Embedded Systems Design using CPU. Alessandro Palla PhD student in Embedded System Design
|
|
|
- Roderick Cannon
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Embedded Systems Design using CPU Alessandro Palla PhD student in Embedded System Design
2 Slides and other stuffs Website: You can find there (maybe) Today s slides (Theoretical lesson) Tomorrow s slides (Practical lesson) Link to some datasheet Cortex M4 STM32F4 STM32F4Discovery Board LIS3DSH (Accelerometer)
3 Lessons Outline Short seminario on STM32F4 Embedded CPU. Theory and simple example Today Challenges and Constraints designing an embedded system using a CPU STM32F4 Introduction Cortex M4 CPU Simple approach to Thumb Instruction Set Memory Model AMBA Bus Clock NVIC
4 Outline (...continue) Power Management DMA Timer Tomorrow Simple application development: USB Mouse controlled by g acceleration. How it works? When user tilts the board, accelerometer detects it and change mouse pointer s position on PC screen. Developing and testing application on STM32F4-Discovery board
5 Software for Tomorrow Unfortunately we have only one developer board :( You can follow software developing by download two software (not mandatory) STM32Cube MX IAR Embedded Workbench -> Kickstarter Edition (free) If you have a STM32F4Discovery board you can take it!!
6 Embedded System Embedded computing systems Computing systems embedded within electronic devices Hard to define. Nearly any computing system other than a desktop computer Billions of units produced yearly, versus millions of desktop units Perhaps 50 per household and per automobile
7 Short list of embedded systems Anti-lock brakes Auto-focus cameras Automatic teller machines Automatic toll systems Automatic transmission Avionic systems Battery chargers Camcorders Cell phones Cell-phone base stations Cordless phones Cruise control Curbside check-in systems Digital cameras Disk drives Electronic card readers Electronic instruments Electronic toys/games Factory control Fax machines Fingerprint identifiers Home security systems Life-support systems Medical testing systems Modems MPEG decoders Network cards Network switches/routers On-board navigation Pagers Photocopiers Point-of-sale systems Portable video games Printers Satellite phones Scanners Smart ovens/dishwashers Speech recognizers Stereo systems Teleconferencing systems Televisions Temperature controllers Theft tracking systems TV set-top boxes VCR s, DVD players Video game consoles Video phones Washers and dryers
8 Common characteristics of embedded systems Single-functioned Executes a single program, repeatedly Tightly-constrained Low cost, low power, small, fast, etc. Reactive and real-time Continually reacts to changes in the system s environment Must compute certain results in real-time without delay
9 Design Example: digital camera Single-functioned -- always a digital camera Tightly-constrained -- Low cost, low power, small, fast Reactive and real-time -- only to a small extent
10 Optimizing design metrics Obvious design goal: Construct an implementation with desired functionality Key design challenge: Simultaneously optimize numerous design metrics Design metric A measurable feature of a system s implementation Optimizing design metrics is a key challenge
11 Design Metrics Common metrics Unit cost: the monetary cost of manufacturing each copy of the system, excluding NRE cost NRE cost (Non-Recurring Engineering cost): The one-time monetary cost of designing the system Size: the physical space required by the system Performance: the execution time or throughput of the system Power: the amount of power consumed by the system Flexibility: the ability to change the functionality of the system without incurring heavy NRE cost
12 Design Metrics Common metrics (continued) Time-to-prototype: the time needed to build a working version of the system Time-to-market: the time required to develop a system to the point that it can be released and sold to customers Maintainability: the ability to modify the system after its initial release Correctness, safety, many more
13 Metrics Trade-Off Expertise with both software and hardware is needed to optimize design metrics Not just a hardware or software expert, as is common A designer must be comfortable with various technologies in order to choose the best for a given application and constraints
14 General-Purpose Processor General-Purpose Processor Processor designed for a variety of computation tasks Low unit cost, in part because manufacturer spreads NRE over large numbers of units Motorola sold half a billion 68HC05 microcontrollers only in 1996 Carefully designed since higher NRE is acceptable Can yield good performance, size and power Low NRE cost, short time-to-market/prototype, high flexibility User just writes software; no processor design No need of complex hardware design, fast prototyping and error detection
15 Case Study: STM32F4 High performance embedded CPU using a Cortex M4 core Low cost development board (STM32F4Discovery costs approx 10$) Well documented Lots of feature and peripherals M in Cortex M4 means Microcontroller. CPU designed for embedded systems that not requires too much computing power. Others Cortex family: R: Realtime CPU, suitable for deep embedded real-time systems. A: Application CPU, generic high performance processor
16 STM32F4 Also for DSP applications
17 Key Features
18 STMicroelectronics One of the world top important productor of Electronics Devices Embedded CPU MEMS Sensor MEMS means Micro-Electro-Mechanical-System, a sensor built in silicon into a chip to reduce dimension, costs and reliability Example: Microphone Accelerometer, Gyro, Inertial Modules Pressure Sensors and so on RFIC (Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit) OPAMP and other analog electronics ecc... An Italian-French company
