Vision: mclouds Computing on Clouds of Mobile Devices
|
|
|
- Abel Stephens
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vision: mclouds Computing on Clouds of Mobile Devices Emiliano Miluzzo, Ramón Cáceres, Yih-Farn Chen AT&T Labs Research, Florham Park, NJ, USA ABSTRACT When we think of mobile cloud computing today, we typically refer to empowering mobile devices in particular smartphones and tablets with the capabilities of stationary resources residing in giant data centers. But what happens when these mobile devices become as powerful as our personal computers or more? This paper presents our vision of a future in which mobile devices become a core component of mobile cloud computing architectures. We envision a world where mobile devices will be capable of forming mobile clouds, or mclouds, to accomplish tasks locally without relying, when possible, on costly and, sometimes, inefficient backend communication. We discuss a possible mclouds architecture, its benefits and tradeoffs, and the user incentive scheme to support the mcloud design. Categories and Subject Descriptors: C.2 [Computer- Communication Networks]: Distributed Systems General Terms: Algorithms, Design Keywords: Mobile Cloud Computing, Mobile Devices, Distributed Systems 1. INTRODUCTION The tremendous explosion of mobile devices is far from over. Smartphones and tablets are at the center of a new modern revolution, one that is taking mobile computing to a whole new level. These devices become even smarter with the introduction of novel and powerful services that can take advantage of the computational resources on both the device itself and on the cloud. The game-changing application markets (Apple App Store and Google Android Market), artificial intelligence breakthroughs (AT&T Watson [2], Apple Siri, Google voice search), sensing and communication capabilities are pushing the envelope for a new class of devices towards the realization, one day, of an ambitious grand vision: all-in-one smart, powerful, and versatile devices the ultimate fusion of phones, tablets, and personal computers. It is not too hard to imagine a world where we will be able to Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. To copy otherwise, to republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. MCS 12, June 25, 2012, Low Wood Bay, Lake District, UK. Copyright 2012 ACM /12/06...$ CPU MEMORY BATTERY 2012 dual-core 1.2 GHz RAM: 1 GB storage: 32 GB cores RAM: 32 GB storage: 1 TB NETWORK WiFi / 4G WiFi / xg 8 h talk time 270 h stand-by - Figure 1: Mobile devices today and in ten years from now. While computation and memory will likely increase considerably, network bandwidth and battery capacity will not grow at the same pace. carry a single device to answer phone calls, use it as our primary personal computer at work by hooking it up to external monitors and keyboards, and install our favorite games as much as we do nowadays on tablets and smartphones. If we then look ten years into the future, how would mobile cloud computing be different from now? Or, putting it differently, how would we redefine it given the enormous capabilities that our future mobile devices will expose? It is guaranteed that the answers to these questions are not straightforward, nor have a single solution. But at the same time, it wouldn t be wise for future mobile cloud computing architects to continue to look at these mobile devices as only capable of thin-layer interactions with remote clouds and not take into account the new exciting opportunities from their extraordinarily powerful hardware support. A schematic and approximate representation of the evolution of these devices characteristics is shown in Figure 1. While computation and storage will most likely continue to increase according to Moore s law, it is not clear if the cellular communication channel and the battery capacity will present similar trends. Battery still remains a bottleneck, not being able to cope with larger screens, computation, and data exchange requirements of many applications, either coming with the device itself or from the market places. Even the cellular wireless bandwidth might not exhibit substantial upgrades in the short term and often a new wireless
2 technology soon experiences lack of capacity given the continuous traffic growth due to the unstoppable demand for new data-intensive applications. It is the case of applications that, for example, nowadays heavily rely on the cloud to accomplish their tasks speech and image processing are examples. Moreover, service providers prefer to design applications that accomplish most of the audio, video, and image processing in the cloud in order to be able to collect (and own) large amounts of user data, a precious resource for building more accurate machine learning classification models, for example. Relying heavily on the backend cloud means, however, paying a cost on the network, where a large fraction of its bandwidth is employed to deliver overhead data (sent to the cloud for remote processing for example), which might overall degrade the network performance. Can we offload some of this traffic from the network when possible? Can we rethink the architecture of mobile computing systems in order to reduce the amount of unnecessary traffic on the cellular wireless links by accomplishing tasks locally? The freed bandwidth would be made available to other services, improving network usability and customers satisfaction. The growing capabilities of mobile devices certainly open a door towards this possibility. This paper presents our vision of mclouds, a mobile cloud computing architecture that runs resource-intensive applications on collections of cooperating mobile devices. Section 2 describes the mclouds design, particularly the mechanisms for managing the distributed computing operations between mcloud members. Section 3 discusses the user incentive scheme for mclouds, an important driver for the adoption of this technology. 2. MCLOUDS In this section, we present the mcloud design and the role of mclouds within the context of future mobile cloud computing system architectures. mclouds are introduced to: take advantage of the improving hardware capabilities on mobile devices; reduce the impact on the cellular data channel, hence reducing bandwidth usage. In what follows, we highlight the mclouds design principles and the motivations driving them. 2.1 Do It Locally If You Can Recent studies on smartphone data usage show that the launch of the latest mobile device generations has triggered an exponential growth of wireless bandwidth demand, while highlighting that Just 1% of all users now consume half of the entire downlink data [5]. As an example of this growth, wireless data traffic handled by AT&T s network went from 0.1 Petabytes in 2006 to 27.1 Petabytes in 2011 a 27,000% increase in 5 years [1]. A major reason for this increase is that many applications and services involving some computation in the speech, image, and audio domains for example heavily rely on the cloud to complete their tasks. The mobile device is in fact often considered only as a thin-layer abstraction for collecting data (audio, pictures, etc.), sending it to the cloud for processing, and receiving the output of this processing back. It s not hard to identify a drawback to this approach: it can suffer from network scalability issues when millions of devices engage in backend communication for cloud processing. With the growing popularity of smart, mobile devices and services, this issue may have an even larger impact in the future. While the preferable repository for long-lived content (e.g., personal files, backups, etc.) will probably remain the backend cloud due to its security, reliability, and availability advantages, much of the processing could be gradually transferred to the mobile devices as their hardware becomes increasingly capable of handling heavy computational loads. Mobile devices will at some point be as powerful as today s backend machines, and task processing will require little or no support from the backend. This hypothesis is already reality for some applications that rely entirely on local processing. It is the case of PocketSphinx, for example, a successful effort of a speech recognition engine implementation for mobile devices without backend interaction [9]. Conti et al. [7] also introduce the opportunistic computing idea as a means to move computation to the mobile devices. It has also been shown that a 3G cellular data interface requires 3 to 5 times more energy than WiFi transmissions [8]. Sending data remotely then not only claims large shares of wireless bandwidth, but also takes its toll on mobile device energy. By promoting local processing, mclouds is intended to: i) syphon data off the cellular data channel, and ii) reduce the backend cloud complexity by pushing intelligence to the edge, i.e., onto the mobile devices. Local data exchanges between mcloud members can occur over free high-bandwidth WiFi networks, both ad-hoc and multicast, or through emerging short-range radio technologies specifically designed for direct interaction between mobile devices [4]. Should any remote data be required to support a local processing task such as machine learning models or specific datasets the data could be transferred to a mobile device opportunistically via WiFi, during offpeak hours via the cellular network, and, possibly, when the device is charging. 2.2 MCloud Processing The mobile devices forming an mcloud are named mdevs. We use the term mtasks to denote the processing tasks carried out by mdevs. An example of an mtask is a speech processing procedure after collecting a voice sample from the user, or an image processing algorithm on a picture taken with the mobile device. We envision mechanisms within the mcloud such that mtasks can be executed either on the single device itself or, when possible, by distributing smaller portions of an mtask among members of the mcloud to parallelize the processing and alleviate the burden on single devices. We thus identify two scenarios: individual and distributed processing. Individual Processing. This is the case of an mtask that can be autonomously accomplished by a single device, without the intervention of external entities. Single device computation is possible for mtasks that do not require too many resources (CPU, RAM, battery) to complete. Pocket- Sphinx [9] is an example of individual processing.
