Linked Lists. Linked Lists
|
|
|
- Lenard Merritt
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Linked Lists Kruse and Ryba Textbook 4.1 and Chapter 6 Linked Lists Linked list of items is arranged in order Size of linked list changes as items are inserted or removed Dynamic memory allocation is often used in linked list implementation Ten fundamental functions are used to manipulate linked lists (see textbook). 1
2 Fundamentals A linked list is a sequence of items arranged one after another. Each item in list is connected to the next item via a link end marker Each item is placed together with the link to the next item, resulting in a simple component called a node. Declaring a Class for Node struct Node typedef double Item; Item data; // data stored in node Node *link; // pointer to next node ; A struct is a special kind of class where all members are public. In this case there are two public member variables: data, link. Whenever a program needs to refer to the item type, we can use the expression Node::Item. 2
3 Head Pointers, Tail Pointers Usually, programs do not actually declare node variables. Instead, the list is accessed through one or more pointers to nodes. tail_ptr end marker Struct Node typedef double Item; Item data; Node *link; ; Node *; Node *tail_ptr; tail_ptr end marker 3
4 Null Pointer The final node in the linked list does not point to a next node. If link does not point to a node, its value is set to. is a special C++ constant, from the standard library facility <stdlib.h> pointer is often written 0 (zero). Use of pointer in last node of linked list: tail_ptr
5 Empty List When the list is empty, both the and tail_ptr are. When creating a new linked list, it starts out empty (both tail and head pointers ). Node *,*tail_ptr; = ; tail_ptr = ; Null tail_ptr Null Any linked list functions you write should handle the case of empty list (head and tail pointers ). Member Selection Operator Suppose a program has built a linked list: tail_ptr is a pointer to a node. How can we get/set the value of the Item inside the node? 5
6 Member Selection Operator One possible syntax: (*).data = 4.5; cout << (*).data; The expression (*).data means the data member of the node pointed to by. Member Selection Operator Preferred syntax: ->data = 4.5; cout << ->data; The symbol -> is considered a single operator. Reminds you of an arrow pointing to the member. The expression ->data means the data member of the node pointed to by. 6
7 Two Common Pointer Bugs Attempting to dereference a pointer via *p or p-> when p=. Attempting to dereference a pointer via *p or p-> when p is not properly initialized. NOTE: this error does not cause a syntax error, but instead causes errors: Bus Error Segmentation violation Address protection violation Computing the Length of a Linked List size_t list_length(node * ) Node *cursor; size_t answer=0; for(cursor=; cursor!= ; cursor=cursor->link) answer++; return answer; 7
8 Computing the Length of a Linked List cursor=; Computing the Length of a Linked List cursor=cursor->link;
9 Computing the Length of a Linked List cursor=cursor->link; Computing the Length of a Linked List cursor=cursor->link=;
10 Computing the Length of a Linked List size_t list_length(node * ) Node *cursor; size_t answer=0; for(cursor=; cursor!= ; cursor=cursor->link) answer++; return answer; Traversing a Linked List Common pattern in functions that need to traverse a linked list: for(cursor=; cursor!= ; cursor=cursor->link) Will this work for an empty list? Always make sure your functions work in the empty list case!! 10
11 Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr; Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr; insert_ptr 11
12 Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr; insert_ptr Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr; insert_ptr
13 Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr; insert_ptr 8.9 Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr; insert_ptr
14 Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr; 8.9 Inserting a Node at List Head void list_head_insert(node*, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: new node is added to front of list containing entry, and // is set to point at new node. insert_ptr->link = ; = insert_ptr;
15 Inserting a Node not at List Head void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to a node in a valid linked list // Postcondition: new node is added after the node pointed to by // previous_ptr prev_ptr insert_ptr->link = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = insert_ptr; Inserting a Node not at List Head void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to a node in a valid linked list // Postcondition: new node is added after the node pointed to by // previous_ptr prev_ptr insert_ptr->link = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = insert_ptr; insert_ptr 15
16 Inserting a Node not at List Head void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to a node in a valid linked list // Postcondition: new node is added after the node pointed to by // previous_ptr prev_ptr insert_ptr->link = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = insert_ptr; insert_ptr Inserting a Node not at List Head void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to a node in a valid linked list // Postcondition: new node is added after the node pointed to by // previous_ptr prev_ptr insert_ptr->link = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = insert_ptr; insert_ptr
17 Inserting a Node not at List Head void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to a node in a valid linked list // Postcondition: new node is added after the node pointed to by // previous_ptr prev_ptr insert_ptr->link = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = insert_ptr; insert_ptr 8.9 Inserting a Node not at List Head void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to a node in a valid linked list // Postcondition: new node is added after the node pointed to by // previous_ptr prev_ptr insert_ptr->link = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = insert_ptr; insert_ptr
18 Inserting a Node not at List Head void list_insert(node* previous_ptr, const Node::Item& entry) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to a node in a valid linked list // Postcondition: new node is added after the node pointed to by // previous_ptr insert_ptr->link = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = insert_ptr; 8.9 List Search Find the first node in a list that contains the specified item. Return pointer to that node. 18
19 Searching List for Item Node* list_search(node*, const Node::Item& target) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: return value is pointer to first node containing // specified target. Returns if no matching node found. Node *cursor; for(cursor = ; cursor!= ; cursor = cursor->link) if(target == cursor->data) return cursor; return ; Locating n th Node in List Node* list_locate(node*, size_t position) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: return value is pointer to node at specified position // first node in list has position=0 Node *cursor; size_t i; cursor = ; for(i=0; (i<position) && (cursor!= ); ++i) cursor = cursor->link; return cursor; 19