19 MEMS Example of MEMS Accelerometer Embedded into a chip, note the scale!
20 CPU Structure Von Neumann Fewer memory wires Harvard Simultaneous program and data memory access In Harvard architecture CPU can access simultaneously both in program and data memory Cortex M4 has Harvard structure in order to improve CPU speed
21 Memory Model Program is stored in a flash memory, data in a volatile memory like SRAM I-bus: This bus is used by the core to fetch instructions. S-bus: This bus is used to access data located in a peripheral or in SRAM D-bus: This bus is used by the core for literal load and debug access. I-bus D-bus S-bus
22 Cortex M4 Structure Key Concept: from processor point of view everything is memory space! Data Memory Program Memory Peripheral registers D-bus CPU access to memory only using LOAD and STORE instruction RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) paradigm I-bus S-bus
23 Memory Map 32 bit memory space (4 GB), byte-addressable, little endian: Not everything of this space is available from user s application Code Internal SRAM External SRAM Peripherals External Device Every peripheral is mapped into a specific address Depending of MSB bits of address bus arbiter selects which memory should be read/write
24 Multi AHB bus matrix Using Bus matrix multiple bus master can perform simultaneously operation on different memory.
25 Multi AHB bus matrix Using Bus matrix multiple bus master can perform simultaneously operation on different memory. For example in the same clock cycle: CPU can fetch instruction from Flash
26 Multi AHB bus matrix Using Bus matrix multiple bus master can perform simultaneously operation on different memory. For example in the same clock cycle: CPU can fetch instruction from Flash CPU can read/write data from SRAM
27 Multi AHB bus matrix Using Bus matrix multiple bus master can perform simultaneously operation on different memory. For example in the same clock cycle: CPU can fetch instruction from Flash CPU can read/write data from SRAM DMA can transfer data from two different peripherals
28 Multi AHB bus matrix Using Bus matrix multiple bus master can perform simultaneously operation on different memory. For example in the same clock cycle: CPU can fetch instruction from Flash CPU can read/write data from SRAM DMA can transfer data from two different peripherals Multi AHB bus matrix automatically manages access arbitration between masters
29 Flash memory latency Flash memory is perfect to store non-volatile data like program s code, static data etc but is typically much slower than SRAM! CPU can t fetch instruction before Flash latency time. Es: fclk = 168 MHz, Tclk ~ 6 ns Flash latency in clock cycle = floor(tr,flash / Tclk) Flash latency time depending on Supply voltage: low voltage increase latency time Flash size: big flash has bigger parasitic capacitance remember delay in CMOS: Tdelay~ Ron-mosfet * Cp Second order effect, voltage scaling is more important
30 Wait states
31 ART Accelerator Adaptive Real-Time memory Accelerator: a proprietary (STM) hardware block designed to reduce wait states in flash read access. Flash memory is organised in 128-bit blocks, up to 8 instruction-block using Thumb instruction set (16 bit x instr.) ART works like a cache memory. Using prefetch of next instruction theoretically it reduces to 0 wait states in sequential statements. For non-sequential instruction (like branch, call etc ) the penalty in terms of number of cycles is at least equal to the number of wait states A dynamic branch prediction system is used to improve performances
32 Cortex M4 Register Map 13 General purpose register Attention! in order to use 16 bit instruction, not all GP register can be used for all instruction
33 Example: ADD/SUBTRACT This instruction can do: Rd = Rs ± Rn Rd = Rs ± Offset3 5 bit opcode flag for immediate operand, 3 bit 3 bit register, from R0 to R7 For more than 3 bit sum: MOV Rn,#num SUM Rd,Rs,Rn Same code size 32 bit Instruction set 2 clock cycle
34 Thumb Instruction Set Thumb instructions in general requires more code than 32 bit RISC instruction set. More instruction for the same code that decreases performance of CPU Otherwise Thumb increases code density Example: only 16 bit instruction size for simple increment like i++ => ADD R0,R0,#1 Thumb code is typically 65% of ARM 32 bit code (infocenter.arm.com) ARM7 and other high end processors can use both Thumb and ARM 32 bit instruction sets
35 Cortex M4 Register Map SP: Stack Pointer PC: Program Counter LR: Link Register, the register that contains return address from PC when Branch and Link (BL) instruction is executed Example:.main BL func ; branch to func label ; after BX CPU execute this instruction.func BX LR ; do stuffs ; branch to LR register value
36 Clock Three different clock sources can be used to drive the system clock HSI oscillator clock (high-speed internal clock signal) HSE oscillator clock (high-speed external clock signal) PLL clock Device has also two secondary clock sources 32 khz low-speed internal clock khz low speed external crystal This two clock can be used to drive Real-Time Clock 215 = 32768, so if this clock feed a 16 bit timer his MSB toggle every second
37 External Clock With crystal/ceramic resonator in range from 4 to 26 MHz Using an external source. It can have a frequency from 1 to 50 MHz
38 Select System Clock
39 Other derived clock APB1 and APB2 are peripheral lower speed buses Usually peripherals don t need to go at maximum speed, so decrease clock frequency can save power. Prescalers can be changed runtime, like clock frequency
40 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC) provides configurable interrupt handling abilities to the processor. Up to 91 maskable interrupt Facilitates low-latency interrupt handling Controls power management Three levels of priority: Interrupt Number Preempt Priority Subpriority
41 Position Number Position number is fixed and set by design Rule: interrupt handler with lower priority/position number is prioritary to others
42 How interrupt priority works It s easy to understand using examples: EXTI0 number = 13, EXTI1 number = 14 Case 1: EXTI0 and EXTI1 pending, same preemption and subpriority CPU executes highest priority interrupt
43 How interrupt priority works Case 2: EXTI0 and EXTI1 pending, same preemption and but different subprioroty: 1 for EXTI0 and 0 for EXTI1 User can change priority interrupt using subpriority
44 How interrupt priority works Case 3: EXTI0 interrupt request while EXTI1 is running, same preemption and subpriority Interrupt service routine (ISR) can be preempted only from interrupt with higher preemption priority
45 How interrupt priority works Case 4: EXTI0 interrupt request while EXTI1 is running, same subpriority but different preemption: 0 for EXTI0 and 1 for EXTI1 In that case EXTI0 has greater preemption priority than EXTI1
46 Priority Stm32 has 4 bits of priority, 16 priority levels User can select how much of this 4 bits are for preemption priority and how much is for subpriority Example: 2 bits for preemption and 2 bits for subpriority In this case we can have 4 levels of preempted ISR and 4 for subpriority Another Example: 0 bit for preemption and 4 for subpriority No-preemptible ISR
47 Interrupt Priority Summary The preempt priority level defines whether an interrupt can be serviced when the processor is already running another interrupt handler. In other words, preempt priority determines if one interrupt can preempt another The subpriority level value is used only when two exception with the same preempt priority level are pending. The exception with the lower subpriority will be handled first. The position number level value is used only when two exception with the same preempt priority and subpriority are pending. The exception with the lower position number will be handled first.
