MAP GENERALIZATION FOR OSMASTERMAP DATA IN LOCATION BASED SERVICES & MOBILE GIS APPLICATIONS
|
|
|
- Dayna Parker
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geoinformatics 2004 Proc. 12th Int. Conf. on Geoinformatics Geospatial Information Research: Bridging the Pacific and Atlantic University of Gävle, Sweden, 7-9 June 2004 MAP GENERALIZATION FOR OSMASTERMAP DATA IN LOCATION BASED SERVICES & MOBILE GIS APPLICATIONS 54 S. Anand 1, J.M. Ware 2 and G.E. Taylor 3 University of Glamorgan, Wales CF37 1DL 1 [email protected], 2 [email protected], 3 [email protected] Abstract This paper looks at how previous solutions to graphic conflict reduction can be adapted and applied to production of schematic maps suitable for MobileGIS applications. Map generalization is the process by which small scale maps are to be derived from large scale maps. With the advent of high-end miniature technology as well as digital geographic data products like OSMasterMap it is essential to devise proper methodologies for map generalization specifically tailored for mobile GIS applications. This paper is concerned with the problem of producing schematic maps suitable for rendering on Mobile GIS display devices (e.g. PDAs). Schematic maps are a diagrammatic representation based on linear abstractions of networks. Transportation networks are the key candidates for applying schematization to help ease the interpretation of information by the process of cartographic abstraction. Schematic maps are built-up from sketches which usually have a close resemblance to verbal descriptions about spatial features. It is desirable to devise suitable generalization techniques for generating schematic maps from large scale datasets for display on small display devices to be used for Mobile GIS applications. INTRODUCTION Map generalization is the process by which small scale maps are derived from large scale maps. This requires the application of operations such as simplification, selection, displacement and amalgamation to map features subsequent to scale reduction (Ware and Jones, 1998). With the advent of high-end miniature technology as well as digital geographic data products like OSMasterMap it is desirable to devise proper methodology for map generalization specifically tailored for mobile GIS applications. The need for understanding and applying cartographic principles suitable for MobileGIS using small display devices is the underlying theme of the study. The main characteristic of these devices is that they have relatively small display areas. This compounded with the need to display map data at scales smaller than its source scale, gives rise to the possibility of graphic conflict. Also scale reduction will often require certain important features for example roads to be exaggerated in size, leading in some cases to overlapping of features. In short it necessitates the need for developing map generalization techniques suitable for Mobile GIS applications. The study is focused on finding suitable map generalization techniques to enable OSMasterMap data to be displayed at different scales with the least graphic conflict of features on small screen display devices. It is intended to further apply the same principle for developing schematic maps for transportation networks using OSCAR dataset that can be used for route finding applications by Mobile GIS users.
2 Map generalization for OSMasterMap data in LBS & mobile GIS applications MOBLIE GIS & LOCATION BASED SERVICES MobileGIS is a relatively new technology but with the arrival of high bandwidth mobile networks its application potential has increased tremendously. There is a huge amount of available geographic information which can be re-purposed for mobile GIS application. This coupled with the ability to filter and personalize content by reference to a user's physical location will provide compelling business opportunities, which can be useful for consumers as well as saving money for businesses through improved efficiencies. Mobile GIS refers to the use of geographic data in the field on mobile devices such as networked Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs). The main components for Mobile GIS are a global positioning system (GPS), a handheld computer (e.g. a PDA) and a communication network, with GIS acting as the backbone (Figure 1). Figure 1: The basic components essential for Mobile GIS application. Location Based Services (LBS) refers to the infrastructure needed to provide various services to a user based on the user s location. LBS applications act according to a geographic trigger like input of a place name, postcode, position of a GPS user, location information from mobile phone network etc. BACKGROUND OF RESEARCH Ordnance Survey through the introduction of OSMasterMap has now made possible a digital map database of UK. With the large scale use and application of mobile devices it is now possible to deliver digital geographic information for mobile GIS applications. The need to deliver the required map information on small display screens of device necessitates the application of appropriate map generalization techniques that are specifically tailored for this purpose. The OS MasterMap data has no scale and features are digital representations of the world. All real world objects are represented as explicit features and each is identified by a unique TOID (Topological Identifier). The attributes will include a survey accuracy ranging from ±1.0 m in urban areas to ±8.0 m in mountain and moorland areas. However, the initial data has been derived from large-scale mapping and the accuracy and resolution of geometry derived from that mapping (Ordnance Survey, 2003). Though the OSMasterMap data should therefore be appropriate for display at 1:1250, 1:2500 and 1:10,000 scales in urban, 55
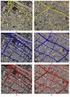
3 S. Anand, J.M. Ware and G.E. Taylor rural and mountain/moorland areas, the practical applicability for small screen devices specifically for LBS is to be verified and optimised to tailor the need. MAP GENERALIZATION ISSUES UNIQUE TO MOBILE DEVICES To understand the unique issues related to generalizing maps for display on small display screen devices it is important to look into the specifications of PDA s and tailor the solutions to suit the need. With the current specification of PDA's available in the market having processing power, memory capacity, screen resolution and display size very much less than PCs, there is a marked difference between the map generalization requirements for display on a typical desktop PC and that of a PDA. The processing capability of PDAs is in the range of 400 MHz.This implies that processor intensive operations like on the fly map generalization need performed on a server and only the final output be transferred for display on the PDA screen. The memory technology of PDA s is range of 64 MB. This highlights the issue associated with storing large-scale voluminous datasets like OSMasterMap (in Gigabytes) in the limited memory space of PDA s. The screen resolution of 240 x 320 pixels of low display resolution of PDA screens makes it necessary to render the final output image based on the generalization carried out as per the small display cartographic specification developed to give maximum clarity and readability. Various tests have been carried out to verify the specification developed. For visual proof see Figure 2 where the image on the left explicitly shows the graphic conflicts between roads and building features at 1:10000 scale rendered without applying specification guidelines and the image on the right rendered as per the map specification guidelines for 1:5000 scale which shows lesser spatial conflicts and better clarity. Figure 2: Figures show OSMasterMap data displayed in a HP ipaq PocketPC h5400 series using ESRI s ArcPad. The image on the left depicting the display in 1:10000 scale explicitly showing spatial conflicts between roads and building features and image on the right displayed at the map specification guidelines for 1:5000 scale. 56
