Options Vs. Futures: Which on Average Will Have the Greater Payoff?
|
|
|
- Shanna Jennings
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Utah State University All Graduate Plan B and other Reports Graduate Studies 2012 Options Vs. Futures: Which on Average Will Have the Greater? Ryan Silvester Utah State University Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Finance Commons Recommended Citation Silvester, Ryan, "Options Vs. Futures: Which on Average Will Have the Greater?" (2012). All Graduate Plan B and other Reports. Paper 208. This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Graduate Studies at DigitalCommons@USU. It has been accepted for inclusion in All Graduate Plan B and other Reports by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@USU. For more information, please contact becky.thoms@usu.edu.
2 Options Vs. Futures: Which on Average Will Have the Greater? Ryan Silvester Introduction The use and idea of futures contracts has been around for almost as long as humans have existed. Many of these contracts can be as simple as the shaking of someone s hand with the agreement to trade an asset for an agreed upon price in the future. These contracts have often been used by farmers to ensure a needed price for an asset, or for a store owner to ensure a needed asset for a given price. The idea of a futures contract is to either buy or sell an asset later on at a specified price. In this paper I will look at both positions. First, wanting to buy an asset in the future is said to be long a futures contract, and to sell an asset in the future is said to be short a futures contract. The benefit of these contracts is that it gives the seller peace of mind to know that they will get paid a specified amount for an asset in the future; or the buyer will not have to pay more than the specified amount for an asset in the future. There can be disadvantages to these types of contracts as well. For example, if in the time between making the contract and the exchange of the asset the price moves in your favor, you will have lost out on the price move. This brings up the idea of the options market. I will focus on the basic European call and put options. A European option means that the options can only be exercised at the expiration date of the options. A call option is used when one is looking to buy an asset in the future, with a desire to put a cap on the amount that will be paid for the asset. A put option is used when someone is looking to sell an asset in the future and wants to put a floor on how much will be received for the asset. There are a couple differences between the options and futures contracts. First, with a futures contract no money is exchanged until the expiration of the contract; whereas with an options contract the person purchasing the contract will pay a fee for the contract up front, similar to an insurance premium. The second difference is with a futures contract, the agreed upon amount must be paid and received whether or not it is to your benefit; whereas with an options contract, the purchaser of the contract has the choice to look for a better price in the market, and if found, they can simply walk away from the contract. Thus, for an options contract, a premium is paid to be able to walk away from the contract. These differences lead to different payoffs for each of the types of contracts. First, to compare the contracts that deal with purchasing an asset in the future, we will look at a call option and a long futures contract. The call option payoff formula is: payoff = Max( P T K, 0) Premuim; This will yield a payoff that looks like figure one, Where P T is the price of the asset at the end of the contract and K is the strike price. It starts negative, the amount of the premium, and continues to stay flat until it reaches the strike price then it increases upward. The long futures contract payoff formula is: payoff = P T K; This will yields a payoff that looks like figure two. It starts negative, the set price, and then continues upward
3 crossing through the zero payoff line at the set price and continues up. One can see that if compared, the call option will outperform the long future contract up until a point just before the strike price and then the future contract will outperform the call option. The call option outperforms the long futures contract by more in the beginning, than the amount that the long futures contract outperforms the call option in the end. Thus the long futures contract has a lot of ground to make up to come out even or on top. Figure one Figure two Now, to look at the contracts that deal with selling of an asset, we look at a put option and a short futures contract. The put option payoff formula is: payoff = Max( K P T, 0) premium; this will yield a payoff that looks like figure three. It starts positive and decreases until it reaches the strike price at which it is negative, the amount of the premium, and then it continues flat. The short futures contract payoff is: payoff = K P T ; this will yield a payoff that looks like figure four. It starts positive, the amount of the set price, and continues down crossing the zero payoff line at the set price and then continues to decrease. One can see that if compared, the short futures contract will outperform the put option until a point just after the strike, at which the put option will then outperform the futures contract. The put option outperforms the short futures contract by more at the end, than the short futures contract outperforms the put option at the beginning, like the call option outperformed the long futures contract. Figure three Figure four Now that I have laid out the different payoffs of these contracts, I want to know which of these contracts on average will outperform the other. In each of the two comparisons, either of the contracts has the possibility of outperforming the other, depending upon what the final price is. Using the
4 examples from before, if I were a farmer trying to get the most out of my harvest which of these contracts should I use? Or, if I were a store owner trying to get the needed assets for my store at the cheapest price, which of these contracts should I use? To answer these questions, I use Monte Carlo simulation to create data. I simulate a year s worth of price changes, where price changes happen on every minute. I do this ten thousand times for each of my models. I then take the ending price and apply the payoff rule for each of the four contracts; a call option, a long future, a put option and a short future contract. I calculated the mean and the standard deviation of these payoffs to compare the difference between the contracts. Research Design I use four different models to simulate from. I use each of these models multiple times with different parameters to check for robustness in the results. The parameters that are needed for the models are: the initial price of the asset, which I will set at $50; the strike price of the contracts, which will also be set at $50; the volatility of the asset, which will take on the values 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5; the risk free rate, which will be set at 0.08; the dividend yield, which will be set at 0; the drift term, which will be set at 0.02; and the time will be one year. I will use the Black- Scholes- Merton model to price the option premium that will be used to calculate the option payoff. I will then compare each of the contracts in the different models to see if any conclusion can be reached as to which of these contracts has the greater payoff. The first model I use is the Geometric Browning Motion. This is a stochastic process that is a random walk in continuous time. A process is said to follow a Geometric Browning Motion if it satisfies the stochastic differential equation ds(t) = µ[s(t)]dt + σ[s(t)]dz(t). Using Itô Lemma we have the analytic solution to this stochastic differential equation and can simulate asset prices using the following formula: S t = S 0 exp[( µ + r δ (σ 2 /2))t + σ*z(t) Where S t is the price of the asset at time t, S 0 is the initial price, µ is the drift term, r is the risk free rate, δ is the continuously compounded dividend of the asset, σ is the volatility of the price, and Z(t) is a random draw from a standard normal distribution. This model is an accurate simulation of prices, but is disadvantaged because of the assumption that volatility is constant and known. The second model is also Geometric Browning Motion, but I add in some microstructure noise, that would come from trading, into the simulations. I do this by taking each S t and multiplying it by α*w(t) to get the final S t. Where α is an amount of micro structure noise that can occur and W(t) is a random draw from a standard normal distribution. The third model I use is the Heston model. This process differs from a Geometric Browning Motion because it does not assume the variance of an asset is constant, but that it follows a random process. The Heston model assumes that the price of an asset, S t, is determined by the stochastic
