Caring for Your Gastrostomy
|
|
|
- Juliet Eaton
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Caring for Your Gastrostomy
2 Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 4 Gastrostomy Feedings... 5 Giving Medicines... 8 Changing a Balloon-Type Gastrostomy Tube... 9 Common Problems Common Questions and Answers Home Supplies List A Ready Reference Guide
3 What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)? It is a tube that enters the stomach through the outer abdomen. It can be used to give food and medicines if you cannot swallow. It can also be used to drain fluids from the stomach. The tube can be placed in surgery or in the clinic. Food, fluids, and medications go into the G-tube, instead of into the mouth and pass down the tube into the stomach. 2
4 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes The type of tube you use may change, depending on your needs. PEG (Percutaneous tube): 1. Used if tube is placed by the GI doctor or surgeon. 2. Must be removed by specially trained doctor or nurse. 3. Life of this type of tube is 1-2 years. Balloon-type G-tube (Foley catheter or replacement tube): 1. Has a balloon that needs to be inflated with water to hold it in place. 2. May be removed and replaced by patient or caretaker. 3. Life of this type of tube is about 2-6 months. Types of Skin-Level Devices Button (mushroom-type device) 1. May be placed a few months after G- tube opening is fully healed. 2. Requires clinic visit for placement and removal. 3. Life of this type of device is 1-2 years. MICKEY or AMT Mini Button (balloon-type) 1. May be placed 3 months after PEG placement when opening is fully healed. 2. Caregiver can be taught to replace as device is secured by a balloon. 3. Life of this type of device is 3-6 months. This may vary due to weight change and/or medicines. 3
5 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site How often should the site be cleaned? Once a day is fine, though more often if there is drainage around the tube. One of the easiest ways to clean your site is in the shower. Be sure to rotate the tube and allow water to flow under the skin disc to clean the area. Soap is not necessary. If you are not able to shower, please use the following steps. What to Do Tips 1. Wash your hands. 2. Clean the skin and tube with gauze pads and water. If there is crust around the tube, dip the gauze in warm water. Wrap it around the crusted area. After about 5 minutes, remove the gauze and wipe away crusting. Dry well. 3. Inspect the skin around the site. Call your doctor or nurse practitioner if you notice: drainage bleeding excess tissue redness swelling 4. For the first three weeks, the skin disc must not be loosened except by your health care provider! After 3 weeks, the skin disc may be moved to a comfortable distance from your skin. Rotate tube daily. Note the numbered marking on tube to make sure the tube is staying in the right place. If there are no markings, note the length of the tube. 5. Tuck the G-tube under your clothing to prevent accidental pulls. 6. Wash your hands when done. Moisture can irritate skin. Avoid dressings. If a dressing is needed, gently place it on top of skin disc. Change morning and night or when soiled. It's normal to have a little clear drainage around the G-tube opening. When this drainage dries, it becomes a light brown crust If the tube is not well secured, it can prevent healing or the balloon can slip into the intestine. This could cause leaking, diarrhea, or vomiting. Try wrapping a piece of tape around the end of the tube. Then, stick a pin through the tape and fasten it to your clothing. 4
6 Gastrostomy Feedings What to Feed: Formula Name: Names of Equivalent Products: Name of Manufacturer: Total amount of formula per day: Total amount of water per day: Additional Vitamins/Minerals/Supplements: When to Feed: Give can/cc of every hours or times per day. Flush the tube with ml/cc water after each feeding. When to delay feeding: If you have nausea, feel full, or the tube does not flush freely, try again in one hour. If this goes on, call your doctor. 5
7 Other Instructions: Supplies: Tube feeding formula 60 ml/cc catheter tip syringe and/or feeding bag Clamp or catheter cap (for G-tube) Adapter tube (for skin level device) Water (Optional) Pump stand or IV pole Feeding pump with feeding bag 3-way stopcock (Lopez enteral valve) 6
