HEMATOLOGY WBC Anaemia classification
|
|
|
- Terence Lambert
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEMATOLOGY WBC Anaemia classification Tropical Laboratory Medecine Unit February 2009 P. Gillet
2 WBC Leukocyte number concentration (WBC count) Man and women (Asia) : leukocytes/µl Man and women (Africa) : leucocytes/µl RBC count : /µl Platelet count : /µl Destruction of the RBC Dilution and counting WBC in a known volume
3 WBC Leukocyte number concentration (WBC count) Destruction of the RBC (hemolysis) TÜRCK SOLUTION dilution 1/20 (v/v) (20 µl blood µl Türck) Dilution and counting WBC in a known volume COUNTING CHAMBER
4 WBC Neubauer counting chamber
5 WBC Neubauer (double improved) counting chamber: Area : 3 mm x 3 mm = 9 mm². Depth : 0,1 mm. 1 4 Field of vue 10x 2 3
6 WBC Neubauer (double improved) counting chamber: Area : 3 mm x 3 mm = 9 mm². Depth : 0,1 mm. Field of vue 40x
7 WBC Leukocyte number concentration (WBC count) Dilution factor : 20 µl of blood µl Turck solution, gives a 20 x blood dilution Volume factor : 4 large squares counted, or 4 x 0.1 mm³. [10/4 = 2,5 x]. Total factor : 50 x Number of leukocytes par mm3 (or µl) of blood = Number of leukocytes counted x 50
8 WBC Count Leukocyte type number fraction (% of the different types of WBC) preparation of thin blood film staining of thin blood films
9 WBC Count Preparation of thin blood film Let dry (fix with methanol) Stain with (May-Grünwald-Giemsa) or with Giemsa
10
11 WBC Count Film too thick Film too thin
12
13 Giemsa Dry thin blood film. Fixation with methanol. Cover the complete preparation with a 3.5 % diluted Giemsa buffered solution [5 drops of concentrated Giemsa + 4 ml of buffered water per slide]. Let stain for 20 to 30 minutes. (coloration) Rinse by gently dripping tap water on the preparation. Let dry and examine under the microscope with an oilimmersion objective 100x
14 May-Grünwald-Giemsa Dry thin blood film. Cover completely with May-Grünwald solution. Let the solution act for 3 minutes. (fixation) Without removing the May-Grünwald solution, add (drop by drop) 4 ml of buffered water. Let the preparation stand for 1 minute (coloration 1). Remove the staining solution. Do not rinse the slide Without rinsing the slide, cover the complete preparation with a 3.5 % diluted Giemsa buffered solution [5 drops of concentrated Giemsa + 4 ml of buffered water per slide]. Let stain for 20 to 30 minutes (coloration 2). Rinse by gently dripping tap water on the preparation. Let dry and examine under the microscope with an oil-immersion objective 100x
15 Differential WBC Count CELL TYPE SIZE NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM GRANULOCYTES µm FORM COLOUR CHROMATIN STRUCTURE QUANTITY COLOUR GRANULES LEUKOCYTES : POLYMORPHONUCLEAR (GRANULOCYTES) IMMATURE NON SEGMENTED NEUTROPHILS Band forms or S shaped Horseshoe, Central curvature is maximum a third part of the width of the lobes Clear blue purple Strands of fine chromatin abundant +++ Dusty rose (=very small granules) Small granules, light purple or violet Not always present SEGMENTED NEUTROPHILS to 5 lobes Deep blue purple Rather thick and coarse +++ Rose Small granules, Pink or pink mauve EOSINOPHILS Usually a bi-lobed nucleus Blue purple Rather thick and coarse +++ Rose Many large, uniform granules, red orange BASOPHILS Hardly visible lobes, not well separated (polymorph) Blue purple Rather thick and coarse, covered by granules +++ Light rose Very large, well separated, variable granules Deep purple Small in number Non segmented Neutrophil Segmented Neutrophil Eosinophil Basophil
