Journal of Neuroscience Methods
|
|
|
- Angela Marsh
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Neuroscience Methods 200 (2011) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Neuroscience Methods j o ur nal homep age: Short communication Anopheles gambiae mosquito isolated neurons: A new biological model for optimizing insecticide/repellent efficacy Céline Lavialle-Defaix a,1, Véronique Apaire-Marchais a,1, Christian Legros a, Cédric Pennetier b, Aly Mohamed a,c, Patricia Licznar a, Vincent Corbel b, Bruno Lapied a, a Laboratoire Récepteurs et Canaux Ioniques Membranaires (RCIM) - UPRES EA 2647/USC INRA 2023, IFR 149 QUASAV, Université d Angers, UFR Sciences, 2 boulevard Lavoisier, Angers Cedex, France b Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD), MIVEGEC (UM1-CNRS 5290-IRD 224), Centre de Recherche Entomologique de Cotonou, 01 BP 4414 RP Cotonou, Benin c Plant Protection Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt a r t i c l e i n f o Article history: Received 13 April 2011 Received in revised form 23 May 2011 Accepted 8 June 2011 Keywords: Malaria Mosquito Isolated neurons Insecticides DEET Vector-borne diseases a b s t r a c t To understand better the mode of action of insecticides and repellents used in vector-borne diseases control, we developed a new biological model based on mosquito neurons isolated from adults Anopheles gambiae heads. This cellular model is well adapted to multidisciplinary approaches: electrophysiology, pharmacology, molecular biology and biochemical assays. Using RT-PCR, we demonstrated that isolated neurons express the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit 1 (Ag 1 nachr), two acetylcholinesterases (AChE-1 and AChE-2) and three voltage-gated ion channels required for membrane excitability (AgCav1, AgNav1 and AgKv1). In order to correlate the expression of the different transcripts, encoding functional AgNav channel, nachr receptor and AChE enzymes detected by RT-PCR, with electrophysiological activity we used patch-clamp technique. We revealed that AgNav and AChE which are targeted by insecticide and/or repellent were sensitive to the pyrethroid permethrin and to the repellent DEET, respectively. In addition, using colorimetric method, we also showed that AChE was sensitive to the carbamate propoxur. These results indicated that this novel neuronal mosquito model will lead to molecular and functional characterization of insecticide/repellent targets and appears as a powerful tool to investigate the development of highly specific and effective strategies for disease vector control Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction Despite considerable efforts in recent years dedicated throughout the world to control vector-borne diseases, malaria is still a major public health problem with nearly 250 million cases a year and 800,000 deaths among them, 85% are children under five years old (WHO, 2010). The only chemicals recommended by World Health Organization (WHO) to control adult mosquito vectors are neurotoxic insecticides, which target the sodium channels (pyrethroids) and the acetylcholinesterases (organophosphates and carbamates) (WHO, 2006). Unfortunately the main malaria vector species Anopheles gambiae developed multiple resistance mechanisms to these insecticides (Ranson et al., 2011). This is worrying because it may impede the WHO Global Action Plan for malaria control and its eradication. In this context, there is an urgent need to deeply investigate insecticide/repellent neurological effects and interactions, at both molecular and cellular levels, Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: [email protected] (B. Lapied). 1 Equally contributed to this work. for developing new research strategies to ensure better control of insecticide-resistant malaria vectors (Lapied et al., 2009). Although, behavior observations, phenotypic and genotypic studies brought important knowledge allowing the development of alternative strategies against mosquitoes (Ranson et al., 2011), there is a real lack of data describing the physiology and pharmacology of insecticide/repellent targets-interactions at mosquito neuronal level. So it is crucial to find out new methods to overcome this limitation. Until now, primary neuronal cultures have been developed from numerous insect species (Beadle, 2006). Because they express membrane receptors and ion channels targeted by insecticides, they constitute ideal biological models to investigate the mode of action of insecticides. More recently, the use of such biological models have highlighted that intracellular regulatory mechanisms have fundamental consequences for the sensitivity of insecticide targets (Lapied et al., 2009; Lavialle-Defaix et al., 2010). However, among insect neuronal preparations available, the fully differentiated Mosquito Isolated Neurons (MIN) model is still lacking. We set up a novel biological model of A. gambiae adult MIN which is offering all facilities to study the mode of action of insecticides/repellents, to investigate the impact of resistance mechanisms at neurologi /$ see front matter 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /j.jneumeth
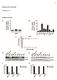
2 C. Lavialle-Defaix et al. / Journal of Neuroscience Methods 200 (2011) Fig. 1. Adult mosquito neuron isolation procedure and characterization. (a) Anopheles gambiae head. (b) Mechanical dissociation of neurons from mosquito head. (c e) Confocal laser-scanning images: (c) counterstaining with acridine orange binds DNA in the nuclei of all cells. (d) HRP-staining in neurons among isolated cells. (e) Fluorescent double-labeling as a result of superimposing (c) and (d) identified cells as neurons (arrows). (f) Light photomicrograph of isolated adult mosquito neurons observed 24 h after dissociation. (g) Electrophoretic analysis of amplicons obtained by multiplex PCR using cdna of isolated neurons (Ag 1 nachr: 548 bp; Ag Cav: 777 bp; AgKv1: 470 bp; ace-1: 558 bp; ace-2: 433 bp; AgNav1: 895 bp). cal level and to characterize intracellular regulation mechanisms involved in the modulation of the sensitivity of insecticide targets. 