Inhibition of caspase-8 activity reduces IFN-γ expression by T cells from Leishmania major infection
|
|
|
- Ernest Maxwell
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências (28) 8(1): (Annals of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences) ISSN Inhibition of caspase-8 activity reduces IFN-γ expression by T cells from Leishmania major infection WÂNIA F. PEREIRA, LANDI V.C. GUILLERMO, FLÁVIA L. RIBEIRO-GOMES and MARCELA F. LOPES Instituto de Biofísica Carlos Chagas Filho, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Av. Carlos Chagas Filho, Ilha do Fundão, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil Manuscript received on July 11, 27; accepted for publication on August 15, 27; presented by ROGERIO MENEGHINI ABSTRACT Following infection with Leishmania major, T cell activation and apoptosis can be detected in draining lymph nodes of C57BL/6-infected mice. We investigated the mechanisms involved in apoptosis and cytokine expression following T cell activation. After two weeks of infection, apoptotic T cells were not detected in draining lymph nodes but activation with anti-cd3 induced apoptosis in both CD4 and CD8 T cells. Treatment with anti-fas Ligand, caspase-8 or caspase- 9 inhibitors did not block activation-induced T-cell death. We also investigated whether the blockade of caspase-8 activity would affect the expression of type-1 or type-2 cytokines. At early stages of infection, both CD4 and CD8 T cells expressed IFN-γ upon activation. Treatment with the caspase-8 inhibitor zietd-fmk (benzyl-oxycarbonyl-ile- Glu(OMe)-Thr-Asp(OMe)-fluoromethyl ketone) reduced the proportion of CD8 T cells and IFN-γ expression in both CD4 and CD8 T cells. We conclude that a non apoptotic role of caspase-8 activity may be required for T cell-mediated type-1 responses during L. major infection. Key words: apoptosis, caspase-8, CD8 T cells, IFN-γ, Leishmaniasis. INTRODUCTION Immunity to Leishmania infection correlates with protective type 1 response in resistant hosts. CD4 Th1 cells have been considered as a major source of IFN-γ, with NK cells and CD8 T cells playing a minor role in primary infection (McMahon-Pratt and Alexander 24). Susceptibility to Leishmania major infection has been associated with type 2 cytokine responses; whereas IL-1 contributes to parasite persistence (Belkaid et al. 22a), the role of IL-4 produced by CD4 Th2 cells remains controversial (Mohrs et al. 1999, Noben-Trauth et al. 1999, Noben-Trauth et al. 23). Apoptosis of both CD4 and CD8 T cells has been observed within cutaneous lesions in human leishmaniasis (Bertho et al. 2), as well as in lymph nodes from mice Correspondence to: Marcela de Freitas Lopes biof.ufrj.br infected with L. major (Desbarats et al. 2). Apoptosis contributes to T cell anergy to Leishmania amazonensis antigens (Pinheiro et al. 24), but the mechanisms involved in T cell death in cutaneous leishmaniasis are not known. T cell apoptosis can be mediated by intrinsic pathway involving growth factor deprivation and caspase-9 activation (Alves et al. 27). By contrast, activationinduced cell death (AICD) occurs upon induction of Fas Ligand (FasL) expression, interaction with death receptor Fas and recruitment of caspase-8 (Lenardo et al. 1999, Krammer 2). Caspase-8 is also involved in T cell signaling for proliferation, IL-2 production and development of CD8 T cell memory (Alam et al. 1999, Kennedy et al. 1999, Chun et al. 22, Wu et al. 24). We investigated the role of caspase-8 in T-cell apoptosis and control of cytokine responses in draining lymph nodes upon L. major infection. Activation-in-
2 13 WÂNIA F. PEREIRA et al. duced T cell death occurs in both CD4 and CD8 T cells from infected mice. Nonetheless, inhibitors of FasL, caspase-8 or caspase-9 did not affect T cell apoptosis, whereas caspase-8 inhibition reduced IFN-γ expression upon stimulation of T cells. These results suggest that caspase-8 activity may be required in the development of protective immune responses to Leishmania infection. MATERIALS AND METHODS MICE AND L. major INFECTION Female C57BL/6 mice were obtained from the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro. L. major LV39 isolated from BALB/c mice were cultured in Schneider s medium at 28 C during 4 days and used at the stationary phase of the culture. Mice, aging 7-9 wk, were infected in the left hind footpad with sc injection of metacyclic promastigotes/3 µl. Mice were killed during the acute phase at 2, 6, and 13 weeks post infection. All experiments and animal handling were conducted according to approved institutional protocols. CELL SUSPENSIONS AND CULTURES Cells were obtained from draining (popliteal) lymph nodes from infected mice or from a pool of inguinal and popliteal lymph nodes from normal mice. Cells were re-suspended in DMEM (Invitrogen Life Technologies), supplemented with 2 mm glutamine, M 2-ME, 1 µg/ml gentamicin, 1 mm sodium pyruvate,.1 mm MEM nonessential amino acids, and 1 mm HEPES plus 1% FBS (Invitrogen Life Technologies). Cells (1 1 6 /.5mL) were cultured in duplicate in medium only or stimulated with 1 µg/ml plate-bound anti-cd3 (mab 2C11; BD Pharmingen) in 48-well vessels. Cultures were set at 37 C and 7% CO 2 in a humid atmosphere for 24 h. In some experiments, cells were activated with anti-cd3 and incubated with 1 µg/ ml anti-fasl (clone MFL3) or IgG control mab (BD Pharmingen), or with 4 µm of caspase-8 inhibitor zi- ETD (zietd-fmk: benzyl-oxycarbonyl-ile-glu(ome)- Thr-Asp(OMe)-fluoromethyl ketone), or caspase-9 inhibitor zlehd (zlehd-fmk: benzyl-oxycarbonyl-leu- Glu(OMe)-His-Asp(OMe)-fmk) from Enzyme System Products, or.4% DMSO as stock diluent control. Apoptosis was evaluated in T cell subsets by flow cytometry as described below. FLOW CYTOMETRY Fresh or cultured cells were washed in sorting buffer (containing 2% FBS) and incubated with anti-cd16/ CD32 for Fc blocking, followed by staining with allophycocyanin-labeled anti-cd8 or anti-cd4 for 3 min at 4 C. All mabs used in flow cytometry are from BD Pharmingen. For apoptosis