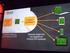
3 mdev 3 mtask 1 output 1 (a) mdev 3 (b) mdev 3 output 3 (c) output 2 Figure 2: Distributed mcloud processing: (a) needs to accomplish mtask 1 and mtask 1 can be split into smaller subtasks; (b) master distributes the subtasks to the surrounding slaves; (c) master collects the results from the slaves. Distributed Processing. There will be situations, however, where mdevs won t be able to act alone because the task requires too many resources. In such a scenario, mdevs could invoke the cooperation of nearby devices to alleviate its computational burden by slicing up a task into smaller subtasks for which independent execution is possible. We call the mobile device requesting the cooperation the master mdev and the others the slave mdevs. This scenario is depicted in Figure 2. If an mtask can be split into subtasks that can be safely executed independently from each other (as for mtask 1 from master in Figure 2a), the master can assign subtasks to those slaves willing to accept them. Examples of mtasks that can be split into independent computation units are image and video processing operations, which can exploit high levels of parallelism. Each slave mdev independently proceeds to the processing of its assigned subtask and returns the result back to the master mdev. After collecting the results from the slaves, the master combines these results to produce the final output. Researchers have already proposed ideas to advance mobile computing, and mobile sensing in particular, to boost machine-learning inference accuracy by promoting inter-device cooperation [14]. Given the growing interest in mobile sensing applications to profile people s context and behavior, machine learning algorithms are among the main drivers for the mcloud technology: typical machine learning routines require heavy computation for which the support of powerful, backend machines is needed. With mclouds these tasks could be accomplished locally without needing to send large quantities of data to the backend cloud. In order to support mcloud operations in any conditions, mdevs can always rely on the backend cloud for completing operations whenever it is not possible to successfully instantiate a distributed processing task in collaboration with nearby mdevs. This might occur because of the heterogeneous mcloud environment, where mdevs might have different capabilities that cannot fulfill the requests of the master. An mcloud is also a highly dynamic ecosystem, where members join and leave with little guarantees about the persistence of some of the resources. It might be also the case that nearby mdevs are not willing to accept a master s task. 2.3 MCloud Management mclouds relies on two important principles. They are the ability to: i) easily manage the mcloud its formation and functionality which we discuss in this section, and ii) identify proper and effective incentive mechanisms for people to lend their devices for other people s computations (see Section 3). An mcloud is an ensemble of mdevs that are usually mobile, dynamically joining and leaving the mcloud formation. Because of this, several questions arise: Would it be ever possible to form and maintain stable mcloud configurations? How do we know if the surrounding mdevs have enough resources to participate in a distributed processing task? What if there aren t enough mdevs in an mcloud to complete a task? This is only a small sample of the questions and challenges that need to be addressed. At a high level, we envision the following procedural steps: Resource Discovery. An mdev (the master) that intends to instantiate a distributed processing task first needs to identify nearby mdevs that could potentially form the mcloud. At this stage, the master initiates a discovery phase by broadcasting solicitation messages, announcing the intent of forming an mcloud and the scope of the task. We only focus on one-hop master-slave interactions. Nearby mdevs willing to join the mcloud and take part in the cooperation, reply to the solicitation messages. If there are no nearby mdevs willing to join the mcloud, or there aren t enough mdevs to receive all the subtasks, the master relies on the backend cloud for the entire task or for the subtasks that cannot be accommodated by the slaves. Formation. The mdevs (the slaves) willing to join respond to the master by sending their unique identifiers. The master maintains a list with the slaves identifiers and the tasks assigned to them. Maintenance. This is probably the most challenging phase, because due to mobility, the topology of the mcloud may vary over time (mdevs may move in and out of the master s short-range radio coverage). To this end, the resource discovery phase needs to be executed multiple times following the mcloud formation. The discovery could be scheduled to run periodically or, to reduce overhead and energy usage for message transmission, only in response to certain activity events. Researchers have shown how to run a user s activity classifiers on mobile devices using the motion sensors [12]. If then a slave detects the user s movement (e.g., walking), it might inform the master that it will be soon out of range and stop the processing. If the master detects its own movement, it would inform the slaves, which would react by halting their processes. Uncompleted tasks could be resumed on other mdevs or on the backend cloud. Release. A release message, announcing the intention to leave the mcloud, can be sent by an mdev at anytime. Triggering factors are the assessment of lack of resources (e.g., the battery is depleting, the user launching a resourceintensive application on the device), mobility, or simply because the mdev doesn t intend to participate anymore without any particular reason. It is the master s responsibility to find other mdevs or involve the backend cloud for processing the tasks that haven t been completed by the released slaves. Naturally, our design for mcloud topology discovery, formation, maintenance, and release can borrow techniques previously introduced and developed in other domains, such as mobile ad-hoc networks for example [6, 3].
4 3. INCENTIVES Proper incentive policies are needed for users with mobile devices to opt-in to mcloud participation. In this section, we analyze possible incentive strategies that may help mclouds become a viable and effective alternative to the current mobile cloud computing model. There has been recent work on managing cellular congestion by using economic incentives to modify the behavior of wireless users. Uninor [17] employs a dynamic pricing plan that gives different discounts based on the location and time of a voice call. TUBE [10] studies how time-shifting the wireless data demand helps the service provider by dynamically varying the incentives. We are interested in finding out what incentives (and from whom) should be provided to mobile device users to encourage them to participate in mclouds since each mdev may bear the cost of cellular wireless bandwidth usage and battery drainage to help complete portions of mtasks. Let s assume that a smartphone user has an mtask that can be distributed to other mdevs. We first start with a simple model (a revision of a classic pricing model proposed by Mendelson [13]) with the following parameters: u utility of a mobile service, a measure of satisfaction perceived by the mobile user, which may be indirectly revealed by the price the user is willing to pay ; T time to complete the service without using mclouds; w cost of waiting per second, which reduces the satisfaction and is highly dependent on the application; p cellular usage payment to carrier without using mclouds. A mobile user will consider a mobile service useful if: u w T p > 0 (1) That is, there is still surplus in the utility after deducting the cost of the waiting time and cellular payment. When the network is congested, the delay component w T becomes a significant factor and fewer users would be willing to use the network. For example, a user may consider the value of watching a 100MB YouTube video of highlights of the latest NBA game to be $5, and the cost of waiting (before continuous streaming starts) to be $0.25 per second. Assuming the wireless service plan to be $25 for 2GB, the cellular payment (without dynamic pricing) would be $1.25. Under this model, the user would have no desire to watch the video if the delay is longer than 15 seconds (waiting cost of $3.75). If mclouds is available, then the user will have the option to distribute its tasks to multiple smartphones to reduce the time to completion. Let s first consider the scenario where the carrier does not provide incentives and the user with the master mdev will have to pay other slave mdevs for their support: t time to completion with mclouds, typically smaller than T because the tasks are distributed; m number of slave mdevs; s average incentive payment to each slave mdev; each slave may price the same subtask differently; q cellular usage payment from the master mdev to carrier when mclouds is used. Note that each slave mdev may handle some of the cellular wireless communications on behalf of the master mdev, and in that case q is likely to be less than p (less data to send to the backend). The payment s is typically made by the master mdev, but the carrier may also decide to pay the incentive to reduce network congestions in certain areas in order to keep the service at an acceptable level. A mobile user with the master mdev will consider a mobile service with mclouds useful if there is surplus in utility after paying the slaves: u w t m s q > 0 (2) And mclouds provides real cost savings (compared to equation 1) only if: w T + p > w t + m s + q (3) That is, the added payment to the slaves should be lower than the savings achieved through reduced waiting time and reduced payment to the wireless carrier by using mclouds. Note that if the carrier is willing to cover the cost to significantly reduce the network congestion, then the slave payment cost (q) from the master is reduced to 0 and mclouds is beneficial to the master as long as: w T + p > w t + q (4) In other words, incentives provided by carriers intended to reduce congestion in their networks may significantly boost the adoption of mclouds. Now we turn the attention to the slave mdev. Note that the benefit of participating in mclous (through the incentives received) must outweigh the cost of the battery drain and cellular wireless bandwidth usage