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Mosquitoes The reference susceptible strain of A. gambiae (Kisumu) provided by CCPV/IRD Montpellier, was used in this study and maintained under laboratory conditions: 26 ± 1 C and 68 ± 1% relative humidity. This strain, originated from Kisumu in Kenya, was colonized many years ago and is free of any detectable insecticide resistance mechanism Cells isolation procedure The adult mosquito heads were carefully cut under a binocular microscope. Antennae, maxillary palps, labium and antennal pedicels were removed. The heads were excised and placed in mosquito saline buffer containing (in mm) 130 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 3 MgCl 2, 2 CaCl 2, 35 sucrose, 5 HEPES, 5% fetal bovine serum, 50 UI ml 1 penicillin and 50 g ml 1 streptomycin. Dissociation of neuronal cells from head was performed mechanically by repetitive gentle suctions through fire-polished Pasteur pipettes (Fig. 1) Cell culture stainings Isolated cells were placed in chamber slides pre-coated with poly-d-lysine hydrobromide (Sigma) and fixed for 15 min with 2% paraformaldehyde containing 2% (w/v) sucrose in phosphatebuffer saline (PBS, ph 7.2). After fixation, cells were washed 3 times for 5 min in PBS and 5 min in PBS containing 0.2% Triton X-100 (PBS-T). In order to block non-specific binding of the primary antibody, cells were pre-incubated with 4% bovine serum albumin (BSA, Sigma) in PBS-T for 1 h. Primary rabbit anti-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) antibodies (Sigma) used at a dilution of 1:5000 in PBS-T, was applied overnight at 4 C. After washing in PBS-T, cells were incubated with secondary antibody (Cy3-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, Chemicon International) used at a dilution of 1:1000 in PBS- T containing 1% BSA for 40 min in the dark at 20 C. Then, the
3 70 C. Lavialle-Defaix et al. / Journal of Neuroscience Methods 200 (2011) Table 1 Biophysical characteristics of the inward sodium current of adult isolated mosquito neurons. Current voltage relationship INa amplitude (pa) at 1 Midpoint of steady-state activation Slope factor of activation, k Midpoint of steady-state inactivation (V 0.5, mv) Slope factor of inactivation, k Time constant of recovery from inactivation (ms) Activation threshold (mv) Reversal potential (mv) 40 ± ± ± ± 0.10 (n = 11) 5.8 ± 0.1 (n = 11) 47.4 ± 0.2 (n = 9) 8.6 ± 0.1 (n = 9) 2.7 ± 0.2 secondary antibody solution was removed and the cells were incubated with acridine orange at 0.01% in PBS for 2 min. Subsequently, the cells were rinsed in PBS and mounted on glass slides using glycerol/pbs. Double-labeled preparations were analyzed using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Olympus BX50). We used the helium/neon laser (excitation wavelength 543 nm, detection range nm) for imaging of Cy3 fluorescence and the argon laser (excitation wavelength 488 nm, detection range nm) for imaging of acridine orange. Typical cells were chosen using the transmitted light scan mode of the confocal microscope (magnification 600 ) Gene expression profiling of mosquito neurons by multiplex PCR Total RNA was extracted from cells isolated from 10 mosquito heads with the NucleoSpin RNA XS system (Macherey-Nagel) including a DNaseI treatment and transcribed into cdna using protocols described previously (Moignot et al., 2009). Amplification was performed by multiplex semi-nested or nested PCR with specific primers sets (Supplementary Table 1) matching genes encoding the 1 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (Ag 1 nachr), the subunit of the voltage-gated Ca 2+ channel (AgCav1), the Shakerrelated K + channel (AgKv1), the acetylcholinesterase 1 (AChE-1), the acetylcholinesterase 2 (AChE-2) and the subunit of the voltage-gated Na + channel (AgNav1). To amplify simultaneously the different cdnas, the first round of PCR was performed in a single tube, containing 2 l cdna, 2 l 10 PCR buffer, 1.5 mm MgCl 2, 0.2 mm dntp, 0.25 M of each gene-specific primer in a 20 l final volume and 0.3 U EuroTaq DNA polymerase (BioCat GmbH). The second round of PCR was done in separate tubes using 0.25 l of the first PCR as template and a second nested or semi-nested gene specific primer set in a 50 l final volume. For both PCR, an initial denaturation was carried out at 94 C for 4 min, followed by 35 cycles (20 s at 94 C, 30 s at 60 C, 1 min at 72 C) of amplification and a final cycle of 10 min at 72 C. The PCR products of expected size were separated on agarose gel and purified using NucleoSpin Extract II (Macherey-Nagel) for direct sequencing (Millegen) Electrophysiological recordings The glass coverslips were mounted in a recording chamber (Warner Instruments) connected to a gravity perfusion system allowing drug application. The isolated neuron cell bodies, maintained at 27 C, were used for recordings 4 h after dissociation. Patch-clamp technique in the whole-cell recording configuration (Hamill et al., 1981) was used to record both voltage-dependent and ACh-induced ionic currents (voltage-clamp mode) Ionic currents were recorded with an Axopatch 200A amplifier (Axon Instruments, Foster City, CA), filtered at 5 khz using a 4-pole lowpass Bessel filter. Patch pipettes were pulled from borosilicate glass capillary tubes (GC 150T-10; Clark Electromedical Instruments, Harvard Apparatus) using a Sutter P-97 (Sutter Instruments). Pipettes had resistances ranging from 6 to 8 M when filled with internal solutions. The liquid junction potential between bath and internal solution was always corrected before the formation of a gigaohm seal (>5 G). In all experimental conditions, cells were bathed in external solution containing (in mm) 130 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 3 MgCl 2, 2 CaCl 2, 5 HEPES, ph was adjusted to 7.2 with NaOH 1 M, except otherwise stated (see below). The internal solution contained (in mm): 140 K-gluconate, 10 NaCl, 3 MgCl 2, 0.1 CaCl 2, 1.5 EGTA, 1 ATP-Mg and 10 HEPES buffer; ph was adjusted to 7.2 with KOH 1 M. The solutions used to record sodium current were designed to eliminate interference from outward potassium and inward calcium currents. The extracellular solution superfusing the cells contained (in mm) 130 NaCl, 50 TEA-Cl, 5 KCl, 2 MgCl 2, 0.5 CaCl 2, 0.5 CdCl 2, 5 4-AP, 10 HEPES, ph was adjusted to 7.2 with NaOH 1 M. Patch pipettes were filled with an internal solution containing (in mm) 140 CsCl, 7 NaCl, 2 MgCl 2, 2 EGTA, 10 HEPES, 1 ATP-Mg, ph was adjusted to 7.2 with CsOH 1 M. Although leak and capacitive currents were compensated electronically at the beginning of each experiment, subtraction of residual capacitive and leakage currents was performed with an on-line P/6 protocol provided by pclamp. Mosquito neurons were voltage-clamped at a steady-state holding potential of 7 and 15-ms test pluses were applied from the holding potential at a frequency of 0.3 Hz. Patch-clamp experiments were conducted at room temperature (20 22 C). Data analyses were presented in Supplementary data Pneumatic pressure ejection application of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine Acetylcholine (ACh, 100 M, Sigma Chemicals) was applied by pneumatic pressure ejection (15 psig, 200-ms pulses), with a pneumatic pressure system (Miniframe, Medical System Corporation, NY) to minimize receptor desensitization resulting from bath application of agonist (Lapied et al., 1990). The pressure ejection was made through a glass micropipette (resistance of 2 M when filled with agonist) positioned in solution within 40 m from the isolated neuron cell body. In no experiment did the pressure ejection of normal saline realized with the same protocol affect the current baseline. Repeated applications of ACh were made with an interval of 2 min between the end of one application and the beginning of the next Biochemical assay of AChE activity Seven heads from A. gambiae mosquito adults were placed in 700 L of the mosquito saline buffer and isolation of neuron cells was performed using mechanical dissociation as described (Fig. 1). Hundred L of the suspension were incubated for 15 min with 10 L of a carbamate insecticide (propoxur). Dilutions (10 4 M to 10 8 M) from the initial concentration (1 M) were used for propoxur. AChE residual activity was determined spectrophotometrically (Ellman et al., 1961) at 405 nm at 30 min using 100 L of 1 mm acetylthiocholine (ATC) (Sigma) and 100 L of 1 mm DTNB (Sigma) for each dilution, and was expressed as a percentage of ini-
