Gastrostomy Tubes Home Care Manual (Corpak, Foley catheter, Genie, Malecot, Mic-G)
|
|
|
- Valerie Poole
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physician who placed the gastrostomy: Date placed: Type of gastrostomy tube: Size of the gastrostomy: Gastrostomy tubes are measured in French (Fr.) sizes. A size 16 Fr. gastrostomy is larger than a 14 Fr. gastrostomy. Your child has a Fr. gastrostomy. Phone number to ask questions after discharge: Call the Surgery Team night or day if your child has any of the following symptoms: If the gastrostomy tube comes out. Call now and look at page 17 of this manual. Has purulent, bloody, bright green, or brown drainage that smells like stool coming from the gastrostomy. Has a temperature over 101 F (38.4 C) Has any of the following for more than 48 hours (2 days): -drainage or leakage around the gastrostomy. -redness larger than the size of a quarter around the gastrostomy. -skin irritation or rashes. -swelling or tenderness. Note: Call the General Surgery Office during office hours. If after hours (nights, weekends, and holidays) call and ask for the Surgery Resident on-call to be paged. Call your child s regular doctor if: Has a swollen or hard stomach. Is throwing up with feeds. Has pain or cramping with feeds. Is crying without tears. Has a dry mouth or cracked lips. Is an infant and has a sunken soft spot. Is more sleepy than normal. Is dizzy. Is an infant and has no wet diapers in 8 hours. Has no urine in 12 hours at any age.
2 Section Table of Contents A. Introduction...3 Page Number B. Placement of the Gastrostomy C. Your Child s Gastrostomy D. Clamping the Gastrostomy.. 6 E. General Guidelines for Care...7 F. When to call the Surgery Office.. 7 G. General Feeding Guidelines...8 H. Relieving Gas in the Stomach. 9 I. How to Feed Your Child Through the Gastrostomy J. Giving Medicines K. Skin Care L. Leaking...16 M. Products that Can Protect Your Child s Skin From Leakage N. Granulation Tissue O. What if gastrostomy button or tube comes out before months after surgery or before your child s surgery clinic surgery appointment? P. Placing the Foley Tube into the Gastrostomy Stoma Q. Frequently Asked Questions R. When to Call Your Child s Medical Provider.. 20 S. Home Care Supplies....20
3 A. Introduction Feedings and/or medications can be given to your child through the gastrostomy. Your child may need the gastrostomy for a short time or for a lifetime. A Home Care company delivers supplies to care for the gastrostomy at home. B. Placement of the Gastrostomy Note: Your child does not have to go to surgery if the gastrostomy needs to be replaced or have button inserted. 1. Your child s medical provider or surgeon will decide how the gastrostomy is placed. A small opening called a stoma is made on your child s abdomen. The gastrostomy goes into the stomach, passes through the muscle and fatty layers, and comes out the stoma. o A path (tract) from the stomach to the abdominal wall forms around the gastrostomy in 6 to 8 weeks. o The healing around the gastrostomy is similar to the tract formation after a body piercing. o Do not turn the gastrostomy. o Unnecessary movement of the gastrostomy in the tract will interfere with the healing process. The end of the gastrostomy in the stomach may look like a mushroom or have a small balloon at the end. The mushroom or balloon keeps the gastrostomy up against the stomach wall.
4 After the Gastrostomy is placed: The area around the gastrostomy may be tender for several days. It is normal to see drainage around the gastrostomy after it is placed. A small plastic container may be attached to the gastrostomy after surgery. o Stomach contents drain into the container. o The container is removed when your child starts feeding. o Some of the tubes will come back with a dressing after surgery. C. Your Child s Gastrostomy There are several types of gastrostomies, but the care is basically the same. You do not have to know the specific name of your child s gastrostomy. Types gastrostomy tubes: The tan gastrostomy tube is a Malecot or Mushroom or de Pezzer. o The tan or red baby nipple around the gastrostomy prevents the tube from moving. o There is no separate port for giving medicines.
5 The clear gastrostomy tube is a Corpak: o There is a cap on the end of tubing. o There may or may not be a separate port for giving medicines. Mic-key (G) gastrostomy tubes are also clear. o The ring around the gastrostomy prevents the tube from moving. o There may or may not be a separate port for giving medicines.