20 Removing a Node at List Head void list_head_remove(node* ) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: first node is removed from front of list, and // is set to point at ->link. Removed node is deleted Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = ; = ->link; delete remove_ptr; 8.9 Removing a Node at List Head void list_head_remove(node* ) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: first node is removed from front of list, and // is set to point at ->link. Removed node is deleted Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = ; = ->link; delete remove_ptr; remove_ptr
21 Removing a Node at List Head void list_head_remove(node* ) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: first node is removed from front of list, and // is set to point at ->link. Removed node is deleted Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = ; = ->link; delete remove_ptr; remove_ptr 8.9 Removing a Node at List Head void list_head_remove(node* ) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: first node is removed from front of list, and // is set to point at ->link. Removed node is deleted Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = ; = ->link; delete remove_ptr; remove_ptr
22 Removing a Node at List Head void list_head_remove(node* ) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: first node is removed from front of list, and // is set to point at ->link. Removed node is deleted Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = ; = ->link; delete remove_ptr; remove_ptr Will it work if =? void list_head_remove(node* ) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: first node is removed from front of list, and // is set to point at ->link. Removed node is deleted Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = ; = ->link; delete remove_ptr; 22
23 Will it work if =? void list_head_remove(node* ) // Precondition: is a head pointer to a linked list // Postcondition: first node is removed from front of list, and // is set to point at ->link. Removed node is deleted Node *remove_ptr; if( == ) return; remove_ptr = ; ->link = ->next; delete remove_ptr; Removing a not Node at List Head void list_remove(node* previous_ptr) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to node in a linked list // Postcondition: node is removed from front of list, and // removed node is deleted previous_ptr Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = remove_ptr->link; remove_ptr delete remove_ptr;
24 Removing a not Node at List Head void list_remove(node* previous_ptr) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to node in a linked list // Postcondition: node is removed from front of list, and // removed node is deleted previous_ptr Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = remove_ptr->link; remove_ptr delete remove_ptr; 8.9 Removing a not Node at List Head void list_remove(node* previous_ptr) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to node in a linked list // Postcondition: node is removed from front of list, and // removed node is deleted previous_ptr Node *remove_ptr; remove_ptr = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = remove_ptr->next; delete remove_ptr; remove_ptr
25 Removing a not Node at List Head void list_remove(node* previous_ptr) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to node in a linked list // Postcondition: node is removed from front of list, and // removed node is deleted previous_ptr Node *remove_ptr; 8.9 remove_ptr = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = remove_ptr->link; delete remove_ptr; remove_ptr 3.5 Removing a not Node at List Head void list_remove(node* previous_ptr) // Precondition: previous_ptr is a pointer to node in a linked list // Postcondition: node is removed from front of list, and // removed node is deleted previous_ptr Node *remove_ptr; 8.9 remove_ptr = previous_ptr->link; previous_ptr->link = remove_ptr->link; delete remove_ptr; remove_ptr
26 Other List Functions list clear: empties a list, deleting all nodes. list copy: copies a list, and all its nodes. list append: appends one list onto the end of another Implementations and interfaces may vary, but the basic operations on lists remain more or less the same. Better implementation: define a list class!! This is object oriented programming after all. 26
BSc (Hons) Business Information Systems, BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security. & BSc. (Hons.) Software Engineering
 BSc (Hons) Business Information Systems, BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security & BSc. (Hons.) Software Engineering Cohort: BIS/05/FT BCNS/05/FT BSE/05/FT Examinations for 2005-2006 / Semester
BSc (Hons) Business Information Systems, BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security & BSc. (Hons.) Software Engineering Cohort: BIS/05/FT BCNS/05/FT BSE/05/FT Examinations for 2005-2006 / Semester
Data Structures Using C++ 2E. Chapter 5 Linked Lists
 Data Structures Using C++ 2E Chapter 5 Linked Lists Test #1 Next Thursday During Class Cover through (near?) end of Chapter 5 Objectives Learn about linked lists Become aware of the basic properties of
Data Structures Using C++ 2E Chapter 5 Linked Lists Test #1 Next Thursday During Class Cover through (near?) end of Chapter 5 Objectives Learn about linked lists Become aware of the basic properties of
Stacks. Linear data structures
 Stacks Linear data structures Collection of components that can be arranged as a straight line Data structure grows or shrinks as we add or remove objects ADTs provide an abstract layer for various operations
Stacks Linear data structures Collection of components that can be arranged as a straight line Data structure grows or shrinks as we add or remove objects ADTs provide an abstract layer for various operations
Lecture 12 Doubly Linked Lists (with Recursion)
 Lecture 12 Doubly Linked Lists (with Recursion) In this lecture Introduction to Doubly linked lists What is recursion? Designing a node of a DLL Recursion and Linked Lists o Finding a node in a LL (recursively)
Lecture 12 Doubly Linked Lists (with Recursion) In this lecture Introduction to Doubly linked lists What is recursion? Designing a node of a DLL Recursion and Linked Lists o Finding a node in a LL (recursively)
MAX = 5 Current = 0 'This will declare an array with 5 elements. Inserting a Value onto the Stack (Push) -----------------------------------------
 =============================================================================================================================== DATA STRUCTURE PSEUDO-CODE EXAMPLES (c) Mubashir N. Mir - www.mubashirnabi.com
=============================================================================================================================== DATA STRUCTURE PSEUDO-CODE EXAMPLES (c) Mubashir N. Mir - www.mubashirnabi.com
Queue Implementations
 Queue Implementations as double 1 2 as double MCS 360 Lecture 17 Introduction to Data Structures Jan Verschelde, 1 October 2010 Queue Implementations as double 1 2 as double a circular as double A can
Queue Implementations as double 1 2 as double MCS 360 Lecture 17 Introduction to Data Structures Jan Verschelde, 1 October 2010 Queue Implementations as double 1 2 as double a circular as double A can
7.1 Our Current Model
 Chapter 7 The Stack In this chapter we examine what is arguably the most important abstract data type in computer science, the stack. We will see that the stack ADT and its implementation are very simple.
Chapter 7 The Stack In this chapter we examine what is arguably the most important abstract data type in computer science, the stack. We will see that the stack ADT and its implementation are very simple.
