The Breast. Simply Health helps me learn more about health care. Simply Health gives me the information I need to talk to my doctors.
|
|
|
- Asher Logan
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
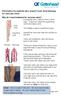
1 Breast Health for Women The Breast What are normal, healthy breasts? Normal, healthy breasts are many shapes.they can be many sizes. Each woman is a different shape. The picture (pick-chur) shows how women are different. Simply Health helps me learn more about health care. Simply Health gives me the information I need to talk to my doctors. What are breasts made of? Breasts have parts to help feed a baby. I have these parts even if I do not have a baby. They are there even if I do not breast-feed. Healthy breasts have these parts: Lobes are the parts that make milk. Milk ducts are tubes. They carry milk to the nipple (nih-pull). Nipples are what a baby sucks from. Areolas (air-ee-oh-lahs) are the pinky-brown part. They are around the nipple. Fat gives shape to the breast. Tissue (tih-shoe) keeps breast shape. Blood vessels run blood and fluid (floo-id) to the breasts. Lymph (limf) tubes help move fluid (floo-id). The Breast This paper will tell me about my breasts. It shows some problems many women can get with their breasts. It tells me what to look for. The paper also shows what I can do to try and keep my breasts healthy. Because the more I know, the better I can take care of my breasts. Parts of the Breast Lobes Nipples Milk Ducts What can I do to help keep my breasts healthy (hell-thee)? Be active (ack-tiv) and keep fit I am active when I move a lot, such as run, swim, play a sport, walk my dog. Active women get less breast cancer. Women who stay still get more breast cancer. So go have fun! I can ask my doctor how I can be active. Good foods I can eat These foods help keep my breasts healthy: Apples Brown Bread Oranges Broccoli Eat good foods Cook good foods. The Canada Food Guide to Healthy Eating (guide sounds like wide) will tell me about good foods. I can ask my doctor what foods help stop breast cancer before it starts. Play soccer Walk your dog Eat fruits and vegetables Do not eat a lot of food from cans. Fruit and vegetables have lots of good things for my body, such as vitamins (vie-ta-minz). Salmon Berries Peas Carrots Brown breads and cereals Brown bread is the best bread. It has more good things for my body than white bread. Cereal, such as bran flakes, is also good for my body. Eat fish Salmon Tuna
2 Will my breasts hurt if something is wrong? Not always. Some breast pain is normal. My breasts can hurt or change shape and it is OK. Even if I do not have a problem, such as my breasts may swell before my period. Sometimes, this hurts a bit. My breasts may hurt if I am pregnant. When I start to breast-feed, my breasts may hurt. In menopause (men-o-paws), my breasts may hurt a bit. When should I go to the doctor? If my breasts hurt for other reasons, it is good to go to my doctor. I can have breast pain from problems. My doctor may be able to help. I may feel a lump in one of my breasts. The lump may not hurt. I should go to the doctor anyway. What are breast lumps? A breast lump is a bump in the breast. Many breast lumps are not cancer, such as: Fibrocystic disease (fy-bro-sis-tic diz-eez). This is when I have lots of cysts (sists). When I have too many hormones, my body can make cysts. Cysts are small bags of fluid (floo-id). Fluid is like water. Fibroadenoma (fi-bro-a-de-no-ma) is a tumour (too-mer). A tumour is a lump. This one is made of breast tissue. It is not cancer. Papilloma (pah pih low-ma) is a small lump. It is like a wart. It grows in the milk duct or nipple. Cancer can also be a lump in your breast. Go to your doctor if you feel a lump! She will find out what the lump is. She will try to get rid of it. Why do I need to do my own breast exam? If I do my own breast exam once a month, I can see if my breasts are healthy. I may feel funny if I look at my breasts. But I have to look at them to find problems. I also must feel them to find problems. How do I do my own breast exam? There are 3 steps to a breast exam. 1. Look for changes in a mirror. 2. Feel for changes when I stand up. 3. Feel for changes when I lie down. How do I look for changes in a mirror? I stand in front of a mirror. I look at my breasts. I look for changes. Do I see any lumps? Do I see dimples (dim-pulls)? Is there a rash on my nipple? Does blood or sticky fluid come out of my nipple? 