4 Map generalization for OSMasterMap data in LBS & mobile GIS applications A display size of 50 cm 2 for PDA screens necessitates that map images are produced and optimised for that size. Most contemporary PDAs are network enabled to handle network connectivity ranging from 9.6 KB cellular connections to 11 MB Wireless LANs. Considering the rate of technological advance, the rate at which network bandwidths are increasing is faster than the rate at which the processing power and storage capacity are increasing. This is encouraging trend for map generalization in MobileGIS applications as it will mean that the processor and storage intensive operations can be handled by the server and final output be transferred to be rendered on the mobile device effectively due to availability of higher network bandwidth. In short PDAs have different form factors such as display resolution, varying numbers of display lines, horizontal or vertical screen orientation and hardware specification when compared to PCs. Hence mobile GIS applications that are specific to PDAs need to be suitably tailored for the requirements of the same. The application of suitable automated map generalization techniques will help in faster and more efficient rendering of maps in small screen display devices as well as filtering redundant data, thereby optimising data transmission in networks and thereby lowering costs DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL DISPLAY MAP SPECIFICATION For verifying the suitability of OSMaster map data for small screen devices, the data for the St. David s area in Wales was loaded on ESRI s ArcPad and tested in a HP ipaq PocketPC h5400 series for display at various scales to find out the extent of spatial conflicts between features. The initial research concentrated on developing cartographic specification for OSMasterMap data suitable for small screen devices, with tests being carried out on a wide range of display scales (Figure 3). Finally scale ranges of 1:2500, 1:5000 and 1:10000 were selected as most appropriate for MobileGIS applications. Figure 3: Example small display cartographic specification developed It was found that there is graphic conflict between features likes roads and buildings during scale reduction (Figure 2) and since the display screen is comparatively of small size the 57
5 S. Anand, J.M. Ware and G.E. Taylor problem becomes much more apparent than when compared for desktop devices. Work has already been done by using simulated annealing to reduce the degree of spatial conflict in desktop systems using GIS. The simulated annealing algorithm which controls operations of displacement, deletion, reduction and enlargement of multiple map objects to help resolve spatial conflict arising due to scale reduction (Ware and Jones, 1998; Ware et al., 2001). It is proposed to further the work in applying Simulated Annealing techniques in map generalization and apply it for the delivery of geographic information for MobileGIS applications (Anand and Ware, 2003). SCHEMATIC MAPS A schematic map is a diagrammatic representation based on linear abstractions of networks. Typically transportation networks are the key candidates for applying schematization to help ease the interpretation of information by the process of cartographic abstraction. Schematic maps are built-up from sketches which usually have close resemblance with verbal descriptions about spatial features (Avelar, 2002) To understand the theory behind schematization process it is important to know the principles of cartographic abstraction that are applied in the process. Figure 4 tries to diagrammatically represent the series of processes of abstraction that take place when the dataset (e.g. OSMasterMap) is to be used for producing suitable LBS Maps. The figure depicting the transformational view of the process of map schematization is extended from the transformational view of cartography (Tobler, 1979; Robinson et al., 1995). Map generalization operators such as selection, classification, simplification, exaggeration, symbolization are applied on the source dataset as per the small display cartographic specification to produce the final LBS map. Surveying Techniques Applying cartographic generalization techniques User interpretation Real World Dataset (OSMasterMap) Generalized LBS Map User s mental image Figure 4: Transformational view of the process of map schematization (extended from the transformational view of cartography Tobler, 1979, and Robinson et al., 1995). KEY GENERALIZATION PROCESSES FOR SCHEMATIC MAPS Key generalizing processes for generating schematic maps is to eliminate all features and networks (or portions of network) that are not functionally relevant. Also all geometric invariants of the network's structure are relaxed except topological accuracy (Elroi, 1988). When generating schematic maps from large scale datasets like OSMasterMap the basic 58
6 Map generalization for OSMasterMap data in LBS & mobile GIS applications user inputs are the initial and final destinations. Based on this the system will have to generate an appropriate schematic map depicting the turning point information with turning directions coupled preferably with map labels for each road and the distance to be traveled in that road. Also if PoI (Points of Interest) dataset is available the local landmarks on the route can also be displayed as a means of enhancing navigation. This is especially important if the system is to be used for generating tourist maps. Also by enabling different levels of schematic maps of the same region the global properties of the route can be conveyed to the user. This acts much like the Zoom In- Zoom Out functionality. The generalization operators that come into play in generating schematic maps are: Length generalization - It is necessary to exaggerate the lengths of shorter roads while shortening longer roads to enable all roads and turning points to be made visible. That is, relative scaling has to be performed to fit road lengths of different orders of magnitude to fit within a small display screen of device like PDA; Shape generalization - Line simplification algorithms like Douglas Peucker algorithm can be applied to road datasets to remove unwanted detail and produce a simplified version of the network. This not only reduces avoidable clutter but also makes tasks such as line labeling more straightforward; Angle generalization - Very often the exact turning angle in not the criterical but the turning directions are. So angular distortions are acceptable while generalizing content for schematic maps. Turn directions should preferably be one of N, S, E, W, SE, SW, NE and NW (at 45 degrees) since people are more easily relate to these representations of angular measurements; Graphic generalization - Colour coding, using different display styles for the point, line, area features etc enhance readability of the generated schematic map as well as improving usability. Other factors that need to be taken into consideration are fixing