Cardiovascular Nursing Education Associates
|
|
|
- Simon Ball
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Carol Jacobson RN, MN Cardiovascular Nursing Education Associates Carol Jacobson RN, MN 1
2 Position I: Chamber Paced Position II: Chamber Sensed Position III: Response to Sensing O = None O = None O = None A = Atrium A = Atrium T = Triggered V = Ventricle V = Ventricle I = Inhibited D = Dual (A + V) D = Dual (A + V) D = Dual (T + I) Position IV: Rate Modulation O = None R = Rate Modulation Position V: Multisite Pacing O = None A = Atria V = Ventricles D = Dual (A & V) Carol Jacobson RN, MN 2
3 Is this pacemaker working right? Yes. It is a dual chamber pacemaker functioning in the atrial tracking state. Chamber Paced Chamber Sensed Response to Sensing DVI Atrium Ventricle Ventricle VDD Ventricle Atrium DDD Atrium Ventricle Ventricle Atrium Ventricle Inhibits Triggers Inhibits Triggers Inhibits Carol Jacobson RN, MN 3
4 D D D Paces: Atria and Ventricle Senses: Atria and Ventricle Response to Sensing: Atrial sensing = inhibits atrial output, triggers ventricular output Ventricular sensing = inhibits all output AVI - AV interval or AV delay ARP - atrial refractory period PVARP - post ventricular atrial refractory period AEI - atrial escape interval VRP - ventricular refractory period MTI - maximum tracking interval Carol Jacobson RN, MN 4
5 Pacing Interval AV Interval Atrial Escape Interval (V-A interval) Interval from a sensed or paced ventricular event to the next atrial output spike Amount of time the pacemaker will wait for an intrinsic P wave before it paces the atrium Not programmable Carol Jacobson RN, MN 5
6 Pacing Interval AV Interval Atrial Escape Interval (V-A interval) Period of time when atrial channel cannot respond to atrial activity Begins with paced or sensed atrial activity AVI AVI PVARP Carol Jacobson RN, MN 6
7 PVARP hides really early P waves from the atrial channel and prevents inappropriate atrial tracking Retrograde P Very short ventricular refractory period ( blink ) that occurs with every atrial pacemaker spike (to prevent crosstalk) Carol Jacobson RN, MN 7
8 Begins with sensed or paced ventricular beat Ventricular channel unable to respond to sensed events so it doesn t respond to T wave potentials or other local potentials in ventricle Maximum rate at which the ventricular channel will track the atrial rate Determines the upper rate limit (URL) of the pacemaker keeps ventricular paced rate <URL PAC Carol Jacobson RN, MN 8
9 AVI ARP AEI VRP MTI Possible underlying rhythm: sinus brady and AV block Carol Jacobson RN, MN 9
10 AVI ARP AEI VRP MTI Possible underlying rhythm: sinus brady but intact AV conduction AVI ARP AEI VRP MTI Possible underlying rhythm: sinus rhythm with 3 rd degree AV block Carol Jacobson RN, MN 10
11 AVI ARP AEI VRP MTI AVI ARP AEI VRP MTI Carol Jacobson RN, MN 11
12 Minimum rate Upper rate limit AV interval PVARP Ventricular refractory period Special programmed parameters Carol Jacobson RN, MN 12
13 Atrial Capture Atrial Sensing Ventricular Capture Ventricular Sensing Atrial spike immediately followed by obvious P wave Atrial spike followed by normal QRS Carol Jacobson RN, MN 13
14 Normal P wave followed by a paced QRS within the programmed AV delay In DDD mode there is no such thing as straight ventricular pacing. There is always either an atrial sensed beat or an atrial paced beat before a ventricular paced beat. Ventricular spike followed immediately by wide QRS Carol Jacobson RN, MN 14
15 Atrial spike followed by normal QRS Resetting of atrial escape interval by a PVC AEI AEI reset by sensed PVC What state of pacing is this? AV sequential Atrial capture? Good Atrial sensing? Can t evaluate Ventricular capture? Good Ventricular sensing? Can t evaluate Carol Jacobson RN, MN 15
16 Practice #2 What state of pacing is this? Atrial tracking (A sense, V pace) Atrial capture? Can t evaluate Atrial sensing? Good Ventricular capture? Good Ventricular sensing? Can t evaluate What state(s) of pacing? Atrial capture? Ventricular capture? Ventricular sensing? AV sequential, Atrial pacing, Atrial tracking Atrial sensing? Good Good (beat 6) Good Good (beats 2, 4, 9) Carol Jacobson RN, MN 16
17 Differential AV Delay Shorter AV delay on sensed beats than on AV paced beats Rate Adaptive AV Delay AV delay shortens as pacing rate increases in response to activity Mode Switching Switches to VVI when atrial fib or flutter occurs Shorter AV delay on sensed beats than on AV paced beats Maintains more consistent atrial contraction to ventricular contraction timing between sensed and paced atrial beats Paced AV delay = 200 ms (.20 sec) Sensed AV delay = 160 ms (0.16 sec) Carol Jacobson RN, MN 17