6 D. Clamping the Gastrostomy Your child s gastrostomy tube may or may not have a clamp. Gastrostomy tubes are clamped when not being used to prevent formula and gastric contents from coming out of the tube. Never use the blue clamps (gizmos) on the gastrostomy! Use the clamp or the end cap on the gastrostomy. OR If the gastrostomy does not have a clamp or an end cap: 1. Take the cover off the end of the feeding syringe. 2. Gently put it into the end of the gastrostomy. 3. If a rubber band is used, change the position every 8 hours.
7 E. General Guidelines for Care The following care is important for all different types of gastrostomies: 1. Prevent the gastrostomy from being pulled or turned. o Dress infants in onsies. o An ace wrap may be used on active children. 2. Keep the balloon or mushroom up against the stomach wall to create a seal. o The balloon or mushroom works like a sandbag in a flood wall. o If the balloon or mushroom is not up against the stomach wall, the seal is broken and formula or gastric juices may leak onto your child s skin. 3. Provide safe and comfortable feedings through the gastrostomy. o Your child s stomach may need to adapt to the volume of the feedings. o Give feedings slowly. Never push in feedings with a syringe. o Giving the feedings too fast is uncomfortable for your child. Your child could cramp, wretch, or vomit. 4. Age appropriate mouth care should be given to a child receiving gastrostomy feedings. F. When to Call the Surgery Office 1. Call the surgery office immediately if you see drainage from the gastrostomy that looks: o Purulent (like pus) o Bloody o Bright green o Brown and smells like stool 2. Gastrostomy sites very seldom get infected. However, look at your child s gastrostomy site daily for any skin changes. Look for: o Drainage or leakage around the gastrostomy. o Redness larger than the size of a quarter. o Skin irritation or rashes. o Swelling or tenderness. o Call the Surgery Office if any of the above last longer than 24 hours.
8 G. General Feeding Guidelines 1. Feeding Orders: In the hospital, your child s medical provider will order the type of feeding, schedule for feedings and method of feeding. Your child s Primary Health Care Provider will monitor the feedings after your child is from the hospital. 2. The Feeding Experience: You and your child should be in a comfortable position during feedings. You can do any of the following: o Hold your child during feedings. o Put your child in an infant seat, wheelchair or chair. o Lay your child on his or her right side. This helps the stomach empty and keeps food from sitting in the stomach for a long time. Provide comfort to your child during feedings: o Offer your child a pacifier during the feeding. o Rock and talk to your child. o Gently stroke your child s lips and cheeks. o Play your child s favorite music or video. 3. Feeding Methods: (Feeding procedures are described later in this tool.) Feeding by gravity (bolus feeds): Amount of formula: Frequency of feedings: every hours Feeding by a feeding pump: Pump feedings may be continuous or intermittent. Continuous feedings: Volume of feedings Time of infusion: Start time End time and/or Intermittent (several times a day): Volume of feeding Infused over minutes every hours 4. Flushing the gastrostomy o Flush the gastrostomy with 5 to 10 ml of tap water after every feeding and medicine. o Flush the gastrostomy once a day with 5 to 10 ml of tap water if the gastrostomy is not needed to give your child feedings or medications.
9 H. Relieving Excess Air in the Stomach: Venting Air (Burping) Most children with gastrostomies can burp or pass gas to relieve air in the stomach. However, some children have problems with excess air in the stomach. Usually gas is the biggest problem the first few days after surgery. A syringe or Farrell bag may be used to relieve gas from the stomach. Using a syringe to relieve gas in the stomach: 1. Close the gastrostomy tubing to keep formula from coming out. 2. Place the feeding syringe (without the plunger) into the gastrostomy. 3. Open the gastrostomy. 4. Hold the syringe above the level of your child s stomach. 5. Excess gas will bubble up in the syringe. It is normal if formula or stomach contents rise into the syringe. 6. Once the gas is relieved, allow the formula or stomach contents to slowly flow back into the stomach. 7. Add 5 to 10 ml of tap water to the syringe to flush the gastrostomy. Close the gastrostomy. Using a Farrell Bag to relieve excess gas in the stomach: Your child s medical provider may order a Farrell bag if your child had a Nissen Fundoplication (anti-reflux procedure). The Farrell bag attaches to the gastrostomy and allows excess gas to come out of your child s stomach while your child is being fed. Refer to the Farrell Bag Teaching Tool.