the aspect ratio of the resulting image to make the effective use of map space when trying to fit and display on a small screen display device of 240 x 320 pixel resolution. Enabling support for vertical and horizontal scrolling will add more flexibility to the user (Agrawala, 2001). Another possibility is to divide the map into steps and display each step separately on the screen. This method is especially useful when the area to be covered becomes large and there is a lot of competition among the various features for the very limited display space CONCLUSION The research proves conclusively the need for developing specific map generalization algorithms for data products like OSMasterMap if intended to be applied for Mobile GIS applications using small screen display devices. Mobile applications using small screen display devices derive benefits of generalization for helping in rendering relevant information legible at a given scale by enhancing the visualization of the large-scale data on small screen display devices and providing essential information for each group of users e.g. tourists, utilities etc. A development of cartographic specification for OSMasterMap suitable for small display cartography has been carried out and various tests performed. The optimal scale ranges and 59
7 S. Anand, J.M. Ware and G.E. Taylor the symbolization suited for the different feature classes in each of the scale ranges were arrived at via experimentation. Graphic conflict between feature classes at the specified scale ranges are to be dealt with by applying simulated annealing technique. It is intended to further apply the same principle for developing schematic maps of road features using OSCAR data for mobile GIS users. It is very important to devise suitable generalization techniques for generating schematic maps from large scale datasets like OSMasterMap for display on small display devices to be used for location based services. By including Points of Interest datasets linked to OSMasterMap along with road datasets (OSCAR) will help create powerful location based services that are particularly tailored for tourism applications. REFERENCES Agrawala, M., 2001: Visualizing Route Maps, PhD Dissertation, Stanford University. Anand, S. and Ware, J.M., 2003: Map Generalization for Automatic Derivation of Location Based Service Maps. Royal Geographic Society. Avelar, S., 2002: Schematic Maps On Demand: Design, Modeling and Visualization. PhD Dissertation, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology. Elroi, D.S., 1988: Designing a network linemap schematization software enhancement package, Proceedings of the Eighth Annual ESRI User Conference, Redlands. Ordnance Survey, 2003: OSMasterMap Technical Information co.uk/products/smastermap/pdf/v4userguidep1.pdf. Robinson, A., Morrison, J., Muehrcke, P., Kimmerling, A. and Guptill, S., 1995: Elements of Cartography. Wiley. Tobler, W., 1979: A transformational view of cartography. The American Cartographer. Ware, J.M. and Jones, C.B., 1998: Conflict reduction in map generalization using iterative improvement. GeoInformatica2:4. Ware, J.M., Jones, C.B. and Thomas, N., 2001: Map generalization, object displacement and simulated annealing: two techniques for execution time improvement. Proceedings of GIS Research UK 2001 Conference (GISRUK 01). 60
REAL-TIME DATA GENERALISATION AND INTEGRATION USING JAVA
 REAL-TIME DATA GENERALISATION AND INTEGRATION USING JAVA Lars Harrie and Mikael Johansson National Land Survey of Sweden SE-801 82 Gävle [email protected], [email protected] KEY WORDS:
REAL-TIME DATA GENERALISATION AND INTEGRATION USING JAVA Lars Harrie and Mikael Johansson National Land Survey of Sweden SE-801 82 Gävle [email protected], [email protected] KEY WORDS:
3D Maps for Boat Tourists
 3D Maps for Boat Tourists Volker Coors a Ove Gjesdal b Jan Rasmus Sulebak b Katri Lakso c a Fraunhofer Institut for Computer Graphics, Germany HfT Stuttgart, University of Applied Sciences, Germany [email protected]
3D Maps for Boat Tourists Volker Coors a Ove Gjesdal b Jan Rasmus Sulebak b Katri Lakso c a Fraunhofer Institut for Computer Graphics, Germany HfT Stuttgart, University of Applied Sciences, Germany [email protected]
A MOBILE GIS APPLICATION FOR HEAVILY RESOURCE-CONSTRAINED DEVICES
 A MOBILE GIS APPLICATION FOR HEAVILY RESOURCE-CONSTRAINED DEVICES Robert P. Biuk-Aghai Faculty of Science and Technology University of Macau P.O. Box 3001 Macau S.A.R., China Phone: (+853) 3974365 Fax:
A MOBILE GIS APPLICATION FOR HEAVILY RESOURCE-CONSTRAINED DEVICES Robert P. Biuk-Aghai Faculty of Science and Technology University of Macau P.O. Box 3001 Macau S.A.R., China Phone: (+853) 3974365 Fax:
MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY ON MANSOURA UNIVERSITY, EGYPT
 MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY ON MANSOURA UNIVERSITY, EGYPT Asmaa Ahmed Hussein 1, Elkhedr Hassan Eibrahim 2, Aziza Asem 1 1 Faculty of Computer Sciences and information systems,
MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY ON MANSOURA UNIVERSITY, EGYPT Asmaa Ahmed Hussein 1, Elkhedr Hassan Eibrahim 2, Aziza Asem 1 1 Faculty of Computer Sciences and information systems,
GEO-VISUALIZATION SUPPORT FOR MULTIDIMENSIONAL CLUSTERING
 Geoinformatics 2004 Proc. 12th Int. Conf. on Geoinformatics Geospatial Information Research: Bridging the Pacific and Atlantic University of Gävle, Sweden, 7-9 June 2004 GEO-VISUALIZATION SUPPORT FOR MULTIDIMENSIONAL
Geoinformatics 2004 Proc. 12th Int. Conf. on Geoinformatics Geospatial Information Research: Bridging the Pacific and Atlantic University of Gävle, Sweden, 7-9 June 2004 GEO-VISUALIZATION SUPPORT FOR MULTIDIMENSIONAL
Parallel Visualization for GIS Applications
 Parallel Visualization for GIS Applications Alexandre Sorokine, Jamison Daniel, Cheng Liu Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Geographic Information Science & Technology, PO Box 2008 MS 6017, Oak Ridge National
Parallel Visualization for GIS Applications Alexandre Sorokine, Jamison Daniel, Cheng Liu Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Geographic Information Science & Technology, PO Box 2008 MS 6017, Oak Ridge National
DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7
 DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7 Contents GIS and maps The visualization process Visualization and strategies
DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7 Contents GIS and maps The visualization process Visualization and strategies
Introduction to ArcPad: Mobile GIS. Originally prepared by Gregory Vandeberg, Ph.D. Department of Geography
 Introduction to ArcPad: Mobile GIS Originally prepared by Gregory Vandeberg, Ph.D. Department of Geography Outline Introduction What is ArcPad? What can you do with ArcPad? What do you need to run it?
Introduction to ArcPad: Mobile GIS Originally prepared by Gregory Vandeberg, Ph.D. Department of Geography Outline Introduction What is ArcPad? What can you do with ArcPad? What do you need to run it?
The automatic generalization of buildings whilst maintaining the settlement structure. A case study based on the 1:50`000 Swiss National Map Series
 The automatic generalization of buildings whilst maintaining the settlement structure A case study based on the 1:50`000 Swiss National Map Series Anna Vetter 05.12.2014 The Structure 1. Introduction 2.
The automatic generalization of buildings whilst maintaining the settlement structure A case study based on the 1:50`000 Swiss National Map Series Anna Vetter 05.12.2014 The Structure 1. Introduction 2.