8 How to Do Feedings What to Do 1. Wash hands with soap and warm water for 30 seconds. 2. Connect syringe or feeding bag to G- tube. If using a skin level device, connect the adapter tube to the device and then the syringe or feeding bag. Flush with ml/cc water. 3. Sitting up or lie on right side with head raised is best. 4. Give the feeding at room temperature. Why Helps remove germs and prevent infection. Flushing before feeding helps you to check if the tube is open This helps the stomach empty and decreases regurgitation. Cold feedings can cause stomach cramps. If using a pump: Connect G-tube to pump tubing, open the flow clamp and turn on pump. Be sure pump is set at the correct rate. The correct rate is. Your nurse or home care provider will show you how to use a pump. Note: Need to use adapter tube with the skin level device. If not using a pump: a) Syringe Method: Remove plunger from syringe and connect syringe to G-tube. Raise syringe 4-5 inches above the stomach and pour the feeding into the syringe. Allow the feeding to drop into the stomach by itself. Feedings should take minutes. For thicker feedings, you may need to gently push the feeding with the plunger. Never force feedings into the G-tube. If a large amount of feeding enters the stomach too quickly, it can cause swelling of the stomach, vomiting, or retching. To slow down the feeding, lower the syringe. 7
9 b) Feeding bag method: Close clamp. Fill the feeding bag with the desired amount of formula. Suspend the feeding bag at least two feet above your head. Run tube feeding through empty tubing. Attach to G- tube. Open clamp and regulate flow. 5. When feeding is done, flush the G-tube with 30 ml of tap water or amount recommended by the dietician to meet your daily water needs. Some people handle their feedings better if the tube is vented (left open and suspended) for 1/2 to 1 hour after feeding to let out excess air. 6. Clamp or cap tube or remove skin level feeding adapter. Adapter tubes and feeding bags are reusable. 7. Clean your supplies by rinsing the syringe, bag, and/or tube with cool water. Then swish with warm water and a small amount of liquid dishwashing detergent. Rinse. Hang to dry. Change tube feeding bags every 3 days. 8. NOTE: If the plunger cannot be easily inserted into the syringe, try a few drops of vegetable oil. Change syringe weekly. Giving Medicines Medicine can be given with a syringe through the G-tube. Crush and dissolve pills in water (not formula) so that they do not clog the tube. You may want to ask your doctor about getting the medicine in liquid form. Never crush enteric-coated or time-release capsules. Flush the tube with ml of water before and after giving medicines. 8
10 Changing a Balloon-Type Gastrostomy Tube The first tube change must be done by a doctor. Change the tube if: It becomes plugged; It accidentally falls out; Your doctor recommends routine changes. Supplies Tips G-tube with inflatable balloon (size will be ordered by doctor or nurse practitioner) Water 2 syringes and needle 1 inch tape Lubricating jelly (water soluble) such as KY jelly or Surgilube (not Vaseline ) It's normal for some stomach juices to spill out during the tube change. It's also common for a few drops of blood to ooze from the site during the change. If there are more than a few drops of blood, call your doctor. 9
11 What to Do Tips 1. Wash your hands. 2. Take a new G-tube and test the balloon for leaks Using a syringe, draw up 5 ml of water. Inject the water into the smaller balloon port. Wait 2 minutes. If there is no leak after 2 minutes, withdraw the water. If the balloon leaks, toss it out and test a new one. 3. To remove the odl tube, unclamp the G- tube. Using a different syringe, withdraw water from the balloon. Discard. 4. Coat the tip of the new tube with a lubricating jelly. Do not use Vaseline. 5. Insert the new tube. While holding the tube at a 90 angle to the stomach, gently insert it about 3-4 inches into the opening. 6. Using the syringe, inject the amount of water specified on package into the balloon port. 7. Make sure that the balloon is against the wall of the stomach by gently pulling the tube back until you meet resistance. 8. Clean the site. Then move the skin disc down to the skin level and tape the tube in place. If you have a skin level device, please refer to the package insert If you meet resistance, remove the tube and try again a little harder. Turn the tube to a different angle. If you cannot insert the tube, call your doctor. A balloon that is placed snugly against the wall of the stomach helps prevent stomach contents from leaking. If the balloon is not well secured, it can slip down into the intestines and cause a blockage. 9. Wash your hands. 10
12 Common Problems 1. Blocked tube 2. Leaking around the tube 3. Leaking from feeding end of tube 4. Redness around the tube 5. Bleeding around tube 6. Tissue buildup around tube 7. Tube falls out 8. Vomiting 9. Diarrhea 10. Dehydration 11. Constipation 12. Gas, bloating, cramping 1. Blocked Tube Milk the tube by squeezing it between your fingers. Start at the top and work toward the stomach. Firmly flush the tube using ml of warm water. If that fails, change the tube if snstructed to do so. Call your doctor or nurse practitioner. Prevent blockage by always thoroughly flushing tube with ml water after feedings and before and after medicines. 