Checking Port Status and Connectivity
|
|
|
- Domenic Scott
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to check switch port status and connectivity on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Checking Module Status, page 7-2 Checking Interfaces Status, page 7-2 Displaying MAC Addresses, page 7-3 Checking Cable Status Using Time Domain Reflectometer, page 7-3 Using Telnet, page 7-5 Changing the Logout Timer, page 7-6 Monitoring User Sessions, page 7-6 Using Ping, page 7-7 Using IP Traceroute, page 7-8 Using Layer 2 Traceroute, page 7-9 Configuring ICMP, page 7-11 For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, first look at the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Reference and related publications at this location: If the command is not found in the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Reference, it will be found in the larger Cisco IOS library. Refer to the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Reference and related publications at this location: 7-1
2 Checking Module Status Chapter 7 Checking Module Status The Catalyst 4500 series switch is a multimodule system. You can see which modules are installed, as well as the MAC address ranges and version numbers for each module, by using the show module command. You can use the [mod_num] argument to specify a particular module number to see detailed information on that module. This example shows how to check module status for all modules on your switch: show module all Mod Ports Card Type Model Serial No BaseX (GBIC) Supervisor Module WS-X4014 JAB012345AB /100/1000BaseTX (RJ45) WS-X4424-GB-RJ45 JAB045304EY /100BaseTX (RJ45) WS-X4148 JAB023402QK M MAC addresses Hw Fw Sw Stat dd46.9f00 to 0004.dd46.a2ff (10r)EW(1.21) 12.1(10)EW(1) Ok e7e.1d70 to e7e.1d Ok f to f10.239f 1.0 Ok Checking Interfaces Status You can view summary or detailed information on the switch ports using the show interfaces status command. To see summary information on all ports on the switch, enter the show interfaces status command with no arguments. Specify a particular module number to see information on the ports on that module only. Enter both the module number and the port number to see detailed information about the specified port. To apply configuration commands to a particular port, you must specify the appropriate logical module. For more information, see the Checking Module Status section on page 7-2. This example shows how to display the status of all interfaces on a Catalyst 4500 series switch, including transceivers. Output of this command displays Unapproved GBIC for non-cisco transceivers: show interfaces status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi1/1 notconnect 1 auto auto No Gbic Gi1/2 notconnect 1 auto auto No Gbic Gi5/1 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100/1000-TX Gi5/2 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100/1000-TX Gi5/3 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100/1000-TX Gi5/4 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100/1000-TX Fa6/1 connected 1 a-full a /100BaseTX Fa6/2 connected 2 a-full a /100BaseTX Fa6/3 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100BaseTX Fa6/4 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100BaseTX This example shows how to display the status of interfaces in error-disabled state: show interfaces status err-disabled Port Name Status Reason Fa9/4 err-disabled link-flap informational error message when the timer expires on a cause 7-2
3 Chapter 7 Displaying MAC Addresses d04h:%PM-SP-4-ERR_RECOVER:Attempting to recover from link-flap err-disable state on Fa9/4 Displaying MAC Addresses In addition to displaying the MAC address range for a module using the show module command, you can display the MAC address table information of a specific MAC address or a specific interface in the switch using the show mac-address-table address and show mac-address-table interface commands. This example shows how to display MAC address table information for a specific MAC address: show mac-address-table address e8d.6400 vlan mac address type protocol qos ports e8d.6400 static assigned -- Switch e8d.6400 static assigned -- Switch e8d.6400 static assigned -- Switch e8d.6400 static ipx -- Switch e8d.6400 static ipx -- Switch e8d.6400 static assigned -- Switch e8d.6400 static assigned -- Switch e8d.6400 static ipx -- Switch e8d.6400 static ipx -- Switch e8d.6400 static ipx -- Switch e8d.6400 static other -- Switch e8d.6400 static other -- Switch e8d.6400 static other -- Switch e8d.6400 static ip -- Switch e8d.6400 static ip -- Route e8d.6400 static other -- Switch e8d.6400 static other -- Switch e8d.6400 static ip -- Switch e8d.6400 static ip -- Switch e8d.6400 static ip -- Switch This example shows how to display MAC address table information for a specific interface: show mac-address-table interface gigabit 1/1 Multicast Entries vlan mac address type ports ffff.ffff.ffff system Switch,Gi6/1,Gi6/2,Gi6/9,Gi1/1 Checking Cable Status Using Time Domain Reflectometer Interfaces on a Supervisor Engine 6-E or Supervisor Engine 6L-E do not support TDR; the line cards do. You can use the Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) feature to determine if cabling is at fault when you cannot establish a link. 7-3