48 Power Management Power consumption is one of the most important constraints in portable embedded device. STM32F4 provides several low-power mode Sleep mode (CPU core stopped) Stop mode (all clocks are stopped) Standby mode (disable 1.2V power supply, lost of volatile data) In addition user can reduce power consumption in run mode Slowing down system clock Disable peripherals clock when they are unused
49 Sleep Mode Sleep Mode Description Mode entry WFI or WFE special instruction Mode Exit Latency Interrupt if WFI was used Event if WFE was used None In sleep mode only CPU clock is stopped. To enter in this mode user can call special instruction WFI (Wait for Interrupt) => wake CPU on any interrupt configured. WFE (Wait for Event) => wake CPU on any event. Event is generated by EXTI peripherals (see documentation or TODO)
50 Stop Mode Stop Mode Description Mode entry WFI or WFE instruction plus configuration of some register Mode Exit Latency EXTI lines configured in Interrupt mode if WFI was used EXTI lines configured in Interrupt mode if WFI was used Oscillator startup time In stop mode all clock are stopped. Voltage is still on User can decide to keep active few low consumption peripherals like RTC, Watchdog and low frequency oscillator (for RTC and Watchdog)
51 Standby Mode Stop Mode Description Mode entry WFI or WFE instruction plus configuration of some register Mode Exit Rising edge on WKUP pin, external reset, RTC or Watchdog reset Latency Oscillator startup time In standby mode device disabled 1.2V regulator. All non volatile data was lost!! After waking up from standby, program execution restarts in the same way as after a Reset! User can decide to keep active few low consumption peripherals like RTC, Watchdog and low frequency oscillator (for RTC and Watchdog)
52 Reset Circuit
53 DMA Direct memory Access(DMA) is used in order to provide high-speed data transfer between peripherals and memory and between memory and memory. Data can be quickly moved by DMA without any CPU action. This keeps CPU resources free for other operations Three modes: Memory-to-Peripheral Peripheral-to-Memory Memory-to-Memory
54 DMA DMA read data from Memory and place it to Peripheral destination address. It automatically increments source/destination address to perform multi-byte transfer, also in circular mode (i = (i+1)%n) 8 stream can be performed simultaneously, coordinated by a bus Arbiter depending on stream priority DMA transfer can be triggered both by software or peripherals.
55 DMA Example
56 Peripheral-to-memory Peripheral to memory transfer controlled by CPU Example: Transfer data array from SD card to memory
57 Peripheral-to-memory Peripheral to memory transfer controlled by peripheral Example: USB data transfer
58 Memory-to-memory Memory to memory transfer. Example: Non blocking memcpy During memory transfer CPU is free to do other stuffs
59 Timer 16-bit Counter Up, down and centred counting modes Auto Reload 4 x 16-bit Capture/Compare Channels Programmable channel direction: input/output Input Capture, PWM Input Capture Modes Output Compare, PWM, One Pulse Modes Independent IRQ/DMA Requests: At each Update Event At each Capture Compare Events At each Input Trigger
60 Clock Selection Clock can be selected from 2 sources Internal clock TIMxCLK provided by the RCC External pin ETR Timer Trigger can be Internal trigger input 1 to 4: ITR1 / ITR2 / ITR3 / ITR4 Using another timer as a prescaler External Capture Compare pins Pin 1: TI1FP1 or TI1F_ED Pin 2: TI2FP2 External pin ETR
61 Counting Modes 3 Counting Modes: Center Aligned Up counting Down Counting All three mode have the same update-event interrupt period
62 Output Compare The Output Compare is used to control an output waveform or indicate when a period of time has elapsed. When a match is found between the capture/compare register and the counter: The corresponding output pin is assigned to the programmable Mode, it can be: Set/Reset/Toggle Remain unchanged Generates an interrupt if the corresponding interrupt mask is set Send a DMA request if the corresponding enable bit is set
63 Output Compare
64 PWM The PWM mode allows to generate 4 independent signals. The frequency and a duty cycle determined as follow: One auto-reload register to defined the PWM period. Each PWM channel has a Capture Compare register to define the duty cycle. There are two configurable PWM modes: Edge-aligned Mode Center-aligned Mode
65 Synchronization Timers can be linked together for synchronization pourposes 1) Cascade Mode: TIM1 used as master timer for TIM2, TIM2 configured as TIM1 slave and master for TIM3
66 Synchronization 2) One Master several slaves: TIM1 used as master for TIM2, TIM2 and TIM4.
67 Synchronization 3) Timers and external trigger synchronization: TIM1, TIM2 and TIM3 are slaves for an external signal connected to respective Timers inputs.
