Stock Assessment 101: Current Practice for Tuna Stocks
|
|
|
- Peter Moore
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stock Assessment 101: Current Practice for Tuna Stocks By Victor Restrepo Chair, ISSF Scientific Advisory Committee January 2011 NOTE: This document is meant to be a simple introduction to stock assessments intended for the general public. Readers interested in more details should refer to the specialized literature on the subject. Q. What is a stock assessment? A stock assessment is a process whereby scientists analyze a variety of relevant data about the fisheries, the species of interest and other variables (such as economic or environmental ones) in order to evaluate the impacts of the fisheries on the stock or population. Stock assessments are not meant to be a research tool (although they can be); they are meant to provide useful information for fishery managers to consider. In many cases, stock assessment models are also used to and to estimate the likely impacts of alternative management options. A stock assessment model uses the information available over a number of years (in many cases since the beginning of industrial fisheries) and reconstructs the evolution of the population and of the fisheries during this time period. By estimating how the population has responded to different levels of fishing, it is possible to predict how it might respond in the future under different management scenarios. Stock assessment is not an exact science. There is much uncertainty due to incomplete (or even biased) data, natural variability and the inability of simplistic models to fully capture a complex reality. Fishery managers need to take this uncertainty into account when making decisions. In many ways, this is similar to what successful business 1
2 managers do in using indicators to track the performance of the company's finances, labor, operations (throughput), legal and regulatory risks. Q. What is a stock? A stock results from management partitioning the population of a species into time- space sub- units that have some degree of coherence biologically and/or ecologically (like genetics, vital rates, spawning or feeding grounds or migratory pathways). This partitioning is done so as to avoid the potential deleterious effects of an over- concentration of fishing mortality on just a portion of the population, and to increase the sustainable yield from the population as a whole. In some cases, the stock and the population are the same. Q. Who conducts the stock assessments? The stock assessments are conducted by the scientific bodies of the tuna Regional Fishery Management Organizations (RFMOs). Each RFMO is structured and mandated in a slightly different way. In the case of IATTC, staff members of the Secretariat conduct the analyses which are later reviewed by the Scientific Advisory Committee before being presented to the Commissioners. WCPFC is similar, except that the analyses are initially conducted by a contracted provider (SPC's Oceanic Fisheries Program). In both ICCAT and IOTC, the analyses are conducted by working groups established by their respective scientific committees that are composed primarily of national scientists. Q. How often are stocks assessed? Most stock assessments of tuna stocks are conducted every two to four years, but there is a lot of variation between species and RFMOs (in fact, some tuna stocks have never been assessed). The frequency with which a stock should be assessed depends on: - The longevity of the species. Shorter- lived species should be assessed more frequently than longer- lived ones. - The management measures in place: Scientific advice based on stock assessments is generally timed so as to match an existing management plan. For example, if conservation measures establish quotas for four years, the assessments tend to be scheduled during the year in which the plan expires. - The status of the stock: As part of the Precautionary Approach, stocks that are overexploited and that continue to be fished heavily should be subject to closer monitoring. Q. What are the inputs used in an assessment? There are a number of data inputs to an assessment, as well as assumptions and modeling choices made by scientists. Data inputs tend to be of three kinds: 2
3 1) Data about the fisheries: Catch and catch rates (also known as CPUE or Catch per- Unit Effort), fishing effort (e.g., number of sets made), size (or weight) composition of the catch, spatial and temporal distribution of fishing. 2) Data about the fish: Any information about the life history of the fish such as growth rates, natural mortality, relationship between size and weight, size at maturity and reproductive rates, etc. 3) Ancillary information about the ecosystem, economic drivers, etc.: These are other factors that the scientists believe should be taken into consideration because they affect some component of the assessment model. Some types of data provide information about both the fishery and the biology of the species. A good example is tagging data which can provide information on growth, behavior, and natural and fishing mortality rates. Assumptions and model choices are often dictated by the situation. The model used to analyze the data, for example, depends on the available data. If the data are highly aggregated (for example annual catch for the entire stock, all gears combined), then only very simple models can be used. If, on the other hand, the data are available at a fine level of operational detail (such as set- by- set), then more sophisticated and complex models can be used. In typical situations there will be a mixture of aggregated data and some disaggregated data, as well as missing information or very incomplete knowledge of some biological or fishery aspect. Ecosystem effects have been incorporated historically in stock assessments as natural variability or as simple feedback terms. However, as long- term data series of ecosystem indicators are becoming available, their use in stock assessments is becoming more common. Q. What are the outputs of a stock assessment? The basic component of a stock assessment model reconstructs the evolution of the population and fisheries during the time period analyzed. Typical model outputs are time series of the following: - Recruitment (the number of fish born each year) 3
4 - Fishing mortality: This is a measure of the rate at which individuals in the population die from fishing. Fishing mortality is usually estimated by age group, by year and by fishing gear (fishery). - Abundance: The number of fish alive, usually estimated by age group and year. - Biomass: This is like abundance, but expressed in fish weight instead of numbers of fish. Biomass is usually estimated by year. - Spawning biomass: This is the portion of the biomass that corresponds to mature fish only, and is used as a proxy for the reproductive output of the population. - Selectivity: This measures how vulnerable different age groups (or size groups) are to fishing by a given fishing gear. - Catchability coefficients: These are model parameters that scale the magnitude of various inputs to various outputs. One example is that catchability links stock abundance (model output) to CPUE (model input); another example is that catchability relates fishing mortality (output) to fishing effort (input). There are other outputs that may or may not be obtained with the same basic model. These are usually derived from two or more of the outputs above, and tend to be very important for the advice to fishery managers. For example, biological reference points such as MSY, FMSY or BMSY (see Appendix 1) which give managers a benchmark against which to compare the current levels of catch, fishing mortality and abundance. Q. What are some of the main sources of uncertainty in an assessment? Fisheries data are often incomplete or biased, which is a source of uncertainty that cannot always be quantified. Some of the reasons for incomplete or bad data include: - Insufficient sampling due to insufficient resources - Historical data gaps (insufficient resources) - Changes in fishing technology and techniques over time that are not recorded - Limited Research on life- history and behavior - Mis- reporting (for example, due to IUU fishing) - Effects of and on the ecosystem In addition, the behavior of fish and fishing fleets (and the interaction between them) is very complex and often highly variable. Coupled with insufficient sampling of fish, fisheries and ecosystems, this results in uncertainty being a common feature in stock assessments. Q. How is uncertainty quantified and expressed? Scientists use statistical tools to measure uncertainty. In general, these try to measure how tight is the match between a model's prediction and the observed data: The tighter the "fit", the lower the uncertainty. In addition, scientists sometimes use different types of models (and alternative sets of data) to see how sensitive the results can be to these choices. 4