4 Checking Cable Status Using Time Domain Reflectometer Chapter 7 This test is especially important when replacing an existing switch, upgrading to Gigabit Ethernet, or installing new cable plants. Overview With TDR, you can check the status of copper cables on the 48-port 10/100/1000 BASE-T modules for the Catalyst 4500 series switch (WS-X4548-GB-RJ45, WS-X4548-GB-RJ45V, WS-X4524-GB-RJ45V, WS-X4548-GB-RJ45V+, WS-X4013+TS, WS-C4948, and WS-C GE). TDR detects a cable fault by sending a signal through the cable and reading the signal that is reflected back. All or part of the signal can be reflected back either by cable defects or by the end of the cable. There are four pairs of standard category 5 cable. Each pair can assume one of the following states: open (not connected), broken, shorted, or terminated. The TDR test detects all four states and displays the first three as Fault conditions, and displays the fourth as Terminated. Although the CLI output is shown, the cable length is shown only if the state is Faulty. Running the TDR Test To start the TDR test, perform this task in privileged mode: Step 1 Step 2 test cable-diagnostics tdr {interface {interface interface-number}} show cable-diagnostics tdr {interface {interface interface-number}} Starts the TDR test. Displays the TDR test counter information. This example shows how to start the TDR test on port 1 on module 2: test cable-diagnostics tdr int gi2/1 This example shows the message that displays when the TDR test is not supported on a module: test cable-diagnostics tdr int gi2/1 00:03:15:%C4K_IOSDIAGMAN-4-TESTNOTSUPPORTEDONMODULE: Online cable diag tdr test is not supported on this module This example shows how to display TDR test results for a port: show cable-diagnostics tdr interface gi4/13 Interface Speed Local pair Cable length Remote channel Status Gi4/13 0Mbps m Unknown Fault m Unknown Fault m Unknown Fault m Unknown Fault This command will be deprecated in future releases of Cisco IOS software. Use the diagnostic start and the show diagnostic result commands to run the TDR test and display the test results. 7-4
5 Chapter 7 Using Telnet TDR is a port test; the port cannot handle traffic for the duration of the test (generally, 1 minute). TDR Guidelines The following guidelines apply to the use of TDR: If you connect a port undergoing a TDR test to an Auto-MDIX enabled port, the TDR result might be invalid. In those instances, the port on the WS-X4148-RJ45V should be administratively down before the start of the TDR test. If you connect a port undergoing a TDR test to a 100BASE-T port such as that on the WS-X4148-RJ45V, the unused pairs (4-5 and 7-8) will be reported as faulty because the remote end does not terminate these pairs. Do not change the port configuration while the TDR test is running. Due to cable characteristics, you should run the TDR test multiple times to get accurate results. Do not change port status (for example, remove the cable at the near or far end) because the results might be inaccurate. Using Telnet You can access the switch command-line interface (CLI) using Telnet. In addition, you can use Telnet from the switch to access other devices in the network. You can have up to eight simultaneous Telnet sessions. Before you can open a Telnet session to the switch, you must first set the IP address (and in some cases the default gateway) for the switch. For information about setting the IP address and default gateway, see Chapter 3, Configuring the Switch for the First Time. To establish a Telnet connection to a host by using the hostname, configure and enable DNS. To establish a Telnet connection to another device on the network from the switch, perform this task: telnet host [port] Opens a Telnet session to a remote host. This example shows how to establish a Telnet connection from the switch to the remote host named labsparc: telnet labsparc Trying Connected to labsparc. Escape character is '^]'. UNIX(r) System V Release 4.0 (labsparc) login: 7-5
6 Changing the Logout Timer Chapter 7 Changing the Logout Timer The logout timer automatically disconnects a user from the switch when the user is idle for longer than the specified time. To set the logout timer, perform this task: logoutwarning number Changes the logout timer value (a timeout value of 0 prevents idle sessions from being disconnected automatically). Use the no keyword to return to the default value. Monitoring User Sessions You can display the currently active user sessions on the switch using the show users command. The command output lists all active console port and Telnet sessions on the switch. To display the active user sessions on the switch, perform this task in privileged EXEC mode: show users [all] Displays the currently active user sessions on the switch. This example shows the output of the show users command when local authentication is enabled for console and Telnet sessions (the asterisk [*] indicates the current session): show users Line User Host(s) Idle Location * 0 con 0 idle 00:00:00 Interface User Mode Idle Peer Address show users all Line User Host(s) Idle Location * 0 con 0 idle 00:00:00 1 vty 0 00:00:00 2 vty 1 00:00:00 3 vty 2 00:00:00 4 vty 3 00:00:00 5 vty 4 00:00:00 Interface User Mode Idle Peer Address To disconnect an active user session, perform this task: disconnect {console ip_addr} Disconnects an active user session on the switch. 7-6
7 Chapter 7 Using Ping This example shows how to disconnect an active console port session and an active Telnet session: Switch> disconnect console Console session disconnected. Console> (enable) disconnect tim-nt.bigcorp.com Telnet session from tim-nt.bigcorp.com disconnected. (1) show users Session User Location telnet jake jake-mac.bigcorp.com * telnet suzy suzy-pc.bigcorp.com Using Ping These sections describe how to use IP ping: Understanding How Ping Works, page 7-7 Running Ping, page 7-7 Understanding How Ping Works You can use the ping command to verify connectivity to remote hosts. If you attempt to ping a host in a different IP subnetwork, you must define a static route to the network or configure a router to route between those subnets. The ping command is configurable from normal executive and privileged EXEC mode. Ping returns one of the following responses: Normal response The normal response (hostname is alive) occurs in 1 to 10 seconds, depending on network traffic. Destination does not respond If the host does not respond, a No Answer message is returned. Unknown host If the host does not exist, an Unknown Host message is returned. Destination unreachable If the default gateway cannot reach the specified network, a Destination Unreachable message is returned. Network or host unreachable If there is no entry in the route table for the host or network, a Network or Host Unreachable message is returned. To stop a ping in progress, press Ctrl-C. Running Ping To ping another device on the network from the switch, perform this task in normal executive and privileged EXEC mode: ping host Checks connectivity to a remote host. 7-7