68 RTC: Real Time Clock Clock sources khz dedicated oscillator (LSE) Low frequency (32kHz), low power internal RC(LSI) HSE divided by Event/Interrupt sources Second Overflow Alarm (also connected to EXTI Line 17 for Auto Wake-Up from STOP)
Lecture 1. Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems
 CENG 314 Lecture 1 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems Asst. Prof. Tolga Ayav, Ph.D. Department of Computer Engineering System A system has a set of one or more inputs entering a black box and a
CENG 314 Lecture 1 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems Asst. Prof. Tolga Ayav, Ph.D. Department of Computer Engineering System A system has a set of one or more inputs entering a black box and a
ARM Cortex STM series
 ARM Cortex board 1 ARM Cortex STM series 2 STM32 Series 3 Abbreviation FS full speed HS high speed MC motor controller MSI multi speed internal oscillator RNG random number generator SDIO secure digital
ARM Cortex board 1 ARM Cortex STM series 2 STM32 Series 3 Abbreviation FS full speed HS high speed MC motor controller MSI multi speed internal oscillator RNG random number generator SDIO secure digital
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 reset and clock controller.
 Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 reset and clock controller. 1 The STM32L4 reset and clock controller manages system and peripheral clocks. STM32L4 devices embed three internal oscillators,
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 reset and clock controller. 1 The STM32L4 reset and clock controller manages system and peripheral clocks. STM32L4 devices embed three internal oscillators,
STM32 F-2 series High-performance Cortex-M3 MCUs
 STM32 F-2 series High-performance Cortex-M3 MCUs STMicroelectronics 32-bit microcontrollers, 120 MHz/150 DMIPS with ART Accelerator TM and advanced peripherals www.st.com/mcu STM32 F-2 series The STM32
STM32 F-2 series High-performance Cortex-M3 MCUs STMicroelectronics 32-bit microcontrollers, 120 MHz/150 DMIPS with ART Accelerator TM and advanced peripherals www.st.com/mcu STM32 F-2 series The STM32
AN4646 Application note
 Application note Peripheral interconnections on STM32F401 and STM32F411 lines Introduction On top of the highest performance and the lowest power consumption of the STM32F4 family, STM32F401/411 peripherals
Application note Peripheral interconnections on STM32F401 and STM32F411 lines Introduction On top of the highest performance and the lowest power consumption of the STM32F4 family, STM32F401/411 peripherals
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors
 Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors White paper Joseph Yiu January 2013 Overview Finite state machines (FSM) are commonly used in electronic designs. FSM can be used
Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors White paper Joseph Yiu January 2013 Overview Finite state machines (FSM) are commonly used in electronic designs. FSM can be used
STM32L. Ultra-low-power Cortex -M3 devices
 STM32L Ultra-low-power Cortex -M3 devices STM32L press release STM32L 32- to 128-Kbyte products are entering full production 2 nd half March 2011 Part of industry s largest ARM Cortex -M 32-bit microcontroller
STM32L Ultra-low-power Cortex -M3 devices STM32L press release STM32L 32- to 128-Kbyte products are entering full production 2 nd half March 2011 Part of industry s largest ARM Cortex -M 32-bit microcontroller
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 13. PIC Family Microcontroller
 Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas
 Technology Trend MSP432 TM microcontrollers: Bringing high performance to low-power applications The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas Instruments leverages its more than 20 years of lowpower leadership
Technology Trend MSP432 TM microcontrollers: Bringing high performance to low-power applications The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas Instruments leverages its more than 20 years of lowpower leadership
Exception and Interrupt Handling in ARM
 Exception and Interrupt Handling in ARM Architectures and Design Methods for Embedded Systems Summer Semester 2006 Author: Ahmed Fathy Mohammed Abdelrazek Advisor: Dominik Lücke Abstract We discuss exceptions
Exception and Interrupt Handling in ARM Architectures and Design Methods for Embedded Systems Summer Semester 2006 Author: Ahmed Fathy Mohammed Abdelrazek Advisor: Dominik Lücke Abstract We discuss exceptions
Overview of the Cortex-M3
 CHAPTER Overview of the Cortex-M3 2 In This Chapter Fundamentals 11 Registers 12 Operation Modes 14 The Built-In Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller 15 The Memory Map 16 The Bus Interface 17 The MPU 18
CHAPTER Overview of the Cortex-M3 2 In This Chapter Fundamentals 11 Registers 12 Operation Modes 14 The Built-In Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller 15 The Memory Map 16 The Bus Interface 17 The MPU 18
Atmel Norway 2005. XMEGA Introduction
 Atmel Norway 005 XMEGA Introduction XMEGA XMEGA targets Leadership on Peripheral Performance Leadership in Low Power Consumption Extending AVR market reach XMEGA AVR family 44-100 pin packages 16K 51K
Atmel Norway 005 XMEGA Introduction XMEGA XMEGA targets Leadership on Peripheral Performance Leadership in Low Power Consumption Extending AVR market reach XMEGA AVR family 44-100 pin packages 16K 51K
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems. 2008 Chapter-1L03: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Chapter 1 Computer System Overview
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
Lesson-16: Real time clock DEVICES AND COMMUNICATION BUSES FOR DEVICES NETWORK
 DEVICES AND COMMUNICATION BUSES FOR DEVICES NETWORK Lesson-16: Real time clock 1 Real Time Clock (RTC) A clock, which is based on the interrupts at preset intervals. An interrupt service routine executes
DEVICES AND COMMUNICATION BUSES FOR DEVICES NETWORK Lesson-16: Real time clock 1 Real Time Clock (RTC) A clock, which is based on the interrupts at preset intervals. An interrupt service routine executes
Building Blocks for PRU Development
 Building Blocks for PRU Development Module 1 PRU Hardware Overview This session covers a hardware overview of the PRU-ICSS Subsystem. Author: Texas Instruments, Sitara ARM Processors Oct 2014 2 ARM SoC
Building Blocks for PRU Development Module 1 PRU Hardware Overview This session covers a hardware overview of the PRU-ICSS Subsystem. Author: Texas Instruments, Sitara ARM Processors Oct 2014 2 ARM SoC
COMPUTER HARDWARE. Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems
 COMPUTER HARDWARE Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems Computer I/O I/O devices commonly found in Computer systems Keyboards Displays Printers Magnetic Drives Compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM)
