COGNITION. Chapter 10: Decision Making. Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology (Kellogg)
|
|
|
- Sherman Banks
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mark Van Selst San Jose State University COGNITION Chapter 10: Decision Making Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology (Kellogg) Fall 2013
2 Decision Making and Problem Solving Algorithm: precise set of rules guaranteed to produce the correct answer Heuristic: rule of thumb, and informal strategy or approach that works under some circumstances (not all)
3 FORMAL LOGIC Induction the process of reasoning from the particular to the general Deduction the process of drawing, by reasoning, particular conclusion from more general principles assumed to be true Francis Bacon proposed logical induction as the logic of scientific discovery and deduction as the logic of argumentation. In fact, both processes are used synergistically in the behavioral sciences: by observation of particular events (induction) and from already known principles (deduction).
4 Syllogistic Reasoning three statement logical form Major Premise Minor Premise Conclusion The logical validity of the conclusion is determined entirely after 'accepting' the premises as true (it is a logical deductive conclusion that is a conclusion that necessarily follows from the premises) All bears are animals Some animals are white Thus, some bears are white (Invalid conclusion) Syllogistic reasoning is highly subject to the confirmation bias; you can guard against this (1) through the use of Euler Circles (Venn diagrams) while (2) trying to falsify the conclusion.
5 Euler Circles
6 Syllogisms Major and Minor Premises All Some None People do poorly with syllogisms, even when the content is meaningless letters.
7 Cognitive Constraints (Syllogistic Reasoning) Atmosphere Hypothesis All, Some incorrectly assume syllogism is valid no, none if conclusion is negative is more likely to be accepted (even though not valid) Illicit Conversion (all A are B does NOT mean all B are A, but people tend to perform this illicit conversion ) Belief Bias: meaningful information can lead to accepting logically invalid conclusions
8 two major parts: conditional clause (if-then) evidence Conditional Reasoning Determine whether the evidence supports, refutes or is irrelevant to the stated relationship. The "if" clause of the conditional is the antecedent The "then" clause of the condition is the consequent The question is whether you can draw a logical conclusion from the evidence
9 The four possible conditional reasoning situations: If P then Q P Thus, Q If P then Q Not P Thus, NOT Q If P then Q Q Thus, P If P then Q Not Q Thus, NOT P valid inference AFFIRM THE ANTECEDENT (modus ponens) invalid inference DENY THE ANTECEDENT invalid inference AFFIRM THE CONSEQUENT valid inference DENY THE CONSEQUENT (modus tollens)**
10 Conditional Reasoning People are generally good about Affirming the Antecedent, but have difficulty denying the consequent. People also have a tendency to engage in the two invalid forms. In addition, people have a tendency to perform an "ILLICIT CONVERSION" and switch the condition from if P, then Q to If Q then P.
11 Conditional Reasoning (Wason card problem) Which card or cards do you need to turn over to test "if VOWEL on one side then EVEN on other side". E K 4 7 Typically subjects will show a confirmation bias avoid seeking evidence in opposition to our beliefs Martini Coke Meaningful material seems to help people. People are not good at abstract logic.
12 Wason (1968) Inductive Reasoning Test 8, 10, 12, Participants are to propose additional elements/sequences to identify the rule The evidence supported the confirmation bias
13 Decisions Under Uncertainty are like Decisions Under Risk (but use subjective odds vs. given odds) The concept of utility (value or gain associated with each possible outcome) One view of human decision making is to maximize utility BUT: bet with 1/3 chance of winning $8 OR bet with 5/6 chance of winning $3
14 Subjective Utility The joy of winning or pain of losing levels off with greater amounts Losses steeper than gains people are risk averse The shape of the function yields Framing Effects -- the way a question is worded has an important effect on people's decisions. This effect is both robust & pervasive. (Asian Disease, theatre ticket, calculator).
15 Framing Effects Making a different decision depending on where people see themselves to be in relation to the curvilinear subjective utility function. e.g., shopping for $15 calculator drive 5 min to save $5? Shopping for $150 jacket drive 5 min to save $5?
16 Once you have lost money it is ok to keep losing more (relatively little added subjective cost) this appears in stock trades for professional brokerage houses! The subjective utility curve has a zero point (reference for gains and losses) after purchase lowered expectations lead to early sell when the stock does well and being late to cut bait
17 Emotion and Thinking When people are in a good mood they try to maintain the good vibe and thus actually become increasingly risk averse Risk averse in the domain of gains
18 Subjective Probability Highly probable events are underestimated Low probability events are overestimated (Kahneman & Tversky, 1982)
19 Kahneman & Tversky In making predictions and judgments under uncertainty, people do not appear to follow the calculus of chance or the statistical theory of prediction. Instead, they rely on a limited number of heuristics which sometimes yield reasonable judgments and sometimes lead to severe and systematic errors (p.237, 1982)
20 Heuristics and Biases Representativeness Heuristic Judgment strategy based on estimates of how similar an event seems to be to its population: whether the event seems similar to the process that produced it, or, how similar is event to the population of events it came from. A sample looks representative if it is similar in important characteristics to the population from which it was selected. For example, a random process should produce a random looking result. Which sequence of coin tosses is more likely? HHHHHH HHHTTT THHTHT The gambler s fallacy: Ignoring the effect of sample size Law of large numbers: the TRUTH is that large samples are very likely to be representative of the population from which they are selected (Central Limit Theorem, etc.); small samples may not be. Law of small numbers: Mistaken belief that small samples will be representative of the population from which they are selected. (this is a mistake that people make... it is not a real law) stereotypes can lead to Base-Rate neglect (failure to obey Bayes Theorem) via a conjunctive fallacy (bank teller)
21 A special case of Representativeness: the Gambler s Fallacy The Gambler's Fallacy and its sibling, the Hot Hand Fallacy, have two distinctions that can be claimed of no other fallacies: They have built a city in the desert (Las Vegas) They are the economic mainstay of Monaco, an entire, albeit tiny, country, from which we get the alias "Monte Carlo" fallacy. Both fallacies are based on the same mistake, namely, a failure to understand statistical independence. Two events are statistically independent when the occurrence of one has no statistical effect upon the occurrence of the other. Statistical independence is connected to the notion of randomness in the following way: what makes a sequence random is that its members are statistically independent of each other. For instance, a list of random numbers is such that one cannot predict better than chance any member of the list based upon a knowledge of the other list members.