Unordered Linked Lists
 Unordered Linked Lists Derive class unorderedlinkedlist from the abstract class linkedlisttype Implement the operations search, insertfirst, insertlast, deletenode See code on page 292 Defines an unordered
Unordered Linked Lists Derive class unorderedlinkedlist from the abstract class linkedlisttype Implement the operations search, insertfirst, insertlast, deletenode See code on page 292 Defines an unordered
Lecture 11 Doubly Linked Lists & Array of Linked Lists. Doubly Linked Lists
 Lecture 11 Doubly Linked Lists & Array of Linked Lists In this lecture Doubly linked lists Array of Linked Lists Creating an Array of Linked Lists Representing a Sparse Matrix Defining a Node for a Sparse
Lecture 11 Doubly Linked Lists & Array of Linked Lists In this lecture Doubly linked lists Array of Linked Lists Creating an Array of Linked Lists Representing a Sparse Matrix Defining a Node for a Sparse
1 Abstract Data Types Information Hiding
 1 1 Abstract Data Types Information Hiding 1.1 Data Types Data types are an integral part of every programming language. ANSI-C has int, double and char to name just a few. Programmers are rarely content
1 1 Abstract Data Types Information Hiding 1.1 Data Types Data types are an integral part of every programming language. ANSI-C has int, double and char to name just a few. Programmers are rarely content
Data Structures Using C++ 2E. Chapter 5 Linked Lists
 Data Structures Using C++ 2E Chapter 5 Linked Lists Doubly Linked Lists Traversed in either direction Typical operations Initialize the list Destroy the list Determine if list empty Search list for a given
Data Structures Using C++ 2E Chapter 5 Linked Lists Doubly Linked Lists Traversed in either direction Typical operations Initialize the list Destroy the list Determine if list empty Search list for a given
Object Oriented Software Design II
 Object Oriented Software Design II Introduction to C++ Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa February 20, 2012 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) C++ Intro February
Object Oriented Software Design II Introduction to C++ Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa February 20, 2012 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) C++ Intro February
Linked Lists Linked Lists, Queues, and Stacks
 Linked Lists Linked Lists, Queues, and Stacks CSE 10: Introduction to C Programming Fall 200 Dynamic data structure Size is not fixed at compile time Each element of a linked list: holds a value points
Linked Lists Linked Lists, Queues, and Stacks CSE 10: Introduction to C Programming Fall 200 Dynamic data structure Size is not fixed at compile time Each element of a linked list: holds a value points
Integrating the C++ Standard Template Library Into the Undergraduate Computer Science Curriculum
 Integrating the C++ Standard Template Library Into the Undergraduate Computer Science Curriculum James P. Kelsh James.Kelsh@cmich.edu Roger Y. Lee lee@cps.cmich.edu Department of Computer Science Central
Integrating the C++ Standard Template Library Into the Undergraduate Computer Science Curriculum James P. Kelsh James.Kelsh@cmich.edu Roger Y. Lee lee@cps.cmich.edu Department of Computer Science Central
CS107L Handout 04 Autumn 2007 October 19, 2007 Custom STL-Like Containers and Iterators
 CS107L Handout 04 Autumn 2007 October 19, 2007 Custom STL-Like Containers and Iterators This handout is designed to provide a better understanding of how one should write template code and architect iterators
CS107L Handout 04 Autumn 2007 October 19, 2007 Custom STL-Like Containers and Iterators This handout is designed to provide a better understanding of how one should write template code and architect iterators
Short Notes on Dynamic Memory Allocation, Pointer and Data Structure
 Short Notes on Dynamic Memory Allocation, Pointer and Data Structure 1 Dynamic Memory Allocation in C/C++ Motivation /* a[100] vs. *b or *c */ Func(int array_size) double k, a[100], *b, *c; b = (double
Short Notes on Dynamic Memory Allocation, Pointer and Data Structure 1 Dynamic Memory Allocation in C/C++ Motivation /* a[100] vs. *b or *c */ Func(int array_size) double k, a[100], *b, *c; b = (double
Common Data Structures
 Data Structures 1 Common Data Structures Arrays (single and multiple dimensional) Linked Lists Stacks Queues Trees Graphs You should already be familiar with arrays, so they will not be discussed. Trees
Data Structures 1 Common Data Structures Arrays (single and multiple dimensional) Linked Lists Stacks Queues Trees Graphs You should already be familiar with arrays, so they will not be discussed. Trees
Software Engineering Concepts: Testing. Pointers & Dynamic Allocation. CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Monday, September 14, 2009
 Software Engineering Concepts: Testing Simple Class Example continued Pointers & Dynamic Allocation CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Monday, September 14, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department
Software Engineering Concepts: Testing Simple Class Example continued Pointers & Dynamic Allocation CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Monday, September 14, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department
Linked List as an ADT (cont d.)
 Linked List as an ADT (cont d.) Default constructor Initializes list to an empty state Destroy the list Deallocates memory occupied by each node Initialize the list Reinitializes list to an empty state
Linked List as an ADT (cont d.) Default constructor Initializes list to an empty state Destroy the list Deallocates memory occupied by each node Initialize the list Reinitializes list to an empty state
Lecture 11 Array of Linked Lists
 Lecture 11 Array of Linked Lists In this lecture Array of Linked Lists Creating an Array of Linked Lists Representing a Sparse Matrix Defining a Node for Sparse Matrix Exercises Solutions An Array of Linked
Lecture 11 Array of Linked Lists In this lecture Array of Linked Lists Creating an Array of Linked Lists Representing a Sparse Matrix Defining a Node for Sparse Matrix Exercises Solutions An Array of Linked
CS 2412 Data Structures. Chapter 2 Stacks and recursion
 CS 2412 Data Structures Chapter 2 Stacks and recursion 1 2.1 Stacks A stack is a data structure in which all insertions and deletions of entries are made at one end, called top of the stack. Examples:
CS 2412 Data Structures Chapter 2 Stacks and recursion 1 2.1 Stacks A stack is a data structure in which all insertions and deletions of entries are made at one end, called top of the stack. Examples:
5. A full binary tree with n leaves contains [A] n nodes. [B] log n 2 nodes. [C] 2n 1 nodes. [D] n 2 nodes.
![5. A full binary tree with n leaves contains [A] n nodes. [B] log n 2 nodes. [C] 2n 1 nodes. [D] n 2 nodes. 5. A full binary tree with n leaves contains [A] n nodes. [B] log n 2 nodes. [C] 2n 1 nodes. [D] n 2 nodes.](/thumbs/40/21353779.jpg) 1. The advantage of.. is that they solve the problem if sequential storage representation. But disadvantage in that is they are sequential lists. [A] Lists [B] Linked Lists [A] Trees [A] Queues 2. The
1. The advantage of.. is that they solve the problem if sequential storage representation. But disadvantage in that is they are sequential lists. [A] Lists [B] Linked Lists [A] Trees [A] Queues 2. The
Object Oriented Software Design II
 Object Oriented Software Design II C++ intro Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa February 26, 2012 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) C++ Intro February 26,
Object Oriented Software Design II C++ intro Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa February 26, 2012 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) C++ Intro February 26,
Course: Programming II - Abstract Data Types. The ADT Stack. A stack. The ADT Stack and Recursion Slide Number 1
 Definition Course: Programming II - Abstract Data Types The ADT Stack The ADT Stack is a linear sequence of an arbitrary number of items, together with access procedures. The access procedures permit insertions
Definition Course: Programming II - Abstract Data Types The ADT Stack The ADT Stack is a linear sequence of an arbitrary number of items, together with access procedures. The access procedures permit insertions
CS 2112 Spring 2014. 0 Instructions. Assignment 3 Data Structures and Web Filtering. 0.1 Grading. 0.2 Partners. 0.3 Restrictions
 CS 2112 Spring 2014 Assignment 3 Data Structures and Web Filtering Due: March 4, 2014 11:59 PM Implementing spam blacklists and web filters requires matching candidate domain names and URLs very rapidly
CS 2112 Spring 2014 Assignment 3 Data Structures and Web Filtering Due: March 4, 2014 11:59 PM Implementing spam blacklists and web filters requires matching candidate domain names and URLs very rapidly
Data Types in the Kernel
 ,ch11.3440 Page 288 Thursday, January 20, 2005 9:25 AM CHAPTER 11 Data Types in the Kernel Chapter 11 Before we go on to more advanced topics, we need to stop for a quick note on portability issues. Modern
,ch11.3440 Page 288 Thursday, January 20, 2005 9:25 AM CHAPTER 11 Data Types in the Kernel Chapter 11 Before we go on to more advanced topics, we need to stop for a quick note on portability issues. Modern
1) The postfix expression for the infix expression A+B*(C+D)/F+D*E is ABCD+*F/DE*++
 Answer the following 1) The postfix expression for the infix expression A+B*(C+D)/F+D*E is ABCD+*F/DE*++ 2) Which data structure is needed to convert infix notations to postfix notations? Stack 3) The
Answer the following 1) The postfix expression for the infix expression A+B*(C+D)/F+D*E is ABCD+*F/DE*++ 2) Which data structure is needed to convert infix notations to postfix notations? Stack 3) The
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2016S-05 Abstract Data Types and Lists David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 05-0: Abstract Data Types Recall that an Abstract Data
Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2016S-05 Abstract Data Types and Lists David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 05-0: Abstract Data Types Recall that an Abstract Data
C++FA 5.1 PRACTICE MID-TERM EXAM
 C++FA 5.1 PRACTICE MID-TERM EXAM This practicemid-term exam covers sections C++FA 1.1 through C++FA 1.4 of C++ with Financial Applications by Ben Van Vliet, available at www.benvanvliet.net. 1.) A pointer
C++FA 5.1 PRACTICE MID-TERM EXAM This practicemid-term exam covers sections C++FA 1.1 through C++FA 1.4 of C++ with Financial Applications by Ben Van Vliet, available at www.benvanvliet.net. 1.) A pointer
Scoping (Readings 7.1,7.4,7.6) Parameter passing methods (7.5) Building symbol tables (7.6)
 Semantic Analysis Scoping (Readings 7.1,7.4,7.6) Static Dynamic Parameter passing methods (7.5) Building symbol tables (7.6) How to use them to find multiply-declared and undeclared variables Type checking
Semantic Analysis Scoping (Readings 7.1,7.4,7.6) Static Dynamic Parameter passing methods (7.5) Building symbol tables (7.6) How to use them to find multiply-declared and undeclared variables Type checking
Linked List Problems
 Linked List Problems By Nick Parlante Copyright 1998-99, Nick Parlante Abstract This document presents 18 linked list problems covering a wide range of difficulty. Most obviously, these problems are useful
Linked List Problems By Nick Parlante Copyright 1998-99, Nick Parlante Abstract This document presents 18 linked list problems covering a wide range of difficulty. Most obviously, these problems are useful
recursion, O(n), linked lists 6/14
 recursion, O(n), linked lists 6/14 recursion reducing the amount of data to process and processing a smaller amount of data example: process one item in a list, recursively process the rest of the list
recursion, O(n), linked lists 6/14 recursion reducing the amount of data to process and processing a smaller amount of data example: process one item in a list, recursively process the rest of the list
Data Structures Using C++
 Data Structures Using C++ 1.1 Introduction Data structure is an implementation of an abstract data type having its own set of data elements along with functions to perform operations on that data. Arrays
Data Structures Using C++ 1.1 Introduction Data structure is an implementation of an abstract data type having its own set of data elements along with functions to perform operations on that data. Arrays
Creating a One-line Diagram
 Creating a One-line Diagram The purpose of this tutorial is to show the fundamentals of building and manipulating a one-line diagram in ETAP. Various elements will be added to the one-line view (OLV),
Creating a One-line Diagram The purpose of this tutorial is to show the fundamentals of building and manipulating a one-line diagram in ETAP. Various elements will be added to the one-line view (OLV),
GDB Tutorial. A Walkthrough with Examples. CMSC 212 - Spring 2009. Last modified March 22, 2009. GDB Tutorial
 A Walkthrough with Examples CMSC 212 - Spring 2009 Last modified March 22, 2009 What is gdb? GNU Debugger A debugger for several languages, including C and C++ It allows you to inspect what the program
A Walkthrough with Examples CMSC 212 - Spring 2009 Last modified March 22, 2009 What is gdb? GNU Debugger A debugger for several languages, including C and C++ It allows you to inspect what the program
DATA STRUCTURES USING C
 DATA STRUCTURES USING C QUESTION BANK UNIT I 1. Define data. 2. Define Entity. 3. Define information. 4. Define Array. 5. Define data structure. 6. Give any two applications of data structures. 7. Give
DATA STRUCTURES USING C QUESTION BANK UNIT I 1. Define data. 2. Define Entity. 3. Define information. 4. Define Array. 5. Define data structure. 6. Give any two applications of data structures. 7. Give
PROBLEM SOLVING SEVENTH EDITION WALTER SAVITCH UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO CONTRIBUTOR KENRICK MOCK UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA, ANCHORAGE PEARSON
 PROBLEM SOLVING WITH SEVENTH EDITION WALTER SAVITCH UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO CONTRIBUTOR KENRICK MOCK UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA, ANCHORAGE PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London
PROBLEM SOLVING WITH SEVENTH EDITION WALTER SAVITCH UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO CONTRIBUTOR KENRICK MOCK UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA, ANCHORAGE PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London
PART-A Questions. 2. How does an enumerated statement differ from a typedef statement?