8 Using IP Traceroute Chapter 7 This example shows how to ping a remote host from normal executive mode: ping labsparc labsparc is alive Switch> ping is alive This example shows how to enter a ping command in privileged EXEC mode specifying the number of packets, the packet size, and the timeout period: ping Target IP Address []: Number of Packets [5]: 10 Datagram Size [56]: 100 Timeout in seconds [2]: 10 Source IP Address [ ]: !!!!!!!!!! PING Statistics packets transmitted, 10 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 1/1/1 Switch Using IP Traceroute These sections describe how to use IP traceroute feature: Understanding How IP Traceroute Works, page 7-8 Running IP Traceroute, page 7-9 Understanding How IP Traceroute Works You can use IP traceroute to identify the path that packets take through the network on a hop-by-hop basis. The command output displays all network layer (Layer 3) devices, such as routers, that the traffic passes through on the way to the destination. Layer 2 switches can participate as the source or destination of the trace command but will not appear as a hop in the trace command output. The trace command uses the Time To Live (TTL) field in the IP header to cause routers and servers to generate specific return messages. Traceroute starts by sending a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) datagram to the destination host with the TTL field set to 1. If a router finds a TTL value of 1 or 0, it drops the datagram and sends back an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Time-Exceeded message to the sender. Traceroute determines the address of the first hop by examining the source address field of the ICMP Time-Exceeded message. To identify the next hop, traceroute sends a UDP packet with a TTL value of 2. The first router decrements the TTL field by 1 and sends the datagram to the next router. The second router sees a TTL value of 1, discards the datagram, and returns the Time-Exceeded message to the source. This process continues until the TTL is incremented to a value large enough for the datagram to reach the destination host or until the maximum TTL is reached. To determine when a datagram reaches its destination, traceroute sets the UDP destination port in the datagram to a very large value that the destination host is unlikely to be using. When a host receives a datagram with an unrecognized port number, it sends an ICMP Port Unreachable error message to the source. The Port Unreachable error message indicates to traceroute that the destination has been reached. 7-8
9 Chapter 7 Using Layer 2 Traceroute Running IP Traceroute To trace the path that packets take through the network, perform this task in EXEC or privileged EXEC mode: trace [protocol] [destination] Runs IP traceroute to trace the path that packets take through the network. This example shows use the trace command to display the route a packet takes through the network to reach its destination: trace ip ABA.NYC.mil Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to ABA.NYC.mil ( ) 1 DEBRIS.CISCO.COM ( ) 1000 msec 8 msec 4 msec 2 BARRNET-GW.CISCO.COM ( ) 8 msec 8 msec 8 msec 3 EXTERNAL-A-GATEWAY.STANFORD.EDU ( ) 8 msec 4 msec 4 msec 4 BB2.SU.BARRNET.NET ( ) 8 msec 8 msec 8 msec 5 SU.ARC.BARRNET.NET ( ) 12 msec 12 msec 8 msec 6 MOFFETT-FLD-MB.in.MIL ( ) 216 msec 120 msec 132 msec 7 ABA.NYC.mil ( ) 412 msec 628 msec 664 msec Using Layer 2 Traceroute The Layer 2 traceroute feature allows the switch to identify the physical path that a packet takes from a source device to a destination device. Layer 2 traceroute supports only unicast source and destination MAC addresses. It determines the path by using the MAC address tables of the switches in the path. When the switch detects a device in the path that does not support Layer 2 traceroute, the switch continues to send Layer 2 trace queries and lets them time out. If you want the switch to trace the path from a host on a source device to a host on a destination device, the switch can identify only the path from the source device to the destination device. It cannot identify the path that a packet takes from source host to the source device or from the destination device to the destination host. These sections describe how to use the Layer 2 traceroute feature: Layer 2 Traceroute Usage Guidelines, page 7-10 Running Layer 2 Traceroute, page
10 Using Layer 2 Traceroute Chapter 7 Layer 2 Traceroute Usage Guidelines These are the Layer 2 traceroute usage guidelines: CDP must be enabled on all the devices in the network. For Layer 2 traceroute to functional properly, do not disable CDP. If any devices in the physical path are transparent to CDP, the switch cannot identify the path through these devices. For more information about enabling CDP, see Chapter 26, Configuring CDP. All switches in the physical path must have IP connectivity. When a switch is reachable from another switch, you can test connectivity by using the ping command in privileged EXEC mode. The maximum number of hops identified in the path is ten. You can enter the traceroute mac or the traceroute mac ip command in privileged EXEC mode on a switch that is not in the physical path from the source device to the destination device. All switches in the path must be reachable from this switch. The traceroute mac command output shows the Layer 2 path only when the specified source and destination MAC addresses belong to the same VLAN. If you specify source and destination MAC addresses that belong to different VLANs, the Layer 2 path is not identified, and an error message appears. If you specify a multicast source or destination MAC address, the path is not identified, and an error message appears. If the source or destination