1. Stand in front of the mirror with my arms down. 2. Raise my arms above my head. How do I feel for changes when I lie down? I lay down on my bed or on the floor. I put one hand up over my head. The picture shows me what to do. I use my other hand to feel for lumps on my breast. I do this like I do when I stand. When I am done one breast, I do the other. I can ask my doctor or nurse to show me how to do my own breast exam. What is a clinical breast exam? This is when my doctor does my breast exam. She checks my breasts for problems. How many times do I have to go for a breast exam? If I am 20 to 30 years old, my doctor should do my breast exam every 1 to 3 years. I can ask my doctor when to go. If there are breast problems in my family, I may need to go more often. My doctor will give me a breast exam every year: If I am 40-years-old or older. If a woman in my family has had breast cancer, such as: my grandma, mom, aunt, or sister. What do I need to do? Once a year, I should get a breast exam from my doctor. Once a month, I should do my own breast exam. After I am 50 years old, I should go for a mammogram (mam-oh-gram). Be active, keep fit, eat good foods, and do not smoke! If I have problems, my doctor may send me for tests, such as: Mammogram (mam-oh-gram) Ultrasound (ul-tra-sownd) Biopsy (bye-opp-see) What is a breast exam? Exam means to look at. In a breast exam, someone checks my breasts. I can be the one who checks. It can also be my doctor. Look for lumps and other problems. 3. Put my hands on my hips. 4. Push my shoulders forward. How do I feel for lumps when I stand? Lift up one of my arms. (See the picture below) Use my fingers to press in little circles below my armpit. Slowly move in toward my nipple. Start at the outside of my breast. Then move in toward the middle and make another circle. After I am done that arm, I lift up my other arm. I can do this in the shower too. It may be easier in the shower. Press in little circles. What happens in a clinical breast exam? I can ask someone I trust to go with me to the doctor. This person can help me feel less afraid. At the clinical breast exam, a nurse will ask me to take off my shirt and bra. She will ask me to lie on a soft table. She will give me a sheet. I can put it over my chest. If my doctor is a man, a female nurse may stay in the room with me. My friend can stay with me for as long as it takes. Stand up breast exam. Clinical breast exam.
3 In a breast exam, does my doctor have to touch my breasts? Yes! It is her job to make sure I am OK. My doctor feels my breasts to see if they are healthy. She feels for lumps that are not normal. What is a mammogram? A mammogram (mam-oh-gram) is black and white picture. It shows the inside of my breast. This picture is like a finger-print. It looks different for all women. What is a mammogram for? A doctor uses it to look for a lump or cyst (sist). The mammogram can help find out if I have cancer. The mammogram shows problems that I do not feel or see. It is best to find cancer when it is small. That is why a mammogram can help me. When should I go for a mammogram? When I am 50 years and older, I should go for a mammogram every 2 years. If my family has breast cancer, I should go for a mammogram. My doctor will know when I need a mammogram. What do I need to know before I go for a mammogram? The best time to go is one week after my period (if I still have them). I should not wear deodorant, baby powder or perfume to the mammogram. - These make white spots on the picture. It can mess up the picture. I should wear a shirt and pants. That way I can take off just my top. I may have had other mammograms or ultrasounds before: - I need to make a list of where, when and what I had done. - I can ask my last doctor to give the last mammograms to the new doctor. The mammogram technician may ask me about my breast problems. - What is my family history? Do other women in my family have breast problems? - How long have I felt problems? - Have I had a breast operation? - Do I take hormones (hore-moans) or birth control? I should tell my doctor or nurse if I find new problems in my breasts. If I do not hear from my doctor in 10 days, I can call her. I can also call the place where I had the mammogram. Who looks at my mammogram? A doctor will look at my mammogram. This doctor knows how to look at x-rays. This doctor will know if there are problems in my mammogram. Another doctor may also look at it too. This doctor knows about breast problems. Mammogram What happens at a mammogram? Like the breast exam, I can bring someone I trust. She can stay with me until the mammogram. Then she can wait outside the x-ray room. A person will take me into an empty room. She is called a mammogram technologist (teck-naw-low-jist). She will give me a paper robe. - She will leave. Then I can take off my shirt and put on the robe. - She will come back and take me to another room. In the new room I will meet a new person. - This person is a mammogram technician (teck-nih-shun). - She will ask me to stand or sit in front of the mammogram machine (ma-sheen). (A machine is an object or thing that does a job. A mammogram machine takes a picture of the breast.) - See the picture below. - She will ask me to set my breast on a square plate. It is part of the mammogram machine (ma-sheen), like in the picture. The machine (ma-sheen) presses my breast between 2 plates. That moves my breast tissue (tih-shoe) apart. - The press uses less x-ray to take the picture. The press can hurt a bit. But it does not last very long. I will have a mammogram of both of my breasts. This woman is having a mammogram. Two doctors will look at my mammogram. They know how to find breast problems.
