Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Guidance to Patients with Primary Immune Deficiencies
|
|
|
- Blaze Hines
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Guidance to Patients with Primary Immune Deficiencies Frank R. DeLeo, Ph.D. 1 and Harry L. Malech, MD 2 1 Laboratory of Human Bacterial Pathogens, Rocky Mountain Laboratories, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Hamilton, MT 2 Laboratory of Host Defenses, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD This work by Frank R. DeLeo, Ph.D. and Harry L. Malech, M.D. was supported by the intramural program of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, DHHS. Lay Language Discussion Background Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, often referred to as MRSA, has become a significant infection problem both in hospitals and in the general community. It is a type of staph that is resistant to methicillin and other commonly used antibiotics in the same class, including penicillin, amoxicillin, and oxacillin. While MRSA is of concern to everyone, patients with a variety of primary immune deficiencies (PID) may be at increased risk for at least three important reasons. First, depending on the kind of PID, some patients may be less capable of defending against infection with either regular Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) or with MRSA. Second, patients with PID in frequent contact with hospitals and other general health care institutions may have a somewhat increased risk of coming in contact with other individuals who are carriers of, or infected with, S. aureus including the MRSA variety. Third, patients with some forms of PID may have eczema or other skin conditions which enhance the tendency to become colonized with S. aureus including the MRSA variety Understanding MRSA To understand the significance of MRSA, it is necessary to know some general information about all S. aureus. Regular everyday S. aureus has been a cause of severe infections in humans for thousands of years. It is a very ancient and durable human pathogen. Even in the antibiotic era of 1950 s to the present, S. aureus has remained a problem and a concern despite the increasing availability of many types of antibiotics that can effectively kill this bacterium. It is important to know that it is very common; in fact, it is the rare person who has not had a S. aureus boil or other infection. It is not unusual for perfectly healthy people to be colonized in their nose with S. aureus. These people comprise the most common source of the bacteria (including the MRSA varieties) in the community. S. aureus, including MRSA varieties, can survive and infect through inanimate damp objects such as dirty towels and shared sports equipment. However, it is most effectively and commonly spread though direct hand and other skin contact with these carriers, as well as by individuals who have actual infections.
2 The first isolated examples of MRSA were found in hospitals where they caused infections only in very debilitated surgical or hemodialysis patients. It was initially thought that these early hospital-associated MRSA strains were both antibiotic resistant and particularly infectious. However, studies in the past few years indicate that it is actually the community-associated MRSA strains, capable of easily infecting healthy individuals that are more infectious. These community-associated (CA) MRSA strains are very infectious and tissue destructive. They cause outbreaks in the general community of healthy individuals in schools, sports teams, gymnasiums and other settings where there is close physical contact. These CA-MRSA strains actually are genetically distinct from the strains causing infections in debilitated hospitalized patients, and appear to have unique genetic factors that allow them to more effectively infect, spread and cause injury in people with perfectly normal immune systems. This ability to easily infect, spread in the body and cause tissue damage is what is meant by saying an organism is more virulent. It is this greater virulence of these CA- MRSA strains that is the major problem causing the current epidemics and severe infections among otherwise healthy individuals. The antibiotic resistance makes it harder to treat and adds to a high level of anxiety, However, it is not the only concern and is not the main reason that CA-MRSA infections has caused epidemics in the schools, among sports teams, and in long term care institutions. Guidance for Patients with Primary Immune Deficiencies (PID) The concern about CA-MRSA in schools, day care centers, sports teams, and health care institutions affects everyone and not just patients with PID. In addition, health care institutions are experiencing problems not just with MRSA but with resistant and virulent strains of a number of other types of bacteria. This has led to increased diligence of hospital epidemiologists in isolating patients with suspect infections and increased training of physicians to be thinking about and recognizing potential problem bacterial infections. Recognition and treatment of health-care workers who may themselves be carriers of resistant bacteria has been improved, and training of physicians to liberally use germicidal hand washes and vigorous hand washing with soap and water has been amplified. Even for the general populace, early attention to boils and other skin infections, use of germicidal lotions, and frequent hand washing can do much to reduce the spread of S. aureus including MRSA strains. At schools and day care centers, and with sports teams, the sharing of personal items of clothing or equipment should be discouraged. Germicidal hand lotions should be available and encouraged, as should hand washing. Very