Cardiac Pacing in First-Degree Atrioventricular Block
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Mason
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cardiac Pacing in First-Degree Atrioventricular Block Serge Barold, Bengt Herweg Florida Heart Rhythm Institute, Tampa, Florida, USA. ABSTRACT This article will summarize the cardiac pacing in first-degree atrioventricular block. KEYWORDS Cardiac pacing, first-degree atrioventricular block Birinci Derece Atriyoventriküler Blokta Kalp Pili ÖZET Bu yazıda birinci derece atriyoventriküler blokta kardiyak pacing özetlenecektir. ANAHTAR KELİMELER Birinci derece atriyoventriküler blok, kardiyak pacing İLETİŞİM ADRESİ Dr. Serge BAROLD Florida Heart Rhythm Institute, Tampa, Florida, USA
2 Cardiac Pacing in First-Degree Atrioventricular Block 45 First-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, often considered a relatively benign arrhythmia, can occasionally be associated with severe symptoms. Although there is little evidence to suggest that pacemakers improve survival in patients with isolated first-degree AV block, it is now recognized that marked (PR sec) first-degree AV block can lead to symptoms similar to those in the pacemaker syndrome even in the absence of higher degrees of AV block (1-4). Uncontrolled trials have shown that many symptomatic patients with a PR interval 0.30 sec can be improved with dual chamber pacing especially in patients with normal left ventricular (LV) function. Echocardiography Prolonged AV conduction causes atrial systole too early in diastole which then causes an ineffective or decreased contribution of atrial systole to cardiac output. Such a decrease in cardiac output is poorly tolerated in heart failure patients. Atrial contraction begins in early diastole resulting in atrial systole superimposed upon the early left ventricular (LV) filling phase and much earlier than the onset of LV systolic pressure. There is therefore delay of the E wave with resultant fusion between the E and A waves producing shortening of the LV diastolic filling time (Fig 1). The delay in AV conduction also induces diastolic mit- FİGURE 1 Pulsed wave Doppler echocardiography coupled with the surface ECG in a patient with a long PR interval. Left panel: The E and A waves are superimposed due to the very late diastole resulting from a very delayed ventricular activation. Right panel: Dual chamber pacing results in shortening of the AV interval (from atrial sensing to onset of ventricular pacing). The E wave now occurs well before the A wave (atrial contraction). This increases the left ventricular filling time and the aortic velocity-time integral (VTI). (Reproduced with permission from Garrigue S. Optimization of cardiac resynchronization therapy: the role of echocardiography in atrioventricular, interventricular and intraventricular delay optimization. In: Yu CM, Hayes DL, Auricchio A (Eds), Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy, Malden, MA, Blackwell-Futura, 2006: ).
3 46 Türk Aritmi, Pacemaker ve Elektrofizyoloji Dergisi ral regurgitation (Fig 2). In a normal heart, atrial systole occurs immediately before ventricular systole. In the setting of a long PR interval, the atrium begins to relax and atrial pressure drops after atrial systole. This causes the mitral valve to remain open because of delayed LV systole. With the mitral valve open, the LV end-diastolic pressure rises and exceeds left atrial pressure thereby producing diastolic mitral regurgitation, a decrease in preload (LV end-diastolic pressure) at the onset of LV systole and, ultimately, a decrease in LV dp/dt max and cardiac output. This type of mitral regurgitation appears inconsequential in the normal heart but may be important in patients with severe LV dysfunction. Pacemaker-like Syndrome AAI(R) pacing with a very long PR interval may produce pacemaker syndrome. This form of pacemaker syndrome has resurfaced more recently in patients with intermittent marked first-degree AV block during managed ventricular pacing to minimize right ventricular pacing. In this pacing mode, a device permits the establishment of very long PR intervals without the emission of a ventricular output. A long PR interval ( 0.30 sec) without a pacemaker shares the same pathophysiology as VVI pacing with retrograde ventriculoatrial conduction or an AAI-induced pacemaker syndrome. Some workers have called the hemodynamic disturbance produced by marked FİGURE 2 Continuous-wave Doppler echocardiographic recording of transmitral blood flow velocity demonstrating diastolic mitral regurgitation in a patient with first degree AV block with a markedly prolonged PR interval of 360 msec. The low velocity regurgitant signal is seen in diastole following the atrial filling wave and prior to the onset of systolic mitral regurgitation.