5 Uncertainty in assessment results can be expressed by a variety of methods. When different models are used, one simple way is to plot the results (for example, the abundance trajectories over time) from the various models. When viewing such results, however, stakeholders should be careful to recognize that not all of the models are equally likely or realistic. For this reason, scientists sometimes weigh the outcomes from different models by some measure of how likely or realistic they are. Q. What is a Kobe Plot? The so- called "Kobe Plot" (the name derives from the original joint meeting of the tuna RFMOs in Kobe, Japan, but now from a subsequent series of meetings in what is known as the "Kobe process") is a way of summarizing stock assessment results in a graphical way that has become widely used. On the X- axis, the plot represents biomass (or spawning biomass), expressed relative to BMSY. And, on the Y- axis, it represents fishing mortality relative to FMSY. See Appendix 1 for more information about BMSY and FMSY. The plot offers a simple way in which managers can quickly infer if the stock is in "good" or "bad" shape, depending on where it falls in one of four quadrants in the plot. A value below 1.0 on the X- axis means that the biomass is below BMSY (in most cases, RFMOs refer to this as the stock being "overfished"). And, a value above 1.0 on the Y- axis means that the fishing mortality is above FMSY (meaning that the stock is "being overfished" or that "overfishing is occurring"). The Kobe plot above on the right is an example (for bigeye tuna in the western and central Pacific Ocean). Each purple dot shows the relative situation of the stock in different years. In the more recent time period (the darker purple dots), overfishing has been occurring. The white dot shows the current situation of the stock, i.e., its status in the last year of the assessment data analyzed. Q. How can stock assessments be improved? Data, data, data! The state- of- the- art of fish stock assessment models today is quite sophisticated and, for the most part, improving stock assessments does not depend on improving modeling techniques. The limiting factor in stock assessments is the quantity 5
6 and quality of data available for the fish, fisheries and their ecosystem. Even in the tuna RFMOs that count with excellent data sets for some fisheries, there are substantial data deficiencies for other fisheries. These are a few ways in which data can be improved: - Increased sampling intensity to cover all fisheries and their associated ecosystems. All ecosystems and some fisheries have inadequate sampling coverage. For example, many artisanal fisheries are poorly sampled and even such basic statistics as total catch are poorly known. Developed nations should assist developing ones to improve their capacity to meet sampling and reporting obligations. - Increased observer coverage. Observer data can be an important complement to other sampling activities, such as logbooks, and can serve as a means of validating other sampling sources. - Enhanced tagging programs. Scientific campaigns where fish are tagged and released, and later recovered in fishing operations, are very valuable as they provide useful information to the stock assessment models. - Enhanced research on fish and fisher behavior, to (1) improve our understanding of the effects of environment on fish population dynamics, (2) better quantify fishing effort (i.e. to find measures of fishing effort that are directly proportional to fishing mortality), and, (3) better assess key parameters such as catchability (which characterizes the interaction between fish and fishers). - Increased involvement by the industry. The industry, both fishing and processing sectors, can help member governments of RFMOs do their job more effectively and efficiently by ensuring that their operations are sampled and reported adequately and in a timely basis. In many cases, the industry has historical records that could be useful to an assessment but that were never collected by government agencies. 6
7 APPENDIX 1 MSY BENCHMARKS Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY) is a reference point that helps guide fisheries management. All of the Tuna RFMOs have as one of their management objectives the aim to maintain tuna populations at levels that can produce MSY. Definitions Notes MSY can be defined as "The largest average catch or yield that can continuously be taken from a stock under existing environmental conditions. (For species with fluctuating recruitment, the maximum might be obtained by taking fewer fish in some years than in others.)" FMSY (also "Fishing Mortality at MSY" or "MSY Fishing Mortality Level"). This is the level of fishing intensity that, if applied constantly year after year, would result in MSY. BMSY (also "Biomass at MSY" or "MSY Biomass Level"). This is the stock size (biomass) that would result on average if FMSY was applied constantly year after year. BMSY is sometimes measured by the total biomass of the stock and sometimes by the biomass of the spawners ("spawning biomass"). "Kobe Plot" (also "phase plot" or "Stock status plot"). This is a plot used to summarize the status of a fishery relative to MSY- based reference points. The X- axis corresponds to the ratio B/BMSY and the Y- axis corresponds to F/FMSY. The four quadrants of the plot are usually colored for simplicity, with Green corresponding to [F<FMSY; B>BMSY], and Red corresponding to [F>FMSY; B<BMSY]. - If FMSY were applied constantly, year after year, neither the stock biomass nor the catches would be constant. The biomass would fluctuate around BMSY and the catches would fluctuate around MSY. The degree of these fluctuations would depend on the characteristics of the stock. The fluctuations would be greater for stocks with high inter- annual variability in recruitment (basically, the number of fish that are born each year). - MSY, FMSY and BMSY levels for a given stock can change due to the selectivity of fishing gears ("selectivity" means the size range that a particular fishing gear tends to catch in a given area and a given season). Generally, if the combined result of all fisheries tends to yield larger fish, MSY will be higher. Some tuna fisheries have experienced substantial changes in selectivity over time as a result of the introduction of different gears of fishing operations. For example, the MSY for bigeye tuna in the western and central Pacific Ocean has been reduced to about one- half of its highest historical level. 7
8 - MSY, FMSY and BMSY levels for a given stock can also change due to environmental reasons. For example, environmental changes could affect the average level of recruits to the population, or the average growth rates, or average natural mortality rates, etc. Sometimes these changes cannot be easily explained. When they are abrupt, scientists often refer to "regime shifts", meaning that there was a large change in the ecosystem that affected the stock. - MSY- based reference points are estimated during the stock assessment process. There are different methods that can be used for estimating these quantities. For most tuna stocks, the estimation involves a combination of two types of models: a) A Yield- per- recruit and Spawner- per- recruit model. This model is used to predict how different levels of Fishing Mortality will affect the average catch (and the average reproductive output) of a fish in the population. b) A stock- recruitment relationship. This model is used to predict the number of recruits that will result, on average, at different population sizes. Typically, due to data limitations and environmental noise, the application of the second type of model requires scientists to make assumptions. Thus, the estimation of MSY- based benchmarks is highly sensitive to the assumed relationship between spawning biomass and recruitment. - When a stock falls somewhat below BMSY, it does not mean that a collapse is imminent. It means that it may be falling below the level at which managers intend to maintain it. The stock should be closely monitored and management measures should be strengthened as needed in order to ensure that it rebuilds again to BMSY or greater. However, if a stock falls substantially below BMSY, e.g. to less than one- half of BMSY, there will be a much increased risk of a serious collapse and managers need to take drastic action to ensure stock rebuilding. - If managers are to embrace the Precautionary Approach, they should manage the fisheries to ensure that fishing mortality does not exceed FMSY. Given that there is uncertainty in the stock assessment results, FMSY should not be their target. Furthermore, if fishing mortality is below FMSY, both the economic rent of the fisheries and the stock biomass will be higher. 8
Marine Stewardship Council
 Marine Stewardship Council MSC Fishery Standard Principles and Criteria for Sustainable Fishing Version 1.1 1 st May 2010 Committees responsible for this Standard This standard is intended to be used on