Multiresolution 3D Rendering on Mobile Devices
 Multiresolution 3D Rendering on Mobile Devices Javier Lluch, Rafa Gaitán, Miguel Escrivá, and Emilio Camahort Computer Graphics Section Departament of Computer Science Polytechnic University of Valencia
Multiresolution 3D Rendering on Mobile Devices Javier Lluch, Rafa Gaitán, Miguel Escrivá, and Emilio Camahort Computer Graphics Section Departament of Computer Science Polytechnic University of Valencia
Visual Interfaces for Geographic Data
 Visual Interfaces for Geographic Data Robert Laurini, INSA-Lyon, http://liris.insa-lyon.fr/robert.laurini SYNONYMS Cartography, Visualizing spatial data, interactive capture, interactive layout DEFINITION
Visual Interfaces for Geographic Data Robert Laurini, INSA-Lyon, http://liris.insa-lyon.fr/robert.laurini SYNONYMS Cartography, Visualizing spatial data, interactive capture, interactive layout DEFINITION
Future Landscapes. Research report CONTENTS. June 2005
 Future Landscapes Research report June 2005 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Original ideas for the project 3. The Future Landscapes prototype 4. Early usability trials 5. Reflections on first phases of development
Future Landscapes Research report June 2005 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Original ideas for the project 3. The Future Landscapes prototype 4. Early usability trials 5. Reflections on first phases of development
An ESRI White Paper May 2007 Mobile GIS for Homeland Security
 An ESRI White Paper May 2007 Mobile GIS for Homeland Security ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100 USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL [email protected] WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2007 ESRI
An ESRI White Paper May 2007 Mobile GIS for Homeland Security ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100 USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL [email protected] WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2007 ESRI
AN ONTOLOGY BASED APPROACH FOR GEOSPATIAL DATA INTEGRATION OF AUTHORITATIVE AND CROWD SOURCED DATASETS
 CO-118 AN ONTOLOGY BASED APPROACH FOR GEOSPATIAL DATA INTEGRATION OF AUTHORITATIVE AND CROWD SOURCED DATASETS DU H.(1), JIANG W.(1), ANAND S.(1), MORLEY J.(1), HART G.(2), LEIBOVICI D.(1), JACKSON M.(1)
CO-118 AN ONTOLOGY BASED APPROACH FOR GEOSPATIAL DATA INTEGRATION OF AUTHORITATIVE AND CROWD SOURCED DATASETS DU H.(1), JIANG W.(1), ANAND S.(1), MORLEY J.(1), HART G.(2), LEIBOVICI D.(1), JACKSON M.(1)
Principles and Practices of Data Integration
 Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
Managing a Geographic Database From Mobile Devices Through OGC Web Services
 Managing a Geographic Database From Mobile Devices Through OGC Web Services Nieves R. Brisaboa 1, Miguel R. Luaces 1, Jose R. Parama 1, and Jose R. Viqueira 2 1 Database Laboratory, University of A Coruña,
Managing a Geographic Database From Mobile Devices Through OGC Web Services Nieves R. Brisaboa 1, Miguel R. Luaces 1, Jose R. Parama 1, and Jose R. Viqueira 2 1 Database Laboratory, University of A Coruña,
Build Panoramas on Android Phones
 Build Panoramas on Android Phones Tao Chu, Bowen Meng, Zixuan Wang Stanford University, Stanford CA Abstract The purpose of this work is to implement panorama stitching from a sequence of photos taken
Build Panoramas on Android Phones Tao Chu, Bowen Meng, Zixuan Wang Stanford University, Stanford CA Abstract The purpose of this work is to implement panorama stitching from a sequence of photos taken
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION GIS Syllabus - Version 1.2 January 2007 Copyright AICA-CEPIS 2009 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION GIS Syllabus - Version 1.2 January 2007 Copyright AICA-CEPIS 2009 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed
ArcGIS Data Models Practical Templates for Implementing GIS Projects
 ArcGIS Data Models Practical Templates for Implementing GIS Projects GIS Database Design According to C.J. Date (1995), database design deals with the logical representation of data in a database. The
ArcGIS Data Models Practical Templates for Implementing GIS Projects GIS Database Design According to C.J. Date (1995), database design deals with the logical representation of data in a database. The
Applications of Dynamic Representation Technologies in Multimedia Electronic Map
 Applications of Dynamic Representation Technologies in Multimedia Electronic Map WU Guofeng CAI Zhongliang DU Qingyun LONG Yi (School of Resources and Environment Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei.
Applications of Dynamic Representation Technologies in Multimedia Electronic Map WU Guofeng CAI Zhongliang DU Qingyun LONG Yi (School of Resources and Environment Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei.
Geovisualization. Geovisualization, cartographic transformation, cartograms, dasymetric maps, scientific visualization (ViSC), PPGIS
 13 Geovisualization OVERVIEW Using techniques of geovisualization, GIS provides a far richer and more flexible medium for portraying attribute distributions than the paper mapping which is covered in Chapter
13 Geovisualization OVERVIEW Using techniques of geovisualization, GIS provides a far richer and more flexible medium for portraying attribute distributions than the paper mapping which is covered in Chapter
A HYBRID APPROACH FOR AUTOMATED AREA AGGREGATION
 A HYBRID APPROACH FOR AUTOMATED AREA AGGREGATION Zeshen Wang ESRI 380 NewYork Street Redlands CA 92373 [email protected] ABSTRACT Automated area aggregation, which is widely needed for mapping both natural
A HYBRID APPROACH FOR AUTOMATED AREA AGGREGATION Zeshen Wang ESRI 380 NewYork Street Redlands CA 92373 [email protected] ABSTRACT Automated area aggregation, which is widely needed for mapping both natural
A System for Capturing High Resolution Images
 A System for Capturing High Resolution Images G.Voyatzis, G.Angelopoulos, A.Bors and I.Pitas Department of Informatics University of Thessaloniki BOX 451, 54006 Thessaloniki GREECE e-mail: [email protected]
A System for Capturing High Resolution Images G.Voyatzis, G.Angelopoulos, A.Bors and I.Pitas Department of Informatics University of Thessaloniki BOX 451, 54006 Thessaloniki GREECE e-mail: [email protected]
SCALABILITY OF CONTEXTUAL GENERALIZATION PROCESSING USING PARTITIONING AND PARALLELIZATION. Marc-Olivier Briat, Jean-Luc Monnot, Edith M.
