Workshop B: Essentials of Neonatal Cardiology and CHD Anthony C. Chang, MD, MBA, MPH CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE
|
|
|
- Marilynn Knight
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SHUNT LESIONS NEONATAL : CONGENITAL CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS AND CARDIAC SURGERY ANTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF ORANGE COUNTY ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY FLOW RV VOLUME OVERLOAD ATRIAL DYSRHYTHMIAS ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT PARTIAL ANOMALOUS PV RETURN LV-RA SHUNT (GERBODE DEFECT) CA-RA FISTULA CEREBRAL AVM VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY FLOW AND PRESSURE LV VOLUME OVERLOAD VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS AORTOPULMONARY WINDOW 1
2 COMMON ATRIOVENTRICULAR CANAL COMMON MIXING INCREASED PULMONARY BLOOD FLOW AND PRESSURE AV VALVE REGURGITATION BIVENTRICULAR VOLUME OVERLOAD COMMON ATRIOVENTRICULAR CANAL PAP PBF PVR PAP PBF PVR Low Normal Low CDH Normal or Low PAP PBF PVR PAP PBF PVR CDH Normal or Low VSD Normal VSD in Premie Low 2
3 PAP PBF PVR VSD in Premie VSD in Neonate Low Normal OBSTRUCTIVE LESIONS PULMONARY STENOSIS TETRALOGY OF FALLOT PREOPERATIVE PHYSIOLOGY UNRESTRICTIVE VSD DYNAMIC RVOT OBSTRUCTION RV HYPERTROPHY R TO L SHUNT WITH DECREASE IN SVR TETRALOGY OF FALLOT PREOPERATIVE PHYSIOLOGY TOF AND WITH STENOTIC SHUNT DORV WITH SUBPS SV WITH SUBPS ANY SV WITH STENOTIC SHUNT TREAT WITH OXYGEN, VOLUME, AND NEOSYNEPHRINE 3
4 TETRALOGY OF FALLOT/PULMONARY ATRESIA TETRALOGY OF FALLOT/ ABSENT PULMONARY VALVE AORTIC STENOSIS LV PRESSURE OVERLOAD LV CONCENTRIC HYPERTROPHY SUBENDOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA COEXISTING LESIONS AORTIC STENOSIS CORONARY ISCHEMIA ROSS LV DYSFUNCTION NEOAORTIC INSUFFICIENCY RV DYSFUNCTION RESIDUAL VSD RVOT NARROWING ROSS-KONNO COARCTATION OF THE AORTA LV PRESSURE OVERLOAD LV HYPERTROPHY MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA CVA DUCTAL DEPENDENT LESIONS 4
5 DUCTAL DEPENDENT LESIONS Pulmonary Blood Flow Critical PS/ PAtresia TOF with PS or PAtresia SV with PS or Patresia Tricuspid Atresia Ebstein s Anomaly TRICUSPID ATRESIA Ebstein s Anomaly Ebstein s Anomaly Preoperative Pathophysiology Severe TR Functional and PS/PAt RV/LV Interaction Pulmonary Hypoplasia Anatomic HETEROTAXY SYNDROME Heterotaxy HETEROTAXY SYNDROME Asplenia Heterotaxy DORV/ CAVC TAPVR SubPS or PAtresia AET 5
6 HETEROTAXY SYNDROME Heterotaxy Polysplenia Primum ASD/ LVOTO Interrupted IVC Ipsilateral SVC/PVs CHB DUCTAL DEPENDENT LESIONS SYSTEMIC BLOOD FLOW CRITICAL AORTIC STENOSIS COARCTATION OF THE AORTA INTERRUPTED AORTIC ARCH HYPOPLASTIC LEFT HEART SYNDROME HYPOPLASTIC LEFT HEART SYNDROME SINGLE VENTRICLE PHYSIOLOGY INCREASED QP:QS RV VOLUME OVERLOAD EXTRACARDIAC ISSUES HYPOPLASTIC LEFT HEART SYNDROME SINGLE VENTRICLE PHYSIOLOGY INCREASED QP:QS RV VOLUME OVERLOAD EXTRACARDIAC ISSUES SINGLE VENTRICLE PHYSIOLOGY CRITERIA SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY VENOUS RETURN TO COMMON MIXING CHAMBER SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY BLOOD FLOW DETERMINED BY SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY VASCULAR RESISTANCE Single Ventricle Physiology Qp:QS Calculation IF AO-MV OXYGEN% IS 25% IF PV OXYGEN% IS 95% THEN QP:QS = AO MV/ PV PA = 25 / 95 PA AND SINCE AO = PA SAT 25 / 95 POX 6