hot water cycles and bleach should be used in the laundering of any shared towels or similar items. In busy, active institutions such as schools, it is neither practical, nor cost effective to have janitors disinfect doorknobs or multiple user desks though out the day. However, showers and sports changing areas are special places where frequent attention to cleanup and use of diluted bleach or other disinfectant may help reduce spread of MRSA. Institutions should make antiseptic cleanser gels more available in a variety of locations so that students use them routinely. Sinks should have pump soaps and not bar soaps available for hand washing. In general S. aureus is spread by contact-- it does not come from the floor or on dust to infect someone, but rather is spread through direct contact. It is usually contracted by hand contact, such as touching an infected individual or coming in contact with their personal items that they have recently used. Patients with PID (depending upon the specific type of PID) may be less capable of defending against infection with S. aureus including the MRSA strains. They may also have frequent contact with hospitals and other general health care institutions where they may be at increased
3 risk of coming in contact with other individuals who are carriers of, or infected with, S. aureus including the MRSA varieties. Patients with PID who have eczema or other skin conditions causing breaks allow for enhanced colonization and infection with S. aureus including the MRSA varieties. Nasal or skin carriage with S. aureus including MRSA varieties is so common in the general populations that generally it is impractical to do routine testing and treatment for carriers. However, in the case of patients with PID, particularly patients who are thought by their physicians to have a type of PID or associated skin condition that makes them more at risk from S. aureus, it may be cost effective to periodically test the patient for carriage. For young children with PID, it may even be reasonable to periodically test their primary care givers to see if they are carriers of S. aureus because of the frequent intimate contact between caregiver and child with PID. There are no studies that provide clear guidance with respect to this, but with some types of PID relationships have been observed between carriage and later infection with the same organism. Thus, treatment of or prevention of nasal carriage by use of nasal application of mupirocin ointment may be reasonable in some cases. On a case by case basis that must be determined by the patient s physician, it may be reasonable to consider treatment to try to eradicate S. aureus carriage in a PID patient or young child PID patient s primary caregiver. The parents of some children with PID have become concerned about even sending their children to school at all because of the new anxiety raised by the CA-MRSA epidemic. This is a complex decision that does not lend itself to a simple answer that will cover every situation. It should be emphasized that most children with a primary immunodeficiency disease are able to attend school safely. The exposure risk for all pathogens, not just CA-MRSA, is somewhat greater for children attending school than those who are home schooled and who also avoid all other contacts with groups of children. In some unusual special instances, home schooling, homebound and even dual enrollment options may be viable alternatives. However the social, psychological and learning benefits to the child enrolled in a general school environment must remain an important part of the equation when considering one s options. The child s physician can help in making this decision, but as a general rule, if children have no restrictions on being in public places, such as movies, malls, and airplanes, they should be able to safely attend school. If it has been determined that school is ordinarily a safe environment for a specific patient, it is usually not advisable to stop schooling because of the current CA-MRSA epidemic, but rather to take the additional precautions outlined above and continue to attend school. The option of requesting that the child be excused from participating in physical education (PE) classes might be considered depending on the type of activities scheduled for those classes. Scientific Language with References about MRSA S. aureus is the most frequent etiologic agent causing bloodstream, skin / soft tissue, and lower respiratory tract infections in the U.S., Canada, Latin America, Western Pacific, and Europe in a reviewed two year period from (Diekema et al., Clin Infect Dis, 2001, 32:S114). Remember that this data precedes the current epidemic of community-associated MRSA, emphasizing that it is S. aureus in general that is a problem, with the MRSA variety raising the additional issues that include the problem of antibiotic resistance. Otherwise healthy people who are colonized (mostly in the nose) with S. aureus are a source of the bacteria (including the MRSA varieties) in the community. In fact, a recent study demonstrated that approximately 20% of individuals in the general population are persistent S. aureus nasal carriers, 30% are intermittent carriers, and 50% non-carriers (Wertheim et al., Lancet Infect Dis, 2005, 5:751).