4 C. Lavialle-Defaix et al. / Journal of Neuroscience Methods 200 (2011) a d f b c -90 IK peak INa TTX Ctr IK sustained 500 pa 4 ms 100 pa 1 ms Potential (mv) Current amplitude (pa) e ms 15 ms 1 ms I/INa max ms 10 ms 1 to 15 ms Time (ms) g pa 1 ms I/Imax Control 200 pa 2 ms Potential (mv) Permethrin (10-5 M) 100 pa 2 ms Fig. 2. Electrophysiological properties of the isolated mosquito neurons studied with the patch-clamp technique in whole-cell recording configuration. (a) Typical example of the whole cell currents activated by a depolarizing pulse to from a holding potential of 9. (b e) Biophysical properties of the TTX-sensitive inward sodium current studied under voltage-clamp condition, in the presence of potassium and calcium channel blockers. (b) Blocking effect of TTX (10 7 M) on the control inward current elicited by a depolarizing pulse to applied from a holding potential of 7 (n = 4). Currents are capacity- and leak-corrected. (d) Current voltage relationship constructed from values of maximum current amplitude shown in (c) and plotted as a function of test pulses. The smooth curve represents the best fit according to Eq. (1) (Supplementary data). (e) Voltage-dependence of the steady-state activation (right curve) and inactivation (left curve) of the TTX-sensitive sodium current according to the protocols shown in inset. Smooth curves were fitted through the data points using single Boltzmann distributions (Eqs. (2) and (3) for activation and inactivation, respectively; see Supplementary data). (f) Time course of recovery from inactivation of the TTX-sensitive sodium current at a holding potential of 7. The inset shows the experimental protocol used. (g) Typical example of the inward sodium currents recorded in control (upper trace) and after application of the pyrethroid insecticide, permethrin (10 5 M, lower trace). Currents were elicited by a depolarizing pulse according to the protocol shown above current traces. In all cases, data are means ± S.E.M. tial activity (without inhibitor). Values obtained are means of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Characterization of the A. gambiae neurons MIN were obtained from adult A. gambiae heads using mechanical dissociation (Fig. 1a and b). The proportion of neurons among dissociated cells was evaluated by a double immunocytochemical labeling method, using a rabbit anti-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) primary antibody as neuronal cell surface marker (Loesel et al., 2006). Counterstaining with acridine orange, that binds to DNA in the nuclei of all cells, yielded the total number of cells. 53.4% of the cell population (n = 196) were double-labeled and were therefore identified as neurons (Fig. 1c e). In this case, neurons appeared as small spherical cells with a mean diameter of 5.1 ± 0.1 m (Fig. 1f). To demonstrate that our new mosquito neuronal model (i) expresses the main targets for insecticides and repellents, including voltage-gated Na + channels (Nav channels), acetylcholinesterases (AChE) and cholinergic receptor and (ii) is suitable for the development of molecular, electrophysiological and biochemical approaches, essential to study the mode of action of insecticides and repellents, we first adapted RT-PCR on such preparation. Using cdna from isolated cell, we performed a multiplex nested or semi-nested PCR with specific primers for genes encoding the 1 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit (Ag 1 nachr), the alpha subunit of voltage-gated Ca 2+ channel (AgCav1), the Shakerrelated K + channel (AgKv1), the acetylcholinesterase-1 (AChE-1), the acetylcholinesterase-2 (AChE-2) and the alpha subunit of Nav channel (AgNav1). The second round of PCR amplification revealed the simultaneous expression of all of these transcripts in the isolated cells from mosquito heads (Fig. 1g). Each PCR product was detected with the expected size and direct sequencing confirmed their molecular identity Electrophysiological properties of A gambiae isolated neurons In addition, in order to correlate the expression of the transcripts detected by RT-PCR with electrophysiological activity, we adapted whole-cell patch-clamp technique to MIN. The isolated neurons were used for electrophysiological recordings 4 h after dissociation. In our experimental conditions, isolated neurons can survive with stable electrophysiological properties for 24 h. According to the double immunocytochemical labeling data, all neurons investigated had spherical diameter cell body geometry of about 5 m in which an adequate space-clamp is easily attained. In 100% of isolated neurons tested, depolarizing pulse from a holding potential
5 72 C. Lavialle-Defaix et al. / Journal of Neuroscience Methods 200 (2011) Fig. 3. Anticholinesterasic effects of the repellent DEET and the carbamate insecticide, propoxur on adult isolated mosquito neurons. (a) Typical examples of steady-state recordings of the acetylcholine-(ach) induced inward current obtained in whole cell voltage-clamp mode at a holding potential of 5 in control and after bath application of the repellent DEET (10 7 M). The cholinergic agonist was applied by pressure-ejection onto isolated neuron from a patch-pipette filled with saline containing 100 M ACh. (b) Histogram illustrating the effects of DEET (10 7 M) on both amplitude and duration of the ACh-induced inward current. Data are means ± S.E.M. (n = 7). (c) Dose-dependent anticholinesterasic effect of the carbamate propoxur on the neuronal residual AChE activity. The inset illustrates the comparative histogram giving the IC 50 value estimated at M. of 9 to elicited global currents consisting of a fast small inward sodium current followed by a biphasic outward potassium current (Fig. 2a). The mean amplitudes of the peak outward current was ± pa (n = 10) and ± 68.8 pa (n = 10) for the sustained component. To isolate the inward sodium current, calcium and potassium current inhibitors were used. As illustrated in Fig. 2b, application of 10 7 M TTX, the well known Nav channel