22 Heuristics and Biases: Availability Heuristic making a decision based on ease of retrieval from memory. You estimate the frequency or probability of an event by how easy or fast it is to think of examples of the event. This is often accurate, but can lead to errors when availability is not correlated with true, objective frequency. Frequency Familiarity Salience Vividness Examples: Words with K 1st vs. 3rd (Tversky & Kahneman, 1973) How many words with K first vs. K third? (people say first-k but really more third-k [harder to think of them])
23 Heuristics and Biases: Simulation Heuristic Simulation Heuristic constructing a mental model of an event and then running the model to make a prediction of some future event, or imagine a different outcome of some event or action. The undoing heuristic - changing events (more likely downhill changes than horizontal or uphill changes [p.375]) Hindsight Bias - because the scenario happened, we feel that the outcome should have been predictable since it is now very easy to picture how the event could have happened. Anticipating Outcomes (using simulation) both positive and negative and then deciding what to do based on these anticipated outcomes tends to produce more realistic (rather than biased) evaluations.
24 Probability or Frequency? A central issue in the use of heuristics is the matter of representation: do we process the PROBABILITY or the RELATIVE FREQUENCY? There are two opinion polls, in one set, 6 include candidate A and A wins 5 of the 6. In another set, 18 include candidate B and B wins 9 of the 18. Who do you expect to win? Bizarrely, people OFTEN claim that B is more likely to win this shows a reliance on raw scores rather than probabilities.
25 More Heuristics and Biases Halo Effect -- Opinion/Evaluation generalized from a high score on one trait to a high score on all traits (also "negative halo effect") Anchoring and Adjustment - People usually begin by guessing a first approximation -- an anchor -- and then make adjustments to that number of the basis of additional information. Often leads to a reasonable answer, but can lead to errors in some cases. It the average price of an undergraduate textbook more than, or less than, $10.00? What is the average price of an undergraduate textbook? typical finding: those with the $10 anchor produce lower estimated prices than those students given a $100 anchor. Part of this is due to the availability heuristic. It also works to bias estimates of frequency or number (e.g., the number of countries in Africa.. anchor at 5 versus anchor at 80...).
26 Terminology Syllogistic reasoning Conditional reasoning Deductive Inductive Illicit conversion Belief bias Affirm the antecedent Deny the consequent Affirm the consequent Deny the antecedent Subjective Probability Subjective utility Decisions under risk Decisions under uncertainty Representativeness Availability Halo effect Gambler s fallacy // law of small numbers Simulation heuristic
27 Assignment #10 Biases in Reasoning and Decision Making Assignment #10 (Biases in Reasoning and Decision Making): GOAL: To have you demonstrate your grasp three different cognitive biases in decisionmaking. One of these must be the "Anchoring and Adjustment" heuristic; another must relate to the work of Kahneman. The remaining one is any cognitive biases in decision-making not already included in your write-up that was discussed in class or which is mentioned in the text (group think, framing, etc.). REQUIREMENT: Write a report discussing the heuristics that have influenced three separate decisions that you have personally made. Provide a brief description of each of three scenarios in which you had to make a decision (or were involved in the decision making) and the cognitive biases that may have been involved (possibly in retrospect). Each of the three sections of this assignment will include a clear definition of the heuristic(s), the description of the situation, and statements that indicate why each heuristic applies to the situation as you have described it. It is possible (but not required) that multiple heuristics may have influenced each decision; you may note this, but you must describe three separate decisionmaking episodes. One of the episodes must use the "anchoring and adjustment" heuristic, another as discussed by Kahneman. The other heuristic is up to you. Due Date: start of class.
28 Assignment #11 Values and Application of Cognitive Psychology GOAL: To have you demonstrate your grasp of the scope and relevance of cognitive psychology. Goal #5 (see syllabus page 3) of the psychology degree objectives focus on the role of the individual within society. REQUIREMENT: Your task is to elucidate (discuss) how the content covered in this course is relevant to GOAL #5 (syllabus page 3). You MUST use different examples and specific discussion questions than addressed in previous written assignments. I expect two to three pages, not more, not less. I do not want you to throw in technical terms where they are not appropriate; I do want you to describe how an increased knowledge of cognitive psychology content impacts your ethics, appreciation for diversity, and development of skepticism.
29 Copyright 2013 / Van Selst
Ignoring base rates. Ignoring base rates (cont.) Improving our judgments. Base Rate Neglect. When Base Rate Matters. Probabilities vs.
 Ignoring base rates People were told that they would be reading descriptions of a group that had 30 engineers and 70 lawyers. People had to judge whether each description was of an engineer or a lawyer.
Ignoring base rates People were told that they would be reading descriptions of a group that had 30 engineers and 70 lawyers. People had to judge whether each description was of an engineer or a lawyer.
Reasoning and Decision Making
 Reasoning and Decision Making Learning Objective Topics Deductive vs. Inductive Reasoning Inductive Reasoning l Heuristics Utility and Emotions Neuroscience l Prefrontal Damage l Neuroeconomics 1 Reasoning
Reasoning and Decision Making Learning Objective Topics Deductive vs. Inductive Reasoning Inductive Reasoning l Heuristics Utility and Emotions Neuroscience l Prefrontal Damage l Neuroeconomics 1 Reasoning
What happens when logic and psychology meet?
 Logic meets psychology 1 What happens when logic and psychology meet? 27 September 2005 Core Logic Logic and Cognition Group m.e.counihan@uva.nl kamer 218 (Vendelstraat 8) tel. 020-525 4531 Logic meets
Logic meets psychology 1 What happens when logic and psychology meet? 27 September 2005 Core Logic Logic and Cognition Group m.e.counihan@uva.nl kamer 218 (Vendelstraat 8) tel. 020-525 4531 Logic meets
def: An axiom is a statement that is assumed to be true, or in the case of a mathematical system, is used to specify the system.