MAC address belongs to multiple VLANs, you must specify the VLAN to which both the source and destination MAC addresses belong. If the VLAN is not specified, the path is not identified, and an error message appears. The traceroute mac ip command output shows the Layer 2 path when the specified source and destination IP addresses belong to the same subnet. When you specify the IP addresses, the switch uses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to associate the IP address with the corresponding MAC address and the VLAN ID. If an ARP entry exists for the specified IP address, the switch uses the associated MAC address and identifies the physical path. If an ARP entry does not exist, the switch sends an ARP query and tries to resolve the IP address. If the IP address is not resolved, the path is not identified, and an error message appears. When multiple devices are attached to one port through hubs (for example, multiple CDP neighbors are detected on a port), the Layer 2 traceroute feature is not supported. When more than one CDP neighbor is detected on a port, the Layer 2 path is not identified, and an error message appears. This feature is not supported in Token Ring VLANs. 7-10
11 Chapter 7 Configuring ICMP Running Layer 2 Traceroute To display the physical path that a packet takes from a source device to a destination device, perform either one of these tasks in privileged EXEC mode: traceroute mac {source-mac-address} {destination-mac-address} Runs Layer 2 traceroute to trace the path that packets take through the network. or traceroute mac ip {source-mac-address} {destination-mac-address} Runs IP traceroute to trace the path that packets take through the network. These examples show how to use the traceroute mac and traceroute mac ip commands to display the physical path a packet takes through the network to reach its destination: traceroute mac Source found on con6[ws-c2950g-24-ei] ( ) con6 ( ) :Fa0/1 => Fa0/3 con5 ( ) : Fa0/3 => Gi0/1 con1 ( ) : Gi0/1 => Gi0/2 con2 ( ) : Gi0/2 => Fa0/1 Destination found on con2[ws-c ] ( ) Layer 2 trace completed traceroute mac ip detail Translating IP to mac => => Source found on con6[ws-c2950g-24-ei] ( ) con6 / WS-C2950G-24-EI / : Fa0/1 [auto, auto] => Fa0/3 [auto, auto] con5 / WS-C2950G-24-EI / : Fa0/3 [auto, auto] => Gi0/1 [auto, auto] con1 / WS-C G / : Gi0/1 [auto, auto] => Gi0/2 [auto, auto] con2 / WS-C / : Gi0/2 [auto, auto] => Fa0/1 [auto, auto] Destination found on con2[ws-c ] ( ) Layer 2 trace completed. Configuring ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) provides many services that control and manage IP connections. ICMP messages are sent by routers or access servers to hosts or other routers when a problem is discovered with the Internet header. For detailed information on ICMP, refer to RFC
12 Configuring ICMP Chapter 7 Enabling ICMP Protocol Unreachable Messages If the Cisco IOS software receives a nonbroadcast packet that uses an unknown protocol, it sends an ICMP Protocol Unreachable message back to the source. Similarly, if the software receives a packet that it is unable to deliver to the ultimate destination because it knows of no route to the destination address, it sends an ICMP Host Unreachable message to the source. This feature is enabled by default. To enable the generation of ICMP Protocol Unreachable and Host Unreachable messages, enter the following command in interface configuration mode: Switch (config-if)# [no] ip unreachables Enables ICMP destination unreachable messages. Use the no keyword to disable the ICMP destination unreachable messages. Caution If you enter the no ip unreachables command, you will break the path MTU discovery functionality. Routers in the middle of the network might be forced to fragment packets. To limit the rate that Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) destination unreachable messages are generated, perform this task: Switch (config)# [no] ip icmp rate-limit unreachable [df] milliseconds Limits the rate that ICMP destination messages are generated. Use the no keyword to remove the rate limit and reduce the CPU usage. Enabling ICMP Redirect Messages Data routes are sometimes less than optimal. For example, it is possible for the router to be forced to resend a packet through the same interface on which it was received. If this occurs, the Cisco IOS software sends an ICMP Redirect message to the originator of the packet telling the originator that the router is on a subnet directly connected to the receiving device, and that it must forward the packet to another system on the same subnet. The software sends an ICMP Redirect message to the packet's originator because the originating host presumably could have sent that packet to the next hop without involving this device at all. The Redirect message instructs the sender to remove the receiving device from the route and substitute a specified device representing a more direct path. This feature is enabled by default. However, when Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is configured on an interface, ICMP Redirect messages are disabled (by default) for the interface. For more information on HSRP, refer to the following URL: guration_guide_chapter.html 7-12
13 Chapter 7 Configuring ICMP To enable the sending of ICMP Redirect messages if the Cisco IOS software is forced to resend a packet through the same interface on which it was received, enter the following command in interface configuration mode: Switch (config-if)# [no] ip redirects Enables ICMP Redirect messages. Use the no keyword to disable the ICMP Redirect messages and reduce CPU usage. Enabling ICMP Mask Reply Messages Occasionally, network devices must know the subnet mask for a particular subnetwork in the internetwork. To obtain this information, devices can send ICMP Mask Request messages. These messages are responded to by ICMP Mask Reply messages from devices that have the requested information. The Cisco IOS software can respond to ICMP Mask Request messages if the ICMP Mask Reply function is enabled. To have the Cisco IOS software respond to ICMP mask requests by sending ICMP Mask Reply messages, perform this task: Switch (config-if)# [no] ip mask-reply Enables response to ICMP destination mask requests. Use the no keyword to disable this functionality. 7-13