4 What is an ultrasound? An ultrasound (ul-tra-sownd) is a picture (pik-cher). It is a picture from inside your breast. Ultrasound uses sound (sownd) to make the picture. It does not use x-rays to make the picture. Why do I need an ultrasound (ul-tra-sownd)? It can show my doctor if a lump is solid or not. If the lump is solid, it may be a tumour. If the lump has water, it may be a cyst. A tumour (too-mer) may or may not be cancer. A cyst is like a small bag of water. A cyst can be inside the breast. It is not cancer, but it may feel the same. What do I need to know before the ultrasound? I should wear a shirt and pants. That way I can just take off my top. I should not use lotion, powder or perfume on my breasts before I go. Do NOT wear lotion, powder or perfume Wear a shirt and pants What happens when I have an ultrasound? I go to a new office for an ultrasound (ul-tra-sownd). I can ask someone I trust to come with me. She can stay with me for as long as it takes. A nurse will take me to an empty room. She will give me a robe to cover up with. She will leave. Then I can take off my shirt and bra. I can put on the robe. The nurse will come back. - She will take me to another room. - The room has a flat bed. - I will lie on my back for the test. Another person, the ultrasound technician (teck-nih-shun), will come in. They will give me the ultrasound. - This person may be a man or a woman. - I can ask them what will happen. She will move the sheet. That way she can see my breasts. - She will ask me to show her where I feel the pain. - Or, she will ask where the problem is. She will use a tool to make the ultrasound picture. - She will put a gel on the tool. The gel helps the tool slide over my breasts. How can the doctor tell if a solid lump is cancer? The doctor takes away part of my lump. This is called a biopsy (bye-opp-see). The doctor tests the lump. That way she finds out if it is cancer or not. How many kinds of biopsy are there? There are two ways to check lumps. I can have a needle. I can have surgery. Needle biopsy What happens when I get a needle? My doctor will give me something so the needle will not hurt. Then, my doctor puts a needle into my lump. She takes away part of the lump in my breast. She then tests the part she took. She tests to see if it is cancer or not. There are two kinds of needles. I can ask my doctor about them. What happens when I get a surgery? This is when I have a small operation (ah-purr-ay-shun). First, my doctor will give me something to make me sleep. Once I am asleep, my doctor cuts out part of the lump in my breast. My doctor will test the part. She will find out if it is cancer or not. Do not smoke! These papers were developed by The VRRI in partnership with Women s Health Centre, Alberta Health Services Calgary Health Region, with funding assistance from Calgary Region Community Board Persons with Developmental Disabilities Community Capacity Initiative Grants. Reprinted by Literacy Alberta in To order copies, please contact Literacy Alberta at PDF copies may also be downloaded for free from Smokers get cancer more than persons who do not. So if I do smoke, I should stop!