Marine Stewardship Council MSC Fishery Standard Principles and Criteria for Sustainable Fishing Version 1.1 1 st May 2010 Committees responsible for this Standard This standard is intended to be used on
John Holmes Chair, ISC-Albacore Working Group Fisheries and Oceans Canada Nanaimo, BC, Canada
 John Holmes Chair, ISC-Albacore Working Group Fisheries and Oceans Canada Nanaimo, BC, Canada (MOW4) Harvest Strategy Workshop 30 November 1 December 2015 Kuta, Bali, Indonesia ** Much of this material
John Holmes Chair, ISC-Albacore Working Group Fisheries and Oceans Canada Nanaimo, BC, Canada (MOW4) Harvest Strategy Workshop 30 November 1 December 2015 Kuta, Bali, Indonesia ** Much of this material
Update of a projection software to represent a stock-recruitment relationship using flexible assumptions
 Update of a projection software to represent a stock-recruitment relationship using flexible assumptions Tetsuya Akita, Isana Tsuruoka, and Hiromu Fukuda National Research Institute of Far Seas Fisheries
Update of a projection software to represent a stock-recruitment relationship using flexible assumptions Tetsuya Akita, Isana Tsuruoka, and Hiromu Fukuda National Research Institute of Far Seas Fisheries
Progress Report on Harmonization and Improvement of T-RFMO Trade Tracking Programs and development of Catch Documentation Systems
 Progress Report on Harmonization and Improvement of T-RFMO Trade Tracking Programs and development of Catch Documentation Systems Jointly Prepared by the Five Secretariats 1. Introduction Kobe Course of
Progress Report on Harmonization and Improvement of T-RFMO Trade Tracking Programs and development of Catch Documentation Systems Jointly Prepared by the Five Secretariats 1. Introduction Kobe Course of
Hake Benchmark Assessment Meeting Schedule
 Hake Benchmark Assessment Meeting Schedule Meeting Date Location Data I Aug. 23 Aquarium Conference Room Ecosystem Consumption (1) 9:00 AM 166 Water St. Data II Sep. 7 10 am 5:30 pm Sep. 8-10 9 am 5:30
Hake Benchmark Assessment Meeting Schedule Meeting Date Location Data I Aug. 23 Aquarium Conference Room Ecosystem Consumption (1) 9:00 AM 166 Water St. Data II Sep. 7 10 am 5:30 pm Sep. 8-10 9 am 5:30
Using Probabilistic MCB Analysis to Determine Uncertainty in a Stock Assessment
 Using the probabilistic MCB runs to set management parameters and determine stock status The existence of uncertainty is a well-accepted and thoroughly documented part of the stock assessment process in
Using the probabilistic MCB runs to set management parameters and determine stock status The existence of uncertainty is a well-accepted and thoroughly documented part of the stock assessment process in
8.3.18 Advice May 2014
 8.3.18 Advice May 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Baltic Sea Sprat in Subdivisions 22 32 (Baltic Sea) Advice for 2015 ICES advises on the basis of the MSY approach that catches in 2015 should be no more than 222
8.3.18 Advice May 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Baltic Sea Sprat in Subdivisions 22 32 (Baltic Sea) Advice for 2015 ICES advises on the basis of the MSY approach that catches in 2015 should be no more than 222
Table 1. Von Bertalanffy growth parameters and length-weight relations for red snapper
 Red snapper, Lutjanus campechanus (Poey, 1860) Red snapper are distributed throughout the Gulf of Mexico and up the U.S. Atlantic coast to North Carolina and, although rarely, to Massachusetts. Gold et
Red snapper, Lutjanus campechanus (Poey, 1860) Red snapper are distributed throughout the Gulf of Mexico and up the U.S. Atlantic coast to North Carolina and, although rarely, to Massachusetts. Gold et
SARC 52 SUMMARY REPORT
 52th Northeast Regional Stock Assessment Review Committee 6 10 June 2011 Northeast Fisheries Science Center Wood s Hole, MA SARC 52 SUMMARY REPORT 6 July 2011 Review Committee Patrick J. Sullivan (chair)
52th Northeast Regional Stock Assessment Review Committee 6 10 June 2011 Northeast Fisheries Science Center Wood s Hole, MA SARC 52 SUMMARY REPORT 6 July 2011 Review Committee Patrick J. Sullivan (chair)
NON-TAR GE T FINFISH SPE CIES AND SMALL TARGET SPECIES
 K obe I I B ycatch W or kshop B ack gr ound Paper NON-TAR GE T FINFISH SPE CIES AND SMALL TARGET SPECIES 1. Overview... 1 2. Information and resources for addressing bycatch... 2 3. Research and management
K obe I I B ycatch W or kshop B ack gr ound Paper NON-TAR GE T FINFISH SPE CIES AND SMALL TARGET SPECIES 1. Overview... 1 2. Information and resources for addressing bycatch... 2 3. Research and management
Carey R. McGilliard November 2014. Executive Summary
 8. Assessment of the Flathead Sole Stock in the Gulf of Alaska Carey R. McGilliard November 2014 Executive Summary Flathead sole (Hippoglossoides elassodon) are assessed on a biennial stock assessment
8. Assessment of the Flathead Sole Stock in the Gulf of Alaska Carey R. McGilliard November 2014 Executive Summary Flathead sole (Hippoglossoides elassodon) are assessed on a biennial stock assessment
9.3.7 Advice December 2014
 9.3.7 Advice December 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Widely distributed and migratory stocks European eel Advice for 2015 The status of eel remains critical and ICES advises that all anthropogenic mortality (e.g.
9.3.7 Advice December 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Widely distributed and migratory stocks European eel Advice for 2015 The status of eel remains critical and ICES advises that all anthropogenic mortality (e.g.
Status of bigeye tuna in the eastern Pacific Ocean in 2001 and outlook for 2002
 SCTB15 Working Paper BET-2 Status of bigeye tuna in the eastern Pacific Ocean in 21 and outlook for 22 Mark N. Maunder and Shelton J. Harley Inter-American Tropical Tuna Commission (IATTC) La Jolla, CA,
SCTB15 Working Paper BET-2 Status of bigeye tuna in the eastern Pacific Ocean in 21 and outlook for 22 Mark N. Maunder and Shelton J. Harley Inter-American Tropical Tuna Commission (IATTC) La Jolla, CA,
ICCAT Newsletter No. 21
 ICCAT Newsletter No. 21 February 2015 MESSAGE FROM THE ICCAT EXECUTIVE SECRETARY The ICCAT Secretariat has the pleasure to present its readers with ICCAT Newsletter No. 21, informing about the latest events
ICCAT Newsletter No. 21 February 2015 MESSAGE FROM THE ICCAT EXECUTIVE SECRETARY The ICCAT Secretariat has the pleasure to present its readers with ICCAT Newsletter No. 21, informing about the latest events
A Guide to Fisheries Stock Assessment using the FMSP Tools
 A Guide to Fisheries Stock Assessment using the FMSP Tools Daniel D. Hoggarth, Christopher C. Mees, Catherine O Neill, James Hindson, Mohan Krishna Copyright 2005, Marine Resources Assessment Group (MRAG),
A Guide to Fisheries Stock Assessment using the FMSP Tools Daniel D. Hoggarth, Christopher C. Mees, Catherine O Neill, James Hindson, Mohan Krishna Copyright 2005, Marine Resources Assessment Group (MRAG),
The Economics of Ecosystem Based Management: The Fishery Case
 The Economics of Ecosystem Based Management: The Fishery Case Fisheries impact on marine ecosystem and policy implications Peder Andersen Co-authors: Lars Ravensbeck Hans S. Frost Department of Food and
The Economics of Ecosystem Based Management: The Fishery Case Fisheries impact on marine ecosystem and policy implications Peder Andersen Co-authors: Lars Ravensbeck Hans S. Frost Department of Food and
A. GULF OF MAINE HADDOCK ASSESSMENT SUMMARY FOR 2014
 A. GULF OF MAINE HADDOCK ASSESSMENT SUMMARY FOR 2014 State of Stock: The Gulf of Maine haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) stock is not overfished and overfishing is not occurring in 2013 (Figure A1). Spawning
A. GULF OF MAINE HADDOCK ASSESSMENT SUMMARY FOR 2014 State of Stock: The Gulf of Maine haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) stock is not overfished and overfishing is not occurring in 2013 (Figure A1). Spawning
Guidance to Stock Assessment Workshop Working Groups (SAW WG) on Preparation/Format of SAW Reports for Peer Review
 Guidance to Stock Assessment Workshop Working Groups (SAW WG) on Preparation/Format of SAW Reports for Peer Review J. Weinberg, SAW Chairman (last revised: 10/16/2014) Stock Assessment Terms of Reference
Guidance to Stock Assessment Workshop Working Groups (SAW WG) on Preparation/Format of SAW Reports for Peer Review J. Weinberg, SAW Chairman (last revised: 10/16/2014) Stock Assessment Terms of Reference
DRAFT MAFMC Assessment Levels - Summary
 Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council 800 North State Street, Suite 201, Dover, DE 19901-3910 Phone: 302-674-2331 ǀ FAX: 302-674-5399 ǀ www.mafmc.org Richard B. Robins, Jr., Chairman ǀ Lee G. Anderson,
Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council 800 North State Street, Suite 201, Dover, DE 19901-3910 Phone: 302-674-2331 ǀ FAX: 302-674-5399 ǀ www.mafmc.org Richard B. Robins, Jr., Chairman ǀ Lee G. Anderson,
How can Fisheries Management Solve the Problem of Biological Sustainability?