incurred by the slave. If b i is the battery drain cost and v i is the cellular data cost (as perceived by the slave i), then the following must hold for an mdev receiving payment s i to be interested in participating: s i > b i + v i (5) For example, a recent measurement we conducted shows that the use of the personal hotspot application on an iphone 4 device to support a WiFi-only ipad device consumes roughly 200MB of data during one hour of usage. In this case, v i would be $2.50 on a 2GB/$25 monthly plan. The battery on the iphone 4 drops by 22% for one hour of usage serving as a hotspot. If the slave mdev i considers every 10% of battery drain to be worth $1, then b i would be $2.20. So the incentive payment s i to the slave must be higher than $4.70 if the task it received consumes the same amount of cellular data and battery usage. Whether the incentives are paid by the master mdev or the carrier, the carrier can serve as the clearinghouse that handles all the transactions (or micro payments) on behalf of the owners of the mobile device participating in mclouds. To help explain how incentives work in a real application scenario, let s consider an mcloud-based real-time conference attendance app, which allows a mobile user to take a snapshot of a crowd (say attendees in a particular session) and match faces in the crowd against the stored photos of all conference attendees to figure out who is attending which session. Furthermore, the conference organizers want to get real-time updates on the distribution of attendees in various sessions for logistics planning. A conference volunteer may decide to use mclouds to quickly recognize all faces in the room since her own device may not have sufficient computation power and communication bandwidth to do that in real time. Let s assume that
5 there are 1000 attendees at the conference and a centralized database of all their faces is stored in the backend cloud. Let s assume that the app allows a user to upload a small image of a face to the backend cloud, which returns the name of the conference attendee. We also assume that there are typically 50 attendees in each session and 10 of them are available to participate in mclouds. If the volunteer (with the master mdev) does it on her own device, the on-device app may take the following steps: (a) detect the number of faces in the snapshot and crop a small image for each face, (b) submit each face separately for recognition, and (c) return the list of attendees to the user. Let s assume that step (a) takes 10 seconds, step (b) takes 5 seconds for each face, and step (c) takes 2 seconds. The volunteer would need 10+5*50+2=262 seconds (T ) without mclouds to accomplish the task. By using mclouds with 10 slave mdevs (each performing 5 face recognition tasks), the time will be reduced significantly since step (b) can be distributed to 10 mdevs. If we assume that the overhead of communicating with all slave mdevs is 2 seconds (through multicast), then the total time (t) with mclouds would be *5+2=39 seconds. Now let s consider the surplus utility of the master mdev without mclouds. Let s assume that the utility of real-time face recognition (u) of 50 users in a conference session is worth $10 to the conference organizers, and it costs $0.03 in cellular payment for any phone to submit a face recognition request to the cloud, and $0.02 is the cost of delay per second (w). Then w T would be $0.02 * 262 =$5.24 and p would be $0.03 * 50 = $1.50. So the surplus in utility (see equation 1) after subtracting the waiting cost and cellular payment would be $10 -$ $1.50 = $3.26. Now we consider the case with mclouds. Let s assume that the average cost equivalent to the battery drainage b i for performing the subtask on each slave mdev i is $0.10. The average cellular payment is simply $0.03*5=$0.15 each. The master mdev may decide to pay $0.3 (> $0.25) to each slave mdev to cover their costs. So the surplus utility for the master mdev (see equation 2) is $10 - $0.02*39-10*$0.3-0 = $6.22. Note that there would be no cellular payment on the master mdev since the tasks have been distributed. The use of mclouds would result in a saving of $2.96. If we further assume that each slave mdev is powerful enough to perform face recognition on its own, then all the cellular payments can be removed; however, each b i would become higher since each slave mdev i would have to work harder to finish its subtask without contacting the cloud. Note that the face recognition application on each slave mdev i will only need a face classification model, with a much smaller memory footprint than the training data, to perform its task. 4. DISCUSSION This paper takes the position that mclouds will be a core component of our future computing landscape. As we have described, running processing and storage-intensive applications on increasingly resourceful mobile devices would reduce demands on rapidly saturating cellular data networks. It is important to note that mclouds will complement, but not replace, other approaches in the spectrum of mobile cloud computing solutions. In particular, we see two other approaches that will also play important roles. One is the currently dominant model of offloading computation and storage from mobile devices to centralized cloud resources. There are many scenarios in which this approach will continue to make sense, for example applications that need access to datasets too large to move away from centralized data centers. The other approach is Cloudlets, which shifts computation and storage to stationary resources close to the edge of the network [15]. This approach promises to reduce latency with respect to the centralized solution, and makes available more computing, storage, and energy resources than are available on mobile devices. It is also important to mention that proper security and trust mechanisms are needed to facilitate the adoption of mclouds. We assume that mclouds are a trusted platform running on trusted devices where any third-party computation is executed within well-defined and secure environments [16]. Any phone-to-phone interaction should be regulated by off-the-shelf authentication and authorization techniques. Finally, local stationary devices such as personal computers, set-top boxes, etc. could also become members of an mcloud. They could lend further computing power and enrich the capabilities of the mcloud. 5. CONCLUSION We have presented mclouds, our vision of mobile cloud computing architectures, where mobile devices become core computing nodes because of their rapidly growing capabilities. We have discussed the advantages of the mclouds approach and provided initial design considerations. Although these ideas are preliminary, we believe that mclouds will play a key role in the future mobile computing landscape. 6. REFERENCES [1] AT&T 2011 Annual Report. us/files/pdf/ar2011_annual_report.pdf. [2] AT&T Watson. [3] Personal Networks. [4] Qualcomm s Flashlinq. [5] Trends in Smartphone Data Use. [6] S. Basagni, et al. Mobile ad hoc Networking. Wiley-IEEE Press, [7] M. Conti and M. Kumar. Opportunities in Opportunistic Computing. Computer, 43(1):42 50, [8] E. Cuervo, et al. Maui: Making Smartphones Last Longer with Code Offload. In Proc. of MobiSys 10. [9] D. Huggins-Daines, et al. PocketSphinx: A Free, Real-Time Continuous Speech Recognition System for Hand-Held Devices. In Proc. of ICASSP [10] C. Joe-Wong, et al. Time-Dependent Broadband Pricing: Feasibility and Benefits. In Proc. of ICDCS 11. [11] E. Koukoumidis, et al. Pocket Cloudlets. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 39(1): , [12] N. Lane, et al. A Survey of Mobile Phone Sensing. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 48(9): , [13] H. Mendelson. Pricing Computer Services: Queuing Effects. Communications of the ACM, [14] E. Miluzzo, et al. Darwin Phones: the Evolution of Sensing and Inference on Mobile Phones. In Proc. of MobiSys 10. [15] M. Satyanarayanan, et al. The Case for VM-Based Cloudlets in Mobile Computing. Pervasive Computing, IEEE, 8(4):14 23, [16] L.P. Cox and P.M. Chen. Pocket Hypervisors: Opportunities and Challenges. ACM HotMobile 07, 46 50, [17] Uninor. Dynamic Pricing Plan with per Second Billing, Feb
Mobile Cloud Computing Challenges
 Mobile Cloud Computing Challenges by Kyung Mun - Tuesday, September 21, 2010 http://www2.alcatel-lucent.com/techzine/mobile-cloud-computing-challenges/ Application usage on mobile devices has exploded
Mobile Cloud Computing Challenges by Kyung Mun - Tuesday, September 21, 2010 http://www2.alcatel-lucent.com/techzine/mobile-cloud-computing-challenges/ Application usage on mobile devices has exploded
Rethinking the Small Cell Business Model
 CASE STUDY Intelligent Small Cell Trial Intel Architecture Rethinking the Small Cell Business Model In 2011 mobile data traffic experienced a 2.3 fold increase, reaching over 597 petabytes per month. 1
CASE STUDY Intelligent Small Cell Trial Intel Architecture Rethinking the Small Cell Business Model In 2011 mobile data traffic experienced a 2.3 fold increase, reaching over 597 petabytes per month. 1
How To Create An Ad Hoc Cloud On A Cell Phone
 Ad Hoc Cloud Computing using Mobile Devices Gonzalo Huerta-Canepa and Dongman Lee KAIST MCS Workshop @ MobiSys 2010 Agenda Smart Phones are not just phones Desire versus reality Why using mobile devices
Ad Hoc Cloud Computing using Mobile Devices Gonzalo Huerta-Canepa and Dongman Lee KAIST MCS Workshop @ MobiSys 2010 Agenda Smart Phones are not just phones Desire versus reality Why using mobile devices
Mobile Cloud Computing: Survey & Discussion. Jianting Yue Sep 27, 2013
 Mobile Cloud Computing: Survey & Discussion Jianting Yue Sep 27, 2013 1 Outline Lead-in Definition Main Functions Architecture Computation Offloading: an example Challenges Potential Ideas Summary 2 3
Mobile Cloud Computing: Survey & Discussion Jianting Yue Sep 27, 2013 1 Outline Lead-in Definition Main Functions Architecture Computation Offloading: an example Challenges Potential Ideas Summary 2 3
Big and small corporations, startups, and academic
 Editor: Yih-Farn Chen Beyond Wires I m Cloud 2.0, and I m Not Just a Data Center AT&T Labs Research Cloud service providers invest significant effort into designing, building, and empowering cloud infrastructures.
Editor: Yih-Farn Chen Beyond Wires I m Cloud 2.0, and I m Not Just a Data Center AT&T Labs Research Cloud service providers invest significant effort into designing, building, and empowering cloud infrastructures.