4 Cardiac Pacing in First-Degree Atrioventricular Block 47 first-degree AV block a pacemaker syndrome without a pacemaker, and others have labeled this entity as pseudopacemaker syndrome. These characterizations are potentially confusing. The term pacemaker-like syndrome is probably more appropriate. Although patients with symptomatic marked first-degree AV block ( 0.30 sec), and normal LV function can benefit from dual chamber pacing. Some patients with a long PR interval and interatrial conduction delay may be already hemodynamically compensated because delayed conduction to the left atrium may be associated with an appropriately timed mechanical left AV synchrony, a situation where improvement would not be expected with pacing. Clinical evaluation. Patients with marked first-degree AV block may or may not be symptomatic at rest. They are more likely to become symptomatic with mild or moderate exercise when the PR interval does not shorten appropriately and atrial systole shifts progressively closer towards the preceding LV systole. Patients with subtle symptoms should undergo a treadmill stress test to determine the hemodynamic disadvantage of the long PR interval (defined as 0.30 sec). In some patients the long PR interval itself may occasionally become manifest only on exercise. Adaptation of the PR interval on exercise is unlikely in patients with a PR interval 0.30 sec. In symptomatic patients with marked 1stdegree AV block (as an isolated abnormality) it is important to realize that the benefit of pacing with optimized AV synchrony (with a shorter AV delay) may outweigh the risk of impaired LV function produced by right ventricular pacing with resultant LV dyssynchrony. This risk is impossible to evaluate on a short-term basis. An acute determination of the clinical status and need for permanent pacing can often be made noninvasively Occasionally a therapeutic decision may be facilitated by an invasive hemodynamic study with temporary right atrial and ventricular pacing to assess the hemodynamic response to AV interval optimization (Fig 3). However, an acute hemodynamic FİGURE 3 Hemodynamic abnormalities in a symptomatic patient with marked first-degree AV block and hemodynamic improvement with temporary dual chamber pacing. A. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure shows large cannon waves during sinus rhythm with a very long PR interval (Scale 0-40 mmhg). B. Note the normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure after temporary dual chamber pacing with a physiologic AV delay (Scale 0-40 mm Hg). (Reproduced with permission from Barold SS. Acquired atrioventricular block. In: Kusomoto FM, Goldschlager N (Eds), Cardiac Pacing for the Clinician, Philadelphia, PA, Lippincott Williams and Williams, 2001; ).
5 48 Türk Aritmi, Pacemaker ve Elektrofizyoloji Dergisi FİGURE 4 Twelve-lead ECG in the same patient as in Fig 3. During sinus tachycardia the sinus P wave is close to the preceding QRS complex on the initial portion of the ST-segment. This pattern mimics a reentrant supraventricular tachycardia.. (Reproduced with permission from Barold SS. Acquired atrioventricular block. In: Kusomoto FM, Goldschlager N (Eds), Cardiac Pacing for the Clinician, Philadelphia, PA, Lippincott Williams and Williams, 2001; ). improvement with a more physiologic AV delay does not guarantee long-term benefit because of the potential risk of harmful long-term effects of continual right ventricular pacing. Furthermore, it may be impossible during a resting pacing study to demonstrate symptomatic improvement, and the performance of an exercise study with a temporary dual-chamber pacemaker in place is difficult. Therefore it is reasonable to recommend a permanent pacemaker in many symptomatic patients without a temporary pacing study which itself carries unnecessary risks and cost. Asymptomatic patients There are no data on the prognosis of asymptomatic patients with a long PR interval ( 0.30 sec). Pacing is generally not recommended in truly asymptomatic patients. Differential diagnosis 1. The diagnosis of marked first-degree AV block can be overlooked when the PR interval is very long because the ECG may be misinterpreted to show a junctional rhythm with retrograde ventriculoatrial conduction (Fig 4). In questionable cases, sinus rhythm can be easily documented during an electrophysiologic study by delineating the pattern of right atrial activation which travels from high to low right atrium in sinus rhythm (Fig 5). 2. Patients with a long PR interval may respond to the abnormal resting hemodynamics with sinus tachycardia which may be misinterpreted as supraventricular tachycardia because the P-wave is placed so close to the preceding QRS complex. AV delay vs. asynchronous ventricular activation Optimization of the AV interval may be harmful in some patients because of deterioration of LV function secondary to paced ventricular depolarization. It is unwise to program a slow pacing rate and a very long AV delay to avoid right ventricular pacing in a patient who remains symptomatic. Programming a short AV