 SCALABILITY OF CONTEXTUAL GENERALIZATION PROCESSING USING PARTITIONING AND PARALLELIZATION Abstract Marc-Olivier Briat, Jean-Luc Monnot, Edith M. Punt Esri, Redlands, California, USA [email protected], [email protected],
SCALABILITY OF CONTEXTUAL GENERALIZATION PROCESSING USING PARTITIONING AND PARALLELIZATION Abstract Marc-Olivier Briat, Jean-Luc Monnot, Edith M. Punt Esri, Redlands, California, USA [email protected], [email protected],
Interactive 3D Visualization As A Tool For Construction Education
 Interactive 3D Visualization As A Tool For Construction Education Dr. Jose L. Perdomo 1, Mohd.Fairuz Shiratuddin 2, Dr. Walid Thabet 3, and Ashwin Ananth 4 Abstract - Throughout the years, various teaching
Interactive 3D Visualization As A Tool For Construction Education Dr. Jose L. Perdomo 1, Mohd.Fairuz Shiratuddin 2, Dr. Walid Thabet 3, and Ashwin Ananth 4 Abstract - Throughout the years, various teaching
Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies. 13 th May 2004. Content. What is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies 13 th May 2004 Content Introduction to GIS Data concepts Data input Analysis Applications selected examples What is GIS? Geographic Information
Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies 13 th May 2004 Content Introduction to GIS Data concepts Data input Analysis Applications selected examples What is GIS? Geographic Information
Trace Desktop Workforce / Fleet Management System
 Trace Desktop Workforce / Fleet Management System Introduction TRACE is an extension of SD s Geographical Information System (SPACE) which incorporates a range of GPS tracking devices that enable users
Trace Desktop Workforce / Fleet Management System Introduction TRACE is an extension of SD s Geographical Information System (SPACE) which incorporates a range of GPS tracking devices that enable users
Automated generalisation of land cover data in a planar topographic map
 14 th Workshop of the ICA commission on Generalisation and Multiple Representation 30 th of June and 1 st of July, Paris Automated generalisation of land cover data in a planar topographic map John van
14 th Workshop of the ICA commission on Generalisation and Multiple Representation 30 th of June and 1 st of July, Paris Automated generalisation of land cover data in a planar topographic map John van
VISUALIZATION OF GEOSPATIAL METADATA FOR SELECTING GEOGRAPHIC DATASETS
 Helsinki University of Technology Publications in Cartography and Geoinformatics Teknillisen korkeakoulun kartografian ja geoinformatiikan julkaisuja Espoo 2005 TKK-ICG-6 VISUALIZATION OF GEOSPATIAL METADATA
Helsinki University of Technology Publications in Cartography and Geoinformatics Teknillisen korkeakoulun kartografian ja geoinformatiikan julkaisuja Espoo 2005 TKK-ICG-6 VISUALIZATION OF GEOSPATIAL METADATA
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION OVERVIEW OF POSTGRESQL AND POSTGIS SESUG 2012. Paper RI-14
 SESUG 2012 Paper RI-14 Creating a Heatmap Visualization of 150 Million GPS Points on Roadway Maps via SAS Shih-Ching Wu, Virginia Tech Transportation Institute, Blacksburg, Virginia Shane McLaughlin, Virginia
SESUG 2012 Paper RI-14 Creating a Heatmap Visualization of 150 Million GPS Points on Roadway Maps via SAS Shih-Ching Wu, Virginia Tech Transportation Institute, Blacksburg, Virginia Shane McLaughlin, Virginia
Storage Guardian Remote Backup Restore and Archive Services
 Storage Guardian Remote Backup Restore and Archive Services Storage Guardian is the unique alternative to traditional backup methods, replacing conventional tapebased backup systems with a fully automated,
Storage Guardian Remote Backup Restore and Archive Services Storage Guardian is the unique alternative to traditional backup methods, replacing conventional tapebased backup systems with a fully automated,
Design and Deployment of Specialized Visualizations for Weather-Sensitive Electric Distribution Operations
 Fourth Symposium on Policy and Socio-Economic Research 4.1 Design and Deployment of Specialized Visualizations for Weather-Sensitive Electric Distribution Operations Lloyd A. Treinish IBM, Yorktown Heights,
Fourth Symposium on Policy and Socio-Economic Research 4.1 Design and Deployment of Specialized Visualizations for Weather-Sensitive Electric Distribution Operations Lloyd A. Treinish IBM, Yorktown Heights,
Usability for the new PC: Mobile Devices
 Usability for the new PC: Mobile Devices By Nikhita Kumar Introduction The mobile phones that we carry with us all the time have evolved a lot with time. They have become increasingly sophisticated and
Usability for the new PC: Mobile Devices By Nikhita Kumar Introduction The mobile phones that we carry with us all the time have evolved a lot with time. They have become increasingly sophisticated and
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS
 INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
MAP PROJECTIONS AND VISUALIZATION OF NAVIGATIONAL PATHS IN ELECTRONIC CHART SYSTEMS
 MAP PROJECTIONS AND VISUALIZATION OF NAVIGATIONAL PATHS IN ELECTRONIC CHART SYSTEMS Athanasios PALLIKARIS [1] and Lysandros TSOULOS [2] [1] Associate Professor. Hellenic Naval Academy, Sea Sciences and
MAP PROJECTIONS AND VISUALIZATION OF NAVIGATIONAL PATHS IN ELECTRONIC CHART SYSTEMS Athanasios PALLIKARIS [1] and Lysandros TSOULOS [2] [1] Associate Professor. Hellenic Naval Academy, Sea Sciences and
Introduction. Mobile GIS emerged in the mid-1990s to meet the needs of field work such as surveying and utility maintenance.
 Mobile GIS Introduction With more than 6.8 billion mobile cellular subscribers, (2013), wireless communication and mobile computing have gained acceptance worldwide with speed that has surpassed many other
Mobile GIS Introduction With more than 6.8 billion mobile cellular subscribers, (2013), wireless communication and mobile computing have gained acceptance worldwide with speed that has surpassed many other
Introduction. Chapter 1
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction Robotics and automation have undergone an outstanding development in the manufacturing industry over the last decades owing to the increasing demand for higher levels of productivity
1 Chapter 1 Introduction Robotics and automation have undergone an outstanding development in the manufacturing industry over the last decades owing to the increasing demand for higher levels of productivity
SOME ASPECTS OF MOBILE GIS
 I.E. Keller, V. Dohotar, S. Naş, G. Bădescu Some Aspects of Mobile GIS SOME ASPECTS OF MOBILE GIS Iulius Eduard KELLER, phd.dipl.eng.lecturer North University Baia Mare, [email protected] Vasile DOHOTAR,
I.E. Keller, V. Dohotar, S. Naş, G. Bădescu Some Aspects of Mobile GIS SOME ASPECTS OF MOBILE GIS Iulius Eduard KELLER, phd.dipl.eng.lecturer North University Baia Mare, [email protected] Vasile DOHOTAR,
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction
 Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Intro to GIS Winter 2011. Data Visualization Part I
 Intro to GIS Winter 2011 Data Visualization Part I Cartographer Code of Ethics Always have a straightforward agenda and have a defining purpose or goal for each map Always strive to know your audience
Intro to GIS Winter 2011 Data Visualization Part I Cartographer Code of Ethics Always have a straightforward agenda and have a defining purpose or goal for each map Always strive to know your audience
TwoDog Forest Inventory Software. Complete Field to Office Forest Inventory Solution for Timber and Non-Timber Values
 TwoDog Forest Inventory Software Complete Field to Office Forest Inventory Solution for Timber and Non-Timber Values TwoDog Forest Inventory Software Complete Field to Office Forest Inventory Solution
TwoDog Forest Inventory Software Complete Field to Office Forest Inventory Solution for Timber and Non-Timber Values TwoDog Forest Inventory Software Complete Field to Office Forest Inventory Solution
An approach to data enrichment of building features using Delaunay triangulation for automatic map generalization
 An approach to data enrichment of building features using Delaunay triangulation for automatic map generalization Rupasinghe K.A.B.S 1, Allan J. Brimicombe 2, Yang Li 3 1,2,3 Centre for Geo-Information
An approach to data enrichment of building features using Delaunay triangulation for automatic map generalization Rupasinghe K.A.B.S 1, Allan J. Brimicombe 2, Yang Li 3 1,2,3 Centre for Geo-Information
Guide To Creating Academic Posters Using Microsoft PowerPoint 2010
 Guide To Creating Academic Posters Using Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 INFORMATION SERVICES Version 3.0 July 2011 Table of Contents Section 1 - Introduction... 1 Section 2 - Initial Preparation... 2 2.1 Overall
Guide To Creating Academic Posters Using Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 INFORMATION SERVICES Version 3.0 July 2011 Table of Contents Section 1 - Introduction... 1 Section 2 - Initial Preparation... 2 2.1 Overall
ArcGIS Mobile Application User s Guide
 ArcGIS Mobile Application User s Guide 1 Contents Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 2 5 5 6 7 7 8 8 11 12 14 15 19 21 22 23 37 38 ArcGIS Mobile User Interface Essentials Title Bar Menu Bar Hardware
ArcGIS Mobile Application User s Guide 1 Contents Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 2 5 5 6 7 7 8 8 11 12 14 15 19 21 22 23 37 38 ArcGIS Mobile User Interface Essentials Title Bar Menu Bar Hardware
Zorba Asset Tracking Solution
 Asset Tracking Solution State-of-the art fleet management and vehicle tracking solution to increase your productivity. Affordable installation and operating costs Easy to install and operate User friendly
Asset Tracking Solution State-of-the art fleet management and vehicle tracking solution to increase your productivity. Affordable installation and operating costs Easy to install and operate User friendly
Digital Orthophoto Production In the Desktop Environment 1
 Digital Orthophoto Production In the Desktop Environment 1 By Dr. Roy A. Welch and Thomas R. Jordan Digital orthophotos are proving suitable for a variety of mapping, GIS and environmental monitoring tasks.
Digital Orthophoto Production In the Desktop Environment 1 By Dr. Roy A. Welch and Thomas R. Jordan Digital orthophotos are proving suitable for a variety of mapping, GIS and environmental monitoring tasks.
Vector tiles for the Swiss Federal Geoportal
 Vector tiles for the Swiss Federal Geoportal Ingensand Jens, Marion Nappez1, Cédric Moullet, Loïc Gasser2,Sarah Composto1 1 GIS Lab, University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland. Route de Cheseaux
Vector tiles for the Swiss Federal Geoportal Ingensand Jens, Marion Nappez1, Cédric Moullet, Loïc Gasser2,Sarah Composto1 1 GIS Lab, University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland. Route de Cheseaux
Amazon Hosted ESRI GeoPortal Server. GeoCloud Project Report
 Amazon Hosted ESRI GeoPortal Server GeoCloud Project Report Description of Application Operating Organization The USDA participated in the FY 2011 Federal Geographic Data Committee (FGDC) GeoCloud Sandbox
Amazon Hosted ESRI GeoPortal Server GeoCloud Project Report Description of Application Operating Organization The USDA participated in the FY 2011 Federal Geographic Data Committee (FGDC) GeoCloud Sandbox
3 hours One paper 70 Marks. Areas of Learning Theory
 GRAPHIC DESIGN CODE NO. 071 Class XII DESIGN OF THE QUESTION PAPER 3 hours One paper 70 Marks Section-wise Weightage of the Theory Areas of Learning Theory Section A (Reader) Section B Application of Design
GRAPHIC DESIGN CODE NO. 071 Class XII DESIGN OF THE QUESTION PAPER 3 hours One paper 70 Marks Section-wise Weightage of the Theory Areas of Learning Theory Section A (Reader) Section B Application of Design
Using Mobile GIS for Water Networks Management The Open Source Approach
 Using Mobile GIS for Water Networks Management The Open Source Approach Iraklis KARAMPOURNIOTIS and Ioannis PARASCHAKIS The GI_Forum Program Committee accepted this paper as reviewed full paper. Abstract
Using Mobile GIS for Water Networks Management The Open Source Approach Iraklis KARAMPOURNIOTIS and Ioannis PARASCHAKIS The GI_Forum Program Committee accepted this paper as reviewed full paper. Abstract
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches
 Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
Cross Platform Mobile Gis System For Data Collection Based On Gps And Emerging Gis Technologies
 International Conference of Advance Research and Innovation (-2014) Cross Platform Mobile Gis System For Data Collection Based On Gps And Emerging Gis Technologies Mohammad Nasim a,*, Prashant Kumar b
International Conference of Advance Research and Innovation (-2014) Cross Platform Mobile Gis System For Data Collection Based On Gps And Emerging Gis Technologies Mohammad Nasim a,*, Prashant Kumar b
Location tracking: technology, methodology and applications
 Location tracking: technology, methodology and applications Marina L. Gavrilova SPARCS Laboratory Co-Director Associate Professor University of Calgary Interests and affiliations SPARCS Lab Co-Founder
Location tracking: technology, methodology and applications Marina L. Gavrilova SPARCS Laboratory Co-Director Associate Professor University of Calgary Interests and affiliations SPARCS Lab Co-Founder
Face detection is a process of localizing and extracting the face region from the
 Chapter 4 FACE NORMALIZATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION Face detection is a process of localizing and extracting the face region from the background. The detected face varies in rotation, brightness, size, etc.
Chapter 4 FACE NORMALIZATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION Face detection is a process of localizing and extracting the face region from the background. The detected face varies in rotation, brightness, size, etc.