Mobile Cloud Computing: Paradigms and Challenges 移 动 云 计 算 : 模 式 与 挑 战
 Mobile Cloud Computing: Paradigms and Challenges 移 动 云 计 算 : 模 式 与 挑 战 Jiannong Cao Internet & Mobile Computing Lab Department of Computing Hong Kong Polytechnic University Email: csjcao@comp.polyu.edu.hk
Mobile Cloud Computing: Paradigms and Challenges 移 动 云 计 算 : 模 式 与 挑 战 Jiannong Cao Internet & Mobile Computing Lab Department of Computing Hong Kong Polytechnic University Email: csjcao@comp.polyu.edu.hk
CSci 8980 Mobile Cloud Computing. MCC Overview
 CSci 8980 Mobile Cloud Computing MCC Overview Papers Students can do: 1 long paper or 2 short papers Extra credit: add another By 8am tomorrow, I will randomly assign papers unless I hear from you Protocol:
CSci 8980 Mobile Cloud Computing MCC Overview Papers Students can do: 1 long paper or 2 short papers Extra credit: add another By 8am tomorrow, I will randomly assign papers unless I hear from you Protocol:
App coverage. ericsson White paper Uen 284 23-3212 Rev B August 2015
 ericsson White paper Uen 284 23-3212 Rev B August 2015 App coverage effectively relating network performance to user experience Mobile broadband networks, smart devices and apps bring significant benefits
ericsson White paper Uen 284 23-3212 Rev B August 2015 App coverage effectively relating network performance to user experience Mobile broadband networks, smart devices and apps bring significant benefits
Mobile Application Performance Testing
 StarBase Insight Mobile Application Performance Testing Introduction Purpose This discussion paper aims to educate the reader about mobile applications and demystify their performance testing needs by
StarBase Insight Mobile Application Performance Testing Introduction Purpose This discussion paper aims to educate the reader about mobile applications and demystify their performance testing needs by
Towards Wearable Cognitive Assistance
 Towards Wearable Cognitive Assistance Kiryong Ha, Zhuo Chen, Wenlu Hu, Wolfgang Richter, Padmanabhan Pillaiy, and Mahadev Satyanarayanan Carnegie Mellon University and Intel Labs Presenter: Saurabh Verma
Towards Wearable Cognitive Assistance Kiryong Ha, Zhuo Chen, Wenlu Hu, Wolfgang Richter, Padmanabhan Pillaiy, and Mahadev Satyanarayanan Carnegie Mellon University and Intel Labs Presenter: Saurabh Verma
IMPLEMENTATION OF CELLULAR NETWORKS WITH LEASING CAPABILITIES FOR LARGE QUERY PROCESS
 IMPLEMENTATION OF CELLULAR NETWORKS WITH LEASING CAPABILITIES FOR LARGE QUERY PROCESS M.surendra 1, T.Sujilatha 2, #1 Student of M.Tech (C.S) and Department Of CSE, GOKULA KRISHNA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
IMPLEMENTATION OF CELLULAR NETWORKS WITH LEASING CAPABILITIES FOR LARGE QUERY PROCESS M.surendra 1, T.Sujilatha 2, #1 Student of M.Tech (C.S) and Department Of CSE, GOKULA KRISHNA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
From Traditional Functional Testing to Enabling Continuous Quality in Mobile App Development
 From Traditional Functional Testing to Enabling Continuous Quality in Mobile App Development Introduction Today s developers are under constant pressure to launch killer apps and release enhancements as
From Traditional Functional Testing to Enabling Continuous Quality in Mobile App Development Introduction Today s developers are under constant pressure to launch killer apps and release enhancements as
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF VIDEO CONFERENCING SOFTWARE IN TECHNOLOGY 802.11N NABILA BINTI RUSLAN
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF VIDEO CONFERENCING SOFTWARE IN TECHNOLOGY 802.11N NABILA BINTI RUSLAN This report is submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Bachelor of Computer Science (Software
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF VIDEO CONFERENCING SOFTWARE IN TECHNOLOGY 802.11N NABILA BINTI RUSLAN This report is submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Bachelor of Computer Science (Software
Steps to Migrating to a Private Cloud
 Deploying and Managing Private Clouds The Essentials Series Steps to Migrating to a Private Cloud sponsored by Introduction to Realtime Publishers by Don Jones, Series Editor For several years now, Realtime
Deploying and Managing Private Clouds The Essentials Series Steps to Migrating to a Private Cloud sponsored by Introduction to Realtime Publishers by Don Jones, Series Editor For several years now, Realtime
Development of a Service Robot System for a Remote Child Monitoring Platform
 , pp.153-162 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsh.2014.8.5.14 Development of a Service Robot System for a Remote Child Monitoring Platform Taewoo Han 1 and Yong-Ho Seo 2, * 1 Department of Game and Multimedia,
, pp.153-162 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsh.2014.8.5.14 Development of a Service Robot System for a Remote Child Monitoring Platform Taewoo Han 1 and Yong-Ho Seo 2, * 1 Department of Game and Multimedia,
Mobile Adaptive Opportunistic Junction for Health Care Networking in Different Geographical Region
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 113-118 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Mobile
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 113-118 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Mobile
3G/Wi-Fi Seamless Offload
 Qualcomm Incorporated March 2010 Table of Contents [1] Introduction... 1 [2] The Role of WLAN... 2 [3] 3G/Wi-Fi Seamless Offload Pathway... 2 [4] Application-Based Switching... 3 [5] Wi-Fi Mobility...
Qualcomm Incorporated March 2010 Table of Contents [1] Introduction... 1 [2] The Role of WLAN... 2 [3] 3G/Wi-Fi Seamless Offload Pathway... 2 [4] Application-Based Switching... 3 [5] Wi-Fi Mobility...
A B S T R A C T. Index Trems- Wi-Fi P2P, WLAN, Mobile Telephony, Piconet I. INTRODUCTION
 Wi-Fi Calling Using Android Phones. Mr.Dnyaneshwar Bhusari, Mr.Gaurav Mokase, Mr.Prasad Waghmare, Ms. Kundan Kumar Department of Information Technology D.Y.Patil College of Engineering, Akurdi, Pune, India
Wi-Fi Calling Using Android Phones. Mr.Dnyaneshwar Bhusari, Mr.Gaurav Mokase, Mr.Prasad Waghmare, Ms. Kundan Kumar Department of Information Technology D.Y.Patil College of Engineering, Akurdi, Pune, India
Mobile Hybrid Cloud Computing Issues and Solutions
 , pp.341-345 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013.29.72 Mobile Hybrid Cloud Computing Issues and Solutions Yvette E. Gelogo *1 and Haeng-Kon Kim 1 1 School of Information Technology, Catholic University
, pp.341-345 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013.29.72 Mobile Hybrid Cloud Computing Issues and Solutions Yvette E. Gelogo *1 and Haeng-Kon Kim 1 1 School of Information Technology, Catholic University
Managing Background Data Traffic in Mobile Devices
 Qualcomm Incorporated January 2012 QUALCOMM is a registered trademark of QUALCOMM Incorporated in the United States and may be registered in other countries. Other product and brand names may be trademarks
Qualcomm Incorporated January 2012 QUALCOMM is a registered trademark of QUALCOMM Incorporated in the United States and may be registered in other countries. Other product and brand names may be trademarks
Mobile Cloud Computing. Chamitha de Alwis, PhD Senior Lecturer University of Sri Jayewardenepura chamitha@sjp.ac.lk
 Mobile Cloud Computing Chamitha de Alwis, PhD Senior Lecturer University of Sri Jayewardenepura chamitha@sjp.ac.lk Mobile Computing Rapid progress of mobile computing have become a powerful trend in the
Mobile Cloud Computing Chamitha de Alwis, PhD Senior Lecturer University of Sri Jayewardenepura chamitha@sjp.ac.lk Mobile Computing Rapid progress of mobile computing have become a powerful trend in the
Smart Wi-Fi A Smart Offload Solution for Smartphones
 Smart Wi-Fi A Smart Offload Solution for Smartphones Kineto Wireless, Inc. 1601 McCarthy Blvd. Milpitas, CA 95035 Tel: +1 408 546 0660 2011 Kineto Wireless, Inc. All rights reserved. www.kineto.com The
Smart Wi-Fi A Smart Offload Solution for Smartphones Kineto Wireless, Inc. 1601 McCarthy Blvd. Milpitas, CA 95035 Tel: +1 408 546 0660 2011 Kineto Wireless, Inc. All rights reserved. www.kineto.com The
Technology Services...Ahead of Times. Enterprise Application on ipad
 Technology Services...Ahead of Times Enterprise Application on ipad Diaspark, 60/2 Babu Labhchand Chhajlani Marg, Indore M.P. (India) 452009 Overview This white paper talks about the capabilities of ipad
Technology Services...Ahead of Times Enterprise Application on ipad Diaspark, 60/2 Babu Labhchand Chhajlani Marg, Indore M.P. (India) 452009 Overview This white paper talks about the capabilities of ipad
IMPROVING QUALITY OF VIDEOS IN VIDEO STREAMING USING FRAMEWORK IN THE CLOUD
 IMPROVING QUALITY OF VIDEOS IN VIDEO STREAMING USING FRAMEWORK IN THE CLOUD R.Dhanya 1, Mr. G.R.Anantha Raman 2 1. Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Adhiyamaan college of Engineering(Hosur).
