An estimated 4.1 million infants are screened annually in the
|
|
|
- Amy Wade
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Newborn Screening Newborn Screening: Current Status Much progress has been made, but the infrastructure needed for comprehensive newborn screening is not yet available. by Pamela H. Arn ABSTRACT: Newborn screening, which represents one of the major advances in child health of the past century, has been carried out in all fifty U.S. states since the 1970s. Newborn screening programs are state-run, and decisions are left to the individual states regarding the conditions to be screened for, the mechanism for confirmatory testing, followup care, and financing of the programs. Laboratory advances in tandem mass spectrometry make it possible to screen newborns for many rare inborn errors of metabolism. This raises many policy issues including screening s cost-effectiveness, ethics, quality, and oversight. [Health Affairs 26, no. 2 (2007): ; /hlthaff ] An estimated 4.1 million infants are screened annually in the United States for genetic metabolic disorders. U.S. newborn screening programs began in the early 1960s with phenylketonuria (PKU), a disorder of protein metabolism that causes mental retardation when untreated. Babies with PKU appear normal at birth, but the severe developmental disabilities associated with the condition can be avoided with early dietary treatment. Screening for PKU was followed by screening for congenital hypothyroidism in the early 1970s, based on the success of PKU screening and treatment and on the ability to prevent severe disability in another group of children. Evolving screening capabilities. Each state is now responsible for its own newborn screening program. State legislatures play a key role in the newborn screening system, since they are (at a minimum) responsible for appropriating funds or authorizing fees to make the screening program possible. In all cases, the primary responsibility for newborn screening resides in the public health system, which faces many challenges as newborn screening capabilities evolve. 1 Until the past few years, there was little controversy regarding state-run newborn screening programs. All fifty states screened for PKU and hypothyroidism; some states included galactosemia (a disorder of lactose metabolism that can cause liver failure and death if untreated) and hemoglobinopathies (such as sickle cell anemia), and a few screened for other rare disorders. Historically, for each dis- Pamela Arn (parn@nemours.org) is chief of genetics and director of education at the Nemours Children s Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida. HEALTH AFFAIRS ~ Volume 26, Number DOI /hlthaff Project HOPE The People-to-People Health Foundation, Inc.
2 DataWatch order screened, a separate test was required, each with its associated costs and the need for a portion of the blood specimen, thus limiting the number of tests that could be done. 2 In the early 1980s, with the advent of the technique of tandem mass spectroscopy (MS/MS), it became possible to screen for a sizable number of conditions on a single blood specimen in a timely fashion. In 1990, David Millington proposed using MS/MS analysis of dried blood spots for newborn screening. 3 With this technique, a profile of as many as fifteen different markers and ratios of metabolites (known as an acylcarnitine profile) can be determined using a very small amount of blood. This allows a single procedure to screen for thirty or more inherited disorders. 4 By the mid-1990s it was possible to screen for amino acid, organic acid, and fatty acid disorders in the same procedure. The increase in the number of inheritedmetabolicdisordersdetectableinthenewbornperiodextendedthepossibilities of early, generally presymptomatic, diagnosis and treatment. This minimized morbidity and mortality for many affected children but also raised questions of cost-effectiveness, treatment efficacy, ethics, and lack of data regarding the natural history of some of the disorders. 5 As a result of funding problems and lack of data regarding outcomes, not every state incorporated the new technologies into their screening programs. Growing disparities in screening programs. Private laboratories began offering newborn screening tests either by contracting with individual hospitals or states, or both, or by offering tests directly to the community as public awareness of these conditions grew. All of these factors contributed to growing disparities in screening programs across states. Pressure to adopt expanded screening has come from physicians, patient advocacy groups, and legal actions brought by the parents of children with genetic disorders that were not detected by screening. By as early as 2003, almost half of the states had implemented MS/MS screening, but the number and types of conditions for which they were screening still varied. Modern Developments In Newborn Screening The criteria of James M.G. Wilson and Gunnar Jungner were proposed in the 1960s to assess the validity of screening for a given condition. These criteria were as follows: (1) The condition being screened for should be an important health problem; (2) the natural history of the condition should be well understood; (3) there should be a detectable early stage; (4) treatment at an early stage should be of more benefit than at a later stage; (5) a suitable test should be devised for the early stage; (6) the test should be acceptable; (7) intervals for repeating the test should be determined; (8) adequate health service provision should be made for the extra clinical workload resulting from screening; and (9) the risks, both physical and psychological, should be less than the benefits. 6 The criteria were proposed before multiplex screening emerged; they consider each disease individually. Also, some aspects of the criteria (such as the importance of the health 560 March/April 2007
3 Newborn Screening problem) are subjective. No standard criteria are consistently used in all programs. The lack of uniformity in newborn screening programs and the complexity of assessment led the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Newborn Screening Task Force to recommend that the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) should engage in a national process involving government, professionals, and consumers to assist in the development and implementation of nationally recognized newborn screening system standards and policies. 7 HRSA s Maternal and Child Health Bureau (MCHB) also commissioned the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) to outline a process to standardize outcomes and guidelines for state newborn screening programs and to define responsibilities for collecting and evaluating outcome data, including a recommended uniform panel of conditions to include in state newborn screening programs. TheACMGformedagroup(theNewbornScreeningExpertGroup)thatincluded subspecialists; primary care physicians; consumers; and experts in law, ethics, and public health to make recommendations regarding newborn screening. The methods used and details of the deliberations were published in a special report; the diseases that the ACMG recommended for screening are listed in Exhibit 1. 8 These twenty-nine conditions were recommended because the group concluded that a screening test and a treatment were available for each, and adequate information about the natural history was known. Many of the diseases chosen are rare individually, but when considered together, they make up a major cause of pediatric morbidity and mortality. Some of the diseases are unfamiliar even to pediatricians, thus complicating diagnosis without screening. The expert group also identified twenty-five additional conditions that may be considered for screening. Metabolites of these conditions may be detected on newborn screening, and the diseases associated with these metabolites may be reported in some programs. Current screening panels for all states can be found at the national newborn screening and genetics resource center. 9 Value Of Screening Programs Genetic diseases involving metabolism, also known as inborn errors of metabolism, generally fall into two broad categories: diseases of intoxication and diseases of fatty acid oxidation. In disorders of intoxication, there is a progressive accumulation of metabolites that are toxic to a newborn because a key enzyme in a metabolic pathway is lacking. Diseases 1 15 and 27 (Exhibit 1) fall into this category. Treatment is available for these disorders, and early intervention prior to the developmentofsymptomsgenerallyresultsinanimprovedoutcome. 10 Disorders of fatty acid oxidation (diseases 16 20, Exhibit 1) include mediumchain acyl-coa dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency. This disorder was an important driver of expanded screening. The most frequent clinical presentation is that of a previously normal toddler with hypoglycemia, coma, and seizures after a short illness. MCAD is one of the most common inborn errors, with incidence estimates HEALTH AFFAIRS ~ Volume 26, Number 2 561