COMPUTER HARDWARE Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems Computer I/O I/O devices commonly found in Computer systems Keyboards Displays Printers Magnetic Drives Compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM)
Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs)
 Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs) Course & Kit Contents LEARN HOW TO: Use of Keil Real View for ARM Use ARM Cortex-M3 MCU for professional embedded application development Understanding
Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs) Course & Kit Contents LEARN HOW TO: Use of Keil Real View for ARM Use ARM Cortex-M3 MCU for professional embedded application development Understanding
Central Processing Unit
 Chapter 4 Central Processing Unit 1. CPU organization and operation flowchart 1.1. General concepts The primary function of the Central Processing Unit is to execute sequences of instructions representing
Chapter 4 Central Processing Unit 1. CPU organization and operation flowchart 1.1. General concepts The primary function of the Central Processing Unit is to execute sequences of instructions representing
Serial Communications
 Serial Communications 1 Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs Operation
Serial Communications 1 Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs Operation
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ
 nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION
 EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION TOPICS TO BE DISCUSSED System Embedded System Components Classifications Processors Other Hardware Software Applications 2 INTRODUCTION What is a system? A system
EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION TOPICS TO BE DISCUSSED System Embedded System Components Classifications Processors Other Hardware Software Applications 2 INTRODUCTION What is a system? A system
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:16 min)
 Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Timer, Interrupt, Exception in ARM
 Timer, Interrupt, Exception in ARM Modifications from Prabal Dutta, University of Michigan 1 Interrupts Merriam-Webster: to break the uniformity or continuity of Informs a program of some external events
Timer, Interrupt, Exception in ARM Modifications from Prabal Dutta, University of Michigan 1 Interrupts Merriam-Webster: to break the uniformity or continuity of Informs a program of some external events
Motor Control using NXP s LPC2900
 Motor Control using NXP s LPC2900 Agenda LPC2900 Overview and Development tools Control of BLDC Motors using the LPC2900 CPU Load of BLDCM and PMSM Enhancing performance LPC2900 Demo BLDC motor 2 LPC2900
Motor Control using NXP s LPC2900 Agenda LPC2900 Overview and Development tools Control of BLDC Motors using the LPC2900 CPU Load of BLDCM and PMSM Enhancing performance LPC2900 Demo BLDC motor 2 LPC2900
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output
 Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE
 8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE Objective: 1. Familiarization with different types of Microcontroller 2. To know 8051 microcontroller in detail 3. Programming and Interfacing 8051 microcontroller Prerequisites:
8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE Objective: 1. Familiarization with different types of Microcontroller 2. To know 8051 microcontroller in detail 3. Programming and Interfacing 8051 microcontroller Prerequisites:
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR 1. What is the purpose of segment registers
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR 1. What is the purpose of segment registers
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 SDMMC controller module. It covers the main features of the controller which is used to connect
 Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 SDMMC controller module. It covers the main features of the controller which is used to connect the CPU to an SD card, MMC card, or an SDIO device.
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 SDMMC controller module. It covers the main features of the controller which is used to connect the CPU to an SD card, MMC card, or an SDIO device.
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation
 Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
AN10850. LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer. Document information. LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode
 LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
8-Bit Flash Microcontroller for Smart Cards. AT89SCXXXXA Summary. Features. Description. Complete datasheet available under NDA
 Features Compatible with MCS-51 products On-chip Flash Program Memory Endurance: 1,000 Write/Erase Cycles On-chip EEPROM Data Memory Endurance: 100,000 Write/Erase Cycles 512 x 8-bit RAM ISO 7816 I/O Port
Features Compatible with MCS-51 products On-chip Flash Program Memory Endurance: 1,000 Write/Erase Cycles On-chip EEPROM Data Memory Endurance: 100,000 Write/Erase Cycles 512 x 8-bit RAM ISO 7816 I/O Port
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems
 ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory
 CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
ARM Architecture. ARM history. Why ARM? ARM Ltd. 1983 developed by Acorn computers. Computer Organization and Assembly Languages Yung-Yu Chuang
 ARM history ARM Architecture Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang 1983 developed by Acorn computers To replace 6502 in BBC computers 4-man VLSI design team Its simplicity it comes
ARM history ARM Architecture Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang 1983 developed by Acorn computers To replace 6502 in BBC computers 4-man VLSI design team Its simplicity it comes
2.0 Command and Data Handling Subsystem
 2.0 Command and Data Handling Subsystem The Command and Data Handling Subsystem is the brain of the whole autonomous CubeSat. The C&DH system consists of an Onboard Computer, OBC, which controls the operation
2.0 Command and Data Handling Subsystem The Command and Data Handling Subsystem is the brain of the whole autonomous CubeSat. The C&DH system consists of an Onboard Computer, OBC, which controls the operation
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
AN3252 Application note
 Application note Building a wave generator using STM8L-DISCOVERY Application overview This application note provides a short description of how to use the STM8L-DISCOVERY as a basic wave generator for
Application note Building a wave generator using STM8L-DISCOVERY Application overview This application note provides a short description of how to use the STM8L-DISCOVERY as a basic wave generator for
Section 29. Real-Time Clock and Calendar (RTCC)
 Section 29. Real-Time Clock and Calendar (RTCC) HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 29.1 Introduction... 29-2 29.2 Status and Control Registers... 29-3 29.3 Modes of Operation...