 1. Distinguish & and && operators. PART-A Questions 2. How does an enumerated statement differ from a typedef statement? 3. What are the various members of a class? 4. Who can access the protected members
1. Distinguish & and && operators. PART-A Questions 2. How does an enumerated statement differ from a typedef statement? 3. What are the various members of a class? 4. Who can access the protected members
ADTs,, Arrays, Linked Lists
 1 ADTs,, Arrays, Linked Lists Outline and Required Reading: ADTs ( 2.1.2) Arrays ( 1.5) Linked Lists ( 4.3.1, 4.3.2) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Abstract Data Type (ADT) 2 abstract
1 ADTs,, Arrays, Linked Lists Outline and Required Reading: ADTs ( 2.1.2) Arrays ( 1.5) Linked Lists ( 4.3.1, 4.3.2) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Abstract Data Type (ADT) 2 abstract
Pointers and Linked Lists
 15 Pointers and Linked Lists 15.1 Nodes and Linked Lists 828 Nodes 828 Linked Lists 834 Inserting a Node at the Head of a List 835 Pitfall:Losing Nodes 839 Searching a Linked List 840 Pointers as Iterators
15 Pointers and Linked Lists 15.1 Nodes and Linked Lists 828 Nodes 828 Linked Lists 834 Inserting a Node at the Head of a List 835 Pitfall:Losing Nodes 839 Searching a Linked List 840 Pointers as Iterators
CS107L Handout 02 Autumn 2007 October 5, 2007 Copy Constructor and operator=
 CS107L Handout 02 Autumn 2007 October 5, 2007 Copy Constructor and operator= Much of the surrounding prose written by Andy Maag, CS193D instructor from years ago. The compiler will supply a default (zero-argument)
CS107L Handout 02 Autumn 2007 October 5, 2007 Copy Constructor and operator= Much of the surrounding prose written by Andy Maag, CS193D instructor from years ago. The compiler will supply a default (zero-argument)
C Dynamic Data Structures. University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell
 C Dynamic Data Structures University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell Data Structures A data structure is a particular organization of data in memory. We want to
C Dynamic Data Structures University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell Data Structures A data structure is a particular organization of data in memory. We want to
Cours de C++ Utilisations des conteneurs
 Cours de C++ Utilisations des conteneurs Cécile Braunstein cecile.braunstein@lip6.fr 1 / 18 Introduction Containers - Why? Help to solve messy problems Provide useful function and data structure Consistency
Cours de C++ Utilisations des conteneurs Cécile Braunstein cecile.braunstein@lip6.fr 1 / 18 Introduction Containers - Why? Help to solve messy problems Provide useful function and data structure Consistency
A binary search tree or BST is a binary tree that is either empty or in which the data element of each node has a key, and:
 Binary Search Trees 1 The general binary tree shown in the previous chapter is not terribly useful in practice. The chief use of binary trees is for providing rapid access to data (indexing, if you will)
Binary Search Trees 1 The general binary tree shown in the previous chapter is not terribly useful in practice. The chief use of binary trees is for providing rapid access to data (indexing, if you will)
Queues. Manolis Koubarakis. Data Structures and Programming Techniques
 Queues Manolis Koubarakis 1 The ADT Queue A queue Q of items of type T is a sequence of items of type T on which the following operations are defined: Initialize the queue to the empty queue. Determine
Queues Manolis Koubarakis 1 The ADT Queue A queue Q of items of type T is a sequence of items of type T on which the following operations are defined: Initialize the queue to the empty queue. Determine
Converting a Number from Decimal to Binary
 Converting a Number from Decimal to Binary Convert nonnegative integer in decimal format (base 10) into equivalent binary number (base 2) Rightmost bit of x Remainder of x after division by two Recursive
Converting a Number from Decimal to Binary Convert nonnegative integer in decimal format (base 10) into equivalent binary number (base 2) Rightmost bit of x Remainder of x after division by two Recursive
Embedded Programming in C/C++: Lesson-1: Programming Elements and Programming in C
 Embedded Programming in C/C++: Lesson-1: Programming Elements and Programming in C 1 An essential part of any embedded system design Programming 2 Programming in Assembly or HLL Processor and memory-sensitive
Embedded Programming in C/C++: Lesson-1: Programming Elements and Programming in C 1 An essential part of any embedded system design Programming 2 Programming in Assembly or HLL Processor and memory-sensitive
Passing 1D arrays to functions.
 Passing 1D arrays to functions. In C++ arrays can only be reference parameters. It is not possible to pass an array by value. Therefore, the ampersand (&) is omitted. What is actually passed to the function,
Passing 1D arrays to functions. In C++ arrays can only be reference parameters. It is not possible to pass an array by value. Therefore, the ampersand (&) is omitted. What is actually passed to the function,
Abstract Data Type. EECS 281: Data Structures and Algorithms. The Foundation: Data Structures and Abstract Data Types
 EECS 281: Data Structures and Algorithms The Foundation: Data Structures and Abstract Data Types Computer science is the science of abstraction. Abstract Data Type Abstraction of a data structure on that
EECS 281: Data Structures and Algorithms The Foundation: Data Structures and Abstract Data Types Computer science is the science of abstraction. Abstract Data Type Abstraction of a data structure on that
CS193D Handout 06 Winter 2004 January 26, 2004 Copy Constructor and operator=
 CS193D Handout 06 Winter 2004 January 26, 2004 Copy Constructor and operator= We already know that the compiler will supply a default (zero-argument) constructor if the programmer does not specify one.
CS193D Handout 06 Winter 2004 January 26, 2004 Copy Constructor and operator= We already know that the compiler will supply a default (zero-argument) constructor if the programmer does not specify one.