16 Differential WBC Count CELL TYPE SIZE NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM AGRANULOCYTES µm FORM COLOUR CHROMATIN STRUCTURE QUANTITY COLOUR GRANULES LEUKOCYTES : MONOMORPHONUCLEAR (AGRANULOCYTES) SMALL LYMPHOCYTES 7-10 Round or oval Or slightly indented Deep purple Big clumps of intensely stained chromatin (-) or + Sky blue (Often absent) LARGE LYMPHOCYTES Round or oval Or slightly indented Red, purple Clumps of deep stained chromatin and other clumps which are less intensely stained ++ Sky blue Absent or a few granules azurophils (rose violet) MONOCYTES Round, oval, indented or bean form Blue to slightly violet Fine, spongy like +++ Vacuoles often demonstrable. Grey or blue grey Very fine granules (dusty like), azurophils (rose violet) ERYTHROCYTES 6,7 7,7 Biconcave discus shape Rose None TROMBOCYTES 1,5 2 (5) Slightly blue Reddish Lymphocyte Monocyte
17
18 Hemato 2
19 Hemato 3
20 Hemato 4
21 Hemato 5
22 2. Anaemia classification Haemoglobin concentration Erythrocyte volume fraction (PCV) RBC count indices
23 Anaemia classification (1) RED CELL INDICES 1 : Haemoglobin and PCV : MCHC Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin Concentration MCHC (g/100 ml) = Haemoglobin concentration (g/100 ml) / PCV (%) x 100 MCHC < 30 g% MCHC between 30 and 36 g% Hypochromic anaemia. Normochromic anaemia.
24 Anaemia classification (2) 2 : PCV and RBC count : MCV Mean Corpuscular Volume PCV (%) MCV (fl) = x 10 x l Red blood cell count per µl (in millions) FOR ADULTS microcytic anaemia < 82 normocytic anaemia > 92 macrocytic anaemia Reference range : 82 to 92 fl (for adults; age related variation for children) [a femtolitre (fl) is of a litre]
25 Anaemia classification (3) 3 : Haemoglobin and RBC count : MCH Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin Haemoglobin (in g/l) MCH (pg) = Red blood cells count per µl (in millions) Reference range : 28 to 32 pg (for adults; age related variation for children) FOR ADULTS > 32 hyperchromic anaemia
26 Other useful tests Thin blood films examination (Giemsa) Test for sickle-cell anaemia Determination of the reticulocyte number fraction/number Parasites detection (faeces, blood, )
27 RED CELL MORPHOLOGY Shape, size or color Inclusions (DNA) (Ribosomes) Anisocytosis : Different sizes (Haemoglobin) Poikilocytosis : Different shapes Anisochromasia : Different colors
28
29 a a : Normal. b : Anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, anisochromasia, microcytes, elliptocytes, c : Anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, microcytes, d: Hypochromia, anisocytosis, microcytes, elliptocytes, fragment, c b d
30 RED CELL MORPHOLOGY Shape, size or color Inclusions (DNA) (Ribosomes) Anisocytosis : Different sizes (Haemoglobin) Poikilocytosis : Different shapes Anisochromasia : Different colors
31 a b c a: b: c: Anisocytosis Anisocytosis, Anisocytosis Spherocytes Target cells, Basophilic stippling Polychromatic macrocytes Poikilocytes, Ovallocytes Howell-Jolly body Acanthocytes Sprerocytes
32 a : Anisocytosis Fragments Acanthocytes a b : Anisocytosis Macrocytes Microcytes b C: Anisocytosis Anisochromasia Sperocytes Macrocytes Microcytes Fragments c
33 Corpuscules de Heinz (haemoglobin) Siderocytes (Pappenheimer) Howell-Jolly body (DNA) Pappenheimer (iron) b c a
34 Acanthocytes Echinocytes
35
36 Hypochromic anaemia : Iron deficiency a and b : moderately severe Hypochromasia Microcytosis Poikilocytosis Anisocytosis Elliptocytes c: very severe Hypochromasia, Microcytosis Poikilocytosis Anisocytosis Elliptocytes
37 Hypochromic anaemia : Iron deficiency Before the treatment During the treatment