detection, cells were washed to remove excess of surface staining reagents, and then stained with FITC-annexin V (apoptosis detection kit; R&D Systems) for 2 min at room temperature in annexin buffer or with 7-AAD, which was added just prior to flow cytometry. Cells were also stained with FITClabeled anti-cd44 as a marker for T cell activation. Cells were washed and acquired on a FACSCalibur system, by using Cell quest software (BD Biosciences). For analysis, FlowJo software was used (TreeStar). INTRACELLULAR CYTOKINES Lymph node cells (1 1 6 /.5 ml) obtained from L. major-infected mice (2 wk upon infection) were cultured in 48 well plates with plate bound anti-cd3 (1 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of IL-4 (1 ng/ml), zietd (4 µm) or.4% DMSO. Upon 72 h, PMA (1 ng/ml) and ionomycin (.5 µg/ml) from Sigma were added to cultures. Some cultures were left without further stimulation. After 1 h, brefeldin A (1 µg/ml, Sigma) was added to all cells. Cells were collected upon 3 h, counted, stained, and analyzed by flow cytometry. For surface markers, cells were treated with allophycocyanin-labeled anti-cd8 or anti-cd4, washed, fixed and stained with PE-anti-IL-1 and FITC-anti-IFNγ. DATA ANALYSIS Results are expressed as average and SEM in figures and the number (n) of animals per group was indicated in figure legend. For in vitro experiments, data are expressed as average of 2-3 determinations per treatment, in each of at least 3 repeat experiments, and significant differences detected in Student s t test were shown for p <.5( ). RESULTS T CELL APOPTOSIS DURING L.major INFECTION We infected B6 mice in the footpads with L. major and followed the onset of activation and apoptosis in T cells from draining (popliteal) lymph nodes. Increased ex-
3 CASPASE-8 AND IFN-γ EXPRESSION IN L. major INFECTION 131 A B CD44 hi cells (%) CD4 T cells: Normal Infected CD44 hi cells (%) CD8 T cells: Normal Infected C 7AAD + cells (%) weeks post infection CD4 T cells: Normal Infected D 7AAD + cells (%) weeks post infection CD8 T cells: Normal Infected weeks post infection weeks post infection Fig. 1 T cell activation and apoptosis during L. major infection. Lymph node cells from normal and L. major-infected mice were analysed by flow cytometry. Activation of CD4 (A) and CD8 (B) T cells was determined by high expression of CD44. Apoptosis was assed upon staining with 7-AAD in CD4 (C) and CD8 (D) T cells. Open bars represents T-cell activation and apoptosis in a pool of (inguinal and popliteal) lymph nodes from normal mice, black bars represent draining (popliteal) lymph nodes from L. major-infected mice. Results are expressed as average and SEM (n=2-3 mice/group). pression of CD44 and staining with 7-AAD were assessed as markers of activation and apoptosis in T cells, respectively. We observed increased activation and apoptosis 6 wk upon L. major infection in both CD4 and CD8 T cells (Fig. 1). After 13 wk of infection, however, activation returned to baseline levels (Fig. 1A and B), whereas apoptosis remained elevated (Fig. 1C and D). We investigated the mechanisms of T cell apoptosis in vitro. Activation with anti-cd3 induced apoptosis in both CD4 and CD8 T cells from draining lymph nodes as early as 2 wk (Fig. 2A and B) upon infection with L. major. AICD was more evident in CD4 than in CD8 T cells upon 2 (Fig. 2A and B) or 6 (Fig. 2C and D) wk of infection. To investigate the role of Fas-death pathway, we treated T cell cultures with anti-fasl or control IgG antibody and assessed apoptosis by annexin V staining upon 24 h. Treatment with anti-fasl did not inhibit apoptosis induced upon T cell activation (Fig. 3A and B). To address whether caspase-8 or caspase-9 were involved in apoptosis, T cells were activated in the presence of caspase-8 (zietd) or caspase-9 (zlehd) inhibitor. Neither zietd nor zlehd inhibited AICD in T cells from L. major infection (Fig. 3C and D). CASPASE-8 AND CYTOKINE EXPRESSION BY TCELLS Previous experiments suggest a non apoptotic role of caspases in T cell signaling for cytokine responses (Sehra et al. 25, Su et al. 25). We addressed by flow cyto-
4 132 WÂNIA F. PEREIRA et al. Fig. 2 Activation-induced cell death upon infection with L. major. Lymph node cells from normal and L. major-infected mice were cultured in the presence of medium only (open bars) or stimulated with anti-cd3 (black bars). After 24 h, cells were stained with anti-cd4 (A and C), anti-cd8 (B and D), 7-AAD and evaluated by flow cytometry. Panels show percentages of apoptotic (7-AAD + ) CD4 and CD8 T cells upon 2 (A and B) or 6 (C and D) weeks of infection. Results are expressed as average and SEM. Significant differences between cells treated with medium and anti-cd3 were indicated for p <.5( ). metry cytokine expression in T cell subsets, and whether caspase-8 controls type-1/type-2 cytokines upon L. major infection. First, T cells from draining lymph nodes (2 wk post infection) were activated with anti-cd3 in the presence of caspase-8 inhibitor zietd or DMSO only during 72 h. Then, T cells were re-stimulated with ionomycin and PMA, in the presence of brefeldin A, to prevent cytokine secretion. The presence of zietd did not affect the number of cells recovered from T cell cultures (not shown). The proportions of CD4 and CD8 T cells were similar (3-4%) in cultures (Fig. 4A and B). Caspase-8 inhibition negatively affected CD8, but not CD4, T cells (Fig. 4A and B) and the proportion of cells expressing IFN-γ, but not IL-1 (Fig. 4C and D). Both CD4 and CD8 T cells expressed IFN-γ (Fig. 5A and B), whereas expression of IL-4 was not detected even upon culture with exogenous IL-4 (not shown). The inhibition of caspase-8 decreased the expression of IFN-γ in both CD4 and CD8 T cells (Fig. 5A and B). These results suggest that caspase-8 plays a role in the control of cytokine responses to L. major infection. DISCUSSION Apoptosis of CD4 T cells has been suggested as a mechanism to reduce Th1 responses in Leishmania donovani infection (Das et al. 1999). In addition, Fas and/or FasL expression has been detected in T cells from lymph nodes (Desbarats et al. 2) or lesions (Eidsmo et al. 25) during L. major infection, and mice with defective Fas/ FasL expression show increased Th1 responses upon L. donovani (Alexander et al. 21) and L. major (Huang