7 Single Ventricle Physiology Qp:QS (Pox 87%) IF AO-MV OXYGEN% IS 25% IF PV OXYGEN% IS 95% THEN QP:QS = AO MV/ PV PA = 25 / 95 PA AND SINCE AO = PA SAT 25 / = 3:1 HYPOPLASTIC LEFT HEART SYNDROME RV DYSFUNCTION (RV-LV) SINGLE VENTRICLE PHYSIOLOGY TRICUSPID REGURGITATION SHUNT STENOSIS/OBSTRUCTION RESIDUAL ARCH OBSTRUCTION RESTRICTIVE ASD NORWOOD HYPOPLASTIC LEFT HEART SYNDROME RV DYSFUNCTION (RV-LV) SINGLE VENTRICLE PHYSIOLOGY TRICUSPID REGURGITATION RVOT STENOSIS/OBSTRUCTION RESIDUAL ARCH OBSTRUCTION SANO Bidirectional Cavopulmonary Anastomosis Normal Profile PA PRESSURE MMHG LA PRESSURE 0-5 MMHG TP < 10 MMHG SATURATION 80 5% FONTAN MISCELLANEOUS 7
8 TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT ARTERIES MIXING ASD (MOST EFFECTIVE) VSD PDA COEXISTING PPHN (REVERSE DIFFERENTIAL CYANOSIS) TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT ARTERIES TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT ARTERIES PA saturation > Aortic saturation During systole (compliance of atria), atrial shunt is mostly L R During diastole (compliance of ventricles), mostly R L atrial shunt is TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT ARTERIES LV PREPAREDNESS CORONARY ISCHEMIA TOTAL ANOMALOUS PULMONARY VENOUS CONNECTION OBSTRUCTIVE TYPE LUNG PATHOLOGY NONOBSTRUCTIVE TYPE RV VOLUME OVERLOAD TOTAL ANOMALOUS PULMONARY VENOUS CONNECTION PULMONARY PATHOLOGY NONCOMPLIANT LV ATRIAL ECTOPIC TACHYCARDIA PV CONFLUENCE NARROWING 8
9 TRUNCUS ARTERIOSUS PEROPERATIVE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY INCREASED PULMONARY BLOOD FLOW AND PRESSURE BIVENTRICULAR VOLUME OVERLOAD TRUNCAL STENOSIS/ INSUFFICIENCY EXTRACARDIAC ISSUES TRUNCUS ARTERIOSUS RV RESTRICTIVE DYSFUNCTION JUNCTIONAL ECTOPIC TACHYCARDIA TRUNCAL STENOSIS/ INSUFFIENCY RESIDUAL VSD THE PRESSURE-VOLUME LOOP CARDIAC OUTPUT MANIPULATION CARDIAC OUTPUT MANIPULATION CARDIAC OUTPUT MANIPULATION PRELOAD 9
10 CARDIAC OUTPUT MANIPULATION AFTERLOAD CARDIAC OUTPUT MANIPULATION CONTRACTILITY VALVE STENOSIS [AORTIC] During ventricular ejection, LV pressure exceeds aortic pressure. Stroke volume is decreased; stroke work can be about the same but potential energy is increased. VALVE STENOSIS [MITRAL] During ventricular filling (diastole), LA pressure exceeds LVEDP. Both stroke volume and stroke work are decreased and the potential energy is unchanged. VALVE INSUFFICIENCY [AORTIC] During ventricular relaxation, blood flows backwards from aorta into to the LV. Pulse pressure widens. Both stroke volume and stroke work are increased but potential energy can be about the same. VALVE INSUFFICIENCY [MITRAL] During systole, LV ejects blood back into the LA as well as into the aorta. The LAP and the v-wave are increased. Both stroke volume and stroke work are increased but potential energy can be about the same. 10
11 VALVE INSUFFICIENCY [MITRAL] Acute- increased LA pressure with pulmonary edema and decreased cardiac output Chronic-increased LA size with little if any pulmonary edema and normal cardiac output Cardiac Cycle of Work/ Career Systole Diastole 11
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Resuscitation in congenital heart disease. Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto
 Resuscitation in congenital heart disease Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto Evolution of Congenital Heart Disease Extraordinary success: Overall
Resuscitation in congenital heart disease Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto Evolution of Congenital Heart Disease Extraordinary success: Overall
Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease. Elliot Krane, M.D.
 Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease Elliot Krane, M.D. Introduction The evolution of medicine to managed care and contracted medical services has often had the effect of shifting a sicker
Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease Elliot Krane, M.D. Introduction The evolution of medicine to managed care and contracted medical services has often had the effect of shifting a sicker
How to get insurance companies to work with you
 Paying for Quality ACHD Care How to get insurance companies to work with you Christy Sillman, RN, MSN ACHD nurse coordinator Inpatient ACHD Nurse Educator The Adult Congenital Heart Program Stanford Lucile
Paying for Quality ACHD Care How to get insurance companies to work with you Christy Sillman, RN, MSN ACHD nurse coordinator Inpatient ACHD Nurse Educator The Adult Congenital Heart Program Stanford Lucile
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology:
 Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Pediatric Cardiology What is Cyanosis? Bluish discoloration of skin that occurs when
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Pediatric Cardiology What is Cyanosis? Bluish discoloration of skin that occurs when
Congenital Heart Defects Initial Diagnosis and
 Congenital Heart Defects Initial Diagnosis and Management age e Linda Risley, RN, MSN, CPNP Congenital Heart Defects Congenital heart defects are the most common type of birth defect ~1 out of 100 live
Congenital Heart Defects Initial Diagnosis and Management age e Linda Risley, RN, MSN, CPNP Congenital Heart Defects Congenital heart defects are the most common type of birth defect ~1 out of 100 live
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Questions FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008
 FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
Congenital Heart Defects
 Congenital Heart Defects 1 Congenital Heart Defects CHD with Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow Patent Ductus Arteriosus - PDA...3 Atrial Septal Defect - ASD...4 Ventricular Septal Defect - VSD...5 Aorto-Pulmonary
Congenital Heart Defects 1 Congenital Heart Defects CHD with Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow Patent Ductus Arteriosus - PDA...3 Atrial Septal Defect - ASD...4 Ventricular Septal Defect - VSD...5 Aorto-Pulmonary
Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation. Ghada El Shahed, MD
 Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation Ghada El Shahed, MD Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams University Flow through systemic & pulmonary circulations is normally balanced and equal. Two circulations
Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation Ghada El Shahed, MD Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams University Flow through systemic & pulmonary circulations is normally balanced and equal. Two circulations
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being
 Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. danjcohen@optonline.net
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. danjcohen@optonline.net
Current status of pediatric cardiac surgery
 Current status of pediatric cardiac surgery Sabine H. Daebritz Dept. of Cardio-vascular Surgery Heart Center Duisburg, Germany Normal circulation 1 Complex cardiac lesions Stenoses Shunts Malconnections
Current status of pediatric cardiac surgery Sabine H. Daebritz Dept. of Cardio-vascular Surgery Heart Center Duisburg, Germany Normal circulation 1 Complex cardiac lesions Stenoses Shunts Malconnections
Cardiology Fellowship Manual. Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page
 Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page 2015-2016 UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION
Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page 2015-2016 UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION
020 // Congenital Heart Disease
 020 // Congenital Heart Disease CONTENTS 188 Basics 188 Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) 191 Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) 192 Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD) 194 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) 195 Coronary Fistulas
020 // Congenital Heart Disease CONTENTS 188 Basics 188 Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) 191 Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) 192 Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD) 194 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) 195 Coronary Fistulas
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
Question 1: Interpret the rhythm strip above (comment on regularity, rate, P wave, PR interval and QRS)?
 It is your first month on your NICU rotation and you are prerounding on your patients. The nurse takes you aside and says she s been seeing something funny on the cardiac monitor. You walk to the bedside
It is your first month on your NICU rotation and you are prerounding on your patients. The nurse takes you aside and says she s been seeing something funny on the cardiac monitor. You walk to the bedside
Pulmonary Atresia With Intact Ventricular Septum - Anatomy, Physiology, and Diagnostic Imaging
 Pulmonary Atresia With Intact Ventricular Septum - Anatomy, Physiology, and Diagnostic Imaging Larry Latson MD Director of Pediatric Interventional Cardiology and Adult CHD Joe DiMaggio Children s Hospital
Pulmonary Atresia With Intact Ventricular Septum - Anatomy, Physiology, and Diagnostic Imaging Larry Latson MD Director of Pediatric Interventional Cardiology and Adult CHD Joe DiMaggio Children s Hospital
Delivery Planning for the Fetus with Congenital Heart Disease
 Delivery Planning for the Fetus with Congenital Heart Disease Mar y T. Donofrio MD, FAAP, FACC, FASE Director of the Fetal Heart Program Children s National Medical Center Washington DC Objectives Review
Delivery Planning for the Fetus with Congenital Heart Disease Mar y T. Donofrio MD, FAAP, FACC, FASE Director of the Fetal Heart Program Children s National Medical Center Washington DC Objectives Review
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb.