5 process ds t = µs t dt + dz s (t) where V t follows a process dv t = Κ( σ V t )dt + θ dz v (t). We simulate from this model using the following formulas: ln(s t ) = ln(s 0 ) + (µ + r δ (V t 2 /2))t + *Z 1 (t) V t = V t- 1 + Κ( Ṽ V t- 1 )t + θ Z 3 (t) Where S t is the price of an asset at time t, S 0 is the initial price of the asset, µ is the drift of the price, r is the risk free rate, δ is the continuously compounded dividend, σ is the long run variance, Κ is the rate at which V t reverts to Ṽ, Ṽ is the mean variance, θ is the volatility of the volatility, Z 1 (t) and Z 2 (t) are random draws from a standard normal distribution, and Z 3 (t) = ρz 1 (t) + Z 2 (t) because Z 1 (t) and Z 3 (t) have correlation of ρ. The fourth model is also a Heston model, but again I add in microstructure noise into the simulations. This is done in the same way as before to get our final S t by multiplying our S t s from the simulations by α*w(t). Results First to look at the results from when I have volatility set at 0.3 (figure five). On average in every model, except the Heston model without microstructure noise, the call option outperforms the long futures contract. The reason the call option doesn t outperform the futures contract in the Heston model, could be from the fact that the Black- Scholes- Merton model overvalue options with stochastic volatility; as shown by Hull and White in The Pricing of Options on Assets with Stochastic Volatilities. Also I noticed that the standard deviation is smaller on the call option, which is not surprising because it has a bottom on the amount it can lose. The call option outperforms the long futures contract by anywhere from fifty cents to almost four dollars in these cases. Hypothetically, if this was scaled up for a small company that needed a thousand of an asset to use throughout the year this would be somewhere between five hundred dollars to four thousand dollars. That would be a significant amount to a small company. Also in every model, except the Heston model without microstructure noise, the put option outperforms the short futures contract. And again, not surprisingly, the put option has a smaller standard deviation. The put option outperforms the short futures contract by around a dollar every time. Again, this would be a significant amount for a farmer or a small company making this contract for a thousand of an asset. Figure Five σ = 0.3 Geometric Browning Motion GBM W/ Heston Model Heston W/ payoff Call Option Long Futures Put Option Short Futures
6 Next, looking at the results from when I raise the volatility to 0.5 (figure six). With a higher volatility, the cost of the options premiums is going to increase. This could offset its ability to outperform the futures contract, but there are similar results to the first time. The call option is outperforming the long futures contract except in the Heston model without microstructure. This could again be from the Black- Scholes- Merton model overvaluing options with stochastic volatility. The put option outperforms the short futures contract in all the models except the Heston model with microstructure noise. Thus the options still seem to, on average, outperform the futures contracts even with the higher premium cost. Figure six σ = 0.5 Geometric Browning Motion GBM W/ Heston Model Heston W/ payoff Call Option Long Futures Put Option Short Futures Finally, to look at the results from when the volatility is reduced to 0.1 (figure seven). With the decreased volatility, the premiums for the options will be reduced, but so will the movement away from the strike price. These results are even more in favor of the options over the futures contracts. The call option outperforms the long futures contract, but the difference is only about twenty cents in this case. Twenty cents on a thousand assets or even hundreds of thousands of assets is a lot of money that could be made. The put option outperforms the short futures contract by over a dollar in every model. Figure seven σ = 0.1 Geometric Browning Motion GBM W/ Heston Model Heston W/ payoff Call Option Long Futures Put Option Short Futures Conclusion
7 Options and futures contracts have been used to ensure a price of an asset for many years. They both can be used to ensure the price to be paid for the asset, or for the price to be received for an asset. They each have a different type of payoff which makes it possible to lose or win at the end of the contract. No one can know which one of these contracts will give the best result in any given time period, but one can look to see which does the best on average. The results in this paper lead to the idea that, on average, options will outperform futures contracts. This is robust over different starting volatilities, from large 0.5 to small 0.1. This suggests those companies, farmers, or anyone that is looking to set a price for an asset they are going to buy or sell in the future should look to the options market rather than the futures market. Another benefit exclusive to options is to set a price that is far away from the current spot rate. Say a farmer doesn t care if the price of his commodity changes a little bit, but he won t be able to survive if the price drops below a certain level. He can buy a put option that has a strike at that level, and because it is a lot lower than the current spot rate it will not cost very much. Therefore, the farmer is protected against an extreme price drop. The reverse can also be done with a call option and an extreme price increase on an asset one needs to buy. References Black, Fischer, Myron Scholes (1973), The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liability, Journal of Political Economy, 81(3): Cox, J.c. and Ross, S.A. (1976), The Valuation of Options for Alternative Stochastic Processes, Journal of Financial Economics, 7(3): Heston, S.L. (1993), A Closed- Form Solution for Options with Stochastic Volatility with Application to Bond and Currency Options, The Review of Financial Studies, 6(3): Hull, J.C. and White, A. (1987), The Pricing of Options on Assets with Stochastic Volatilities, Journal of Finance, 43: Merton, R.C. (1973), Theory of Rational Option Pricing, Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science (The RAND Corperation), 4(1):
Caput Derivatives: October 30, 2003
 Caput Derivatives: October 30, 2003 Exam + Answers Total time: 2 hours and 30 minutes. Note 1: You are allowed to use books, course notes, and a calculator. Question 1. [20 points] Consider an investor
Caput Derivatives: October 30, 2003 Exam + Answers Total time: 2 hours and 30 minutes. Note 1: You are allowed to use books, course notes, and a calculator. Question 1. [20 points] Consider an investor
CS 522 Computational Tools and Methods in Finance Robert Jarrow Lecture 1: Equity Options
 CS 5 Computational Tools and Methods in Finance Robert Jarrow Lecture 1: Equity Options 1. Definitions Equity. The common stock of a corporation. Traded on organized exchanges (NYSE, AMEX, NASDAQ). A common
CS 5 Computational Tools and Methods in Finance Robert Jarrow Lecture 1: Equity Options 1. Definitions Equity. The common stock of a corporation. Traded on organized exchanges (NYSE, AMEX, NASDAQ). A common
第 9 讲 : 股 票 期 权 定 价 : B-S 模 型 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes Model
 1 第 9 讲 : 股 票 期 权 定 价 : B-S 模 型 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes Model Outline 有 关 股 价 的 假 设 The B-S Model 隐 性 波 动 性 Implied Volatility 红 利 与 期 权 定 价 Dividends and Option Pricing 美 式 期 权 定 价 American
1 第 9 讲 : 股 票 期 权 定 价 : B-S 模 型 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes Model Outline 有 关 股 价 的 假 设 The B-S Model 隐 性 波 动 性 Implied Volatility 红 利 与 期 权 定 价 Dividends and Option Pricing 美 式 期 权 定 价 American
Betting on Volatility: A Delta Hedging Approach. Liang Zhong
 Betting on Volatility: A Delta Hedging Approach Liang Zhong Department of Mathematics, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden April, 211 Abstract In the financial market, investors prefer to estimate the stock price
Betting on Volatility: A Delta Hedging Approach Liang Zhong Department of Mathematics, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden April, 211 Abstract In the financial market, investors prefer to estimate the stock price
Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes-Merton Model. Chapter 13
 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes-Merton Model Chapter 13 Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets, 8th Ed, Ch 13, Copyright John C. Hull 2013 1 The Black-Scholes-Merton Random Walk Assumption
Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes-Merton Model Chapter 13 Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets, 8th Ed, Ch 13, Copyright John C. Hull 2013 1 The Black-Scholes-Merton Random Walk Assumption
2. Exercising the option - buying or selling asset by using option. 3. Strike (or exercise) price - price at which asset may be bought or sold
 Chapter 21 : Options-1 CHAPTER 21. OPTIONS Contents I. INTRODUCTION BASIC TERMS II. VALUATION OF OPTIONS A. Minimum Values of Options B. Maximum Values of Options C. Determinants of Call Value D. Black-Scholes
Chapter 21 : Options-1 CHAPTER 21. OPTIONS Contents I. INTRODUCTION BASIC TERMS II. VALUATION OF OPTIONS A. Minimum Values of Options B. Maximum Values of Options C. Determinants of Call Value D. Black-Scholes
On Black-Scholes Equation, Black- Scholes Formula and Binary Option Price
 On Black-Scholes Equation, Black- Scholes Formula and Binary Option Price Abstract: Chi Gao 12/15/2013 I. Black-Scholes Equation is derived using two methods: (1) risk-neutral measure; (2) - hedge. II.
