Tube Feeding by Gravity
|
|
|
- Gilbert Doyle
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tube Feeding by Gravity UHN Information for patients and families Read this book to learn: how to use your feeding tube how to keep it clean common problems what you can do about them Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: University Health Network. All rights reserved. This information is to be used for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult your health care provider for advice about a specific medical condition. A single copy of these materials may be reprinted for non-commercial personal use only. Author: UHN Clinical Nutrition Created: 04/2006 Form: D-5319 (03/2014) C034-D
2 Table of contents Section A: Your tube feeding schedule Page 3 Section B: Parts of your feeding tube Page 4 Section C: Before you use your feeding tube Page 5 Section D: How to use your feeding tube Page 9 Section E: After using your feeding container tubing Page 20 Section F: Common problems and what to do Page 22 Patient s Name: Date: Registered Dietitian: Phone: 2
3 Section A: Your tube feeding schedule Time: Amount of formula: Amount of water to flush: Time: Amount of formula: Amount of water to flush: Time: Amount of formula: Amount of water to flush: Time: Amount of formula: Amount of water to flush: Time: Amount of formula: Amount of water to flush: This will give you calories and ml of water each day. 3
4 Section B: Parts of your feeding tube 4
5 Section C: Before you use your feeding tube Read this section to learn: ;; what to collect before you use your feeding tube ;; how you need to prepare Follow these steps before you use your feeding tube: Step 1: Clean your work surface. This will help reduce contact with harmful bacteria (germs). Step 2: Collect these things. Formula Formula is liquid food. It usually comes in a can or a Tetra Pak box. The formula has all the nutrients, vitamins and minerals you need to stay healthy. Store the formula at room temperature when unopened. Keep it away from direct sunlight or heat. If you have leftover formula, store it in the fridge. Let it come to room temperature before you use it. 5
6 Feeding container with tubing The feeding container is the plastic container or bag. The container holds the formula. The formula flows from the container through the tubing into your feeding tube. A complete set contains: Container to hold the formula. Drip chamber that connects the container to the tubing. The drip chamber lets you see how fast the formula is flowing through the tubing. Roller clamp to control the rate the formula flows into the tubing. Plastic tube with a tip that connects the feeding container tubing to the feeding tube in your body. 6
7 Catheter-tip syringe (60 ml, equal to 2 ounces) This is a plastic syringe that has a 3 cm (1 inch) tip on it. You will use this to flush your feeding tube with water and to give medicine. Glass of room temperature water Use room temperature water to flush your feeding tube. Flush your feeding tube to make sure it does not get blocked. Do not use cold water. Cold water can give you stomach pain or cramps. Clean paper towels Use paper towels to protect your clothes from spills. Something to hang your feeding container from You can hang your container from many things. Try using: An IV stand A coat rack A hook in the wall or ceiling A clothes hanger over a door 7
8 Step 3: Wash your hands. Wash your hands with soap and water. Dry your hands using a clean towel. Step 4: Get comfortable. Make sure you are comfortable and entertained while receiving your feeding. It will help make the time more pleasant. It can take a long time to finish your feeding. Be prepared and plan ahead. Use these tips to make your feeding more comfortable: Choose a room that is bright and cheerful to have your feeding. Entertain yourself with books or crossword puzzles. Watch your favourite programs or movies on TV. Listen to relaxing music. Invite a friend or family member to keep you company. Sit in a comfortable chair. You can also sit up in bed. Use pillows to prop yourself up. Your upper body should be raised at least 30 to 45 degrees. 8
9 Section D: How to use your feeding tube Read this section to learn: ;; how to flush your feeding tube ;; how to feed yourself through your tube Follow the 7 steps below to use your feeding tube: Step 1: Put the formula in the feeding container. Do not put blended or pureed food or other liquids into the feeding container. Only use store-bought formula approved by your dietitian. A. Close the roller clamp on your feeding container. This will stop the formula from flowing into the tube. B. Shake the formula. Wipe the cover with a clean cloth. Open the formula. 9
10 C. Use 1 hand to hold the container and the end of the tube. Hold them in a vertical upright position so that the tube makes a U shape. D. Open the lid of the feeding container. Pour the formula into the container. E. Close the lid on the feeding container. F. Keep the empty can or Tetra Pak because you will use it later. 10
11 Step 2: Hang the feeding container. Hang the container. Hang it above your shoulder when you are seated. Step 3: Let the formula flow through the tubing. A. Slowly open the roller clamp. The formula should start to flow down the tube. 11