2. Leaking Around Tube Be sure the balloon is snugly against the wall of the stomach. This provides a seal, which helps prevent leakage. Leaking is often a signal that tissue build-up has started or the tube is out of place. Please call your doctor. If there is leakage, protect the skin with zinc oxide ointment, and change the dressing when it is wet. The acid in the leaking stomach juices can irritate the skin. For relief, change dressing often and wash irritated skin with water. You may need to see your doctor or nurse if it becomes a problem. Measure the tube to check its placement in the stomach. (A tube that moves up and down in the stomach can cause irritation and widen the opening.) When you change the tube, remove the old tube and wait minutes before placing the new tube. This lets the opening close a bit so that the new tube will fit more tightly. 3. Leaking from feeding end of tube Call your nurse or doctor. 4. Redness around the Tube Keep skin around the tube clean and dry. (Some redness is normal, but moisture can irritate the skin and lead to an infection.) Clean the skin around the site more often using plain water. Keep irritated areas open to air if possible. Ask a nurse about other ways to fasten the tube in place. Call the nurse or doctor if you see signs of infection (redness, swelling, rash, unusual drainage). 11
13 5. Bleeding Around the Tube If you notice more than a few drops of blood, call your doctor or nurse. Some bleeding is normal during the tube change due to irritation. Keep the tube well secured to prevent accidental pulling. 6. Tissue Buildup around Tube The growth of tissue around the tube is normal because the body tries to repair itself. The nurse practitioner may need to remove some of this excess tissue. This can be done in the clinic. Call the clinic if tissue builds up or bleeding occurs. 7. Tube Falls Out If the tube has not been changed by a doctor for the first time, cover the opening with a clean dressing. Call your clinic or go to the local emergency room for the tube change. If the tube has been changed before, simply change the tube as usual at home. If a few hours have passed and the same sized tube will not go in easily, use a smaller sized tube. Then, wait a week to change the tube again and insert the correct sized tube. NOTE: Although this is not an emergency, if the tube is not put in shortly after coming out, the opening can begin to close. It is best for the tube to be replaced within 2 hours of coming out. You may even use the old tube until you can have a new one put in. Tape the old tube in place, as the balloon will not stay inflated. 8. Vomiting Check the tube placement to be sure that the balloon is against the wall of the stomach, not slipping in and out. If the balloon slips into the intestine, it can cause a blockage and vomiting and swelling of the stomach. Do the feeding sitting upright or propped up on pillows (45) if lying down. Try smaller feedings more often. Make sure the total amount for the day is the same. Infection may cause vomiting. Be sure equipment is well cleaned and rinsed between feedings. Wash your hands between contacts with persons who are ill. Call your doctor if vomiting persists more than once. The type or strength of the formula may need to be changed. 9. Diarrhea Diarrhea means frequent, loose, watery stools. Looser stools may be normal with certain types of tube feeding. A few loose stools in a 24-hour period are not a problem. Avoid formula hanging for longer than 6-8 hours. 12
14 Check the tube to be sure that the balloon is against the wall of the stomach. If the tube is too low in the stomach, the feeding will enter the intestine too quickly, causing diarrhea. Give the tube feeding more slowly. Give more water after each feeding to replace water lost in the diarrhea. If the diarrhea does not stop after 2 or 3 days, call your doctor. NOTE: Consult your dietician. Changing to a tube feeding with fiber may help. 10 Dehydration Vomiting, diarrhea, a fever and sweating cause the body to lose fluids. You may not get thirsty so you must be very careful to note the signs of dehydration and call your doctor. They will tell you what kind of extra fluid to give. Symptoms include: Decreased or more concentrated urine Crying with no tears Dry skin that has no recoil when squeezed Fatigue or irritability 11. Constipation Dizziness Dry mouth and lips Sunken eyes Headache Constipation may be due to a low fluid intake, too little fiber in the feeding or a side effect of medicine. This is common in the elderly or those with limited activity. Giving extra water or fruit juice (especially prune or apple juice) between feedings may be helpful. If you have chronic constipation, call your nurse or doctor. Often, a different formula may be prescribed. 12. Gas, Bloating, Cramping Consider the points outlined for diarrhea. Also, try to get rid of all air from the tube feeding system before connecting to the G-tube. You may open the tube while it s raised to allow extra air to escape. It s best done if lying down with the tube held straight up. Be sure to have a towel handy in case fluid is released. Recap once the air is out and fluid starts to come out. 13