 The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
Normal Intracardiac Pressures. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
ACYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS
 ACYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS Acyanotic congenital heart defects may be due to obstructive lesions (stenosis) or left-to-right shunts. Lesions with left-to-right shunts include atrial septal defect, ventricular
ACYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS Acyanotic congenital heart defects may be due to obstructive lesions (stenosis) or left-to-right shunts. Lesions with left-to-right shunts include atrial septal defect, ventricular
25 Anomalies and Diseases of the Fetal Heart
 270 25 Anomalies and Diseases of the Fetal Heart Epidemiology and Indications for Fetal Echocardiography Epidemiologic Aspects It is generally known that approximately 15 20% of pregnancies in the second
270 25 Anomalies and Diseases of the Fetal Heart Epidemiology and Indications for Fetal Echocardiography Epidemiologic Aspects It is generally known that approximately 15 20% of pregnancies in the second
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Disclosures. Not as Pink as You Think 3/17/2014. Not As Pink As You Think: Pulse Oximetry Screening For Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 March of Dimes New York State Chapter 36th Annual Perinatal Nurses Conference Promoting Perinatal Health Through Evidence Based Practice Not As Pink As You Think: Pulse Oximetry Screening For Critical
March of Dimes New York State Chapter 36th Annual Perinatal Nurses Conference Promoting Perinatal Health Through Evidence Based Practice Not As Pink As You Think: Pulse Oximetry Screening For Critical
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
How To Treat A Single Ventricle And Fontan
 COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
ANESTHESIA FOR PATIENTS POST CHD REPAIR
 ANESTHESIA FOR PATIENTS POST CHD REPAIR ABDULLAH HALAWANI, MBBS, FRCPC. Consultant CVT Anesthesiologist Head, Section of Pediatric Anesthesia KFSH & RC, Riyadh 1 Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) is one of
ANESTHESIA FOR PATIENTS POST CHD REPAIR ABDULLAH HALAWANI, MBBS, FRCPC. Consultant CVT Anesthesiologist Head, Section of Pediatric Anesthesia KFSH & RC, Riyadh 1 Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) is one of
Chromosome Syndromes associated with Congenital Heart Defects
 National Birth Defects Prevention Network (NBPDN)/NBDPS Annual Meeting Feb. 26-29. 2012 Arlington, VA Chromosome Syndromes associated with Congenital Heart Defects Angela E. Lin, MD, FAAP, FACMG Associate
National Birth Defects Prevention Network (NBPDN)/NBDPS Annual Meeting Feb. 26-29. 2012 Arlington, VA Chromosome Syndromes associated with Congenital Heart Defects Angela E. Lin, MD, FAAP, FACMG Associate
Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology. Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital
 Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital Topics Who needs Nutrition support? Energy Requirements Meeting Energy and growth requirements Feeding Issues
Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital Topics Who needs Nutrition support? Energy Requirements Meeting Energy and growth requirements Feeding Issues
Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013. Director, Intraoperative TEE Program. Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
 Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013 Mary Beth Brady, MD, FASE Director, Intraoperative TEE Program Johns Hopkins School of Medicine At the conclusion of the workshop, the participants
Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013 Mary Beth Brady, MD, FASE Director, Intraoperative TEE Program Johns Hopkins School of Medicine At the conclusion of the workshop, the participants
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery
 Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Congenital heart defects
 CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART
 CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART Charles White MD Director of Thoracic Imaging Department of Radiology University of Maryland NO DISCLOSURES CWHITE@UMM.EDU CARDIAC CASE DISTRIBUTION Coronary CTA 30% ED chest
CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART Charles White MD Director of Thoracic Imaging Department of Radiology University of Maryland NO DISCLOSURES CWHITE@UMM.EDU CARDIAC CASE DISTRIBUTION Coronary CTA 30% ED chest
HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD
 HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD Frances R. Zappalla, D.O. Nemours Cardiac Center A.I. du Pont Hospital for Children Wilmington, DE Definition: HEART MURMURS An extra abnormal heart sound usually detected
HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD Frances R. Zappalla, D.O. Nemours Cardiac Center A.I. du Pont Hospital for Children Wilmington, DE Definition: HEART MURMURS An extra abnormal heart sound usually detected
1p36 and the Heart. John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA
 1p36 and the Heart John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy Services Associate Professor, Pediatric Cardiology and Adult Cardiovascular Diseases Associate
1p36 and the Heart John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy Services Associate Professor, Pediatric Cardiology and Adult Cardiovascular Diseases Associate
The Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease among Neonates Referred for Echocardiography
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 ABSTRACT The Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease among Neonates Referred for Echocardiography Hussain Al Khawahur, MD* Hussain Al Sowaiket, MD** Thuria
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 ABSTRACT The Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease among Neonates Referred for Echocardiography Hussain Al Khawahur, MD* Hussain Al Sowaiket, MD** Thuria
Presentation of Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate and Young Infant
 Presentation of Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate and Young Infant Article cardiology Michael Silberbach, MD,* David Hannon, MD Author Disclosure Drs Silberbach and Hannon did not disclose any financial
Presentation of Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate and Young Infant Article cardiology Michael Silberbach, MD,* David Hannon, MD Author Disclosure Drs Silberbach and Hannon did not disclose any financial
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Failure EXERCISES. Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it.
 Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
Confirmed CCHD What next?
 Confirmed CCHD What next? Herbert J. Stern MD, FACC, FSCAI Children s Cardiology Associates and Dell Children s Hospital Catheter Based Therapy: Spectrum of Procedures Tear PFO to enhance mixing (D-TGA)
Confirmed CCHD What next? Herbert J. Stern MD, FACC, FSCAI Children s Cardiology Associates and Dell Children s Hospital Catheter Based Therapy: Spectrum of Procedures Tear PFO to enhance mixing (D-TGA)
Congenital Heart Disease. Mary Rummell, RN, MN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery
 Congenital Heart Disease Mary Rummell, RN, MN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery Objectives The learner will: Identify 3 areas in the developing heart that result
Congenital Heart Disease Mary Rummell, RN, MN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery Objectives The learner will: Identify 3 areas in the developing heart that result
CURRICULUM VITAE MUTHU JOTHI
 CURRICULUM VITAE MUTHU JOTHI Nationality: Indian Date of Birth: 2 st April 965 Residential Address: A-32 Mayflower Shakthi Gardens Nanjundapuram Road, Coimbatore Pin :64036 Phone: 0(9)422-2325532 Mobile
CURRICULUM VITAE MUTHU JOTHI Nationality: Indian Date of Birth: 2 st April 965 Residential Address: A-32 Mayflower Shakthi Gardens Nanjundapuram Road, Coimbatore Pin :64036 Phone: 0(9)422-2325532 Mobile
Anaesthesia and Heart Failure
 Anaesthesia and Heart Failure Andrew Baldock, Specialist Registrar, Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust E mail: ajbaldock@doctors.org.uk Self-assessment The following true/false questions may be
Anaesthesia and Heart Failure Andrew Baldock, Specialist Registrar, Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust E mail: ajbaldock@doctors.org.uk Self-assessment The following true/false questions may be
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition
 Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition Nevine Mahmoud, MD John Ludtke, MD Maj, USAFR, MC, FS RAM Class 2014 Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine Division of Aerospace Medicine Dayton,
Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition Nevine Mahmoud, MD John Ludtke, MD Maj, USAFR, MC, FS RAM Class 2014 Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine Division of Aerospace Medicine Dayton,
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia By Dr. N. Robert Payne
 The following material was developed prior to RGA s acquisition on January 1, 2010 of the Group Reinsurance Business formerly formerly owned owned by ReliaStar by Life ReliaStar Insurance Life Company
The following material was developed prior to RGA s acquisition on January 1, 2010 of the Group Reinsurance Business formerly formerly owned owned by ReliaStar by Life ReliaStar Insurance Life Company
Mr GH: Pericardial Window. Anaesthetic Management of Cardiac Tamponade
 Mr GH: Pericardial Window Anaesthetic Management of Cardiac Tamponade Mr GH 56 yo M HOPCx Asbestosis, adenoca R lung 8/52 6/52 cisplatin/ taxol chemo Weekly pleural taps for effusions Sent from Bendigo
Mr GH: Pericardial Window Anaesthetic Management of Cardiac Tamponade Mr GH 56 yo M HOPCx Asbestosis, adenoca R lung 8/52 6/52 cisplatin/ taxol chemo Weekly pleural taps for effusions Sent from Bendigo
What is echo? CHAPTER 1 1.1 BASIC NOTIONS. Ultrasound production and detection
 What is echo? CHAPTER 1 1.1 BASIC NOTIONS Echocardiography (echo) the use of ultrasound to examine the heart is a safe, powerful, non-invasive and painless technique. Echo is easy to understand as many
What is echo? CHAPTER 1 1.1 BASIC NOTIONS Echocardiography (echo) the use of ultrasound to examine the heart is a safe, powerful, non-invasive and painless technique. Echo is easy to understand as many
Cardiac Disorders of the Newborn
 Cardiac Disorders of the Newborn Lance A. Parton, MD, FAAP Associate Director Regional NICU Maria Fareri Children s Hospital at Westchester Medical Center Professor of Pediatrics OB/Gyn, Anesthesiology
Cardiac Disorders of the Newborn Lance A. Parton, MD, FAAP Associate Director Regional NICU Maria Fareri Children s Hospital at Westchester Medical Center Professor of Pediatrics OB/Gyn, Anesthesiology
1 Congestive Heart Failure & its Pharmacological Management
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Prof. Keith Baker 1 Congestive Heart Failure & its Pharmacological Management Keith Baker, M.D., Ph.D.