 Section 1.5 Methods of Proof 1.5.1 1.5 METHODS OF PROOF Some forms of argument ( valid ) never lead from correct statements to an incorrect. Some other forms of argument ( fallacies ) can lead from true
Section 1.5 Methods of Proof 1.5.1 1.5 METHODS OF PROOF Some forms of argument ( valid ) never lead from correct statements to an incorrect. Some other forms of argument ( fallacies ) can lead from true
CHAPTER 3. Methods of Proofs. 1. Logical Arguments and Formal Proofs
 CHAPTER 3 Methods of Proofs 1. Logical Arguments and Formal Proofs 1.1. Basic Terminology. An axiom is a statement that is given to be true. A rule of inference is a logical rule that is used to deduce
CHAPTER 3 Methods of Proofs 1. Logical Arguments and Formal Proofs 1.1. Basic Terminology. An axiom is a statement that is given to be true. A rule of inference is a logical rule that is used to deduce
Deductive reasoning is the kind of reasoning in which, roughly, the truth of the input
 Forthcoming in The Encyclopedia of the Mind, edited by Hal Pashler, SAGE Publishing. Editorial Board: Tim Crane, Fernanda Ferreira, Marcel Kinsbourne, and Rich Zemel. Deductive Reasoning Joshua Schechter
Forthcoming in The Encyclopedia of the Mind, edited by Hal Pashler, SAGE Publishing. Editorial Board: Tim Crane, Fernanda Ferreira, Marcel Kinsbourne, and Rich Zemel. Deductive Reasoning Joshua Schechter
The Binomial Distribution
 The Binomial Distribution James H. Steiger November 10, 00 1 Topics for this Module 1. The Binomial Process. The Binomial Random Variable. The Binomial Distribution (a) Computing the Binomial pdf (b) Computing
The Binomial Distribution James H. Steiger November 10, 00 1 Topics for this Module 1. The Binomial Process. The Binomial Random Variable. The Binomial Distribution (a) Computing the Binomial pdf (b) Computing
Chapter 6: Probability
 Chapter 6: Probability In a more mathematically oriented statistics course, you would spend a lot of time talking about colored balls in urns. We will skip over such detailed examinations of probability,
Chapter 6: Probability In a more mathematically oriented statistics course, you would spend a lot of time talking about colored balls in urns. We will skip over such detailed examinations of probability,
Mathematical goals. Starting points. Materials required. Time needed
 Level S2 of challenge: B/C S2 Mathematical goals Starting points Materials required Time needed Evaluating probability statements To help learners to: discuss and clarify some common misconceptions about
Level S2 of challenge: B/C S2 Mathematical goals Starting points Materials required Time needed Evaluating probability statements To help learners to: discuss and clarify some common misconceptions about
Independent samples t-test. Dr. Tom Pierce Radford University
 Independent samples t-test Dr. Tom Pierce Radford University The logic behind drawing causal conclusions from experiments The sampling distribution of the difference between means The standard error of
Independent samples t-test Dr. Tom Pierce Radford University The logic behind drawing causal conclusions from experiments The sampling distribution of the difference between means The standard error of
What Is Induction and Why Study It?
 1 What Is Induction and Why Study It? Evan Heit Why study induction, and indeed, why should there be a whole book devoted to the study of induction? The first reason is that inductive reasoning corresponds
1 What Is Induction and Why Study It? Evan Heit Why study induction, and indeed, why should there be a whole book devoted to the study of induction? The first reason is that inductive reasoning corresponds
Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley
 Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley Word Count: 2,486 Definition Prospect Theory is a psychological account that describes how people make decisions under conditions of uncertainty. These may
Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley Word Count: 2,486 Definition Prospect Theory is a psychological account that describes how people make decisions under conditions of uncertainty. These may
Mgmt 301 Managers as Decision Makers. Exploring Management. [Nathan Neale]
![Mgmt 301 Managers as Decision Makers. Exploring Management. [Nathan Neale] Mgmt 301 Managers as Decision Makers. Exploring Management. [Nathan Neale]](/thumbs/40/21390726.jpg) Mgmt 301 Managers as Decision Makers Exploring Management [Nathan Neale] Slide # 1 Slide Title: WSU Online Title Slide [piano introduction] Slide #2 Slide Title: Chapter 4 Managers as Decisions Makers
Mgmt 301 Managers as Decision Makers Exploring Management [Nathan Neale] Slide # 1 Slide Title: WSU Online Title Slide [piano introduction] Slide #2 Slide Title: Chapter 4 Managers as Decisions Makers
Teaching & Learning Plans. Plan 1: Introduction to Probability. Junior Certificate Syllabus Leaving Certificate Syllabus
 Teaching & Learning Plans Plan 1: Introduction to Probability Junior Certificate Syllabus Leaving Certificate Syllabus The Teaching & Learning Plans are structured as follows: Aims outline what the lesson,
Teaching & Learning Plans Plan 1: Introduction to Probability Junior Certificate Syllabus Leaving Certificate Syllabus The Teaching & Learning Plans are structured as follows: Aims outline what the lesson,
DISCRETE MATH: LECTURE 3
 DISCRETE MATH: LECTURE 3 DR. DANIEL FREEMAN 1. Chapter 2.2 Conditional Statements If p and q are statement variables, the conditional of q by p is If p then q or p implies q and is denoted p q. It is false
DISCRETE MATH: LECTURE 3 DR. DANIEL FREEMAN 1. Chapter 2.2 Conditional Statements If p and q are statement variables, the conditional of q by p is If p then q or p implies q and is denoted p q. It is false
Comparison of frequentist and Bayesian inference. Class 20, 18.05, Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom
 Comparison of frequentist and Bayesian inference. Class 20, 18.05, Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1 Learning Goals 1. Be able to explain the difference between the p-value and a posterior
Comparison of frequentist and Bayesian inference. Class 20, 18.05, Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1 Learning Goals 1. Be able to explain the difference between the p-value and a posterior
Making Financial Education More Effective: Lessons From Behavioral Economics
 Making Financial Education More Effective: Lessons From Behavioral Economics Joanne Yoong Prepared for the OECD-Bank of Italy International Symposium on Financial Literacy June 2010 Overview Project background
Making Financial Education More Effective: Lessons From Behavioral Economics Joanne Yoong Prepared for the OECD-Bank of Italy International Symposium on Financial Literacy June 2010 Overview Project background
P1. All of the students will understand validity P2. You are one of the students -------------------- C. You will understand validity
 Validity Philosophy 130 O Rourke I. The Data A. Here are examples of arguments that are valid: P1. If I am in my office, my lights are on P2. I am in my office C. My lights are on P1. He is either in class
Validity Philosophy 130 O Rourke I. The Data A. Here are examples of arguments that are valid: P1. If I am in my office, my lights are on P2. I am in my office C. My lights are on P1. He is either in class
Eliminating Over-Confidence in Software Development Effort Estimates
 Eliminating Over-Confidence in Software Development Effort Estimates Magne Jørgensen 1 and Kjetil Moløkken 1,2 1 Simula Research Laboratory, P.O.Box 134, 1325 Lysaker, Norway {magne.jorgensen, kjetilmo}@simula.no
Eliminating Over-Confidence in Software Development Effort Estimates Magne Jørgensen 1 and Kjetil Moløkken 1,2 1 Simula Research Laboratory, P.O.Box 134, 1325 Lysaker, Norway {magne.jorgensen, kjetilmo}@simula.no
2 What is Rational: Normative. 4 Lottery & Gambling
 1 Decision Making 2 What is Rational: Normative Key Question: Are you Rational? Deviations from rationality: Value is subjective (utility, and more..). Value is multidimensional (multiple budgets, not
1 Decision Making 2 What is Rational: Normative Key Question: Are you Rational? Deviations from rationality: Value is subjective (utility, and more..). Value is multidimensional (multiple budgets, not
Five High Order Thinking Skills
 Five High Order Introduction The high technology like computers and calculators has profoundly changed the world of mathematics education. It is not only what aspects of mathematics are essential for learning,
Five High Order Introduction The high technology like computers and calculators has profoundly changed the world of mathematics education. It is not only what aspects of mathematics are essential for learning,