5 CASPASE-8 AND IFN-γ EXPRESSION IN L. major INFECTION 133 Fig. 3 T-cell death pathways during L. major infection. Lymph node cells from infected (2 wk) mice were cultured with medium only (open bars) or stimulated with anti-cd3 (black bars) in the presence of anti-fasl or control IgG (A and B) or in the presence of zietd, zlehd or stock diluent DMSO (C and D). After 24 h, cultured cells were stained with anti-cd4, anti-cd8, and annexin V. Panels show percentages of apoptotic (annexin V + ) CD4 (A and C) and CD8 (B and D) T cells. Results are expressed as average and SEM. et al. 1998) infections. We observed increased apoptosis in both CD4 and CD8 T cells from draining lymph nodes only at later stages of L. major infection. T cell apoptosis can also be induced by stimulation in vitro (AICD) as early as 2 wk and after 6 wk, at the peak of lymphocyte activation in vivo. Nonetheless, AICD was not blocked by inhibitors of FasL, caspase-8 or caspase- 9, although these reagents have been successfully used at the same doses in previous unrelated experiments (Silva et al. 25, Guillermo et al. 27). Therefore, AICD in lymph nodes from L. major infection may be mediated by other mechanisms, such as granzyme-b-induced apoptosis (Devadas et al. 26). By contrast, caspase-8 inhibition by zietd peptide negatively affected CD8 T cells and the expression of IFN-γ in T cells from L. major-infected mice. Similarly, CD8 T cells have defective survival and IFN-γ expression in mice bearing a T cell-restricted transgene for the viral-flice/caspase-8 inhibitory protein (vflip) (Wu et al. 24). These results suggest a paradoxical role of caspase-8 preventing, rather than inducing T cell death. Although caspase-8 inhibition could affect CD8 T-cell responses during L. major infection, the role of CD8 T cells as an important source of IFN-γ in the immunity to primary L. major infection is disputed (Huber et al. 1998, Belkaid et al. 22b). However, it has been suggested that CD8 T cells can favor IFN-γ expression by protective CD4 Th1 cells during L. major infection. (Herath et al. 23). Based on evidence suggesting a non apoptotic role of caspase-8 in T cell signaling for cytokine expression (Su et al. 25), we studied how caspase-8 inhibition would affect the development of type-1 vs type-2 responses following L. major infection. Caspase-8 inhibition decreased the expression of IFN-γ by both CD4 and CD8 T cells. It is possible that these effects are due to defective signaling for cytokine expression upon caspase-8 inhibition as previously observed for NF-κB activation
6 134 WÂNIA F. PEREIRA et al. A CD4 + cells (%) 5 Lymph node: medium Ion + PMA B CD8 + cells (%) 5 4 Lymph node: medium Ion + PMA 3 * 2 1 C - DMSO IETD D - DMSO IETD 6 Lymph node: medium 4 Lymph node: medium IL-1 + cells (%) Ion+PMA IFN + cells (%) Ion+PMA * - DMSO IETD - DMSO IETD Fig. 4 Expression of type 1 and type 2 cytokines in L. major infection. Lymph node cells from infected (2 wk) mice were stimulated with anti-cd3 only or in the presence of zietd or stock diluent DMSO for 72 h. Cells were re-stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 4 h, in the presence of brefeldin A. Cells were stained with anti-cd4 (A), anti-cd8 (B) or permeabilized and stained with anti-il-1 (C) and anti-ifn-γ (D). Results are expressed as average and SEM. Significant differences between cells treated with zietd and DMSO were indicated for p <.5( ). and IL-2 secretion (Silva et al. 25, Su et al. 25). In agreement with this idea, defective NF-κB activation affects negatively both proliferation and the production of IFN-γ by T cells (Corn et al. 23). By contrast, IL- 1 expression in T cells from L. major infection was not affected by inhibition of caspase-8 even in the presence of IL-4 (not shown). Therefore, non apoptotic activity of caspase-8 is not necessary for the expression of type- 2 cytokines, but may be required for the induction of protective type-1 response in L. major infection. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank George A. DosReis (IBCCF-UFRJ) for helpful suggestions. This investigation received financial support from the UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Program for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases (TDR) (grant A6281), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), and Institute for Investigation in Immunology (iii), Millennium Institutes, Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology. W.F.P. receives an MSc fellowship from Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). M.F.L. is a research fellow at CNPq, Brazil. RESUMO A ativação e a morte por apoptose de linfócitos T foram observadas em linfonodos drenantes de camundongos C57BL/6 infectados com Leishmania major. Investigamos os mecanismos envolvidos na apoptose e na expressão de citocinas após a ativação de linfócitos T. Após duas semanas de infecção, embora as células apoptóticas ainda não sejam detectadas em linfonodos drenantes, células T CD4 e CD8 sofrem apoptose após ativação com anti-cd3. O tratamento com anticorpo antagonista anti-ligante de Fas, ou com inibidores das caspases-8 e 9, não