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Prof. Keith Baker 1 Congestive Heart Failure & its Pharmacological Management Keith Baker, M.D., Ph.D.
Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Surgery
 Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Surgery in New York State 2006 2009 New York State Department of Health October 2011 Members of the New York State Cardiac Advisory Committee Chair Spencer King, M.D. Executive
Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Surgery in New York State 2006 2009 New York State Department of Health October 2011 Members of the New York State Cardiac Advisory Committee Chair Spencer King, M.D. Executive
Social Security Administration Compassionate Allowances Outreach Hearing on Cardiovascular Disease and Multiple Organ Transplants November 9, 2010
 Social Security Administration Compassionate Allowances Outreach Hearing on Cardiovascular Disease and Multiple Organ Transplants November 9, 2010 Ileana Piña, MD, MPH American Heart Association/American
Social Security Administration Compassionate Allowances Outreach Hearing on Cardiovascular Disease and Multiple Organ Transplants November 9, 2010 Ileana Piña, MD, MPH American Heart Association/American
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in the Apparently Healthy Newborn
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in the Apparently Healthy Newborn A presentation of Texas Pulse Oximetry Project: A Joint Educational Initiative of The University of Texas Health Science
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in the Apparently Healthy Newborn A presentation of Texas Pulse Oximetry Project: A Joint Educational Initiative of The University of Texas Health Science
Auscultation of the Heart
 Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease
 Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease Pei-NiJone, MD a, Kenneth O. Schowengerdt, Jr., MD b, * KEYWORDS Fetal echocardiography Prenatal diagnosis Neonatal heart disease Fetal echocardiography,
Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease Pei-NiJone, MD a, Kenneth O. Schowengerdt, Jr., MD b, * KEYWORDS Fetal echocardiography Prenatal diagnosis Neonatal heart disease Fetal echocardiography,
HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D.
 CHAPTER 20 HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D. INTRODUCTION Congenital heart defects are relatively rare; seriously debilitating heart abnormalities rarer still. Approximately 8 babies
CHAPTER 20 HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D. INTRODUCTION Congenital heart defects are relatively rare; seriously debilitating heart abnormalities rarer still. Approximately 8 babies
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects
 Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
Definitions. Child LifeAdvance. Critical Illness Insurance Plan
 Definitions Child LifeAdvance Critical Illness Insurance Plan Child LifeAdvance This is specimen wording only and is not binding. In the event of any inconsistency between the information contained in
Definitions Child LifeAdvance Critical Illness Insurance Plan Child LifeAdvance This is specimen wording only and is not binding. In the event of any inconsistency between the information contained in
Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Patient Information
 Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patient Information WHAT IS CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE? Congenital heart disease (CHD) refers to a defect of the heart or major blood vessels
Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patient Information WHAT IS CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE? Congenital heart disease (CHD) refers to a defect of the heart or major blood vessels
Introduction to CV Pathophysiology. Introduction to Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
 Introduction to CV Pathophysiology Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Introduction to Cardiovascular Pathophysiology 1. Basic Anatomy 2. Excitation Contraction Coupling
Introduction to CV Pathophysiology Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Introduction to Cardiovascular Pathophysiology 1. Basic Anatomy 2. Excitation Contraction Coupling
THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS
 MEDICAL CENTER ARCHIVES OF NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN/WEILL CORNELL 1300 York Avenue # 34 New York, NY 10065 Finding Aid To THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS Dates of Papers: 1948-1991 52.5 Linear
MEDICAL CENTER ARCHIVES OF NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN/WEILL CORNELL 1300 York Avenue # 34 New York, NY 10065 Finding Aid To THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS Dates of Papers: 1948-1991 52.5 Linear
Working Towards Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening to Detect Critical CHD
 Working Towards Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening to Detect Critical CHD Dalhousie Fall Refresher Course 2015 Kenny K Wong, MD, FRCPC Pediatric Cardiologist Associate Professor of Pediatrics Objectives
Working Towards Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening to Detect Critical CHD Dalhousie Fall Refresher Course 2015 Kenny K Wong, MD, FRCPC Pediatric Cardiologist Associate Professor of Pediatrics Objectives
Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs. Acknowledgement. Disclosures Real or Potential Conflicts of Interest
 Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs W. Lane Edwards, Jr., MSN, ARNP, ANP Hospitalist Group of Southwest Florida Affiliate Professor of Nursing, University of Alaska at Anchorage Acknowledgement
Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs W. Lane Edwards, Jr., MSN, ARNP, ANP Hospitalist Group of Southwest Florida Affiliate Professor of Nursing, University of Alaska at Anchorage Acknowledgement
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Sao Paulo Brazil UNIDADE FETAL
 Simone R. F. Fontes Pedra, MD Si R F F P d MD Sao Paulo Brazil UNIDADE FETAL FROM CONCEPTION TO MATURITY: BUILDING A FETAL THERAPY PROGRAM Simone R F Fontes Simone R. F. Fontes Simone R. F. FontesPedra
Simone R. F. Fontes Pedra, MD Si R F F P d MD Sao Paulo Brazil UNIDADE FETAL FROM CONCEPTION TO MATURITY: BUILDING A FETAL THERAPY PROGRAM Simone R F Fontes Simone R. F. Fontes Simone R. F. FontesPedra
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Feeding in Infants with Complex Congenital Heart Disease. Rachel Torok, MD Southeastern Pediatric Cardiology Society Conference September 6, 2014
 Feeding in Infants with Complex Congenital Heart Disease Rachel Torok, MD Southeastern Pediatric Cardiology Society Conference September 6, 2014 Objectives Discuss common feeding issues in patients with
Feeding in Infants with Complex Congenital Heart Disease Rachel Torok, MD Southeastern Pediatric Cardiology Society Conference September 6, 2014 Objectives Discuss common feeding issues in patients with
Review of the Cardiac Unit at the Royal Liverpool Children s Hospital NHS Trust Alder Hey
 I N F O R M A T I O N Review of the Cardiac Unit at the Royal Liverpool Children s Hospital NHS Trust Alder Hey by Professor John R. Ashton CBE Regional Director of Public Health, National Health Service,
I N F O R M A T I O N Review of the Cardiac Unit at the Royal Liverpool Children s Hospital NHS Trust Alder Hey by Professor John R. Ashton CBE Regional Director of Public Health, National Health Service,
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen
 RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
Fetal and neonatal mortality in patients with isolated congenital heart diseases and heart conditions associated with extracardiac abnormalities
 Original article Arch Argent Pediatr 2013;111(5):418-422 / 418 Fetal and neonatal mortality in patients with isolated congenital heart diseases and heart conditions associated with extracardiac abnormalities
Original article Arch Argent Pediatr 2013;111(5):418-422 / 418 Fetal and neonatal mortality in patients with isolated congenital heart diseases and heart conditions associated with extracardiac abnormalities
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease
 Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS
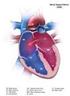 Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Consider the following 2 cases and discuss the questions below before reading the tutorial.