Section 29. Real-Time Clock and Calendar (RTCC) HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 29.1 Introduction... 29-2 29.2 Status and Control Registers... 29-3 29.3 Modes of Operation...
Palaparthi.Jagadeesh Chand. Associate Professor in ECE Department, Nimra Institute of Science & Technology, Vijayawada, A.P.
 Patient Monitoring Using Embedded Palaparthi.Jagadeesh Chand Associate Professor in ECE Department, Nimra Institute of Science & Technology, Vijayawada, A.P Abstract The aim of this project is to inform
Patient Monitoring Using Embedded Palaparthi.Jagadeesh Chand Associate Professor in ECE Department, Nimra Institute of Science & Technology, Vijayawada, A.P Abstract The aim of this project is to inform
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
Tutorial for MPLAB Starter Kit for PIC18F
 Tutorial for MPLAB Starter Kit for PIC18F 2006 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. WebSeminar Title Slide 1 Welcome to the tutorial for the MPLAB Starter Kit for PIC18F. My name is
Tutorial for MPLAB Starter Kit for PIC18F 2006 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. WebSeminar Title Slide 1 Welcome to the tutorial for the MPLAB Starter Kit for PIC18F. My name is
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
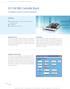 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
AVR Butterfly Training. Atmel Norway, AVR Applications Group
 AVR Butterfly Training Atmel Norway, AVR Applications Group 1 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...3 GETTING STARTED...4 REQUIRED SOFTWARE AND HARDWARE...4 SETTING UP THE HARDWARE...4 SETTING UP THE SOFTWARE...5
AVR Butterfly Training Atmel Norway, AVR Applications Group 1 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...3 GETTING STARTED...4 REQUIRED SOFTWARE AND HARDWARE...4 SETTING UP THE HARDWARE...4 SETTING UP THE SOFTWARE...5
Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs
 Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs AN033101-0412 Abstract This describes how to interface the Dallas 1-Wire bus with Zilog s Z8F1680 Series of MCUs as master devices. The Z8F0880,
Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs AN033101-0412 Abstract This describes how to interface the Dallas 1-Wire bus with Zilog s Z8F1680 Series of MCUs as master devices. The Z8F0880,
Keil C51 Cross Compiler
 Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
Software engineering for real-time systems
 Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX
 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
Chapter 6. Inside the System Unit. What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future. What You Will Learn... Describing Hardware Performance
 What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
STM32F411xC STM32F411xE
 STM32F411xC STM32F411xE ARM Cortex -M4 32b MCU+FPU, 125 DMIPS, 512KB Flash, 128KB RAM, USB OTG FS, 11 TIMs, 1 ADC, 13 comm. interfaces Features Datasheet - production data Dynamic Efficiency Line with
STM32F411xC STM32F411xE ARM Cortex -M4 32b MCU+FPU, 125 DMIPS, 512KB Flash, 128KB RAM, USB OTG FS, 11 TIMs, 1 ADC, 13 comm. interfaces Features Datasheet - production data Dynamic Efficiency Line with
Chapter 02: Computer Organization. Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures
 Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications
 Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture
 An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture Trevor Martin CEng, MIEE Technical Director This article gives an overview of the ARM 7 architecture and a description of its major features for a developer new
An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture Trevor Martin CEng, MIEE Technical Director This article gives an overview of the ARM 7 architecture and a description of its major features for a developer new
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
AN2586 Application note
 AN2586 Application note STM32F10xxx hardware development: getting started Introduction This application note is intended for system designers who require a hardware implementation overview of the development
AN2586 Application note STM32F10xxx hardware development: getting started Introduction This application note is intended for system designers who require a hardware implementation overview of the development
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501. Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2
 Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
CHAPTER 6: Computer System Organisation 1. The Computer System's Primary Functions
 CHAPTER 6: Computer System Organisation 1. The Computer System's Primary Functions All computers, from the first room-sized mainframes, to today's powerful desktop, laptop and even hand-held PCs, perform
CHAPTER 6: Computer System Organisation 1. The Computer System's Primary Functions All computers, from the first room-sized mainframes, to today's powerful desktop, laptop and even hand-held PCs, perform
Hello and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 Firewall. It covers the main features of this system IP used to secure sensitive code and data.
 Hello and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 Firewall. It covers the main features of this system IP used to secure sensitive code and data. 1 Here is an overview of the Firewall s implementation
Hello and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 Firewall. It covers the main features of this system IP used to secure sensitive code and data. 1 Here is an overview of the Firewall s implementation
Hello and welcome to this training module for the STM32L4 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) controller. This controller can be used in a wide range of
 Hello and welcome to this training module for the STM32L4 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) controller. This controller can be used in a wide range of applications such as home appliances, medical, automotive,
Hello and welcome to this training module for the STM32L4 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) controller. This controller can be used in a wide range of applications such as home appliances, medical, automotive,
An Introduction to MPLAB Integrated Development Environment
 An Introduction to MPLAB Integrated Development Environment 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated An introduction to MPLAB Integrated Development Environment Slide 1 This seminar is an introduction to
An Introduction to MPLAB Integrated Development Environment 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated An introduction to MPLAB Integrated Development Environment Slide 1 This seminar is an introduction to
Microcontroller Basics A microcontroller is a small, low-cost computer-on-a-chip which usually includes:
 Microcontroller Basics A microcontroller is a small, low-cost computer-on-a-chip which usually includes: An 8 or 16 bit microprocessor (CPU). A small amount of RAM. Programmable ROM and/or flash memory.