Cpt S 223. School of EECS, WSU
 Abstract Data Types 1 Topics Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Some basic ADTs: Lists Stacks Queues 2 Primitive Data Type vs. Abstract Data Types Primitive DT: ADT: programmer progra ammer Interface (API) e.g.,
Abstract Data Types 1 Topics Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Some basic ADTs: Lists Stacks Queues 2 Primitive Data Type vs. Abstract Data Types Primitive DT: ADT: programmer progra ammer Interface (API) e.g.,
C++ INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
 C++ INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these C++ Interview Questions have been designed specially to get
C++ INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these C++ Interview Questions have been designed specially to get
Data Structures and Data Manipulation
 Data Structures and Data Manipulation What the Specification Says: Explain how static data structures may be used to implement dynamic data structures; Describe algorithms for the insertion, retrieval
Data Structures and Data Manipulation What the Specification Says: Explain how static data structures may be used to implement dynamic data structures; Describe algorithms for the insertion, retrieval
Quiz 4 Solutions EECS 211: FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER PROGRAMMING II. 1 Q u i z 4 S o l u t i o n s
 Quiz 4 Solutions Q1: What value does function mystery return when called with a value of 4? int mystery ( int number ) { if ( number
Quiz 4 Solutions Q1: What value does function mystery return when called with a value of 4? int mystery ( int number ) { if ( number
Glossary of Object Oriented Terms
 Appendix E Glossary of Object Oriented Terms abstract class: A class primarily intended to define an instance, but can not be instantiated without additional methods. abstract data type: An abstraction
Appendix E Glossary of Object Oriented Terms abstract class: A class primarily intended to define an instance, but can not be instantiated without additional methods. abstract data type: An abstraction
Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server
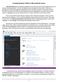 Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database server that stores and retrieves data for multi-user network-based applications. SQL Server databases are
Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database server that stores and retrieves data for multi-user network-based applications. SQL Server databases are
Optimizing object definitions with @Select and @Where functions
 Designer 4.0 and 5.0 Optimizing object definitions with @Select and @Where functions You can use @Functions in Designer to allow you to use more flexible methods to specify SQL in object definitions. The
Designer 4.0 and 5.0 Optimizing object definitions with @Select and @Where functions You can use @Functions in Designer to allow you to use more flexible methods to specify SQL in object definitions. The
Data Structure with C
 Subject: Data Structure with C Topic : Tree Tree A tree is a set of nodes that either:is empty or has a designated node, called the root, from which hierarchically descend zero or more subtrees, which
Subject: Data Structure with C Topic : Tree Tree A tree is a set of nodes that either:is empty or has a designated node, called the root, from which hierarchically descend zero or more subtrees, which
Object Oriented Software Design II
 Object Oriented Software Design II Real Application Design Christian Nastasi http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~chris/cpp Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa April 25, 2012 C. Nastasi (Scuola
Object Oriented Software Design II Real Application Design Christian Nastasi http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~chris/cpp Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa April 25, 2012 C. Nastasi (Scuola
Variable Base Interface
 Chapter 6 Variable Base Interface 6.1 Introduction Finite element codes has been changed a lot during the evolution of the Finite Element Method, In its early times, finite element applications were developed
Chapter 6 Variable Base Interface 6.1 Introduction Finite element codes has been changed a lot during the evolution of the Finite Element Method, In its early times, finite element applications were developed
Software Development Phases
 Software Development Phases Specification of the task Design of a solution Implementation of solution Analysis of solution Testing and debugging Maintenance and evolution of the system Obsolescence Specification
Software Development Phases Specification of the task Design of a solution Implementation of solution Analysis of solution Testing and debugging Maintenance and evolution of the system Obsolescence Specification
Programming languages C
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 9899:1999 TECHNICAL CORRIGENDUM 2 Published 2004-11-15 INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION МЕЖДУНАРОДНАЯ ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ ПО СТАНДАРТИЗАЦИИ ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 9899:1999 TECHNICAL CORRIGENDUM 2 Published 2004-11-15 INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION МЕЖДУНАРОДНАЯ ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ ПО СТАНДАРТИЗАЦИИ ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE
C++ DATA STRUCTURES. Defining a Structure: Accessing Structure Members:
 C++ DATA STRUCTURES http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_data_structures.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com C/C++ arrays allow you to define variables that combine several data items of the same kind
C++ DATA STRUCTURES http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_data_structures.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com C/C++ arrays allow you to define variables that combine several data items of the same kind
The following themes form the major topics of this chapter: The terms and concepts related to trees (Section 5.2).
 CHAPTER 5 The Tree Data Model There are many situations in which information has a hierarchical or nested structure like that found in family trees or organization charts. The abstraction that models hierarchical
CHAPTER 5 The Tree Data Model There are many situations in which information has a hierarchical or nested structure like that found in family trees or organization charts. The abstraction that models hierarchical
Programming by Contract. Programming by Contract: Motivation. Programming by Contract: Preconditions and Postconditions
 COMP209 Object Oriented Programming Designing Classes 2 Mark Hall Programming by Contract (adapted from slides by Mark Utting) Preconditions Postconditions Class invariants Programming by Contract An agreement
COMP209 Object Oriented Programming Designing Classes 2 Mark Hall Programming by Contract (adapted from slides by Mark Utting) Preconditions Postconditions Class invariants Programming by Contract An agreement
Lecture Notes on Stacks & Queues
 Lecture Notes on Stacks & Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons Lecture 9 February 12, 2013 1 Introduction In this lecture we introduce queues and
Lecture Notes on Stacks & Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons Lecture 9 February 12, 2013 1 Introduction In this lecture we introduce queues and
Programming Database lectures for mathema
 Programming Database lectures for mathematics students April 25, 2015 Functions Functions are defined in Postgres with CREATE FUNCTION name(parameter type,...) RETURNS result-type AS $$ function-body $$
Programming Database lectures for mathematics students April 25, 2015 Functions Functions are defined in Postgres with CREATE FUNCTION name(parameter type,...) RETURNS result-type AS $$ function-body $$
SQLITE C/C++ TUTORIAL
 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/sqlite/sqlite_c_cpp.htm SQLITE C/C++ TUTORIAL Copyright tutorialspoint.com Installation Before we start using SQLite in our C/C++ programs, we need to make sure that we have
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/sqlite/sqlite_c_cpp.htm SQLITE C/C++ TUTORIAL Copyright tutorialspoint.com Installation Before we start using SQLite in our C/C++ programs, we need to make sure that we have
Sources: On the Web: Slides will be available on:
 C programming Introduction The basics of algorithms Structure of a C code, compilation step Constant, variable type, variable scope Expression and operators: assignment, arithmetic operators, comparison,
C programming Introduction The basics of algorithms Structure of a C code, compilation step Constant, variable type, variable scope Expression and operators: assignment, arithmetic operators, comparison,
Working with Visio Connectors
 Working with Visio Connectors Overview Connectors are lines that connect your shapes. Once a connection has been made, when the shape is moved, the connector points stay connected and move with the shape.