12 If the formula is not flowing, try: Squeezing the bag lightly. Opening up the lid on the feeding container to allow some air in. Squeezing the drip chamber. B. Turn the drip chamber upside down. Let the formula fill it half full. Then turn the drip chamber upright again. C. Remove the cap of the feeding container tubing. Place the end into the empty formula can or Tetra Pak that you saved. 12
13 D. Let the formula run through the tubing to push out any extra air. E. Close the roller clamp when the formula gets to the end of the tubing. 13
14 F. Put the cap back on the end of the tubing. Step 4: Flush your feeding tube. Flush the feeding tube in your body with water once your feeding container is ready. Flushing your tube will make sure it is working well and is not blocked. A. Remove the cap from your syringe. B. Place the tip of the syringe below the waterline. This will help make sure no air goes into the syringe. Fill the syringe with millilitres of room temperature water. 14
15 C. Aim the tip of the syringe up in the air. Squeeze a tiny bit of water out of the tip. Make sure there is no air left in the syringe. D. Remove the cap from your feeding tube. E. Insert the tip of the syringe into the end of your feeding tube. 15
16 F. Slowly push the plunger on the syringe. The water from the syringe will go into your feeding tube. G. Remove the syringe and place the caps back on the feeding tube and the syringe. Step 5: Connect the feeding container tubing to your feeding tube. After you flush your feeding tube, you are ready to connect the feeding container tubing to the feeding tube in your body. A. Remove the cap from the feeding container tubing and the cap from your feeding tube. 16
17 B. Put the tip of the feeding container tubing into your feeding tube. C. Open the roller clamp on the feeding container tubing. Let the feeding formula drip at a steady rate. Check the flow of the formula from time to time. You can expect it to take about an hour for each box of feed. You can adjust the speed to go slower or faster. It depends on your comfort and how your body reacts to the feeds. Moving the roller clamp: up ( ) will make the formula drip faster down ( ) will make the formula drip slower 17
18 Step 6: Finish your feeding. A. Close the roller clamp on the feeding container tubing. B. Pull out the tip of the feeding container tubing. Replace the cap on your feeding tube and the feeding container tubing. Step 7: Flush your feeding tube again. Repeat step 4 (page 14). 18
19 Do these things to stay safe: ;; Wash your hands with soap and water before you begin your feeding. ;; Stay in a sitting position during your feeding. Don't lay down flat. ;; Raise your upper body at least 30 to 45 degrees. ;; Stay upright after your feeding. Don't lie flat for 1 hour after your feeding is finished. If you lie flat the feeding formula could back up from your stomach and into your throat. 19
20 Section E: After using your feeding container tubing Read this section to learn: ;; how to clean your feeding container after feeding ;; when to use a new container and tubing Follow these steps to clean your feeding container and tubing: Step 1: Rinse your feeding container and tubing. After each feeding, the feeding container needs to be rinsed with water. This is so no formula is left in the container or tube. A. Take your feeding container down and bring it to a sink. B. Remove the tip cover from the tubing and open the roller clamp. Put the end of the tubing into the sink. C. Open the top of the feeding container and pour water into the container. Hold the container above your head to get the water to run through the tubing. Make sure you hold the end of the tubing into the sink. D. Repeat the rinsing until there is no formula left in the feeding container or tubing. 20
21 Step 2: Clean your feeding container and tubing at the end of each day. A. Repeat Step 1, but add a small amount of liquid dish soap to the water. B. Rinse well to make sure all of the soap is removed. C. Hang the feeding container and tubing to dry. D. Your feeding container and tubing are ready for use the next day. When do I need a new container and tubing? You will get a new feeding container each day while you are in the hospital. You can use a feeding container longer when at home. Throw away your feeding container if formula gets built up inside the container. If you have a feeding container with tubing attached to it, change the container once a week. If you have a feeding container with separate tubing, change the container once a month and the tubing once a week. 21
22 Section F: Common problems and what to do Here are some common problems you may have with your feeding tube: nausea and/or vomiting diarrhea constipation blocked feeding tube Nausea and vomiting Nausea and vomiting are unpleasant symptoms that can happen with illness. They can also be related to your tube feeding. Give yourself your feeding at the rate suggested by your dietitian to help prevent nausea and vomiting. If you are doing this and still have nausea, the rate may be too fast for you. Slow the rate of your feeding by rolling the roller clamp down ( ) a little bit on the tubing. If you continue to have nausea after slowing the rate you should call your CCAC dietitian or nurse. Diarrhea Diarrhea can be caused by many things. Run your formula at the rate suggested by your dietitian. If you are doing this and still have loose bowel movements after your feeding, the rate may be too fast for you. Slow the rate of your feeds by rolling the clamp down ( ) a little bit on the tubing. You can easily get dehydrated when you have diarrhea. Contact your CCAC dietitian or nurse if you have diarrhea. 22