 How can Fisheries Management Solve the Problem of Biological Sustainability? Workshop in Akureyri Iceland 11.-12. October 2007 Niels Vestergaard Department of Environmental and Business Economics Centre
How can Fisheries Management Solve the Problem of Biological Sustainability? Workshop in Akureyri Iceland 11.-12. October 2007 Niels Vestergaard Department of Environmental and Business Economics Centre
BESTTuna. Paul A.M. van Zwieten, Simon R. Bush
 BESTTuna Benefiting from Innovations in Sustainable and Equitable Management of Fisheries on Trans boundary Tuna s in the Coral Triangle and Western Pacific Paul A.M. van Zwieten, Simon R. Bush WWFs broken
BESTTuna Benefiting from Innovations in Sustainable and Equitable Management of Fisheries on Trans boundary Tuna s in the Coral Triangle and Western Pacific Paul A.M. van Zwieten, Simon R. Bush WWFs broken
3.13.5.b Gear selectivity in the directed cod fishery (BACOMA project)
 3.13.5.b Gear selectivity in the directed cod fishery (BACOMA project) IBSFC has asked ICES to: i) evaluate the potential improvement in the gear selectivity in the directed cod fisheries as concluded
3.13.5.b Gear selectivity in the directed cod fishery (BACOMA project) IBSFC has asked ICES to: i) evaluate the potential improvement in the gear selectivity in the directed cod fisheries as concluded
The need to ban fish aggregating devices (FADs) to save juvenile baby tunas. Greenpeace uncovers trade in juvenile tuna in General Santos Fish Port
 The need to ban fish aggregating devices (FADs) to save juvenile baby tunas 2 December 2014 Quezon City, Philippines Greenpeace uncovers trade in juvenile tuna in General Santos Fish Port Introduction
The need to ban fish aggregating devices (FADs) to save juvenile baby tunas 2 December 2014 Quezon City, Philippines Greenpeace uncovers trade in juvenile tuna in General Santos Fish Port Introduction
Management Strategy Evaluation and Management Procedures
 Please cite this paper as: Holland, D. S. (2010), Management Strategy Evaluation and Management Procedures: Tools for Rebuilding and Sustaining Fisheries, OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Working Papers,
Please cite this paper as: Holland, D. S. (2010), Management Strategy Evaluation and Management Procedures: Tools for Rebuilding and Sustaining Fisheries, OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Working Papers,
Northern Territory Fisheries Resource Sharing Framework
 Northern Territory Fisheries Resource Sharing Framework Page 1 of 11 Introduction Fishing is important in the Northern Territory (Territory). Coastal Aboriginal people recognise sea country out to the
Northern Territory Fisheries Resource Sharing Framework Page 1 of 11 Introduction Fishing is important in the Northern Territory (Territory). Coastal Aboriginal people recognise sea country out to the
Shark, Skate and Ray Conservation Plan
 Shark, Skate and Ray Conservation Plan Introduction Sharks, skates and rays, collectively known as elasmobranchs are caught in fisheries worldwide, including in EU and UK waters. Many have been depleted
Shark, Skate and Ray Conservation Plan Introduction Sharks, skates and rays, collectively known as elasmobranchs are caught in fisheries worldwide, including in EU and UK waters. Many have been depleted
MADAGASCAR REPORT MADAGASCAR FISHERIES DATA MANAGEMENT
 44 MADAGASCAR REPORT MADAGASCAR FISHERIES DATA MANAGEMENT Total production statistics have various sources, particularly from logbook, from activities report, from evaluations and projections. It is 120
44 MADAGASCAR REPORT MADAGASCAR FISHERIES DATA MANAGEMENT Total production statistics have various sources, particularly from logbook, from activities report, from evaluations and projections. It is 120
Fisheries Management: Arctic principles
 Fisheries Management: Arctic principles Spatial issues in the Arctic Marine Resource Management Stockholm 4-6 September 2014 Niels Vestergaard Department of Environmental and Business Economics Centre
Fisheries Management: Arctic principles Spatial issues in the Arctic Marine Resource Management Stockholm 4-6 September 2014 Niels Vestergaard Department of Environmental and Business Economics Centre
Marine Fisheries Stock Assessment Improvement Plan
 Marine Fisheries Stock Assessment Improvement Plan Report of the National Marine Fisheries Service National Task Force for Improving Fish Stock Assessments Pamela M. Mace (Chair), Norman W. Bartoo, Anne
Marine Fisheries Stock Assessment Improvement Plan Report of the National Marine Fisheries Service National Task Force for Improving Fish Stock Assessments Pamela M. Mace (Chair), Norman W. Bartoo, Anne
Paper prepared by Consultancy Team Paul Wallis and Nick Wyatt
 TECHNICAL AND COMPLIANCE COMMITTEE Seventh Regular Session 28 September - 4 October 2011 Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia OPTIMIZATION OF COST OF COMMISSION OPERATIONS WCPFC-TCC7-2011/09 Rev 1 30
TECHNICAL AND COMPLIANCE COMMITTEE Seventh Regular Session 28 September - 4 October 2011 Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia OPTIMIZATION OF COST OF COMMISSION OPERATIONS WCPFC-TCC7-2011/09 Rev 1 30
POPULATION DYNAMICS. Zoo 511 Ecology of Fishes
 POPULATION DYNAMICS Zoo 511 Ecology of Fishes Today s goals Understand why and how population dynamics are important in fisheries ecology Gain experience in a variety of mark-recapture methods What are
POPULATION DYNAMICS Zoo 511 Ecology of Fishes Today s goals Understand why and how population dynamics are important in fisheries ecology Gain experience in a variety of mark-recapture methods What are
National Marine Fisheries Service Electronic Monitoring Cooperative Research and Implementation Program
 National Marine Fisheries Service Electronic Monitoring Cooperative Research and Implementation Program Introduction This cooperative research program has been developed to be responsive both to the implementation
National Marine Fisheries Service Electronic Monitoring Cooperative Research and Implementation Program Introduction This cooperative research program has been developed to be responsive both to the implementation
Columbia River Project Water Use Plan. Monitoring Program Terms of Reference LOWER COLUMBIA RIVER FISH MANAGEMENT PLAN
 Columbia River Project Water Use Plan LOWER COLUMBIA RIVER FISH MANAGEMENT PLAN CLBMON-45 Lower Columbia River Fish Indexing Surveys 31 August 2007 1.0 OVERVIEW LOWER COLUMBIA RIVER FISH MANAGEMENT PLAN
Columbia River Project Water Use Plan LOWER COLUMBIA RIVER FISH MANAGEMENT PLAN CLBMON-45 Lower Columbia River Fish Indexing Surveys 31 August 2007 1.0 OVERVIEW LOWER COLUMBIA RIVER FISH MANAGEMENT PLAN
6.3.2 Advice June 2014. Mixed-fisheries advice for Subarea IV (North Sea) and Divisions IIIa North (Skagerrak) and VIId (Eastern Channel)
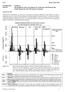 6.3.2 Advice June 2014 ECOREGION STOCK North Sea Mixed-fisheries advice for Subarea IV (North Sea) and Divisions IIIa North (Skagerrak) and VIId (Eastern Channel) Scenarios for 2015 Mixed-fisheries considerations
6.3.2 Advice June 2014 ECOREGION STOCK North Sea Mixed-fisheries advice for Subarea IV (North Sea) and Divisions IIIa North (Skagerrak) and VIId (Eastern Channel) Scenarios for 2015 Mixed-fisheries considerations
AP Biology Unit I: Ecological Interactions
 AP Biology Unit I: Ecological Interactions Essential knowledge 1.C.1: Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth s history. Species extinction rates are rapid at times of ecological stress.
AP Biology Unit I: Ecological Interactions Essential knowledge 1.C.1: Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth s history. Species extinction rates are rapid at times of ecological stress.