Microcontroller Basics A microcontroller is a small, low-cost computer-on-a-chip which usually includes: An 8 or 16 bit microprocessor (CPU). A small amount of RAM. Programmable ROM and/or flash memory.
ZigBee Technology Overview
 ZigBee Technology Overview Presented by Silicon Laboratories Shaoxian Luo 1 EM351 & EM357 introduction EM358x Family introduction 2 EM351 & EM357 3 Ember ZigBee Platform Complete, ready for certification
ZigBee Technology Overview Presented by Silicon Laboratories Shaoxian Luo 1 EM351 & EM357 introduction EM358x Family introduction 2 EM351 & EM357 3 Ember ZigBee Platform Complete, ready for certification
Learning Outcomes. Simple CPU Operation and Buses. Composition of a CPU. A simple CPU design
 Learning Outcomes Simple CPU Operation and Buses Dr Eddie Edwards eddie.edwards@imperial.ac.uk At the end of this lecture you will Understand how a CPU might be put together Be able to name the basic components
Learning Outcomes Simple CPU Operation and Buses Dr Eddie Edwards eddie.edwards@imperial.ac.uk At the end of this lecture you will Understand how a CPU might be put together Be able to name the basic components
AN3371 Application note
 Application note Using the hardware real-time clock (RTC) in STM32 F0, F2, F3, F4 and L1 series of MCUs Introduction Note: A real-time clock (RTC) is a computer clock that keeps track of the current time.
Application note Using the hardware real-time clock (RTC) in STM32 F0, F2, F3, F4 and L1 series of MCUs Introduction Note: A real-time clock (RTC) is a computer clock that keeps track of the current time.
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Microtronics technologies Mobile: 99707 90092
 For more Project details visit: http://www.projectsof8051.com/rfid-based-attendance-management-system/ Code Project Title 1500 RFid Based Attendance System Synopsis for RFid Based Attendance System 1.
For more Project details visit: http://www.projectsof8051.com/rfid-based-attendance-management-system/ Code Project Title 1500 RFid Based Attendance System Synopsis for RFid Based Attendance System 1.
Implementation of a Wimedia UWB Media Access Controller
 Implementation of a Wimedia UWB Media Access Controller Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Zurich University of Applied Sciences Technikumstrasse 20/22 CH-8401,Winterthur, Switzerland hans.gelke@zhaw.ch
Implementation of a Wimedia UWB Media Access Controller Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Zurich University of Applied Sciences Technikumstrasse 20/22 CH-8401,Winterthur, Switzerland hans.gelke@zhaw.ch
Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board
 Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board 1 Introduction The aim of this course ECE 425L is to help you understand and utilize the functionalities of ARM7TDMI LPC2148 microcontroller. To do that,
Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board 1 Introduction The aim of this course ECE 425L is to help you understand and utilize the functionalities of ARM7TDMI LPC2148 microcontroller. To do that,
AN3265 Application note
 Application note Handling hardware and software failures with the STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application is based on the STM8S-DISCOVERY. It demonstrates how to use the STM8S window watchdog
Application note Handling hardware and software failures with the STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application is based on the STM8S-DISCOVERY. It demonstrates how to use the STM8S window watchdog
Application Note 195. ARM11 performance monitor unit. Document number: ARM DAI 195B Issued: 15th February, 2008 Copyright ARM Limited 2007
 Application Note 195 ARM11 performance monitor unit Document number: ARM DAI 195B Issued: 15th February, 2008 Copyright ARM Limited 2007 Copyright 2007 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Application Note
Application Note 195 ARM11 performance monitor unit Document number: ARM DAI 195B Issued: 15th February, 2008 Copyright ARM Limited 2007 Copyright 2007 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Application Note
Quiz for Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 3.10
 Date: 3.10 Not all questions are of equal difficulty. Please review the entire quiz first and then budget your time carefully. Name: Course: Solutions in Red 1. [6 points] Give a concise answer to each
Date: 3.10 Not all questions are of equal difficulty. Please review the entire quiz first and then budget your time carefully. Name: Course: Solutions in Red 1. [6 points] Give a concise answer to each
AVR Timer/Counter. Prof Prabhat Ranjan DA-IICT, Gandhinagar
 AVR Timer/Counter Prof Prabhat Ranjan DA-IICT, Gandhinagar 8-bit Timer/Counter0 with PWM Single Compare Unit Counter Clear Timer on Compare Match (Auto Reload) Glitch-free, Phase Correct Pulse Width Modulator
AVR Timer/Counter Prof Prabhat Ranjan DA-IICT, Gandhinagar 8-bit Timer/Counter0 with PWM Single Compare Unit Counter Clear Timer on Compare Match (Auto Reload) Glitch-free, Phase Correct Pulse Width Modulator
ARM Cortex -A8 SBC with MIPI CSI Camera and Spartan -6 FPGA SBC1654
 ARM Cortex -A8 SBC with MIPI CSI Camera and Spartan -6 FPGA SBC1654 Features ARM Cortex-A8 processor, 800MHz Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA expands vision processing capabilities Dual MIPI CSI-2 CMOS camera ports,
ARM Cortex -A8 SBC with MIPI CSI Camera and Spartan -6 FPGA SBC1654 Features ARM Cortex-A8 processor, 800MHz Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA expands vision processing capabilities Dual MIPI CSI-2 CMOS camera ports,
CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II
 CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II 6 - Microprocessor Interfacing - Memory and Peripheral Dr. Tim Ferguson, Monash University. AUSTRALIA. Tel: +61-3-99053227 FAX: +61-3-99053574
CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II 6 - Microprocessor Interfacing - Memory and Peripheral Dr. Tim Ferguson, Monash University. AUSTRALIA. Tel: +61-3-99053227 FAX: +61-3-99053574