18 AV interval shortens as pacing rate increases in response to activity Pacing rate = 68 AV delay with no activity: 160 ms Pacing rate = 94 AV delay with activity: 120 ms Device switches from tracking (DDD/R) to nontracking (DDI/R) mode when atrial arrhythmias occur Prevents pacer from trying to track rapid atrial rates symptom relief Atrial tracking Onset of atrial flutter MS Pacer tracks atrial rate for a few beats Switches to non-tracking mode paced rate slows Carol Jacobson RN, MN 18
19 One channel of the pacemaker senses something that is occurring in the other chamber o Ventricular channel senses atrial output spike or intrinsic P wave o Ventricular channel thinks the atrial pacing spike is a QRS and fails to pace the ventricle Causes atrial pacing at a rate equal to the atrial escape interval and can result in ventricular asystole if there is no intrinsic conduction to the ventricle Normal Operation Crosstalk Carol Jacobson RN, MN 19
20 Delivery of ventricular pacing stimulus at a short AV delay ( ms) if a signal is sensed early in the AV delay Short AV interval allows for a ventricular output but prevents it from falling on the T wave Used to prevent crosstalk inhibition of ventricular output PVC #1: Early enough to inhibit all pacing PVC #2: Inhibits ventricular pacing PVC #3: Occurs during blanking period and causes safety pace Carol Jacobson RN, MN 20
21 Occur when the intrinsic atrial rate exceeds the upper rate limit Goal is to limit the rate at which the ventricle will pace in response to rapid atrial rates Wenckebach response 2:1 block Maximum tracking interval will not allow ventricular pacing to occur before it times out Max track interval is determined by programmed upper rate of pacemaker In this example there is a sinus tachycardia at rate of about 136. Upper rate limit is 120 (green arrow at bottom). AV delay progressively increases (white part of arrow at top) because max track won t allow a V pace to occur until it times out. The increase in AV delay pushes PVARP (red arrow at top) closer to the next P wave until finally a P wave occurs in PVARP ( ) and is not sensed and therefore does not initiate a V pace, resulting in a pause which keeps the ventricular rate below upper rate limit. Carol Jacobson RN, MN 21
22 When the atrial rate is faster than the total atrial refractory period, every other P wave falls in PVARP and 2:1 block occurs Carol Jacobson RN, MN 22
23 Reentrant tachycardia that occurs only with dual chamber pacemakers Antegrade limb of circuit is the pacemaker Retrograde limb of circuit is retrograde conduction through the AV node or an accessory pathway Caused by anything that causes loss of AV synchrony PVC with retrograde conduction to atria PAC that prolongs AVI Loss of atrial capture Removal of a magnet after pacemaker testing Myopotential tracking Atrial sensing circuit Ventricular output circuit Carol Jacobson RN, MN 23
24 A PVC conducts retrograde to the atrium The atrial channel senses the retrograde P wave and triggers a V pace after a long AV delay (caused by the maximum tracking interval) The V pace results in retrograde conduction to the atrium which is sensed, another V pace is triggered, and PMT occurs Carol Jacobson RN, MN 24
25 PMT Prevention Algorithms + PVARP or ARE (atrial refractory extension) o Automatic extension of PVARP after a PVC to prevent sensing of a retrograde P wave by the atrial channel DVI on PVC o Switches to DVI mode when a PVC occurs (turns off atrial sensing circuit to prevent sensing of retrograde P) PMT Termination Algorithms Interrupts PMT after programmable number of beats by extending PVARP or switching to DVI Carol Jacobson RN, MN 25
26 Dual Chamber Atrial Ventricular Bi-ventricular Right ventricular apex Left ventricle via left cardiac vein Patients with all of the following should receive CRT with or without ICD unless contraindicated: EF < 35% Sinus rhythm LBBB with QRS > 150ms NYHA class II, III or ambulatory class IV despite optimal medical therapy Carol Jacobson RN, MN 26
27 CRT can be useful for the following patients with EF < 35% LBBB with a QRS duration 120 to 149 ms (IIa) Non-LBBB pattern with a QRS duration >150 ms and NYHA class III/ambulatory class IV symptoms (IIa) Atrial fibrillation if near 100% pacing expected (IIa) Non-LBBB pattern with QRS duration 120 to 149 ms, and NYHA class III/ambulatory class IV (IIb) Non-LBBB pattern with a QRS duration >150 ms and NYHA class II symptoms (IIb) LVEF < 30%, ischemic etiology of heart failure, sinus rhythm, LBBB with a QRS duration of >150 ms, and NYHA class I symptoms (IIb) Abnormal ventricular conduction resulting in abnormal mechanical function Poor systolic function Impaired diastolic function Interventricular dyssynchrony - time delay between contraction of right and left ventricles Intraventricular dyssynchrony - abnormal segmental contraction within the LV Carol Jacobson RN, MN 27