38 Hypochromic anaemia : β thalassaemia minor (a, b) β thalassaemia major (c) a : microcytosis, anisocytosis, poikilocytosis b : microcytosis, anisocytosis, Poikilocytosis Basophilic stippling (Hypochromic cells) a : normoblasts, double population (trf) Howell Jolly Basophilic stippling
39 Hypochromic anaemia : β thalassaemia minor a b
40
41 Normochromic anaemia : Sickel cells
42 Other useful tests Thin blood films examination (Giemsa) Test for sickle-cell anaemia Determination of the reticulocyte number fraction/number Parasites detection (faeces, blood, )
43 SS AS
44
45 hyperchromic anaemia: MACROCYTIC ANAEMIA i
46 Hyperchromic anaemia : Megaloblastic anaemia
47
48 Other useful tests Thin blood films examination (Giemsa) Test for sickle-cell anaemia Determination of the reticulocyte number fraction/number Parasites detection (faeces, blood, )
49 Determination of the reticulocyte number fraction/number Reticulocytes can be distinguished from mature RBCs because they still contain remnant genetic material (RNA) inside them, a characteristic not found in mature RBCs Blood briefly incubated with supravital stain, the RNA is precipitated as a dye-rna-protein complex that can be seen microscopically as a dark blue network (reticulum) or as dark blue granules on a thin blood film.
50 Determination of the reticulocyte number fraction/number count the number of reticulocytes in 5 fields of 200 RBCs. Must be a thin area where cells are evenly distributed and not touching each other.
51 Reticulocytes count Percentage : Adults and children : Infants at birth : 2-15 / RBC / RBC Absolute number : Adults and children : / µl Infants at birth : up to /µl
Hematology Morphology Critique
 Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010
 NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY
 9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - GRANULOCYTE FORMATION AND CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Preparation of Blood Films
 Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains)
 LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
A Clinical Pathology 201 Study Module
 Tutorial - Blood Cell Morphology A Clinical Pathology 201 Study Module by Carolyn Sue Walters, MHS, MT(ASCP) Department of Pathology School of Medicine Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center
Tutorial - Blood Cell Morphology A Clinical Pathology 201 Study Module by Carolyn Sue Walters, MHS, MT(ASCP) Department of Pathology School of Medicine Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center
Exercise 9: Blood. Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826.
 Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Evaluation of Cell Morphology and Introduction to Platelet and White Blood Cell Morphology
 Evaluation of Cell Morphology and Introduction to Platelet and White Blood Cell Morphology Kathy W. Jones, MS, MT(ASCP), CLS(NCA) Chapter 5 Introduction Examination of the Peripheral Blood Smear The Normal
Evaluation of Cell Morphology and Introduction to Platelet and White Blood Cell Morphology Kathy W. Jones, MS, MT(ASCP), CLS(NCA) Chapter 5 Introduction Examination of the Peripheral Blood Smear The Normal
Atlas of Hematology and Analysis of Peripheral Blood Smears
 CHAPTER e17 Atlas of Hematology and Analysis of Peripheral Blood Smears Dan L. Longo Some of the relevant findings in peripheral blood, enlarged lymph nodes, and bone marrow are illustrated in this chapter.
CHAPTER e17 Atlas of Hematology and Analysis of Peripheral Blood Smears Dan L. Longo Some of the relevant findings in peripheral blood, enlarged lymph nodes, and bone marrow are illustrated in this chapter.