4 It is important to appreciate the distinction between virulence and antibiotic resistance. Much of the confusion in the general community and even by some physicians regarding understanding of MRSA arises from failure to appreciate that the virulence and antibiotic resistance characteristics of the bacteria are entirely separate traits that may differ significantly in different strains of S. aureus, including the MRSA varieties. Virulence refers to the ability of the bacteria to infect, to spread in the patient and to cause tissue damage. Antibiotic resistance with respect to MRSA refers to resistance to methicillin, oxacillin and some other related antibiotics that previously were very effective against regular S. aureus. Many healthcare-associated MRSA strains are multi-drug resistant, i.e., resistant to methicillin and a wide range of antibiotics unrelated to methicillin, including aminoglycosides, tetracycline, bleomycin, erythromycin and spectinomycin (Kuroda et al., Lancet. 2001, 357:1225 and Holden et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004, 101:9786). Although this is a problem for treatment, there still are several types of intravenous and oral antibiotics available that effectively can treat MRSA strains (vancomycin and linezolid, for example), but the bacteria s MRSA characteristic must be identified so a physician may choose the appropriate antibiotic. The best way to describe the situation is that among regular S. aureus bacteria and among the MRSA strains there are varieties that are modestly infectious, and epidemic strains that are highly virulent tending to be easily spread to others and causing severe infections even in otherwise healthy individuals. To summarize this important background and provide published references, these are the key points relating to healthcare-associated MRSA and community-associated MRSA: Features of healthcare-associated S. aureus infections (these are now primarily MRSA) Healthcare-associated S. aureus infections occur typically in individuals with risk factors for disease (e.g., surgery, hemodialysis). Methicillin resistance per se is not associated with virulence it is a problem for treatment. Clinically, MRSA and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) are indistinguishable (Miller et al., Clin Infect Dis, 2007, 44:471; Zahar et la., Clin Infect Dis, 2005, 41:1224). However, earlier reports did appear to link MRSA in hospitals with higher death rates (Melzer et al., Clin Infect Dis, 2003, 37: ). The proportion of S. aureus isolates that were MRSA in intensive care units (ICUs) increased from 35.9% in 1992 to 64.4% in 2003 (Klevens et al., Clin Infect Dis, 2006, 42:389). Hospital-associated infections are predominantly caused by strains designated by the genetic types known as USA100 & USA200 (MRSA252) (McDougal et al., J Clin Microbiol, 2003, 41: 5113). More recently another genetic strain known as USA300 has moved into hospitals from the community, and it has blurred the line of distinction between healthcare-associated and community-associated because as will be noted below it is actually a strain that has the high virulence characteristic of community-associated MRSA (see below). U.S. economic burden in hospitals in 2003 was $14.5 billion (Noskin et al., Clin Infect Dis, 2007, 45:1132) Incidence rate of all invasive MRSA infections is 31.3 per 100,000 persons. Approximately 20% (estimated 18,650 deaths out of 94,360 invasive infections) caused death (Klevens et al., JAMA, 2007, 298:1763)
5 Features of the recent community-associated (CA) methcillin resistant S. aureus infections (CA-MRSA) The first notable recognition of CA-MRSA in the U.S. was four pediatric deaths in the Midwest (CDC, JAMA, 1999, 282:1123) caused by a strain known as MW2 (pulsed-field gel electrophoresis type [PFGE] USA400). CA-MRSA is partly defined by the fact that it causes disease in otherwise healthy individuals in the community, and includes areas in which individuals are in close physical proximity (schools, daycare, athletic teams, prisons, etc). Infections with CA-MRSA are predominantly skin and soft tissue infections (~75%), but invasive disease when it occurs is severe and can lead to death. For example, CA-MRSA can cause necrotizing fasciitis (a type of flesh eating destruction of tissues) (Miller et al., NEJM, 2005, 352:14) or Waterhouse-Friderichsen Syndrome (a type of widespread shock and bleeding) (Adem et al., NEJM, 2005, 353:12). The most prevalent CA-MRSA genotypes are PFGE USA400 and USA300 (McDougal et al., J Clin Microbiol, 2003, 41: 5113). USA300 isolates now account for most of the community infections, up to 98% of all CA-MRSA infections (King et al., Ann Intern Med, 2006, 144:309 and Moran et al., NEJM, 2006, 355:7), and is the leading current cause of infections among patients coming in to emergency departments (Moran et al., NEJM, 2006, 355:7). As previously noted above this USA300 strain now has also appeared in hospitals, blurring the distinction between CA-MRSA and hospital-associated MRSA. It is more accurate and informative to refer to the specific strain/isolate causing the infection. Epidemic CA-MRSA strains USA300 and USA400 are highly virulent and typically have enhanced virulence (ability to infect and cause tissue destruction) compared with the prominent original hospital strains of MRSA (Voyich et al., J Immunol, 2005, 175:3907). The enhanced ability of CA-MRSA strains to circumvent killing by human blood neutrophils (by causing destruction of the blood neutrophils) is linked to the enhanced virulence of CA-MRSA (Voyich et al., J Immunol, 2005, 175:3907). It previously was thought that a protein produced by CA-MRSA called Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) was the cause of their high virulence, but it now appears not to be the cause of their high virulence (Voyich et al., J Infect Dis, 2006, 194:1761). Instead it appears that CA-MRSA produce small peptides that cause human blood neutrophils to burst open (a process call cell lysis), thereby explaining why CA-MRSA are so good at evading normal immune defenses and causing such severe infections and epidemics (Wang et al., Nat. Med., Nov 11, 2007, electronic publication ahead of print).