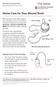
10 I. How to Feed Your Child Through the Gastrostomy Note: Clean supplies with warm water. Rinse and air dry. DO NOT boil or place them in a dishwasher. Feeding by Gravity 1. Gather supplies: formula feeding syringe without the plunger water (5 to 10 ml) for flushing 2. Wash your hands. 3. Attach the syringe to the gastrostomy. 4. Open the gastrostomy. 5. Lower the syringe and pour the formula in. 6. Raise the syringe until the formula flows in slowly. 7. Raise the syringe to increase the flow of feeding. Lower the syringe to decrease the flow of the feeding. 8. Feedings should go in over 15 to 20 minutes. o The feeding will come back into they syringe if your child is crying or fussy. o Wait a few minutes and comfort your child. The feeding will go in again once your child is quiet. o If the formula is not going down and your child is quiet, put the plunger into the syringe and gently push the plunger about one-half inch to start the flow of the formula. Do not push hard. Take the plunger out after the feeding starts to flow in. 9. Flush the gastrostomy with 5 to 10 ml of tap water after the feeding is finished. 10. Close the gastrostomy.
11 Intermittent pump feedings for (several times a day) feedings NOTE: Your child s home health company will review the pump with you. 1. Gather supplies: feeding pump and tubing formula feeding syringe without the plunger for flushing tap water (5 to 10 ml) for flushing 2. Wash your hands. 3. Pour formula into the feeding bag. 4. Open the clamp on the feeding bag, fill the pump tubing, then close the clamp. 5. Place the pump tubing into the pump. 6. Attach the pump tubing to the gastrostomy. 7. Make sure the tubing connections are secure. 8. Open the gastrostomy. 9. Open the clamp on the pump tubing. 10. Check the feeding rate on the pump. 11. Start the feeding pump. 12. Flush the gastrostomy after the feeding is done: a) Turn off the pump. b) Close the gastrostomy. c) Remove the pump tubing. d) Attach the feeding syringe (without the plunger) to the gastrostomy. e) Open the gastrostomy. f) Flush the gastrostomy with 5 to 10 ml of tap water. g) Remove the syringe. h) Close the gastrostomy after flushing.
12 Continuous feedings (during the day and/or night time) by the pump Use the syringe method to relieve gas (as explained above) before continuous feeds if your child is not using the Farrell bag. NOTE: Your child s home health company will review the pump with you. 1. Gather supplies: feeding pump and tubing formula feeding syringe without the plunger for flushing tap water (5 to 10 ml) for flushing 2. Wash your hands. 3. Pour formula into the feeding bag. 4. Open the clamp on the feeding bag, fill the pump tubing, then close the clamp. 5. Place the pump tubing into the pump. 6. Attach the pump tubing to the gastrostomy. 7. Make sure the tubing connections are secure. 8. Open the gastrostomy. 9. Open the clamp on the pump tubing. 10. Check the feeding rate on the pump. 11. Start the feeding pump. 12. Flush the gastrostomy after the feeding is done: a) Turn off the pump. b) Close the gastrostomy. c) Remove the pump tubing. d) Attach the feeding syringe (without the plunger) to the gastrostomy. e) Open the gastrostomy. f) Flush the gastrostomy with 5 to 10 ml of tap water. g) Remove the syringe.
13 J. Giving Medicines Flush the gastrostomy with 5 to 10 ml of tap water after giving medications. Ask your pharmacist to dispense all medications in a liquid form if possible. If your child s Primary Care Provider or Pharmacist tells you to crush pills or open capsules, dissolve the medications in water before giving. Using the medication port on the extension set for feeding: Mic-key G 1. Be sure the feeding port is closed when using the medicine port. 2. Put the medicine syringe (with medicine in it) into the small port on the gastrostomy. 3. Open the gastrostomy. 4. Slowly push the medicine into the gastrostomy. 5. Close the gastrostomy. 6. Disconnect the medicine syringe. 7. Attach a syringe with 5 to 10 ml of water. 8. Open the gastrostomy. 9. Slowly push the water into the gastrostomy to flush it. 10. Close the gastrostomy. 11. Disconnect the syringe. 12. Close the medicine port. If the Gastrostomy does not have a medicine port: 1. Attach the feeding syringe without the plunger directly into the gastrostomy. 2. Open the gastrostomy. 3. Put medicine into the feeding syringe and allow it to flow into the gastrostomy. 4. Put 5 to 10 ml of water into the feeding syringe and flush the gastrostomy. 5. Close the gastrostomy.