SMART FISHING INITIATIVE RESULTS 2010 - JUNE 2016 RESULTS 2010-2016. WWF s 2020 VISION Our oceans are wellmanaged,
 Brent Stirtion/Getty Images RESULTS 2010-2016 WWF s 2020 VISION Our oceans are wellmanaged, healthy, robust and full of life, providing valuable services for the well-being of humanity. SMART FISHING INITIATIVE
Brent Stirtion/Getty Images RESULTS 2010-2016 WWF s 2020 VISION Our oceans are wellmanaged, healthy, robust and full of life, providing valuable services for the well-being of humanity. SMART FISHING INITIATIVE
Marine biological diversity beyond areas of national jurisdiction. Legal and policy framework
 Marine biological diversity beyond areas of national jurisdiction Legal and policy framework 1. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) provides the legal framework within which all
Marine biological diversity beyond areas of national jurisdiction Legal and policy framework 1. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) provides the legal framework within which all
Skjal 2. The Faroe Plateau Ecosystem. ICES 2016
 Skjal 2. The Faroe Plateau Ecosystem. ICES 2016 ICES Advice on fishing opportunities, catch, and effort Faroes Ecoregion Published 10 June 2016 4.3.1 Cod (Gadus morhua) in Subdivision 5.b.1 (Faroe Plateau)
Skjal 2. The Faroe Plateau Ecosystem. ICES 2016 ICES Advice on fishing opportunities, catch, and effort Faroes Ecoregion Published 10 June 2016 4.3.1 Cod (Gadus morhua) in Subdivision 5.b.1 (Faroe Plateau)
EUROPEAN COMMISSION. Better Regulation "Toolbox" This Toolbox complements the Better Regulation Guideline presented in in SWD(2015) 111
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Better Regulation "Toolbox" This Toolbox complements the Better Regulation Guideline presented in in SWD(2015) 111 It is presented here in the form of a single document and structured
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Better Regulation "Toolbox" This Toolbox complements the Better Regulation Guideline presented in in SWD(2015) 111 It is presented here in the form of a single document and structured
5 Year Strategic Plan
 Mid Atlantic Fishery Management Council 5 Year Strategic Plan 2014 2018 DRAFT 5/31/2013 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 The Mid Atlantic Fishery Management Council... 2 Rationale
Mid Atlantic Fishery Management Council 5 Year Strategic Plan 2014 2018 DRAFT 5/31/2013 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 The Mid Atlantic Fishery Management Council... 2 Rationale
Past, Present and Future
 EBFMtuna 2012 Towards ecosystem based management of tuna fisheries Evolution Of RadiobuoysTechnology For FADs Past, Present and Future Francisco Pino R&D Director Montpellier, October 2012 Beginnings Tunaseiner
EBFMtuna 2012 Towards ecosystem based management of tuna fisheries Evolution Of RadiobuoysTechnology For FADs Past, Present and Future Francisco Pino R&D Director Montpellier, October 2012 Beginnings Tunaseiner
Therefore, this is a very important question, which encourages consideration of the current management of the resource.
 Aalisarnermut, Piniarnermut Nunalerinermullu Naalakkersuisoqarfik Department of Fisheries, Hunting and Agriculture Finn's speech to NAFMC Climate change in the North Atlantic has become a reality which
Aalisarnermut, Piniarnermut Nunalerinermullu Naalakkersuisoqarfik Department of Fisheries, Hunting and Agriculture Finn's speech to NAFMC Climate change in the North Atlantic has become a reality which
NOAA Fisheries Office of International Affairs. Dr. Rebecca Lent
 NOAA Fisheries Office of International Affairs Dr. Rebecca Lent 1 International Responsibilities Magnuson-Stevens Act (MSA) Marine Mammal Protection Act Endangered Species Act Implementing legislation
NOAA Fisheries Office of International Affairs Dr. Rebecca Lent 1 International Responsibilities Magnuson-Stevens Act (MSA) Marine Mammal Protection Act Endangered Species Act Implementing legislation
The various relationships between the spawning stock and recruits may be: exploitation K. Limburg, lecture notes, Fisheries Science
 S-R II: More about stockrecruitment relationships & exploitation K. Limburg, lecture notes, Fisheries Science Last time, we discussed the following concepts about exploited populations of fish. We identified
S-R II: More about stockrecruitment relationships & exploitation K. Limburg, lecture notes, Fisheries Science Last time, we discussed the following concepts about exploited populations of fish. We identified
2016 Outlook and Management -Pre-season outlook / expectations and early indications - General overview of in-season management approach
 Salmon Briefing 2016 Outlook and Management -Pre-season outlook / expectations and early indications - General overview of in-season management approach Pacific Salmon Species Size and age at return varies
Salmon Briefing 2016 Outlook and Management -Pre-season outlook / expectations and early indications - General overview of in-season management approach Pacific Salmon Species Size and age at return varies
3.3.3 Capelin (Mallotus villosus) in Subareas I and II (Northeast Arctic), excluding Division IIa west of 5 W (Barents Sea capelin)
 ICES Advice on fishing opportunities, catch, and effort Barents Sea and Norwegian Sea Ecoregions Published 8 October 2015 3.3.3 Capelin (Mallotus villosus) in Subareas I and II (Northeast Arctic), excluding
ICES Advice on fishing opportunities, catch, and effort Barents Sea and Norwegian Sea Ecoregions Published 8 October 2015 3.3.3 Capelin (Mallotus villosus) in Subareas I and II (Northeast Arctic), excluding
Decision-support tools for economic optimization of Western Rock Lobster fishery
 Fisheries Research Report No. 257, 2014 Decision-support tools for economic optimization of Western Rock Lobster fishery Nick Caputi, Simon de Lestang, Chris Reid, Alex Hesp, Jason How and Peter Stephenson
Fisheries Research Report No. 257, 2014 Decision-support tools for economic optimization of Western Rock Lobster fishery Nick Caputi, Simon de Lestang, Chris Reid, Alex Hesp, Jason How and Peter Stephenson
Removal fishing to estimate catch probability: preliminary data analysis
 Removal fishing to estimate catch probability: preliminary data analysis Raymond A. Webster Abstract This project examined whether or not removal sampling was a useful technique for estimating catch probability
Removal fishing to estimate catch probability: preliminary data analysis Raymond A. Webster Abstract This project examined whether or not removal sampling was a useful technique for estimating catch probability
A FRAMEWORK FOR THE APPLICATION OF PRECAUTION IN SCIENCE-BASED DECISION MAKING ABOUT RISK
 Government of Canada Gouvernement du Canada A FRAMEWORK FOR THE APPLICATION OF PRECAUTION IN SCIENCE-BASED DECISION MAKING ABOUT RISK National Library of Canada cataloguing in publication data Main entry
Government of Canada Gouvernement du Canada A FRAMEWORK FOR THE APPLICATION OF PRECAUTION IN SCIENCE-BASED DECISION MAKING ABOUT RISK National Library of Canada cataloguing in publication data Main entry
ICCAT Newsletter No. 22
 ICCAT Newsletter No. 22 September 2015 MESSAGE FROM THE ICCAT EXECUTIVE SECRETARY The ICCAT Secretariat is pleased to present its readers with ICCAT Newsletter No. 22, informing about the latest events
ICCAT Newsletter No. 22 September 2015 MESSAGE FROM THE ICCAT EXECUTIVE SECRETARY The ICCAT Secretariat is pleased to present its readers with ICCAT Newsletter No. 22, informing about the latest events
Fair Trade USA Data-Limited Stock Assessment Decision Tree
 Fair Trade USA Data-Limited Stock Assessment Decision Tree January 31, 2014 Introduction This stock assessment decision tree may be used to determine which data-limited stock assessment methodology is
Fair Trade USA Data-Limited Stock Assessment Decision Tree January 31, 2014 Introduction This stock assessment decision tree may be used to determine which data-limited stock assessment methodology is
Practice Questions 1: Evolution
 Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