IMPROVING QUALITY OF VIDEOS IN VIDEO STREAMING USING FRAMEWORK IN THE CLOUD R.Dhanya 1, Mr. G.R.Anantha Raman 2 1. Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Adhiyamaan college of Engineering(Hosur).
How To Make Internet Available For Free
 Is Connectivity A Human Right? For almost ten years, Facebook has been on a mission to make the world more open and connected. For us, that means the entire world not just the richest, most developed countries.
Is Connectivity A Human Right? For almost ten years, Facebook has been on a mission to make the world more open and connected. For us, that means the entire world not just the richest, most developed countries.
QoS Provision in a Cloud-Based Multimedia Storage System
 ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 QoS Provision in a Cloud-Based Multimedia Storage System Minal Padwal1, Manjushri Mahajan2 M.E. (C.E.), G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering & Management, Wagholi, Pune, India Assistant
ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 QoS Provision in a Cloud-Based Multimedia Storage System Minal Padwal1, Manjushri Mahajan2 M.E. (C.E.), G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering & Management, Wagholi, Pune, India Assistant
White paper. Mobile broadband with HSPA and LTE capacity and cost aspects
 White paper Mobile broadband with HSPA and LTE capacity and cost aspects Contents 3 Radio capacity of mobile broadband 7 The cost of mobile broadband capacity 10 Summary 11 Abbreviations The latest generation
White paper Mobile broadband with HSPA and LTE capacity and cost aspects Contents 3 Radio capacity of mobile broadband 7 The cost of mobile broadband capacity 10 Summary 11 Abbreviations The latest generation
Amdocs Smart Net Solution
 Amdocs Smart Net Solution With the explosive growth of mobile data and the popularity of Wi-Fi as an access technology, Wi-Fi services have become a key strategy for service providers to alleviate network
Amdocs Smart Net Solution With the explosive growth of mobile data and the popularity of Wi-Fi as an access technology, Wi-Fi services have become a key strategy for service providers to alleviate network
MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING On Gaming Applications PRASAD REDDY
 MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING On Gaming Applications PRASAD REDDY Outline Introduction for mobile gaming Difference between mobile cloud game and normal Challenges in the design of mobile games Mobile cloud gaming
MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING On Gaming Applications PRASAD REDDY Outline Introduction for mobile gaming Difference between mobile cloud game and normal Challenges in the design of mobile games Mobile cloud gaming
Intelligent Content Delivery Network (CDN) The New Generation of High-Quality Network
 White paper Intelligent Content Delivery Network (CDN) The New Generation of High-Quality Network July 2001 Executive Summary Rich media content like audio and video streaming over the Internet is becoming
White paper Intelligent Content Delivery Network (CDN) The New Generation of High-Quality Network July 2001 Executive Summary Rich media content like audio and video streaming over the Internet is becoming
The Way to Wi-Fi in a New Age of Roaming. How to Harness Wi-Fi Solutions to Realize the Next Phase of Mobile Communications
 The Way to Wi-Fi in a New Age of Roaming How to Harness Wi-Fi Solutions to Realize the Next Phase of Mobile Communications 1 Table of Contents Introduction...2 The New Age of Roaming...2 Why Wi-Fi?...3
The Way to Wi-Fi in a New Age of Roaming How to Harness Wi-Fi Solutions to Realize the Next Phase of Mobile Communications 1 Table of Contents Introduction...2 The New Age of Roaming...2 Why Wi-Fi?...3
Automation of Smartphone Traffic Generation in a Virtualized Environment. Tanya Jha Rashmi Shetty
 Automation of Smartphone Traffic Generation in a Virtualized Environment Tanya Jha Rashmi Shetty Abstract Scalable and comprehensive analysis of rapidly evolving mobile device application traffic is extremely
Automation of Smartphone Traffic Generation in a Virtualized Environment Tanya Jha Rashmi Shetty Abstract Scalable and comprehensive analysis of rapidly evolving mobile device application traffic is extremely
networks Live & On-Demand Video Delivery without Interruption Wireless optimization the unsolved mystery WHITE PAPER
 Live & On-Demand Video Delivery without Interruption Wireless optimization the unsolved mystery - Improving the way the world connects - WHITE PAPER Live On-Demand Video Streaming without Interruption
Live & On-Demand Video Delivery without Interruption Wireless optimization the unsolved mystery - Improving the way the world connects - WHITE PAPER Live On-Demand Video Streaming without Interruption
Mobile Cloud Computing for Data-Intensive Applications
 Mobile Cloud Computing for Data-Intensive Applications Senior Thesis Final Report Vincent Teo, vct@andrew.cmu.edu Advisor: Professor Priya Narasimhan, priya@cs.cmu.edu Abstract The computational and storage
Mobile Cloud Computing for Data-Intensive Applications Senior Thesis Final Report Vincent Teo, vct@andrew.cmu.edu Advisor: Professor Priya Narasimhan, priya@cs.cmu.edu Abstract The computational and storage
LTE Test: EE 4G Network Performance
 LTE Test: EE 4G Network Performance An Analysis of Coverage, Speed, Latency and related key performance indicators, from October 31 st to December 20 th, 2012. Disclaimer Epitiro has used its best endeavours
LTE Test: EE 4G Network Performance An Analysis of Coverage, Speed, Latency and related key performance indicators, from October 31 st to December 20 th, 2012. Disclaimer Epitiro has used its best endeavours
3G smartphones. ericsson White paper Uen 284 23-3250 February 2015
 ericsson White paper Uen 284 23-3250 February 2015 3G smartphones optimizing user experience and network efficiency Rapid global smartphone uptake is creating new mobile data traffic patterns. There is
ericsson White paper Uen 284 23-3250 February 2015 3G smartphones optimizing user experience and network efficiency Rapid global smartphone uptake is creating new mobile data traffic patterns. There is
Mobile Enterprise and IPv6 Consumerization of IT
 Mobile Enterprise and IPv6 Consumerization of IT Yanick Pouffary Distinguished Technologist - Technology Services - Networking HP IPv6 Global Leader April 18, 2013 Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development
Mobile Enterprise and IPv6 Consumerization of IT Yanick Pouffary Distinguished Technologist - Technology Services - Networking HP IPv6 Global Leader April 18, 2013 Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development
STeP-IN SUMMIT 2014. June 2014 at Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune - INDIA. Mobile Performance Testing
 STeP-IN SUMMIT 2014 11 th International Conference on Software Testing June 2014 at Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune - INDIA Mobile Performance Testing by Sahadevaiah Kola, Senior Test Lead and Sachin Goyal
STeP-IN SUMMIT 2014 11 th International Conference on Software Testing June 2014 at Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune - INDIA Mobile Performance Testing by Sahadevaiah Kola, Senior Test Lead and Sachin Goyal
Smart Anytime, Safe Anywhere. Climax Home Portal Platform. Envisage and Enable a Connected Future
 Smart Anytime, Safe Anywhere Climax Home Portal Platform Envisage and Enable a Connected Future Climax Home Portal Platform An IP/GPRS-Based Solution to Deliver Smart Home and Mobile Control Services Reliable
Smart Anytime, Safe Anywhere Climax Home Portal Platform Envisage and Enable a Connected Future Climax Home Portal Platform An IP/GPRS-Based Solution to Deliver Smart Home and Mobile Control Services Reliable
Megapixel Surveillance
 White Paper The Latest Advances in Megapixel Surveillance Table of Contents Development of IP Surveillance 03 Benefits of IP Surveillance 03 Development of Megapixel Surveillance 04 Benefits of Megapixel
White Paper The Latest Advances in Megapixel Surveillance Table of Contents Development of IP Surveillance 03 Benefits of IP Surveillance 03 Development of Megapixel Surveillance 04 Benefits of Megapixel
Forecast of Mobile Broadband Bandwidth Requirements
 Forecast of Mobile Broadband Bandwidth Requirements s Executive Summary The consumption of video content is creating a shift from use in the home to mobile devices. This is driving exponential increases
Forecast of Mobile Broadband Bandwidth Requirements s Executive Summary The consumption of video content is creating a shift from use in the home to mobile devices. This is driving exponential increases
Potted History of the Mobile Phone
 Ever wondered why your parents are lacking in knowledge of the functionality of your mobile wizardry? Well, it might surprise you to know that mobile phone technology has only really developed over the
Ever wondered why your parents are lacking in knowledge of the functionality of your mobile wizardry? Well, it might surprise you to know that mobile phone technology has only really developed over the
STMicroelectronics is pleased to present the. SENSational. Attend a FREE One-Day Technical Seminar Near YOU!