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
RDW-- Interpreting the Full Blood Count
 RDW-- Interpreting the Full Blood Count The most important components of a Full Blood Count report are, of course, the Haemoglobin, the White Cell Count and Differential and the Platelet Count. However,
RDW-- Interpreting the Full Blood Count The most important components of a Full Blood Count report are, of course, the Haemoglobin, the White Cell Count and Differential and the Platelet Count. However,
MICROKROM MICROKROM. Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains
 MICROKROM M I C R O S C O P Y S TA I N S MICROKROM Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains Coral Clinical Systems A3, Gitanjali Tulip Block, Dr. A. Do Rego Bagh, Alto Santacruz, Bambolim
MICROKROM M I C R O S C O P Y S TA I N S MICROKROM Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains Coral Clinical Systems A3, Gitanjali Tulip Block, Dr. A. Do Rego Bagh, Alto Santacruz, Bambolim
Professor Emeritus Paul J Canfield Faculty of Veterinary Science University of Sydney HAEMATOLOGY PRACTICAL NOTES FOR VETERINARY NURSES INTRODUCTION
 Pathology in Practice NSW Far South Coast Branch NSW Division, Australian Veterinary Association REGIONAL CONTINUING EDUCATION CONFERENCE AT BATEMAN S BAY, 10-12 September 2010 Professor Emeritus Paul
Pathology in Practice NSW Far South Coast Branch NSW Division, Australian Veterinary Association REGIONAL CONTINUING EDUCATION CONFERENCE AT BATEMAN S BAY, 10-12 September 2010 Professor Emeritus Paul
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells
 Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Hematology Sequence. Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES. c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral Blood Smear (several parts)
 Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
BLOOD FILM STAINING EFFECTS
 An Educational Supplement prepared by ALQEP May 2004 Introduction The stained peripheral blood film is one of the world s most widely and frequently used tests. Since its introduction in the late nineteenth
An Educational Supplement prepared by ALQEP May 2004 Introduction The stained peripheral blood film is one of the world s most widely and frequently used tests. Since its introduction in the late nineteenth
MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES OF THE ERYTHROCYTE
 MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES OF THE ERYTHROCYTE 68 Assignment: VIEW the RBC Morphology Slides located on Blackboard as you read/refer to the following pages 67-73 regarding Morphologic Abnormalities of the
MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES OF THE ERYTHROCYTE 68 Assignment: VIEW the RBC Morphology Slides located on Blackboard as you read/refer to the following pages 67-73 regarding Morphologic Abnormalities of the
Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF BLOOD CELLS
 Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF BLOOD CELLS April - 2012 ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF RED BLOOD CELL When a blood smear is inspected for abnormal
Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF BLOOD CELLS April - 2012 ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF RED BLOOD CELL When a blood smear is inspected for abnormal
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD
 ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY. Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab
 HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY RED BLOOD CELLS AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS IN URINALYSIS
 URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points)
 Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood
 70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
SEED Haematology. Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013
 SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory Automated haematology cell counting The laboratory
SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory Automated haematology cell counting The laboratory
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT
 MANUAL PLATELET COUNT Principle Whole blood is diluted with a 1% ammonium oxalate solution. The isotonic balance of the diluent is such that all erythrocytes are lysed while the leukocytes, platelets,
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT Principle Whole blood is diluted with a 1% ammonium oxalate solution. The isotonic balance of the diluent is such that all erythrocytes are lysed while the leukocytes, platelets,
Keywords: RBC histogram, Peripheral blood smear, red cell disorders.
 Research article Automated red blood cell analysis compared with routine red blood cell morphology by smear review Dr.Poonam Radadiya*, Dr.Nandita Mehta*, Dr.Hansa Goswami***, Dr.R.N.Gonsai**** *3 rd year
Research article Automated red blood cell analysis compared with routine red blood cell morphology by smear review Dr.Poonam Radadiya*, Dr.Nandita Mehta*, Dr.Hansa Goswami***, Dr.R.N.Gonsai**** *3 rd year
serology Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification
 Serology: Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification S erology is a branch of immunology dealing with techniques to identify and measure antigens, and to detect serum antibodies. Agglutination
Serology: Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification S erology is a branch of immunology dealing with techniques to identify and measure antigens, and to detect serum antibodies. Agglutination
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Young fetus: site of hematopoiesis together with the liver and bone marrow. Hgb WBC >----------< Plt Hct. Retic =
 Learning Objectives At the completion of this program, the participants will be able to: 1. Identify the components of the CBC and Differential and their clinical implications. 2. Identify normal pediatric
Learning Objectives At the completion of this program, the participants will be able to: 1. Identify the components of the CBC and Differential and their clinical implications. 2. Identify normal pediatric
Haematology what does your blood test mean?
 Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e. Chapter 17: Blood
 Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink
 A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink Chris Thomas, 3 Hall End, Milton, Cambridge CB24 6AQ, [email protected] Published in: Micscape http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artsep15/ct-quink-blood-stain.pdf
A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink Chris Thomas, 3 Hall End, Milton, Cambridge CB24 6AQ, [email protected] Published in: Micscape http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artsep15/ct-quink-blood-stain.pdf
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT
 MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
Mean cell volume (MCV)- reference range 79-101 fl Red cell distribution width (RDW)- reference range <15.1
 Anaemia Mean cell volume and red cell distribution width helped diagnose anaemia cause. Red cell distribution width went up with deficiencies (whether iron, folate or B-12), and the anaemic haemoglobinopathies.
Anaemia Mean cell volume and red cell distribution width helped diagnose anaemia cause. Red cell distribution width went up with deficiencies (whether iron, folate or B-12), and the anaemic haemoglobinopathies.
A&P 2 Blood Lab Guide In-Lab Exercises
 A&P 2 Blood Lab Guide In-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking at the blood and some common blood tests.
A&P 2 Blood Lab Guide In-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking at the blood and some common blood tests.
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
LAB: Blood Exploration
 Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE
 MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual white blood cell counts using the Unopette system. PRINCIPLE Free-flowing
MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual white blood cell counts using the Unopette system. PRINCIPLE Free-flowing
Laboratory Studies in the Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency, Latent Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficient Erythropoiesis
 Laboratory Studies in the Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency, Latent Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficient Erythropoiesis General Comments The laboratory studies listed below are helpful in the diagnosis and management
Laboratory Studies in the Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency, Latent Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficient Erythropoiesis General Comments The laboratory studies listed below are helpful in the diagnosis and management
Key Words: Erythrocytes, reticulocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, platelets, CBC
 HEMATOPOIETIC SYSTEM I: PERIPHERAL BLOOD READING: Gartner and Hiatt, pages 89-101 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the composition of normal peripheral blood, including the relative quantities of the blood
HEMATOPOIETIC SYSTEM I: PERIPHERAL BLOOD READING: Gartner and Hiatt, pages 89-101 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the composition of normal peripheral blood, including the relative quantities of the blood
HM_09_336 v1.0. Atlas of Pediatric Peripheral Blood Smears
 Atlas of Pediatric Peripheral Blood Smears Atlas of Pediatric Peripheral Blood Smears Taru Hays, MD Pediatric Hematologist Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders The Children s Hospital of Denver Professor
Atlas of Pediatric Peripheral Blood Smears Atlas of Pediatric Peripheral Blood Smears Taru Hays, MD Pediatric Hematologist Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders The Children s Hospital of Denver Professor
Complete Blood Count in Primary Care
 Complete Blood Count in Primary Care bpac nz better medicine Editorial Team Tony Fraser Professor Murray Tilyard Clinical Advisory Group Dr Dave Colquhoun Michele Cray Dr Rosemary Ikram Dr Peter Jensen
Complete Blood Count in Primary Care bpac nz better medicine Editorial Team Tony Fraser Professor Murray Tilyard Clinical Advisory Group Dr Dave Colquhoun Michele Cray Dr Rosemary Ikram Dr Peter Jensen
California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Distance Learning Program
 California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Distance Learning Program NEUTROPHILIA by Helen M. Sowers, MA, CLS Dept. of Biological Science (retired) California State University, East Bay Hayward,
California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Distance Learning Program NEUTROPHILIA by Helen M. Sowers, MA, CLS Dept. of Biological Science (retired) California State University, East Bay Hayward,
Cells. Introduction WSBCTC 1
 Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
EVALUATING BLOOD FILMS