14 K. Skin Care Mic-key G and Corpak o Clean the skin around the gastrostomy at least three times a week with soap and warm water. Rinse well and pat dry. o A dressing may not be needed unless the gastrostomy is leaking. Dressing Change You may be instructed to place small dressing under the Mic-Key G to protect your child s skin if there is leaking around the tube. Stomahesive powder should be sprinkled on your child s skin before placing the dressing (see below). 1. Gather Supplies: Washcloth Soap and water Stomahesive powder Pre-cut 2x2 gauze (1 package) Hypafix tape Scissors 2. Remove the tape on the silicone ring. Take out the gauze 3. Hold the gastrostomy tube straight up and clean the skin around the gastrostomy with warm soapy water 4. Rinse the area and pat it dry. 5. Sprinkle stomahesive powder around the gastrostomy. 6. Separate the 2x2 gauze- there are 2 pieces in each package. Put one gauze around the tube 7. Place four pieces of tape to cover the ring, gauze and skin.
15 Malecot, Mushroom, or de Pezzer with Nipple Dressing o Change the dressing 3 times a week unless it is wet or the skin is reddened. o Bath time is a good time to change the dressing. Dressing Change Gather Supplies: Washcloth Soap and water Pre-cut 2X2 gauze (1 package) Tape Scissors 1. Remove the tape on the nipple. Take out the gauze. 2. Hold the gastrostomy tube straight up and gently lift up the nipple. 3. Clean the skin around the gastrostomy with warm soapy water. 4. Rinse the area and pat it dry. 5. Separate the 2x 2 gauze there are 2 pieces in each package. Put one gauze around the gastrostomy tube. Put the second piece of gauze around the tube facing the opposite direction. 6. Hold the tube and gently push the nipple down on the gauze. 7. Place four pieces of tape on the nipple, gauze and skin. (see picture).
16 L. Leaking Feedings or stomach contents (greenish, yellowish in color) can leak around the gastrostomy onto your child s skin. Leaking can happen if the end of the gastrostomy in the stomach is not up against the stomach wall. If the gastrostomy easily moves up and down. Hold the gastrostomy in one hand and gently push the nipple or ring down on the skin. This will re-create the seal. Call the service that placed the gastrostomy if the leaking persists. M. Products that Can Protect Your Child s Skin from Leakage 1. Stomahesive Powder o Stomahesive powder can be sprinkled around the buttom. o The powder absorbs some of the drainage and helps protect your child s skin o Use a small amount of powder to prevent clumping on the skin. o It will not hurt your child if some of the powder goes into the gastrostomy site. Call the surgery office if the leaking persists. The nurse may discuss the use of the following supplies to protect your child s skin. Do not use any of these supplies without talking to a nurse from the surgery office. 2. Dressings o A dressing may be placed over the powder to absorb leakage around the gastrostomy (2x2 split gauze or panty-line cut to fit). o Foam dressings may be ordered to place around your child s gastrostomy if leaking increases.
17 3. Stomahesive paste o Do not use the stomahesive paste unless you are told to do so by the Surgery Office. o Stomahesive paste is a putty-like substance used around the gastrostomy to help prevent leaking. The stomahesive paste comes in a tube similar to toothpaste. o The paste is used around the gastrostomy to help prevent persistent leaking. How to apply the paste: 1. Take the plunger out of a small syringe. 2. Squeeze the paste into the barrel of the syringe. 3. Replace the plunger. 4. Sprinkle stomahesive powder where you will put the paste if the skin is irritated. 5. Push the plunger and put a small dab of paste around the gastrostomy. 6. Do not smooth the paste with your finger. This removes the paste. 7. Too much stomahesive paste is difficult to remove from the skin. 8. Replace the cap on the syringe. You can save this for another time. N. Granulation Tissue Sometimes, extra tissue called granulation tissue grows around the gastrostomy. You cannot prevent granulation tissue from forming. Granulation tissue contains many capillaries (small blood vessels). The tissue may be red or pink. It looks like the inside of the mouth. Granulation tissue is not an infection but it can have yellow/green drainage that smells like stinky feet. Do not worry if you see tiny spots of blood if the tissue becomes irritated. Granulation tissue is more likely to form if the gastrostomy is turned a lot. Granulation tissue may go away but it can return. Call the surgery office if the granulation tissue becomes tender and painful to your child or if the drainage increases. A nurse from the Surgery Office or Home Care will gently roll a small q-tip with medicine on it over the granulation tissue. This medicine is called silver nitrate. This medicine will help the granulation tissue shrink and dry up. The tissue may turn dark or white.