 SENSational STMicroelectronics is pleased to present the SENSational Seminar Attend a FREE One-Day Technical Seminar Near YOU! Seminar Sensors and the Internet of Things are changing the way we interact
SENSational STMicroelectronics is pleased to present the SENSational Seminar Attend a FREE One-Day Technical Seminar Near YOU! Seminar Sensors and the Internet of Things are changing the way we interact
ICT Development Trends (2014): Embracing the Era of Mobile-ICT
 ICT Development Trends (2014): Embracing the Era of Mobile-ICT ZTE COPORATION In our fast-growing global information society, technology has had a profound effect on every aspect of society and each individual's
ICT Development Trends (2014): Embracing the Era of Mobile-ICT ZTE COPORATION In our fast-growing global information society, technology has had a profound effect on every aspect of society and each individual's
Business Startups - Advantages of Using Automation
 CLOUD AUTOMATION How Cloud Automation Can Help You Scale Your IT Services TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 03 Business Benefits 07 Administrator Benefits 11 Technical Considerations 14 Conclusion 17 2 INTRODUCTION
CLOUD AUTOMATION How Cloud Automation Can Help You Scale Your IT Services TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 03 Business Benefits 07 Administrator Benefits 11 Technical Considerations 14 Conclusion 17 2 INTRODUCTION
Gaming as a Service. Prof. Victor C.M. Leung. The University of British Columbia, Canada www.ece.ubc.ca/~vleung
 Gaming as a Service Prof. Victor C.M. Leung The University of British Columbia, Canada www.ece.ubc.ca/~vleung International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications 4 February, 2014 Outline
Gaming as a Service Prof. Victor C.M. Leung The University of British Columbia, Canada www.ece.ubc.ca/~vleung International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications 4 February, 2014 Outline
Cloud Apps HCSS Software Hosting & Data Security
 Cloud Apps HCSS Software Hosting & Data Security Innovative Software for the Construction Industry SOLUTION Productivity in the cloud. We expect you to be the experts when it comes to building roads and
Cloud Apps HCSS Software Hosting & Data Security Innovative Software for the Construction Industry SOLUTION Productivity in the cloud. We expect you to be the experts when it comes to building roads and
Mobile Performance Testing Approaches and Challenges
 NOUS INFOSYSTEMS LEVERAGING INTELLECT Mobile Performance Testing Approaches and Challenges ABSTRACT Mobile devices are playing a key role in daily business functions as mobile devices are adopted by most
NOUS INFOSYSTEMS LEVERAGING INTELLECT Mobile Performance Testing Approaches and Challenges ABSTRACT Mobile devices are playing a key role in daily business functions as mobile devices are adopted by most
MOBILE APPLICATIONS AND CLOUD COMPUTING. Roberto Beraldi
 MOBILE APPLICATIONS AND CLOUD COMPUTING Roberto Beraldi Course Outline 6 CFUs Topics: Mobile application programming (Android) Cloud computing To pass the exam: Individual working and documented application
MOBILE APPLICATIONS AND CLOUD COMPUTING Roberto Beraldi Course Outline 6 CFUs Topics: Mobile application programming (Android) Cloud computing To pass the exam: Individual working and documented application
Offloading file search operation for performance improvement of smart phones
 Offloading file search operation for performance improvement of smart phones Ashutosh Jain mcs112566@cse.iitd.ac.in Vigya Sharma mcs112564@cse.iitd.ac.in Shehbaz Jaffer mcs112578@cse.iitd.ac.in Kolin Paul
Offloading file search operation for performance improvement of smart phones Ashutosh Jain mcs112566@cse.iitd.ac.in Vigya Sharma mcs112564@cse.iitd.ac.in Shehbaz Jaffer mcs112578@cse.iitd.ac.in Kolin Paul
Business aware traffic steering
 Nokia Networks Business aware traffic steering Nokia Networks white paper Business aware traffic steering Contents 1. Executive Summary 3 2. Static load or QoS-based traffic steering alone is no longer
Nokia Networks Business aware traffic steering Nokia Networks white paper Business aware traffic steering Contents 1. Executive Summary 3 2. Static load or QoS-based traffic steering alone is no longer
Giving life to today s media distribution services
 Giving life to today s media distribution services FIA - Future Internet Assembly Athens, 17 March 2014 Presenter: Nikolaos Efthymiopoulos Network architecture & Management Group Copyright University of
Giving life to today s media distribution services FIA - Future Internet Assembly Athens, 17 March 2014 Presenter: Nikolaos Efthymiopoulos Network architecture & Management Group Copyright University of
In the pursuit of becoming smart
 WHITE PAPER In the pursuit of becoming smart The business insight into Comarch IoT Platform Introduction Businesses around the world are seeking the direction for the future, trying to find the right solution
WHITE PAPER In the pursuit of becoming smart The business insight into Comarch IoT Platform Introduction Businesses around the world are seeking the direction for the future, trying to find the right solution
Results from MyConnection SG Pilot (October 2014 March 2015)
 Results from MyConnection SG Pilot (October 2014 March 2015) IDA launched the MyConnection SG mobile application in October 2014 to complement the IDA Quality of Service ( QoS ) framework to allow IDA
Results from MyConnection SG Pilot (October 2014 March 2015) IDA launched the MyConnection SG mobile application in October 2014 to complement the IDA Quality of Service ( QoS ) framework to allow IDA
How the emergence of OpenFlow and SDN will change the networking landscape
 How the emergence of OpenFlow and SDN will change the networking landscape Software-defined networking (SDN) powered by the OpenFlow protocol has the potential to be an important and necessary game-changer
How the emergence of OpenFlow and SDN will change the networking landscape Software-defined networking (SDN) powered by the OpenFlow protocol has the potential to be an important and necessary game-changer
SMALL BUSINESS. the basics. in telecommunications solutions
 SMALL BUSINESS the basics in telecommunications solutions 1 2 Mobility Innovation, transformation and the cloud Security and business continuity At AT&T, we understand the unique needs that small businesses
SMALL BUSINESS the basics in telecommunications solutions 1 2 Mobility Innovation, transformation and the cloud Security and business continuity At AT&T, we understand the unique needs that small businesses
Enhance Service Delivery and Accelerate Financial Applications with Consolidated Market Data
 White Paper Enhance Service Delivery and Accelerate Financial Applications with Consolidated Market Data What You Will Learn Financial market technology is advancing at a rapid pace. The integration of
White Paper Enhance Service Delivery and Accelerate Financial Applications with Consolidated Market Data What You Will Learn Financial market technology is advancing at a rapid pace. The integration of
Establishing How Many VoIP Calls a Wireless LAN Can Support Without Performance Degradation
 Establishing How Many VoIP Calls a Wireless LAN Can Support Without Performance Degradation ABSTRACT Ángel Cuevas Rumín Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Department of Telematic Engineering Ph.D Student
Establishing How Many VoIP Calls a Wireless LAN Can Support Without Performance Degradation ABSTRACT Ángel Cuevas Rumín Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Department of Telematic Engineering Ph.D Student
Opportunism and Symbiosis in Mobile Cloud Computing: The Promise and the Challenges
 Opportunism and Symbiosis in Mobile Cloud Computing: The Promise and the Challenges Mostafa Ammar School of Computer Science Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA In Collaboration with: Ellen Zegura,
Opportunism and Symbiosis in Mobile Cloud Computing: The Promise and the Challenges Mostafa Ammar School of Computer Science Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA In Collaboration with: Ellen Zegura,
Chapter 19 Cloud Computing for Multimedia Services
 Chapter 19 Cloud Computing for Multimedia Services 19.1 Cloud Computing Overview 19.2 Multimedia Cloud Computing 19.3 Cloud-Assisted Media Sharing 19.4 Computation Offloading for Multimedia Services 19.5
Chapter 19 Cloud Computing for Multimedia Services 19.1 Cloud Computing Overview 19.2 Multimedia Cloud Computing 19.3 Cloud-Assisted Media Sharing 19.4 Computation Offloading for Multimedia Services 19.5
Next-Generation Mobile Apps 7 Critical Success Factors
 Mobile marketing is still the new kid on the block. Some marketers have tried a variety of mobile tactics and found Next-Generation Mobile Apps 7 Critical Success Factors Introduction There are literally