5 What the hard words mean Areola (air-ee-oh-la): The dark brown or pink circle of skin around the nipple. Benign (buh-nine): This means a lump that is not cancer. Biopsy (bi-op-see): When the doctor takes a bit of the tumour. She does this to find out if it is cancer or benign. Breast: Part of a woman s body. It makes milk to feed a baby. Breast exam: Exam means to look at. In a breast exam, I check my breasts. I look for lumps and other problems. My doctor can also do this. When a doctor does it, we call it a clinical breast exam. Breast-feed: Some mothers can feed a baby from their breasts. The breast makes milk. The baby sucks the breast and drinks the milk. Breast lumps: Bumps that we feel inside our breasts. We cannot see them on the outside. Breast tissue (tih-shoe): This is what my breasts are made of, such as lobes, glands, and skin. It gives my breast shape. Cancer: Cancer is cells in a body that grow and do not stop. Cancer cells can make big lumps in our bodies. They can move to other parts of our bodies. Cancer can stop parts of our body from working right. Clinical breast exam: When the doctor looks at and feels my breasts. The doctor looks for lumps or other problems. Cyst (sist): Small bag of fluid (floo-id). The fluid is like water. A cyst feels like a lump. Dimple: A spot that looks pushed in. It may look like a shadowy spot. Fibrocystic disease (fy-bro-sis-tic diz-eez): When you have too many hormones, your body can make cysts (sists). Cysts are small bags of fluid (floo-id). The fluid is like water. Fibroadenoma (fi-bro-a-de-no-ma): A tumour (too-mer). A tumour is a lump. This one is made of breast tissue. It is not cancer. Machine (ma-sheen): An object or thing that does a job. A mammogram machine takes a picture of the breast. Mammogram (mam-oh-gram): An x-ray picture of the breast. Mammogram technician (mam-oh-gram teck-nih-shun): A person who knows how to take an x-ray of breasts. Milk duct: A tube that takes the milk from the lobe to the nipple. Nipple (nih-pull): The raised skin on the breast. It is the opening to the breast. Milk can come out of the nipple to feed a baby. Nutritionist (new-trih-shun-ist): A person who goes to school. She learns about the best healthy foods to eat. Operation (ah-purr-ay-shun): see surgery. Papilloma (pah pih low-ma): A small lump. It is like a wart. It grows in the milk duct or nipple. Pucker: Same as a dimple. Radiologist (ray-dee-all-oh-jist): A person who is trained to look for problems in a mammogram. Rash: Itchy, red or brown coloured spots on skin. Surgery (sur-jur-ee): This is when I have a small operation (ah-purr-ay-shun). First, my doctor will give me something to make me sleep. Once I am asleep, my doctor cuts out part of the lump in my breast. Tumour (too-mer): A tumour is a lump. It is made only of tissue. It is not fluid. Ultrasound (ull-tra-sownd): A way to look inside a breast. It uses sound to make a picture. The picture is of the inside of my breast. Ultrasound technician (ull-tra-sownd teck-nih-shun): The person who gives ultrasounds. X-rays: Black and white pictures. They are of the inside of your breasts. They are not the same as ultrasounds. Fluid (floo-id): Wet stuff, such as water. Healthy (hell-thee): When you are OK and not sick. Copyright 2004 VRRI Hormones (hore-moans): Stuff that the brain makes to send a message to different parts of your body, such as your ovaries or breasts. Lobes: The part of the breast that makes milk. Lymph tubes (limf): Tubes that carry fluid to and from different parts of the body.
Feeling Your Way To Healthy Breast. Lisa Barnes, BSN, RN Ruth Fay,B.A.,M.B.A.,RN Mary Grady, BSN, RN Margaret Richmond, MA, RN
 Feeling Your Way To Healthy Breast Lisa Barnes, BSN, RN Ruth Fay,B.A.,M.B.A.,RN Mary Grady, BSN, RN Margaret Richmond, MA, RN WHAT ARE MY BREASTS MADE OF? A breast is made of three main parts: glands,
Feeling Your Way To Healthy Breast Lisa Barnes, BSN, RN Ruth Fay,B.A.,M.B.A.,RN Mary Grady, BSN, RN Margaret Richmond, MA, RN WHAT ARE MY BREASTS MADE OF? A breast is made of three main parts: glands,
Your Protection Starts with Breast Cancer Early Screening
 Your Protection Starts with Breast Cancer Early Screening Basics You Need to Know Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women. Breast cancer can develop in men at a much lower rate. Breast cancer
Your Protection Starts with Breast Cancer Early Screening Basics You Need to Know Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women. Breast cancer can develop in men at a much lower rate. Breast cancer
Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer
 Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer There was no history in my family. But the test was positive and it was breast cancer. I was so shocked, I couldn t believe it. ~ Colette
Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer There was no history in my family. But the test was positive and it was breast cancer. I was so shocked, I couldn t believe it. ~ Colette
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate Patient information: Breast cancer screening (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is breast cancer screening? Breast
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate Patient information: Breast cancer screening (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is breast cancer screening? Breast
Mammography AND CLINICAL BREAST EXAMS. joytolife.org WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT BREAST CANCER HOW TO DO A BREAST SELF-EXAM EARLY DETECTION SAVES LIVES