 Idea Exchange Mind Over Miller 2004 Annual Index Clinical Solutions for Companion-Animal Practitioners www.vetmedpub.com DECEMBER 2004 EVALUATING BLOOD FILMS Take 3 minutes to bring abnormalities to light
Idea Exchange Mind Over Miller 2004 Annual Index Clinical Solutions for Companion-Animal Practitioners www.vetmedpub.com DECEMBER 2004 EVALUATING BLOOD FILMS Take 3 minutes to bring abnormalities to light
BioSciences. Peripheral Blood Smear Preparation. Blood Smear Preparation Materials
 PolyFacts Vol. 5 No. 1 BioSciences Use the Wright Stain High Quality StainRITE Ready-to-Use Stains for Hematology Peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated with
PolyFacts Vol. 5 No. 1 BioSciences Use the Wright Stain High Quality StainRITE Ready-to-Use Stains for Hematology Peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated with
 Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions
 Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
OBJECTIVES PROCEDURE. Lab 2- Bio 160. Name:
 Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
EDF Extended Depth of Field
 EDF Extended Depth of Field An upgrade for the ImageStream system Think outside the dot. Break the classic depth of field barrier Improve precision Enhance discrimination Simplify analysis Increase resolution
EDF Extended Depth of Field An upgrade for the ImageStream system Think outside the dot. Break the classic depth of field barrier Improve precision Enhance discrimination Simplify analysis Increase resolution
Pentra DX Nexus. Process efficiency in Hematology
 Pentra DX Nexus Process efficiency in Hematology Pentra DX Nexus Be productive and flexible 120 samples per hour 28 parameters Automatic reflex testing Automatic validation of results Integrated cytology
Pentra DX Nexus Process efficiency in Hematology Pentra DX Nexus Be productive and flexible 120 samples per hour 28 parameters Automatic reflex testing Automatic validation of results Integrated cytology
Clinical Laboratory Parameters for Crl:CD(SD) Rats. March, 2006. Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis, Ph.D. Charles B. Clifford, D.V.M., Ph.D.
 Clinical Laboratory Parameters for Crl:CD(SD) Rats March, 2006 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis, Ph.D. Charles B. Clifford, D.V.M., Ph.D. CHARLES RIVER LABORATORIES Clinical Laboratory Parameters
Clinical Laboratory Parameters for Crl:CD(SD) Rats March, 2006 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis, Ph.D. Charles B. Clifford, D.V.M., Ph.D. CHARLES RIVER LABORATORIES Clinical Laboratory Parameters
Gram Staining. The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain. Advantages:
 Gram Staining The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain Advantages: Can observe size and morphology (like other staining) Can find out additional information about the organism- primarily what type of
Gram Staining The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain Advantages: Can observe size and morphology (like other staining) Can find out additional information about the organism- primarily what type of
Approach to the child with anemia
 1 of 43 6/8/2010 2:17 PM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Your UpToDate subscription will expire in 22 day(s). Click here to renew. Approach to the child with anemia Author
1 of 43 6/8/2010 2:17 PM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Your UpToDate subscription will expire in 22 day(s). Click here to renew. Approach to the child with anemia Author
Hematology. Diagnostic Value of CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 22 Diagnostic Value of Hematology JAIME SAMOUR, MVZ, P hd, D ipl ECAMS Hematology is the discipline of medical science that studies the blood and blood-forming tissues, and is currently considered
CHAPTER 22 Diagnostic Value of Hematology JAIME SAMOUR, MVZ, P hd, D ipl ECAMS Hematology is the discipline of medical science that studies the blood and blood-forming tissues, and is currently considered
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Hair & Fiber. (Unit 5)
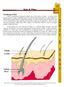 37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
What Does My Bone Marrow Do?
 What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI
 Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Blood Questions. 8. A reduced ability to produce thrombin would cause the time required for blood clot formation to:
 Answer the first 40 items with: a. Increase b. Decrease c. Stay the same 1. An increase in plasma levels of erythropoietin will cause blood viscosity to: 2. The activation of plasminogen will cause the
Answer the first 40 items with: a. Increase b. Decrease c. Stay the same 1. An increase in plasma levels of erythropoietin will cause blood viscosity to: 2. The activation of plasminogen will cause the
Subtypes of AML follow branches of myeloid development, making the FAB classificaoon relaovely simple to understand.