IMPLEMENTATION NOTE. Validating Risk Rating Systems at IRB Institutions
 IMPLEMENTATION NOTE Subject: Category: Capital No: A-1 Date: January 2006 I. Introduction The term rating system comprises all of the methods, processes, controls, data collection and IT systems that support
IMPLEMENTATION NOTE Subject: Category: Capital No: A-1 Date: January 2006 I. Introduction The term rating system comprises all of the methods, processes, controls, data collection and IT systems that support
Bio-Economic Tradeoffs among Gears and Fleet Dynamics of Tuna Purse-Seiner Fishery
 TECHNICAL EXPERTS WORKSHOP ON THE MANAGEMENT OF THE CAPACITY OF THE TUNA FISHING FLEET IN THE EPO, Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, 23-25 April 2014 Bio-Economic Tradeoffs among Gears and Fleet Dynamics
TECHNICAL EXPERTS WORKSHOP ON THE MANAGEMENT OF THE CAPACITY OF THE TUNA FISHING FLEET IN THE EPO, Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, 23-25 April 2014 Bio-Economic Tradeoffs among Gears and Fleet Dynamics
Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements
 National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Handbook for Quality Assurance and Accreditation in Saudi Arabia PART 2 Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements Version 2.0 Internal Quality
National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Handbook for Quality Assurance and Accreditation in Saudi Arabia PART 2 Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements Version 2.0 Internal Quality
Consultation Document: Guidance on Assessment of Management Performance Indicators in Small-scale Fisheries
 MSC - Marine Stewardship Council Consultation Document: Guidance on Assessment of Management Performance Indicators in Small-scale Fisheries Consultation Dates: 1 st April-3 rd May, 2011 MSC Contact: Yemi
MSC - Marine Stewardship Council Consultation Document: Guidance on Assessment of Management Performance Indicators in Small-scale Fisheries Consultation Dates: 1 st April-3 rd May, 2011 MSC Contact: Yemi
APPLICATION OF MULTIFAN-CL IN THE STOCK ASSESSMENT OF ALBACORE
 SCRS/2003/072 Col. Vol. Sci. Pap. ICCAT, 56(6): 1391-1401 (2004) APPLICATION OF MULTIFAN-CL IN THE STOCK ASSESSMENT OF ALBACORE D. García 1, V. Restrepo 2, H. Arrizabalaga 3, C. Palma 2, I. Mosqueira 1,
SCRS/2003/072 Col. Vol. Sci. Pap. ICCAT, 56(6): 1391-1401 (2004) APPLICATION OF MULTIFAN-CL IN THE STOCK ASSESSMENT OF ALBACORE D. García 1, V. Restrepo 2, H. Arrizabalaga 3, C. Palma 2, I. Mosqueira 1,
Biological Diversity and Tourism: Development of Guidelines for Sustainable Tourism in Vulnerable Ecosystems
 Biological Diversity and Tourism: Development of Guidelines for Sustainable Tourism in Vulnerable Ecosystems Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Foreword The rapid and often uncontrolled
Biological Diversity and Tourism: Development of Guidelines for Sustainable Tourism in Vulnerable Ecosystems Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Foreword The rapid and often uncontrolled
Report on the SARC 45 on Gulf of Maine Northern Shrimp and Atlantic Sea Scallops, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, June 4-6, 2007
 J.-J. Maguire CIE Review SARC 45 Page 1 Report on the SARC 45 on Gulf of Maine Northern Shrimp and Atlantic Sea Scallops, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, June 4-6, 2007 Jean-Jacques Maguire CIE Reviewer Prepared
J.-J. Maguire CIE Review SARC 45 Page 1 Report on the SARC 45 on Gulf of Maine Northern Shrimp and Atlantic Sea Scallops, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, June 4-6, 2007 Jean-Jacques Maguire CIE Reviewer Prepared
How To Measure Performance
 How to Write Great Performance Measures Part of a Continuing Series on: Performance Monitoring and Program Evaluation Sponsored by NOAA s SEE Evaluation Committee John Bortniak Member, SEE Evaluation Committee
How to Write Great Performance Measures Part of a Continuing Series on: Performance Monitoring and Program Evaluation Sponsored by NOAA s SEE Evaluation Committee John Bortniak Member, SEE Evaluation Committee
How To Write A Listing Policy For A Species At Risk Act
 Fisheries and Oceans Canada Species at Risk Act Listing Policy and Directive for Do Not List Advice DFO SARA Listing Policy Preamble The Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) Species at Risk Act (SARA) Listing
Fisheries and Oceans Canada Species at Risk Act Listing Policy and Directive for Do Not List Advice DFO SARA Listing Policy Preamble The Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) Species at Risk Act (SARA) Listing
MPA NETWORKS MODULE 2 2.1 INTRODUCTION TO MPA NETWORKS. Advantages of Networks 2.2 TYPES OF MPA NETWORKS. Social Networks. Ecological Networks
 2.1 INTRODUCTION TO MPA NETWORKS Advantages of Networks 2.2 TYPES OF MPA NETWORKS Social Networks Ecological Networks Management-based Networks Case Study: A Regional Approach to MPA Development in West
2.1 INTRODUCTION TO MPA NETWORKS Advantages of Networks 2.2 TYPES OF MPA NETWORKS Social Networks Ecological Networks Management-based Networks Case Study: A Regional Approach to MPA Development in West
COMMITTEE ON FISHERIES
 May 2016 COFI/2016/Inf.15 E COMMITTEE ON FISHERIES Thirty-second Session Rome, 11-15 July 2016 ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE ON RIGHTS-BASED APPROACHES FOR FISHERIES: A GLOBAL WORK PROGRAMME FOR ENHANCING FOOD SECURITY
May 2016 COFI/2016/Inf.15 E COMMITTEE ON FISHERIES Thirty-second Session Rome, 11-15 July 2016 ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE ON RIGHTS-BASED APPROACHES FOR FISHERIES: A GLOBAL WORK PROGRAMME FOR ENHANCING FOOD SECURITY
Advance and unedited
 Advance and unedited Outcome of the Ad Hoc Open-ended Informal Working Group to study issues relating to the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity beyond national jurisdiction
Advance and unedited Outcome of the Ad Hoc Open-ended Informal Working Group to study issues relating to the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity beyond national jurisdiction
Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission
 Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission ADDENDUM VII TO THE INTERSTATE FISHERY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR HORSESHOE CRABS FOR PUBLIC COMMENT ADAPTIVE RESOURCE MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK ASMFC Vision Statement:
Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission ADDENDUM VII TO THE INTERSTATE FISHERY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR HORSESHOE CRABS FOR PUBLIC COMMENT ADAPTIVE RESOURCE MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK ASMFC Vision Statement:
Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain. An Oracle White Paper December 2001
 Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain An Oracle White Paper December 2001 Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW This white paper illustrates why a fusion
Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain An Oracle White Paper December 2001 Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW This white paper illustrates why a fusion
CANADIAN ASSESSMENT OF PACIFIC HAKE IN U.S. AND CANADIAN WATERS IN 2009
 Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Science Response 2009/002 CANADIAN ASSESSMENT OF PACIFIC HAKE IN U.S. AND CANADIAN WATERS IN 2009 Context The Pacific hake, also referred to as Pacific whiting (Merluccius
Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Science Response 2009/002 CANADIAN ASSESSMENT OF PACIFIC HAKE IN U.S. AND CANADIAN WATERS IN 2009 Context The Pacific hake, also referred to as Pacific whiting (Merluccius
BEFORE THE SUBCOMMITTEE ON FISHERIES, WILDLIFE, OCEANS AND INSULAR AFFAIRS COMMITTEE ON NATURAL RESOURCES U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES APRIL 3, 2014
 WRITTEN TESTIMONY OF RUSSELL F. SMITH III DEPUTY ASSISTANT SECRETARY FOR INTERNATIONAL FISHERIES NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE LEGISLATIVE HEARING ON H.R.