15 Common Questions and Answers Is there anything special I should know about the percutaneous gastrostomy (the one placed in the clinic)? Yes. The first time the tube is changed a GI specialist must do it. A special procedure is needed to remove the internal bumper that holds the G-tube in the stomach. What happens when I no longer need the gastrostomy tube? Your doctor can explain the medical reasons for the tube and when it is no longer needed. Most often, after the tube is removed, the holeclose over in a few days. Sometimes it may take several weeks to close. Surgery is not needed to close the gastrostomy tube site in most cases. Does someone who can change the gastrostomy tube always need to be with me in case the tube accidentally comes out? No, if the tube comes out, you will be all right. However, because the opening starts to close soon, the tube should be replaced within 2 hours by someone trained to do so. Is there anything special I should know about traveling? Remember to take all the supplies needed for feeding: syringe, formula, tubing, bottled water, etc. Opened formula can be stored in a cooler to prevent spoilage. It is a good idea to also take along an extra tube, some tape, and supplies for changing the tube in case it comes out. Some families use a small canvas bag that is always filled with supplies needed for travel. Can I sleep on my stomach? Yes. After the surgical site has healed, most people are quite comfortable on their stomachs. 14
16 Home Supplies List Tube Feeding Formula: For gastrostomy tubes: 60 ml catheter tip syringe Feeding bag (optional) Tube clamp if needed Cap for end of tube Tape 1" Cotton swabs or gauze Smaller syringes for medicines Lubricating jelly (water soluble) For G-Tube skin level devices: 60 ml catheter tip syringe Feeding bag (optional) Tube clamp if needed Cap for end of tube Tape, 1" Cotton swabs or gauze Smaller syringes for medicines Lubricating jelly (water soluble) Adapter tube Additional supplies for pump feedings: Pump Feeding bags You will be given a 3-day supply before discharge from the nursing staff. Future supplies may be obtained through your home care provider. The special G-tubes, buttons, etc. can be ordered by the GI clinic. Please check with your nurse or doctor. 15
17 You and Your Feeding Tube A Ready Reference Guide Tube Type: Site Care (daily): 1. Cleanse skin and tube with water. 2. Remove any encrusted material with a warm, wet cloth. Tube Feedings 1. Formula 2. Amount and Frequency 3. Method: Syringe Feeding Bag Feeding Bag and Pump Things to watch for 1. Blocked tube. 2. Signs/symptoms of infection - redness, swelling, unusual drainage. 3. Leakage or bleeding around tube. 4. Tissue buildup around tube. 5. Problems with vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, or constipation. Phone Numbers Please call if you have concerns or questions. Doctor: Local Doctor: Nurse Practitioner Dietitian: Home Health Agency: Phone Number: Phone Number: Phone Number: Phone Number: Phone Number: Your health care team may have given you this information as part of your care. If so, please use it and call if you have any questions. If this information was not given to you as part of your care, please check with your doctor. This is not medical advice. This is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Because each person s health needs are different, you should talk with your doctor or others on your health care team when using this information. If you have an emergency, please call 911. Copyright 10/2015. University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics Authority. All rights reserved. Produced by the Department of Nursing. HF#
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube
 Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
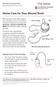
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care
 GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Gastrostomy Tubes Home Care Manual (Corpak, Foley catheter, Genie, Malecot, Mic-G)
 Physician who placed the gastrostomy: Date placed: Type of gastrostomy tube: Size of the gastrostomy: Gastrostomy tubes are measured in French (Fr.) sizes. A size 16 Fr. gastrostomy is larger than a 14
Physician who placed the gastrostomy: Date placed: Type of gastrostomy tube: Size of the gastrostomy: Gastrostomy tubes are measured in French (Fr.) sizes. A size 16 Fr. gastrostomy is larger than a 14
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Patients First. Tube Feeding Guidelines. Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS & CARERS. Accessory items. Freka UK Funnel Adapter. Fixation Plate CH9. Male Luer Lock Adapter
 Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
Are any artificial parts used in the ACE Malone surgery?
 ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG. By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service
 Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter
 Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role. Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake
 Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter
 Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding
 Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME
 TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter
 Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Urinary Indwelling Catheter. The Urinary System
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women
 Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women This handout has been prepared to help you learn about self-catheterization after bladder surgery. Step-by-step instructions are given. Please write
Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women This handout has been prepared to help you learn about self-catheterization after bladder surgery. Step-by-step instructions are given. Please write
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: Doing Peritoneal Dialysis at Home
 Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
Home Care for Your Wound Drain
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions
 Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
A Guide to Help You Manage Your Catheter and Drainage Bags
 A Guide to Help You Manage Your Catheter and Drainage Bags A catheter can make a difference to your health and quality of life. We understand that it can be a big adjustment for you. This information will
A Guide to Help You Manage Your Catheter and Drainage Bags A catheter can make a difference to your health and quality of life. We understand that it can be a big adjustment for you. This information will
Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery.
 JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector
 HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the HICKMAN Catheter... 2 Part 2 Caring for Your Hickman Catheter... 3 A. Preventing Infection... 3 B. Bathing...
HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the HICKMAN Catheter... 2 Part 2 Caring for Your Hickman Catheter... 3 A. Preventing Infection... 3 B. Bathing...
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
online version Understanding Indwelling Urinary Catheters and Drainage Systems Useful information When to call for help
 When to call for help This will depend on the individual situation, but usually help should be sought if any of the following occurs: 1. The catheter does not start to drain, despite trying the problem
When to call for help This will depend on the individual situation, but usually help should be sought if any of the following occurs: 1. The catheter does not start to drain, despite trying the problem
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION
 SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Care of Your Hickman Catheter
 Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males
 Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males CEAC 0371 January 2016 Intermittent Self Catheterization This involves inserting a catheter (small tube) into your bladder at regular intervals to help empty
Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males CEAC 0371 January 2016 Intermittent Self Catheterization This involves inserting a catheter (small tube) into your bladder at regular intervals to help empty
How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter
 The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
After Your Abdominal Surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Abdominal Surgery Self-care and follow-up You recently had abdominal surgery. This handout explains what to expect during your recovery. Please read these instructions
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Abdominal Surgery Self-care and follow-up You recently had abdominal surgery. This handout explains what to expect during your recovery. Please read these instructions
FOLFOX Chemotherapy. This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy.
 FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information
 Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Recto-vaginal Fistula Repair
 What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
My patient has a feeding tube
 My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator (December, 2014) Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG
My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator (December, 2014) Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG
PATIENT GUIDE. Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL
 PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter
 Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Achieving Independence
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Section 4: Your Vascular Access. What is vascular access?