4 DataWatch EXHIBIT 1 Twenty-Nine Disorders For Which To Screen Newborns 1. Phenylketonuria 2. Maple syrup urine disease 3. Homocystinuria 4. Citrullinemia 5. Argininosuccinic acidemia 6. Tyrosinemia type I 7. Isovaleric acidemia 8. Glutaric acidemia type I 9. Hydroxymethylglutaric aciduria or HMG-CoA lyase deficiency 10. Multiple carboxylase deficiency 11. Methylmalonic acidemia due to mutase deficiency 12. Methylmalonic acidemia cbia and cbib forms Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency 14. Propionic acidemia 15. Beta-ketothiolase deficiency 16. Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency 17. Very long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency 18. Long-chain 3-OH acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency 19. Trifunctional protein deficiency 20. Carnitine uptake defect 21. Sickle cell anemia 22. HB S/Beta-Thalassemia 23. HB S/C disease 24. Congenital hypothyroidism 25. Biotinidase deficiency 26. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia 27. Classical galactosemia 28. Hearing loss 29. Cystic fibrosis SOURCE: K. Johnson et al., Financing State Newborn Screening Programs: Sources and Uses of Funds, Pediatrics 117, no. 5, Part 2 (2006): S270 S279. of 1 per 10,000 births in some populations. Approximately 20 percent of undiagnosed children will die during the initial episode, and 20 percent more will suffer irreversible neurological damage related to coma and hypoglycemia. 11 In a report from Australia, 21 percent of unscreened children with MCAD died, while only one child who had been screened died. Once parents are informed of a child s diagnosis, the risk of coma, seizures, and death can be essentially eliminated if the child is not allowed to fast. 12 Current Program Issues Scientific issues. Because of the success of treating MCAD and other diseases, it has been hoped that early intervention in other inborn errors will also result in improved outcomes. The aim of newborn screening is, after all, to improve outcomes by early detection of disease. Data are lacking, however, in the areas of the cost-effectiveness of screening, treatment efficacy, and natural history for some conditions. It has been pointed out that evidence in inborn errors of metabolism in general is either not available or difficult to locate. 13 This does not mean that there can be no evidence-based policy in newborn screening, however. Although randomized controlled trials (RCTs) might not be feasible in the case of rare conditions, observation and expert opinion contribute to evidence and are valuable for informing screening decisions. Policymakers often must make decisions when evidence is in dispute or not available. In these cases, they must be explicit about the elements of thedecision-makingprocessandtheevidencebaseforpolicy. 14 Efforts are under way to gather information after screening is implemented through the National Coordinating Center for the Genetics and Newborn Screen- 562 March/April 2007
5 Newborn Screening ing Regional Collaborative Groups. This is the result of a partnership among the Genetic Services Branch, HRSA, the MCHB, and the ACMG. Participation by states and regions is voluntary. 15 Funding issues. Only a few studies have attempted to do a comprehensive cost-utility analysis of newborn screening. MCAD has been the most commonly analyzed disorder. It has been the most commonly cited for cost-effectiveness, since the treatment for MCAD is quite effective and has been shown to prevent severe neurologic sequelae. Almost all of the additional costs of screening for MCAD are offset by avoided sequelae in some models. A study that looked at a cost-utility analysis of MS/MS screening in a more comprehensive disease panel of diseases concluded, Newborn screening seems to be one of the rare health care interventions that is beneficial to patients, and, with some assumptions, cost saving. 16 Long-term evidence is lacking in many areas, however. False positive results consume resources that might be difficult to quantify. Each state newborn screening program is unique in its administrative and financing structure. The majority of states collect fees as the primary source of program funding. These fees may be collected from hospitals, patients, or third-party payers. To a lesser extent, Medicaid, Title V Maternal and Child Health Services Block Grants, and state general revenue funding are used. Most newborn screening funds, however, do not come from federal or state general revenues (Exhibit 2). Nationwide data on funding sources and uses for services related to newborn screening are not collected routinely. A 2003 report by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) noted that in state fiscal year 2001, more than $120 million was spent on screening programs. This averaged approximately $30 per infant screened, and most of the fees collected are used to support laboratory analysis. Fewer than half of the states provide financing for genetic or nutritional counseling and long-term follow-up. 17 Health system needs. Care of children with metabolic diseases is complex, involving primary care physicians, metabolic specialists, genetic counselors, and EXHIBIT 2 Sources Of Funding For Newborn Screening, 2003 Other funds 5% Other state funding 20% Fees 60% Medicaid 10% Title V MCH Services Block Grant 5% SOURCE: K. Johnson et al., Financing State Newborn Screening Programs: Sources and Uses of Funds, Pediatrics 117, no. 5, Part 2 (2006): S271 (reprinted with permission). NOTE: MCH is Maternal and Child Health. HEALTH AFFAIRS ~ Volume 26, Number 2 563
6 DataWatch metabolic nutritionists. Even when the initial screening is successfully funded and completed, confirmation of diagnosis and long-term management are challenging. Actual laboratories are often not part of the state system, thus requiring insurance approvals to access necessary testing in a timely fashion. Few states have an integrated system of care that allows screening, confirmation, and follow-up to occur seamlessly. Newborn screening involves education of physicians and parents, definitive diagnosis, long-term management, and quality evaluation. If all of these components of a program are not in place, cost-savings benefits might not be fully realized, and optimal patient outcomes might not be achieved. Quality and training needs. Considerable need exists for education and training throughout the health care system, since very few physicians have been trained to manage children with inborn errors of metabolism. There are also very few people trained to oversee biochemical genetics testing laboratories. Since the 1980s there has been a progressive decline in the number of biochemical specialty laboratories, and clinical biochemical specialists are in short supply. The biochemical specialty laboratories that traditionally provided diagnostic services for these rare diseases had limited capacity and limited services, which made it difficult for them to compete financially. Few labs in the country, therefore, are equipped to quickly and accurately provide definitive diagnostics for a positive newborn screen. Also, enrollment of young physicians and people with doctorates in biochemical genetics programs declined in the 1990s because of funding problems and greater interest in molecular genetics. 