Working with Visio Connectors Overview Connectors are lines that connect your shapes. Once a connection has been made, when the shape is moved, the connector points stay connected and move with the shape.
Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Deques. It s time for a chainge!
 Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Deques It s time for a chainge! Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Differentiate an abstraction from an implementation. Define and give examples of problems
Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Deques It s time for a chainge! Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Differentiate an abstraction from an implementation. Define and give examples of problems
Course: Programming II - Abstract Data Types. The ADT Queue. (Bobby, Joe, Sue, Ellen) Add(Ellen) Delete( ) The ADT Queues Slide Number 1
 Definition Course: Programming II - Abstract Data Types The ADT Queue The ADT Queue is a linear sequence of an arbitrary number of items, together with access procedures. The access procedures permit addition
Definition Course: Programming II - Abstract Data Types The ADT Queue The ADT Queue is a linear sequence of an arbitrary number of items, together with access procedures. The access procedures permit addition
Lecture Notes on Binary Search Trees
 Lecture Notes on Binary Search Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 17 March 17, 2010 1 Introduction In the previous two lectures we have seen how to exploit the structure
Lecture Notes on Binary Search Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 17 March 17, 2010 1 Introduction In the previous two lectures we have seen how to exploit the structure
Help on the Embedded Software Block
 Help on the Embedded Software Block Powersim Inc. 1. Introduction The Embedded Software Block is a block that allows users to model embedded devices such as microcontrollers, DSP, or other devices. It
Help on the Embedded Software Block Powersim Inc. 1. Introduction The Embedded Software Block is a block that allows users to model embedded devices such as microcontrollers, DSP, or other devices. It
root node level: internal node edge leaf node CS@VT Data Structures & Algorithms 2000-2009 McQuain
 inary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from each
inary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from each
TREE BASIC TERMINOLOGIES
 TREE Trees are very flexible, versatile and powerful non-liner data structure that can be used to represent data items possessing hierarchical relationship between the grand father and his children and
TREE Trees are very flexible, versatile and powerful non-liner data structure that can be used to represent data items possessing hierarchical relationship between the grand father and his children and
Questions 1 through 25 are worth 2 points each. Choose one best answer for each.
 Questions 1 through 25 are worth 2 points each. Choose one best answer for each. 1. For the singly linked list implementation of the queue, where are the enqueues and dequeues performed? c a. Enqueue in
Questions 1 through 25 are worth 2 points each. Choose one best answer for each. 1. For the singly linked list implementation of the queue, where are the enqueues and dequeues performed? c a. Enqueue in
Coding Rules. Encoding the type of a function into the name (so-called Hungarian notation) is forbidden - it only confuses the programmer.
 Coding Rules Section A: Linux kernel style based coding for C programs Coding style for C is based on Linux Kernel coding style. The following excerpts in this section are mostly taken as is from articles
Coding Rules Section A: Linux kernel style based coding for C programs Coding style for C is based on Linux Kernel coding style. The following excerpts in this section are mostly taken as is from articles
Lecture Notes on Binary Search Trees
 Lecture Notes on Binary Search Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning André Platzer Lecture 17 October 23, 2014 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will continue considering associative
Lecture Notes on Binary Search Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning André Platzer Lecture 17 October 23, 2014 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will continue considering associative
Chapter 2: Elements of Java
 Chapter 2: Elements of Java Basic components of a Java program Primitive data types Arithmetic expressions Type casting. The String type (introduction) Basic I/O statements Importing packages. 1 Introduction
Chapter 2: Elements of Java Basic components of a Java program Primitive data types Arithmetic expressions Type casting. The String type (introduction) Basic I/O statements Importing packages. 1 Introduction
MicroStrategy Desktop
 MicroStrategy Desktop Quick Start Guide MicroStrategy Desktop is designed to enable business professionals like you to explore data, simply and without needing direct support from IT. 1 Import data from
MicroStrategy Desktop Quick Start Guide MicroStrategy Desktop is designed to enable business professionals like you to explore data, simply and without needing direct support from IT. 1 Import data from
- Easy to insert & delete in O(1) time - Don t need to estimate total memory needed. - Hard to search in less than O(n) time
 Skip Lists CMSC 420 Linked Lists Benefits & Drawbacks Benefits: - Easy to insert & delete in O(1) time - Don t need to estimate total memory needed Drawbacks: - Hard to search in less than O(n) time (binary
Skip Lists CMSC 420 Linked Lists Benefits & Drawbacks Benefits: - Easy to insert & delete in O(1) time - Don t need to estimate total memory needed Drawbacks: - Hard to search in less than O(n) time (binary
vector vec double # in # cl in ude <s ude tdexcept> tdexcept> // std::ou std t_of ::ou _range t_of class class V Vector { ector {
 Software Design (C++) 3. Resource management and exception safety (idioms and technicalities) Juha Vihavainen University of Helsinki Preview More on error handling and exceptions checking array indices
Software Design (C++) 3. Resource management and exception safety (idioms and technicalities) Juha Vihavainen University of Helsinki Preview More on error handling and exceptions checking array indices
Queue ADT. March 16, 2000
 Queue ADT March 6, 2000 The Queue ADT Queue represent another form of linear data structure. As in the case of the list, the idea of a queue is to represent sequences of elements, all having the same type.
Queue ADT March 6, 2000 The Queue ADT Queue represent another form of linear data structure. As in the case of the list, the idea of a queue is to represent sequences of elements, all having the same type.