ABSTRACT Utilizing Mobile GIS for Hydrology and Hydraulics Field Reconnaissance
 ABSTRACT Utilizing Mobile GIS for Hydrology and Hydraulics Field Reconnaissance Jessica D. Baker 1, EIT, CFM and Noelle Gaspard 1, CFM Advances in technology have dramatically improved traditional methods
ABSTRACT Utilizing Mobile GIS for Hydrology and Hydraulics Field Reconnaissance Jessica D. Baker 1, EIT, CFM and Noelle Gaspard 1, CFM Advances in technology have dramatically improved traditional methods
Abstract. Introduction
 Data Replication and Data Sharing Integrating Heterogeneous Spatial Databases Mark Stoakes and Katherine Irwin Professional Services, Safe Software Inc. Abstract Spatial data warehouses are becoming more
Data Replication and Data Sharing Integrating Heterogeneous Spatial Databases Mark Stoakes and Katherine Irwin Professional Services, Safe Software Inc. Abstract Spatial data warehouses are becoming more
Efficient Storage, Compression and Transmission
 Efficient Storage, Compression and Transmission of Complex 3D Models context & problem definition general framework & classification our new algorithm applications for digital documents Mesh Decimation
Efficient Storage, Compression and Transmission of Complex 3D Models context & problem definition general framework & classification our new algorithm applications for digital documents Mesh Decimation
SECONDARY STORAGE TERRAIN VISUALIZATION IN A CLIENT-SERVER ENVIRONMENT: A SURVEY
 SECONDARY STORAGE TERRAIN VISUALIZATION IN A CLIENT-SERVER ENVIRONMENT: A SURVEY Kai Xu and Xiaofang Zhou School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering The University of Queensland, Brisbane,
SECONDARY STORAGE TERRAIN VISUALIZATION IN A CLIENT-SERVER ENVIRONMENT: A SURVEY Kai Xu and Xiaofang Zhou School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering The University of Queensland, Brisbane,
GEOSPATIAL DIGITAL ASSET MANAGEMENT A SOLUTION INTEGRATING IMAGERY AND GIS WHERE WILL ALL THE PIXELS GO?(AND HOW WILL WE EVER FIND THEM?
 GEOSPATIAL DIGITAL ASSET MANAGEMENT A SOLUTION INTEGRATING IMAGERY AND GIS WHERE WILL ALL THE PIXELS GO?(AND HOW WILL WE EVER FIND THEM?) Dr. Joan Lurie, GCC, Inc. 30 West 61 st Street, Apt 9A New York,
GEOSPATIAL DIGITAL ASSET MANAGEMENT A SOLUTION INTEGRATING IMAGERY AND GIS WHERE WILL ALL THE PIXELS GO?(AND HOW WILL WE EVER FIND THEM?) Dr. Joan Lurie, GCC, Inc. 30 West 61 st Street, Apt 9A New York,
Data Modeling Basics. John Auel GIS Technician II United Services Group
 Data Modeling Basics John Auel GIS Technician II United Services Group Background Bachelor of Science at University of Wisconsin, Steven s Point Area of Emphasis -- Cartography Been at United Services
Data Modeling Basics John Auel GIS Technician II United Services Group Background Bachelor of Science at University of Wisconsin, Steven s Point Area of Emphasis -- Cartography Been at United Services
SPATIAL ANALYSIS IN GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. A DATA MODEL ORffiNTED APPROACH
 POSTER SESSIONS 247 SPATIAL ANALYSIS IN GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. A DATA MODEL ORffiNTED APPROACH Kirsi Artimo Helsinki University of Technology Department of Surveying Otakaari 1.02150 Espoo,
POSTER SESSIONS 247 SPATIAL ANALYSIS IN GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. A DATA MODEL ORffiNTED APPROACH Kirsi Artimo Helsinki University of Technology Department of Surveying Otakaari 1.02150 Espoo,
Technology Trends In Geoinformation
 Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: [email protected] www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: [email protected] www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
System Development and Life-Cycle Management (SDLCM) Methodology
 System Development and Life-Cycle Management (SDLCM) Methodology Subject Type Standard Approval CISSCO Program Director A. PURPOSE This standard specifies the format and conventions to be used in developing
System Development and Life-Cycle Management (SDLCM) Methodology Subject Type Standard Approval CISSCO Program Director A. PURPOSE This standard specifies the format and conventions to be used in developing
Responsive Web Design. vs. Mobile Web App: What s Best for Your Enterprise? A WhitePaper by RapidValue Solutions
 Responsive Web Design vs. Mobile Web App: What s Best for Your Enterprise? A WhitePaper by RapidValue Solutions The New Design Trend: Build a Website; Enable Self-optimization Across All Mobile De vices
Responsive Web Design vs. Mobile Web App: What s Best for Your Enterprise? A WhitePaper by RapidValue Solutions The New Design Trend: Build a Website; Enable Self-optimization Across All Mobile De vices
ILLUMINATED CHOROPLETH MAPS
 CO-144 ILLUMINATED CHOROPLETH MAPS KENNELLY P. Long Island University, BROOKVILLE, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Choropleth maps are commonly used to show statistical variation among map enumerations such as
CO-144 ILLUMINATED CHOROPLETH MAPS KENNELLY P. Long Island University, BROOKVILLE, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Choropleth maps are commonly used to show statistical variation among map enumerations such as
Digital data collection and registration on geographical names during field work*
 UNITED NATIONS WORKING PAPER GROUP OF EXPERTS NO. 13 ON GEOGRAPHICAL NAMES Twenty-sixth session Vienna, 2-6 May 2011 Item 20 of the Provisional Agenda Other toponymic issues Digital data collection and
UNITED NATIONS WORKING PAPER GROUP OF EXPERTS NO. 13 ON GEOGRAPHICAL NAMES Twenty-sixth session Vienna, 2-6 May 2011 Item 20 of the Provisional Agenda Other toponymic issues Digital data collection and
GIS and Mapping Solutions for Developers. ESRI Developer Network (EDN SM)
 GIS and Mapping Solutions for Developers ESRI Developer Network (EDN SM) GIS and Mapping Solutions for Developers If you are a software developer looking for an effective way to bring geographic and mapping
GIS and Mapping Solutions for Developers ESRI Developer Network (EDN SM) GIS and Mapping Solutions for Developers If you are a software developer looking for an effective way to bring geographic and mapping
Basic Understandings
 Activity: TEKS: Exploring Transformations Basic understandings. (5) Tools for geometric thinking. Techniques for working with spatial figures and their properties are essential to understanding underlying
Activity: TEKS: Exploring Transformations Basic understandings. (5) Tools for geometric thinking. Techniques for working with spatial figures and their properties are essential to understanding underlying
Introduction to GIS. Dr F. Escobar, Assoc Prof G. Hunter, Assoc Prof I. Bishop, Dr A. Zerger Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
 Introduction to GIS 1 Introduction to GIS http://www.sli.unimelb.edu.au/gisweb/ Dr F. Escobar, Assoc Prof G. Hunter, Assoc Prof I. Bishop, Dr A. Zerger Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