On Black-Scholes Equation, Black- Scholes Formula and Binary Option Price Abstract: Chi Gao 12/15/2013 I. Black-Scholes Equation is derived using two methods: (1) risk-neutral measure; (2) - hedge. II.
Black-Scholes Equation for Option Pricing
 Black-Scholes Equation for Option Pricing By Ivan Karmazin, Jiacong Li 1. Introduction In early 1970s, Black, Scholes and Merton achieved a major breakthrough in pricing of European stock options and there
Black-Scholes Equation for Option Pricing By Ivan Karmazin, Jiacong Li 1. Introduction In early 1970s, Black, Scholes and Merton achieved a major breakthrough in pricing of European stock options and there
A Comparison of Option Pricing Models
 A Comparison of Option Pricing Models Ekrem Kilic 11.01.2005 Abstract Modeling a nonlinear pay o generating instrument is a challenging work. The models that are commonly used for pricing derivative might
A Comparison of Option Pricing Models Ekrem Kilic 11.01.2005 Abstract Modeling a nonlinear pay o generating instrument is a challenging work. The models that are commonly used for pricing derivative might
OPTIONS and FUTURES Lecture 2: Binomial Option Pricing and Call Options
 OPTIONS and FUTURES Lecture 2: Binomial Option Pricing and Call Options Philip H. Dybvig Washington University in Saint Louis binomial model replicating portfolio single period artificial (risk-neutral)
OPTIONS and FUTURES Lecture 2: Binomial Option Pricing and Call Options Philip H. Dybvig Washington University in Saint Louis binomial model replicating portfolio single period artificial (risk-neutral)
Valuation of Asian Options
 Valuation of Asian Options - with Levy Approximation Master thesis in Economics Jan 2014 Author: Aleksandra Mraovic, Qian Zhang Supervisor: Frederik Lundtofte Department of Economics Abstract Asian options
Valuation of Asian Options - with Levy Approximation Master thesis in Economics Jan 2014 Author: Aleksandra Mraovic, Qian Zhang Supervisor: Frederik Lundtofte Department of Economics Abstract Asian options
Exam MFE Spring 2007 FINAL ANSWER KEY 1 B 2 A 3 C 4 E 5 D 6 C 7 E 8 C 9 A 10 B 11 D 12 A 13 E 14 E 15 C 16 D 17 B 18 A 19 D
 Exam MFE Spring 2007 FINAL ANSWER KEY Question # Answer 1 B 2 A 3 C 4 E 5 D 6 C 7 E 8 C 9 A 10 B 11 D 12 A 13 E 14 E 15 C 16 D 17 B 18 A 19 D **BEGINNING OF EXAMINATION** ACTUARIAL MODELS FINANCIAL ECONOMICS
Exam MFE Spring 2007 FINAL ANSWER KEY Question # Answer 1 B 2 A 3 C 4 E 5 D 6 C 7 E 8 C 9 A 10 B 11 D 12 A 13 E 14 E 15 C 16 D 17 B 18 A 19 D **BEGINNING OF EXAMINATION** ACTUARIAL MODELS FINANCIAL ECONOMICS
A Genetic Algorithm to Price an European Put Option Using the Geometric Mean Reverting Model
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol 8, 14, no 143, 715-7135 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/11988/ams144644 A Genetic Algorithm to Price an European Put Option Using the Geometric Mean Reverting
Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol 8, 14, no 143, 715-7135 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/11988/ams144644 A Genetic Algorithm to Price an European Put Option Using the Geometric Mean Reverting
Model-Free Boundaries of Option Time Value and Early Exercise Premium
 Model-Free Boundaries of Option Time Value and Early Exercise Premium Tie Su* Department of Finance University of Miami P.O. Box 248094 Coral Gables, FL 33124-6552 Phone: 305-284-1885 Fax: 305-284-4800
Model-Free Boundaries of Option Time Value and Early Exercise Premium Tie Su* Department of Finance University of Miami P.O. Box 248094 Coral Gables, FL 33124-6552 Phone: 305-284-1885 Fax: 305-284-4800
Moreover, under the risk neutral measure, it must be the case that (5) r t = µ t.
 LECTURE 7: BLACK SCHOLES THEORY 1. Introduction: The Black Scholes Model In 1973 Fisher Black and Myron Scholes ushered in the modern era of derivative securities with a seminal paper 1 on the pricing
LECTURE 7: BLACK SCHOLES THEORY 1. Introduction: The Black Scholes Model In 1973 Fisher Black and Myron Scholes ushered in the modern era of derivative securities with a seminal paper 1 on the pricing
Application of options in hedging of crude oil price risk
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SOCIAL AND MANAGEMEN SCIENCES ISSN rint: 156-154, ISSN Online: 151-1559 doi:1.551/ajsms.1.1.1.67.74 1, ScienceHuβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsms Application of options in hedging of crude
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SOCIAL AND MANAGEMEN SCIENCES ISSN rint: 156-154, ISSN Online: 151-1559 doi:1.551/ajsms.1.1.1.67.74 1, ScienceHuβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsms Application of options in hedging of crude
Lecture 4: The Black-Scholes model
 OPTIONS and FUTURES Lecture 4: The Black-Scholes model Philip H. Dybvig Washington University in Saint Louis Black-Scholes option pricing model Lognormal price process Call price Put price Using Black-Scholes
OPTIONS and FUTURES Lecture 4: The Black-Scholes model Philip H. Dybvig Washington University in Saint Louis Black-Scholes option pricing model Lognormal price process Call price Put price Using Black-Scholes
American and European. Put Option
 American and European Put Option Analytical Finance I Kinda Sumlaji 1 Table of Contents: 1. Introduction... 3 2. Option Style... 4 3. Put Option 4 3.1 Definition 4 3.2 Payoff at Maturity... 4 3.3 Example
American and European Put Option Analytical Finance I Kinda Sumlaji 1 Table of Contents: 1. Introduction... 3 2. Option Style... 4 3. Put Option 4 3.1 Definition 4 3.2 Payoff at Maturity... 4 3.3 Example
FIN 411 -- Investments Option Pricing. Options: Definitions. Arbitrage Restrictions on Call Prices. Arbitrage Restrictions on Call Prices
 FIN 411 -- Investments Option Pricing imple arbitrage relations s to call options Black-choles model Put-Call Parity Implied Volatility Options: Definitions A call option gives the buyer the right, but
FIN 411 -- Investments Option Pricing imple arbitrage relations s to call options Black-choles model Put-Call Parity Implied Volatility Options: Definitions A call option gives the buyer the right, but
The Intuition Behind Option Valuation: A Teaching Note
 The Intuition Behind Option Valuation: A Teaching Note Thomas Grossman Haskayne School of Business University of Calgary Steve Powell Tuck School of Business Dartmouth College Kent L Womack Tuck School
The Intuition Behind Option Valuation: A Teaching Note Thomas Grossman Haskayne School of Business University of Calgary Steve Powell Tuck School of Business Dartmouth College Kent L Womack Tuck School
Review of Basic Options Concepts and Terminology
 Review of Basic Options Concepts and Terminology March 24, 2005 1 Introduction The purchase of an options contract gives the buyer the right to buy call options contract or sell put options contract some
Review of Basic Options Concepts and Terminology March 24, 2005 1 Introduction The purchase of an options contract gives the buyer the right to buy call options contract or sell put options contract some
Session X: Lecturer: Dr. Jose Olmo. Module: Economics of Financial Markets. MSc. Financial Economics. Department of Economics, City University, London
 Session X: Options: Hedging, Insurance and Trading Strategies Lecturer: Dr. Jose Olmo Module: Economics of Financial Markets MSc. Financial Economics Department of Economics, City University, London Option
Session X: Options: Hedging, Insurance and Trading Strategies Lecturer: Dr. Jose Olmo Module: Economics of Financial Markets MSc. Financial Economics Department of Economics, City University, London Option
DETERMINING THE VALUE OF EMPLOYEE STOCK OPTIONS. Report Produced for the Ontario Teachers Pension Plan John Hull and Alan White August 2002
 DETERMINING THE VALUE OF EMPLOYEE STOCK OPTIONS 1. Background Report Produced for the Ontario Teachers Pension Plan John Hull and Alan White August 2002 It is now becoming increasingly accepted that companies
DETERMINING THE VALUE OF EMPLOYEE STOCK OPTIONS 1. Background Report Produced for the Ontario Teachers Pension Plan John Hull and Alan White August 2002 It is now becoming increasingly accepted that companies