 Mammography AND CLINICAL BREAST EXAMS WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT BREAST CANCER HOW TO DO A BREAST SELF-EXAM joytolife.org EARLY DETECTION SAVES LIVES As a woman, you face many special concerns that call
Mammography AND CLINICAL BREAST EXAMS WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT BREAST CANCER HOW TO DO A BREAST SELF-EXAM joytolife.org EARLY DETECTION SAVES LIVES As a woman, you face many special concerns that call
Mammograms & Breast Health. An Information Guide for Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mammograms & Breast Health An Information Guide for Women This booklet was developed by the Centers for Disease Control
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mammograms & Breast Health An Information Guide for Women This booklet was developed by the Centers for Disease Control
BREAST CANCER. How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk. cruk.org
 BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
A Guide to Breast Screening
 A Guide to Breast Screening Contents Information for Carers, Family, Friends and Medical Guardians of Care Introduction Information on BreastCheck Information on Attending Screening The Screening Story
A Guide to Breast Screening Contents Information for Carers, Family, Friends and Medical Guardians of Care Introduction Information on BreastCheck Information on Attending Screening The Screening Story
Common Concerns About Breastfeeding
 Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Breast Cancer Screening
 Breast Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team October Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Breast Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team October Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
REDUCING YOUR RISK OF BREAST CANCER
 REDUCING YOUR RISK OF BREAST CANCER Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. One in eight women develop the disease at some stage in their lifetimes. Breast cancer is rare in men, with around
REDUCING YOUR RISK OF BREAST CANCER Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. One in eight women develop the disease at some stage in their lifetimes. Breast cancer is rare in men, with around
Breast cancer and how to spot it
 Breast cancer and how to spot it EasyRead version 1 This leaflet tells you how to spot signs of breast cancer. It also tells you to go and see your doctor straight away if you think you have any of these
Breast cancer and how to spot it EasyRead version 1 This leaflet tells you how to spot signs of breast cancer. It also tells you to go and see your doctor straight away if you think you have any of these
Supporting people with learning disabilities to take care of their breasts - a guide for supporters. Your breasts, your health
 Supporting people with learning disabilities to take care of their breasts - a guide for supporters Your breasts, your health 1 Why be breast aware? We hope this booklet will help you assist the person
Supporting people with learning disabilities to take care of their breasts - a guide for supporters Your breasts, your health 1 Why be breast aware? We hope this booklet will help you assist the person
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast. September 2012
 Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Breast Cancer. Presentation by Dr Mafunga
 Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are the
NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are the
Preparing for your Ultrasound-Guided Core Biopsy
 Preparing for your Ultrasound-Guided Core Biopsy UHN For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre Read this resource to learn: How to prepare What to expect during the biopsy What you need to do after When
Preparing for your Ultrasound-Guided Core Biopsy UHN For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre Read this resource to learn: How to prepare What to expect during the biopsy What you need to do after When
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Thyroid Cancer Finding It and Treating It Using Radioiodine
 Thyroid Cancer Finding It and Treating It Using Radioiodine Your doctor has referred you to Nuclear Medicine to learn more about the extent of your thyroid cancer, and perhaps even for treatment of the
Thyroid Cancer Finding It and Treating It Using Radioiodine Your doctor has referred you to Nuclear Medicine to learn more about the extent of your thyroid cancer, and perhaps even for treatment of the
Breast cancer in the family
 Birmingham Women's NHS Foundation Trust Breast cancer in the family Information for women with a slightly increased risk of breast cancer This is a no smoking hospital Breast cancer in the family what
Birmingham Women's NHS Foundation Trust Breast cancer in the family Information for women with a slightly increased risk of breast cancer This is a no smoking hospital Breast cancer in the family what
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
Breast Cancer in the Family
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Breast Cancer in the Family Information for women with a moderately increased risk of breast cancer Breast cancer in the family
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Breast Cancer in the Family Information for women with a moderately increased risk of breast cancer Breast cancer in the family
Breast cancer affects one in eight Australian women. It is the most common cancer for Victorian women, with almost 3,700 diagnoses in 2012.