18 Lack of quality assurance systems. Managing diagnostic and confirmatory testing has pitfalls, since the abnormal analyte increases found in MS/MS screening are not always diagnostic of a single disorder; therefore, additional molecular and biochemical testing often must be performed. Comprehensive quality assurance systems are not yet in place to define targets and perform interlaboratory comparisons, although some programs do address technical aspects of the testing. Most of these quality assurance programs are voluntary. To address this issue, Pierro Rinaldo and colleagues proposed laboratory standards that include targets reflecting analytical and postanalytical performance markers, such as detection rate, positive predictive value, and false positive rate. The proposed false positive rate is <0.3 percent, with a positive predictive value of >20 percent. 19 False positive results and their effect on families have been a concern raised by physicians and policymakers. Beth Tarini and colleagues published estimates of the theoretical number of false positive results in expanded screening programs. 20 Although these estimates call attention to the potential negative impact on the public and on the newborn screening system, actual data need to be collected and reported. At least one study has directly shown that false positive screening results increase parental stress and may increase risk for abnormal parent-child interactions. 21 Theincreaseduseofasecondtieroftestingwithinthenewborn screening laboratory might help lower the false positive rate but also must not de- 564 March/April 2007
7 Newborn Screening lay diagnosis in an affected child. This has become possible because of progress in humangenetics,sincenowthemostcommongenemutationsareknownformany diseases (cystic fibrosis and MCAD, for example). Mutation analysis can be performed using the blood from the newborn screening card, thus increasing specificity. However, families and physicians might still be left to cope with results that have uncertain clinical significance. Future Directions Although progress has been made in the adoption of expanded screening over the past few years, more needs to be done to achieve a consistent, equitable, and high-quality national newborn screening program. Up to 23 percent of U.S. newborns are still not screened for MCAD, a disease that is diagnosed by a test that most models generally agree is clinically sound and cost-effective. At the same time, infants are being screened for conditions that are rarer and less treatable than MCAD. As advances in biochemical and molecular genetics occur, it becomes technically possible to add more diseases to the list that can be considered for testing. Already, there is discussion about adding even more diseases in some states. 22 Policymakers will continue to struggle with these issues and that there is need for continuing national discussion. To assist in improving screening and outcome measures, it has been suggested that the new technology should be introduced within a research paradigm, to facilitate data collection. 23 This is difficult, however, given the existence of fifty independent state programs. Regionalization of screening and the laboratories that are able to diagnose, confirm, and monitor metabolite levels would facilitate quality assurance and improve the consistency of data collection. The needed infrastructure is not available, and education of the public and the medical community is lacking. Implementation of newborn screening in a way that will eventually lead to a true evidence-based approach will require collaboration, education, adequate funding for research, and an infrastructure that provides a larger role for a central body (likely the federal government). Until data are collected and available, an evidence-based approach is not possible. Policymakers must try to balance the costs and the benefits, taking into account the weight that the medical community and the public place on screening. NOTES 1. D. Marsden, C. Larson, and H.L. Levy, Newborn Screening for Metabolic Disorders, Journal of Pediatrics 148, no. 5 (2006): L. Sweetman, Newborn Screening by Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Gaining Experience, Clinical Chemistry 47, no. 11 (2001): D.S. Millington et al., Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A New Method for Acylcarnitine Profiling with Potential for Neonatal Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism, Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 13, no. 3 (1990): D.S. Millington et al., The Analysis of Diagnostic Markers of Genetic Disorders to Human Blood and Urine Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Liquid Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry, International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes 111 (1991): ; and E.W. Naylor and D.H. Chace, Automated HEALTH AFFAIRS ~ Volume 26, Number 2 565
8 DataWatch Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Mass Newborn Screening for Disorders in Fatty Acid, Organic Acid, and Amino Acid Metabolism, Journal of Child Neurology 14, no. 1 Supp. (1999): S4 S8. 5. B. Wilcken et al., Screening Newborns for Inborn Errors of Metabolism by Tandem Mass Spectrometry, New England Journal of Medicine 348, no. 23 (2003): J.M. Wilson and G. Jungner, Principles and Practice of Screening for Disease, Public Health Paper no. 34 (Geneva: World Health Organization, 1968). 7. Serving the Family from Birth to the Medical Home: A Report from the Newborn Screening Task Force Convened in Washington, D.C., May 1999, Pediatrics 106, no. 2, Part 2 (2000): M.S. Watson et al., Newborn Screening: Toward a Uniform Screening Panel and System, Genetics in Medicine 8, Supp. 1 (2006): 1S 53S. 9. National Newborn Screening and Genetics Resource Center, National Newborn Screening Status Report, 2 November 2006, (accessed 2 January 2007). 10. J.M. Saudubray et al., Clinical Approach to Inherited Metabolic Disorders in Neonates: An Overview, Seminars in Neonatalogy 7,no.1(2002): T.G. Derks et al., The Natural History of Medium-Chain Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency in the Netherlands: Clinical Presentation and Outcome, Journal of Pediatrics 148, no. 5 (2006): C.J. Wilson et al., Outcome of Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency after Diagnosis, Archives of Disease in Childhood 80, no. 5 (1999): ; and R.R. Howell, We Need Expanded Newborn Screening, Pediatrics 117, no. 5 (2006): R.D. Steiner, Evidence Based Medicine in Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Is There Any and How to Find It, American Journal of Medical Genetics, Part A 134, no. 2 (2005): D. Atkins, J. Siegel, and J. Slutsky, Making Policy When the Evidence Is in Dispute, Health Affairs 24, no. 1 (2005): For more information, go to the National Coordinating Center s home page, A. Pandor et al., Clinical Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Neonatal Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism using Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Systematic Review (Executive Summary), Health Technology Assessment 8, no. 12 (2004): 1 121; L.N. Venditti et al., Newborn Screening by Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis, Pediatrics 112, no. 5 (2003): ; and A.E. Carroll and S.M. Downs, Comprehensive Cost-Utility Analysis of Newborn Screening Strategies, Pediatrics 117, no. 5, Part 2 (2006): S287 S K. Johnson et al., Financing State Newborn Screening Programs: Sources and Uses of Funds, Pediatrics 117, no. 5, Part 2 (2006): S270 S P. Rinaldo, S. Hahn, and D. Matern, Clinical Biochemical Genetics in the Twenty-first Century, Acta Paediatrica 93, no. 445 Supp. (2004): P. Rinaldo et al., Making the Case for Objective Performance Metrics in Newborn Screening by Tandem Mass Spectrometry, Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities (forthcoming). 20. B.A. Tarini, D.A. Christakis, and H.G. Welch, State Newborn Screening in the Tandem Mass SpectrometryEra:MoreTests,MoreFalse-PositiveResults, Pediatrics 118, no. 2 (2006): S.E. Waisbren et al., Effect of Expanded Newborn Screening for Biochemical Genetic Disorders on Child Outcomes and Parental Stress, Journal of the American Medical Association 290, no. 19 (2003): M.H. Gelb et al., Direct Multiplex Assay of Enzymes in Dried Blood Spots by Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Newborn Screening of Lysosomal Storage Disorders, Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 29,nos.2 3 (2006): J.R. Botkin et al., Newborn Screening Technology: Proceed with Caution, Pediatrics 117, no. 5 (2006): March/April 2007