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao, David Tse Note 10
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao, David Tse Note 10 Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability theory has its origins in gambling analyzing card games, dice,
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao, David Tse Note 10 Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability theory has its origins in gambling analyzing card games, dice,
1.2 Forms and Validity
 1.2 Forms and Validity Deductive Logic is the study of methods for determining whether or not an argument is valid. In this section we identify some famous valid argument forms. Argument Forms Consider
1.2 Forms and Validity Deductive Logic is the study of methods for determining whether or not an argument is valid. In this section we identify some famous valid argument forms. Argument Forms Consider
Decision Making under Uncertainty
 6.825 Techniques in Artificial Intelligence Decision Making under Uncertainty How to make one decision in the face of uncertainty Lecture 19 1 In the next two lectures, we ll look at the question of how
6.825 Techniques in Artificial Intelligence Decision Making under Uncertainty How to make one decision in the face of uncertainty Lecture 19 1 In the next two lectures, we ll look at the question of how
Software Project Scheduling under Uncertainties
 Copyright Notice: Materials published by Intaver Institute Inc. may not be published elsewhere without prior written consent of Intaver Institute Inc. Requests for permission to reproduce published materials
Copyright Notice: Materials published by Intaver Institute Inc. may not be published elsewhere without prior written consent of Intaver Institute Inc. Requests for permission to reproduce published materials
A Few Basics of Probability
 A Few Basics of Probability Philosophy 57 Spring, 2004 1 Introduction This handout distinguishes between inductive and deductive logic, and then introduces probability, a concept essential to the study
A Few Basics of Probability Philosophy 57 Spring, 2004 1 Introduction This handout distinguishes between inductive and deductive logic, and then introduces probability, a concept essential to the study
Hypothetical Syllogisms 1
 Phil 2302 Intro to Logic Dr. Naugle Hypothetical Syllogisms 1 Compound syllogisms are composed of different kinds of sentences in their premises and conclusions (not just categorical propositions, statements
Phil 2302 Intro to Logic Dr. Naugle Hypothetical Syllogisms 1 Compound syllogisms are composed of different kinds of sentences in their premises and conclusions (not just categorical propositions, statements
Forex Success Formula. Presents. Secure Your Money. www.forexsuccessformula.com - 1 -
 Forex Success Formula Presents Secure Your Money www.forexsuccessformula.com - 1 - Risk Disclosure Statement The contents of this e-book are for informational purposes only. No Part of this publication
Forex Success Formula Presents Secure Your Money www.forexsuccessformula.com - 1 - Risk Disclosure Statement The contents of this e-book are for informational purposes only. No Part of this publication
Lecture 2: Moral Reasoning & Evaluating Ethical Theories
 Lecture 2: Moral Reasoning & Evaluating Ethical Theories I. Introduction In this ethics course, we are going to avoid divine command theory and various appeals to authority and put our trust in critical
Lecture 2: Moral Reasoning & Evaluating Ethical Theories I. Introduction In this ethics course, we are going to avoid divine command theory and various appeals to authority and put our trust in critical
Banking on a Bad Bet: Probability Matching in Risky Choice Is Linked to Expectation Generation
 Research Report Banking on a Bad Bet: Probability Matching in Risky Choice Is Linked to Expectation Generation Psychological Science 22(6) 77 711 The Author(s) 11 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Research Report Banking on a Bad Bet: Probability Matching in Risky Choice Is Linked to Expectation Generation Psychological Science 22(6) 77 711 The Author(s) 11 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Book Review of Rosenhouse, The Monty Hall Problem. Leslie Burkholder 1
 Book Review of Rosenhouse, The Monty Hall Problem Leslie Burkholder 1 The Monty Hall Problem, Jason Rosenhouse, New York, Oxford University Press, 2009, xii, 195 pp, US $24.95, ISBN 978-0-19-5#6789-8 (Source
Book Review of Rosenhouse, The Monty Hall Problem Leslie Burkholder 1 The Monty Hall Problem, Jason Rosenhouse, New York, Oxford University Press, 2009, xii, 195 pp, US $24.95, ISBN 978-0-19-5#6789-8 (Source
HOW TO CHANGE NEGATIVE THINKING
 HOW TO CHANGE NEGATIVE THINKING For there is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare, Hamlet, Act 2, Scene 2, 239 251. Although you may not be fully aware of it, our minds
HOW TO CHANGE NEGATIVE THINKING For there is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare, Hamlet, Act 2, Scene 2, 239 251. Although you may not be fully aware of it, our minds
psychology and economics
 psychology and economics lecture 9: biases in statistical reasoning tomasz strzalecki failures of Bayesian updating how people fail to update in a Bayesian way how Bayes law fails to describe how people
psychology and economics lecture 9: biases in statistical reasoning tomasz strzalecki failures of Bayesian updating how people fail to update in a Bayesian way how Bayes law fails to describe how people
NATURAL AND CONTRIVED EXPERIENCE IN A REASONING PROBLEM
 Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology (1971) 23, 63-71 NATURAL AND CONTRIVED EXPERIENCE IN A REASONING PROBLEM P. C. WASON AND DIANA SHAPIRO Psycholinguistics Research Unit, Department of Phonetics,
Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology (1971) 23, 63-71 NATURAL AND CONTRIVED EXPERIENCE IN A REASONING PROBLEM P. C. WASON AND DIANA SHAPIRO Psycholinguistics Research Unit, Department of Phonetics,
MATH 140 Lab 4: Probability and the Standard Normal Distribution
 MATH 140 Lab 4: Probability and the Standard Normal Distribution Problem 1. Flipping a Coin Problem In this problem, we want to simualte the process of flipping a fair coin 1000 times. Note that the outcomes
MATH 140 Lab 4: Probability and the Standard Normal Distribution Problem 1. Flipping a Coin Problem In this problem, we want to simualte the process of flipping a fair coin 1000 times. Note that the outcomes
Review. Bayesianism and Reliability. Today s Class
 Review Bayesianism and Reliability Models and Simulations in Philosophy April 14th, 2014 Last Class: Difference between individual and social epistemology Why simulations are particularly useful for social
Review Bayesianism and Reliability Models and Simulations in Philosophy April 14th, 2014 Last Class: Difference between individual and social epistemology Why simulations are particularly useful for social
CRITICAL THINKING REASONS FOR BELIEF AND DOUBT (VAUGHN CH. 4)
 CRITICAL THINKING REASONS FOR BELIEF AND DOUBT (VAUGHN CH. 4) LECTURE PROFESSOR JULIE YOO Claims Without Arguments When Claims Conflict Conflicting Claims Conflict With Your Background Information Experts
CRITICAL THINKING REASONS FOR BELIEF AND DOUBT (VAUGHN CH. 4) LECTURE PROFESSOR JULIE YOO Claims Without Arguments When Claims Conflict Conflicting Claims Conflict With Your Background Information Experts
Sample Size Issues for Conjoint Analysis
 Chapter 7 Sample Size Issues for Conjoint Analysis I m about to conduct a conjoint analysis study. How large a sample size do I need? What will be the margin of error of my estimates if I use a sample
Chapter 7 Sample Size Issues for Conjoint Analysis I m about to conduct a conjoint analysis study. How large a sample size do I need? What will be the margin of error of my estimates if I use a sample
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING TECHNIQUES
 NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING TECHNIQUES PRESENTED BY Name: WINNIE MUGERA Reg No: L50/62004/2013 RESEARCH METHODS LDP 603 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI Date: APRIL 2013 SAMPLING Sampling is the use of a subset of the
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING TECHNIQUES PRESENTED BY Name: WINNIE MUGERA Reg No: L50/62004/2013 RESEARCH METHODS LDP 603 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI Date: APRIL 2013 SAMPLING Sampling is the use of a subset of the
Likewise, we have contradictions: formulas that can only be false, e.g. (p p).