14 Configuring ICMP Chapter
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. 1. IP address for this host computer 2. Subnet mask 3. Default gateway address
 Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
IPv6 Diagnostic and Troubleshooting
 8 IPv6 Diagnostic and Troubleshooting Contents Introduction.................................................. 8-2 ICMP Rate-Limiting........................................... 8-2 Ping for IPv6 (Ping6)..........................................
8 IPv6 Diagnostic and Troubleshooting Contents Introduction.................................................. 8-2 ICMP Rate-Limiting........................................... 8-2 Ping for IPv6 (Ping6)..........................................
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
IP Routing Features. Contents
 7 IP Routing Features Contents Overview of IP Routing.......................................... 7-3 IP Interfaces................................................ 7-3 IP Tables and Caches........................................
7 IP Routing Features Contents Overview of IP Routing.......................................... 7-3 IP Interfaces................................................ 7-3 IP Tables and Caches........................................
- Basic Router Security -
 1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
Troubleshooting IP Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
Configuring the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway This chapter describes how to configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For
CHAPTER 3 Configuring the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway This chapter describes how to configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For
Configuring PROFINET
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Troubleshooting Tools
 Troubleshooting Tools An overview of the main tools for verifying network operation from a host Fulvio Risso Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Turin) see page 2 Notes n The commands/programs
Troubleshooting Tools An overview of the main tools for verifying network operation from a host Fulvio Risso Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Turin) see page 2 Notes n The commands/programs
Configuring Denial of Service Protection
 24 CHAPTER This chapter contains information on how to protect your system against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The information covered in this chapter is unique to the Catalyst 6500 series switches,
24 CHAPTER This chapter contains information on how to protect your system against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The information covered in this chapter is unique to the Catalyst 6500 series switches,
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
IP - The Internet Protocol
 Orientation IP - The Internet Protocol IP (Internet Protocol) is a Network Layer Protocol. IP s current version is Version 4 (IPv4). It is specified in RFC 891. TCP UDP Transport Layer ICMP IP IGMP Network
Orientation IP - The Internet Protocol IP (Internet Protocol) is a Network Layer Protocol. IP s current version is Version 4 (IPv4). It is specified in RFC 891. TCP UDP Transport Layer ICMP IP IGMP Network
Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3
 Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3 ARP - RFC 826, STD 37 DHCP - RFC 2131 ICMP - RFC 0792, STD 05 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Bootstrapping an end host Learning its own configuration parameters
Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3 ARP - RFC 826, STD 37 DHCP - RFC 2131 ICMP - RFC 0792, STD 05 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Bootstrapping an end host Learning its own configuration parameters
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR
 Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
Technical Support Information Belkin internal use only
 The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks. Chapter 5: Ethernet
 CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE
 How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE Summary This document attempts to standardize the methods used to configure Intrauve in situations where there is little or no understanding of
How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE Summary This document attempts to standardize the methods used to configure Intrauve in situations where there is little or no understanding of
Homework 3 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management
 Homework 3 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw3 Assigned on 2013/9/13, Due 2013/9/24 Hand In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw3_WebSys.docx) using the ECET Lab report
Homework 3 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw3 Assigned on 2013/9/13, Due 2013/9/24 Hand In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw3_WebSys.docx) using the ECET Lab report
Lehrstuhl für Informatik 4 Kommunikation und verteilte Systeme. Auxiliary Protocols
 Auxiliary Protocols IP serves only for sending packets with well-known addresses. Some questions however remain open, which are handled by auxiliary protocols: Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Reverse
Auxiliary Protocols IP serves only for sending packets with well-known addresses. Some questions however remain open, which are handled by auxiliary protocols: Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Reverse
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers
 Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
Course Overview: Learn the essential skills needed to set up, configure, support, and troubleshoot your TCP/IP-based network.