blocker, completely inhibited the residual inward current, indicating that this latter resulted of Na + influx through voltagegated channel. The TTX-sensitive Na + current had an amplitude of ± 23.2 pa (n = 21) in response to a depolarizing pulse from a holding potential of 7 to. Fig. 2c shows a typical example of a transient inward current from an isolated neuron in response to a series of voltage-clamp steps applied from a holding potential of 7. The corresponding peak current voltage (I V) relationship was illustrated in Fig. 2d. The voltage-dependence of the steady-state inactivation and activation of the sodium current together with the recovery time from inactivation were studied according to the protocols shown in Fig. 2e and f. All the biophysical characteristics of the voltage dependence of the Na + current were summarized in Table 1. These results indicate that the Nav channels expressed in A. gambiae MIN were functional with an inward current which displayed general electrophysiological properties very similar to those of other invertebrate neurons (Wicher et al., 2001) Neurotoxic effects of insecticide and repellent on A. gambiae isolated neurons Nav channels represent the key target sites for the insecticide pyrethroids (Soderlund, 2008). Permethrin is one of the most used insecticides among pyrethroids used in vector control (WHO, 2006). Application of permethrin on MIN evidenced that the Na + current is sensitive to this pyrethroid. As shown in Fig. 2g, compared to the control current, the decrease of the Na + current recorded in the presence of permethrin (10 5 M) presented a biphasic aspect composed of a fast component followed by the development of a slow maintained one. The deactivation of the slow component was represented by a large inward tail current when the membrane was stepped back to the holding potential. These typical effects of permethrin observed on the Na + current fit well with the effect of pyrethroids described in numerous insect neuronal preparations (Soderlund, 2008). Altogether, our results confirm that MIN are a suitable model to investigate the effects of insecticides acting on the Nav channels. This is of great interest in order to understand further the neurological and molecular processes involved in target-site resistance to pyrethroids (Kdr and super-kdr) and contribute to the design of novel insecticidal compounds on the same target. We next focused on the characterization of AChE, another crucial target involved in the cholinergic neurotransmission in insect by specifically hydrolyzing ACh in the cholinergic synapses. AChE is the molecular target for insecticides including organophosphates, carbamates and more recently the most commonly used insect repellent, DEET (N,N-diethyl-3-methylbenzamide) (Corbel et al., 2009). To show that the different transcripts encoded functional nachr and AChEs, we investigated the anticholinesterasic effects of DEET on MIN. We used the whole-cell patch-clamp technique combined with the pneumatic pressure ejection of the neurotransmitter ACh, as previously described elsewhere (Lapied et al., 1990). As expected, the results illustrated in Fig. 3a and b demonstrated a clear and significant inhibition of AChE after bath application of DEET (10 7 M). The ACh-induced inward current recorded under voltage-clamp condition following pressure ejection of ACh onto the isolated cell was significantly increased in both amplitude and duration (Fig. 3a and b), in accordance with a typical anti-cholinesterasic effect. At the same time, we implemented a biochemical assay to demonstrate that it is possible to measure the AChE enzymatic activity on MIN. The enzymatic activity was measured by using colorimetric method in the presence of the carbamate propoxur. AChE residual activity of mosquito neurons was determined for increasing concentrations of propoxur. The inhibitory concentration 50 (IC 50 ) value of propoxur was estimated at about M and a decrease of 42.4% of AChE activity was observed in the presence of 10 7 M of propoxur (Fig. 3c). Altogether, these data indicate that MIN express functional nachr and AChE. 4. Conclusion We proposed the first mosquito neuronal model for the malaria vector A. gambiae. By using electrophysiology, pharmacology, molecular biology and biochemistry, we demonstrated that A. gambiae MIN express some of the most important functional receptors, ion channels and enzymes targeted by insecticides and repellents. Such approach can be used to build neuronal models of the other major mosquito vectors such as Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus (Dengue and Chikungunya viruses) or Culex quinquefasciatus (Filar-
6 C. Lavialle-Defaix et al. / Journal of Neuroscience Methods 200 (2011) iasis). The development of this neuronal mosquito model will have direct practical applications on insecticidal treatment. It will be a powerful neurobiological tool to bring new highlights on (i) the mode of action of both insecticides and repellents, (ii) the effect of mixtures of two unrelated insecticides and/or insecticide/repellent, which are proposed as promising novel strategies for the control of vector-borne diseases (Pennetier et al., 2009) and (iii) the management of insecticide-resistant malaria vectors. Acknowledgements Céline Lavialle-Defaix was supported by a post-doctoral grant of the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR, programme REAC SEST ). We thank Sophie Quinchard from RCIM laboratory, Angers University and Robert Filmon from the microscopy department, SCIAM, Angers University, for technical assistance. Anopheles gambiae eggs were provided by IRD, UR016, Montpellier, France. Aly Mohamed was supported by a doctoral fellowship of the Egyptian Government. Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: /j.jneumeth References Beadle DJ. Insect neuronal cultures: an experimental vehicle for studies of physiology, pharmacology and cell interactions. Invert Neurosci 2006;6: Corbel V, Stankiewicz M, Pennetier C, Fournier D, Stojan J, Girard E, Dimitrov M, Molgo J, Hougard JM, Lapied B. Evidence for inhibition of cholinesterases in insect and mammalian nervous systems by the insect repellent DEET. BMC Biol 2009;7:47. Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres JV, Featherstone BB. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 1961;7: Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflüger Arch 1981;391: Lapied B, Le Corronc H, Hue B. Sensitive nicotinic and mixed nicotinic muscarinic receptors in insect neurosecretory cells. Brain Res 1990;533: Lapied B, Pennetier C, Apaire-Marchais V, Licznar P, Corbel V. Innovative applications for insect viruses: towards insecticide sensitization. Trends Biotechnol 2009;27: Lavialle-Defaix C, Moignot B, Legros C, Lapied B. How does calcium-dependant intracellular regulation of voltage-dependant sodium current increase the sensitivity to the oxadiazine insecticide indoxacarb metabolite decarbomethoxylated JW062 (DCJW) in insect pacemaker neurons? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2010;333: Loesel R, Weigel S, Braunig P. A simple fluorescent double staining method for distinguishing neuronal from non-neuronal cells in the insect central nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 2006;155: Moignot B, Lemaire C, Quinchard S, Lapied B, Legros C. The discovery of a novel sodium channel in the cockroach Periplaneta americana: evidence for an early duplication of the para-like gene. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2009;39: Pennetier C, Constantini C, Corbel V, Licciardi S, Dabiré RK, Lapied B, Chandre F, Hougard JM. Synergy between repellents and organophosphates on bed nets: efficacy and behavioural response of natural free-flying Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes. PLoS One 2009;4:e7896. Ranson H, N Guessan R, Lines J, Moiroux N, Nkuni Z, Corbel V. Pyrethroid resistance in African Anopheline mosquitoes: what are the implications for malaria control? Trends Parasitol 2011;27:91 8. Soderlund DM. Pyrethroids, knockdown resistance and sodium channels. Pest Manag Sci 2008;64: Wicher D, Walther C, Wicher C. Non-synaptic ion channels in insects basic properties of currents and their modulation in neurons and skeletal muscles. Prog Neurobiol 2001;64: WHO. Guidelines for testing mosquito adulticides for indoor residual spraying and treatment of mosquito nets. In: WHO/CDS/NTD/WHOPES/GCDDP/ Geneva: WHO Press; p. 60. World Health Organization (WHO). World Malaria Report Geneva: WHO Press; 2010: p. 204.
BIOPHYSICS OF NERVE CELLS & NETWORKS
 UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MSci EXAMINATION May 2007 for Internal Students of Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship
UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MSci EXAMINATION May 2007 for Internal Students of Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship
Electrophysiological Recording Techniques
 Electrophysiological Recording Techniques Wen-Jun Gao, PH.D. Drexel University College of Medicine Goal of Physiological Recording To detect the communication signals between neurons in real time (μs to
Electrophysiological Recording Techniques Wen-Jun Gao, PH.D. Drexel University College of Medicine Goal of Physiological Recording To detect the communication signals between neurons in real time (μs to
huwentoxin-iv; TTX, tetrodotoxin; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; HWTX-I, huwentoxin-i; HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293; WT, wild type.
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 40, pp. 27300 27313, October 3, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Tarantula Huwentoxin-IV
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 40, pp. 27300 27313, October 3, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Tarantula Huwentoxin-IV
PROTOCOL. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
 PROTOCOL Immunocytochemistry (ICC) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 11-07 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Materials: MitoSciences primary monoclonal antibody/antibodies Fluorophore-conjugated
PROTOCOL Immunocytochemistry (ICC) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 11-07 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Materials: MitoSciences primary monoclonal antibody/antibodies Fluorophore-conjugated
Running protein gels and detection of proteins
 Running protein gels and detection of proteins 1. Protein concentration determination using the BIO RAD reagent This assay uses a colour change reaction to give a direct measurement of protein concentration.
Running protein gels and detection of proteins 1. Protein concentration determination using the BIO RAD reagent This assay uses a colour change reaction to give a direct measurement of protein concentration.
Bi 360: Midterm Review
 Bi 360: Midterm Review Basic Neurobiology 1) Many axons are surrounded by a fatty insulating sheath called myelin, which is interrupted at regular intervals at the Nodes of Ranvier, where the action potential
Bi 360: Midterm Review Basic Neurobiology 1) Many axons are surrounded by a fatty insulating sheath called myelin, which is interrupted at regular intervals at the Nodes of Ranvier, where the action potential
TRPM8 on QPatch HTX. Cold sensitive ion channels. Application Report:
 Application Report: TRPM8 on QPatch HTX Cold sensitive ion channels Pharmacological characteristics of two TRPM8 expressing cell lines, in multi-hole and single-hole mode on QPatch 16 and QPatch HTX. AR_PUBLIC14585-9
Application Report: TRPM8 on QPatch HTX Cold sensitive ion channels Pharmacological characteristics of two TRPM8 expressing cell lines, in multi-hole and single-hole mode on QPatch 16 and QPatch HTX. AR_PUBLIC14585-9
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
protocol handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel
 handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides
 Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and subsequent analyses are common tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. This Application
Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and subsequent analyses are common tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. This Application
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Action Potentials I Generation. Reading: BCP Chapter 4
 Action Potentials I Generation Reading: BCP Chapter 4 Action Potentials Action potentials (AP s) aka Spikes (because of how they look in an electrical recording of Vm over time). Discharges (descriptive
Action Potentials I Generation Reading: BCP Chapter 4 Action Potentials Action potentials (AP s) aka Spikes (because of how they look in an electrical recording of Vm over time). Discharges (descriptive
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法
 竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
HEK 293 K V 7.1/minK Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH HEK 293 K V 7.1/minK Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH HEK 293 K V 7.1/minK Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. BACKGROUND...3 1.1. The cardiac IKs current is encoded by K V
B SYS GmbH HEK 293 K V 7.1/minK Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH HEK 293 K V 7.1/minK Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. BACKGROUND...3 1.1. The cardiac IKs current is encoded by K V
User Manual. CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit. Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube
 User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
First Strand cdna Synthesis
 380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Insecticide resistance in Aedes aegypti populations of New Caledonia: what is the future for vector control?