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED
 METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY. Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting
 EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
MRSA, Hand Hygiene and Contact Precautions
 MRSA, Hand Hygiene and Contact Precautions Wesley Medical Center Department of Education May 2007 Authors: Lois Rahal, RN, BSN, CIC Brandy Jackson, RN, BSN Hope Helferich, RNC, BSN 1 Objectives Upon completion
MRSA, Hand Hygiene and Contact Precautions Wesley Medical Center Department of Education May 2007 Authors: Lois Rahal, RN, BSN, CIC Brandy Jackson, RN, BSN Hope Helferich, RNC, BSN 1 Objectives Upon completion
Black Hills Healthcare System
 Black Hills Healthcare System Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcal Aureus (MRSA) Patient and Family Information What is MRSA? Staphylococcus Aureus, often referred to simply as staph, is a bacteria commonly
Black Hills Healthcare System Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcal Aureus (MRSA) Patient and Family Information What is MRSA? Staphylococcus Aureus, often referred to simply as staph, is a bacteria commonly
Pre-operative M.R.S.A. Screening Information for Patients
 Infection Prevention and Control Pre-operative M.R.S.A. Screening Information for Patients This information is designed for patients undergoing MRSA screening before coming into hospital for a planned
Infection Prevention and Control Pre-operative M.R.S.A. Screening Information for Patients This information is designed for patients undergoing MRSA screening before coming into hospital for a planned
Living healthy with MRSA
 Stamford Health System Having MRSA means what? Living healthy with MRSA Discharge information for patients and families WASHING YOUR HANDS IS THE KEY!!! Staph aureus is a bacteria that lives on your skin
Stamford Health System Having MRSA means what? Living healthy with MRSA Discharge information for patients and families WASHING YOUR HANDS IS THE KEY!!! Staph aureus is a bacteria that lives on your skin
Introduction to Infection Control
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
Protecting Myself from MRSA By Angela Ulferts RN, BSN
 Protecting Myself from MRSA By Angela Ulferts RN, BSN What is MRSA? MRSA stands for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. This is an infection that has been around for some time. But it has always
Protecting Myself from MRSA By Angela Ulferts RN, BSN What is MRSA? MRSA stands for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. This is an infection that has been around for some time. But it has always
Environmental Management of Staph and MRSA in Community Settings July 2008
 Page 1 of 7 Environmental Management of Staph and MRSA in Community Settings July 2008 Questions addressed on this page What are Staph and MRSA? How is Staph and MRSA spread? What is the role of the environment
Page 1 of 7 Environmental Management of Staph and MRSA in Community Settings July 2008 Questions addressed on this page What are Staph and MRSA? How is Staph and MRSA spread? What is the role of the environment
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital
 Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this leaflet provides information and advice for managing your day-to-day life. 1 About MRSA There are lots of different types or
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this leaflet provides information and advice for managing your day-to-day life. 1 About MRSA There are lots of different types or
VRE. Living with. Learning how to control the spread of Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE)
 VRE Living with Learning how to control the spread of Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) CONTENTS IMPORTANT VRE is a serious infection that may become life-threatening if left untreated. If you or
VRE Living with Learning how to control the spread of Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) CONTENTS IMPORTANT VRE is a serious infection that may become life-threatening if left untreated. If you or
Moving to a hospital or skilled nursing facility
 H Moving to a hospital or skilled nursing facility What to expect when you have MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) A booklet for patients, residents, family members, and caregivers About
H Moving to a hospital or skilled nursing facility What to expect when you have MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) A booklet for patients, residents, family members, and caregivers About
Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol
 Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol PURPOSE: To provide guidance for personnel in order to prevent the spread of Antibiotic Resistant Microorganisms
Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol PURPOSE: To provide guidance for personnel in order to prevent the spread of Antibiotic Resistant Microorganisms
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM
 ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
MRSA. Living with. Acknowledgements. (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
 How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
3.0 Treatment of Infection
 3.0 Treatment of Infection Antibiotics and Medicine National Curriculum Link SCN 3-13b SCN 3-20b HWB 3-15a HWB 3-16a HWB 3-17a Learning Outcomes All students will know: Most common infections will get
3.0 Treatment of Infection Antibiotics and Medicine National Curriculum Link SCN 3-13b SCN 3-20b HWB 3-15a HWB 3-16a HWB 3-17a Learning Outcomes All students will know: Most common infections will get
Living with MRSA. Things to remember about living with MRSA: This is really serious. I need to do something about this now!
 Things to remember about living with MRSA: 1. Wash your hands often. 2. Take care of yourself: Eat right, exercise, quit smoking, and avoid stress. 3. Take good care of your skin. 4. Keep skin infections
Things to remember about living with MRSA: 1. Wash your hands often. 2. Take care of yourself: Eat right, exercise, quit smoking, and avoid stress. 3. Take good care of your skin. 4. Keep skin infections
Learning About MRSA. 6 How is MRSA treated? 7 When should I seek medical care?
 IMPORTANT MRSA is a serious infection that can become life-threatening if left untreated. If you or someone in your family has been diagnosed with MRSA, there are steps you need to take now to avoid spreading
IMPORTANT MRSA is a serious infection that can become life-threatening if left untreated. If you or someone in your family has been diagnosed with MRSA, there are steps you need to take now to avoid spreading
Interim Guidelines for the Management of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Primary Care February 2006
 Table of Contents 1. Background... 2 2. Diagnosis... 2 3. Susceptibility Patterns of MRSA... 3 4. Management... 3 5. Decolonization of the Patient... 4 6. Prevention and Control... 5 7. Information for
Table of Contents 1. Background... 2 2. Diagnosis... 2 3. Susceptibility Patterns of MRSA... 3 4. Management... 3 5. Decolonization of the Patient... 4 6. Prevention and Control... 5 7. Information for
What Is. Norovirus? Learning how to control the spread of norovirus. Web Sites
 Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PVL ASSOCIATED STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS IN THE HOSPITAL ENVIRONMENT
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PVL ASSOCIATED STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS IN THE HOSPITAL ENVIRONMENT Post holder responsible for Policy: Directorate/Department responsible for Policy: Lead Nurse
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PVL ASSOCIATED STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS IN THE HOSPITAL ENVIRONMENT Post holder responsible for Policy: Directorate/Department responsible for Policy: Lead Nurse
Methicillin-resistant S taphylococcus
 Nevio Cimolai, MD, FRCPC Community-acquired MRSA infection: An emerging trend The use of culture as backup to empiric treatment of staphylococcal infection can help deal with widespread antibiotic resistance.