18 O. What if the Gastrostomy Comes Out Before 2 Months after Surgery or Before Your Child s Surgery Clinic Appointment? Gastrostomies, on very rare occasions, may come out. Formula or food may leak from the stoma and you may see a small amount of blood. There is no immediate danger to your child. Cover the opening with a washcloth or towel. Prepare to insert the replacement tube. DO NOT place the old tube back in! Two (2) replacement tubes (Foley tubes) will be in your take-home bag. One Foley tube is the same size as your child s old gastrostomy and the other tube is one size smaller. The Foley tube is inserted to keep the stoma and gastrostomy tract open. When you get home with your child, take the Foley tubes and lubricant out of the take- home bag and put them in a handy location. P. Placing the Foley Tube into the Gastrostomy Stoma 1. Get the Foley tube that is the same size as your child s gastrostomy. 2. Put a dab of water soluble lubricant from the take home package or KY Jelly on the narrow tip of the Foley. 3. Gently insert the appropriate length of the Foley into the gastrostomy stoma. 4. How far do you put the Foley Tube in the stomach? 1¼ inch (3 cm) for a child under 30kg (66lbs) 2 ½ inches (6cm) for a child over 30 kg (66 lbs) 5. Your child may cry, wiggle, or kick causing the abdominal muscles to contract. 6. Take a deep breath, try to relax and comfort your child. When your child breathes out, the abdominal muscles relax and the Foley tube should slide into the stoma. 7. Never force the tube into the stoma. Try the smaller size Foley if needed. 8. Do not take more than 10 to 15 min to try to insert the Foley.
19 9. Tape the Foley tube to your child s abdomen after it is in the stoma. 10. Do not blow up the balloon on the Foley! 11. Do not feed, give water, or give medicine to your child! 12. Call the Surgery Office or the Surgical Resident on Call (after office hours and on the weekends) when the Foley is in the stoma. 13. Take your child to. 14. If you are unable to insert the Foley, take your child to the nearest emergency room! 15. Have the local Emergency Room physician call the Surgical Resident on Call. Q. Frequently Asked Questions 1. Can my child swim or take a bath? After 2 weeks, the gastrostomy site should be healed and your child can take a bath or swim in chlorinated water. After 4 weeks, your child can swim in lakes, rivers or the ocean. Clean the gastrostomy site immediately after swimming. Water my leak into your child s stomach. This is okay for most children. 2. Can my child lay on the gastrostomy? Yes, after the site is no longer tender after placement. Infants can lie on their stomachs for tummy time. Older children can sleep on their stomachs. 3. Does my child have to go back to surgery to remove the gastrostomy? No. Most gastrostomies are removed in the Surgery Clinic. Some leaking from the stoma is normal after the gastrostomy is removed. You will be shown how to put a dressing over your child s old gastrostomy site. Your child may need to have surgery to close the stoma if the gastrostomy has been in place over a year or does not close on its own.
20 R. Call Your Child s Medical Provider if: Your child s abdomen (stomach) is hard or distended (bulging) or your child vomits with feedings. Your child has pain or cramping with feeding. Your child has a fever. Your child has signs and symptoms of dehydration: o No urine in 12 hours for toddlers o No urine in 8 hours for infants o Crying without tears o Very dry mouth or cracked lips o Sunken soft spot (infants less than 1 year) o Your child is more sleepy than usual o Your child feels dizzy S. Home Care Supplies Replacement gastrostomy tube For Skin Care: Stomahesive powder Stomahesive paste (optional) 2X2 gauze Skin barrier wipes Tape of choice Adhesive remover For feedings: Feeding syringe Farrell bag if ordered For General Health Information and Resources: Call or visit the Family Resource Center, a health information library on the 3rd floor of the hospital. Call , at frc@bjc.org, or check out the FREE St. Louis Children's Hospital Kid Care App.