 Insecticide resistance in Aedes aegypti populations of New Caledonia: what is the future for vector control? IPNC/L. Guillaumot Guillaumot L., Vernudachi A., Mphande F., Husson M., Teurlai M., Millet L.,
Insecticide resistance in Aedes aegypti populations of New Caledonia: what is the future for vector control? IPNC/L. Guillaumot Guillaumot L., Vernudachi A., Mphande F., Husson M., Teurlai M., Millet L.,
RT-PCR: Two-Step Protocol
 RT-PCR: Two-Step Protocol We will provide both one-step and two-step protocols for RT-PCR. We recommend the twostep protocol for this class. In the one-step protocol, the components of RT and PCR are mixed
RT-PCR: Two-Step Protocol We will provide both one-step and two-step protocols for RT-PCR. We recommend the twostep protocol for this class. In the one-step protocol, the components of RT and PCR are mixed
ECL Western Blotting Substrate INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS W1001 AND W1015.
 Technical Manual ECL Western Blotting Substrate INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS W1001 AND W1015. PRINTED IN USA. 6/09 ECL Western Blotting Substrate All technical literature is available on the Internet
Technical Manual ECL Western Blotting Substrate INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS W1001 AND W1015. PRINTED IN USA. 6/09 ECL Western Blotting Substrate All technical literature is available on the Internet
Activity 5: The Action Potential: Measuring Its Absolute and Relative Refractory Periods. 250 20 Yes. 125 20 Yes. 60 20 No. 60 25 No.
 3: Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses (Part 2) Activity 5: The Action Potential: Measuring Its Absolute and Relative Refractory Periods Interval between stimuli Stimulus voltage (mv) Second action potential?
3: Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses (Part 2) Activity 5: The Action Potential: Measuring Its Absolute and Relative Refractory Periods Interval between stimuli Stimulus voltage (mv) Second action potential?
Application Note. Single Cell PCR Preparation
 Application Note Single Cell PCR Preparation From Automated Screening to the Molecular Analysis of Single Cells The AmpliGrid system is a highly sensitive tool for the analysis of single cells. In combination
Application Note Single Cell PCR Preparation From Automated Screening to the Molecular Analysis of Single Cells The AmpliGrid system is a highly sensitive tool for the analysis of single cells. In combination
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
 Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Title: Direct Fluorescent Antibody Test (DFAT) for the detection of Renibacterium salmoninarum in tissues Number: BACT-3 Version: 02 Created December 14, 2011 Approval:
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Title: Direct Fluorescent Antibody Test (DFAT) for the detection of Renibacterium salmoninarum in tissues Number: BACT-3 Version: 02 Created December 14, 2011 Approval:
Synaptophysin Regulates the Kinetics of Synaptic Vesicle Endocytosis in Central Neurons
 Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Synaptophysin Regulates the Kinetics of Synaptic Vesicle Endocytosis in Central Neurons Sung E. Kwon and Edwin R. Chapman Supplemental Figure Legends Figure
Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Synaptophysin Regulates the Kinetics of Synaptic Vesicle Endocytosis in Central Neurons Sung E. Kwon and Edwin R. Chapman Supplemental Figure Legends Figure
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR
 Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
CHAPTER- 6. Okadaic acid induced neurotoxicity leads to central cholinergic dysfunction in rats. 1. Introduction. 2. Methods
 CHAPTER- 6 Okadaic acid induced neurotoxicity leads to central cholinergic dysfunction in rats 1. Introduction Neurodegenerative disorders, such as AD are often characterized by the degeneration of the
CHAPTER- 6 Okadaic acid induced neurotoxicity leads to central cholinergic dysfunction in rats 1. Introduction Neurodegenerative disorders, such as AD are often characterized by the degeneration of the
The Neuron and the Synapse. The Neuron. Parts of the Neuron. Functions of the neuron:
 The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
Systemic Pesticides as a Causal Factor of Developmental Brain Disorders (ADHD, autism, etc.)
 2012 9 2 浸 透 性 農 薬 フォーラム 脳 の 発 達 障 害 (ADHD 自 閉 症 など) の 原 因 としての 浸 透 性 農 薬 : ネオニコチノイド Systemic Pesticides as a Causal Factor of Developmental Brain Disorders (ADHD, autism, etc.) 環 境 脳 神 経 科 学 情 報 センター
2012 9 2 浸 透 性 農 薬 フォーラム 脳 の 発 達 障 害 (ADHD 自 閉 症 など) の 原 因 としての 浸 透 性 農 薬 : ネオニコチノイド Systemic Pesticides as a Causal Factor of Developmental Brain Disorders (ADHD, autism, etc.) 環 境 脳 神 経 科 学 情 報 センター
PROTOCOL. Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry. Background. Materials and equipment required.
 PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized
 Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
Cloning GFP into Mammalian cells
 Protocol for Cloning GFP into Mammalian cells Studiepraktik 2013 Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine Aarhus University Produced by the instructors: Tobias Holm Bønnelykke, Rikke Mouridsen, Steffan
Protocol for Cloning GFP into Mammalian cells Studiepraktik 2013 Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine Aarhus University Produced by the instructors: Tobias Holm Bønnelykke, Rikke Mouridsen, Steffan
INSTRUCTION Probemaker
 INSTRUCTION Probemaker Instructions for Duolink In Situ Probemaker PLUS (Art. no. 92009-0020) and Duolink In Situ Probemaker MINUS (Art. no. 92010-0020) Table of content 1. Introduction 4 2. Applications
INSTRUCTION Probemaker Instructions for Duolink In Situ Probemaker PLUS (Art. no. 92009-0020) and Duolink In Situ Probemaker MINUS (Art. no. 92010-0020) Table of content 1. Introduction 4 2. Applications
Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit
 USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
Supplemental Information. McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data
 1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
Reverse Transcription System
 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Reverse Transcription System Instruc ons for use of Product A3500 Revised 1/14 TB099 Reverse Transcription System All technical literature is available on the Internet at: www.promega.com/protocols/
TECHNICAL BULLETIN Reverse Transcription System Instruc ons for use of Product A3500 Revised 1/14 TB099 Reverse Transcription System All technical literature is available on the Internet at: www.promega.com/protocols/
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Dot Blot Analysis. Teacher s Guidebook. (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences www.gbiosciences.com
 PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Highly specific and sensitive quantitation
 PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection
 Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin
 6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Objectives: A) To separate a mixture of casein and bovine serum albumin B) to characterize these proteins based on their solubilities as a function
6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Objectives: A) To separate a mixture of casein and bovine serum albumin B) to characterize these proteins based on their solubilities as a function
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
SOLIDscript Solid Phase cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual
 Toll Free: 866-252-7771 752A Lincoln Blvd. Phone: 732-469-7771 Fax: 732-469-7782 Middlesex, NJ 08846 Web: www.purebiotechllc.com SOLIDscript Solid Phase cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual Product: SOLIDscript
Toll Free: 866-252-7771 752A Lincoln Blvd. Phone: 732-469-7771 Fax: 732-469-7782 Middlesex, NJ 08846 Web: www.purebiotechllc.com SOLIDscript Solid Phase cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual Product: SOLIDscript
Neurophysiology. 2.1 Equilibrium Potential
 2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
In vitro analysis of pri-mirna processing. by Drosha-DGCR8 complex. (Narry Kim s lab)
 In vitro analysis of pri-mirna processing by Drosha-DGCR8 complex (Narry Kim s lab) 1-1. Preparation of radiolabeled pri-mirna transcript The RNA substrate for a cropping reaction can be prepared by in
In vitro analysis of pri-mirna processing by Drosha-DGCR8 complex (Narry Kim s lab) 1-1. Preparation of radiolabeled pri-mirna transcript The RNA substrate for a cropping reaction can be prepared by in
RT31-020 20 rxns. RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl
 Components RT31-020 20 rxns RT31-050 50 rxns RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl 2x RT Master Mix (2) 200 µl 2 x 250 µl 5 x 200 µl RNase H (E. coli) 20 µl 2 x 25 µl
Components RT31-020 20 rxns RT31-050 50 rxns RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl 2x RT Master Mix (2) 200 µl 2 x 250 µl 5 x 200 µl RNase H (E. coli) 20 µl 2 x 25 µl
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date. The Resting Membrane Potential
 REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman)
 Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
 Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 430 (2013) 1066 1071 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 430 (2013) 1066 1071 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc
WESTERN BLOT PROTOCOL FOR LICOR ODYSSEY SCANNER (HAKE S LAB)
 WESTERN BLOT PROTOCOL FOR LICOR ODYSSEY SCANNER (HAKE S LAB) WESTERN BLOT FOR ANALYSIS ON LICOR ODYSSEY SCANNER. 1) The Licor Odyssey protein marker is optimal as it is visible on channel 700 (2ul is enough
WESTERN BLOT PROTOCOL FOR LICOR ODYSSEY SCANNER (HAKE S LAB) WESTERN BLOT FOR ANALYSIS ON LICOR ODYSSEY SCANNER. 1) The Licor Odyssey protein marker is optimal as it is visible on channel 700 (2ul is enough
JBS FUNDAMENT Thermofluor Screen
 Cat. No. CS-330 Amount 1 Kit For in vitro use only. Quality guaranteed for 3 months. Store at 4 C. Application Screen for thermal stability of proteins as a function of the FUNDAMENTAL variables ph and
Cat. No. CS-330 Amount 1 Kit For in vitro use only. Quality guaranteed for 3 months. Store at 4 C. Application Screen for thermal stability of proteins as a function of the FUNDAMENTAL variables ph and
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red)
 ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red) Instructions for Use For the detection of Rabbit and Mouse Primary antibodies on Rodent Tissue. This product is for research
ab183294 TripleStain IHC Kit: M&M&R on rodent tissue (DAB, DAB/Ni & AP/Red) Instructions for Use For the detection of Rabbit and Mouse Primary antibodies on Rodent Tissue. This product is for research
Western Blotting: Mini-gels
 Western Blotting: Mini-gels Materials a Protein Extraction Buffer (for callus or kernel), Solution Stock Final Volume Tris-HCl ph 80 1 M 200 mm 20 ml NaCl 4 M 100 mm 25 ml Sucrose 2 M 400 mm 20 ml EDTA
Western Blotting: Mini-gels Materials a Protein Extraction Buffer (for callus or kernel), Solution Stock Final Volume Tris-HCl ph 80 1 M 200 mm 20 ml NaCl 4 M 100 mm 25 ml Sucrose 2 M 400 mm 20 ml EDTA
EdU Flow Cytometry Kit. User Manual
 User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
Table of Contents. I. Description... 2. II. Kit Components... 2. III. Storage... 2. IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3
 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers
 Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers Brad Larson 1, Karen Kleman-Leyer 1, Xavier Amouretti 2 1 BellBrook Labs, Madison, WI,
Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers Brad Larson 1, Karen Kleman-Leyer 1, Xavier Amouretti 2 1 BellBrook Labs, Madison, WI,
Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated Antibodies
 USER GUIDE Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated Antibodies Catalog Numbers R933-25, R953-25, R963-25 Document Part Number 25-0376 Publication Number MAN0000194 Revision 2.0 For Research Use Only.
USER GUIDE Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated Antibodies Catalog Numbers R933-25, R953-25, R963-25 Document Part Number 25-0376 Publication Number MAN0000194 Revision 2.0 For Research Use Only.
The mhr model is described by 30 ordinary differential equations (ODEs): one. ion concentrations and 23 equations describing channel gating.