 Breast cancer Summary Breast cancer affects one in nine Australian women. It is important for all women to get to know the normal look and feel of their breasts. Although most breast changes aren t caused
Breast cancer Summary Breast cancer affects one in nine Australian women. It is important for all women to get to know the normal look and feel of their breasts. Although most breast changes aren t caused
Surgery Choices. National Cancer Institute. For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer. National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute Surgery Choices For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health The National Cancer Institute is grateful for our
National Cancer Institute Surgery Choices For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health The National Cancer Institute is grateful for our
Raising awareness, saving lives. Breast cancer and women over 70
 North Trent Cancer Network Joan Brown, cancer survivor Raising awareness, saving lives. Breast cancer and women over 70 Barnsley Bassetlaw North Derbyshire Doncaster Rotherham Sheffield a Contents Introduction
North Trent Cancer Network Joan Brown, cancer survivor Raising awareness, saving lives. Breast cancer and women over 70 Barnsley Bassetlaw North Derbyshire Doncaster Rotherham Sheffield a Contents Introduction
Breast Pain. National Cancer Helpline 1800 200 700
 General information Breast Pain Breast Pain This factsheet gives information on breast pain in women. It explains the different types and causes of breast pain and how it can be diagnosed and treated.
General information Breast Pain Breast Pain This factsheet gives information on breast pain in women. It explains the different types and causes of breast pain and how it can be diagnosed and treated.
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
Preparing for your Breast Tomosynthesis
 Preparing for your Breast Tomosynthesis For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre UHN Read this resource to learn: How to prepare What to expect during breast tomosynthesis What questions to ask your
Preparing for your Breast Tomosynthesis For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre UHN Read this resource to learn: How to prepare What to expect during breast tomosynthesis What questions to ask your
What is DCIS? Contents. The breasts
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding ductal carinoma in situ (DCIS). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents The breasts What is
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding ductal carinoma in situ (DCIS). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents The breasts What is
Radiation Therapy and Caring for Your Skin
 Patient Information Radiation Therapy and Caring for Your Skin Comments, Feedback? Contact Patient and Professional Education 519-685-8742 Email: lrcpeducation@lhsc.on.ca Reviewed by the LRCP Patient Education
Patient Information Radiation Therapy and Caring for Your Skin Comments, Feedback? Contact Patient and Professional Education 519-685-8742 Email: lrcpeducation@lhsc.on.ca Reviewed by the LRCP Patient Education
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained
 Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as excision or open biopsy of a breast lump. It explains
Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as excision or open biopsy of a breast lump. It explains
Hysterectomy Vaginal hysterectomy Abdominal hysterectomy
 Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgery to remove a woman s uterus. The uterus is one of the organs of the female reproductive system and is about the size of a closed hand. You can no longer have children
Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgery to remove a woman s uterus. The uterus is one of the organs of the female reproductive system and is about the size of a closed hand. You can no longer have children
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
breast cancer awareness
 breast cancer awareness Wendy with Matthew Gough Wendy Gough s son Matthew died of Testicular Cancer at just 19, having ignored signs of cancer for 6-7 weeks, before going to see his doctor. He was angry
breast cancer awareness Wendy with Matthew Gough Wendy Gough s son Matthew died of Testicular Cancer at just 19, having ignored signs of cancer for 6-7 weeks, before going to see his doctor. He was angry
Breast Cancer Toolkit. Marion DePuit, MSN, Faith Community Nurse. Leslie Brown, BA, Community Advocate 9/2014. Understanding Breast Cancer
 GENERAL: Breast Cancer Toolkit Marion DePuit, MSN, Faith Community Nurse Leslie Brown, BA, Community Advocate 9/2014 Understanding Breast Cancer (Adapted from the American Cancer Society and Breast Cancer.org)
GENERAL: Breast Cancer Toolkit Marion DePuit, MSN, Faith Community Nurse Leslie Brown, BA, Community Advocate 9/2014 Understanding Breast Cancer (Adapted from the American Cancer Society and Breast Cancer.org)
Florida Breast Health Specialists Breast Cancer Information and Facts
 Definition Breast cancer is a cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer: Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (ducts) that move milk from the breast to
Definition Breast cancer is a cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer: Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (ducts) that move milk from the breast to
Let s talk aboutpuberty
 Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
Finding out about BreastScreen Queensland
 Finding out about BreastScreen Queensland Presentation Outline Breast Cancer Statistics About BreastScreen Queensland What is Breast Cancer? Who should have a breastscreen? Risk Factors Women Under 40
Finding out about BreastScreen Queensland Presentation Outline Breast Cancer Statistics About BreastScreen Queensland What is Breast Cancer? Who should have a breastscreen? Risk Factors Women Under 40