7 CASPASE-8 AND IFN-γ EXPRESSION IN L. major INFECTION 135 A DMSO IETD 36.7% 18.3% B CD8 CD4 34.1% 25.2% IFN-γ Fig. 5 Inhibition of caspase-8 reduces IFN-γ expression by T cells from L. major infected mice. Lymph node cells from infected (2 wk) mice were stimulated with anti-cd3 in the presence of zietd (right panels) or stock diluent DMSO (left panels), re-stimulated as described above and stained with anti-cd4 (A), anti-cd8 (B) and anti-ifn-γ (A and B). Panels show percentages of IFN-γ + CD4 T cells (A), and IFN-γ + CD8 T cells (B) as assessed by flow cytometry. bloqueou a morte induzida por ativação das células T. Investigamos também se a inibição da atividade da caspase-8 poderia afetar a expressão de citocinas tipo-1 ou tipo-2. Nos estágios iniciais da infecção, células T CD4 e CD8 de animais infectados com L. major expressaram IFN-γ após ativação. O tratamento com o inibidor de caspase-8 zietd (benzoil-oxicarbonil-ile- Glu(OMe)-Thr-Asp(OMe)-fluorometilcetona) durante a estimulação de células T reduziu a proporção de células T CD8 e a expressão de IFN-γ por células T CD4 e CD8. Concluimos que a atividade não apoptótica de caspase-8 pode ser necessária para o estabelecimento da imunidade mediada por células T durante a infecção por L. major. Palavras-chave: apoptose, caspase-8, células T CD8, IFNgama, Leishmanioses. REFERENCES ALAM A, COHEN LY, AOUAD S AND SEKALY RP Early activation of caspases during T lymphocyte stimulation results in selective substrate cleavage in nonapoptotic cells. J Exp Med 19: ALEXANDER CE, KAYE PM AND ENGWERDA CR. 21. CD95 is required for the early control of parasite burden in the liver of Leishmania donovani-infected mice. Eur J Immunol 31: ALVES NL, VAN LIER RA AND ELDERING E. 27. Withdrawal symptoms on display: Bcl-2 members under investigation. Trends Immunol 28: BELKAID Y, PICCIRILLO CA, MENDEZ S, SHEVACH EM AND SACKS DL. 22a. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature 42: BELKAID Y, VON STEBUT E, MENDEZ S, LIRA R, CALER E, BERTHOLET S, UDEY MC AND SACKS D. 22b. CD8+ T cells are required for primary immunity in C57BL/6 mice following low-dose, intradermal challenge with Leishmania major. J Immunol 168: BERTHO AL, SANTIAGO MA, DA-CRUZ AM AND COU- TINHO SG. 2. Detection of early apoptosis and cell
8 136 WÂNIA F. PEREIRA et al. death in T CD4+ and CD8+ cells from lesions of patients with localized cutaneous leishmaniasis. Braz J Med Biol Res 33: CHUN HJ ET AL. 22. Pleiotropic defects in lymphocyte activation caused by caspase-8 mutations lead to human immunodeficiency. Nature 419: CORN RA ET AL. 23. T cell-intrinsic requirement for NF-κB induction in postdifferentiation IFN-γ production and clonal expansion in a Th1 response. J Immunol 171: DAS G, VOHRA H, RAO K, SAHA B AND MISHRA GC Leishmania donovani infection of a susceptible host results in CD4+ T-cell apoptosis and decreased Th1 cytokine production. Scand J Immunol 49: DESBARATS J, STONE JE, LIN L, ZAKERI ZF, DAVIS GS, PFEIFFER LM, TITUS RG AND NEWELL MK. 2. Rapid early onset lymphocyte cell death in mice resistant, but not susceptible to Leishmania major infection. Apoptosis 5: DEVADAS S, DAS J, LIU C, ZHANG L, ROBERTS AI, PAN Z, MOORE PA, DAS G AND SHI Y. 26. Granzyme B is critical for T cell receptor-induced cell death of type 2 helper T cells. Immunity 25: EIDSMO L, NYLEN S, KHAMESIPOUR A, HEDBLAD MA, CHIODI F AND AKUFFO H. 25. The contribution of the Fas/FasL apoptotic pathway in ulcer formation during Leishmania major-induced cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Am J Pathol 166: GUILLERMO LV, SILVA EM, RIBEIRO-GOMES FL, DE MEIS J, PEREIRA WF, YAGITA H, DOSREIS GA AND LOPES MF. 27. The Fas death pathway controls coordinated expansions of type 1 CD8 and type 2 CD4 T cells in Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Leukoc Biol 81: HERATH S, KROPF P AND MULLER I. 23. Cross-talk between CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells in experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis: CD8(+) T cells are required for optimal IFN-γ production by CD4(+) T cells. Parasite Immunol 25: HUANG FP, XU D, ESFANDIARI EO, SANDS W, WEI XQ AND LIEW FY Mice defective in Fas are highly susceptible to Leishmania major infection despite elevated IL-12 synthesis, strong Th1 responses, and enhanced nitric oxide production. J Immunol 16: HUBER M, TIMMS E, MAK TW, ROLLINGHOFF M AND LOHOFF M Effective and long-lasting immunity against the parasite Leishmania major in CD8-deficient mice. Infect Immun 66: KENNEDY NJ, KATAOKA T, TSCHOPP J AND BUDD RC Caspase activation is required for T cell proliferation. J Exp Med 19: KRAMMER PH. 2. CD95 s deadly mission in the immune system. Nature 47: LENARDO M, CHAN KM, HORNUNG F, MCFARLAND H, SIEGEL R, WANG J AND ZHENG L Mature T lymphocyte apoptosis immune regulation in a dynamic and unpredictable antigenic environment. Annu Rev Immunol 17: MCMAHON-PRATT D AND ALEXANDER J. 24. Does the Leishmania major paradigm of pathogenesis and protection hold for New World cutaneous leishmaniases or the visceral disease? Immunol Rev 21: MOHRS M, LEDERMANN B, KOHLER G, DORFMULLER A, GESSNER A AND BROMBACHER F Differences between IL-4- and IL-4 receptor alpha-deficient mice in chronic leishmaniasis reveal a protective role for IL-13 receptor signaling. J Immunol 162: NOBEN-TRAUTH N, PAUL WE AND SACKS DL IL- 4- and IL-4 receptor-deficient BALB/c mice reveal differences in susceptibility to Leishmania major parasite substrains. J Immunol 162: NOBEN-TRAUTH N, LIRA R, NAGASE H, PAUL WE AND SACKS DL. 23. The relative contribution of IL-4 receptor signaling and IL-1 to susceptibility to Leishmania major. J Immunol 17: PINHEIRO RO, PINTO EF, BENEDITO AB, LOPES UG AND ROSSI-BERGMANN B. 24. The T-cell anergy induced by Leishmania amazonensis antigens is related with defective antigen presentation and apoptosis. An Acad Bras Cienc 76: SEHRA S, PATEL D, KUSAM S, WANG ZY, CHANG CH AND DENT AL. 25. A role for caspases in controlling IL-4 expression in T cells. J Immunol 174: SILVA EM ET AL. 25. Caspase-8 activity prevents type 2 cytokine responses and is required for protective T cellmediated immunity against Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Immunol 174: SU H, BIDERE N, ZHENG L, CUBRE A, SAKAI K, DALE J, SALMENA L, HAKEM R, STRAUS S AND LENARDO M. 25. Requirement for caspase-8 in NF-κB activation by antigen receptor. Science 37: WU Z ET AL. 24. Viral FLIP impairs survival of activated T cells and generation of CD8+ T cell memory. J Immunol 172:
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Determination of specificity of intracellular detection of IL-7Rα by flow cytometry
 CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS.
 TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Introduction to Flow Cytometry
 Outline Introduction to Flow Cytometry Basic Concept of Flow Cytometry Introduction to Instrument Subsystems Daisy Kuo Assistant Product Manager E-mail: daisy_kuo@bd.com BDBiosciences Application Examples
Outline Introduction to Flow Cytometry Basic Concept of Flow Cytometry Introduction to Instrument Subsystems Daisy Kuo Assistant Product Manager E-mail: daisy_kuo@bd.com BDBiosciences Application Examples
The Costimulatory Molecule CD27 Maintains Clonally
 Immunity, Volume 35 Supplemental Information The Costimulatory Molecule CD7 Maintains Clonally Diverse CD8 + T Cell Responses of Low Antigen Affinity to Protect against Viral Variants Klaas P.J.M. van
Immunity, Volume 35 Supplemental Information The Costimulatory Molecule CD7 Maintains Clonally Diverse CD8 + T Cell Responses of Low Antigen Affinity to Protect against Viral Variants Klaas P.J.M. van
EFFECTS OF IRON ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 EFFECTS OF IRON ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Gert Mayer Department of Internal Medicine IV (Nephrology and Hypertension) Medical University Innsbruck Austria Conflicts of interest Research Support: Amgen, Roche,
EFFECTS OF IRON ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Gert Mayer Department of Internal Medicine IV (Nephrology and Hypertension) Medical University Innsbruck Austria Conflicts of interest Research Support: Amgen, Roche,
Identification of T-cell epitopes of SARS-coronavirus for development of peptide-based vaccines and cellular immunity assessment methods
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES PKS Chan 陳 基 湘 S Ma 文 子 光 SM Ngai 倪 世 明 Key Messages 1. Subjects recovered from SARS-CoV infection retain memory of cellular immune response to epitopes
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES PKS Chan 陳 基 湘 S Ma 文 子 光 SM Ngai 倪 世 明 Key Messages 1. Subjects recovered from SARS-CoV infection retain memory of cellular immune response to epitopes
PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens
 www.iqproducts.nl PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens IFN- γ PURE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160P s 50 tests FITC [RUO] [REF] IQP-160F s 50 tests R-PE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160R s 50
www.iqproducts.nl PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens IFN- γ PURE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160P s 50 tests FITC [RUO] [REF] IQP-160F s 50 tests R-PE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160R s 50
Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication. Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic
 Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Why do Waldenstrom s cells need to communicate? Waldenstrom s cells need activating signals to stay alive. WM cells
Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Why do Waldenstrom s cells need to communicate? Waldenstrom s cells need activating signals to stay alive. WM cells
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit
 Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells. Effector T cells. After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells
 After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
The importance of the CD4
 CD4 T Cells Are Required for the Development of Cytotoxic CD8 T Cells During Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection 1 Natalya V. Serbina, 2 Vanja Lazarevic, and JoAnne L. Flynn 3 The control of acute and
CD4 T Cells Are Required for the Development of Cytotoxic CD8 T Cells During Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection 1 Natalya V. Serbina, 2 Vanja Lazarevic, and JoAnne L. Flynn 3 The control of acute and
RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method)
 Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory
 Immunology and Cell Biology (1999) 77, 559 564 Special Feature Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory DA FULCHER
Immunology and Cell Biology (1999) 77, 559 564 Special Feature Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory DA FULCHER
CD4 Th1 Cells Induced by Dendritic Cell-Based Immunotherapy in Mice Chronically Infected with Leishmania amazonensis Do Not Promote Healing
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2004, p. 4455 4463 Vol. 72, No. 8 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4455 4463.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. CD4 Th1
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2004, p. 4455 4463 Vol. 72, No. 8 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4455 4463.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. CD4 Th1
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
The nonobese diabetic (NOD)
 Low CD86 Expression in the Nonobese Diabetic Mouse Results in the Impairment of Both T Cell Activation and CTLA-4 Up-Regulation Eva Dahlén, 1 Gunnar Hedlund, and Kim Dawe The nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse
Low CD86 Expression in the Nonobese Diabetic Mouse Results in the Impairment of Both T Cell Activation and CTLA-4 Up-Regulation Eva Dahlén, 1 Gunnar Hedlund, and Kim Dawe The nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse
Flow Cytometric Analysis of Leishmania Reactive CD4 + /CD8 + Lymphocyte Proliferation in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
 Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 3, No.4, 28, pp. 9-18 Original Article Flow Cytometric Analysis of Leishmania Reactive CD4 + /CD8 + Lymphocyte Proliferation in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis M Nateghi Rostami 1, A
Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 3, No.4, 28, pp. 9-18 Original Article Flow Cytometric Analysis of Leishmania Reactive CD4 + /CD8 + Lymphocyte Proliferation in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis M Nateghi Rostami 1, A
Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity. Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands
 Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands CBER/NIAID/WHO, Bethesda MD, December 11 2007 A working model of an antiviral
Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands CBER/NIAID/WHO, Bethesda MD, December 11 2007 A working model of an antiviral
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit
 Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Islet Viability Assessment by Single Cell Flow Cytometry
 Islet Viability Assessment by Single Cell Flow Cytometry Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To comprehensively assess the viability of the islet cell preparation prior to transplantation. Tissue Samples: A sample containing
Islet Viability Assessment by Single Cell Flow Cytometry Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To comprehensively assess the viability of the islet cell preparation prior to transplantation. Tissue Samples: A sample containing
International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005
 Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Cell viability assays were represented as mean ± S.E. (n=3). Comparisons between the
 Supplemental Data 1 Online supplemental information Statistical analysis Cell viability assays were represented as mean ± S.E. (n=3). Comparisons between the groups were performed using repeated measures
Supplemental Data 1 Online supplemental information Statistical analysis Cell viability assays were represented as mean ± S.E. (n=3). Comparisons between the groups were performed using repeated measures
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Analysis of Apoptosis by Flow-cytometry
 Analysis of Apoptosis by Flow-cytometry Marie-Lise GOUGEON Antiviral Immunity, Biotherapy and Vaccine Unit 2nd training course on Concepts and Methods in Programmed Cell Death «Genetic Pathways and Techniques
Analysis of Apoptosis by Flow-cytometry Marie-Lise GOUGEON Antiviral Immunity, Biotherapy and Vaccine Unit 2nd training course on Concepts and Methods in Programmed Cell Death «Genetic Pathways and Techniques
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit
 Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Dr Malkit S Riyat. MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit
 Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Summary and Conclusions This study has attempted to document the following effects of targeting protein antigens to the macrophage scavenger receptors by maleylation. 1. Modification
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Summary and Conclusions This study has attempted to document the following effects of targeting protein antigens to the macrophage scavenger receptors by maleylation. 1. Modification
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center
 Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TABLE OF CONTENT. Page ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. iii ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT. vii LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES. xvi ABBREVIATIONS.
 x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
Signaling monitoring and flow cytometry
 Signaling monitoring and flow cytometry Coultry Club, FIAP Paris April 8, 2014 Dr Jacques Nunès Lymphocyte Activation Group 1 PLAN I Signalisation intracellulaire & «signal monitoring» II Méthodologie
Signaling monitoring and flow cytometry Coultry Club, FIAP Paris April 8, 2014 Dr Jacques Nunès Lymphocyte Activation Group 1 PLAN I Signalisation intracellulaire & «signal monitoring» II Méthodologie
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
A. FSC and SSC gating of total BM cells. B. Gating strategy used to identify the Lin -
 Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Multiparametric analysis of HSC Populations. A. FSC and SSC gating of total BM cells. B. Gating strategy used to identify the Lin - cell population. BM cells were
Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Multiparametric analysis of HSC Populations. A. FSC and SSC gating of total BM cells. B. Gating strategy used to identify the Lin - cell population. BM cells were
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
02/08/2010. 1. Background. Outline
 Identification of immunodominant T-cell eptitopes in matrix protein of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Ya-Xin Wang, PhD Student Outline 1. Background 2. Research Contents
Identification of immunodominant T-cell eptitopes in matrix protein of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Ya-Xin Wang, PhD Student Outline 1. Background 2. Research Contents
BrdU Flow Kits. Instruction Manual. FITC BrdU Flow Kit. APC BrdU Flow Kit. BD Pharmingen. Cat. No. 559619 (50 tests) Cat. No. 557891 (4 50 tests)
 BD Pharmingen BrdU Flow Kits Instruction Manual FITC BrdU Flow Kit Cat. No. 559619 (50 tests) Cat. No. 557891 (4 50 tests) APC BrdU Flow Kit Cat. No. 552598 (50 tests) Cat. No. 557892 (4 50 tests) BD flow
BD Pharmingen BrdU Flow Kits Instruction Manual FITC BrdU Flow Kit Cat. No. 559619 (50 tests) Cat. No. 557891 (4 50 tests) APC BrdU Flow Kit Cat. No. 552598 (50 tests) Cat. No. 557892 (4 50 tests) BD flow
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy
 Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy
 CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
QuickTiter FeLV Core Antigen ELISA Kit (FeLV p27)
 Product Manual QuickTiter FeLV Core Antigen ELISA Kit (FeLV p27) Catalog Numbers VPK-155 96 wells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) is
Product Manual QuickTiter FeLV Core Antigen ELISA Kit (FeLV p27) Catalog Numbers VPK-155 96 wells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) is
LPG2 parasites and their interaction With Leishmania Major
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2009, p. 3272 3283 Vol. 77, No. 8 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01447-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Leishmania major Phosphoglycans
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2009, p. 3272 3283 Vol. 77, No. 8 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01447-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Leishmania major Phosphoglycans
低 剂 量 辐 射 对 脐 血 T 淋 巴 细 胞 膜 分 子 表 达 的 影 响 EFFECT OF LOW DOSE IRRADIATION ON EXPRESSION OF MEMBRANE MOLECULES OF T LYMPHOCYTES IN CORD BLOOD