 On-line Supplement: Computer Modeling Chris Clausen, PhD and Ira S. Cohen, MD, PhD Computer models of canine ventricular action potentials The mhr model is described by 30 ordinary differential equations
On-line Supplement: Computer Modeling Chris Clausen, PhD and Ira S. Cohen, MD, PhD Computer models of canine ventricular action potentials The mhr model is described by 30 ordinary differential equations
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit
 ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
PyroPhage 3173 DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus (Exo-)
 PyroPhage 3173 DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus (Exo-) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608)
PyroPhage 3173 DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus (Exo-) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608)
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Day 1 A) DNA shearing 1. Samples Dissect tissue (One Mouse OBs) of interest and transfer to an eppendorf containing 0.5 ml of dissecting media (on ice) or PBS but without
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Day 1 A) DNA shearing 1. Samples Dissect tissue (One Mouse OBs) of interest and transfer to an eppendorf containing 0.5 ml of dissecting media (on ice) or PBS but without
RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method)
 Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
1.Gene Synthesis. 2.Peptide & Phospho-P. Assembly PCR. Design & Synthesis. Advantages. Specifications. Advantages
 1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D4010 & D4011
 Page 0 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. D4010 & D4011 Highlights Quick (5 minute) spin column recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC), viral, phage, (wga)dna, etc.)
Page 0 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. D4010 & D4011 Highlights Quick (5 minute) spin column recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC), viral, phage, (wga)dna, etc.)
Introduction to flow cytometry
 Introduction to flow cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology. Discover more with our introduction to flow cytometry. Flow cytometry is now a widely used method for analyzing the expression
Introduction to flow cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology. Discover more with our introduction to flow cytometry. Flow cytometry is now a widely used method for analyzing the expression
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis
 ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
Outline. 1. Experiment. 2. Sample analysis and storage. 3. Image analysis and presenting data. 4. Probemaker
 Tips and tricks Note: this is just an informative document with general recommendations. Please contact [email protected] should you have any queries. Document last reviewed 2011-11-17 Outline 1. Experiment
Tips and tricks Note: this is just an informative document with general recommendations. Please contact [email protected] should you have any queries. Document last reviewed 2011-11-17 Outline 1. Experiment
UltraClean PCR Clean-Up Kit
 UltraClean PCR Clean-Up Kit Catalog No. Quantity 12500-50 50 Preps 12500-100 100 Preps 12500-250 250 Preps Instruction Manual Please recycle Version: 02212013 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Protocol
UltraClean PCR Clean-Up Kit Catalog No. Quantity 12500-50 50 Preps 12500-100 100 Preps 12500-250 250 Preps Instruction Manual Please recycle Version: 02212013 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Protocol
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit
 ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
Measuring Protein Concentration through Absorption Spectrophotometry
 Measuring Protein Concentration through Absorption Spectrophotometry In this lab exercise you will learn how to homogenize a tissue to extract the protein, and then how to use a protein assay reagent to
Measuring Protein Concentration through Absorption Spectrophotometry In this lab exercise you will learn how to homogenize a tissue to extract the protein, and then how to use a protein assay reagent to
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays.
 Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix. Protocol
 TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE
 ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and the Action of Nicotine, Cocaine, and Marijuana in the Brain Te a c h e r s G u i d e Films for the Humanities & Sciences Background Information This program, made entirely of
ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and the Action of Nicotine, Cocaine, and Marijuana in the Brain Te a c h e r s G u i d e Films for the Humanities & Sciences Background Information This program, made entirely of
SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus-
 Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Problem Sets: Questions and Answers
 BI 360: Neurobiology Fall 2014 Problem Sets: Questions and Answers These problems are provided to aid in your understanding of basic neurobiological concepts and to guide your focus for in-depth study.
BI 360: Neurobiology Fall 2014 Problem Sets: Questions and Answers These problems are provided to aid in your understanding of basic neurobiological concepts and to guide your focus for in-depth study.
Simulation of an Action Potential using the Hodgkin-Huxley Model in Python. Nathan Law 250560559. Medical Biophysics 3970
 Simulation of an Action Potential using the Hodgkin-Huxley Model in Python Nathan Law 250560559 Medical Biophysics 3970 Instructor: Dr. Ian MacDonald TA: Nathaniel Hayward Project Supervisor: Dr. Andrea
Simulation of an Action Potential using the Hodgkin-Huxley Model in Python Nathan Law 250560559 Medical Biophysics 3970 Instructor: Dr. Ian MacDonald TA: Nathaniel Hayward Project Supervisor: Dr. Andrea
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit
 Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
Real-time monitoring of rolling circle amplification using aggregation-induced emission: applications for biological detection
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Supplementary Information Real-time monitoring of rolling circle amplification using aggregation-induced
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Supplementary Information Real-time monitoring of rolling circle amplification using aggregation-induced
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR. A = B (1+e) n. A=amplified products, B=input templates, n=cycle number, and e=amplification efficiency.
 QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR Application: Quantitative RT-PCR is used to quantify mrna in both relative and absolute terms. It can be applied for the quantification of mrna expressed from endogenous genes, and
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR Application: Quantitative RT-PCR is used to quantify mrna in both relative and absolute terms. It can be applied for the quantification of mrna expressed from endogenous genes, and
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products
 Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit
 Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit Store kit at -20 C on receipt (ver. 3-060901) A limited-use label license covers this product. By use of this product, you accept the terms and conditions outlined in
Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit Store kit at -20 C on receipt (ver. 3-060901) A limited-use label license covers this product. By use of this product, you accept the terms and conditions outlined in
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling
 Protocol Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-97893-117 Order per fax: +49-30-97893-299 Or e-mail: [email protected] www: www.jpt.com
Protocol Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-97893-117 Order per fax: +49-30-97893-299 Or e-mail: [email protected] www: www.jpt.com
Biology 309 Lab Notebook
 Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
MystiCq microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C
 microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna
 All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a
 Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr
 DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit
 ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse
 PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes:
 icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Introduction Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis The skeletal muscle is one of the
icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Introduction Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis The skeletal muscle is one of the