Lecture Notes: Basic Concepts in Option Pricing - The Black and Scholes Model
 Brunel University Msc., EC5504, Financial Engineering Prof Menelaos Karanasos Lecture Notes: Basic Concepts in Option Pricing - The Black and Scholes Model Recall that the price of an option is equal to
Brunel University Msc., EC5504, Financial Engineering Prof Menelaos Karanasos Lecture Notes: Basic Concepts in Option Pricing - The Black and Scholes Model Recall that the price of an option is equal to
Option Portfolio Modeling
 Value of Option (Total=Intrinsic+Time Euro) Option Portfolio Modeling Harry van Breen www.besttheindex.com E-mail: h.j.vanbreen@besttheindex.com Introduction The goal of this white paper is to provide
Value of Option (Total=Intrinsic+Time Euro) Option Portfolio Modeling Harry van Breen www.besttheindex.com E-mail: h.j.vanbreen@besttheindex.com Introduction The goal of this white paper is to provide
Jung-Soon Hyun and Young-Hee Kim
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 43 (2006), No. 4, pp. 845 858 TWO APPROACHES FOR STOCHASTIC INTEREST RATE OPTION MODEL Jung-Soon Hyun and Young-Hee Kim Abstract. We present two approaches of the stochastic interest
J. Korean Math. Soc. 43 (2006), No. 4, pp. 845 858 TWO APPROACHES FOR STOCHASTIC INTEREST RATE OPTION MODEL Jung-Soon Hyun and Young-Hee Kim Abstract. We present two approaches of the stochastic interest
2 Stock Price. Figure S1.1 Profit from long position in Problem 1.13
 Problem 1.11. A cattle farmer expects to have 12, pounds of live cattle to sell in three months. The livecattle futures contract on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange is for the delivery of 4, pounds of cattle.
Problem 1.11. A cattle farmer expects to have 12, pounds of live cattle to sell in three months. The livecattle futures contract on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange is for the delivery of 4, pounds of cattle.
Call Price as a Function of the Stock Price
 Call Price as a Function of the Stock Price Intuitively, the call price should be an increasing function of the stock price. This relationship allows one to develop a theory of option pricing, derived
Call Price as a Function of the Stock Price Intuitively, the call price should be an increasing function of the stock price. This relationship allows one to develop a theory of option pricing, derived
BINOMIAL OPTIONS PRICING MODEL. Mark Ioffe. Abstract
 BINOMIAL OPTIONS PRICING MODEL Mark Ioffe Abstract Binomial option pricing model is a widespread numerical method of calculating price of American options. In terms of applied mathematics this is simple
BINOMIAL OPTIONS PRICING MODEL Mark Ioffe Abstract Binomial option pricing model is a widespread numerical method of calculating price of American options. In terms of applied mathematics this is simple
CHAPTER 5 OPTION PRICING THEORY AND MODELS
 1 CHAPTER 5 OPTION PRICING THEORY AND MODELS In general, the value of any asset is the present value of the expected cash flows on that asset. In this section, we will consider an exception to that rule
1 CHAPTER 5 OPTION PRICING THEORY AND MODELS In general, the value of any asset is the present value of the expected cash flows on that asset. In this section, we will consider an exception to that rule
Monte Carlo simulations and option pricing
 Monte Carlo simulations and option pricing by Bingqian Lu Undergraduate Mathematics Department Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA 16802 Project Supervisor: Professor Anna Mazzucato July,
Monte Carlo simulations and option pricing by Bingqian Lu Undergraduate Mathematics Department Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA 16802 Project Supervisor: Professor Anna Mazzucato July,
Monte Carlo Simulation
 Monte Carlo Simulation Palisade User Conference 2007 Real Options Analysis Dr. Colin Beardsley, Managing Director Risk-Return Solutions Pty Limited www.riskreturnsolutions.com The Plot Today We will review
Monte Carlo Simulation Palisade User Conference 2007 Real Options Analysis Dr. Colin Beardsley, Managing Director Risk-Return Solutions Pty Limited www.riskreturnsolutions.com The Plot Today We will review
One Period Binomial Model
 FIN-40008 FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS SPRING 2008 One Period Binomial Model These notes consider the one period binomial model to exactly price an option. We will consider three different methods of pricing
FIN-40008 FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS SPRING 2008 One Period Binomial Model These notes consider the one period binomial model to exactly price an option. We will consider three different methods of pricing
Return to Risk Limited website: www.risklimited.com. Overview of Options An Introduction
 Return to Risk Limited website: www.risklimited.com Overview of Options An Introduction Options Definition The right, but not the obligation, to enter into a transaction [buy or sell] at a pre-agreed price,
Return to Risk Limited website: www.risklimited.com Overview of Options An Introduction Options Definition The right, but not the obligation, to enter into a transaction [buy or sell] at a pre-agreed price,
The interest volatility surface
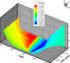 The interest volatility surface David Kohlberg Kandidatuppsats i matematisk statistik Bachelor Thesis in Mathematical Statistics Kandidatuppsats 2011:7 Matematisk statistik Juni 2011 www.math.su.se Matematisk
The interest volatility surface David Kohlberg Kandidatuppsats i matematisk statistik Bachelor Thesis in Mathematical Statistics Kandidatuppsats 2011:7 Matematisk statistik Juni 2011 www.math.su.se Matematisk
The Valuation of Currency Options
 The Valuation of Currency Options Nahum Biger and John Hull Both Nahum Biger and John Hull are Associate Professors of Finance in the Faculty of Administrative Studies, York University, Canada. Introduction
The Valuation of Currency Options Nahum Biger and John Hull Both Nahum Biger and John Hull are Associate Professors of Finance in the Faculty of Administrative Studies, York University, Canada. Introduction
Lecture 4: Futures and Options Steven Skiena. http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena
 Lecture 4: Futures and Options Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena Foreign Currency Futures Assume that
Lecture 4: Futures and Options Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena Foreign Currency Futures Assume that
Assessing Credit Risk for a Ghanaian Bank Using the Black- Scholes Model
 Assessing Credit Risk for a Ghanaian Bank Using the Black- Scholes Model VK Dedu 1, FT Oduro 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana. Abstract
Assessing Credit Risk for a Ghanaian Bank Using the Black- Scholes Model VK Dedu 1, FT Oduro 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana. Abstract
The Behavior of Bonds and Interest Rates. An Impossible Bond Pricing Model. 780 w Interest Rate Models
 780 w Interest Rate Models The Behavior of Bonds and Interest Rates Before discussing how a bond market-maker would delta-hedge, we first need to specify how bonds behave. Suppose we try to model a zero-coupon
780 w Interest Rate Models The Behavior of Bonds and Interest Rates Before discussing how a bond market-maker would delta-hedge, we first need to specify how bonds behave. Suppose we try to model a zero-coupon
Research on Option Trading Strategies
 Research on Option Trading Strategies An Interactive Qualifying Project Report: Submitted to the Faculty of the WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree
Research on Option Trading Strategies An Interactive Qualifying Project Report: Submitted to the Faculty of the WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree
Valuation of Razorback Executive Stock Options: A Simulation Approach
 Valuation of Razorback Executive Stock Options: A Simulation Approach Joe Cheung Charles J. Corrado Department of Accounting & Finance The University of Auckland Private Bag 92019 Auckland, New Zealand.