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers 2 Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Since the mid-1960s, health care providers have offered newborn screening
Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers 2 Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Since the mid-1960s, health care providers have offered newborn screening
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Alabama Newborn Screening Program
 Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Your newborn baby s blood test
 Newborn Screening Free health checks for your baby Your newborn baby s blood test The Newborn Metabolic Screening Programme All babies are checked at birth to see that all is well. Some of your baby s
Newborn Screening Free health checks for your baby Your newborn baby s blood test The Newborn Metabolic Screening Programme All babies are checked at birth to see that all is well. Some of your baby s
Newborn Screening Test
 Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project
 Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project Susan Tanksley, PhD MSGRCC Annual Meeting July 14, 2011 The Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measure Project (TNSPMP) is funded through a cooperative
Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project Susan Tanksley, PhD MSGRCC Annual Meeting July 14, 2011 The Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measure Project (TNSPMP) is funded through a cooperative
Newborn Screening Issues
 Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM
 Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Newborn screening policy and guidelines
 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233
 State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233 Welcome and Introductions Review of Agenda Approval of December 2011 Minutes Commissioner
State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233 Welcome and Introductions Review of Agenda Approval of December 2011 Minutes Commissioner
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners
 Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
NEWBORN GENETIC SCREENING: EVOLVING TECHNOLOGIES AND PUBLIC HEALTH POLICY
 NEWBORN GENETIC SCREENING: EVOLVING TECHNOLOGIES AND PUBLIC HEALTH POLICY Patricia C. Kuszler, MD, JD * University of Washington School of Law William H. Gates Hall, Box 353020 Seattle, Washington U.S.A
NEWBORN GENETIC SCREENING: EVOLVING TECHNOLOGIES AND PUBLIC HEALTH POLICY Patricia C. Kuszler, MD, JD * University of Washington School of Law William H. Gates Hall, Box 353020 Seattle, Washington U.S.A
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners. Newborn screening
 Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Newborn Screening In America:
 Newborn Screening In America: Problems and Policies Vani Kilakkathi 2012 Council for Responsible Genetics 5 Upland Road, Suite 3 Cambridge, MA 02140 Email: crg@gene-watch.org www.councilforresponsiblegenetics.org
Newborn Screening In America: Problems and Policies Vani Kilakkathi 2012 Council for Responsible Genetics 5 Upland Road, Suite 3 Cambridge, MA 02140 Email: crg@gene-watch.org www.councilforresponsiblegenetics.org
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS
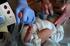 COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484
 Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484 An act to amend Sections 124977 and 125055 of, to add Sections 1604.6 and 125002 to, and to add Article 4 (commencing with Section 123370) to Chapter 1 of Part 2 of Division
Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484 An act to amend Sections 124977 and 125055 of, to add Sections 1604.6 and 125002 to, and to add Article 4 (commencing with Section 123370) to Chapter 1 of Part 2 of Division
Newborn Screening and Health Information Technology
 Newborn Screening and Health Information Technology Alan E Zuckerman MD FAAP Georgetown University Medical Center SACHDNC HIT Workgroup Co-Chair AAP Council on Clinical Information Technology (COCIT) Executive
Newborn Screening and Health Information Technology Alan E Zuckerman MD FAAP Georgetown University Medical Center SACHDNC HIT Workgroup Co-Chair AAP Council on Clinical Information Technology (COCIT) Executive
State Policy and Finance Framework for Newborn Screening Programs:
 State Policy and Finance Framework for Newborn Screening Programs: Case Studies of Select States Presentation by: Kay Johnson, MPH, EdM President, Johnson Group Consulting Research Assistant Professor,
State Policy and Finance Framework for Newborn Screening Programs: Case Studies of Select States Presentation by: Kay Johnson, MPH, EdM President, Johnson Group Consulting Research Assistant Professor,
PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP
 PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP PUBLIC HEALTH ACTIVITIES & SERVICES INVENTORY TECHNICAL NOTES HEALTHY FAMILY DEVELOPMENT Nurse-Family Partnership Nurse-Family Partnership is a voluntary program of
PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP PUBLIC HEALTH ACTIVITIES & SERVICES INVENTORY TECHNICAL NOTES HEALTHY FAMILY DEVELOPMENT Nurse-Family Partnership Nurse-Family Partnership is a voluntary program of
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy
 MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
STATE STATUTES AND REGULATIONS ON DIETARY TREATMENT OF DISORDERS IDENTIFIED THROUGH NEWBORN SCREENING JURISDICTION AND CITATION
 Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
Colorado s Integrated Data System: one state s approach to a comprehensive health information exchange for short-term and long-term follow-up
 Colorado s Integrated Data System: one state s approach to a comprehensive health information exchange for short-term and long-term follow-up Erica L. Wright, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor, Instructor
Colorado s Integrated Data System: one state s approach to a comprehensive health information exchange for short-term and long-term follow-up Erica L. Wright, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor, Instructor
June 20, 2012. Testimony of. Vera F. Tait MD, FAAP. On behalf of the. American Academy of Pediatrics. Before the
 Testimony of Vera F. Tait MD, FAAP On behalf of the Before the Subcommittee on Personnel, Senate Armed Services Committee Department of Federal Affairs 601 13th Street NW, Suite 400 North Washington, DC
Testimony of Vera F. Tait MD, FAAP On behalf of the Before the Subcommittee on Personnel, Senate Armed Services Committee Department of Federal Affairs 601 13th Street NW, Suite 400 North Washington, DC
STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE
 STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE LIST OF REVISIONS REVISION NO. DATE REVISED BY: PAGE/S DESCRIPTION 1 TBD GDSP 13 Initial Version II STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER
STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE LIST OF REVISIONS REVISION NO. DATE REVISED BY: PAGE/S DESCRIPTION 1 TBD GDSP 13 Initial Version II STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER
One Hundred Tenth Congress of the United States of America
 S. 1858 One Hundred Tenth Congress of the United States of America AT THE SECOND SESSION Begun and held at the City of Washington on Thursday, the third day of January, two thousand and eight An Act To
S. 1858 One Hundred Tenth Congress of the United States of America AT THE SECOND SESSION Begun and held at the City of Washington on Thursday, the third day of January, two thousand and eight An Act To
National Survey of Pre- and Post- Analytical Performance Measures Used in Newborn Screening Programs
 National Survey of Pre- and Post- Analytical Performance Measures Used in Newborn Screening Programs Simran Tiwana, MBA* Susan Tanksley, PhD* Brad Therrell, PhD Donna Williams, BS* Mirsa Douglass, MBA*
National Survey of Pre- and Post- Analytical Performance Measures Used in Newborn Screening Programs Simran Tiwana, MBA* Susan Tanksley, PhD* Brad Therrell, PhD Donna Williams, BS* Mirsa Douglass, MBA*
Exhibit A Scope of Work. Vendor agrees to provide to the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) the services described herein.