6 Cardiac Pacing in First-Degree Atrioventricular Block 49 FİGURE 5 Figure 5. Surface ECG and intracardiac recording from a patient with symptomatic marked first-degree AV block. Same patient as in Figures 3 and 4. RA = high right atrial electrogram, HBE = electrogram at site of His bundle recording. Note the sequence of atrial activation (RA to HBE) is consistent with sinus rhythm and rules out retrograde atrial activation. The AH interval is markedly prolonged. (Reproduced with permission from Barold SS. Acquired atrioventricular block. In: Kusomoto FM, Goldschlager N (Eds), Cardiac Pacing for the Clinician, Philadelphia, PA, Lippincott Williams and Williams, 2001; ). delay for hemodynamic benefit requires periodic evaluation of LV function to determine the cumulative effect of right ventricular pacing. Long PR interval, and congestive heart failure Studies with conventional DDD pacing and a short AV delay in heterogeneous groups of patients with LV systolic function and congestive heart failure of various etiologies have generally yielded disappointing results. In only a few patients with severe congestive heart failure and first-degree AV block, implantation of a conventional dual chamber pacemaker may occasionally improve cardiac performance but DDD pacing may also cause further longterm deterioration of LV function secondary to pacing-induced abnormal LV depolarization.. Conventional DDD pacing abolishes presystolic mitral regurgitation and increases the time for forward flow. However, elimination of diastolic mitral regurgitation plays as yet an undefined but probably small role in the overall he- modynamic benefit but it may result in more optimal hemodynamic performance because of a lower left atrial pressure and higher LV preload at the onset of systole. Long-term deterioration of LV function during DDD or DDDR pacing may eventually necessitate an upgrade to biventricular pacing. Indications for Pacing The 2008 ACC/AHA/HRS Guidelines (3) state: Although there is little evidence to suggest that pacemakers improve survival in patients with isolated first-degree AV block, it is now recognized that marked (PR more than 300 milliseconds) first-degree AV block can lead to symptoms even in the absence of higher degrees of AV block. When marked first-degree AV block for any reason causes atrial systole in close proximity to the preceding ventricular systole and produces hemodynamic consequences usually associated with retrograde (ventriculoatrial) conduction, signs and symptoms similar to the pacemaker syndrome may occur. With
7 50 Türk Aritmi, Pacemaker ve Elektrofizyoloji Dergisi marked first-degree AV block, atrial contraction occurs before complete atrial filling, ventricular filling is compromised, and an increase in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure and a decrease in cardiac output follow. Small uncontrolled trials have suggested some symptomatic and functional improvement by pacing of patients with PR intervals more than 0.30 seconds by decreasing the time for AV conduction. Finally, a long PR interval may identify a subgroup of patients with LV dysfunction, some of whom may benefit from dual-chamber pacing with a short(er) AV delay. Although echocardiographic or invasive techniques may be used to assess hemodynamic improvement before permanent pacemaker implantation, such studies are not required. The table in the guidelines shows that first-degree AV block is a class IIa indication as follows: Permanent pacemaker implantation is reasonable for first- or second-degree AV block with symptoms similar to those of pacemaker syndrome or hemodynamic compromise. It would seem more prudent at this juncture to consider the initial implantation of a biventricular DDD device when the LV ejection fraction is 35% even in the presence of a narrow QRS complex. The guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology (4) state that: In patients with firstdegree AV block, cardiac pacing is not recommended unless the PR interval fails to adapt to heart rate during exercise and is long enough (usually.300 ms) to cause symptoms becauseof inadequate LV filling, or an increase in wedge pressure, as the left atrial systole occurs close to or simultaneous with the previous LV systole. In such cases small, uncontrolled studies have shown an improvement in patients symptoms. The guidelines also recommend pacing with a IIa indication. REFERENCES 1. Barold SS. Indications for permanent cardiac pacing in first-degree AV block: class I, II, or III? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 1996;19: Barold SS, Ilercil A, Leonelli F, Herweg B. Firstdegree atrioventricular block. Clinical manifestations, indications for pacing, pacemaker management & consequences during cardiac resynchronization. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2006;17: Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Ellenbogen KA, et al. Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices); American Association for Thoracic Surgery; Society of Thoracic Surgeons. ACC/ AHA/HRS 2008 Guidelines for Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices) developed in collaboration with the American Association for Thoracic Surgery and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51:e Vardas PE, Auricchio A, Blanc JJ, et al. European Society of Cardiology; European Heart Rhythm Association. Guidelines for cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. The Task Force for Cardiac Pacing and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2007;9:95
Schüller and Brandt1 defined the pacemaker
 Hellenic J Cardiol 43: 101-106, 2002 Marked First-Degree Atrioventricular Block: A New Indication for Cardiac Pacing S. SERGE BAROLD 1, I. ELI OVSYSHCHER 2 1 Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, Florida, USA
Hellenic J Cardiol 43: 101-106, 2002 Marked First-Degree Atrioventricular Block: A New Indication for Cardiac Pacing S. SERGE BAROLD 1, I. ELI OVSYSHCHER 2 1 Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, Florida, USA
GERIATRYCZNE PROBLEMY KLINICZNE/GERIATRICS MEDICAL PROBLEMS
 65 G E R I A T R I A 2011; 5: 65-69 GERIATRYCZNE PROBLEMY KLINICZNE/GERIATRICS MEDICAL PROBLEMS Otrzymano/Submitted: 24.02.2011 Poprawiono/Corrected: 01.03.2011 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 06.03.2011 Akademia
65 G E R I A T R I A 2011; 5: 65-69 GERIATRYCZNE PROBLEMY KLINICZNE/GERIATRICS MEDICAL PROBLEMS Otrzymano/Submitted: 24.02.2011 Poprawiono/Corrected: 01.03.2011 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 06.03.2011 Akademia
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Unusual Electrocardiogram During Cardiac Resynchronization. What is the Mechanism?
 Unusual Electrocardiogram During Cardiac Resynchronization. What is the Mechanism? S. Serge BAROLD, M.D. Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, FL, USA ABSTRACT Figure 1 shows the ECG of a patient with a cardiac
Unusual Electrocardiogram During Cardiac Resynchronization. What is the Mechanism? S. Serge BAROLD, M.D. Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, FL, USA ABSTRACT Figure 1 shows the ECG of a patient with a cardiac
Normal Intracardiac Pressures. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Richard(Su+on(DSc( Emeritus(Professor(of(Clinical(Cardiology,( Na<onal(Heart(&(Lung(Ins<tute,(( Imperial(College,(London,(UK.(
 Richard(Su+on(DSc( Emeritus(Professor(of(Clinical(Cardiology,( Na
Richard(Su+on(DSc( Emeritus(Professor(of(Clinical(Cardiology,( Na
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients with and without Atrial Fibrillation
 Original Article CRT in Patients with and without AF Acta Cardiol Sin 2011;27:46 51 Electrophysiology Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients with and without Atrial Fibrillation Hung-Ta Wo, Po-Cheng
Original Article CRT in Patients with and without AF Acta Cardiol Sin 2011;27:46 51 Electrophysiology Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients with and without Atrial Fibrillation Hung-Ta Wo, Po-Cheng
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery
 Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
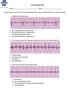 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013. Director, Intraoperative TEE Program. Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
 Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013 Mary Beth Brady, MD, FASE Director, Intraoperative TEE Program Johns Hopkins School of Medicine At the conclusion of the workshop, the participants
Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013 Mary Beth Brady, MD, FASE Director, Intraoperative TEE Program Johns Hopkins School of Medicine At the conclusion of the workshop, the participants
Updated Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Guidelines
 The Ohio State University Heart and Vascular Center Updated Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Guidelines William T. Abraham, MD, FACP, FACC, FAHA, FESC Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Cell Biology
The Ohio State University Heart and Vascular Center Updated Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Guidelines William T. Abraham, MD, FACP, FACC, FAHA, FESC Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Cell Biology
Low-gradient severe aortic stenosis with normal LVEF: A disturbing clinical entity
 Low-gradient severe aortic stenosis with normal LVEF: A disturbing clinical entity Jean-Luc MONIN, MD, PhD Henri Mondor University Hospital Créteil, FRANCE Disclosures : None 77-year-old woman, mild dyspnea