 CHAPTER 4. STATEMENT LOGIC 59 The rightmost column of this truth table contains instances of T and instances of F. Notice that there are no degrees of contingency. If both values are possible, the formula
CHAPTER 4. STATEMENT LOGIC 59 The rightmost column of this truth table contains instances of T and instances of F. Notice that there are no degrees of contingency. If both values are possible, the formula
MTH6120 Further Topics in Mathematical Finance Lesson 2
 MTH6120 Further Topics in Mathematical Finance Lesson 2 Contents 1.2.3 Non-constant interest rates....................... 15 1.3 Arbitrage and Black-Scholes Theory....................... 16 1.3.1 Informal
MTH6120 Further Topics in Mathematical Finance Lesson 2 Contents 1.2.3 Non-constant interest rates....................... 15 1.3 Arbitrage and Black-Scholes Theory....................... 16 1.3.1 Informal
A Statistical Analysis of Popular Lottery Winning Strategies
 CS-BIGS 4(1): 66-72 2010 CS-BIGS http://www.bentley.edu/csbigs/vol4-1/chen.pdf A Statistical Analysis of Popular Lottery Winning Strategies Albert C. Chen Torrey Pines High School, USA Y. Helio Yang San
CS-BIGS 4(1): 66-72 2010 CS-BIGS http://www.bentley.edu/csbigs/vol4-1/chen.pdf A Statistical Analysis of Popular Lottery Winning Strategies Albert C. Chen Torrey Pines High School, USA Y. Helio Yang San
How to Develop a Research Protocol
 How to Develop a Research Protocol Goals & Objectives: To explain the theory of science To explain the theory of research To list the steps involved in developing and conducting a research protocol Outline:
How to Develop a Research Protocol Goals & Objectives: To explain the theory of science To explain the theory of research To list the steps involved in developing and conducting a research protocol Outline:
A Hands-On Exercise Improves Understanding of the Standard Error. of the Mean. Robert S. Ryan. Kutztown University
 A Hands-On Exercise 1 Running head: UNDERSTANDING THE STANDARD ERROR A Hands-On Exercise Improves Understanding of the Standard Error of the Mean Robert S. Ryan Kutztown University A Hands-On Exercise
A Hands-On Exercise 1 Running head: UNDERSTANDING THE STANDARD ERROR A Hands-On Exercise Improves Understanding of the Standard Error of the Mean Robert S. Ryan Kutztown University A Hands-On Exercise
MONT 107N Understanding Randomness Solutions For Final Examination May 11, 2010
 MONT 07N Understanding Randomness Solutions For Final Examination May, 00 Short Answer (a) (0) How are the EV and SE for the sum of n draws with replacement from a box computed? Solution: The EV is n times
MONT 07N Understanding Randomness Solutions For Final Examination May, 00 Short Answer (a) (0) How are the EV and SE for the sum of n draws with replacement from a box computed? Solution: The EV is n times
Clinical Study Design and Methods Terminology
 Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
A Case Study In Behavioral Finance
 A Case Study In Behavioral Finance We Are All Human Behavioral Finance is a field of study that combines psychology, economics, and finance to offer an explanation for why investors make irrational financial
A Case Study In Behavioral Finance We Are All Human Behavioral Finance is a field of study that combines psychology, economics, and finance to offer an explanation for why investors make irrational financial
Algebra 2 C Chapter 12 Probability and Statistics
 Algebra 2 C Chapter 12 Probability and Statistics Section 3 Probability fraction Probability is the ratio that measures the chances of the event occurring For example a coin toss only has 2 equally likely
Algebra 2 C Chapter 12 Probability and Statistics Section 3 Probability fraction Probability is the ratio that measures the chances of the event occurring For example a coin toss only has 2 equally likely
Software Metrics. Lord Kelvin, a physicist. George Miller, a psychologist
 Software Metrics 1. Lord Kelvin, a physicist 2. George Miller, a psychologist Software Metrics Product vs. process Most metrics are indirect: No way to measure property directly or Final product does not
Software Metrics 1. Lord Kelvin, a physicist 2. George Miller, a psychologist Software Metrics Product vs. process Most metrics are indirect: No way to measure property directly or Final product does not
Customer Analysis I. Session 3 Marketing Management Prof. Natalie Mizik
 Customer Analysis I Session 3 Marketing Management Prof. Natalie Mizik Outline How do you think about customers? How do customers think? Overview of approaches. Focus on behavioral economics. Useful in
Customer Analysis I Session 3 Marketing Management Prof. Natalie Mizik Outline How do you think about customers? How do customers think? Overview of approaches. Focus on behavioral economics. Useful in
Consumers Preference for Flat Rates: A Case of Media Access Fees
 Consumers Preference for Flat Rates: A Case of Media Access Fees Hitoshi MITOMO Tokio OTSUKA Dr., Professor, Graduate School of Global Information and Telecommunication Studies, Waseda University, Japan
Consumers Preference for Flat Rates: A Case of Media Access Fees Hitoshi MITOMO Tokio OTSUKA Dr., Professor, Graduate School of Global Information and Telecommunication Studies, Waseda University, Japan
Testing Research and Statistical Hypotheses
 Testing Research and Statistical Hypotheses Introduction In the last lab we analyzed metric artifact attributes such as thickness or width/thickness ratio. Those were continuous variables, which as you
Testing Research and Statistical Hypotheses Introduction In the last lab we analyzed metric artifact attributes such as thickness or width/thickness ratio. Those were continuous variables, which as you
IAI : Expert Systems
 IAI : Expert Systems John A. Bullinaria, 2005 1. What is an Expert System? 2. The Architecture of Expert Systems 3. Knowledge Acquisition 4. Representing the Knowledge 5. The Inference Engine 6. The Rete-Algorithm
IAI : Expert Systems John A. Bullinaria, 2005 1. What is an Expert System? 2. The Architecture of Expert Systems 3. Knowledge Acquisition 4. Representing the Knowledge 5. The Inference Engine 6. The Rete-Algorithm
Tom wants to find two real numbers, a and b, that have a sum of 10 and have a product of 10. He makes this table.