Mobile marketing is still the new kid on the block. Some marketers have tried a variety of mobile tactics and found Next-Generation Mobile Apps 7 Critical Success Factors Introduction There are literally
Efficient DNS based Load Balancing for Bursty Web Application Traffic
 ISSN Volume 1, No.1, September October 2012 International Journal of Science the and Internet. Applied However, Information this trend leads Technology to sudden burst of Available Online at http://warse.org/pdfs/ijmcis01112012.pdf
ISSN Volume 1, No.1, September October 2012 International Journal of Science the and Internet. Applied However, Information this trend leads Technology to sudden burst of Available Online at http://warse.org/pdfs/ijmcis01112012.pdf
app design & development
 FOR MOBILE BUSINESS app design & development SMARTPHONES AND TABLETS App Market Revolution $9B $8B $7B $6B $5B $4B News and Business $3B $2B $1B $0B 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 From Apple s App
FOR MOBILE BUSINESS app design & development SMARTPHONES AND TABLETS App Market Revolution $9B $8B $7B $6B $5B $4B News and Business $3B $2B $1B $0B 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 From Apple s App
Cloud Based Application Architectures using Smart Computing
 Cloud Based Application Architectures using Smart Computing How to Use this Guide Joyent Smart Technology represents a sophisticated evolution in cloud computing infrastructure. Most cloud computing products
Cloud Based Application Architectures using Smart Computing How to Use this Guide Joyent Smart Technology represents a sophisticated evolution in cloud computing infrastructure. Most cloud computing products
Windows Server Performance Monitoring
 Spot server problems before they are noticed The system s really slow today! How often have you heard that? Finding the solution isn t so easy. The obvious questions to ask are why is it running slowly
Spot server problems before they are noticed The system s really slow today! How often have you heard that? Finding the solution isn t so easy. The obvious questions to ask are why is it running slowly
Mobile Cloud Status, challenges, applications. Calin Curescu Senior Researcher, Ericsson Cloud Program
 Mobile Cloud Status, challenges, applications Calin Curescu Senior Researcher, Ericsson Cloud Program THE new ICT industry + + MOBILITY BROADBAND CLOUD DISRUPTIVE COMBINATION CLOUD 1.0: CONSOLIDATION CONSOLIDATION
Mobile Cloud Status, challenges, applications Calin Curescu Senior Researcher, Ericsson Cloud Program THE new ICT industry + + MOBILITY BROADBAND CLOUD DISRUPTIVE COMBINATION CLOUD 1.0: CONSOLIDATION CONSOLIDATION
Increase visibility, control and performance of field resources in the Utilities Industry
 Increase visibility, control and performance of field resources in the Utilities Industry Using low cost mobile phone technology to empower the utility workforce and enhance operational effectiveness.
Increase visibility, control and performance of field resources in the Utilities Industry Using low cost mobile phone technology to empower the utility workforce and enhance operational effectiveness.
Web Application Deployment in the Cloud Using Amazon Web Services From Infancy to Maturity
 P3 InfoTech Solutions Pvt. Ltd http://www.p3infotech.in July 2013 Created by P3 InfoTech Solutions Pvt. Ltd., http://p3infotech.in 1 Web Application Deployment in the Cloud Using Amazon Web Services From
P3 InfoTech Solutions Pvt. Ltd http://www.p3infotech.in July 2013 Created by P3 InfoTech Solutions Pvt. Ltd., http://p3infotech.in 1 Web Application Deployment in the Cloud Using Amazon Web Services From
Cars, Broadband, Internet: And why the road to innovation may go through Washington DC
 Cars, Broadband, Internet: And why the road to innovation may go through Washington DC Jon M. Peha Carnegie Mellon University www.ece.cmu.edu/~peha/bio.html Keynote for IEEE CCNC / Consumer Electronics
Cars, Broadband, Internet: And why the road to innovation may go through Washington DC Jon M. Peha Carnegie Mellon University www.ece.cmu.edu/~peha/bio.html Keynote for IEEE CCNC / Consumer Electronics
The Next Generation Network:
 JULY, 2012 The Next Generation Network: Why the Distributed Enterprise Should Consider Multi-circuit WAN VPN Solutions versus Traditional MPLS Tolt Solutions Network Services 125 Technology Drive Suite
JULY, 2012 The Next Generation Network: Why the Distributed Enterprise Should Consider Multi-circuit WAN VPN Solutions versus Traditional MPLS Tolt Solutions Network Services 125 Technology Drive Suite
Quick Reference for:
 Quick Reference for: Optimum Online Boost Plus Optimum Link SM Optimum app Advanced Wireless Router Por español, vea al revérso Version 1.0 9815001CAP0311COL Table of Contents Optimum Online Boost Plus...................
Quick Reference for: Optimum Online Boost Plus Optimum Link SM Optimum app Advanced Wireless Router Por español, vea al revérso Version 1.0 9815001CAP0311COL Table of Contents Optimum Online Boost Plus...................
Efficient Energy Reduction and Enhancing Security Privacy in Mobile Cloud Computing
 Efficient Energy Reduction and Enhancing Security Privacy in Mobile Cloud Computing B.Sudhanantham 1, M.Shankar 2 PG Scholar, Dept. of CSE, Angel College of Engineering and Technology, Tirupur, India 1
Efficient Energy Reduction and Enhancing Security Privacy in Mobile Cloud Computing B.Sudhanantham 1, M.Shankar 2 PG Scholar, Dept. of CSE, Angel College of Engineering and Technology, Tirupur, India 1
MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING: OPEN ISSUES Pallavi 1, Pardeep Mehta 2
 MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING: OPEN ISSUES Pallavi 1, Pardeep Mehta 2 1 Asst Prof,Dept of Computer Science, Apeejay College of Fine Arts, Jalandhar 144001 2 Asst Prof,Dept of Computer Science,HMV,Jalandhar 144001
MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING: OPEN ISSUES Pallavi 1, Pardeep Mehta 2 1 Asst Prof,Dept of Computer Science, Apeejay College of Fine Arts, Jalandhar 144001 2 Asst Prof,Dept of Computer Science,HMV,Jalandhar 144001
The 5G Infrastructure Public-Private Partnership
 The 5G Infrastructure Public-Private Partnership NetFutures 2015 5G PPP Vision 25/03/2015 19/06/2015 1 5G new service capabilities User experience continuity in challenging situations such as high mobility
The 5G Infrastructure Public-Private Partnership NetFutures 2015 5G PPP Vision 25/03/2015 19/06/2015 1 5G new service capabilities User experience continuity in challenging situations such as high mobility
Social Data Mining through Distributed Mobile Sensing: A Position Paper
 Social Data Mining through Distributed Mobile Sensing: A Position Paper John Gekas, Eurobank Research, Athens, GR Abstract. In this article, we present a distributed framework for collecting and analyzing
Social Data Mining through Distributed Mobile Sensing: A Position Paper John Gekas, Eurobank Research, Athens, GR Abstract. In this article, we present a distributed framework for collecting and analyzing
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 1: Introduction to Mobile Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo About Me In this course The course will include aspects related to general understanding of Mobile and ubiquitous
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 1: Introduction to Mobile Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo About Me In this course The course will include aspects related to general understanding of Mobile and ubiquitous
Enabling Modern Telecommunications Services via Internet Protocol and Satellite Technology Presented to PTC'04, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA
 CASE STUDY Enabling Modern Telecommunications Services via Internet Protocol and Satellite Technology Presented to PTC'04, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA Stephen Yablonski and Steven Spreizer Globecomm Systems,
CASE STUDY Enabling Modern Telecommunications Services via Internet Protocol and Satellite Technology Presented to PTC'04, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA Stephen Yablonski and Steven Spreizer Globecomm Systems,
Real Time Network Server Monitoring using Smartphone with Dynamic Load Balancing
 www.ijcsi.org 227 Real Time Network Server Monitoring using Smartphone with Dynamic Load Balancing Dhuha Basheer Abdullah 1, Zeena Abdulgafar Thanoon 2, 1 Computer Science Department, Mosul University,
www.ijcsi.org 227 Real Time Network Server Monitoring using Smartphone with Dynamic Load Balancing Dhuha Basheer Abdullah 1, Zeena Abdulgafar Thanoon 2, 1 Computer Science Department, Mosul University,
www.wipro.com ACCOMMODATING IOT / M2M REQUIREMENTS IN THE CELLULAR ECOSYSTEM Mahendra Agarwal Architect, Wipro Tecnologies