Nevio Cimolai, MD, FRCPC Community-acquired MRSA infection: An emerging trend The use of culture as backup to empiric treatment of staphylococcal infection can help deal with widespread antibiotic resistance.
MRSA Positive. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Tasmanian Rural Hospitals and Non Acute Health Settings
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Tasmanian Rural Hospitals and Non Acute Health Settings Guidance for the management of patients with MRSA in Tasmania's rural hospitals and non acute
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Tasmanian Rural Hospitals and Non Acute Health Settings Guidance for the management of patients with MRSA in Tasmania's rural hospitals and non acute
Kean University BS Degree Program in Athletic Training BLOOD BORN PATHOGENS POLICY
 Kean University BS Degree Program in Athletic Training BLOOD BORN PATHOGENS POLICY Effective September 2, 2014 The following policy will apply to students taking classes and faculty teaching those classes
Kean University BS Degree Program in Athletic Training BLOOD BORN PATHOGENS POLICY Effective September 2, 2014 The following policy will apply to students taking classes and faculty teaching those classes
DHS: SENIORS AND PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES DIVISION
 DHS: SENIORS AND PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES DIVISION Nurse to Nurse Oregon s community-based care nursing newsletter Winter 2009 Vol. 6 No. 1 Infection control Standard Precautions are measures used to protect
DHS: SENIORS AND PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES DIVISION Nurse to Nurse Oregon s community-based care nursing newsletter Winter 2009 Vol. 6 No. 1 Infection control Standard Precautions are measures used to protect
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
Clinic Infectious Disease Control
 Chapter 2 - Lesson 4 Clinic Infectious Disease Control Introduction Infectious and parasitic disease control is important in veterinary clinics. The main objective is to prevent the spread of infections
Chapter 2 - Lesson 4 Clinic Infectious Disease Control Introduction Infectious and parasitic disease control is important in veterinary clinics. The main objective is to prevent the spread of infections
Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips
 Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
 Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Patient information Service: Infection Control Team Divison: Intergrated Medical and Rehabiltitation Services Infectioncontrol@homerton.nhs.uk Telephone
Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Patient information Service: Infection Control Team Divison: Intergrated Medical and Rehabiltitation Services Infectioncontrol@homerton.nhs.uk Telephone
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey
 2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
Management of Communicable Diseases In a School Setting
 Maryland State Department of Education Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Management of Communicable
Maryland State Department of Education Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Management of Communicable
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
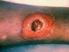 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
The Disease is a commonly diagnosed infectious disease that affects all equidae worldwide. Caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi (S.equi), this d
 ADVICE ON The Disease is a commonly diagnosed infectious disease that affects all equidae worldwide. Caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi (S.equi), this disease is highly contagious and is spread
ADVICE ON The Disease is a commonly diagnosed infectious disease that affects all equidae worldwide. Caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi (S.equi), this disease is highly contagious and is spread
Introduction. 1 Centres for Disease Control. Overview of healthcare related MRSA 2 Invasive Methicillin-Resistant Staphyloccus aureus
 An Alternative Approach in The Treatment of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), using Classical Homeopathy. Pierre Fontaine RSHom CCH. Introduction MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
An Alternative Approach in The Treatment of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), using Classical Homeopathy. Pierre Fontaine RSHom CCH. Introduction MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
Bacteria: The good, the bad, and the ugly. SEPA BioScience Montana Module 2
 Bacteria: The good, the bad, and the ugly. SEPA BioScience Montana Module 2 Introduction: The following reading will give you a basic introduction to bacteria and their role in illness. It will explore
Bacteria: The good, the bad, and the ugly. SEPA BioScience Montana Module 2 Introduction: The following reading will give you a basic introduction to bacteria and their role in illness. It will explore
Healthcare workers report that various factors contribute to poor compliance with hand hygiene. These include:
 RISKTOPICS Hand hygiene in the healthcare setting January 2013 Proper hand hygiene is the best way to keep from getting sick and prevent germs from being spread to others. For hospitals, nursing homes
RISKTOPICS Hand hygiene in the healthcare setting January 2013 Proper hand hygiene is the best way to keep from getting sick and prevent germs from being spread to others. For hospitals, nursing homes
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF CONTAGIOUS ILLNESS
 PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF CONTAGIOUS ILLNESS This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF CONTAGIOUS ILLNESS This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program
 Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Borderless Diseases By Sunny Thai