 Sum and Product This problem gives you the chance to: use arithmetic and algebra to represent and analyze a mathematical situation solve a quadratic equation by trial and improvement Tom wants to find
Sum and Product This problem gives you the chance to: use arithmetic and algebra to represent and analyze a mathematical situation solve a quadratic equation by trial and improvement Tom wants to find
CRITICAL THINKING. Induction v Deduction. Enumerative Induction and Inductive Generalization Sample Size Representativeness Mean, Median, Mode,
 CRITICAL THINKING INDUCTIVE REASONING LECTURE PROFESSOR JULIE YOO Induction v Deduction Enumerative Induction and Inductive Generalization Sample Size Representativeness Mean, Median, Mode, Analogical
CRITICAL THINKING INDUCTIVE REASONING LECTURE PROFESSOR JULIE YOO Induction v Deduction Enumerative Induction and Inductive Generalization Sample Size Representativeness Mean, Median, Mode, Analogical
Conn Valuation Services Ltd.
 CAPITALIZED EARNINGS VS. DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW: Which is the more accurate business valuation tool? By Richard R. Conn CMA, MBA, CPA, ABV, ERP Is the capitalized earnings 1 method or discounted cash flow
CAPITALIZED EARNINGS VS. DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW: Which is the more accurate business valuation tool? By Richard R. Conn CMA, MBA, CPA, ABV, ERP Is the capitalized earnings 1 method or discounted cash flow
Descriptive Statistics and Measurement Scales
 Descriptive Statistics 1 Descriptive Statistics and Measurement Scales Descriptive statistics are used to describe the basic features of the data in a study. They provide simple summaries about the sample
Descriptive Statistics 1 Descriptive Statistics and Measurement Scales Descriptive statistics are used to describe the basic features of the data in a study. They provide simple summaries about the sample
STA 371G: Statistics and Modeling
 STA 371G: Statistics and Modeling Decision Making Under Uncertainty: Probability, Betting Odds and Bayes Theorem Mingyuan Zhou McCombs School of Business The University of Texas at Austin http://mingyuanzhou.github.io/sta371g
STA 371G: Statistics and Modeling Decision Making Under Uncertainty: Probability, Betting Odds and Bayes Theorem Mingyuan Zhou McCombs School of Business The University of Texas at Austin http://mingyuanzhou.github.io/sta371g
The Best-Kept Secret of Forex
 The Best-Kept Secret of Forex Many traders go through trading system after trading system, only to find that most of them don t work. The truth of the matter is that there are many effective trading systems
The Best-Kept Secret of Forex Many traders go through trading system after trading system, only to find that most of them don t work. The truth of the matter is that there are many effective trading systems
"Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1
 BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY / 3 CHAPTER ONE BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY "Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1 Medicine
BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY / 3 CHAPTER ONE BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY "Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1 Medicine
Modern Science vs. Ancient Philosophy. Daniel Gilbert s theory of happiness as presented in his book, Stumbling on Happiness,
 Laura Katharine Norwood Freshman Seminar Dr. Golden 10/21/10 Modern Science vs. Ancient Philosophy Daniel Gilbert s theory of happiness as presented in his book, Stumbling on Happiness, has many similarities
Laura Katharine Norwood Freshman Seminar Dr. Golden 10/21/10 Modern Science vs. Ancient Philosophy Daniel Gilbert s theory of happiness as presented in his book, Stumbling on Happiness, has many similarities
Chapter 8 Subjective Probability
 Making Hard Decisions Chapter 8 Subjective Probability Slide 1 of 45 A Subjective Interpretation Frequentist interpretation of probability: Probability = Relative frequency of occurrence of an event Frequentist
Making Hard Decisions Chapter 8 Subjective Probability Slide 1 of 45 A Subjective Interpretation Frequentist interpretation of probability: Probability = Relative frequency of occurrence of an event Frequentist
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
Conditional Probability, Hypothesis Testing, and the Monty Hall Problem
 Conditional Probability, Hypothesis Testing, and the Monty Hall Problem Ernie Croot September 17, 2008 On more than one occasion I have heard the comment Probability does not exist in the real world, and
Conditional Probability, Hypothesis Testing, and the Monty Hall Problem Ernie Croot September 17, 2008 On more than one occasion I have heard the comment Probability does not exist in the real world, and
Elementary Statistics and Inference. Elementary Statistics and Inference. 17 Expected Value and Standard Error. 22S:025 or 7P:025.
 Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Lecture Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Chapter 7 A. The Expected Value In a chance process (probability experiment) the outcomes of
Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Lecture Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Chapter 7 A. The Expected Value In a chance process (probability experiment) the outcomes of
FRC Risk Reporting Requirements Working Party Case Study (Pharmaceutical Industry)
 FRC Risk Reporting Requirements Working Party Case Study (Pharmaceutical Industry) 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 Background and Scope... 3 Company Background and Highlights... 3 Sample Risk Register...
FRC Risk Reporting Requirements Working Party Case Study (Pharmaceutical Industry) 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 Background and Scope... 3 Company Background and Highlights... 3 Sample Risk Register...
Video Poker in South Carolina: A Mathematical Study
 Video Poker in South Carolina: A Mathematical Study by Joel V. Brawley and Todd D. Mateer Since its debut in South Carolina in 1986, video poker has become a game of great popularity as well as a game
Video Poker in South Carolina: A Mathematical Study by Joel V. Brawley and Todd D. Mateer Since its debut in South Carolina in 1986, video poker has become a game of great popularity as well as a game
APP INVENTOR. Test Review
 APP INVENTOR Test Review Main Concepts App Inventor Lists Creating Random Numbers Variables Searching and Sorting Data Linear Search Binary Search Selection Sort Quick Sort Abstraction Modulus Division
APP INVENTOR Test Review Main Concepts App Inventor Lists Creating Random Numbers Variables Searching and Sorting Data Linear Search Binary Search Selection Sort Quick Sort Abstraction Modulus Division
The Mozart effect Methods of Scientific Research
 The Mozart effect Methods of Scientific Research Chapter 2 Experimental Research: p42 49 http://www.mozarteffect.com/ http://www.amazon.com/mozart-sonata-pianos-schubert-fantasia/dp/b0000cf330 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hhqn2qjhlcm
The Mozart effect Methods of Scientific Research Chapter 2 Experimental Research: p42 49 http://www.mozarteffect.com/ http://www.amazon.com/mozart-sonata-pianos-schubert-fantasia/dp/b0000cf330 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hhqn2qjhlcm
What Is Circular Reasoning?