WRITTEN TESTIMONY OF RUSSELL F. SMITH III DEPUTY ASSISTANT SECRETARY FOR INTERNATIONAL FISHERIES NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE LEGISLATIVE HEARING ON H.R.
COMMISSION TENTH REGULAR SESSION Cairns, Australia 2-6 December 2013
 COMMISSION TENTH REGULAR SESSION Cairns, Australia 2-6 December 2013 CONSERVATION AND MANAGEMENT MEASURE FOR BIGEYE, YELLOWFIN AND SKIPJACK TUNA IN THE WESTERN AND CENTRAL PACIFIC OCEAN Conservation and
COMMISSION TENTH REGULAR SESSION Cairns, Australia 2-6 December 2013 CONSERVATION AND MANAGEMENT MEASURE FOR BIGEYE, YELLOWFIN AND SKIPJACK TUNA IN THE WESTERN AND CENTRAL PACIFIC OCEAN Conservation and
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic
 AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
Electronic management and exchange of fishery information
 FLUX Electronic management and exchange of fishery information Dr Heiner Lehr heiner@syntesa.eu 1 INTRODUCTION 2 Global seafood trade Global seafood trade is estimated to be worth about 140 billion USD
FLUX Electronic management and exchange of fishery information Dr Heiner Lehr heiner@syntesa.eu 1 INTRODUCTION 2 Global seafood trade Global seafood trade is estimated to be worth about 140 billion USD
MMP Goal - effectively manage the (manatee) population in perpetuity throughout Florida by securing habitat and minimizing threats
 Statewide Monitoring of the Florida Manatee Presentation for the Marine Mammal Commission 2015 Annual Meeting Leslie Ward-Geiger, Marine Mammal Research Program Leader Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation
Statewide Monitoring of the Florida Manatee Presentation for the Marine Mammal Commission 2015 Annual Meeting Leslie Ward-Geiger, Marine Mammal Research Program Leader Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation
INTERIM MEASURES ADOPTED BY PARTICIPANTS IN NEGOTIATIONS TO ESTABLISH SOUTH PACIFIC REGIONAL FISHERIES MANAGEMENT ORGANISATION
 INTERIM MEASURES ADOPTED BY PARTICIPANTS IN NEGOTIATIONS TO ESTABLISH SOUTH PACIFIC REGIONAL FISHERIES MANAGEMENT ORGANISATION Participants in the negotiations to establish a South Pacific Regional Fisheries
INTERIM MEASURES ADOPTED BY PARTICIPANTS IN NEGOTIATIONS TO ESTABLISH SOUTH PACIFIC REGIONAL FISHERIES MANAGEMENT ORGANISATION Participants in the negotiations to establish a South Pacific Regional Fisheries
Indicator fact sheet Fishing fleet trends
 Indicator fact sheet Fishing fleet trends Key message: The big EU 15 fishing fleet (1989 2000) has decreased in numbers of vessels (10 %), in tonnage (6 %) and power (12 %) The much smaller EFTA fishing
Indicator fact sheet Fishing fleet trends Key message: The big EU 15 fishing fleet (1989 2000) has decreased in numbers of vessels (10 %), in tonnage (6 %) and power (12 %) The much smaller EFTA fishing
22. Assessment of the Octopus Stock Complex in the Bering Sea and Aleutian Islands
 22. Assessment of the Octopus Stock Complex in the Bering Sea and Aleutian Islands M. Elizabeth Conners, Christina Conrath, and Kerim Aydin Alaska Fisheries Science Center November 2015 Executive Summary
22. Assessment of the Octopus Stock Complex in the Bering Sea and Aleutian Islands M. Elizabeth Conners, Christina Conrath, and Kerim Aydin Alaska Fisheries Science Center November 2015 Executive Summary
REGIONAL ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES IMPLEMENTATION PLAN FOR WEST COAST MARINE FISHERIES DRAFT JANUARY 27, 2015
 REGIONAL ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES IMPLEMENTATION PLAN FOR WEST COAST MARINE FISHERIES DRAFT JANUARY 27, 2015 Introduction In recent years, the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) and the Pacific Fishery
REGIONAL ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES IMPLEMENTATION PLAN FOR WEST COAST MARINE FISHERIES DRAFT JANUARY 27, 2015 Introduction In recent years, the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) and the Pacific Fishery
CHAPTER 8 FISHERY MONITORING, CONTROL AND SURVEILLANCE. Per Erik BERGH 1 and Sandy DAVIES 2
 CHAPTER 8 FISHERY MONITORING, CONTROL AND SURVEILLANCE by Per Erik BERGH 1 and Sandy DAVIES 2 1 Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources, Namibia 2 Marine Fisheries and Resources Sector Co-ordinating
CHAPTER 8 FISHERY MONITORING, CONTROL AND SURVEILLANCE by Per Erik BERGH 1 and Sandy DAVIES 2 1 Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources, Namibia 2 Marine Fisheries and Resources Sector Co-ordinating
Economic Research Division
 July Economic Commentary Number Why is the Rate of Decline in the GDP Deflator So Large? Exploring the background against the discrepancy from the Consumer Price Index Economic Research Division Maiko
July Economic Commentary Number Why is the Rate of Decline in the GDP Deflator So Large? Exploring the background against the discrepancy from the Consumer Price Index Economic Research Division Maiko
Peer review on manuscript "Predicting environmental gradients with..." by Peer 410
 Peer review on manuscript "Predicting environmental gradients with..." by Peer 410 ADDED INFO ABOUT FEATURED PEER REVIEW This peer review is written by Dr. Richard Field, Associate Professor of Biogeography
Peer review on manuscript "Predicting environmental gradients with..." by Peer 410 ADDED INFO ABOUT FEATURED PEER REVIEW This peer review is written by Dr. Richard Field, Associate Professor of Biogeography
Data Collection and Management Program Review Northeast Fisheries Science Center Summary and Response November 2013
 Northeast Fisheries Science Center Introduction Data Collection and Management Program Review Northeast Fisheries Science Center Summary and Response November 2013 During August 5-8, 2013, six peer reviewers
Northeast Fisheries Science Center Introduction Data Collection and Management Program Review Northeast Fisheries Science Center Summary and Response November 2013 During August 5-8, 2013, six peer reviewers
The use of echo-sounder buoys in purse seine fleets fishing with DFADs in the eastern Pacific Ocean
 The use of echo-sounder buoys in purse seine fleets fishing with DFADs in the eastern Pacific Ocean Moreno 1, G., Murua 2, J., Restrepo 1, V. Summary Tuna purse seine fishers utilizing Drifting Fish Aggregating
The use of echo-sounder buoys in purse seine fleets fishing with DFADs in the eastern Pacific Ocean Moreno 1, G., Murua 2, J., Restrepo 1, V. Summary Tuna purse seine fishers utilizing Drifting Fish Aggregating
SABLEFISH PERMIT STACKING PROGRAM- ACTION ISSUES, ELECTRONIC FISH TICKET ANALYSIS
 Agenda Item C.6.a Supplemental Attachment 3 April 2014 SABLEFISH PERMIT STACKING PROGRAM- ACTION ISSUES, ELECTRONIC FISH TICKET ANALYSIS In the Draft Council Decision Analysis Document for the sablefish
Agenda Item C.6.a Supplemental Attachment 3 April 2014 SABLEFISH PERMIT STACKING PROGRAM- ACTION ISSUES, ELECTRONIC FISH TICKET ANALYSIS In the Draft Council Decision Analysis Document for the sablefish
JARPA II* Research Fleet Departs for the Antarctic
 THE INSTITUTE OF CETACEAN RESEARCH 4-5 TOYOMI-CHO, CHUO-KU, TOKYO 104-0055 JAPAN PHONE: +81-3-3536-6521 FAX: +81-3536-6522 MEDIA RELEASE 7 November 2005 JARPA II* Research Fleet Departs for the Antarctic
THE INSTITUTE OF CETACEAN RESEARCH 4-5 TOYOMI-CHO, CHUO-KU, TOKYO 104-0055 JAPAN PHONE: +81-3-3536-6521 FAX: +81-3536-6522 MEDIA RELEASE 7 November 2005 JARPA II* Research Fleet Departs for the Antarctic
Improving accountability and performance in international fisheries management
 A series of papers on policy options, prepared for the third meeting of the Global Ocean Commission, November 2013 Policy Options Paper # 9: Improving accountability and performance in international fisheries
A series of papers on policy options, prepared for the third meeting of the Global Ocean Commission, November 2013 Policy Options Paper # 9: Improving accountability and performance in international fisheries
Ellen Hey Professor of Public International Law, Erasmus School of Law, Erasmus University Rotterdam
 THE PRINCIPLE OF COMMON BUT DIFFERENTIATED RESPONSIBILITIES Ellen Hey Professor of Public International Law, Erasmus School of Law, Erasmus University Rotterdam Short summary This lecture discusses the
THE PRINCIPLE OF COMMON BUT DIFFERENTIATED RESPONSIBILITIES Ellen Hey Professor of Public International Law, Erasmus School of Law, Erasmus University Rotterdam Short summary This lecture discusses the
Study suggests the Mediterranean Sea may be losing large predatory sharks.