 CNIC-01513 PUTH-0001 低 剂 量 辐 射 对 脐 血 T 淋 巴 细 胞 膜 分 子 表 达 的 影 响 EFFECT OF LOW DOSE IRRADIATION ON EXPRESSION OF MEMBRANE MOLECULES OF T LYMPHOCYTES IN CORD BLOOD 中 国 核 情 报 中 心 China Nuclear Information
CNIC-01513 PUTH-0001 低 剂 量 辐 射 对 脐 血 T 淋 巴 细 胞 膜 分 子 表 达 的 影 响 EFFECT OF LOW DOSE IRRADIATION ON EXPRESSION OF MEMBRANE MOLECULES OF T LYMPHOCYTES IN CORD BLOOD 中 国 核 情 报 中 心 China Nuclear Information
DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM TO EXCHANGE ATTENUATORS OF THE OB85/1 GAMMA IRRADIATOR
 2011 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2011 Belo Horizonte,MG, Brazil, October 24-28, 2011 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-04-5 DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION
2011 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2011 Belo Horizonte,MG, Brazil, October 24-28, 2011 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-04-5 DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION
SYNERGISTIC ROLE OF IL-15 IN THE EPITHELIUM AND THE LAMINA PROPRIA IN CELIAC DISEASE PATHOGENESIS
 SYNERGISTIC ROLE OF IL-15 IN THE EPITHELIUM AND THE LAMINA PROPRIA IN CELIAC DISEASE PATHOGENESIS Bana Jabri Department of Medicine Celiac Disease Center University of Chicago Ingested gluten Environmental
SYNERGISTIC ROLE OF IL-15 IN THE EPITHELIUM AND THE LAMINA PROPRIA IN CELIAC DISEASE PATHOGENESIS Bana Jabri Department of Medicine Celiac Disease Center University of Chicago Ingested gluten Environmental
Combining Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy in Melanoma
 Combining Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy in Melanoma 8:45 am - 9:15 am Antoni Ribas, M.D., h.d. rofessor of Medicine rofessor of Surgery rofessor of Molecular and Medical harmacology Director, Tumor
Combining Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy in Melanoma 8:45 am - 9:15 am Antoni Ribas, M.D., h.d. rofessor of Medicine rofessor of Surgery rofessor of Molecular and Medical harmacology Director, Tumor
LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Flow Cytometry. What is Flow Cytometry? What Can a Flow Cytometer Tell Us About a Cell? Particle Size. Flow = Fluid Cyto = Cell Metry = Measurement
 What is Flow Cytometry? Flow Cytometry Basic Principle and Applications BD Biosciences Daisy Kuo (daisy_kuo@bd.com) Flow = Fluid Cyto = Cell Metry = Measurement A variety of measurements are made on cells,
What is Flow Cytometry? Flow Cytometry Basic Principle and Applications BD Biosciences Daisy Kuo (daisy_kuo@bd.com) Flow = Fluid Cyto = Cell Metry = Measurement A variety of measurements are made on cells,
How do plasma cells survive
 How do plasma cells survive Claudia Berek Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft Immune response Naive B cell Peripheral lymphoid organs Memory B cell Germinal T
How do plasma cells survive Claudia Berek Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft Immune response Naive B cell Peripheral lymphoid organs Memory B cell Germinal T
PROTOCOL. Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry. Background. Materials and equipment required.
 PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
Les interactions parasites eucaryotes-hôtes: * * transient pathogenic processes in humans. How does Leishmania Adaptive
 Les interactions parasites eucaryotes-hôtes: l exemple de Leishmania * * t = 24h Geneviève Milon * * * Leishmania major : first recognized as the etiological agent of transient pathogenic processes in
Les interactions parasites eucaryotes-hôtes: l exemple de Leishmania * * t = 24h Geneviève Milon * * * Leishmania major : first recognized as the etiological agent of transient pathogenic processes in
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS
 EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
Selection of Cell Lines for Manufacturing Therapeutic Antibodies by Flow Cytometric Cell Sorting. Andrew Racher Lonza Biologics
 Selection of Cell Lines for Manufacturing Therapeutic Antibodies by Flow Cytometric Cell Sorting Andrew Racher Lonza Biologics Structure of Talk 1. The Problem 2. Possible Solutions 3. Solution Chosen
Selection of Cell Lines for Manufacturing Therapeutic Antibodies by Flow Cytometric Cell Sorting Andrew Racher Lonza Biologics Structure of Talk 1. The Problem 2. Possible Solutions 3. Solution Chosen
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service
 KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
2.1.2 Characterization of antiviral effect of cytokine expression on HBV replication in transduced mouse hepatocytes line
 i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
Analysis of the adaptive immune response to West Nile virus
 Analysis of the adaptive immune response to West Nile virus Jonathan Bramson (PI) Robin Parsons Alina Lelic Galina Denisova Lesley Latham Carole Evelegh Dmitri Denisov Strategy for characterizing T cell
Analysis of the adaptive immune response to West Nile virus Jonathan Bramson (PI) Robin Parsons Alina Lelic Galina Denisova Lesley Latham Carole Evelegh Dmitri Denisov Strategy for characterizing T cell
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
This presentation may contain forward-looking statements, which reflect Trillium's current expectation regarding future events. These forward-looking
 Q1/2016 This presentation may contain forward-looking statements, which reflect Trillium's current expectation regarding future events. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties
Q1/2016 This presentation may contain forward-looking statements, which reflect Trillium's current expectation regarding future events. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties
Anti-CD38 anti-cd3 bispecific antibody in multiple myeloma
 Anti-CD38 anti-cd3 bispecific antibody in multiple myeloma David E. Szymkowski Senior Director, Biotherapeutics Proteins by Design 1960s...1980s...2000s... Where are the bispecific antibody drugs? J Exp.
Anti-CD38 anti-cd3 bispecific antibody in multiple myeloma David E. Szymkowski Senior Director, Biotherapeutics Proteins by Design 1960s...1980s...2000s... Where are the bispecific antibody drugs? J Exp.