 What Is Circular Reasoning? Logical fallacies are a type of error in reasoning, errors which may be recognized and corrected by observant thinkers. There are a large number of informal fallacies that are
What Is Circular Reasoning? Logical fallacies are a type of error in reasoning, errors which may be recognized and corrected by observant thinkers. There are a large number of informal fallacies that are
FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING: VISIONARY THINKING OR OXYMORON? Aswath Damodaran
 FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING: VISIONARY THINKING OR OXYMORON? Aswath Damodaran Three big questions about fair value accounting Why fair value accounting? What is fair value? What are the first principles that
FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING: VISIONARY THINKING OR OXYMORON? Aswath Damodaran Three big questions about fair value accounting Why fair value accounting? What is fair value? What are the first principles that
How to Use Problem-Solving Simulations to Improve Knowledge, Skills, and Teamwork
 How to Use Problem-Solving Simulations to Improve Knowledge, Skills, and Teamwork By Janet L. Szumal, Ph.D. Human Synergistics/Center for Applied Research, Inc. Reprinted from Mel Silberman and Pat Philips
How to Use Problem-Solving Simulations to Improve Knowledge, Skills, and Teamwork By Janet L. Szumal, Ph.D. Human Synergistics/Center for Applied Research, Inc. Reprinted from Mel Silberman and Pat Philips
Practical Research. Paul D. Leedy Jeanne Ellis Ormrod. Planning and Design. Tenth Edition
 Practical Research Planning and Design Tenth Edition Paul D. Leedy Jeanne Ellis Ormrod 2013, 2010, 2005, 2001, 1997 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 1 The Nature and Tools of Research
Practical Research Planning and Design Tenth Edition Paul D. Leedy Jeanne Ellis Ormrod 2013, 2010, 2005, 2001, 1997 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 1 The Nature and Tools of Research
Lecture 9 Maher on Inductive Probability
 Lecture 9 Maher on Inductive Probability Patrick Maher Scientific Thought II Spring 2010 Two concepts of probability Example You know that a coin is either two-headed or two-tailed but you have no information
Lecture 9 Maher on Inductive Probability Patrick Maher Scientific Thought II Spring 2010 Two concepts of probability Example You know that a coin is either two-headed or two-tailed but you have no information
Pascal is here expressing a kind of skepticism about the ability of human reason to deliver an answer to this question.
 Pascal s wager So far we have discussed a number of arguments for or against the existence of God. In the reading for today, Pascal asks not Does God exist? but Should we believe in God? What is distinctive
Pascal s wager So far we have discussed a number of arguments for or against the existence of God. In the reading for today, Pascal asks not Does God exist? but Should we believe in God? What is distinctive
Mathematical Induction
 Mathematical Induction (Handout March 8, 01) The Principle of Mathematical Induction provides a means to prove infinitely many statements all at once The principle is logical rather than strictly mathematical,
Mathematical Induction (Handout March 8, 01) The Principle of Mathematical Induction provides a means to prove infinitely many statements all at once The principle is logical rather than strictly mathematical,
John Kerrich s coin-tossing Experiment. Law of Averages - pg. 294 Moore s Text
 Law of Averages - pg. 294 Moore s Text When tossing a fair coin the chances of tails and heads are the same: 50% and 50%. So, if the coin is tossed a large number of times, the number of heads and the
Law of Averages - pg. 294 Moore s Text When tossing a fair coin the chances of tails and heads are the same: 50% and 50%. So, if the coin is tossed a large number of times, the number of heads and the
Expect the Unexpected When Teaching Probability
 Boise State University ScholarWorks Curriculum, Instruction, and Foundational Studies Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Curriculum, Instruction, and Foundational Studies 3-1-2015 Expect
Boise State University ScholarWorks Curriculum, Instruction, and Foundational Studies Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Curriculum, Instruction, and Foundational Studies 3-1-2015 Expect
Philosophy 104. Chapter 8.1 Notes
 Philosophy 104 Chapter 8.1 Notes Inductive reasoning - The process of deriving general principles from particular facts or instances. - "induction." The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language,
Philosophy 104 Chapter 8.1 Notes Inductive reasoning - The process of deriving general principles from particular facts or instances. - "induction." The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language,
ECON 459 Game Theory. Lecture Notes Auctions. Luca Anderlini Spring 2015
 ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2015 These notes have been used before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please let me know. 1
ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2015 These notes have been used before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please let me know. 1
Perception and Individual Decision Making
 Robbins & Judge Organizational Behavior 13th Edition Perception and Individual Decision Making Bob Stretch Southwestern College 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 5-0 Chapter Learning Objectives
Robbins & Judge Organizational Behavior 13th Edition Perception and Individual Decision Making Bob Stretch Southwestern College 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 5-0 Chapter Learning Objectives
Social Perception and Attribution
 4 Social Perception and Attribution Chapter An Information Processing Model of Perception Stereotypes: Perceptions about Groups of People Self-Fulfilling Prophecy: The Pygmalion Effect Causal Attribution
4 Social Perception and Attribution Chapter An Information Processing Model of Perception Stereotypes: Perceptions about Groups of People Self-Fulfilling Prophecy: The Pygmalion Effect Causal Attribution
DEVELOPING HYPOTHESIS AND
 Shalini Prasad Ajith Rao Eeshoo Rehani DEVELOPING 500 METHODS SEPTEMBER 18 TH 2001 DEVELOPING HYPOTHESIS AND Introduction Processes involved before formulating the hypotheses. Definition Nature of Hypothesis
Shalini Prasad Ajith Rao Eeshoo Rehani DEVELOPING 500 METHODS SEPTEMBER 18 TH 2001 DEVELOPING HYPOTHESIS AND Introduction Processes involved before formulating the hypotheses. Definition Nature of Hypothesis
1. I have 4 sides. My opposite sides are equal. I have 4 right angles. Which shape am I?
 Which Shape? This problem gives you the chance to: identify and describe shapes use clues to solve riddles Use shapes A, B, or C to solve the riddles. A B C 1. I have 4 sides. My opposite sides are equal.
Which Shape? This problem gives you the chance to: identify and describe shapes use clues to solve riddles Use shapes A, B, or C to solve the riddles. A B C 1. I have 4 sides. My opposite sides are equal.