 Course Name: TCP/IP Networking Course Overview: Learn the essential skills needed to set up, configure, support, and troubleshoot your TCP/IP-based network. TCP/IP is the globally accepted group of protocols
Course Name: TCP/IP Networking Course Overview: Learn the essential skills needed to set up, configure, support, and troubleshoot your TCP/IP-based network. TCP/IP is the globally accepted group of protocols
Configuring NetFlow-lite
 CHAPTER 55 Note NetFlow-lite is only supported on Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch. This chapter describes how to configure NetFlow-lite on the Catalyst 4948E switch. NetFlow-lite provides traffic monitoring
CHAPTER 55 Note NetFlow-lite is only supported on Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch. This chapter describes how to configure NetFlow-lite on the Catalyst 4948E switch. NetFlow-lite provides traffic monitoring
Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP
 The feature addresses the limitation of qualifying Internet Control Management Protocol (ICMP) messages into either a malicious or benign category by allowing the Cisco IOS firewall to use stateful inspection
The feature addresses the limitation of qualifying Internet Control Management Protocol (ICMP) messages into either a malicious or benign category by allowing the Cisco IOS firewall to use stateful inspection
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline
 www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS
 BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Communication analysis provides powerful tool for maintenance, performance monitoring, attack detection, and problems fixing in computer networks. Today networks
BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Communication analysis provides powerful tool for maintenance, performance monitoring, attack detection, and problems fixing in computer networks. Today networks
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING
 CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
NetFlow Subinterface Support
 NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
NETWORK LAYER/INTERNET PROTOCOLS
 CHAPTER 3 NETWORK LAYER/INTERNET PROTOCOLS You will learn about the following in this chapter: IP operation, fields and functions ICMP messages and meanings Fragmentation and reassembly of datagrams IP
CHAPTER 3 NETWORK LAYER/INTERNET PROTOCOLS You will learn about the following in this chapter: IP operation, fields and functions ICMP messages and meanings Fragmentation and reassembly of datagrams IP
Hands On Activities: TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management
 Hands On Activities: TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management 1. TCP/IP Network Management Tasks TCP/IP network management tasks include Examine your physical and IP network address Traffic monitoring
Hands On Activities: TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management 1. TCP/IP Network Management Tasks TCP/IP network management tasks include Examine your physical and IP network address Traffic monitoring
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
Configuring EtherChannels
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
Guide to TCP/IP, Third Edition. Chapter 3: Data Link and Network Layer TCP/IP Protocols
 Guide to TCP/IP, Third Edition Chapter 3: Data Link and Network Layer TCP/IP Protocols Objectives Understand the role that data link protocols, such as SLIP and PPP, play for TCP/IP Distinguish among various
Guide to TCP/IP, Third Edition Chapter 3: Data Link and Network Layer TCP/IP Protocols Objectives Understand the role that data link protocols, such as SLIP and PPP, play for TCP/IP Distinguish among various
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
IPv6 for Cisco IOS Software, File 2 of 3: Configuring
 IPv6 for Cisco IOS Software, File 2 of 3: Configuring This document provides configuration tasks for the Cisco implementation of IP version 6 (IPv6) in the Cisco IOS software and includes the following
IPv6 for Cisco IOS Software, File 2 of 3: Configuring This document provides configuration tasks for the Cisco implementation of IP version 6 (IPv6) in the Cisco IOS software and includes the following
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
8.2 The Internet Protocol
 TCP/IP Protocol Suite HTTP SMTP DNS RTP Distributed applications Reliable stream service TCP UDP User datagram service Best-effort connectionless packet transfer Network Interface 1 IP Network Interface
TCP/IP Protocol Suite HTTP SMTP DNS RTP Distributed applications Reliable stream service TCP UDP User datagram service Best-effort connectionless packet transfer Network Interface 1 IP Network Interface
Firewall Load Balancing
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes the (FWLB) feature. It includes the following sections: FWLB Overview, page 6-1 FWLB Features, page 6-2 FWLB Configuration Tasks, page 6-3 Monitoring and Maintaining FWLB,
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes the (FWLB) feature. It includes the following sections: FWLB Overview, page 6-1 FWLB Features, page 6-2 FWLB Configuration Tasks, page 6-3 Monitoring and Maintaining FWLB,
"Charting the Course...
 Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Chapter 3 Configuring Basic IPv6 Connectivity
 Chapter 3 Configuring Basic IPv6 Connectivity This chapter explains how to get a ProCurve Routing Switch that supports IPv6 up and running. To configure basic IPv6 connectivity, you must do the following:
Chapter 3 Configuring Basic IPv6 Connectivity This chapter explains how to get a ProCurve Routing Switch that supports IPv6 up and running. To configure basic IPv6 connectivity, you must do the following:
CCNA Discovery 4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, In Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, In Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
- IPv4 Addressing and Subnetting -
 1 Hardware Addressing - IPv4 Addressing and Subnetting - A hardware address is used to uniquely identify a host within a local network. Hardware addressing is a function of the Data-Link layer of the OSI
1 Hardware Addressing - IPv4 Addressing and Subnetting - A hardware address is used to uniquely identify a host within a local network. Hardware addressing is a function of the Data-Link layer of the OSI
How To Learn Cisco Cisco Ios And Cisco Vlan
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching
 CCNP3 v5 - Chapter 5 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing High Availability in a Campus Environment Routing issues Hosts rely on a router to find the best path Issues with established
CCNP3 v5 - Chapter 5 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing High Availability in a Campus Environment Routing issues Hosts rely on a router to find the best path Issues with established
IP Application Services Commands show vrrp. This command was introduced. If no group is specified, the status for all groups is displayed.
 show vrrp show vrrp To display a brief or detailed status of one or all configured Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) groups on the router, use the show vrrp command in privileged EXEC mode. show
show vrrp show vrrp To display a brief or detailed status of one or all configured Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) groups on the router, use the show vrrp command in privileged EXEC mode. show
Troubleshooting the Firewall Services Module
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
ccna question and answers
 ccna question and answers 46 Which addresses are valid host addresses? A. 201.222.5.17 B. 201.222.5.18 C. 201.222.5.16 D. 201.222.5.19 E. 201.222.5.31,B & D Subnet addresses in this situation are all in
ccna question and answers 46 Which addresses are valid host addresses? A. 201.222.5.17 B. 201.222.5.18 C. 201.222.5.16 D. 201.222.5.19 E. 201.222.5.31,B & D Subnet addresses in this situation are all in
IP Addressing and Subnetting. 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
Instructor Notes for Lab 3
 Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
IP addressing and forwarding Network layer
 The Internet Network layer Host, router network layer functions: IP addressing and forwarding Network layer Routing protocols path selection RIP, OSPF, BGP Transport layer: TCP, UDP forwarding table IP
The Internet Network layer Host, router network layer functions: IP addressing and forwarding Network layer Routing protocols path selection RIP, OSPF, BGP Transport layer: TCP, UDP forwarding table IP
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
VRRPv3: Object Tracking Integration
 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) enables a group of devices to form a single virtual device to provide redundancy. The LAN clients then can be configured with the virtual device as the default
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) enables a group of devices to form a single virtual device to provide redundancy. The LAN clients then can be configured with the virtual device as the default
IOS Server Load Balancing
 IOS Server Load Balancing This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Server Load Balancing (SLB) feature. It includes the following sections: Feature Overview, page 1 Supported Platforms, page 5 Supported
IOS Server Load Balancing This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Server Load Balancing (SLB) feature. It includes the following sections: Feature Overview, page 1 Supported Platforms, page 5 Supported
Administrative Distance
 RIP is a distance vector routing protocol. It shares routing information through the local broadcast in every 30 seconds. In this tutorial we will explain RIP routing fundamentals with examples such as
RIP is a distance vector routing protocol. It shares routing information through the local broadcast in every 30 seconds. In this tutorial we will explain RIP routing fundamentals with examples such as
Monitoring Traffic Interception
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to use traffic interception to monitor your WAAS devices and contains the following sections: Verifying WCCPv2 Interception, page 2-1 Verifying Inline Interception,
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to use traffic interception to monitor your WAAS devices and contains the following sections: Verifying WCCPv2 Interception, page 2-1 Verifying Inline Interception,
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
 Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Network Protocol Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring IP Addressing... 1 1.1 IP Introduction... 1 1.1.1 IP... 1 1.1.2 IP Routing Protocol... 1 1.2 Configuring IP Address Task List... 2 1.3 Configuring
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring IP Addressing... 1 1.1 IP Introduction... 1 1.1.1 IP... 1 1.1.2 IP Routing Protocol... 1 1.2 Configuring IP Address Task List... 2 1.3 Configuring
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Using Link Layer Discovery Protocol in Multivendor Networks
 Using Link Layer Discovery Protocol in Multivendor Networks Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), standardized by the IEEE as part of 802.1ab, enables standardized discovery of nodes, which in turn facilitates
Using Link Layer Discovery Protocol in Multivendor Networks Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), standardized by the IEEE as part of 802.1ab, enables standardized discovery of nodes, which in turn facilitates
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting
 Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter provides troubleshooting tips and information for your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. After each problem description, instructions are provided
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter provides troubleshooting tips and information for your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. After each problem description, instructions are provided