 1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
Pathology No: SHS-CASE No. Date of Procedure: Client Name Address
 TEL #: (650) 725-5604 FAX #: (650) 725-7409 Med. Rec. No.: Date of Procedure: Sex: A ge: Date Received: Date of Birth: Account No.: Physician(s): Client Name Address SPECIMEN SUBMITTED: LEFT PIC BONE MARROW,
TEL #: (650) 725-5604 FAX #: (650) 725-7409 Med. Rec. No.: Date of Procedure: Sex: A ge: Date Received: Date of Birth: Account No.: Physician(s): Client Name Address SPECIMEN SUBMITTED: LEFT PIC BONE MARROW,
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist
 Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
IDEXX LaserCyte Hematology Analyzer Case Study Book and Technical Guide
 IDEXX LaserCyte Hematology Analyzer Case Study Book and Technical Guide Fold out for normal dot plot comparison Feline Canine Equine 496 496 496 12288 16384 496 12288 16384 Red Blood Cells White Blood
IDEXX LaserCyte Hematology Analyzer Case Study Book and Technical Guide Fold out for normal dot plot comparison Feline Canine Equine 496 496 496 12288 16384 496 12288 16384 Red Blood Cells White Blood
BC-5800. Auto Hematology Analyzer
 BC-5800 Auto Hematology Analyzer BC-5800 Auto Hematology Analyzer 5-part differentiation, 29 parameters, 2 histograms + 2 scattergrams Up to 90 samples per hour Laser scatter + Chemical dye + Flow cytometry
BC-5800 Auto Hematology Analyzer BC-5800 Auto Hematology Analyzer 5-part differentiation, 29 parameters, 2 histograms + 2 scattergrams Up to 90 samples per hour Laser scatter + Chemical dye + Flow cytometry
BLOOD COUNT INTERPRETATION. J. Bačovský
 BLOOD COUNT INTERPRETATION J. Bačovský Sysmex XE 5000 + software + staining ) CellaVision DM 96 (automatic digitál morphology of peripheral blood smears Hematology Cell Counter Counts cells by electronic
BLOOD COUNT INTERPRETATION J. Bačovský Sysmex XE 5000 + software + staining ) CellaVision DM 96 (automatic digitál morphology of peripheral blood smears Hematology Cell Counter Counts cells by electronic
HEMATOLOGICAL CHANGES IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA
 Analele tiinifice ale Universitii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Seciunea Genetic i Biologie Molecular, TOM XII, 2011 HEMATOLOGICAL CHANGES IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA MIHAI BULARDA MOROZAN ¹*, COSTIC MISIL ² Keywords:
Analele tiinifice ale Universitii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Seciunea Genetic i Biologie Molecular, TOM XII, 2011 HEMATOLOGICAL CHANGES IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA MIHAI BULARDA MOROZAN ¹*, COSTIC MISIL ² Keywords:
XE-2100 Automated Hematology System. Fast, Accurate, Dependable
 XE-2100 Automated Hematology System Fast, Accurate, Dependable Advanced Technology Solutions to Meet your Lab s Needs Even with these challenges, the need for hematology testing has remained steady or
XE-2100 Automated Hematology System Fast, Accurate, Dependable Advanced Technology Solutions to Meet your Lab s Needs Even with these challenges, the need for hematology testing has remained steady or
Compartmentalization of the Cell. Objectives. Recommended Reading. Professor Alfred Cuschieri. Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
EQUINE CLINICAL PATHOLOGY NOTES
 EQUINE CLINICAL PATHOLOGY NOTES Kathleen P.Freeman, DVM, BS, MS, PhD, DipECVCP, FRCPath, MRCVS RCVS Specialist in Veterinary Pathology (Clinical Pathology) European Veterinary Specialist in Clinical Pathology
EQUINE CLINICAL PATHOLOGY NOTES Kathleen P.Freeman, DVM, BS, MS, PhD, DipECVCP, FRCPath, MRCVS RCVS Specialist in Veterinary Pathology (Clinical Pathology) European Veterinary Specialist in Clinical Pathology
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood. Short Answer. Figure 10.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Short Answer Figure 10.1 Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Short Answer Figure 10.1 Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref:
whole blood consists of two main elements: the formed elements
 bloodc components TERI JUNGE, CST/CFA whole blood consists of two main elements: the formed elements and the liquid element. The formed elements are cell fragments and cells, known as corpuscles, which