Understanding Lead Poisoning
 Understanding Lead Poisoning A guide for parents of children with high lead levels FOR MORE INFORMATION, CONTACT: Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program (CLPPP) Massachusetts Department of Public
Understanding Lead Poisoning A guide for parents of children with high lead levels FOR MORE INFORMATION, CONTACT: Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program (CLPPP) Massachusetts Department of Public
Inflammatory breast cancer
 april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader. Two years ago, I was working as a bedside nurse. One of my colleagues felt
 Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Module 7 Talking With Mothers About Breastfeeding...During Pregnancy
 Module 7 Talking With Mothers About Breastfeeding...During Pregnancy Overview This seventh module introduces peer counselors to the various physical and emotional changes that occur throughout a woman
Module 7 Talking With Mothers About Breastfeeding...During Pregnancy Overview This seventh module introduces peer counselors to the various physical and emotional changes that occur throughout a woman
Managing Constipation
 Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Surgery for breast cancer in men
 Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
about Why You Should Know Melanoma
 about Why You Should Know Melanoma Why You Should Know about Melanoma Each year, more than 3 million Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer. This is the most common form of cancer. Of these, more than
about Why You Should Know Melanoma Why You Should Know about Melanoma Each year, more than 3 million Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer. This is the most common form of cancer. Of these, more than
Breastfeeding Your Baby
 Getting the Help You Need If you have questions or problems, don t wait. Another nursing mother or mothers support group can often help. Your hospital, WIC office, baby s doctor, midwife, or obstetrician/gynecologist
Getting the Help You Need If you have questions or problems, don t wait. Another nursing mother or mothers support group can often help. Your hospital, WIC office, baby s doctor, midwife, or obstetrician/gynecologist
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease
 TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Having a Trans-Arterial Embolisation
 Having a Trans-Arterial Embolisation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Having a Trans-Arterial Embolisation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Breast Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Breast Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Breast Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and
Breast Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Breast Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and
Lung cancer (non-small-cell)
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
Goiter. This reference summary explains goiters. It covers symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Radiation Therapy What It Is, How It Helps
 Radiation Therapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best
Radiation Therapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best
Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Breast Cancer Awareness Month Issue 12 October 2015 In this Issue 2 Cancer Statistics in Kenya 3 What is Breast Cancer? 4 Symptoms of Breast
Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Breast Cancer Awareness Month Issue 12 October 2015 In this Issue 2 Cancer Statistics in Kenya 3 What is Breast Cancer? 4 Symptoms of Breast
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body
 How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
DISCOVERY HEALTH MATTERS. Breast cancer the facts
 DISCOVERY HEALTH MATTERS Breast cancer the facts Vol 12 2013 Discovery Health Matters Discovery Health Matters is a layman s guide to important, but often misunderstood topics in healthcare. The information
DISCOVERY HEALTH MATTERS Breast cancer the facts Vol 12 2013 Discovery Health Matters Discovery Health Matters is a layman s guide to important, but often misunderstood topics in healthcare. The information
Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
APGO Clinical Skills Curriculum. The Breast Exam
 APGO Clinical Skills Curriculum The Breast Exam Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO) Undergraduate Medical Education Committee 2008 The Breast Exam Table of Contents Intended Learning
APGO Clinical Skills Curriculum The Breast Exam Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO) Undergraduate Medical Education Committee 2008 The Breast Exam Table of Contents Intended Learning
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have had surgery for
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have had surgery for
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Having a Breast Biopsy. A Guide for Women and Their Families
 Having a Breast Biopsy A Guide for Women and Their Families Fast Facts n n Most women who have a breast biopsy do not have breast cancer. About 4 out of every 5 breast biopsies are negative for cancer.
Having a Breast Biopsy A Guide for Women and Their Families Fast Facts n n Most women who have a breast biopsy do not have breast cancer. About 4 out of every 5 breast biopsies are negative for cancer.
Peripheral Bypass Surgery
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Peripheral Bypass Surgery www.nshealth.ca Peripheral Bypass Surgery Your surgeon has arranged for you to have surgery. This pamphlet will help you learn about your operation.
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Peripheral Bypass Surgery www.nshealth.ca Peripheral Bypass Surgery Your surgeon has arranged for you to have surgery. This pamphlet will help you learn about your operation.