Valuation of Razorback Executive Stock Options: A Simulation Approach Joe Cheung Charles J. Corrado Department of Accounting & Finance The University of Auckland Private Bag 92019 Auckland, New Zealand.
The Black-Scholes Formula
 FIN-40008 FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS SPRING 2008 The Black-Scholes Formula These notes examine the Black-Scholes formula for European options. The Black-Scholes formula are complex as they are based on the
FIN-40008 FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS SPRING 2008 The Black-Scholes Formula These notes examine the Black-Scholes formula for European options. The Black-Scholes formula are complex as they are based on the
Valuing equity-based payments
 E Valuing equity-based payments Executive remuneration packages generally comprise many components. While it is relatively easy to identify how much will be paid in a base salary a fixed dollar amount
E Valuing equity-based payments Executive remuneration packages generally comprise many components. While it is relatively easy to identify how much will be paid in a base salary a fixed dollar amount
Pricing complex options using a simple Monte Carlo Simulation
 A subsidiary of Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation Pricing complex options using a simple Monte Carlo Simulation Peter Fink Among the different numerical procedures for valuing options, the Monte Carlo
A subsidiary of Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation Pricing complex options using a simple Monte Carlo Simulation Peter Fink Among the different numerical procedures for valuing options, the Monte Carlo
Forward Price. The payoff of a forward contract at maturity is S T X. Forward contracts do not involve any initial cash flow.
 Forward Price The payoff of a forward contract at maturity is S T X. Forward contracts do not involve any initial cash flow. The forward price is the delivery price which makes the forward contract zero
Forward Price The payoff of a forward contract at maturity is S T X. Forward contracts do not involve any initial cash flow. The forward price is the delivery price which makes the forward contract zero
Monte-Carlo Option Pricing. Victor Podlozhnyuk vpodlozhnyuk@nvidia.com
 Monte-Carlo Option Pricing Victor Podlozhnyuk vpodlozhnyuk@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 1. 3//7 vpodlozhnyuk Initial release Abstract The pricing of options
Monte-Carlo Option Pricing Victor Podlozhnyuk vpodlozhnyuk@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 1. 3//7 vpodlozhnyuk Initial release Abstract The pricing of options
Pricing Interest-Rate- Derivative Securities
 Pricing Interest-Rate- Derivative Securities John Hull Alan White University of Toronto This article shows that the one-state-variable interest-rate models of Vasicek (1977) and Cox, Ingersoll, and Ross
Pricing Interest-Rate- Derivative Securities John Hull Alan White University of Toronto This article shows that the one-state-variable interest-rate models of Vasicek (1977) and Cox, Ingersoll, and Ross
15.401 Finance Theory
 Finance Theory MIT Sloan MBA Program Andrew W. Lo Harris & Harris Group Professor, MIT Sloan School Lectures 10 11 11: : Options Critical Concepts Motivation Payoff Diagrams Payoff Tables Option Strategies
Finance Theory MIT Sloan MBA Program Andrew W. Lo Harris & Harris Group Professor, MIT Sloan School Lectures 10 11 11: : Options Critical Concepts Motivation Payoff Diagrams Payoff Tables Option Strategies
Binomial lattice model for stock prices
 Copyright c 2007 by Karl Sigman Binomial lattice model for stock prices Here we model the price of a stock in discrete time by a Markov chain of the recursive form S n+ S n Y n+, n 0, where the {Y i }
Copyright c 2007 by Karl Sigman Binomial lattice model for stock prices Here we model the price of a stock in discrete time by a Markov chain of the recursive form S n+ S n Y n+, n 0, where the {Y i }
Jorge Cruz Lopez - Bus 316: Derivative Securities. Week 11. The Black-Scholes Model: Hull, Ch. 13.
 Week 11 The Black-Scholes Model: Hull, Ch. 13. 1 The Black-Scholes Model Objective: To show how the Black-Scholes formula is derived and how it can be used to value options. 2 The Black-Scholes Model 1.
Week 11 The Black-Scholes Model: Hull, Ch. 13. 1 The Black-Scholes Model Objective: To show how the Black-Scholes formula is derived and how it can be used to value options. 2 The Black-Scholes Model 1.