28 Both ventricles depolarize at same time Septum moves leftwards and functions as part of LV Mitral valve closes and blood is ejected into aorta Abnormal ventricular depolarization due to LBBB: RV depolarizes normally Septum depolarizes from right side instead of from left side LV depolarizes late and abnormally slowly due to muscle cell-to-cell conduction Carol Jacobson RN, MN 28
29 Abnormal Mechanical Function Septum depolarizes before LV When LV contracts, septum is already relaxed and bulges into RV (paradoxical septal wall motion) LV papillary muscles contract late, allowing mitral valve to evert into LA Reduced forwards flow through aortic valve due to mitral regurgitation LV contraction is delayed, causing LV to contract at same time as LA, reducing LV filling LV relaxes late, causing reduced LV filling during diastole Pacing of RV and LV together Coordinates ventricular contraction Forces septum to contract with LV Reduces both inter and intraventricular dyssynchrony Papillary muscles contract with LV Reduces amount of mitral regurgitation Dual chamber pacing Improves AV timing to optimize ventricular filling Carol Jacobson RN, MN 29
30 Improved systolic and diastolic function Increased stroke volume and improved LVEF Reduced LV volume & dimension (reverse LV remodeling noted with 3 months of CRT) Decreased mitral regurgitation Improved exercise capacity Improved functional class Improved quality of life Decreased hospitalization for HF Reduced mortality (especially when combined with ICD) 36% reduction of all-cause mortality in CARE-HF study From this: To this: Carol Jacobson RN, MN 30
31 Not as easy as your regular RV pacing!! Loss of capture in one ventricle can change the QRS axis and/or QRS shape in multiple leads V 1 Bi ventricular capture Loss of RV capture Intrinsic LBBB conduction (no pacing) 4 ECGs recommended Baseline intrinsic conduction (showing LBBB) RV pacing only LV pacing only Bi-V pacing Use of marker channels on programmers makes it easier to evaluate pacemaker function during follow-up visits Carol Jacobson RN, MN 31
32 Intrinsic conduction V1 II RV Pacing LV Pacing V1 II Bi-V Pacing With biventricular pacing the idea is to FORCE ventricular pacing so that both ventricles contract together AV delays programmed on the short side to force ventricular pacing rather than allowing intrinsic conduction to occur Carol Jacobson RN, MN 32
33 So what s the problem with right ventricular pacing? Ventricular pacing from the RV apex creates the same inter and intraventricular conduction delay as LBBB and causes similar mechanical malfunctions The goal then is to PREVENT ventricular pacing whenever possible Carol Jacobson RN, MN 33
34 Left ventricular electrical and mechanical dyssynchrony (iatrogenic LBBB) LV remodeling LV systolic and diastolic dysfunction Regional wall motion abnormalities Mitral regurgitation Increased risk of atrial fibrillation Increased risk of developing heart failure (even with normal heart function prior to pacemaker insertion) Increased incidence of hospitalization due to HF Left atrial enlargement Promotion of ventricular arrhythmias SNS activation Reduced exercise capacity Sweeney MO, Hellkamp AS, Ellenbogen KA, et al. Adverse effect of ventricular pacing on heart failure and atrial fibrillation among patients with normal baseline QRS duration in a clinical trial of pacemaker therapy for sinus node dysfunction. Circulation. 2003;107:2932 Sweeney, M. O., & Prinzen, F. W. (2006). A new paradigm for physiologic ventricular pacing. J Am Coll Cardiol 47(2), Carol Jacobson RN, MN 34
35 Incidence of atrial fibrillation increases with increasing % of ventricular pacing in both VVI and DDD modes Why? RV pacing delays LV contraction and relaxation Left atrial pressures have to be higher to fill the not yet relaxed LV. Elevated LA pressure causes atrial enlargement which increases risk of AF Alternate pacing sites His Bundle RVOT RV septal sites Bifocal RV pacing (apex and RVOT) LV pacing alone Biventricular pacing Triventricular pacing (RV apex, RVOT, LV) Carol Jacobson RN, MN 35
36 Programming to reduce RV pacing Long AV delay to encourage intrinsic conduction AAI/R mode whenever possible VVI at rate of 40 instead of DDD as backup mode in ICD patients with no indications for pacing Special Pacemaker Functions MVP mode (Managed Ventricular Pacing) AV Search Hysteresis (AVSH) VIP (Ventricular Intrinsic Preference) Provides AAI/R pacing with dual chamber pacing support if transient or persistent AV block occurs Functions as AAI/R and allows intrinsic AV conduction to occur (long AV interval) Monitors ventricle each beat to verify intact conduction Carol Jacobson RN, MN 36