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Breast Reduction Surgery. For the Patients of Dr. Morris
 2015 Breast Reduction Surgery For the Patients of Dr. Morris Breast Reduction Surgery for the Patients of Dr. Morris Please bring this booklet with you to the hospital on the day of surgery. What happens
2015 Breast Reduction Surgery For the Patients of Dr. Morris Breast Reduction Surgery for the Patients of Dr. Morris Please bring this booklet with you to the hospital on the day of surgery. What happens
BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
 BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre December 2014 Contents About this booklet 1 Your First Oncology Consultation
BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre December 2014 Contents About this booklet 1 Your First Oncology Consultation
Radiotherapy for breast cancer
 Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Information for patients who require Foam Sclerotherapy for Varicose Veins
 Information for patients who require Foam Sclerotherapy for Varicose Veins Why do I need treatment for varicose veins? Deep veins Everybody has 2 sets of veins in their legs. These are called the superficial
Information for patients who require Foam Sclerotherapy for Varicose Veins Why do I need treatment for varicose veins? Deep veins Everybody has 2 sets of veins in their legs. These are called the superficial
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
My Sister Got Cancer. Forward
 My Sister Got Cancer Forward Approximately 1 in 315 children in the United States will develop cancer before the age of 15. The cancers that children typically develop differ from those that occur in adults.
My Sister Got Cancer Forward Approximately 1 in 315 children in the United States will develop cancer before the age of 15. The cancers that children typically develop differ from those that occur in adults.
LiveHealthy! Health questions are not easy to answer alone. See inside! 24/7 Nurse Advice Line for Health Choice Members. Speak with registered nurses
 LiveHealthy! Spring 2014 24/7 Nurse Advice Line for Health Choice Members Health questions are not easy to answer alone. Get the help you need to make the right choices. Speak with registered nurses Toll-free,
LiveHealthy! Spring 2014 24/7 Nurse Advice Line for Health Choice Members Health questions are not easy to answer alone. Get the help you need to make the right choices. Speak with registered nurses Toll-free,
Testing for Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
CT Scan UHN. Information for patients and families
 CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide
 NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
Laparoscopic Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy
 Laparoscopic Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy What is a? This is a surgery where your doctor uses a thin, lighted camera and small surgical tool placed through a small (1/2 inch) incision usually in the
Laparoscopic Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy What is a? This is a surgery where your doctor uses a thin, lighted camera and small surgical tool placed through a small (1/2 inch) incision usually in the
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma
 GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
The symptoms of HIV infection
 2 The symptoms of HIV infection Saleema s story HIV infection and HIV disease The first weeks of HIV infection The quiet stage of HIV infection The beginning of HIV disease Answering Saleema s questions
2 The symptoms of HIV infection Saleema s story HIV infection and HIV disease The first weeks of HIV infection The quiet stage of HIV infection The beginning of HIV disease Answering Saleema s questions
Having a kidney biopsy
 Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
If you have questions about DCIS, call the Cancer Prevention and Treatment Fund s DCIS hotline at 202-223-4000 or write us at info@stopcancerfund.
 This free booklet was developed and produced by the Cancer Prevention and Treatment Fund CFC # 11967 If you have questions about DCIS, call the Cancer Prevention and Treatment Fund s DCIS hotline at 202-223-4000
This free booklet was developed and produced by the Cancer Prevention and Treatment Fund CFC # 11967 If you have questions about DCIS, call the Cancer Prevention and Treatment Fund s DCIS hotline at 202-223-4000
Breast Reduction Post-Operative Instructions
 Breast Reduction Post-Operative Instructions What are my post-operative instructions? Have someone drive you home after surgery and help you at home for 1-2 days. Get plenty of rest and follow a balanced
Breast Reduction Post-Operative Instructions What are my post-operative instructions? Have someone drive you home after surgery and help you at home for 1-2 days. Get plenty of rest and follow a balanced
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Changes to Your Baby and Your Body During Pregnancy
 Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Breast Reconstruction
 Breast Reconstruction by Editorial Staff and Contributors En Español (Spanish Version) Click here to view an animated version of this procedure. Definition Breast reconstruction is plastic surgery to rebuild
Breast Reconstruction by Editorial Staff and Contributors En Español (Spanish Version) Click here to view an animated version of this procedure. Definition Breast reconstruction is plastic surgery to rebuild
Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Breast Cancer or Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) of the Breast
 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Breast Cancer or Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) of the Breast Why is radiation therapy used to treat breast cancer or DCIS? Breast cancer or DCIS
Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Breast Cancer or Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) of the Breast Why is radiation therapy used to treat breast cancer or DCIS? Breast cancer or DCIS