Introduction to GIS 1 Introduction to GIS http://www.sli.unimelb.edu.au/gisweb/ Dr F. Escobar, Assoc Prof G. Hunter, Assoc Prof I. Bishop, Dr A. Zerger Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
Introduction. C 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd
 1 Introduction The purpose of this text on stereo-based imaging is twofold: it is to give students of computer vision a thorough grounding in the image analysis and projective geometry techniques relevant
1 Introduction The purpose of this text on stereo-based imaging is twofold: it is to give students of computer vision a thorough grounding in the image analysis and projective geometry techniques relevant
Prentice Hall: Middle School Math, Course 1 2002 Correlated to: New York Mathematics Learning Standards (Intermediate)
 New York Mathematics Learning Standards (Intermediate) Mathematical Reasoning Key Idea: Students use MATHEMATICAL REASONING to analyze mathematical situations, make conjectures, gather evidence, and construct
New York Mathematics Learning Standards (Intermediate) Mathematical Reasoning Key Idea: Students use MATHEMATICAL REASONING to analyze mathematical situations, make conjectures, gather evidence, and construct
Extending Enterprise GIS Into The Field with Mobile GIS Technology
 Extending Enterprise GIS Into The Field with Mobile GIS Technology A White Paper January 10, 2014 1525 Oregon Pike Suite 202 Lancaster, PA 17601-7300 Phone (717) 399-7007 Fax (717) 399-7015 www.geographit.com
Extending Enterprise GIS Into The Field with Mobile GIS Technology A White Paper January 10, 2014 1525 Oregon Pike Suite 202 Lancaster, PA 17601-7300 Phone (717) 399-7007 Fax (717) 399-7015 www.geographit.com
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA
 A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - [email protected]
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - [email protected]
Mobile GIS strategies for disseminating thematic tourist information: Examples of spatial narratives
 Mobile GIS strategies for disseminating thematic tourist information: Examples of spatial narratives Lasse Møller-Jensen Department of Geography and Geology, University of Copenhagen, Denmark Øster Voldgade
Mobile GIS strategies for disseminating thematic tourist information: Examples of spatial narratives Lasse Møller-Jensen Department of Geography and Geology, University of Copenhagen, Denmark Øster Voldgade
Web Map Context Service for Adaptive Geospatial Data Visualization
 Web Map Context Service for Adaptive Geospatial Data Visualization Miloš Bogdanović, Danilo Vulović, Leonid Stoimenov INTRODUCTION Faculty of Electronic Engineering, University of Niš, Serbia {milos.bogdanovic,
Web Map Context Service for Adaptive Geospatial Data Visualization Miloš Bogdanović, Danilo Vulović, Leonid Stoimenov INTRODUCTION Faculty of Electronic Engineering, University of Niš, Serbia {milos.bogdanovic,
What is GIS. What is GIS? University of Tsukuba. What do you image of GIS? Copyright(C) ESRI Japan Corporation. All rights reserved.
 What is GIS University of Tsukuba Graduate School of Life and Environmental Science April 21 st, 2011 What is GIS? What do you image of GIS? Gas Insulated Switch Groupe Interventional Speciale Geographic
What is GIS University of Tsukuba Graduate School of Life and Environmental Science April 21 st, 2011 What is GIS? What do you image of GIS? Gas Insulated Switch Groupe Interventional Speciale Geographic
Localization Testing in Mobile World Software Testing Conference, 2013
 Localization Testing in Mobile World Software Testing Conference, 2013 In the recent past, there has been tremendous growth of smart phones and tablets. Due to this continuous growth, mobile applications
Localization Testing in Mobile World Software Testing Conference, 2013 In the recent past, there has been tremendous growth of smart phones and tablets. Due to this continuous growth, mobile applications
CIS 467/602-01: Data Visualization
 CIS 467/602-01: Data Visualization Maps Dr. David Koop Assignment 3 http://www.cis.umassd.edu/ ~dkoop/cis467/assignment3.html Networks and Maps Little East Women's Basketball data Network of games with
CIS 467/602-01: Data Visualization Maps Dr. David Koop Assignment 3 http://www.cis.umassd.edu/ ~dkoop/cis467/assignment3.html Networks and Maps Little East Women's Basketball data Network of games with
Screen Design : Navigation, Windows, Controls, Text,
 Overview Introduction Fundamentals of GUIs - methods - Some examples Screen : Navigation, Windows, Controls, Text, Evaluating GUI Performance 1 Fundamentals of GUI What kind of application? - Simple or
Overview Introduction Fundamentals of GUIs - methods - Some examples Screen : Navigation, Windows, Controls, Text, Evaluating GUI Performance 1 Fundamentals of GUI What kind of application? - Simple or
Branch of Geospatial Support. GEOSPATIAL TRAINING SCHEDULE APRIL 2015 SEPTEMBER 2015 Version: 27 APRIL 2015
 UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR BUREAU OF INDIAN AFFAIRS Office of Trust Services Division of Land Titles and Records Branch of Geospatial Support 13922 Denver West Parkway, Building 54, Suite
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR BUREAU OF INDIAN AFFAIRS Office of Trust Services Division of Land Titles and Records Branch of Geospatial Support 13922 Denver West Parkway, Building 54, Suite
ThinPrint.print Server Engine installation and architecture
 ActiveAnswers iss solutions september 2003 installation guide ThinPrint.print Server Engine installation and architecture contents introduction... 3 SBC printing challenges... 3 enterprise computing printing
ActiveAnswers iss solutions september 2003 installation guide ThinPrint.print Server Engine installation and architecture contents introduction... 3 SBC printing challenges... 3 enterprise computing printing
DATA QUALITY AND SCALE IN CONTEXT OF EUROPEAN SPATIAL DATA HARMONISATION
 DATA QUALITY AND SCALE IN CONTEXT OF EUROPEAN SPATIAL DATA HARMONISATION Katalin Tóth, Vanda Nunes de Lima European Commission Joint Research Centre, Ispra, Italy ABSTRACT The proposal for the INSPIRE
DATA QUALITY AND SCALE IN CONTEXT OF EUROPEAN SPATIAL DATA HARMONISATION Katalin Tóth, Vanda Nunes de Lima European Commission Joint Research Centre, Ispra, Italy ABSTRACT The proposal for the INSPIRE
Real Time Bus Monitoring System by Sharing the Location Using Google Cloud Server Messaging
 Real Time Bus Monitoring System by Sharing the Location Using Google Cloud Server Messaging Aravind. P, Kalaiarasan.A 2, D. Rajini Girinath 3 PG Student, Dept. of CSE, Anand Institute of Higher Technology,
Real Time Bus Monitoring System by Sharing the Location Using Google Cloud Server Messaging Aravind. P, Kalaiarasan.A 2, D. Rajini Girinath 3 PG Student, Dept. of CSE, Anand Institute of Higher Technology,