37 Provides ventricular backup pacing only as needed if transient AV block occurs A-A interval with no sensed ventricular event Transient loss of conduction Ventricular backup safety pace AAI/R pacing continues Switches to DDD/R for one minute if AV block is persistent 2 out of 4 A-A intervals without a ventricular event Persistent loss of conduction Switches to DDD/R Carol Jacobson RN, MN 37
38 When in DDD mode, performs AV conduction check every 1,2,4,8 min up to 16 hrs after switch to DDD/R) Inhibits one V pace to check for intrinsic conduction If conduction check fails, continues in DDD/R mode Failed conduction check Continues in DDD/R Next conduction check scheduled to occur at 2x the previous time interval (1, 2, 4, 8 min hrs) If conduction check passes, device switches to AAI/R mode and continues in that mode until conduction fails again Conduction test passes Switches to AAI/R Carol Jacobson RN, MN 38
39 Is this pacemaker working right? Is this pacemaker working right? Atrial pacing with very long AV delay conducting to ventricle normally Failed conduction Failed conduction Backup ventricular safety pace Backup safety pace Switches to DDD/R pacing Carol Jacobson RN, MN 39
40 Functions in DDD/R mode and automatically searches for intrinsic AV conduction Extends the AV delay by 10% - 100% (programmable value) every X cycles (programmable number from 32 to 1024 cycles) to look for intrinsic conduction Searches for 8 cycles Maximum AV delay is 400 ms If intrinsic conduction is present, AV delay remains long until conduction fails, then pacer returns to DDD/R mode Functions as DDD/R pacer Carol Jacobson RN, MN 40
41 Every 32 beats (or programmed number) it extends AV delay by a programmed value for 8 cycles or until intrinsic conduction occurs Search begins Intrinsic conduction occurs ms AV delay remains long until intrinsic conduction fails to occur within the programmed upper AV delay length DDD/R operation returns with conduction failure Long AV delay continues Conduction fails so V pace occurs 240 ms 240 ms 300 ms DDD/R pacing resumes at programmed parameters for another 32 beats, then search starts again Carol Jacobson RN, MN 41
42 V backup safety pace (probably due to loss of conduction on previous A pace) A pace with long PR, intrinsic conduction A pace, loss of conduction (2 nd one) A pace, V backup safety pace, probable junctional escape beat Switch to DDD (2 out of 4 atrial events not conducted) Normal MVP Pacemaker Function! Carol Jacobson RN, MN 42
43 No matter how weird it looks, its probably working right!!! As long as the patient is hemodynamically stable DON T WAKE THE DOC UP IN THE MIDDLE OF THE NIGHT TO REPORT PACEMAKER MALFUNCTION! The only real emergency is loss of ventricular capture resulting in asystole or symptomatic bradycardia Carol Jacobson RN, MN 43
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Updated Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Guidelines
 The Ohio State University Heart and Vascular Center Updated Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Guidelines William T. Abraham, MD, FACP, FACC, FAHA, FESC Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Cell Biology
The Ohio State University Heart and Vascular Center Updated Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Guidelines William T. Abraham, MD, FACP, FACC, FAHA, FESC Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Cell Biology
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
GERIATRYCZNE PROBLEMY KLINICZNE/GERIATRICS MEDICAL PROBLEMS
 65 G E R I A T R I A 2011; 5: 65-69 GERIATRYCZNE PROBLEMY KLINICZNE/GERIATRICS MEDICAL PROBLEMS Otrzymano/Submitted: 24.02.2011 Poprawiono/Corrected: 01.03.2011 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 06.03.2011 Akademia
65 G E R I A T R I A 2011; 5: 65-69 GERIATRYCZNE PROBLEMY KLINICZNE/GERIATRICS MEDICAL PROBLEMS Otrzymano/Submitted: 24.02.2011 Poprawiono/Corrected: 01.03.2011 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 06.03.2011 Akademia
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
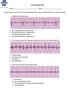 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure
 Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Pacemaker Counter and Histogram Operation and Interpretation. Percentage of total count. Figure 2. Detailed ALTRUA Paced and Sensed Event Counters
 A Closer Look SUMMARY This article provides information regarding the operation and interpretation of Event Counters and Histograms available in ALTRUA, INSIGNIA, PULSAR MAX II, and DISCOVERY II pacemakers.
A Closer Look SUMMARY This article provides information regarding the operation and interpretation of Event Counters and Histograms available in ALTRUA, INSIGNIA, PULSAR MAX II, and DISCOVERY II pacemakers.