23 Constipation Constipation can be caused by many things. Constipation is most commonly caused by: pain medicine not taking enough fluid through your feeding tube If you are constipated, try giving yourself more water through your feeding tube during the day. Contact your CCAC dietitian or nurse if your constipation does not get better. Blocked feeding tube How do I keep my feeding tube from becoming blocked? Flush your feeding tube with at least 60 millilitres of room temperature water before and after you finish a feeding. Also flush with 60 millilitres of water after any crushed medicine you give yourself. Make sure to crush your medicine well. What should I do if my feeding tube becomes blocked? If your feeding tube becomes blocked or if the flow is slower than normal: Try to flush your tube with warm water. Use gentle pressure. Contact your CCAC nurse or doctor if flushing does not unblock your tube. What should I do if my feeding tube falls out? If your tube falls out: Don t try to flush or replace the feeding tube yourself. Cover the area where the tube was in your body with a clean paper towel or piece of gauze. Call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department. 23
24 Call your health care team right away if: you have nausea and vomiting for 2 days you have 3 or more loose bowel movements per day you have not had a bowel movement for 4 days flushing does not unblock your tube your feeding tube falls out 24
25 Notes: 25
26
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding
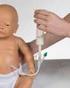 Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME
 TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
Patients First. Tube Feeding Guidelines. Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care
 GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
Caring for Your Gastrostomy
 Caring for Your Gastrostomy Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 4 Gastrostomy Feedings... 5 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Gastrostomy Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 4 Gastrostomy Feedings... 5 Giving Medicines...
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube
 Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter
 Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Urinary Indwelling Catheter. The Urinary System
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Care of a Foley Catheter
 Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males
 Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males CEAC 0371 January 2016 Intermittent Self Catheterization This involves inserting a catheter (small tube) into your bladder at regular intervals to help empty
Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males CEAC 0371 January 2016 Intermittent Self Catheterization This involves inserting a catheter (small tube) into your bladder at regular intervals to help empty
Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS & CARERS. Accessory items. Freka UK Funnel Adapter. Fixation Plate CH9. Male Luer Lock Adapter
 Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter
 Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
What to Do When Receiving Radiation Therapy to the Pelvis
 What to Do When Receiving Radiation Therapy to the Pelvis UHN For patients with gynecological cancer Learn the main steps in planning radiation treatment and how to manage side effects during radiation
What to Do When Receiving Radiation Therapy to the Pelvis UHN For patients with gynecological cancer Learn the main steps in planning radiation treatment and how to manage side effects during radiation
How to prepare your baby s bottle
 How to prepare your baby s bottle Cleaning and Sterilising Using or storing sterilised bottles Preparing a bottle feed Storing and warming feeds Feeding your baby Crèches, childminders and other childcare
How to prepare your baby s bottle Cleaning and Sterilising Using or storing sterilised bottles Preparing a bottle feed Storing and warming feeds Feeding your baby Crèches, childminders and other childcare
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter
 Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter
 The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG. By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service
 Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Clostridium difficile (C. difficile)
 Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) UHN Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn about: What is C. difficile How people get infected with C. difficile Treatment and medicine How
Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) UHN Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn about: What is C. difficile How people get infected with C. difficile Treatment and medicine How
Changing Your Central Line Catheter Cap
 Changing Your Central Line Catheter Cap The catheter cap on each lumen of your central line needs to be changed once a week. A lumen is a small tube within your catheter. These same steps can be used for
Changing Your Central Line Catheter Cap The catheter cap on each lumen of your central line needs to be changed once a week. A lumen is a small tube within your catheter. These same steps can be used for
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube
 Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION
 SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME
 Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
After Your Gastrectomy
 After Your Gastrectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a gastrectomy is how to care for yourself what problems to look out for who to call if you have any
After Your Gastrectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a gastrectomy is how to care for yourself what problems to look out for who to call if you have any
HUMULIN (HU-mu-lin) N
 Instructions for Use HUMULIN (HU-mu-lin) N (human insulin [rdna origin] isophane suspension) vial (100 Units/mL, U-100) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN N and each time you
Instructions for Use HUMULIN (HU-mu-lin) N (human insulin [rdna origin] isophane suspension) vial (100 Units/mL, U-100) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN N and each time you
Foot or Ankle Surgery
 Foot or Ankle Surgery Instructions for patients going home UHN You had a general anesthetic. Do not drive a car or drink alcohol for 24 hours. What can I eat and drink after my operation? You can go back
Foot or Ankle Surgery Instructions for patients going home UHN You had a general anesthetic. Do not drive a car or drink alcohol for 24 hours. What can I eat and drink after my operation? You can go back
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve. Discharge Instructions
 Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
 SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter
 Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women
 Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women This handout has been prepared to help you learn about self-catheterization after bladder surgery. Step-by-step instructions are given. Please write
Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women This handout has been prepared to help you learn about self-catheterization after bladder surgery. Step-by-step instructions are given. Please write
ENTERALITE INFINITY PUMP Instructions for use
 ENTERALITE INFINITY PUMP Instructions for use Key points: 1. Wash your hands with antibacterial soap before handling your feeding tube and supplies. 2. If you have more than one catheter (example: feeding
ENTERALITE INFINITY PUMP Instructions for use Key points: 1. Wash your hands with antibacterial soap before handling your feeding tube and supplies. 2. If you have more than one catheter (example: feeding
Are any artificial parts used in the ACE Malone surgery?
 ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women
 2014 Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women What is intermittent catheterization? Intermittent catheterization is a way to drain urine (pee) from your
2014 Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women What is intermittent catheterization? Intermittent catheterization is a way to drain urine (pee) from your
After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery
 After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment
After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. Read this information before you start. Important things to know about your SmartJect autoinjector. Important things to remember
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SIMPONI (SIM-po-nee) (golimumab) SmartJect autoinjector If your doctor decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of SIMPONI at home, you should receive training
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SIMPONI (SIM-po-nee) (golimumab) SmartJect autoinjector If your doctor decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of SIMPONI at home, you should receive training
Managing Constipation
 Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: Doing Peritoneal Dialysis at Home
 Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
Home Care for Your Wound Drain
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
Gastrostomy Tubes Home Care Manual (Corpak, Foley catheter, Genie, Malecot, Mic-G)
 Physician who placed the gastrostomy: Date placed: Type of gastrostomy tube: Size of the gastrostomy: Gastrostomy tubes are measured in French (Fr.) sizes. A size 16 Fr. gastrostomy is larger than a 14
Physician who placed the gastrostomy: Date placed: Type of gastrostomy tube: Size of the gastrostomy: Gastrostomy tubes are measured in French (Fr.) sizes. A size 16 Fr. gastrostomy is larger than a 14
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Step by Step Guide for Men and Women
 Inside this book Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Step by Step Guide for Men and Women 1986 2005 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Hamilton, Ontario Contributors: Jennifer Skelly Paula Eyles Linda Hilts
Inside this book Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Step by Step Guide for Men and Women 1986 2005 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Hamilton, Ontario Contributors: Jennifer Skelly Paula Eyles Linda Hilts
Cytotoxic Precautions at Home A Guide for Cancer Patients and Families
 Cytotoxic Precautions at Home A Guide for Cancer Patients and Families Your cancer treatment... 1 What are cytotoxic precautions?... 1 What body fluids are cytotoxic?... 1 How do I handle my body wastes?...
Cytotoxic Precautions at Home A Guide for Cancer Patients and Families Your cancer treatment... 1 What are cytotoxic precautions?... 1 What body fluids are cytotoxic?... 1 How do I handle my body wastes?...