Using IPM to Measure Network Performance
 CHAPTER 3 Using IPM to Measure Network Performance This chapter provides details on using IPM to measure latency, jitter, availability, packet loss, and errors. It includes the following sections: Measuring
CHAPTER 3 Using IPM to Measure Network Performance This chapter provides details on using IPM to measure latency, jitter, availability, packet loss, and errors. It includes the following sections: Measuring
Configuring CSS Remote Access Methods
 CHAPTER 11 Configuring CSS Remote Access Methods This chapter describes how to configure the Secure Shell Daemon (SSH), Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS), and the Terminal Access Controller
CHAPTER 11 Configuring CSS Remote Access Methods This chapter describes how to configure the Secure Shell Daemon (SSH), Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS), and the Terminal Access Controller
Ethernet. Ethernet. Network Devices
 Ethernet Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design Ethernet Ethernet is a term used to refer to a diverse set of frame based networking
Ethernet Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design Ethernet Ethernet is a term used to refer to a diverse set of frame based networking
Configuring Flexible NetFlow
 CHAPTER 62 Note Flexible NetFlow is only supported on Supervisor Engine 7-E, Supervisor Engine 7L-E, and Catalyst 4500X. Flow is defined as a unique set of key fields attributes, which might include fields
CHAPTER 62 Note Flexible NetFlow is only supported on Supervisor Engine 7-E, Supervisor Engine 7L-E, and Catalyst 4500X. Flow is defined as a unique set of key fields attributes, which might include fields
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA
 642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
IOS Server Load Balancing
 IOS Server Load Balancing This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Server Load Balancing (SLB) feature. It includes the following sections: Feature Overview, page 1 Supported Platforms, page 5 Supported
IOS Server Load Balancing This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Server Load Balancing (SLB) feature. It includes the following sections: Feature Overview, page 1 Supported Platforms, page 5 Supported
BIT COMMANDER. Serial RS232 / RS485 to Ethernet Converter
 BIT COMMANDER Serial RS232 / RS485 to Ethernet Converter (Part US2000A) Copyrights U.S. Converters 1 Contents Overview and Features... 3 Functions..5 TCP Server Mode... 5 Httpd Client Mode.5 TCP Auto mode....6
BIT COMMANDER Serial RS232 / RS485 to Ethernet Converter (Part US2000A) Copyrights U.S. Converters 1 Contents Overview and Features... 3 Functions..5 TCP Server Mode... 5 Httpd Client Mode.5 TCP Auto mode....6
Zarząd (7 osób) F inanse (13 osób) M arketing (7 osób) S przedaż (16 osób) K adry (15 osób)
 QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1)
 INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Configuring the Transparent or Routed Firewall
 5 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. This chapter also includes information about customizing
5 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. This chapter also includes information about customizing
Troubleshooting the Firewall Services Module
 CHAPTER 25 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
CHAPTER 25 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet
 Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
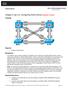 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT)
 ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
You can probably work with decimal. binary numbers needed by the. Working with binary numbers is time- consuming & error-prone.
 IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
Guide to Network Defense and Countermeasures Third Edition. Chapter 2 TCP/IP
 Guide to Network Defense and Countermeasures Third Edition Chapter 2 TCP/IP Objectives Explain the fundamentals of TCP/IP networking Describe IPv4 packet structure and explain packet fragmentation Describe
Guide to Network Defense and Countermeasures Third Edition Chapter 2 TCP/IP Objectives Explain the fundamentals of TCP/IP networking Describe IPv4 packet structure and explain packet fragmentation Describe
IPv6 Fundamentals: A Straightforward Approach
 IPv6 Fundamentals: A Straightforward Approach to Understanding IPv6 Rick Graziani Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 IPv6 Fundamentals Contents Introduction xvi Part I: Background
IPv6 Fundamentals: A Straightforward Approach to Understanding IPv6 Rick Graziani Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 IPv6 Fundamentals Contents Introduction xvi Part I: Background
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications
 Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service
 27 CHAPTER Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service This chapter describes how to configure the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and Location Service
27 CHAPTER Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service This chapter describes how to configure the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and Location Service
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN
 Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer
 Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Networking Test 4 Study Guide
 Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
Configuring Health Monitoring
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure the health monitoring on the CSM and contains these sections: Configuring Probes for Health Monitoring, page 6-1 Configuring Route Health Injection, page
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure the health monitoring on the CSM and contains these sections: Configuring Probes for Health Monitoring, page 6-1 Configuring Route Health Injection, page
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme
 Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Finding Feature Information Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: August 15, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Finding Feature Information Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: August 15, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
1000 CCNA Certification Exam Preparation Questions and Answers:
 1000 CCNA Certification Exam Preparation Questions and Answers: One Thousand Practice Questions for Passing the CCNA Exams - Pass On Your First Try 1 Copyright 2009 Notice of rights All rights reserved.
1000 CCNA Certification Exam Preparation Questions and Answers: One Thousand Practice Questions for Passing the CCNA Exams - Pass On Your First Try 1 Copyright 2009 Notice of rights All rights reserved.