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
Basic principles of pacing
 CHAPTER 1 Basic principles of pacing Malcolm Kirk The aim of this chapter is to give sufficient background and information about cardiac pacemakers to allow interpretation of electrocardiograms (ECGs)
CHAPTER 1 Basic principles of pacing Malcolm Kirk The aim of this chapter is to give sufficient background and information about cardiac pacemakers to allow interpretation of electrocardiograms (ECGs)
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Normal Intracardiac Pressures. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Flash, Rocking on others Added value in DCM and CRT. C. Parsai Polyclinique des Fleurs France
 Flash, Rocking on others Added value in DCM and CRT C. Parsai Polyclinique des Fleurs France Cleland JGF et al. (2007) Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 4: 90 101 Predicting CRT Response Device Related Patient
Flash, Rocking on others Added value in DCM and CRT C. Parsai Polyclinique des Fleurs France Cleland JGF et al. (2007) Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 4: 90 101 Predicting CRT Response Device Related Patient
For more information about the use of the Propaq monitor, refer to the Propaq Directions For Use.
 Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
 Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
CCAD Training Manual. Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM)
 CCAD Training Manual Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM) Version 1.0 A D Cunningham 19/3/2008 Introduction This manual is intended to assist users of the Notes Client version of the CCAD Cardiac Rhythm Management
CCAD Training Manual Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM) Version 1.0 A D Cunningham 19/3/2008 Introduction This manual is intended to assist users of the Notes Client version of the CCAD Cardiac Rhythm Management
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen
 RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery
 Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
Lecture Outline. Cardiovascular Physiology. Cardiovascular System Function. Functional Anatomy of the Heart
 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI
 Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
PSIO 603/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 2007 MRB 422; 626-6833 jburt@u.arizona.edu. MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle
 SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
Pacers use a 5-letter code: first 3 letters most important
 PACEMAKERS 2 Pacemakers: Nomenclature Pacers use a 5-letter code: first 3 letters most important t First Letter: Chamber Paced A= Atrium V= Ventricle D= Dual (A+V) 2nd Letter: Chamber Sensed A= Atrium
PACEMAKERS 2 Pacemakers: Nomenclature Pacers use a 5-letter code: first 3 letters most important t First Letter: Chamber Paced A= Atrium V= Ventricle D= Dual (A+V) 2nd Letter: Chamber Sensed A= Atrium
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Introduction. Planned surgical procedures
 Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure
 Disadvantages of AV Junction Ablation Persistent AFib- no AV synchrony Ongoing risk of thromboembolism Life-long dependency on pacemaker Comparison of LA Ablation vs. AVN Ablation LA Ablation AVN Ablation
Disadvantages of AV Junction Ablation Persistent AFib- no AV synchrony Ongoing risk of thromboembolism Life-long dependency on pacemaker Comparison of LA Ablation vs. AVN Ablation LA Ablation AVN Ablation
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation
 Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Clinical Trials In Cardiac Rhythm Management
 Clinical Trials In Cardiac Rhythm Management Stuart Allen Principal Cardiac Physiologist Manchester Heart Centre HRUK Council Physiologist Representative stuart.allen@cmft.nhs.uk Clinical Trials Pacemakers
Clinical Trials In Cardiac Rhythm Management Stuart Allen Principal Cardiac Physiologist Manchester Heart Centre HRUK Council Physiologist Representative stuart.allen@cmft.nhs.uk Clinical Trials Pacemakers
Schüller and Brandt1 defined the pacemaker
 Hellenic J Cardiol 43: 101-106, 2002 Marked First-Degree Atrioventricular Block: A New Indication for Cardiac Pacing S. SERGE BAROLD 1, I. ELI OVSYSHCHER 2 1 Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, Florida, USA
Hellenic J Cardiol 43: 101-106, 2002 Marked First-Degree Atrioventricular Block: A New Indication for Cardiac Pacing S. SERGE BAROLD 1, I. ELI OVSYSHCHER 2 1 Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, Florida, USA
What Are Arrhythmias?