 www.wipro.com ACCOMMODATING IOT / M2M REQUIREMENTS IN THE CELLULAR ECOSYSTEM Mahendra Agarwal Architect, Wipro Tecnologies Table of Contents Abstract... 03 What s new in Cellular Technology?... 03 Device
www.wipro.com ACCOMMODATING IOT / M2M REQUIREMENTS IN THE CELLULAR ECOSYSTEM Mahendra Agarwal Architect, Wipro Tecnologies Table of Contents Abstract... 03 What s new in Cellular Technology?... 03 Device
Is Your Network Ready for VoIP? > White Paper
 > White Paper Tough Questions, Honest Answers For many years, voice over IP (VoIP) has held the promise of enabling the next generation of voice communications within the enterprise. Unfortunately, its
> White Paper Tough Questions, Honest Answers For many years, voice over IP (VoIP) has held the promise of enabling the next generation of voice communications within the enterprise. Unfortunately, its
Considerations when Implementing Cloud Based Document Management
 Considerations when Implementing 2013 Square 9 Softworks All rights Reserved The copyright for all material provided herein is held by Square 9 Softworks. None of the material may be copied, reproduced,
Considerations when Implementing 2013 Square 9 Softworks All rights Reserved The copyright for all material provided herein is held by Square 9 Softworks. None of the material may be copied, reproduced,
How To Understand The Power Of The Internet Of Things
 Next Internet Evolution: Getting Big Data insights from the Internet of Things Internet of things are fast becoming broadly accepted in the world of computing and they should be. Advances in Cloud computing,
Next Internet Evolution: Getting Big Data insights from the Internet of Things Internet of things are fast becoming broadly accepted in the world of computing and they should be. Advances in Cloud computing,
Profiting from the Rise of Wi-Fi
 Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG) Cisco IBSG 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Profiting from the Rise of Wi-Fi New, Innovative Business Models for Service Providers Authors
Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG) Cisco IBSG 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Profiting from the Rise of Wi-Fi New, Innovative Business Models for Service Providers Authors
Computer-Aided Disaster Recovery Planning Tools (CADRP)
 Computer-Aided Disaster Recovery Planning Tools (CADRP) Omar H. Alhazmi Department of Computer Science Taibah University Medina, Saudi Arabia ohhazmi@taibahu.edu.sa Abstract Information Technology Disaster
Computer-Aided Disaster Recovery Planning Tools (CADRP) Omar H. Alhazmi Department of Computer Science Taibah University Medina, Saudi Arabia ohhazmi@taibahu.edu.sa Abstract Information Technology Disaster
Mobile Commerce and Ubiquitous Computing. Chapter 6
 Mobile Commerce and Ubiquitous Computing Chapter 6 Learning Objectives 1. Discuss the value-added attributes, benefits, and fundamental drivers of m-commerce. 2. Describe the mobile computing infrastructure
Mobile Commerce and Ubiquitous Computing Chapter 6 Learning Objectives 1. Discuss the value-added attributes, benefits, and fundamental drivers of m-commerce. 2. Describe the mobile computing infrastructure
Best Practices in Enterprise Smartphone Development
 Best Practices in Enterprise Smartphone Development Rhomobile White Paper This white paper was written by Adam Blum, Founder and CEO of Rhomobile 12/16/2010 Best Practices in Enterprise Smartphone Development
Best Practices in Enterprise Smartphone Development Rhomobile White Paper This white paper was written by Adam Blum, Founder and CEO of Rhomobile 12/16/2010 Best Practices in Enterprise Smartphone Development
HTML5 : carrier grade
 HTML5 : carrier grade Alex Rutgers / CTO@Momac / February 2013. Introduction Since HTML5 became mainstream media around April 2010 and I decided to create an overview article on HTML5 in the mobile space,
HTML5 : carrier grade Alex Rutgers / CTO@Momac / February 2013. Introduction Since HTML5 became mainstream media around April 2010 and I decided to create an overview article on HTML5 in the mobile space,
Accelerating Cloud Based Services
 Accelerating Cloud Based Services A White Paper February 2011 1.1 Replify 2011 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 The Network a Barrier to Cloud Adoption... 4 Current Solutions...
Accelerating Cloud Based Services A White Paper February 2011 1.1 Replify 2011 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 The Network a Barrier to Cloud Adoption... 4 Current Solutions...
1 Executive Summary... 3. 2 Document Structure... 5. 3 Business Context... 6
 Contents 1 Executive Summary... 3 2 Document Structure... 5 3 Business Context... 6 4 Strategic Response... 8 4.1 Platform... 8 4.2 Network... 10 4.3 Unified Communications... 11 5 Implementation status...
Contents 1 Executive Summary... 3 2 Document Structure... 5 3 Business Context... 6 4 Strategic Response... 8 4.1 Platform... 8 4.2 Network... 10 4.3 Unified Communications... 11 5 Implementation status...
Intelligent Systems for Health Solutions
 Bringing People, Systems, and Information Together Today s health organizations are increasingly challenged to accomplish what we call the triple aim of effective healthcare: deliver higher quality care
Bringing People, Systems, and Information Together Today s health organizations are increasingly challenged to accomplish what we call the triple aim of effective healthcare: deliver higher quality care
Operating from the middle of the digital economy: Integrated Digital Service Providers. By Ed Bae, Sumit Banerjee and Tom Loozen
 Operating from the middle of the digital economy: Integrated Digital Service Providers By Ed Bae, Sumit Banerjee and Tom Loozen 2 Operating from the middle of the digital economy: Integrated Digital Service
Operating from the middle of the digital economy: Integrated Digital Service Providers By Ed Bae, Sumit Banerjee and Tom Loozen 2 Operating from the middle of the digital economy: Integrated Digital Service
Why Choose Desktop as a Service (DaaS)? A TCO Study
 Why Choose Desktop as a Service (DaaS)? A TCO Study by Warning: reading and acting on the advice in this document could save you 25% of your current desktop service delivery costs Introduction Physical
Why Choose Desktop as a Service (DaaS)? A TCO Study by Warning: reading and acting on the advice in this document could save you 25% of your current desktop service delivery costs Introduction Physical
The Value of a Content Delivery Network
 September 2010 White Paper The Value of a Content Delivery Network Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Performance... 3 The Second Generation of CDNs... 6 Conclusion... 7 About NTT America... 8 Introduction
September 2010 White Paper The Value of a Content Delivery Network Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Performance... 3 The Second Generation of CDNs... 6 Conclusion... 7 About NTT America... 8 Introduction
FutureWorks 5G use cases and requirements
 Nokia Networks FutureWorks 5G use cases and requirements White paper - 5G Use Cases and Requirements CONTENTS 1. What 5G will be and why it will come 3 2. Use cases 6 2.1 Mobile broadband 6 2.2 Automotive
Nokia Networks FutureWorks 5G use cases and requirements White paper - 5G Use Cases and Requirements CONTENTS 1. What 5G will be and why it will come 3 2. Use cases 6 2.1 Mobile broadband 6 2.2 Automotive
Device-centric Code is deployed to individual devices, mostly preprovisioned
 Programming Device Ensembles in the Web of Things A Position Paper for the W3C Workshop on the Web of Things Matias Cuenca, Marcelo Da Cruz, Ricardo Morin Intel Services Division (ISD), Software and Services
Programming Device Ensembles in the Web of Things A Position Paper for the W3C Workshop on the Web of Things Matias Cuenca, Marcelo Da Cruz, Ricardo Morin Intel Services Division (ISD), Software and Services
www.rackwareinc.com RackWare Solutions Disaster Recovery
 RackWare Solutions Disaster Recovery RackWare Solutions Disaster Recovery Overview Business Continuance via Disaster Recovery is an essential element of IT and takes on many forms. The high end consists
RackWare Solutions Disaster Recovery RackWare Solutions Disaster Recovery Overview Business Continuance via Disaster Recovery is an essential element of IT and takes on many forms. The high end consists
DATA SYNCHRONIZATION ON MOBILE DEVICES
 JUNE 16, 2015 FINAL BACHELOR PROJECT AT UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NORTHERN DENMARK SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT DATA SYNCHRONIZATION ON MOBILE DEVICES UNDER THE SUPERVISION OF MOGENS HOLM IVERSEN ZLATIMIR ZAHARIEV
JUNE 16, 2015 FINAL BACHELOR PROJECT AT UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NORTHERN DENMARK SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT DATA SYNCHRONIZATION ON MOBILE DEVICES UNDER THE SUPERVISION OF MOGENS HOLM IVERSEN ZLATIMIR ZAHARIEV