 1. Service Overview Vendor agrees to provide to the (CDPH) the services described herein. The Vendor shall provide diagnosis, treatment, and outcome data for metabolic patients identified through the Newborn
1. Service Overview Vendor agrees to provide to the (CDPH) the services described herein. The Vendor shall provide diagnosis, treatment, and outcome data for metabolic patients identified through the Newborn
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Newborn screening: the genomic challenge
 Newborn screening: the genomic challenge The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
Newborn screening: the genomic challenge The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
WRITTEN STATEMENT ON BEHALF OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS PRESENTED TO THE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE COMMITTEE ON DISABILITY IN AMERICA
 WRITTEN STATEMENT ON BEHALF OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS PRESENTED TO THE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE COMMITTEE ON DISABILITY IN AMERICA JANUARY 9, 2006 PAUL LIPKIN, MD, FAAP CHAIR, AAP COUNCIL ON CHILDREN
WRITTEN STATEMENT ON BEHALF OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS PRESENTED TO THE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE COMMITTEE ON DISABILITY IN AMERICA JANUARY 9, 2006 PAUL LIPKIN, MD, FAAP CHAIR, AAP COUNCIL ON CHILDREN
and Krabbe Disease: A Systematic Program Evaluation Roberta Salveson
 Expansion of the New York State Newborn Screening Panel and Krabbe Disease: A Systematic Program Evaluation Roberta Salveson Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Expansion of the New York State Newborn Screening Panel and Krabbe Disease: A Systematic Program Evaluation Roberta Salveson Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia
 Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory
 NEWBORN SCREENING August 2001 Be Kind To Tiny Feet A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory HEMOGLOBINOPATHIES Second Edition Follow-up procedures for hemoglobinopathy
NEWBORN SCREENING August 2001 Be Kind To Tiny Feet A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory HEMOGLOBINOPATHIES Second Edition Follow-up procedures for hemoglobinopathy
Newborn Screening Steering Committee. Newborn Screening Expert Group
 NEWBORN SCREENING: TOWARD A UNIFORM SCREENING PANEL AND SYSTEM 1 Jose Cordero, MD, MPH Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Resources and Services Administration Newborn Screening Steering
NEWBORN SCREENING: TOWARD A UNIFORM SCREENING PANEL AND SYSTEM 1 Jose Cordero, MD, MPH Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Resources and Services Administration Newborn Screening Steering
Newborn Screening Program Study On Comprehensive and Sustainable Long-Term Storage and Use
 Public Health Laboratory, Newborn Screening Program 601 Robert Street North St. Paul, MN 55155-2531 651-201-5466 www.health.state.mn.us/newbornscreening Newborn Screening Program Study On Comprehensive
Public Health Laboratory, Newborn Screening Program 601 Robert Street North St. Paul, MN 55155-2531 651-201-5466 www.health.state.mn.us/newbornscreening Newborn Screening Program Study On Comprehensive
GENETIC COUNSELING IS IT A CAREER FOR YOU? Judith L Miller, MS, LGC April 8, 2014
 GENETIC COUNSELING IS IT A CAREER FOR YOU? Judith L Miller, MS, LGC April 8, 2014 What is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives. Most
GENETIC COUNSELING IS IT A CAREER FOR YOU? Judith L Miller, MS, LGC April 8, 2014 What is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives. Most
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Part I Failure to Thrive
 Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
How to Code Well-Care Visits for Children and Adolescents
 How to Code Well-Care Visits for Children and Adolescents to meet NCQA s HEDIS Quality Goals and Receive Appropriate Reimbursement and Credit for Providing Quality Care TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...
How to Code Well-Care Visits for Children and Adolescents to meet NCQA s HEDIS Quality Goals and Receive Appropriate Reimbursement and Credit for Providing Quality Care TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...