 Recognising Cardiac Disease in Children Name: Hospital: E-mail: Elizabeth Storey Leeds Teaching Hospitals, UK kate@medex.org.uk Consider the following 2 cases and discuss the questions below before reading
Recognising Cardiac Disease in Children Name: Hospital: E-mail: Elizabeth Storey Leeds Teaching Hospitals, UK kate@medex.org.uk Consider the following 2 cases and discuss the questions below before reading
CARDIAC DISORDERS. Circulatory Changes at Birth 7/3/2008
 CARDIAC DISORDERS Circulatory Changes at Birth When the umbilical cord is clamped, the blood supply from the placenta is cut off, and oxygenation must then take place in the infant s lungs As the lungs
CARDIAC DISORDERS Circulatory Changes at Birth When the umbilical cord is clamped, the blood supply from the placenta is cut off, and oxygenation must then take place in the infant s lungs As the lungs
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
North Dakota Birth Defects Monitoring System
 North Dakota Birth Defects Monitoring System Summary Report 1995-1999 North Dakota Department of Health North Dakota Birth Defects Monitoring System Summary Report 1995 1999 John Hoeven, Governor Dr. Terry
North Dakota Birth Defects Monitoring System Summary Report 1995-1999 North Dakota Department of Health North Dakota Birth Defects Monitoring System Summary Report 1995 1999 John Hoeven, Governor Dr. Terry
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Pediatric Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider. Mary Anne Milbert, RN, MSN, CPNP-PC
 Pediatric Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider Mary Anne Milbert, RN, MSN, CPNP-PC 22nd Annual Northeast Regional Nurse Practitioner Conference May 6-8, 2015 DISCLOSURES There has been no commercial
Pediatric Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider Mary Anne Milbert, RN, MSN, CPNP-PC 22nd Annual Northeast Regional Nurse Practitioner Conference May 6-8, 2015 DISCLOSURES There has been no commercial
Cardiovascular surgery: Overview and outcomes
 Cardiovascular surgery: Overview and outcomes Heart Services Health 1 s vision for cardiovascular care provides cardiovascular services that: Produce superior outcomes Design care around the patient experience
Cardiovascular surgery: Overview and outcomes Heart Services Health 1 s vision for cardiovascular care provides cardiovascular services that: Produce superior outcomes Design care around the patient experience
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Results From the New Jersey Statewide Critical Congenital Heart Defects Screening Program
 Results From the New Jersey Statewide Critical Congenital Heart Defects Screening Program WHAT S KNOWN ON THIS SUBJECT: Prenatal diagnosis and clinical examination do not identify all infants with critical
Results From the New Jersey Statewide Critical Congenital Heart Defects Screening Program WHAT S KNOWN ON THIS SUBJECT: Prenatal diagnosis and clinical examination do not identify all infants with critical
The Congenital Heart Surgeons Society (CHSS) Datacenter
 The Congenital Heart Surgeons Society Datacenter: Unique Attributes as a Research Organization Christopher A. Caldarone, MD, and William G. Williams, MD Over the last 25 years, the Congenital Heart Surgeons
The Congenital Heart Surgeons Society Datacenter: Unique Attributes as a Research Organization Christopher A. Caldarone, MD, and William G. Williams, MD Over the last 25 years, the Congenital Heart Surgeons
Anatomy Review. Heart Murmurs. Surface Topography of the Heart 7/19/2011. The Base of the Heart and Erb s Point
 James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease
 5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Adult Cardiac Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks
 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 TETRALOGY OF FALLOT ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 219 18 TH APRIL 2011 Dr Lucy Hepburn Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS Trust Correspondence to: HepbuL@gosh.nhs.uk QUESTIONS Before continuing, try to
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 219 18 TH APRIL 2011 Dr Lucy Hepburn Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS Trust Correspondence to: HepbuL@gosh.nhs.uk QUESTIONS Before continuing, try to
Heart Murmurs. Outline. Basic Pathophysiology
 Heart Murmurs David Leder Outline I. Basic Pathophysiology II. Describing murmurs III. Systolic murmurs IV. Diastolic murmurs V. Continuous murmurs VI. Summary Basic Pathophysiology Murmurs = Math Q =
Heart Murmurs David Leder Outline I. Basic Pathophysiology II. Describing murmurs III. Systolic murmurs IV. Diastolic murmurs V. Continuous murmurs VI. Summary Basic Pathophysiology Murmurs = Math Q =
Fetal echocardiography at 11 13 weeks by transabdominal high-frequency ultrasound
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 296 301 Published online 10 February 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8934 Fetal echocardiography at 11 13 weeks by transabdominal
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 296 301 Published online 10 February 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8934 Fetal echocardiography at 11 13 weeks by transabdominal
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Introduction Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common congenital disorder in newborns [1]. Due to definitional issues, there are large variations in prevalence estimates.
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Introduction Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common congenital disorder in newborns [1]. Due to definitional issues, there are large variations in prevalence estimates.
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery
 Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery Stanford Health Care offers leading, superior options in cardiac surgery, including the latest techniques and research for Minimally Invasive Cardiac surgery. Advanced
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery Stanford Health Care offers leading, superior options in cardiac surgery, including the latest techniques and research for Minimally Invasive Cardiac surgery. Advanced
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April 15, 2008
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