 Borderless Diseases By Sunny Thai Millennium Development Goal #6 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other borderless diseases. A. Halt and begin reversing spread of HIV by 2015. B. Achieve universal access
Borderless Diseases By Sunny Thai Millennium Development Goal #6 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other borderless diseases. A. Halt and begin reversing spread of HIV by 2015. B. Achieve universal access
Develop an understanding of the differential diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION
 JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
COMMON BACTERIAL SKIN INFECTIONS IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 COMMON BACTERIAL SKIN INFECTIONS IN GENERAL PRACTICE The two most common bacteria to cause skin infections are staphylococcus aureus (staph aureus ) and streptococcus pyogenes ( strep) (see Table 1). Staphylococcus
COMMON BACTERIAL SKIN INFECTIONS IN GENERAL PRACTICE The two most common bacteria to cause skin infections are staphylococcus aureus (staph aureus ) and streptococcus pyogenes ( strep) (see Table 1). Staphylococcus
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices
 Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I)
 ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Annual Report, Part I The annual
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Annual Report, Part I The annual
North Carolina Statewide Program for Infection Control and Prevention (SPICE) Objectives. Healthcare-Associated Infections: Impact
 North Carolina Statewide Program for Infection Control and Prevention (SPICE) Karen K. Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC, FSHEA U School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC Objectives Describe how and why SPICE was created.
North Carolina Statewide Program for Infection Control and Prevention (SPICE) Karen K. Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC, FSHEA U School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC Objectives Describe how and why SPICE was created.
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008
 Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu)
 Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu) The United States declared a public health emergency in response to the recent reports of swine flu. UMR wants to help you understand some important facts about H1N1
Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu) The United States declared a public health emergency in response to the recent reports of swine flu. UMR wants to help you understand some important facts about H1N1
The Legal Cost of Getting Infection Prevention and Control Wrong
 The Legal Cost of Getting Infection Prevention and Control Wrong Phil Barnes, Associate Anthony Collins LLP What Are Healthcare Associated Infections? Infections acquired as a consequence of receiving
The Legal Cost of Getting Infection Prevention and Control Wrong Phil Barnes, Associate Anthony Collins LLP What Are Healthcare Associated Infections? Infections acquired as a consequence of receiving
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Solid Organ Transplantation
 Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
MRSA Superbugs: What Every BODY Needs To Know!
 1 There s a new bug in town and not a good one. The antibiotic-resistant staph infection called MRSA has been increasing exponentially the last few years. While many times able to be treated on an outpatient
1 There s a new bug in town and not a good one. The antibiotic-resistant staph infection called MRSA has been increasing exponentially the last few years. While many times able to be treated on an outpatient
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital. If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life.
 Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life. Easy read This booklet is about a germ called MRSA. It is an Easy
Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life. Easy read This booklet is about a germ called MRSA. It is an Easy
33 Infection Control Techniques
 CHAPTER 33 Infection Control Techniques Learning Outcomes 33.1 Describe the medical assistant s role in infection control. 33.2 Describe methods of infection control. 33.3 Compare and contrast medical
CHAPTER 33 Infection Control Techniques Learning Outcomes 33.1 Describe the medical assistant s role in infection control. 33.2 Describe methods of infection control. 33.3 Compare and contrast medical
GUIDELINES TO PREVENT TRANSMISSION INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN SCHOOLS
 GUIDELINES TO PREVENT TRANSMISSION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN SCHOOLS May 1991 Precautions, Procedures and Instructions for Handling Body Fluids DUVAL COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...
GUIDELINES TO PREVENT TRANSMISSION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN SCHOOLS May 1991 Precautions, Procedures and Instructions for Handling Body Fluids DUVAL COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...
Yale New Haven Health System Center for Healthcare Solutions
 Table of Contents Education and Training Yale New Haven Health System Center for Healthcare Solutions 2009-2010 Fall/Winter Course Guide TOPICS center@ynhh.org www.yalenewhavenhealth.org/healthcaresolutions
Table of Contents Education and Training Yale New Haven Health System Center for Healthcare Solutions 2009-2010 Fall/Winter Course Guide TOPICS center@ynhh.org www.yalenewhavenhealth.org/healthcaresolutions
Information for patients and relatives
 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks MRSA Information for patients and relatives This leaflet explains how we treat infections with a bacterium called MRSA (meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). If
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks MRSA Information for patients and relatives This leaflet explains how we treat infections with a bacterium called MRSA (meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). If
Canine Influenza. What do I need to know?