FRANCIS XAVIER ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 EC2042-Embedded and Real time Systems Unit I - I INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED COMPUTING Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is an embedded system? An embedded system employs a combination of hardware & software (a computational
EC2042-Embedded and Real time Systems Unit I - I INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED COMPUTING Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is an embedded system? An embedded system employs a combination of hardware & software (a computational
Real-Time Clock. * Real-Time Computing, edited by Duncan A. Mellichamp, Van Nostrand Reinhold
 REAL-TIME CLOCK Real-Time Clock The device is not a clock! It does not tell time! It has nothing to do with actual or real-time! The Real-Time Clock is no more than an interval timer connected to the computer
REAL-TIME CLOCK Real-Time Clock The device is not a clock! It does not tell time! It has nothing to do with actual or real-time! The Real-Time Clock is no more than an interval timer connected to the computer
UPS PIco. to be used with. Raspberry Pi B+, A+, B, and A. HAT Compliant. Raspberry Pi is a trademark of the Raspberry Pi Foundation
 UPS PIco Uninterruptible Power Supply with Peripherals and I 2 C control Interface to be used with Raspberry Pi B+, A+, B, and A HAT Compliant Raspberry Pi is a trademark of the Raspberry Pi Foundation
UPS PIco Uninterruptible Power Supply with Peripherals and I 2 C control Interface to be used with Raspberry Pi B+, A+, B, and A HAT Compliant Raspberry Pi is a trademark of the Raspberry Pi Foundation
Computer and Set of Robots
 Lesson 11:DESIGN PROCESS EXAMPLES Mobile-Phone, Mobile- Computer and Set of Robots 1 Mobile Phone 2 Mobile phone SoC (System-on-Chip) Hardware units Microcontroller or ASIP (Application Specific Instruction
Lesson 11:DESIGN PROCESS EXAMPLES Mobile-Phone, Mobile- Computer and Set of Robots 1 Mobile Phone 2 Mobile phone SoC (System-on-Chip) Hardware units Microcontroller or ASIP (Application Specific Instruction
Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376
 Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376 General Peripheral Programming Model Each peripheral has a range of addresses in the memory map peripheral has base address (i.e. 0x00A0) each register used in the peripheral
Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376 General Peripheral Programming Model Each peripheral has a range of addresses in the memory map peripheral has base address (i.e. 0x00A0) each register used in the peripheral
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O
 Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
ontroller LSI with Built-in High- Performance Graphic Functions for Automotive Applications
 C ontroller LSI with Built-in High- Performance Graphic Functions for Automotive Applications 1-chip solution for color display, video input and meter control with built-in highperformance CPU core FR81S
C ontroller LSI with Built-in High- Performance Graphic Functions for Automotive Applications 1-chip solution for color display, video input and meter control with built-in highperformance CPU core FR81S
PART B QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I
 PART B QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I 1. Explain the architecture of 8085 microprocessor? Logic pin out of 8085 microprocessor Address bus: unidirectional bus, used as high order bus Data bus: bi-directional
PART B QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I 1. Explain the architecture of 8085 microprocessor? Logic pin out of 8085 microprocessor Address bus: unidirectional bus, used as high order bus Data bus: bi-directional
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization
 Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Network connectivity controllers
 Network connectivity controllers High performance connectivity solutions Factory Automation The hostile environment of many factories can have a significant impact on the life expectancy of PCs, and industrially
Network connectivity controllers High performance connectivity solutions Factory Automation The hostile environment of many factories can have a significant impact on the life expectancy of PCs, and industrially
8-bit Microcontroller. Application Note. AVR134: Real-Time Clock (RTC) using the Asynchronous Timer. Features. Theory of Operation.
 AVR134: Real-Time Clock (RTC) using the Asynchronous Timer Features Real-Time Clock with Very Low Power Consumption (4µA @ 3.3V) Very Low Cost Solution Adjustable Prescaler to Adjust Precision Counts Time,
AVR134: Real-Time Clock (RTC) using the Asynchronous Timer Features Real-Time Clock with Very Low Power Consumption (4µA @ 3.3V) Very Low Cost Solution Adjustable Prescaler to Adjust Precision Counts Time,
DS1307ZN. 64 x 8 Serial Real-Time Clock
 DS137 64 x 8 Serial Real-Time Clock www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Real-time clock (RTC) counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap-year compensation valid
DS137 64 x 8 Serial Real-Time Clock www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Real-time clock (RTC) counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap-year compensation valid
Computer Organization and Architecture
 Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Instruction Set Design One goal of instruction set design is to minimize instruction length Another goal
Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Instruction Set Design One goal of instruction set design is to minimize instruction length Another goal
The I2C Bus. NXP Semiconductors: UM10204 I2C-bus specification and user manual. 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 1
 The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