Pricing Barrier Option Using Finite Difference Method and MonteCarlo Simulation
 Pricing Barrier Option Using Finite Difference Method and MonteCarlo Simulation Yoon W. Kwon CIMS 1, Math. Finance Suzanne A. Lewis CIMS, Math. Finance May 9, 000 1 Courant Institue of Mathematical Science,
Pricing Barrier Option Using Finite Difference Method and MonteCarlo Simulation Yoon W. Kwon CIMS 1, Math. Finance Suzanne A. Lewis CIMS, Math. Finance May 9, 000 1 Courant Institue of Mathematical Science,
Walking Through Some Examples of Futures and Options Contracts Speculation and Hedging
 Walking Through Some Examples of Futures and Options Contracts Speculation and Hedging As Dr. Cogley said in class the other day, sometimes futures contracts and options are hard to wrap your head around
Walking Through Some Examples of Futures and Options Contracts Speculation and Hedging As Dr. Cogley said in class the other day, sometimes futures contracts and options are hard to wrap your head around
Lecture 12: The Black-Scholes Model Steven Skiena. http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena
 Lecture 12: The Black-Scholes Model Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena The Black-Scholes-Merton Model
Lecture 12: The Black-Scholes Model Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena The Black-Scholes-Merton Model
Options (1) Class 19 Financial Management, 15.414
 Options (1) Class 19 Financial Management, 15.414 Today Options Risk management: Why, how, and what? Option payoffs Reading Brealey and Myers, Chapter 2, 21 Sally Jameson 2 Types of questions Your company,
Options (1) Class 19 Financial Management, 15.414 Today Options Risk management: Why, how, and what? Option payoffs Reading Brealey and Myers, Chapter 2, 21 Sally Jameson 2 Types of questions Your company,
Merton-Black-Scholes model for option pricing. Peter Denteneer. 22 oktober 2009
 Merton-Black-Scholes model for option pricing Instituut{Lorentz voor Theoretische Natuurkunde, LION, Universiteit Leiden 22 oktober 2009 With inspiration from: J. Tinbergen, T.C. Koopmans, E. Majorana,
Merton-Black-Scholes model for option pricing Instituut{Lorentz voor Theoretische Natuurkunde, LION, Universiteit Leiden 22 oktober 2009 With inspiration from: J. Tinbergen, T.C. Koopmans, E. Majorana,
Hedging Variable Annuity Guarantees
 p. 1/4 Hedging Variable Annuity Guarantees Actuarial Society of Hong Kong Hong Kong, July 30 Phelim P Boyle Wilfrid Laurier University Thanks to Yan Liu and Adam Kolkiewicz for useful discussions. p. 2/4
p. 1/4 Hedging Variable Annuity Guarantees Actuarial Society of Hong Kong Hong Kong, July 30 Phelim P Boyle Wilfrid Laurier University Thanks to Yan Liu and Adam Kolkiewicz for useful discussions. p. 2/4
Valuation of Lease Contracts In Continuous Time With Stochastic Asset Values
 Valuation of Lease Contracts In Continuous Time With Stochastic Asset Values Riaz Hussain *+ * The University of Scranton Abstract A lease is a derivative security the value of which depends upon the value
Valuation of Lease Contracts In Continuous Time With Stochastic Asset Values Riaz Hussain *+ * The University of Scranton Abstract A lease is a derivative security the value of which depends upon the value
Schonbucher Chapter 9: Firm Value and Share Priced-Based Models Updated 07-30-2007
 Schonbucher Chapter 9: Firm alue and Share Priced-Based Models Updated 07-30-2007 (References sited are listed in the book s bibliography, except Miller 1988) For Intensity and spread-based models of default
Schonbucher Chapter 9: Firm alue and Share Priced-Based Models Updated 07-30-2007 (References sited are listed in the book s bibliography, except Miller 1988) For Intensity and spread-based models of default
Monte Carlo Methods in Finance
 Author: Yiyang Yang Advisor: Pr. Xiaolin Li, Pr. Zari Rachev Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics State University of New York at Stony Brook October 2, 2012 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction
Author: Yiyang Yang Advisor: Pr. Xiaolin Li, Pr. Zari Rachev Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics State University of New York at Stony Brook October 2, 2012 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction
1 The Black-Scholes Formula
 1 The Black-Scholes Formula In 1973 Fischer Black and Myron Scholes published a formula - the Black-Scholes formula - for computing the theoretical price of a European call option on a stock. Their paper,
1 The Black-Scholes Formula In 1973 Fischer Black and Myron Scholes published a formula - the Black-Scholes formula - for computing the theoretical price of a European call option on a stock. Their paper,
LIBRARY OF THE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 LIBRARY OF THE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Digitized by the Internet Archive in 2011 with funding from Boston Library Consortium IVIember Libraries http://www.archive.org/details/calloptionpricinoofisc
LIBRARY OF THE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Digitized by the Internet Archive in 2011 with funding from Boston Library Consortium IVIember Libraries http://www.archive.org/details/calloptionpricinoofisc
Compare and Contrast of Option Decay Functions. Nick Rettig and Carl Zulauf *,**
 Compare and Contrast of Option Decay Functions Nick Rettig and Carl Zulauf *,** * Undergraduate Student (rettig.55@osu.edu) and Professor (zulauf.1@osu.edu) Department of Agricultural, Environmental, and
Compare and Contrast of Option Decay Functions Nick Rettig and Carl Zulauf *,** * Undergraduate Student (rettig.55@osu.edu) and Professor (zulauf.1@osu.edu) Department of Agricultural, Environmental, and
Option pricing. Vinod Kothari
 Option pricing Vinod Kothari Notation we use this Chapter will be as follows: S o : Price of the share at time 0 S T : Price of the share at time T T : time to maturity of the option r : risk free rate
Option pricing Vinod Kothari Notation we use this Chapter will be as follows: S o : Price of the share at time 0 S T : Price of the share at time T T : time to maturity of the option r : risk free rate
The Fair Valuation of Life Insurance Participating Policies: The Mortality Risk Role
 The Fair Valuation of Life Insurance Participating Policies: The Mortality Risk Role Massimiliano Politano Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Naples Federico II Via Cinthia, Monte S.Angelo
The Fair Valuation of Life Insurance Participating Policies: The Mortality Risk Role Massimiliano Politano Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Naples Federico II Via Cinthia, Monte S.Angelo
Black-Scholes-Merton approach merits and shortcomings
 Black-Scholes-Merton approach merits and shortcomings Emilia Matei 1005056 EC372 Term Paper. Topic 3 1. Introduction The Black-Scholes and Merton method of modelling derivatives prices was first introduced
Black-Scholes-Merton approach merits and shortcomings Emilia Matei 1005056 EC372 Term Paper. Topic 3 1. Introduction The Black-Scholes and Merton method of modelling derivatives prices was first introduced
Likewise, the payoff of the better-of-two note may be decomposed as follows: Price of gold (US$/oz) 375 400 425 450 475 500 525 550 575 600 Oil price
 Exchange Options Consider the Double Index Bull (DIB) note, which is suited to investors who believe that two indices will rally over a given term. The note typically pays no coupons and has a redemption
Exchange Options Consider the Double Index Bull (DIB) note, which is suited to investors who believe that two indices will rally over a given term. The note typically pays no coupons and has a redemption
Article from: Risk Management. June 2009 Issue 16
 Article from: Risk Management June 2009 Issue 16 CHAIRSPERSON S Risk quantification CORNER Structural Credit Risk Modeling: Merton and Beyond By Yu Wang The past two years have seen global financial markets
Article from: Risk Management June 2009 Issue 16 CHAIRSPERSON S Risk quantification CORNER Structural Credit Risk Modeling: Merton and Beyond By Yu Wang The past two years have seen global financial markets
A SNOWBALL CURRENCY OPTION
 J. KSIAM Vol.15, No.1, 31 41, 011 A SNOWBALL CURRENCY OPTION GYOOCHEOL SHIM 1 1 GRADUATE DEPARTMENT OF FINANCIAL ENGINEERING, AJOU UNIVERSITY, SOUTH KOREA E-mail address: gshim@ajou.ac.kr ABSTRACT. I introduce
J. KSIAM Vol.15, No.1, 31 41, 011 A SNOWBALL CURRENCY OPTION GYOOCHEOL SHIM 1 1 GRADUATE DEPARTMENT OF FINANCIAL ENGINEERING, AJOU UNIVERSITY, SOUTH KOREA E-mail address: gshim@ajou.ac.kr ABSTRACT. I introduce
where N is the standard normal distribution function,
 The Black-Scholes-Merton formula (Hull 13.5 13.8) Assume S t is a geometric Brownian motion w/drift. Want market value at t = 0 of call option. European call option with expiration at time T. Payout at
The Black-Scholes-Merton formula (Hull 13.5 13.8) Assume S t is a geometric Brownian motion w/drift. Want market value at t = 0 of call option. European call option with expiration at time T. Payout at
TABLE OF CONTENTS. A. Put-Call Parity 1 B. Comparing Options with Respect to Style, Maturity, and Strike 13
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. McDonald 9: "Parity and Other Option Relationships" A. Put-Call Parity 1 B. Comparing Options with Respect to Style, Maturity, and Strike 13 2. McDonald 10: "Binomial Option Pricing:
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. McDonald 9: "Parity and Other Option Relationships" A. Put-Call Parity 1 B. Comparing Options with Respect to Style, Maturity, and Strike 13 2. McDonald 10: "Binomial Option Pricing:
24. Pricing Fixed Income Derivatives. through Black s Formula. MA6622, Ernesto Mordecki, CityU, HK, 2006. References for this Lecture:
 24. Pricing Fixed Income Derivatives through Black s Formula MA6622, Ernesto Mordecki, CityU, HK, 2006. References for this Lecture: John C. Hull, Options, Futures & other Derivatives (Fourth Edition),
24. Pricing Fixed Income Derivatives through Black s Formula MA6622, Ernesto Mordecki, CityU, HK, 2006. References for this Lecture: John C. Hull, Options, Futures & other Derivatives (Fourth Edition),
The Evaluation of Barrier Option Prices Under Stochastic Volatility. BFS 2010 Hilton, Toronto June 24, 2010
 The Evaluation of Barrier Option Prices Under Stochastic Volatility Carl Chiarella, Boda Kang and Gunter H. Meyer School of Finance and Economics University of Technology, Sydney School of Mathematics
The Evaluation of Barrier Option Prices Under Stochastic Volatility Carl Chiarella, Boda Kang and Gunter H. Meyer School of Finance and Economics University of Technology, Sydney School of Mathematics
Two-State Option Pricing
 Rendleman and Bartter [1] present a simple two-state model of option pricing. The states of the world evolve like the branches of a tree. Given the current state, there are two possible states next period.