Low-gradient severe aortic stenosis with normal LVEF: A disturbing clinical entity Jean-Luc MONIN, MD, PhD Henri Mondor University Hospital Créteil, FRANCE Disclosures : None 77-year-old woman, mild dyspnea
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease
 5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
NASPE Training Requirements for Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Selection, Implantation, and Follow-Up
 NASPE Training Requirements for Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Selection, Implantation, and Follow-Up DAVID L. HAYES, GERALD V. NACCARELLI, SEYMOUR FURMAN, VICTOR PARSONNET, DWIGHT REYNOLDS, NORA
NASPE Training Requirements for Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Selection, Implantation, and Follow-Up DAVID L. HAYES, GERALD V. NACCARELLI, SEYMOUR FURMAN, VICTOR PARSONNET, DWIGHT REYNOLDS, NORA
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY. Charles Jazra
 RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
STANDARDS FOR IMPLANTATION AND FOLLOW-UP OF CARDIAC RHYTHM MANAGEMENT DEVICES IN ADULTS January 2013
 1. INTRODUCTION STANDARDS FOR IMPLANTATION AND FOLLOW-UP OF CARDIAC RHYTHM MANAGEMENT DEVICES IN ADULTS January 2013 This document replaces the previous Heart Rhythm UK documents Clinical Guidance by Consensus
1. INTRODUCTION STANDARDS FOR IMPLANTATION AND FOLLOW-UP OF CARDIAC RHYTHM MANAGEMENT DEVICES IN ADULTS January 2013 This document replaces the previous Heart Rhythm UK documents Clinical Guidance by Consensus
Reimbursement Information For Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Service Procedures 1
 GE Healthcare Information For Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Procedures 1 2011 Update www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage, and payment for electrophysiology procedures
GE Healthcare Information For Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Procedures 1 2011 Update www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage, and payment for electrophysiology procedures
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY
 BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
Name: Age: Resting BP: Wt. kg: Est. HR max : 85%HR max : Resting HR:
 Bruce Protocol - Submaximal GXT Name: Age: Resting BP: Wt. kg: Est. HR max : 85%HR max : Resting HR: Stage Min. % Grade MPH METs 2min HR 3min HR BP RPE 1 0-3 10 1.7 4.7 2 3-6 12 2.5 7.0 3 6-9 14 3.4 10.1
Bruce Protocol - Submaximal GXT Name: Age: Resting BP: Wt. kg: Est. HR max : 85%HR max : Resting HR: Stage Min. % Grade MPH METs 2min HR 3min HR BP RPE 1 0-3 10 1.7 4.7 2 3-6 12 2.5 7.0 3 6-9 14 3.4 10.1
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery
 Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation
 Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Heart Disease: Diagnosis & Treatment
 How I Treat Cardiology Peer Reviewed Heart Disease: Diagnosis & Treatment Amara Estrada, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology) University of Florida Background Clinical heart disease is the stage of disease when a
How I Treat Cardiology Peer Reviewed Heart Disease: Diagnosis & Treatment Amara Estrada, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology) University of Florida Background Clinical heart disease is the stage of disease when a
How to control atrial fibrillation in 2013 The ideal patient for a rate control strategy
 How to control atrial fibrillation in 2013 The ideal patient for a rate control strategy L. Pison, MD Advances in Cardiac Arrhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology - Torino, September 28 th 2013
How to control atrial fibrillation in 2013 The ideal patient for a rate control strategy L. Pison, MD Advances in Cardiac Arrhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology - Torino, September 28 th 2013
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
CCAD Training Manual. Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM)
 CCAD Training Manual Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM) Version 1.0 A D Cunningham 19/3/2008 Introduction This manual is intended to assist users of the Notes Client version of the CCAD Cardiac Rhythm Management
CCAD Training Manual Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM) Version 1.0 A D Cunningham 19/3/2008 Introduction This manual is intended to assist users of the Notes Client version of the CCAD Cardiac Rhythm Management
Pacemaker Counter and Histogram Operation and Interpretation. Percentage of total count. Figure 2. Detailed ALTRUA Paced and Sensed Event Counters
 A Closer Look SUMMARY This article provides information regarding the operation and interpretation of Event Counters and Histograms available in ALTRUA, INSIGNIA, PULSAR MAX II, and DISCOVERY II pacemakers.
A Closer Look SUMMARY This article provides information regarding the operation and interpretation of Event Counters and Histograms available in ALTRUA, INSIGNIA, PULSAR MAX II, and DISCOVERY II pacemakers.