 research series april 2008 Study suggests the Mediterranean may be losing large predatory sharks. SHARK DECLINES IN THE MEDITERRANEAN SEA A Summary of New Scientific Analysis: Ferretti, F., Myers, R.A.,
research series april 2008 Study suggests the Mediterranean may be losing large predatory sharks. SHARK DECLINES IN THE MEDITERRANEAN SEA A Summary of New Scientific Analysis: Ferretti, F., Myers, R.A.,
RECREATIONAL FISHERIES MANAGEMENT. The National Marine Fisheries Service Should Develop a Comprehensive Strategy to Guide Its Data Collection Efforts
 United States Government Accountability Office Report to Congressional Requesters December 2015 RECREATIONAL FISHERIES MANAGEMENT The National Marine Fisheries Service Should Develop a Comprehensive Strategy
United States Government Accountability Office Report to Congressional Requesters December 2015 RECREATIONAL FISHERIES MANAGEMENT The National Marine Fisheries Service Should Develop a Comprehensive Strategy
CASE STUDY OF A TRAVEL-COST ANALYSIS: THE MICHIGAN ANGLING DEMAND MODEL 15
 CASE STUDY OF A TRAVEL-COST ANALYSIS: THE MICHIGAN ANGLING DEMAND MODEL 15 Background This case study estimates the demand for recreational angling in Michigan using the travel-cost model. By demand for
CASE STUDY OF A TRAVEL-COST ANALYSIS: THE MICHIGAN ANGLING DEMAND MODEL 15 Background This case study estimates the demand for recreational angling in Michigan using the travel-cost model. By demand for
5.0 ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT METHODS
 5.0 ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT METHODS The methods that are used to conduct the environmental impact assessment (EIA) of the Project are described in this section. The EIA uses a methodological framework
5.0 ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT METHODS The methods that are used to conduct the environmental impact assessment (EIA) of the Project are described in this section. The EIA uses a methodological framework
Subactivity: Habitat Conservation Program Element: National Wetlands Inventory
 HABITAT CONSERVATION FY 29 BUDGET JUSTIFICATION Subactivity: Habitat Conservation Program Element: National Wetlands Inventory National Wetlands Inventory ($) FTE 27 4,7 2 28 Enacted 5,255 2 Fixed Costs
HABITAT CONSERVATION FY 29 BUDGET JUSTIFICATION Subactivity: Habitat Conservation Program Element: National Wetlands Inventory National Wetlands Inventory ($) FTE 27 4,7 2 28 Enacted 5,255 2 Fixed Costs
Introduction to protection goals, ecosystem services and roles of risk management and risk assessment. Lorraine Maltby
 Introduction to protection goals, ecosystem services and roles of risk management and risk assessment. Lorraine Maltby Problem formulation Risk assessment Risk management Robust and efficient environmental
Introduction to protection goals, ecosystem services and roles of risk management and risk assessment. Lorraine Maltby Problem formulation Risk assessment Risk management Robust and efficient environmental
5.5 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL
 0 0 0. QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL.. Introduction The IPCC Good Practice Guidance and Uncertainty Management (GPG000, IPCC, 000), Chapter, Quality Assurance and Quality Control, defines quality
0 0 0. QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL.. Introduction The IPCC Good Practice Guidance and Uncertainty Management (GPG000, IPCC, 000), Chapter, Quality Assurance and Quality Control, defines quality
Guidance on the management of interest rate risk arising from nontrading
 Guidance on the management of interest rate risk arising from nontrading activities Introduction 1. These Guidelines refer to the application of the Supervisory Review Process under Pillar 2 to a structured
Guidance on the management of interest rate risk arising from nontrading activities Introduction 1. These Guidelines refer to the application of the Supervisory Review Process under Pillar 2 to a structured
NOAA. Fisheries Information System Program. The FIS Mission
 Fisheries Information System Program NOAA The FIS Mission In order to support sound science and effective stewardship of our living marine resources, we work collaboratively through partnerships to provide
Fisheries Information System Program NOAA The FIS Mission In order to support sound science and effective stewardship of our living marine resources, we work collaboratively through partnerships to provide
The Physical and Economic Accounts for UK Fisheries
 The Physical and Economic Accounts for UK Fisheries Report by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) March 2003 Acknowledgements The author of this report is Charles Palmer (formerly ONS). The author
The Physical and Economic Accounts for UK Fisheries Report by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) March 2003 Acknowledgements The author of this report is Charles Palmer (formerly ONS). The author
Status of the Fishing Industry
 BELIZE FISHERIES DEPARTMENT Status of the Fishing Industry Mauro Gongora, MSc. Email: megongora@gmail.com Coordinator -Capture Fisheries Unit Belize City, Belize. June 8, 2012. State of the Coastal Zone
BELIZE FISHERIES DEPARTMENT Status of the Fishing Industry Mauro Gongora, MSc. Email: megongora@gmail.com Coordinator -Capture Fisheries Unit Belize City, Belize. June 8, 2012. State of the Coastal Zone
Getting Involved: Cooperative Program and Grant Opportunities for Fishermen in the South Atlantic Region An Overview
 Getting Involved: Cooperative Program and Grant Opportunities for Fishermen in the South Atlantic Region An Overview Fisheries managers often receive questions from fishermen regarding opportunities to
Getting Involved: Cooperative Program and Grant Opportunities for Fishermen in the South Atlantic Region An Overview Fisheries managers often receive questions from fishermen regarding opportunities to
Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing
 Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing Learning Objectives To understand the meanings of marginal cost and marginal costing To distinguish between marginal costing and absorption costing To ascertain
Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing Learning Objectives To understand the meanings of marginal cost and marginal costing To distinguish between marginal costing and absorption costing To ascertain
Ecosystems and Food Webs
 Ecosystems and Food Webs How do AIS affect our lakes? Background Information All things on the planet both living and nonliving interact. An Ecosystem is defined as the set of elements, living and nonliving,
Ecosystems and Food Webs How do AIS affect our lakes? Background Information All things on the planet both living and nonliving interact. An Ecosystem is defined as the set of elements, living and nonliving,
13. Steps 3.1 & 3.2. Develop objectives, indicators and benchmarks. Essential EAFM Date Place. Version 1
 13. Steps 3.1 & 3.2 Develop objectives, indicators and benchmarks Essential EAFM Date Place Version 1 Session objectives After this session you will be able to: Develop management objectives Develop indicators
13. Steps 3.1 & 3.2 Develop objectives, indicators and benchmarks Essential EAFM Date Place Version 1 Session objectives After this session you will be able to: Develop management objectives Develop indicators