Rendleman and Bartter [1] present a simple two-state model of option pricing. The states of the world evolve like the branches of a tree. Given the current state, there are two possible states next period.
Part V: Option Pricing Basics
 erivatives & Risk Management First Week: Part A: Option Fundamentals payoffs market microstructure Next 2 Weeks: Part B: Option Pricing fundamentals: intrinsic vs. time value, put-call parity introduction
erivatives & Risk Management First Week: Part A: Option Fundamentals payoffs market microstructure Next 2 Weeks: Part B: Option Pricing fundamentals: intrinsic vs. time value, put-call parity introduction
How to Value Employee Stock Options
 John Hull and Alan White One of the arguments often used against expensing employee stock options is that calculating their fair value at the time they are granted is very difficult. This article presents
John Hull and Alan White One of the arguments often used against expensing employee stock options is that calculating their fair value at the time they are granted is very difficult. This article presents
American Options. An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan. J. Robert Buchanan American Options
 American Options An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan 2010 Early Exercise Since American style options give the holder the same rights as European style options plus
American Options An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan 2010 Early Exercise Since American style options give the holder the same rights as European style options plus
Hedging Illiquid FX Options: An Empirical Analysis of Alternative Hedging Strategies
 Hedging Illiquid FX Options: An Empirical Analysis of Alternative Hedging Strategies Drazen Pesjak Supervised by A.A. Tsvetkov 1, D. Posthuma 2 and S.A. Borovkova 3 MSc. Thesis Finance HONOURS TRACK Quantitative
Hedging Illiquid FX Options: An Empirical Analysis of Alternative Hedging Strategies Drazen Pesjak Supervised by A.A. Tsvetkov 1, D. Posthuma 2 and S.A. Borovkova 3 MSc. Thesis Finance HONOURS TRACK Quantitative
Pricing Corn Calendar Spread Options. Juheon Seok and B. Wade Brorsen
 Pricing Corn Calendar Spread Options by Juheon Seok and B. Wade Brorsen Suggested citation format: Seok, J., and B. W. Brorsen. 215. Pricing Corn Calendar Spread Options. Proceedings of the NCCC-134 Conference
Pricing Corn Calendar Spread Options by Juheon Seok and B. Wade Brorsen Suggested citation format: Seok, J., and B. W. Brorsen. 215. Pricing Corn Calendar Spread Options. Proceedings of the NCCC-134 Conference
Assignment 2: Option Pricing and the Black-Scholes formula The University of British Columbia Science One CS 2015-2016 Instructor: Michael Gelbart
 Assignment 2: Option Pricing and the Black-Scholes formula The University of British Columbia Science One CS 2015-2016 Instructor: Michael Gelbart Overview Due Thursday, November 12th at 11:59pm Last updated
Assignment 2: Option Pricing and the Black-Scholes formula The University of British Columbia Science One CS 2015-2016 Instructor: Michael Gelbart Overview Due Thursday, November 12th at 11:59pm Last updated
Option Pricing. Chapter 11 Options on Futures. Stefan Ankirchner. University of Bonn. last update: 13/01/2014 at 14:25
 Option Pricing Chapter 11 Options on Futures Stefan Ankirchner University of Bonn last update: 13/01/2014 at 14:25 Stefan Ankirchner Option Pricing 1 Agenda Forward contracts Definition Determining forward
Option Pricing Chapter 11 Options on Futures Stefan Ankirchner University of Bonn last update: 13/01/2014 at 14:25 Stefan Ankirchner Option Pricing 1 Agenda Forward contracts Definition Determining forward
How To Price A Call Option
 Now by Itô s formula But Mu f and u g in Ū. Hence τ θ u(x) =E( Mu(X) ds + u(x(τ θ))) 0 τ θ u(x) E( f(x) ds + g(x(τ θ))) = J x (θ). 0 But since u(x) =J x (θ ), we consequently have u(x) =J x (θ ) = min
Now by Itô s formula But Mu f and u g in Ū. Hence τ θ u(x) =E( Mu(X) ds + u(x(τ θ))) 0 τ θ u(x) E( f(x) ds + g(x(τ θ))) = J x (θ). 0 But since u(x) =J x (θ ), we consequently have u(x) =J x (θ ) = min
Chapter 5 Financial Forwards and Futures
 Chapter 5 Financial Forwards and Futures Question 5.1. Four different ways to sell a share of stock that has a price S(0) at time 0. Question 5.2. Description Get Paid at Lose Ownership of Receive Payment
Chapter 5 Financial Forwards and Futures Question 5.1. Four different ways to sell a share of stock that has a price S(0) at time 0. Question 5.2. Description Get Paid at Lose Ownership of Receive Payment
Understanding N(d 1 ) and N(d 2 ): Risk-Adjusted Probabilities in the Black-Scholes Model 1
 Understanding N(d 1 ) and N(d 2 ): Risk-Adjusted Probabilities in the Black-Scholes Model 1 Lars Tyge Nielsen INSEAD Boulevard de Constance 77305 Fontainebleau Cedex France E-mail: nielsen@freiba51 October
Understanding N(d 1 ) and N(d 2 ): Risk-Adjusted Probabilities in the Black-Scholes Model 1 Lars Tyge Nielsen INSEAD Boulevard de Constance 77305 Fontainebleau Cedex France E-mail: nielsen@freiba51 October
Discussions of Monte Carlo Simulation in Option Pricing TIANYI SHI, Y LAURENT LIU PROF. RENATO FERES MATH 350 RESEARCH PAPER
 Discussions of Monte Carlo Simulation in Option Pricing TIANYI SHI, Y LAURENT LIU PROF. RENATO FERES MATH 350 RESEARCH PAPER INTRODUCTION Having been exposed to a variety of applications of Monte Carlo
Discussions of Monte Carlo Simulation in Option Pricing TIANYI SHI, Y LAURENT LIU PROF. RENATO FERES MATH 350 RESEARCH PAPER INTRODUCTION Having been exposed to a variety of applications of Monte Carlo
Consider a European call option maturing at time T
 Lecture 10: Multi-period Model Options Black-Scholes-Merton model Prof. Markus K. Brunnermeier 1 Binomial Option Pricing Consider a European call option maturing at time T with ihstrike K: C T =max(s T
Lecture 10: Multi-period Model Options Black-Scholes-Merton model Prof. Markus K. Brunnermeier 1 Binomial Option Pricing Consider a European call option maturing at time T with ihstrike K: C T =max(s T
Lecture 12. Options Strategies
 Lecture 12. Options Strategies Introduction to Options Strategies Options, Futures, Derivatives 10/15/07 back to start 1 Solutions Problem 6:23: Assume that a bank can borrow or lend money at the same
Lecture 12. Options Strategies Introduction to Options Strategies Options, Futures, Derivatives 10/15/07 back to start 1 Solutions Problem 6:23: Assume that a bank can borrow or lend money at the same