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Workshop B: Essentials of Neonatal Cardiology and CHD Anthony C. Chang, MD, MBA, MPH CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE
 SHUNT LESIONS NEONATAL : CONGENITAL CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS AND CARDIAC SURGERY ANTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF ORANGE COUNTY ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY
SHUNT LESIONS NEONATAL : CONGENITAL CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS AND CARDIAC SURGERY ANTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF ORANGE COUNTY ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY
Type II Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension due to Left Heart Disease
 Heart Failure Center Hadassah University Hospital Type II Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension due to Left Heart Disease Israel Gotsman MD The Heart Failure Center, Heart Institute Hadassah University
Heart Failure Center Hadassah University Hospital Type II Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension due to Left Heart Disease Israel Gotsman MD The Heart Failure Center, Heart Institute Hadassah University
Introduction. Planned surgical procedures
 Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Echo-Web.Com. Planning for Success in the Field of Echocardiography. Echo-Web Catalog and the iechoschool Curriculum
 Planning for Success in the Field of Echocardiography Echo-Web.Com Echo-Web Catalog and the iechoschool Curriculum Richard Keith H. Duncan, RDCS, RCS, RCIS, BBA Contents The Echo-Web Course Catalog...
Planning for Success in the Field of Echocardiography Echo-Web.Com Echo-Web Catalog and the iechoschool Curriculum Richard Keith H. Duncan, RDCS, RCS, RCIS, BBA Contents The Echo-Web Course Catalog...
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Percutaneous mitral valve leaflet repair for mitral regurgitation April 2013. Reference: NHSCB/A09/PS/b
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Percutaneous mitral valve leaflet repair for mitral regurgitation April 2013 Reference: NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Percutaneous
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Percutaneous mitral valve leaflet repair for mitral regurgitation April 2013 Reference: NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Percutaneous
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. John Whitaker, Conn Sugihara and Michael Cooklin (Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust)
 Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome John Whitaker, Conn Sugihara and Michael Cooklin (Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust) A 38 year old paramedic was admitted with symptoms
Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome John Whitaker, Conn Sugihara and Michael Cooklin (Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust) A 38 year old paramedic was admitted with symptoms
How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure
 Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI
 Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm
 Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona
 Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging. Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469)
 Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
TABLE 1 Clinical Classification of AF. New onset AF (first detected) Paroxysmal (<7 days, mostly < 24 hours)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Auscultation of the Heart
 Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a. Diastolic Heart Failure. By Michel D Astous, MD, FRCPC
 Diastolic Heart Failure The evaluation of both systolic and diastolic functions is of great importance among patients presenting with signs of CHF, as the treatment may be quite different depending on
Diastolic Heart Failure The evaluation of both systolic and diastolic functions is of great importance among patients presenting with signs of CHF, as the treatment may be quite different depending on
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
SECTION III: HEMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES
 10/5/00 3:36 PM 10 Calculation of Stenotic Valve Orifice Area Blase A. Carabello and William Grossman BAC: Baylor University, Department of Medicine, Houston Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Houston, Texas
10/5/00 3:36 PM 10 Calculation of Stenotic Valve Orifice Area Blase A. Carabello and William Grossman BAC: Baylor University, Department of Medicine, Houston Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Houston, Texas
The new generation in ECG interpretation
 The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome
 Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Stress Test (CPET) Archived Medical Policy
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
For more information about the use of the Propaq monitor, refer to the Propaq Directions For Use.
 Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013
 Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
TOP 5. The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac. Arrhythmias in Dogs & Cats. Sinus Arrhythmia. TOP 5 Arrhythmias Seen in Dogs & Cats
 Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography
 GUIDELINES AND STANDARDS Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography Sherif F. Nagueh, MD, Chair, Christopher P. Appleton, MD, Thierry C. Gillebert, MD,*
GUIDELINES AND STANDARDS Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography Sherif F. Nagueh, MD, Chair, Christopher P. Appleton, MD, Thierry C. Gillebert, MD,*
CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges
 CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges APPLICANT: INITIAL APPOINTMENT REQUIREMENTS: BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. from an accredited school of medicine or osteopathy. Successful completion of an ACGME or
CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges APPLICANT: INITIAL APPOINTMENT REQUIREMENTS: BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. from an accredited school of medicine or osteopathy. Successful completion of an ACGME or
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen
 RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular
 Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
The Australian Intervention Randomized Control of Rate in Atrial Fibrillation Trial (AIRCRAFT)
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 10, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00338-3
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 10, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00338-3
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