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care
 GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
Caring for Your Gastrostomy
 Caring for Your Gastrostomy Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 4 Gastrostomy Feedings... 5 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Gastrostomy Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 4 Gastrostomy Feedings... 5 Giving Medicines...
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
My patient has a feeding tube
 My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator (December, 2014) Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG
My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator (December, 2014) Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube
 Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter
 Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women
 2014 Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women What is intermittent catheterization? Intermittent catheterization is a way to drain urine (pee) from your
2014 Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women Intermittent Clean Catheterization for Women What is intermittent catheterization? Intermittent catheterization is a way to drain urine (pee) from your
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter
 Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Are any artificial parts used in the ACE Malone surgery?
 ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter
 Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women
 Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women This handout has been prepared to help you learn about self-catheterization after bladder surgery. Step-by-step instructions are given. Please write
Self-Catheterization after Bladder Surgery For Women This handout has been prepared to help you learn about self-catheterization after bladder surgery. Step-by-step instructions are given. Please write
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Males
 The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Males Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 male patient
The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Males Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 male patient
Home Care for Your Wound Drain
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
Patients First. Tube Feeding Guidelines. Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve. Discharge Instructions
 Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery.
 JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) For Females What it is:
 The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catherterization (CIC) for Females Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 female
The Emily Center Clean Intermittent Catherterization (CIC) for Females Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #200 female
Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males
 Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males CEAC 0371 January 2016 Intermittent Self Catheterization This involves inserting a catheter (small tube) into your bladder at regular intervals to help empty
Intermittent Self Catheterization for Males CEAC 0371 January 2016 Intermittent Self Catheterization This involves inserting a catheter (small tube) into your bladder at regular intervals to help empty
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions
 Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role. Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake
 Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG. By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service
 Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector
 HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the HICKMAN Catheter... 2 Part 2 Caring for Your Hickman Catheter... 3 A. Preventing Infection... 3 B. Bathing...
HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the HICKMAN Catheter... 2 Part 2 Caring for Your Hickman Catheter... 3 A. Preventing Infection... 3 B. Bathing...
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
After Your Abdominal Surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Abdominal Surgery Self-care and follow-up You recently had abdominal surgery. This handout explains what to expect during your recovery. Please read these instructions
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Abdominal Surgery Self-care and follow-up You recently had abdominal surgery. This handout explains what to expect during your recovery. Please read these instructions
PATIENT GUIDE. Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL
 PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION
 www.southerarizonaspine.com POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns,
www.southerarizonaspine.com POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns,
CATHETER for Hemodialysis
 CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery
 Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine www.happypatient.org Updated 5/10 Why? To Help Control Postoperative Pain at Home A pump connected
Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine www.happypatient.org Updated 5/10 Why? To Help Control Postoperative Pain at Home A pump connected
Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS & CARERS. Accessory items. Freka UK Funnel Adapter. Fixation Plate CH9. Male Luer Lock Adapter
 Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter
 The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding
 Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
The temporary haemodialysis catheter
 The temporary haemodialysis catheter Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information in this booklet is for: People have renal failure and who require urgent haemodialysis.
The temporary haemodialysis catheter Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information in this booklet is for: People have renal failure and who require urgent haemodialysis.
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: Doing Peritoneal Dialysis at Home
 Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME
 TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
 SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
After Your Gastrectomy
 After Your Gastrectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a gastrectomy is how to care for yourself what problems to look out for who to call if you have any
After Your Gastrectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a gastrectomy is how to care for yourself what problems to look out for who to call if you have any
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION
 SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives stepby-step instructions for changing a Foley catheter, a tube in the bladder to drain urine.