 Canine Influenza What do I need to know? What is canine influenza? Canine influenza is a newly emerging infectious disease caused by a flu virus. In dogs, a highly contagious strain of the influenza A
Canine Influenza What do I need to know? What is canine influenza? Canine influenza is a newly emerging infectious disease caused by a flu virus. In dogs, a highly contagious strain of the influenza A
INFECTION CONTROL POLICY
 INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Infection control is the name given to a wide range of policies, procedures and techniques intended to prevent the spread of infectious diseases amongst staff and service users.
INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Infection control is the name given to a wide range of policies, procedures and techniques intended to prevent the spread of infectious diseases amongst staff and service users.
The Basics of Drug Resistance:
 CONTACT: Lisa Rossi +1-412-641-8940 +1-412- 916-3315 (mobile) rossil@upmc.edu The Basics of Drug Resistance: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS HIV Drug Resistance and ARV-Based Prevention 1. What is drug resistance?
CONTACT: Lisa Rossi +1-412-641-8940 +1-412- 916-3315 (mobile) rossil@upmc.edu The Basics of Drug Resistance: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS HIV Drug Resistance and ARV-Based Prevention 1. What is drug resistance?
Name Date Class. This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread.
 Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Immunization Healthcare Branch. Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers. Prepared by
 Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations
 GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education AQA SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a AQA BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a BLY1A (Human Biology) (Human Biology) FOUNDATION TIER Specimen Paper Time
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education AQA SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a AQA BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a BLY1A (Human Biology) (Human Biology) FOUNDATION TIER Specimen Paper Time
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General. The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England
 Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England HC 230 Session 1999-00 17 February 2000 Report by the Comptroller
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England HC 230 Session 1999-00 17 February 2000 Report by the Comptroller
Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe
 POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
 Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
How can you protect yourself from infections?
 How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
Blood Transfusion. There are three types of blood cells: Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets.
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
A review of the evidence for pathogenic contamination in the nonhospital. implications for infection transmission
 A review of the evidence for pathogenic contamination in the nonhospital environment and implications for infection transmission Elizabeth Scott Simmons College, Boston Simmons Center for Hygiene and Health
A review of the evidence for pathogenic contamination in the nonhospital environment and implications for infection transmission Elizabeth Scott Simmons College, Boston Simmons Center for Hygiene and Health
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org
 Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Infection Prevention
 Infection Prevention Dear HSS Patient: The Hospital for Special Surgery is committed to patient safety and quality patient care and is proud to have achieved one of the lowest infection rates in New York
Infection Prevention Dear HSS Patient: The Hospital for Special Surgery is committed to patient safety and quality patient care and is proud to have achieved one of the lowest infection rates in New York
NURSING SKILLS FAIR GAME QUESTIONS
 NURSING SKILLS FAIR GAME QUESTIONS FOR UNLICENSED NURSING STAFF The questions contained in this document are intended to be used during a long-term care facility (LTCF) nursing education or skills fair
NURSING SKILLS FAIR GAME QUESTIONS FOR UNLICENSED NURSING STAFF The questions contained in this document are intended to be used during a long-term care facility (LTCF) nursing education or skills fair
RSV infection. Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection.
 RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
Guidelines on Skin Infections Including Community Associated Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)
 Guidelines on Skin Infections Including Community Associated Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Erie County Department of Health (ECDOH) in collaboration with Erie 1 BOCES and Erie
Guidelines on Skin Infections Including Community Associated Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Erie County Department of Health (ECDOH) in collaboration with Erie 1 BOCES and Erie
Cholera / Response / 1. Response to an Epidemic of Cholera
 Cholera / Response / 1 Response to an Epidemic of Cholera Goal of Response Activities Reduce deaths good case management mobilizing staff and supplies increasing access to care Prevent new cases intensive
Cholera / Response / 1 Response to an Epidemic of Cholera Goal of Response Activities Reduce deaths good case management mobilizing staff and supplies increasing access to care Prevent new cases intensive
Management of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections
 Management of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections Federal Bureau of Prisons Clinical Practice Guidelines April 2012 Clinical guidelines are made available to the public for informational
Management of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections Federal Bureau of Prisons Clinical Practice Guidelines April 2012 Clinical guidelines are made available to the public for informational
Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile
 Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile MDRO and CDI Module Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA), Vancomycinresistant Enterococcus(VRE), certain gram negative bacilli, Clostridium
Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile MDRO and CDI Module Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA), Vancomycinresistant Enterococcus(VRE), certain gram negative bacilli, Clostridium
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital
 Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I)
 ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia annual report, part I The format
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia annual report, part I The format
TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE:
 Chapter 9 TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE: Gauze Wound care represents a major area of concern for the rural health provider. This chapter discusses the treatment of open wounds, with emphasis on dressing
Chapter 9 TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE: Gauze Wound care represents a major area of concern for the rural health provider. This chapter discusses the treatment of open wounds, with emphasis on dressing
Bacteria vs. Virus: What s the Difference? Grade 11-12
 Bacteria vs. Virus: What s the Difference? Grade 11-12 Subject: Biology Topic: Bacteria, viruses, and the differences between them. The role that water plays in spreading bacteria and viruses, and the
Bacteria vs. Virus: What s the Difference? Grade 11-12 Subject: Biology Topic: Bacteria, viruses, and the differences between them. The role that water plays in spreading bacteria and viruses, and the
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline
 Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
Approaches to Infection Control
 Approaches to Infection Control Considerations for PTAs in the Clinic Objectives Describe the basic characteristics of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Discuss the locations, advantages, and disadvantages
Approaches to Infection Control Considerations for PTAs in the Clinic Objectives Describe the basic characteristics of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Discuss the locations, advantages, and disadvantages
MRSA in companion animals: frequently asked questions
 MRSA in companion animals: frequently asked questions 1. What is MRSA? MRSA stands for methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (although oxacillin is now used, the terminology has stuck). Over 1400
MRSA in companion animals: frequently asked questions 1. What is MRSA? MRSA stands for methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (although oxacillin is now used, the terminology has stuck). Over 1400
Strep Throat. Group Members: Rebecca Okinczyc
 Strep Throat Group Members: Rebecca Okinczyc Andrew Miclat Joshua Savage Introduction It is the purpose of this paper to present a comprehensive and exhaustive description of the disease Streptococcal
Strep Throat Group Members: Rebecca Okinczyc Andrew Miclat Joshua Savage Introduction It is the purpose of this paper to present a comprehensive and exhaustive description of the disease Streptococcal
Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- Sept 17, 2015
 Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- Sept 17, 2015 Charles Krasner, M.D. UNR School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Hospital Growing problem of pseudomembranous colitis MMWR-
Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- Sept 17, 2015 Charles Krasner, M.D. UNR School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Hospital Growing problem of pseudomembranous colitis MMWR-
Wound Care on the Field. Objectives
 Wound Care on the Field Brittany Witte, PT, DPT Cook Children s Medical Center Objectives Name 3 different types of wounds commonly seen in sports and how to emergently provide care for them. Name all
Wound Care on the Field Brittany Witte, PT, DPT Cook Children s Medical Center Objectives Name 3 different types of wounds commonly seen in sports and how to emergently provide care for them. Name all
C. difficile. Answers to frequently asked questions about. at the Jewish General Hospital. www.jgh.ca SIR MORTIMER B. DAVIS JEWISH GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Answers to frequently asked questions about C. difficile at the Jewish General Hospital SIR MORTIMER B. DAVIS JEWISH GENERAL HOSPITAL A McGill University Teaching Hospital www.jgh.ca 1. CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE
Answers to frequently asked questions about C. difficile at the Jewish General Hospital SIR MORTIMER B. DAVIS JEWISH GENERAL HOSPITAL A McGill University Teaching Hospital www.jgh.ca 1. CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE
Guidelines for the Management of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Infections in the US Navy and Marine Corps
 Guidelines for the Management of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Infections in the US Navy and Marine Corps AUGUST 2005 Navy Environmental Health Center 620 John
Guidelines for the Management of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Infections in the US Navy and Marine Corps AUGUST 2005 Navy Environmental Health Center 620 John
Provincial Hand Hygiene Campaign 2012. Clean Hands Across the Land
 Provincial Hand Hygiene Campaign 2012 Clean Hands Across the Land 1 Overview Welcome/Introduction History Hand Hygiene: the basics Definitions Technique Monitoring Hand Hygiene in the Schools Hand Hygiene
Provincial Hand Hygiene Campaign 2012 Clean Hands Across the Land 1 Overview Welcome/Introduction History Hand Hygiene: the basics Definitions Technique Monitoring Hand Hygiene in the Schools Hand Hygiene
Bloodborne Pathogens
 Bloodborne Pathogens Learning Objectives By the end of this section, the participant should be able to: Name 3 bloodborne pathogens Identify potentially contaminated bodily fluids Describe 3 safe work
Bloodborne Pathogens Learning Objectives By the end of this section, the participant should be able to: Name 3 bloodborne pathogens Identify potentially contaminated bodily fluids Describe 3 safe work
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine
 FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
How MRSA Impacts Your Practice
 How MRSA Impacts Your Practice By Shirley Henderson Apollo Correspondence Classes 1 Copyright 2008 by Apollo Correspondence Classes All rights reserved. Apollo Correspondence Classes 21162 Banff Lane Huntington
How MRSA Impacts Your Practice By Shirley Henderson Apollo Correspondence Classes 1 Copyright 2008 by Apollo Correspondence Classes All rights reserved. Apollo Correspondence Classes 21162 Banff Lane Huntington
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU Updated 5/6/09 ER FAQ What is swine flu? Swine flu is common disease of pigs and is caused by the same category of influenza virus (influenza A) that causes flu in
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU Updated 5/6/09 ER FAQ What is swine flu? Swine flu is common disease of pigs and is caused by the same category of influenza virus (influenza A) that causes flu in