 Section 4: Your Vascular Access What is vascular access? What is a fistula? Taking care of a new fistula What is a graft? Taking care of a new graft What is a hemodialysis catheter? Taking care of a hemodialysis
Section 4: Your Vascular Access What is vascular access? What is a fistula? Taking care of a new fistula What is a graft? Taking care of a new graft What is a hemodialysis catheter? Taking care of a hemodialysis
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Urinary Catheter Care and Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Urinary Catheter Care and Prostate Cancer Treatment The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions
Urinary Catheter Care and Prostate Cancer Treatment The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve. Discharge Instructions
 Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube
 Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
CARING FOR YOUR URINARY CATHETER GRAMPIANS REGIONAL CONTINENCE SERVICE. Author: GRCS Date: 20/06/09 Catalogue No: 712438
 CARING FOR YOUR URINARY CATHETER GRAMPIANS REGIONAL CONTINENCE SERVICE Author: GRCS Date: 20/06/09 Catalogue No: 712438 What is a urinary catheter? A urinary catheter is a hollow tube which drains urine
CARING FOR YOUR URINARY CATHETER GRAMPIANS REGIONAL CONTINENCE SERVICE Author: GRCS Date: 20/06/09 Catalogue No: 712438 What is a urinary catheter? A urinary catheter is a hollow tube which drains urine
Fact Sheet. Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) Queensland Spinal Cord Injuries Service
 and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips
 Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Having a circumcision information for men
 Having a circumcision information for men This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a circumcision. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you
Having a circumcision information for men This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a circumcision. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
 SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME
 Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter
 Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Maintaining Proper Bowel Elimination
 Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
How to care for a Midline Catheter
 How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
Percutaneous Nephrostomy. Care of your Nephrostomy. Department of Urology
 Percutaneous Nephrostomy Care of your Nephrostomy Department of Urology You may encounter some problems at home but these are usually easily overcome. Listed below are some questions patients commonly
Percutaneous Nephrostomy Care of your Nephrostomy Department of Urology You may encounter some problems at home but these are usually easily overcome. Listed below are some questions patients commonly
Tracheostomy Care at Home
 Tracheostomy Care at Home Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT This information will help you understand how to care for a person with a tracheostomy at home. It is a supplement to the teaching offered
Tracheostomy Care at Home Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT This information will help you understand how to care for a person with a tracheostomy at home. It is a supplement to the teaching offered
Information for patients and nurses
 Information for patients and nurses Rocket IPC Pleural Catheter Indwelling Catheter Rocket Indwelling Pleural Catheter (IPC) Contents Contact Information...03 What s in the Rocket Dressing Pack and Bottle
Information for patients and nurses Rocket IPC Pleural Catheter Indwelling Catheter Rocket Indwelling Pleural Catheter (IPC) Contents Contact Information...03 What s in the Rocket Dressing Pack and Bottle
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Medication Administration Quick Guide
 Medication Administration Quick Guide Catholic Mutual Group INDEX INDEX 1. Common Medical Abbreviations 2. Oral Medication Skill Competency 3. Topical Skill Competency 4. Ear Medication Skill Competency
Medication Administration Quick Guide Catholic Mutual Group INDEX INDEX 1. Common Medical Abbreviations 2. Oral Medication Skill Competency 3. Topical Skill Competency 4. Ear Medication Skill Competency
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide
 PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Excision of Vaginal Mesh
 What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement A tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) is a special type of intravenous (IV) line that is placed into a large
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement A tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) is a special type of intravenous (IV) line that is placed into a large
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
After your gastric banding
 After your gastric banding Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered 2 Please call J Ward at Southmead Hospital on 0117 323 5132 if you have any questions or concerns soon after discharge. You may be
After your gastric banding Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered 2 Please call J Ward at Southmead Hospital on 0117 323 5132 if you have any questions or concerns soon after discharge. You may be
Care of a Foley Catheter
 Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
Looking after your urinary catheter at home
 Looking after your urinary catheter at home Information for patients and carers Useful contacts to keep: Name and title of community nurse Single point of access (SPA) for community nursing 24 hour service
Looking after your urinary catheter at home Information for patients and carers Useful contacts to keep: Name and title of community nurse Single point of access (SPA) for community nursing 24 hour service
The temporary haemodialysis catheter
 The temporary haemodialysis catheter Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information in this booklet is for: People have renal failure and who require urgent haemodialysis.
The temporary haemodialysis catheter Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information in this booklet is for: People have renal failure and who require urgent haemodialysis.
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION UROLOGICAL DRAINAGE. Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance. Patient Education Guide
 BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin
 The Emily Center How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin Child Care/Health Promotion Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: How
The Emily Center How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin Child Care/Health Promotion Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: How
Having a urinary catheter information for men
 Having a urinary catheter information for men This leaflet explains what a catheter is, why you need it and how you should look after it. If you have any further questions, please contact your district
Having a urinary catheter information for men This leaflet explains what a catheter is, why you need it and how you should look after it. If you have any further questions, please contact your district
PICC Catheter for IV Therapy
 PICC Catheter for IV Therapy A Patient Guide for: PATIENT PICC A PICC is defined as a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter. A PICC is a special IV Catheter. It is put in an arm vein and ends in a large
PICC Catheter for IV Therapy A Patient Guide for: PATIENT PICC A PICC is defined as a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter. A PICC is a special IV Catheter. It is put in an arm vein and ends in a large
How To Prepare and Give a Prefilled Syringe Injection
 Diablo Valley Onc&Hem Med Grp, Inc Phone Number: (925)6775041 How To Prepare and Give a Prefilled Syringe Injection Patient Education Quick Reference Guide The following are instructions for use of prefilled
Diablo Valley Onc&Hem Med Grp, Inc Phone Number: (925)6775041 How To Prepare and Give a Prefilled Syringe Injection Patient Education Quick Reference Guide The following are instructions for use of prefilled
Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home
 Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust What is a suprapubic catheter? A suprapubic
Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust What is a suprapubic catheter? A suprapubic
However, each person may be managed in a different way as bowel pattern is different in each person.