Feeding. Baby. Your. Infant. Formula
 Feeding Your Infant Baby Formula 1 Feeding Your Baby Infant Formula There are many reasons why some mothers don t breastfeed. If you feel sad and/or disappointed that you are not fully breastfeeding your
Feeding Your Infant Baby Formula 1 Feeding Your Baby Infant Formula There are many reasons why some mothers don t breastfeed. If you feel sad and/or disappointed that you are not fully breastfeeding your
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body
 How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery.
 JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Taking Care of Your Skin During Radiation Therapy
 Taking Care of Your Skin During Radiation Therapy Princess Margaret Information for patients who are having radiation therapy Read this pamphlet to learn about: What a radiation skin reaction is How to
Taking Care of Your Skin During Radiation Therapy Princess Margaret Information for patients who are having radiation therapy Read this pamphlet to learn about: What a radiation skin reaction is How to
How to care for a Midline Catheter
 How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
FOLFOX Chemotherapy. This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy.
 FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions
 Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patients First. Total Parenteral Nutrition: Discharge Instructions. Handwashing is a very important step in preventing infection.
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Handwashing is a very important step in preventing infection. Total Parenteral Nutrition: Discharge Instructions This information will help guide you in learning about
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Handwashing is a very important step in preventing infection. Total Parenteral Nutrition: Discharge Instructions This information will help guide you in learning about
1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child
 1 Drug Name: _Meropenem 1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child Dosage: milligrams every hours over 5 minutes Key Points: FLUSHING: Meropenem Heparin flush 1. Always wash your hands with an
1 Drug Name: _Meropenem 1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child Dosage: milligrams every hours over 5 minutes Key Points: FLUSHING: Meropenem Heparin flush 1. Always wash your hands with an
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter
 Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
How to Prepare Formula for Bottle-Feeding at Home
 How to Prepare Formula for Bottle-Feeding at Home Printed in Ireland This document is published by the Department of Food Safety, Zoonoses and Foodborne Diseases, WHO, in collaboration with the Food and
How to Prepare Formula for Bottle-Feeding at Home Printed in Ireland This document is published by the Department of Food Safety, Zoonoses and Foodborne Diseases, WHO, in collaboration with the Food and
Deluxe Bottle Warmer
 Deluxe Bottle Warmer IMPORTANT SAFEGUARDS This product is for household use only. When using electrical appliances, basic safety precautions should always be followed including the following: Read all
Deluxe Bottle Warmer IMPORTANT SAFEGUARDS This product is for household use only. When using electrical appliances, basic safety precautions should always be followed including the following: Read all
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM
 ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
CYTOTOXIC PRECAUTIONS A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS & FAMILIES
 Perth and Smiths Falls District Hospital Attention: Manager, Quality 60 Cornelia Street, West Smiths Falls, Ontario K7A 2H9 CYTOTOXIC PRECAUTIONS A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS & FAMILIES This guide has been prepared
Perth and Smiths Falls District Hospital Attention: Manager, Quality 60 Cornelia Street, West Smiths Falls, Ontario K7A 2H9 CYTOTOXIC PRECAUTIONS A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS & FAMILIES This guide has been prepared
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Fact Sheet. Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) Queensland Spinal Cord Injuries Service
 and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
GRASP. Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program. Exercise manual. Level. This research project is funded by UBC and the Heart and Stroke Foundation
 GRASP Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program Exercise manual Level 1 This research project is funded by UBC and the Heart and Stroke Foundation 1 Welcome to the Grasp study! Thank you for volunteering
GRASP Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program Exercise manual Level 1 This research project is funded by UBC and the Heart and Stroke Foundation 1 Welcome to the Grasp study! Thank you for volunteering
Bydureon 2 mg powder and solvent for prolonged-release suspension for injection
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE USER Your step by step guide Bydureon 2 mg powder and solvent for prolonged-release suspension for injection If you have questions about taking Bydureon Refer to the Common questions
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE USER Your step by step guide Bydureon 2 mg powder and solvent for prolonged-release suspension for injection If you have questions about taking Bydureon Refer to the Common questions
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Catheterization for Women Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
How to prepare your baby s bottle feed
 How to prepare your baby s bottle feed New Safety Advice Powdered infant formula is not sterile. It may contain bacteria that can make your baby sick. You can reduce the risk to your baby if you prepare
How to prepare your baby s bottle feed New Safety Advice Powdered infant formula is not sterile. It may contain bacteria that can make your baby sick. You can reduce the risk to your baby if you prepare