Colorado Legislative Council Staff
 Colorado Legislative Council Staff Room 029 State Capitol, Denver, CO 80203-1784 (303) 866-3521 FAX: 866-3855 TDD: 866-3472 MEMORANDUM July 1, 2011 TO: Interested Persons FROM: Kelly Stapleton, Senior
Colorado Legislative Council Staff Room 029 State Capitol, Denver, CO 80203-1784 (303) 866-3521 FAX: 866-3855 TDD: 866-3472 MEMORANDUM July 1, 2011 TO: Interested Persons FROM: Kelly Stapleton, Senior
On behalf of the Association of Maternal and Child Health Programs (AMCHP), I am
 Christopher Kus, M.D., M.P.H. Association of Maternal and Child Health Programs, Public Witness Testimony House Labor, Health and Human Services and Education Appropriations Subcommittee March 13, 2013
Christopher Kus, M.D., M.P.H. Association of Maternal and Child Health Programs, Public Witness Testimony House Labor, Health and Human Services and Education Appropriations Subcommittee March 13, 2013
Children s Medical Services Program Overview
 Children s Medical Services Program Overview 1 Children s Medical Services Family-centered, comprehensive, coordinated statewide managed system of care that links community-based health care with multidisciplinary,
Children s Medical Services Program Overview 1 Children s Medical Services Family-centered, comprehensive, coordinated statewide managed system of care that links community-based health care with multidisciplinary,
New Estimates of the Economic Benefits of Newborn Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism in the US
 The findings and conclusions in this presentation have not been formally disseminated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and should not be construed to represent any agency determination
The findings and conclusions in this presentation have not been formally disseminated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and should not be construed to represent any agency determination
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD
 FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
Birth defects. Report by the Secretariat
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
Newborn Screening Public Health Service, Research and Public Trust
 Newborn Screening Public Health Service, Research and Public Trust Anne Marie Comeau, Ph.D Deputy Director, New England Newborn Screening Program Professor of Pediatrics, UMMS A National Conversation on
Newborn Screening Public Health Service, Research and Public Trust Anne Marie Comeau, Ph.D Deputy Director, New England Newborn Screening Program Professor of Pediatrics, UMMS A National Conversation on
- 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D.
 - 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D. We used the following sources to construct indicators for sickle cell disease screening for newborns
- 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D. We used the following sources to construct indicators for sickle cell disease screening for newborns
Differential Diagnosis of NAFLD- A Short Summary:
 Differential Diagnosis of NAFLD- A Short Summary: Almost a fifth of our general pediatric population is now classified as overweight in the United States. When such children present with elevated liver
Differential Diagnosis of NAFLD- A Short Summary: Almost a fifth of our general pediatric population is now classified as overweight in the United States. When such children present with elevated liver
Child Abuse and Neglect AAP Policy Recommendations
 Child Abuse and Neglect AAP Policy Recommendations When Inflicted Skin Injuries Constitute Child Abuse Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect PEDIATRICS Vol. 110 No. 3 September 2002, pp. 644-645 Recommendations
Child Abuse and Neglect AAP Policy Recommendations When Inflicted Skin Injuries Constitute Child Abuse Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect PEDIATRICS Vol. 110 No. 3 September 2002, pp. 644-645 Recommendations
Administrative Code. Title 23: Medicaid Part 223
 Title 23: Medicaid Administrative Code Title 23: Medicaid Part 223 Table of Contents Table of Contents Title 23: Medicaid... 1 Table of Contents... 1 Title 23: Division of Medicaid... 1 Part 223: Early
Title 23: Medicaid Administrative Code Title 23: Medicaid Part 223 Table of Contents Table of Contents Title 23: Medicaid... 1 Table of Contents... 1 Title 23: Division of Medicaid... 1 Part 223: Early
Four Years of Expanded Newborn Screening in. Portugal with MS/MS. National Institute of Health Portugal www.insa.pt 1
 Four Years of Expanded Newborn Screening in Portugal with MS/MS National Institute of Health Portugal www.insa.pt 1 Laura Vilarinho PhD, Hugo Rocha MSc, Carmen Sousa MSc, Ana Marcão PhD, Helena Fonseca
Four Years of Expanded Newborn Screening in Portugal with MS/MS National Institute of Health Portugal www.insa.pt 1 Laura Vilarinho PhD, Hugo Rocha MSc, Carmen Sousa MSc, Ana Marcão PhD, Helena Fonseca
Learning Objectives (Part 2)
 Learning Objectives Describe public health nutrition and differentiate it from clinical nutrition practice List organizations that employ public health/community nutrition personnel Locate and contact
Learning Objectives Describe public health nutrition and differentiate it from clinical nutrition practice List organizations that employ public health/community nutrition personnel Locate and contact
Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
 Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP Kozmac@georgetown.edu cck2@gunet.georgetown.edu Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP Kozmac@georgetown.edu cck2@gunet.georgetown.edu Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Epidemiology 521. Epidemiology of Maternal and Child Health Problems. Winter / Spring, 2010
 Extended MPH Degree Program School of Public Health Department of Epidemiology University of Washington Epidemiology 521 Epidemiology of Maternal and Child Health Problems Winter / Spring, 2010 Instructor:
Extended MPH Degree Program School of Public Health Department of Epidemiology University of Washington Epidemiology 521 Epidemiology of Maternal and Child Health Problems Winter / Spring, 2010 Instructor:
Practitioner s Manual
 Oregon Practitioner s Manual The Oregon Practitioner s Manual Oregon Health & Science University Cary Harding, MD Stephen L. LaFranchi, MD Gregory Thomas, MD Michael Wall, MD Oregon Health Authority Public
Oregon Practitioner s Manual The Oregon Practitioner s Manual Oregon Health & Science University Cary Harding, MD Stephen L. LaFranchi, MD Gregory Thomas, MD Michael Wall, MD Oregon Health Authority Public
Oregon s Strategic Plan for Genetics and Public Health
 Oregon s Strategic Plan for Genetics and Public Health November 2002 Supported by a grant from the Maternal and Child Health Bureau Grant # 4 H46 MC 00172-02-1 Introduction to Oregon s Strategic Plan for
Oregon s Strategic Plan for Genetics and Public Health November 2002 Supported by a grant from the Maternal and Child Health Bureau Grant # 4 H46 MC 00172-02-1 Introduction to Oregon s Strategic Plan for
Editorial Commentary ~ The Case for Universal Newborn Screening Charles P. Hehmeyer