 Department of colorectal surgery Reversal of ileostomy A guide for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to tell you about your reversal of ileostomy operation and how your bowels might work after
Department of colorectal surgery Reversal of ileostomy A guide for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to tell you about your reversal of ileostomy operation and how your bowels might work after
CATHETER for Hemodialysis
 CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
Vesico-Vaginal Fistula
 Saint Mary s Hospital The Warrell Unit Vesico-Vaginal Fistula Information For Patients Contents Page What is a vesico-vaginal fistula? 3 How does a fistula develop? 3 What tests will I need? 3 How can
Saint Mary s Hospital The Warrell Unit Vesico-Vaginal Fistula Information For Patients Contents Page What is a vesico-vaginal fistula? 3 How does a fistula develop? 3 What tests will I need? 3 How can
1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child
 1 Drug Name: _Meropenem 1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child Dosage: milligrams every hours over 5 minutes Key Points: FLUSHING: Meropenem Heparin flush 1. Always wash your hands with an
1 Drug Name: _Meropenem 1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child Dosage: milligrams every hours over 5 minutes Key Points: FLUSHING: Meropenem Heparin flush 1. Always wash your hands with an
Emergency Care for Patients of The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
Going home with a urinary cathether
 Going home with a urinary cathether A patient s guide 1 Your doctor has advised that you require a urinary catheter so that urine can be drained from your bladder. This leaflet provides advice to help
Going home with a urinary cathether A patient s guide 1 Your doctor has advised that you require a urinary catheter so that urine can be drained from your bladder. This leaflet provides advice to help
Foley Catheter Experiences and What I Learned:
 Foley Catheter Experiences and What I Learned: A Male Perspective Copyright May 1, 2005 All rights are reserved by the author Unfortunately, I've had quite a few experiences with the Foley urinary catheter
Foley Catheter Experiences and What I Learned: A Male Perspective Copyright May 1, 2005 All rights are reserved by the author Unfortunately, I've had quite a few experiences with the Foley urinary catheter
Hemodialysis Access: What You Need to Know
 Hemodialysis Access: What You Need to Know Hemodialysis Access: What You Need To Know Whether you already get hemodialysis treatment, or you will need to start dialysis soon, this booklet will help you
Hemodialysis Access: What You Need to Know Hemodialysis Access: What You Need To Know Whether you already get hemodialysis treatment, or you will need to start dialysis soon, this booklet will help you
Central Venous Catheter Care For Haemodialysis
 Central Venous Catheter Care For Haemodialysis Information For Parents and Carers Haemodialysis Unit 01 878 4757 Main Hospital Number 01 878 4200 Central Venous Catheters We hope this booklet will help
Central Venous Catheter Care For Haemodialysis Information For Parents and Carers Haemodialysis Unit 01 878 4757 Main Hospital Number 01 878 4200 Central Venous Catheters We hope this booklet will help
Hysteroscopy. What is a hysteroscopy? When is this surgery used? How do I prepare for surgery?
 What is a hysteroscopy? This is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin tube with a tiny camera to look inside the uterus. There are no incisions. Saline solution is used to expand the uterus in order to
What is a hysteroscopy? This is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin tube with a tiny camera to look inside the uterus. There are no incisions. Saline solution is used to expand the uterus in order to
Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery
 Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine www.happypatient.org Updated 5/10 Why? To Help Control Postoperative Pain at Home A pump connected
Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine www.happypatient.org Updated 5/10 Why? To Help Control Postoperative Pain at Home A pump connected