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role. Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake
 Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Males
 The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Males Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 male patient
The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Males Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 male patient
Bottle Feeding Puppies and Kittens
 Bottle Feeding Puppies and Kittens Formula Goats milk works as a temporary substitute, but it can get expensive. Goats milk is sold at Wal-Mart and most grocery stores. Cow s milk is not an alternative;
Bottle Feeding Puppies and Kittens Formula Goats milk works as a temporary substitute, but it can get expensive. Goats milk is sold at Wal-Mart and most grocery stores. Cow s milk is not an alternative;
Ear Infections Gastroenteritis gastroenteritis
 Ear Gastroenteritis Infections gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis can be caused by many different germs, and the effects of gastro on babies and children depend on several things including: the age of the
Ear Gastroenteritis Infections gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis can be caused by many different germs, and the effects of gastro on babies and children depend on several things including: the age of the
Maintaining Proper Bowel Elimination
 Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen
 1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN 70/30 and each
1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN 70/30 and each
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION UROLOGICAL DRAINAGE. Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance. Patient Education Guide
 BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
Long Term Tube Feeding. Sunnybrook. A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers VETERANS & COMMUNITY
 Long Term Tube Feeding A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY This brochure has been produced by: Sunnybrook Health Sciences
Long Term Tube Feeding A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY This brochure has been produced by: Sunnybrook Health Sciences
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Going home with a urinary cathether
 Going home with a urinary cathether A patient s guide 1 Your doctor has advised that you require a urinary catheter so that urine can be drained from your bladder. This leaflet provides advice to help
Going home with a urinary cathether A patient s guide 1 Your doctor has advised that you require a urinary catheter so that urine can be drained from your bladder. This leaflet provides advice to help
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Using Insulin. Basic facts about insulin and self-injection. What is insulin? How does diabetes affect the body?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Using Insulin Basic facts about insulin and self-injection This handout explains what insulin is, the different types of insulin, how to store it, how to give an injection
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Using Insulin Basic facts about insulin and self-injection This handout explains what insulin is, the different types of insulin, how to store it, how to give an injection
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE
 Page 1/5 EXPECTED OUTCOMES TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE ROOT BEER PRODUCTION Taken from IFT Experiments in Food Science Series This activity will allow student an opportunity to explore yeast fermentation by
Page 1/5 EXPECTED OUTCOMES TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE ROOT BEER PRODUCTION Taken from IFT Experiments in Food Science Series This activity will allow student an opportunity to explore yeast fermentation by
Above Knee Amputee Exercise Program
 Above Knee Amputee Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent any complications. After an above the
Above Knee Amputee Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent any complications. After an above the
General food hygiene rules
 General food hygiene rules Why food hygiene is important? Good food hygiene is essential to ensure that the food you and your family eats is safe. Poor hygiene procedures in your home can put you at risk.
General food hygiene rules Why food hygiene is important? Good food hygiene is essential to ensure that the food you and your family eats is safe. Poor hygiene procedures in your home can put you at risk.
Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Females What it is:
 The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catherterization (CIC) for Females Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 female
The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catherterization (CIC) for Females Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 female
Care of Your Hickman Catheter
 Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
Percutaneous Nephrostomy. Care of your Nephrostomy. Department of Urology
 Percutaneous Nephrostomy Care of your Nephrostomy Department of Urology You may encounter some problems at home but these are usually easily overcome. Listed below are some questions patients commonly
Percutaneous Nephrostomy Care of your Nephrostomy Department of Urology You may encounter some problems at home but these are usually easily overcome. Listed below are some questions patients commonly
CARING FOR YOUR URINARY CATHETER GRAMPIANS REGIONAL CONTINENCE SERVICE. Author: GRCS Date: 20/06/09 Catalogue No: 712438
 CARING FOR YOUR URINARY CATHETER GRAMPIANS REGIONAL CONTINENCE SERVICE Author: GRCS Date: 20/06/09 Catalogue No: 712438 What is a urinary catheter? A urinary catheter is a hollow tube which drains urine
CARING FOR YOUR URINARY CATHETER GRAMPIANS REGIONAL CONTINENCE SERVICE Author: GRCS Date: 20/06/09 Catalogue No: 712438 What is a urinary catheter? A urinary catheter is a hollow tube which drains urine