Vitamin D deficiency exacerbates ischemic cell loss and sensory motor dysfunction in an experimental stroke model
 Vitamin D deficiency exacerbates ischemic cell loss and sensory motor dysfunction in an experimental stroke model Robyn Balden & Farida Sohrabji Texas A&M Health Science Center- College of Medicine ISC
Vitamin D deficiency exacerbates ischemic cell loss and sensory motor dysfunction in an experimental stroke model Robyn Balden & Farida Sohrabji Texas A&M Health Science Center- College of Medicine ISC
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
CHAPTER 8 IMMUNOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS OF PEPTIDE CARBOHYDRATE MIMICRY
 CHAPTER 8 IMMUNOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS OF PEPTIDE CARBOHYDRATE MIMICRY Immunological Implications of Peptide-Carbohydrate Mimicry 8.1 Introduction The two chemically dissimilar molecules, a peptide (12mer)
CHAPTER 8 IMMUNOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS OF PEPTIDE CARBOHYDRATE MIMICRY Immunological Implications of Peptide-Carbohydrate Mimicry 8.1 Introduction The two chemically dissimilar molecules, a peptide (12mer)
Correction Between B and H, and the Analysis of the Magnetization Into Uniaxial Superconductor in the Limit at Large Values of B
 ISSN 0029-3865 CBPF CENTRO BRASILEIRO DE PESQUISAS FÍSICAS Rio de Janeiro Notas de Física CBPF-NF-031/94 April 1994 Correction Between B and H, and the Analysis of the Magnetization Into Uniaxial Superconductor
ISSN 0029-3865 CBPF CENTRO BRASILEIRO DE PESQUISAS FÍSICAS Rio de Janeiro Notas de Física CBPF-NF-031/94 April 1994 Correction Between B and H, and the Analysis of the Magnetization Into Uniaxial Superconductor
Automation of Cell Staining Technical Information Bulletin
 Automation of Cell Staining Technical Information Bulletin Automation of Cell Staining Using the Biomek 4000 Laboratory Automation Workstation Amy N. Yoder, Sr. Development Scientist and Li Liu, Sr. Development
Automation of Cell Staining Technical Information Bulletin Automation of Cell Staining Using the Biomek 4000 Laboratory Automation Workstation Amy N. Yoder, Sr. Development Scientist and Li Liu, Sr. Development
Supplemental Fig. S1. The schematic diagrams of the expression constructs used in this study.
 1 Supplemental data Supplemental Fig. S1. The schematic diagrams of the expression constructs used in this study. Supplemental Fig. S2. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of the 56 putative caspase substrates
1 Supplemental data Supplemental Fig. S1. The schematic diagrams of the expression constructs used in this study. Supplemental Fig. S2. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of the 56 putative caspase substrates
Immunity and how vaccines work
 1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
Chapter 2 Antibodies. Contents. Introduction
 Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
Classic Immunoprecipitation
 292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
Oncos Therapeutics: ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy. March 2015. Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder
 Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers
 Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers Brad Larson 1, Karen Kleman-Leyer 1, Xavier Amouretti 2 1 BellBrook Labs, Madison, WI,
Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers Brad Larson 1, Karen Kleman-Leyer 1, Xavier Amouretti 2 1 BellBrook Labs, Madison, WI,
Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi
 Author Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi Zhu Judy Wei Biological Sciences Though she hopes to attend medical school, Judy Wei
Author Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi Zhu Judy Wei Biological Sciences Though she hopes to attend medical school, Judy Wei
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Disclosures Outline Starting with the Immune System The Innate Immune System The Adaptive Immune System
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
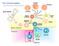 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
NCL Method ITA-14. Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro
 NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a
 Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
CyTOF2. Mass cytometry system. Unveil new cell types and function with high-parameter protein detection
 CyTOF2 Mass cytometry system Unveil new cell types and function with high-parameter protein detection DISCOVER MORE. IMAGINE MORE. MASS CYTOMETRY. THE FUTURE OF CYTOMETRY TODAY. Mass cytometry resolves
CyTOF2 Mass cytometry system Unveil new cell types and function with high-parameter protein detection DISCOVER MORE. IMAGINE MORE. MASS CYTOMETRY. THE FUTURE OF CYTOMETRY TODAY. Mass cytometry resolves
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
THE. Cutting Edge: Neutrophil Granulocyte Serves as a Vector for Leishmania Entry into Macrophages 1
 THE JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY CUTTING EDGE Cutting Edge: Neutrophil Granulocyte Serves as a Vector for Leishmania Entry into Macrophages 1 Ger van Zandbergen, 2 * Matthias Klinger, Antje Mueller, Sonja Dannenberg,*
THE JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY CUTTING EDGE Cutting Edge: Neutrophil Granulocyte Serves as a Vector for Leishmania Entry into Macrophages 1 Ger van Zandbergen, 2 * Matthias Klinger, Antje Mueller, Sonja Dannenberg,*
Hepatitis C Vaccines: Are we making progress?
 Hepatitis C Vaccines: Are we making progress? Second International Hepatitis Cure and Eradication Meeting. Vancouver November, 2015 Objectives: Review the need for a preventive vaccine in 2015. Identify
Hepatitis C Vaccines: Are we making progress? Second International Hepatitis Cure and Eradication Meeting. Vancouver November, 2015 Objectives: Review the need for a preventive vaccine in 2015. Identify
OKT3. ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody. used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~
 g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
On the origin of giant multinuclear Reed-Sternberg cells and the role of CD4 T cells in Hodgkin lymphoma
 On the origin of giant multinuclear Reed-Sternberg cells and the role of CD4 T cells in Hodgkin lymphoma Uber die Entstehung von multinuklearen Reed-Sternberg Riesenzellen und die Rolle von CD4 T-Zellen
On the origin of giant multinuclear Reed-Sternberg cells and the role of CD4 T cells in Hodgkin lymphoma Uber die Entstehung von multinuklearen Reed-Sternberg Riesenzellen und die Rolle von CD4 T-Zellen
Standard Operating Procedure
 1.0 Purpose: 1.1 The characterisation of of main leukocyte subsets in peripheral blood cells from mice by flow cytometry. Reliable values of frequencies of leukocyte clusters are very much dependent on
1.0 Purpose: 1.1 The characterisation of of main leukocyte subsets in peripheral blood cells from mice by flow cytometry. Reliable values of frequencies of leukocyte clusters are very much dependent on