 EP (Exceptional Parent) rarely endorses the positions expressed in a guest editorial but in this case, we not only concur with Mr. Hehmeyer's position on Universal Newborn Screening but we wholeheartedly
EP (Exceptional Parent) rarely endorses the positions expressed in a guest editorial but in this case, we not only concur with Mr. Hehmeyer's position on Universal Newborn Screening but we wholeheartedly
Newborn Blood Spot Standards for newborn blood spot screening
 Newborn Blood Spot Standards for newborn blood spot screening Version 1.0 / August 2013 About the NHS Newborn Blood Spot Screening Programme The NHS Newborn Blood Spot Screening Programme has responsibility
Newborn Blood Spot Standards for newborn blood spot screening Version 1.0 / August 2013 About the NHS Newborn Blood Spot Screening Programme The NHS Newborn Blood Spot Screening Programme has responsibility
Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrometry
 DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
Evaluation and Assessment and Eligibility Regulations 2011
 303.10 Developmental delay. As used in this part, developmental delay, when used with respect to an individual residing in a State, has the meaning given to that term under 303.300. 303.10 Developmental
303.10 Developmental delay. As used in this part, developmental delay, when used with respect to an individual residing in a State, has the meaning given to that term under 303.300. 303.10 Developmental
Insurance coverage of medical foods for treatment of inherited metabolic disorders
 May 18, 2012 Insurance coverage of medical foods for treatment of inherited metabolic disorders Secretary s Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns and Children (SACHDNC) Susan A. Berry,
May 18, 2012 Insurance coverage of medical foods for treatment of inherited metabolic disorders Secretary s Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns and Children (SACHDNC) Susan A. Berry,
On Time / Every Time. A Partnership of Safety and Reliability for Newborn Screening
 On Time / Every Time A Partnership of Safety and Reliability for Newborn Screening Welcome As a result of this program, the participant will be able to: Discuss the importance of obtaining a quality specimen
On Time / Every Time A Partnership of Safety and Reliability for Newborn Screening Welcome As a result of this program, the participant will be able to: Discuss the importance of obtaining a quality specimen
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program
 Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
Career Spotlight - Genetic Counselling
 Career Spotlight - Genetic Counselling Interview conducted by Career Services, University of Manitoba October 25, 2011 Genetic Counsellors featured/interviewed: Sherri Burnett, Genetics & Metabolism Program
Career Spotlight - Genetic Counselling Interview conducted by Career Services, University of Manitoba October 25, 2011 Genetic Counsellors featured/interviewed: Sherri Burnett, Genetics & Metabolism Program
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
The Search for Causes and Cures
 ISSUE REPORT BIRTH DEFECTS AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES: The Search for Causes and Cures JULY 2005 PREVENTING EPIDEMICS. PROTECTING PEOPLE. REPORT AUTHORS Kim Elliott, MA Deputy Director Trust for America
ISSUE REPORT BIRTH DEFECTS AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES: The Search for Causes and Cures JULY 2005 PREVENTING EPIDEMICS. PROTECTING PEOPLE. REPORT AUTHORS Kim Elliott, MA Deputy Director Trust for America
LOUISIANA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HOSPITALS MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH (MCH) BLOCK GRANT*
 LOUISIANA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HOSPITALS MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH (MCH) BLOCK GRANT* What is the MCH Block Grant? It is a grant from the U.S. government to State governments. The state must supply
LOUISIANA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HOSPITALS MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH (MCH) BLOCK GRANT* What is the MCH Block Grant? It is a grant from the U.S. government to State governments. The state must supply
Genetic testing. The difference diagnostics can make. The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association
 6 Genetic testing The difference diagnostics can make The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association Genetic INTRODUCTION testing The Department of Health published Our Inheritance, Our Future - Realising
6 Genetic testing The difference diagnostics can make The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association Genetic INTRODUCTION testing The Department of Health published Our Inheritance, Our Future - Realising
Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings
 Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings Ira M. Lubin, PhD, FACMG Division of Laboratory Systems NCPDCID, CCID Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia Disclaimers
Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings Ira M. Lubin, PhD, FACMG Division of Laboratory Systems NCPDCID, CCID Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia Disclaimers
UPLC/MSMS in the analysis of physiological steroids. May 2012. Anders Feldthus. Anders_Feldthus@Waters.com. 2012 Waters Corporation 1
 UPLC/MSMS in the analysis of physiological steroids Anders Feldthus Anders_Feldthus@Waters.com May 2012 2012 Waters Corporation 1 Clinical Chemistry Mass Spectrometry Citations (1955-2006) 70 Number of
UPLC/MSMS in the analysis of physiological steroids Anders Feldthus Anders_Feldthus@Waters.com May 2012 2012 Waters Corporation 1 Clinical Chemistry Mass Spectrometry Citations (1955-2006) 70 Number of
Ammonia (plasma, blood)
 Ammonia (plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Ammonia 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Ammonia has the formula NH 3. At physiological
Ammonia (plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Ammonia 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Ammonia has the formula NH 3. At physiological
ABC Fax + 41 61 306 12 34 E-Mail karger@karger.ch www.karger.com. Report
 Report Community Genet 2001;4:175 196 Integrating Genetic Services into Public Health Guidance for State and Territorial Programs from the National Newborn Screening and Genetics Resource Center (NNSGRC)
Report Community Genet 2001;4:175 196 Integrating Genetic Services into Public Health Guidance for State and Territorial Programs from the National Newborn Screening and Genetics Resource Center (NNSGRC)
ROUTINE HEART EXAM AND
 INFORMATION FOR PARENTS ROUTINE HEART EXAM AND BIOBANK IN ALL NEWBORNS In the Copenhagen area 2016-2018 You have the option to let your child join a research study conducted by doctors with expertise in
INFORMATION FOR PARENTS ROUTINE HEART EXAM AND BIOBANK IN ALL NEWBORNS In the Copenhagen area 2016-2018 You have the option to let your child join a research study conducted by doctors with expertise in
CCS - Does CCS provide Counseling or Support Services? CCS - Are there any costs to me? CCS - What papers should I bring?