AP Computer Science A 2004 Free-Response Questions
 AP Computer Science A 2004 Free-Response Questions The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use
AP Computer Science A 2004 Free-Response Questions The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use
ECDL. European Computer Driving Licence. Spreadsheet Software BCS ITQ Level 2. Syllabus Version 5.0
 European Computer Driving Licence Spreadsheet Software BCS ITQ Level 2 Using Microsoft Excel 2010 Syllabus Version 5.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, includes
European Computer Driving Licence Spreadsheet Software BCS ITQ Level 2 Using Microsoft Excel 2010 Syllabus Version 5.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, includes
Lecture 3. Arrays. Name of array. c[0] c[1] c[2] c[3] c[4] c[5] c[6] c[7] c[8] c[9] c[10] c[11] Position number of the element within array c
![Lecture 3. Arrays. Name of array. c[0] c[1] c[2] c[3] c[4] c[5] c[6] c[7] c[8] c[9] c[10] c[11] Position number of the element within array c Lecture 3. Arrays. Name of array. c[0] c[1] c[2] c[3] c[4] c[5] c[6] c[7] c[8] c[9] c[10] c[11] Position number of the element within array c](/thumbs/40/21186926.jpg) Lecture 3 Data structures arrays structs C strings: array of chars Arrays as parameters to functions Multiple subscripted arrays Structs as parameters to functions Default arguments Inline functions Redirection
Lecture 3 Data structures arrays structs C strings: array of chars Arrays as parameters to functions Multiple subscripted arrays Structs as parameters to functions Default arguments Inline functions Redirection
6.088 Intro to C/C++ Day 4: Object-oriented programming in C++ Eunsuk Kang and Jean Yang
 6.088 Intro to C/C++ Day 4: Object-oriented programming in C++ Eunsuk Kang and Jean Yang Today s topics Why objects? Object-oriented programming (OOP) in C++ classes fields & methods objects representation
6.088 Intro to C/C++ Day 4: Object-oriented programming in C++ Eunsuk Kang and Jean Yang Today s topics Why objects? Object-oriented programming (OOP) in C++ classes fields & methods objects representation
St S a t ck a ck nd Qu Q eue 1
 Stack and Queue 1 Stack Data structure with Last-In First-Out (LIFO) behavior In Out C B A B C 2 Typical Operations Pop on Stack Push isempty: determines if the stack has no elements isfull: determines
Stack and Queue 1 Stack Data structure with Last-In First-Out (LIFO) behavior In Out C B A B C 2 Typical Operations Pop on Stack Push isempty: determines if the stack has no elements isfull: determines
MyOra 3.0. User Guide. SQL Tool for Oracle. Jayam Systems, LLC
 MyOra 3.0 SQL Tool for Oracle User Guide Jayam Systems, LLC Contents Features... 4 Connecting to the Database... 5 Login... 5 Login History... 6 Connection Indicator... 6 Closing the Connection... 7 SQL
MyOra 3.0 SQL Tool for Oracle User Guide Jayam Systems, LLC Contents Features... 4 Connecting to the Database... 5 Login... 5 Login History... 6 Connection Indicator... 6 Closing the Connection... 7 SQL
Analysis of a Search Algorithm
 CSE 326 Lecture 4: Lists and Stacks 1. Agfgd 2. Dgsdsfd 3. Hdffdsf 4. Sdfgsfdg 5. Tefsdgass We will review: Analysis: Searching a sorted array (from last time) List ADT: Insert, Delete, Find, First, Kth,
CSE 326 Lecture 4: Lists and Stacks 1. Agfgd 2. Dgsdsfd 3. Hdffdsf 4. Sdfgsfdg 5. Tefsdgass We will review: Analysis: Searching a sorted array (from last time) List ADT: Insert, Delete, Find, First, Kth,
Data Structures and Algorithms Lists
 Data Structures and Algorithms Lists Chris Brooks Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco p.1/19 5-0: Abstract Data Types An
Data Structures and Algorithms Lists Chris Brooks Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco p.1/19 5-0: Abstract Data Types An
Module 816. File Management in C. M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University
 M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University Aim Learning objectives Content After working through this module you should be able to create C programs that create an use both text and binary files. After working
M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University Aim Learning objectives Content After working through this module you should be able to create C programs that create an use both text and binary files. After working
The C Programming Language course syllabus associate level
 TECHNOLOGIES The C Programming Language course syllabus associate level Course description The course fully covers the basics of programming in the C programming language and demonstrates fundamental programming
TECHNOLOGIES The C Programming Language course syllabus associate level Course description The course fully covers the basics of programming in the C programming language and demonstrates fundamental programming
Ordered Lists and Binary Trees
 Data Structures and Algorithms Ordered Lists and Binary Trees Chris Brooks Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco p.1/62 6-0:
Data Structures and Algorithms Ordered Lists and Binary Trees Chris Brooks Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco p.1/62 6-0:
LINKED DATA STRUCTURES
 LINKED DATA STRUCTURES 1 Linked Lists A linked list is a structure in which objects refer to the same kind of object, and where: the objects, called nodes, are linked in a linear sequence. we keep a reference
LINKED DATA STRUCTURES 1 Linked Lists A linked list is a structure in which objects refer to the same kind of object, and where: the objects, called nodes, are linked in a linear sequence. we keep a reference
PL/SQL (Cont d) Let s start with the mail_order database, shown here:
 PL/SQL (Cont d) Let s start with the mail_order database, shown here: 1 Table schemas for the Mail Order database: 2 The values inserted into zipcodes table: The values inserted into employees table: 3
PL/SQL (Cont d) Let s start with the mail_order database, shown here: 1 Table schemas for the Mail Order database: 2 The values inserted into zipcodes table: The values inserted into employees table: 3
Data Structures using OOP C++ Lecture 1
 References: 1. E Balagurusamy, Object Oriented Programming with C++, 4 th edition, McGraw-Hill 2008. 2. Robert Lafore, Object-Oriented Programming in C++, 4 th edition, 2002, SAMS publishing. 3. Robert
References: 1. E Balagurusamy, Object Oriented Programming with C++, 4 th edition, McGraw-Hill 2008. 2. Robert Lafore, Object-Oriented Programming in C++, 4 th edition, 2002, SAMS publishing. 3. Robert
Intel EP80579 Software for Security Applications on Intel QuickAssist Technology Cryptographic API Reference
 Intel EP80579 Software for Security Applications on Intel QuickAssist Technology Cryptographic API Reference Automatically generated from sources, May 19, 2009. Reference Number: 320184, Revision -003
Intel EP80579 Software for Security Applications on Intel QuickAssist Technology Cryptographic API Reference Automatically generated from sources, May 19, 2009. Reference Number: 320184, Revision -003