CFSD 21 ST CENTURY SKILL RUBRIC CRITICAL & CREATIVE THINKING
 Critical and creative thinking (higher order thinking) refer to a set of cognitive skills or strategies that increases the probability of a desired outcome. In an information- rich society, the quality
Critical and creative thinking (higher order thinking) refer to a set of cognitive skills or strategies that increases the probability of a desired outcome. In an information- rich society, the quality
Decision & Risk Analysis Lecture 6. Risk and Utility
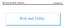 Risk and Utility Risk - Introduction Payoff Game 1 $14.50 0.5 0.5 $30 - $1 EMV 30*0.5+(-1)*0.5= 14.5 Game 2 Which game will you play? Which game is risky? $50.00 Figure 13.1 0.5 0.5 $2,000 - $1,900 EMV
Risk and Utility Risk - Introduction Payoff Game 1 $14.50 0.5 0.5 $30 - $1 EMV 30*0.5+(-1)*0.5= 14.5 Game 2 Which game will you play? Which game is risky? $50.00 Figure 13.1 0.5 0.5 $2,000 - $1,900 EMV
CONSTRUCTING A LOGICAL ARGUMENT
 Sloan Communication Program Teaching Note CONSTRUCTING A LOGICAL ARGUMENT The purpose of most business writing is to recommend some course of action ("we should open a branch office in Duluth"; "management
Sloan Communication Program Teaching Note CONSTRUCTING A LOGICAL ARGUMENT The purpose of most business writing is to recommend some course of action ("we should open a branch office in Duluth"; "management
Current Standard: Mathematical Concepts and Applications Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary
 Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary A student shall apply concepts of shape, space, and measurement to solve problems involving two- and three-dimensional shapes by demonstrating an understanding of:
Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary A student shall apply concepts of shape, space, and measurement to solve problems involving two- and three-dimensional shapes by demonstrating an understanding of:
Structured Interviewing:
 Structured Interviewing: Interview Board Guide How to conduct structured interviews in the appointment process Assessment Oversight and Personnel Psychology Centre TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 SECTION
Structured Interviewing: Interview Board Guide How to conduct structured interviews in the appointment process Assessment Oversight and Personnel Psychology Centre TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 SECTION
Rules of Inference Friday, January 18, 2013 Chittu Tripathy Lecture 05
 Rules of Inference Today s Menu Rules of Inference Quantifiers: Universal and Existential Nesting of Quantifiers Applications Old Example Re-Revisited Our Old Example: Suppose we have: All human beings
Rules of Inference Today s Menu Rules of Inference Quantifiers: Universal and Existential Nesting of Quantifiers Applications Old Example Re-Revisited Our Old Example: Suppose we have: All human beings
Problem of the Month: Fair Games
 Problem of the Month: The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common Core State Standards:
Problem of the Month: The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common Core State Standards:
Pay for performance. Intrinsic (interested in the job as such) Extrinsic motivation. Pay Work environment, non-pay characteristics, benefits
 Pay for performance Motivation Intrinsic (interested in the job as such) Extrinsic motivation Pay Work environment, non-pay characteristics, benefits Inefficient to rely on intrinsic motivation only Workers
Pay for performance Motivation Intrinsic (interested in the job as such) Extrinsic motivation Pay Work environment, non-pay characteristics, benefits Inefficient to rely on intrinsic motivation only Workers
psychology the science of psychology CHAPTER third edition Psychology, Third Edition Saundra K. Ciccarelli J. Noland White
 psychology third edition CHAPTER 1 the science of psychology Learning Objectives LO 1.1 Definition and Goals of Psychology LO 1.2 Structuralism and Functionalism LO 1.3 Early Gestalt, Psychoanalysis, and
psychology third edition CHAPTER 1 the science of psychology Learning Objectives LO 1.1 Definition and Goals of Psychology LO 1.2 Structuralism and Functionalism LO 1.3 Early Gestalt, Psychoanalysis, and
PHILOSOPHY 101: CRITICAL THINKING
 PHILOSOPHY 101: CRITICAL THINKING [days and times] [classroom] [semester] 20YY, [campus] [instructor s name] [office hours: days and times] [instructor s e-mail] COURSE OBJECTIVES AND OUTCOMES 1. Identify
PHILOSOPHY 101: CRITICAL THINKING [days and times] [classroom] [semester] 20YY, [campus] [instructor s name] [office hours: days and times] [instructor s e-mail] COURSE OBJECTIVES AND OUTCOMES 1. Identify
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing OPRE 6301
 Introduction to Hypothesis Testing OPRE 6301 Motivation... The purpose of hypothesis testing is to determine whether there is enough statistical evidence in favor of a certain belief, or hypothesis, about
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing OPRE 6301 Motivation... The purpose of hypothesis testing is to determine whether there is enough statistical evidence in favor of a certain belief, or hypothesis, about
Organizational Behavior and Organizational Change Decisions. Roger N. Nagel Senior Fellow & Wagner Professor. Lehigh University
 Organizational Behavior and Organizational Change Decisions Roger N. Nagel Senior Fellow & Wagner Professor 1 Topics This Presentation Decision making in OB Steps in the Decision-Making Model Common Biases
Organizational Behavior and Organizational Change Decisions Roger N. Nagel Senior Fellow & Wagner Professor 1 Topics This Presentation Decision making in OB Steps in the Decision-Making Model Common Biases
Test Bias. As we have seen, psychological tests can be well-conceived and well-constructed, but
 Test Bias As we have seen, psychological tests can be well-conceived and well-constructed, but none are perfect. The reliability of test scores can be compromised by random measurement error (unsystematic
Test Bias As we have seen, psychological tests can be well-conceived and well-constructed, but none are perfect. The reliability of test scores can be compromised by random measurement error (unsystematic
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS AND INFERENCE. Lecture 12
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Logic and Reasoning Practice Final Exam Spring 2015. Section Number
 Logic and Reasoning Practice Final Exam Spring 2015 Name Section Number The final examination is worth 100 points. 1. (5 points) What is an argument? Explain what is meant when one says that logic is the
Logic and Reasoning Practice Final Exam Spring 2015 Name Section Number The final examination is worth 100 points. 1. (5 points) What is an argument? Explain what is meant when one says that logic is the
Reasoning in Anxiety, OCD and Related Disorders: Can Formal Reasoning Theories Inform Us About Psychopathology?
 Reasoning in Anxiety, OCD and Related Disorders: Can Formal Reasoning Theories Inform Us About Psychopathology? 4 Kieron P. O Connor 1,2 and Marie-Claude Pélissier 1 1 Centre de recherche Fernand-Seguin,
Reasoning in Anxiety, OCD and Related Disorders: Can Formal Reasoning Theories Inform Us About Psychopathology? 4 Kieron P. O Connor 1,2 and Marie-Claude Pélissier 1 1 Centre de recherche Fernand-Seguin,