bloodc components TERI JUNGE, CST/CFA whole blood consists of two main elements: the formed elements and the liquid element. The formed elements are cell fragments and cells, known as corpuscles, which
CHAPTER 14: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: BLOOD. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. 2. Define the term hematology. 3. Name the average volume of blood in a human. 4. Name the two major components of blood
OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. 2. Define the term hematology. 3. Name the average volume of blood in a human. 4. Name the two major components of blood
Microscopic Haematology
 Microscopic Haematology 3e a practical guide for the laboratory Gillian Rozenberg Gillian Rozenberg Sydney Edinburgh London New York Philadelphia St Louis Toronto Churchill Livingstone is an imprint
Microscopic Haematology 3e a practical guide for the laboratory Gillian Rozenberg Gillian Rozenberg Sydney Edinburgh London New York Philadelphia St Louis Toronto Churchill Livingstone is an imprint
Blood. Blood. Blood Composition. Blood Composition. Fractionation & Hemopoesis
 Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC
 The Complete Blood Count and Associated Tests WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed December, 2015, Expires December, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited
The Complete Blood Count and Associated Tests WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed December, 2015, Expires December, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
 1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Note Students are expected to review the corresponding information in the course textbook(s) as well as the classroom notes in preparation for this lab and to aid in
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Note Students are expected to review the corresponding information in the course textbook(s) as well as the classroom notes in preparation for this lab and to aid in
A.L. Wafa a sameer 2014 Circulatory system / Physiology. Physiology of blood
 Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) Physiology of blood E rythrocytes : are the most abundant cells of the blood and are necessary for the delivery of oxygen to the tissues. The major function of red blood
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) Physiology of blood E rythrocytes : are the most abundant cells of the blood and are necessary for the delivery of oxygen to the tissues. The major function of red blood
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction
 Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
SERUM B12 AND FOLATE LEVELS IN PATIENTS WITH MEGALOBLASTIC CHANGE IN THE BONE MARROW
 SERUM B12 AND FOLATE LEVELS IN PATIENTS WITH MEGALOBLASTIC CHANGE IN THE BONE MARROW SALMA HAQ, NASIR IQBAL, FATIMA FAYYAZ AND TAHIRA TASNEEM Department of Pathology, Services Institute of Medical Sciences,
SERUM B12 AND FOLATE LEVELS IN PATIENTS WITH MEGALOBLASTIC CHANGE IN THE BONE MARROW SALMA HAQ, NASIR IQBAL, FATIMA FAYYAZ AND TAHIRA TASNEEM Department of Pathology, Services Institute of Medical Sciences,
Cytology of Lymph Nodes
 Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM
 INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM Inflammation is a response of a tissue to injury, often caused by invading microorganisms. The suffix which indicates inflammation is "-itis" (the
INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM Inflammation is a response of a tissue to injury, often caused by invading microorganisms. The suffix which indicates inflammation is "-itis" (the
No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer
 APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Standard methods for isolating and detecting leukocytes
APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Standard methods for isolating and detecting leukocytes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY
 EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Technical Information DF30
 Technical Information DF30 Performance Pigments and Colors Lead Free Onglaze Colours for Porcelain, Bone China, Vitreous China, Earthenware, and Enamel In this leaflet, Ferro presents SAMBA100, the next
Technical Information DF30 Performance Pigments and Colors Lead Free Onglaze Colours for Porcelain, Bone China, Vitreous China, Earthenware, and Enamel In this leaflet, Ferro presents SAMBA100, the next