HPCFinance: New Thinking in Finance. Calculating Variable Annuity Liability Greeks Using Monte Carlo Simulation
 HPCFinance: New Thinking in Finance Calculating Variable Annuity Liability Greeks Using Monte Carlo Simulation Dr. Mark Cathcart, Standard Life February 14, 2014 0 / 58 Outline Outline of Presentation
HPCFinance: New Thinking in Finance Calculating Variable Annuity Liability Greeks Using Monte Carlo Simulation Dr. Mark Cathcart, Standard Life February 14, 2014 0 / 58 Outline Outline of Presentation
An Introduction to Exotic Options
 An Introduction to Exotic Options Jeff Casey Jeff Casey is entering his final semester of undergraduate studies at Ball State University. He is majoring in Financial Mathematics and has been a math tutor
An Introduction to Exotic Options Jeff Casey Jeff Casey is entering his final semester of undergraduate studies at Ball State University. He is majoring in Financial Mathematics and has been a math tutor
Terminology and Scripts: what you say will make a difference in your success
 Terminology and Scripts: what you say will make a difference in your success Terminology Matters! Here are just three simple terminology suggestions which can help you enhance your ability to make your
Terminology and Scripts: what you say will make a difference in your success Terminology Matters! Here are just three simple terminology suggestions which can help you enhance your ability to make your
THE BLACK-SCHOLES MODEL AND EXTENSIONS
 THE BLAC-SCHOLES MODEL AND EXTENSIONS EVAN TURNER Abstract. This paper will derive the Black-Scholes pricing model of a European option by calculating the expected value of the option. We will assume that
THE BLAC-SCHOLES MODEL AND EXTENSIONS EVAN TURNER Abstract. This paper will derive the Black-Scholes pricing model of a European option by calculating the expected value of the option. We will assume that
The Heston Model. Hui Gong, UCL http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/ ucahgon/ May 6, 2014
 Hui Gong, UCL http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/ ucahgon/ May 6, 2014 Generalized SV models Vanilla Call Option via Heston Itô s lemma for variance process Euler-Maruyama scheme Implement in Excel&VBA 1.
Hui Gong, UCL http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/ ucahgon/ May 6, 2014 Generalized SV models Vanilla Call Option via Heston Itô s lemma for variance process Euler-Maruyama scheme Implement in Excel&VBA 1.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Los Angeles. A Monte Carlo Approach to Pricing An Exotic Currency Derivative Structure
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Los Angeles A Monte Carlo Approach to Pricing An Exotic Currency Derivative Structure A thesis submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Master of
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Los Angeles A Monte Carlo Approach to Pricing An Exotic Currency Derivative Structure A thesis submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Master of
The Black-Scholes pricing formulas
 The Black-Scholes pricing formulas Moty Katzman September 19, 2014 The Black-Scholes differential equation Aim: Find a formula for the price of European options on stock. Lemma 6.1: Assume that a stock
The Black-Scholes pricing formulas Moty Katzman September 19, 2014 The Black-Scholes differential equation Aim: Find a formula for the price of European options on stock. Lemma 6.1: Assume that a stock
Black Scholes Merton Approach To Modelling Financial Derivatives Prices Tomas Sinkariovas 0802869. Words: 3441
 Black Scholes Merton Approach To Modelling Financial Derivatives Prices Tomas Sinkariovas 0802869 Words: 3441 1 1. Introduction In this paper I present Black, Scholes (1973) and Merton (1973) (BSM) general
Black Scholes Merton Approach To Modelling Financial Derivatives Prices Tomas Sinkariovas 0802869 Words: 3441 1 1. Introduction In this paper I present Black, Scholes (1973) and Merton (1973) (BSM) general
FINANCIAL ECONOMICS OPTION PRICING
 OPTION PRICING Options are contingency contracts that specify payoffs if stock prices reach specified levels. A call option is the right to buy a stock at a specified price, X, called the strike price.
OPTION PRICING Options are contingency contracts that specify payoffs if stock prices reach specified levels. A call option is the right to buy a stock at a specified price, X, called the strike price.
Untangling F9 terminology
 Untangling F9 terminology Welcome! This is not a textbook and we are certainly not trying to replace yours! However, we do know that some students find some of the terminology used in F9 difficult to understand.
Untangling F9 terminology Welcome! This is not a textbook and we are certainly not trying to replace yours! However, we do know that some students find some of the terminology used in F9 difficult to understand.
How To Price Garch
 2011 3rd International Conference on Information and Financial Engineering IPEDR vol.12 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Study on Heston-Nandi GARCH Option Pricing Model Suk Joon Byun KAIST Business
2011 3rd International Conference on Information and Financial Engineering IPEDR vol.12 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Study on Heston-Nandi GARCH Option Pricing Model Suk Joon Byun KAIST Business
Currency-Linked-Notes
 Department of Business Studies Author: Master Thesis Jesper Bo Jensen Advisor: Peter Løchte Jørgensen Currency-Linked-Notes An analysis of products issued on the Danish market in 2009 and 2010 Aarhus School
Department of Business Studies Author: Master Thesis Jesper Bo Jensen Advisor: Peter Løchte Jørgensen Currency-Linked-Notes An analysis of products issued on the Danish market in 2009 and 2010 Aarhus School
CORPORATE VALUATIONS AND THE MERTON MODEL
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI ROMA TRE DIPARTIMENTO DI ECONOMIA CORPORATE VALUATIONS AND THE MERTON MODEL Andrea Gheno Working Paper n 55, 2005 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI ROMA TRE DIPARTIMENTO DI ECONOMIA Working
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI ROMA TRE DIPARTIMENTO DI ECONOMIA CORPORATE VALUATIONS AND THE MERTON MODEL Andrea Gheno Working Paper n 55, 2005 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI ROMA TRE DIPARTIMENTO DI ECONOMIA Working