 CCS - Does CCS provide Counseling or Support Services? CCS - Are there any costs to me? CCS - What papers should I bring? CCS - What are the steps to CCS services? CCS - How is my privacy protected? CCS
CCS - Does CCS provide Counseling or Support Services? CCS - Are there any costs to me? CCS - What papers should I bring? CCS - What are the steps to CCS services? CCS - How is my privacy protected? CCS
LEGISLATION. Maryland CCHD Screening AMCHP Annual Conference Washington DC 02/12/13 1/30/2013 THE JOURNEY BEGINS
 Maryland CCHD Screening AMCHP Annual Conference Washington DC 02/12/13 Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Prevention and Health Promotion Administration Debbie Badawi, MD Medical Director,
Maryland CCHD Screening AMCHP Annual Conference Washington DC 02/12/13 Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Prevention and Health Promotion Administration Debbie Badawi, MD Medical Director,
Program on Child Development and Preventive Care
 Annual Report 2007 Program on Child Development and Preventive Care Children s success in school and later in life depends on their early experiences and the ability of their parents and caretakers to
Annual Report 2007 Program on Child Development and Preventive Care Children s success in school and later in life depends on their early experiences and the ability of their parents and caretakers to
ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR SERIES
 ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR SERIES CLASS TITLE MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR I OPTION C 26400 MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR I OPTION D 26401 MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR
ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR SERIES CLASS TITLE MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR I OPTION C 26400 MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR I OPTION D 26401 MEDICAL ADMINISTRATOR
ARMENIA. Albert Matevosyan MD,PhD
 Albert Matevosyan MD,PhD Neurohereditary Diseases Charity Association Head of Republic Center of Medical Genetic and Department of Medical Genetic Yerevan State Medical University Rome EUROPLAN (Italy)
Albert Matevosyan MD,PhD Neurohereditary Diseases Charity Association Head of Republic Center of Medical Genetic and Department of Medical Genetic Yerevan State Medical University Rome EUROPLAN (Italy)
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines
 Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Failure to Thrive: Rethinking Our Treatment Goals Darren Fiore, MD 2013 Advances & Controversies in Clinical Pediatrics. Tips and Reference Sheet
 Failure to Thrive: Rethinking Our Treatment Goals Darren Fiore, MD 2013 Advances & Controversies in Clinical Pediatrics Tips and Reference Sheet Various Definitions of FTT: Weight < 5th percentile for
Failure to Thrive: Rethinking Our Treatment Goals Darren Fiore, MD 2013 Advances & Controversies in Clinical Pediatrics Tips and Reference Sheet Various Definitions of FTT: Weight < 5th percentile for
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism. Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology
 A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
Maggie Dreon, MS, CGC Jessica Tarnowski
 Communicating incidental findings of sickle cell trait on the newborn screen: A Community-Needs Based Assessment Minnesota Department of Health Newborn Screening Program Maggie Dreon, MS, CGC Jessica Tarnowski
Communicating incidental findings of sickle cell trait on the newborn screen: A Community-Needs Based Assessment Minnesota Department of Health Newborn Screening Program Maggie Dreon, MS, CGC Jessica Tarnowski
House Resolution No. 37
 california legislature regular session House Resolution No. Introduced by Assembly Member Hill August, House Resolution No. Relative to umbilical cord blood banking. WHEREAS, Since the first umbilical
california legislature regular session House Resolution No. Introduced by Assembly Member Hill August, House Resolution No. Relative to umbilical cord blood banking. WHEREAS, Since the first umbilical
Section IX Special Needs & Case Management
 Section IX Special Needs & Case Management Special Needs and Case Management 179 Integrated Care Management/Complex Case Management The Case Management/Care Coordination (CM/CC) program is a population-based
Section IX Special Needs & Case Management Special Needs and Case Management 179 Integrated Care Management/Complex Case Management The Case Management/Care Coordination (CM/CC) program is a population-based
Testimony on New Jersey s Maternal and Child Health Services Title V Block Grant 2016 Application
 Testimony on New Jersey s Maternal and Child Health Services Title V Block Grant 2016 Application On Behalf of The Boggs Center on Developmental Disabilities New Jersey s University Center for Excellence
Testimony on New Jersey s Maternal and Child Health Services Title V Block Grant 2016 Application On Behalf of The Boggs Center on Developmental Disabilities New Jersey s University Center for Excellence
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU)
 DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
Essential Nursing Competencies and Curricula Guidelines for Genetics and Genomics: Outcome Indicators
 Essential Nursing Competencies and Curricula Guidelines for Genetics and Genomics: Outcome Indicators Introduction The Outcome Indicators are an adjunct to the Essential Nursing Competencies and Curricula
Essential Nursing Competencies and Curricula Guidelines for Genetics and Genomics: Outcome Indicators Introduction The Outcome Indicators are an adjunct to the Essential Nursing Competencies and Curricula
The National Survey of Children s Health 2011-2012 The Child
 The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
Objectives. What is undernutrition? What is undernutrition? What does undernutrition look like?
 Objectives Basics Jean-Pierre Habicht, MD, PhD Professor Division of Nutritional Sciences Cornell University Types and causes Determinants Consequences Global occurrence and progress Way forward What is
Objectives Basics Jean-Pierre Habicht, MD, PhD Professor Division of Nutritional Sciences Cornell University Types and causes Determinants Consequences Global occurrence and progress Way forward What is
CLINICAL COURSE PROGRESSION AND CLINICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FAMILY NURSE PRACTITIONER (FNP) STUDENTS
 CLINICAL COURSE PROGRESSION AND CLINICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FAMILY NURSE PRACTITIONER (FNP) STUDENTS Any licensed healthcare provider with the following qualifications may serve as a preceptor for a Nurse
CLINICAL COURSE PROGRESSION AND CLINICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FAMILY NURSE PRACTITIONER (FNP) STUDENTS Any licensed healthcare provider with the following qualifications may serve as a preceptor for a Nurse
Underwriting Practices
 Chapter 3 Underwriting Practices An underwriter s objective is to know as much cants. A majority of BC/BS plans (20 of 25) about the applicant s health status as the applicant. represented by an underwriter
Chapter 3 Underwriting Practices An underwriter s objective is to know as much cants. A majority of BC/BS plans (20 of 25) about the applicant s health status as the applicant. represented by an underwriter
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011
 The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
Florida Medicaid and Implementation of SB 2654
 Florida Medicaid and Implementation of SB 2654 Shachi Mankodi Counsel to the Chief of Staff Florida Agency for Health Care Administration Autism Compact Presentation September 18, 2008 Overview What is
Florida Medicaid and Implementation of SB 2654 Shachi Mankodi Counsel to the Chief of Staff Florida Agency for Health Care Administration Autism Compact Presentation September 18, 2008 Overview What is
RuSH: Sickle Cell Surveillance and Registry Program
 RuSH: Sickle Cell Surveillance and Registry Program CDR Althea M Grant, PhD Chief, Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch Division of Blood Disorders National Center for Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
RuSH: Sickle Cell Surveillance and Registry Program CDR Althea M Grant, PhD Chief, Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch Division of Blood Disorders National Center for Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
Delivering the Promise of Genetic and Genomic Medicine. From Research to Clinical Care:
 A m e r i c a n C o l l e g e o f M e d i c a l G e n e t i c s a n d G e n o m i c s Tr a n s l a t i n g G e n e s I n t o H e a l t h From Research to Clinical Care: Delivering the Promise of Genetic
A m e r i c a n C o l l e g e o f M e d i c a l G e n e t i c s a n d G e n o m i c s Tr a n s l a t i n g G e n e s I n t o H e a l t h From Research to Clinical Care: Delivering the Promise of Genetic