 What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
Pacemakers 12/04. Pacemakers. 1. What is a pacemaker?
 Pacemakers 12/04 1-What is a pacemaker? 2- What does intrinsic mean? 3- How exactly do pacemakers work on the heart? 4- What are the parts of a pacemaker? 5- Are there different kinds of pacemakers? 6-
Pacemakers 12/04 1-What is a pacemaker? 2- What does intrinsic mean? 3- How exactly do pacemakers work on the heart? 4- What are the parts of a pacemaker? 5- Are there different kinds of pacemakers? 6-
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY. Charles Jazra
 RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Electrophysiology study (EPS)
 Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
1 Meet Your AliveCor Heart Monitor
 GETTING STARTED HOW TO RECORD YOUR FIRST ECG 1 Meet Your AliveCor Heart Monitor UNPACK Take your AliveCor out of the box. The device is already connected to an attachment plate that can adhere to the back
GETTING STARTED HOW TO RECORD YOUR FIRST ECG 1 Meet Your AliveCor Heart Monitor UNPACK Take your AliveCor out of the box. The device is already connected to an attachment plate that can adhere to the back
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013
 Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular
 Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA
 Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA Intrinsic Conduction Automaticity-cardiac cells ability to spontaneously depolarize and initiate impulse Depolarization-cardiac cells go to a+ intracellular and
Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA Intrinsic Conduction Automaticity-cardiac cells ability to spontaneously depolarize and initiate impulse Depolarization-cardiac cells go to a+ intracellular and
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter
 Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
The Heart Rhythm Charity
 The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2006 Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rhythm)
The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2006 Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rhythm)
Detection of Heart Diseases by Mathematical Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Using Phonocardiogram Signals
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
UCSF Anesthesia Resident Pearls: Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Pacemakers and ICDs Table of Contents
 UCSF Anesthesia Resident Pearls: Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Pacemakers and ICDs Table of Contents Page 1 Intro Indications for Pacers and ICDs Page 2 Differentiating between Pacers and ICDs
UCSF Anesthesia Resident Pearls: Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Pacemakers and ICDs Table of Contents Page 1 Intro Indications for Pacers and ICDs Page 2 Differentiating between Pacers and ICDs
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Dual Chamber Temporary Pacemaker
 5388 Dual Chamber Temporary Pacemaker Technical Manual Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by c or on the order of a physician. 0123 MODEL 5388 0 Technical Manual 0 Dual Chamber Temporary
5388 Dual Chamber Temporary Pacemaker Technical Manual Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by c or on the order of a physician. 0123 MODEL 5388 0 Technical Manual 0 Dual Chamber Temporary
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
Premature Ventricular Contractions. Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS
 Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect. Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs. Acknowledgement. Disclosures Real or Potential Conflicts of Interest
 Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs W. Lane Edwards, Jr., MSN, ARNP, ANP Hospitalist Group of Southwest Florida Affiliate Professor of Nursing, University of Alaska at Anchorage Acknowledgement
Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs W. Lane Edwards, Jr., MSN, ARNP, ANP Hospitalist Group of Southwest Florida Affiliate Professor of Nursing, University of Alaska at Anchorage Acknowledgement
Auscultation of the Heart
 Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