Fact Sheet. Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) Queensland Spinal Cord Injuries Service
 and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Urinary Indwelling Catheter. The Urinary System
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
Achieving Independence
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials Giving a subcutaneous injection
 NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
Percutaneous Nephrostomy. Care of your Nephrostomy. Department of Urology
 Percutaneous Nephrostomy Care of your Nephrostomy Department of Urology You may encounter some problems at home but these are usually easily overcome. Listed below are some questions patients commonly
Percutaneous Nephrostomy Care of your Nephrostomy Department of Urology You may encounter some problems at home but these are usually easily overcome. Listed below are some questions patients commonly
Information for patients and nurses
 Information for patients and nurses Rocket IPC Pleural Catheter Indwelling Catheter Rocket Indwelling Pleural Catheter (IPC) Contents Contact Information...03 What s in the Rocket Dressing Pack and Bottle
Information for patients and nurses Rocket IPC Pleural Catheter Indwelling Catheter Rocket Indwelling Pleural Catheter (IPC) Contents Contact Information...03 What s in the Rocket Dressing Pack and Bottle
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION UROLOGICAL DRAINAGE. Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance. Patient Education Guide
 BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
Abdominal Wall (Ventral, Incisional, Umbilical) Hernia Repair Postoperative Instructions
 Abdominal Wall (Ventral, Incisional, Umbilical) Hernia Repair Postoperative Instructions No lifting greater than 10 15 lbs for the first three weeks following your surgery. Walking around the house, office
Abdominal Wall (Ventral, Incisional, Umbilical) Hernia Repair Postoperative Instructions No lifting greater than 10 15 lbs for the first three weeks following your surgery. Walking around the house, office
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter
 Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement A tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) is a special type of intravenous (IV) line that is placed into a large
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement A tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) is a special type of intravenous (IV) line that is placed into a large
You have been sent home with. Suprapubic Catheter
 You have been sent home with Suprapubic Catheter 1 SUPRAPUBIC CATHETER 1.- What is a suprapubic catheter? 2.- What do you need on discharge. 3.- Basic care 4.- Choosing your bag and bag care 5.- Possible
You have been sent home with Suprapubic Catheter 1 SUPRAPUBIC CATHETER 1.- What is a suprapubic catheter? 2.- What do you need on discharge. 3.- Basic care 4.- Choosing your bag and bag care 5.- Possible
Urinary Catheter Care and Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Urinary Catheter Care and Prostate Cancer Treatment The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions
Urinary Catheter Care and Prostate Cancer Treatment The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions
A Guide to Help You Manage Your Catheter and Drainage Bags
 A Guide to Help You Manage Your Catheter and Drainage Bags A catheter can make a difference to your health and quality of life. We understand that it can be a big adjustment for you. This information will
A Guide to Help You Manage Your Catheter and Drainage Bags A catheter can make a difference to your health and quality of life. We understand that it can be a big adjustment for you. This information will
call 811 to get advice from a nurse, or have someone drive the patient to a hospital Emergency Department. Patients should NOT drive themselves.
 Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
III-701 Urinary Catheterization/Bladder Irrigation Original Date: 3/1/1977 Last Review Date: 10/28/2004
 III-701 Urinary Catheterization/Bladder Irrigation Original Date: 3/1/1977 Last Review Date: 10/28/2004 Purpose A. Allow for precise measurement of urine output. B. Collect a sterile urine specimen. C.
III-701 Urinary Catheterization/Bladder Irrigation Original Date: 3/1/1977 Last Review Date: 10/28/2004 Purpose A. Allow for precise measurement of urine output. B. Collect a sterile urine specimen. C.
Care of a Foley Catheter
 Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
Common Concerns About Breastfeeding
 Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy PICO Single Use System
 Patient & Family Guide 2015 Negative Pressure Wound Therapy PICO Single Use System www.nshealth.ca Negative Pressure Wound Therapy PICO Single Use System What is Negative Pressure Wound Closure Therapy?
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Negative Pressure Wound Therapy PICO Single Use System www.nshealth.ca Negative Pressure Wound Therapy PICO Single Use System What is Negative Pressure Wound Closure Therapy?
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for the night will have their procedure cancelled immediately.
 Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME
 Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
How To Care For A Stoma
 People who have a stoma often share many of the same questions and concerns. This best practice document provides answers to some of the common questions that people ask about the day to day care of the
People who have a stoma often share many of the same questions and concerns. This best practice document provides answers to some of the common questions that people ask about the day to day care of the
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide
 PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
Information and advice following placement of seton for anal fistula
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Information and advice following placement of seton for anal fistula page 2 What is a fistula? You can get an anal fistula as a result of an infection or a collection
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Information and advice following placement of seton for anal fistula page 2 What is a fistula? You can get an anal fistula as a result of an infection or a collection
Changing Your Central Line Catheter Cap
 Changing Your Central Line Catheter Cap The catheter cap on each lumen of your central line needs to be changed once a week. A lumen is a small tube within your catheter. These same steps can be used for
Changing Your Central Line Catheter Cap The catheter cap on each lumen of your central line needs to be changed once a week. A lumen is a small tube within your catheter. These same steps can be used for
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. Read this information before you start. Important things to know about your SmartJect autoinjector. Important things to remember
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SIMPONI (SIM-po-nee) (golimumab) SmartJect autoinjector If your doctor decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of SIMPONI at home, you should receive training
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SIMPONI (SIM-po-nee) (golimumab) SmartJect autoinjector If your doctor decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of SIMPONI at home, you should receive training
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube
 Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness. and pain
 TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
AXIRON (AXE-e-RON) CIII
 Medication Guide 1 AXIRON (AXE-e-RON) CIII (testosterone) topical solution Read this Medication Guide before you start using AXIRON and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information
Medication Guide 1 AXIRON (AXE-e-RON) CIII (testosterone) topical solution Read this Medication Guide before you start using AXIRON and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information
A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization. Boys
 A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization Boys Introduction Probably you have just heard that you have to learn to catheterize your bladder. Most children are worried, frightened or scared
A Child s guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization Boys Introduction Probably you have just heard that you have to learn to catheterize your bladder. Most children are worried, frightened or scared
Having a supra pubic urinary catheter
 Having a supra pubic urinary catheter Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Having a supra pubic urinary catheter Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home
 Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust What is a suprapubic catheter? A suprapubic
Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust What is a suprapubic catheter? A suprapubic
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Section 4: Your Vascular Access. What is vascular access?
 Section 4: Your Vascular Access What is vascular access? What is a fistula? Taking care of a new fistula What is a graft? Taking care of a new graft What is a hemodialysis catheter? Taking care of a hemodialysis
Section 4: Your Vascular Access What is vascular access? What is a fistula? Taking care of a new fistula What is a graft? Taking care of a new graft What is a hemodialysis catheter? Taking care of a hemodialysis
Epigastric Hernia Repair
 Epigastric Hernia Repair WHAT IS EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES IT? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 2 WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF THE HERNIA WAS NOT TREATED? 3 EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR 3 WHAT
Epigastric Hernia Repair WHAT IS EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES IT? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 2 WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF THE HERNIA WAS NOT TREATED? 3 EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR 3 WHAT
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter
 Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
HALO ORTHOSIS. 1. The ring and pins. 2. The vest. 3. The superstructure (uprights that connect the ring to the vest)
 UM Orthotics & Prosthetics Center UM Orthopaedics UM Neurosurgery HALO ORTHOSIS HALO Front View HALO Back View You have been placed in a halo vest. This orthosis (brace) is used to immobilize a neck fracture
UM Orthotics & Prosthetics Center UM Orthopaedics UM Neurosurgery HALO ORTHOSIS HALO Front View HALO Back View You have been placed in a halo vest. This orthosis (brace) is used to immobilize a neck fracture
Femoral Hernia Repair
 Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips
 Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients
 let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
Recto-vaginal Fistula Repair
 What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
A Guide for Families and Caregivers
 A Guide for Families and Caregivers May 2003 Fourth Edition, 2003 The practices of nutrition support are continually evolving with new knowledge and guidelines from expert authorities. This booklet is
A Guide for Families and Caregivers May 2003 Fourth Edition, 2003 The practices of nutrition support are continually evolving with new knowledge and guidelines from expert authorities. This booklet is
Frequently Asked Questions: REDEFINE ACUTE CARE Skincare for Expression Lines
 Frequently Asked Questions: REDEFINE ACUTE CARE Skincare for Expression Lines 1. How does REDEFINE ACUTE CARE work? REDEFINE ACUTE CARE quickly and comfortably smoothes targeted lines and wrinkles using
Frequently Asked Questions: REDEFINE ACUTE CARE Skincare for Expression Lines 1. How does REDEFINE ACUTE CARE work? REDEFINE ACUTE CARE quickly and comfortably smoothes targeted lines and wrinkles using
