Chapter 15: The Special Senses
|
|
|
- Elwin Rogers
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
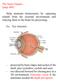
1 Chapter 15: The Special Senses Objectives: 1. Describe the structure and function of accessory eye structures, eye layers, the lens, and humors of the eye. 2. Trace that pathway of light through the eye to the retina, and explain how light is focused for distant and close vision. 3. Describe the events involved in the stimulation of photoreceptors by light, and compare and contrast the roles of rods and cones in vision. 4. Note the cause and consequence of astigmatism, cataract, glaucoma, hyperopia, myopia, presbyopia and color blindness. 5. Compare and contrast light and dark adaptation. 6. Trace the visual pathway to the visual cortex, and briefly describe the steps in visual processing. 7. Describe the location, structure, and afferent pathways of taste and smell receptors, and explain how these receptors are activated. 8. Describe the structure and general function of the outer, middle and internal ears. 9. Describe the sound conduction pathway to the fluids of the internal ear, and follow the auditory pathway from the spiral organ (of Corti) to the temporal cortex. 10. Explain how one is able to differentiate pitch and loudness and localize the source of sounds. 11. Explain how the balance organs of the semicircular canals and the vestibule help maintain dynamic and static equilibrium. 12. List possible causes and symptoms of otitis media, deafness, Ménière s syndrome, and motion sickness. 13. List changes that occur in the special sense organs with aging. I. The Eye and Vision A. Eye and Associated Structures 1. 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye 2. Most of the eye is protected by a cushion of fat and the bony orbit 3. Accessory structures include a. Eyebrows b. Eyelids c. Conjunctiva 1
2 d. Lacrimal apparatus e. Extrinsic eye muscles B. Eyebrows 1. Coarse hairs that overlie the supraorbital margins 2. Functions include: a. Shading the eye b. Preventing perspiration from reaching the eye C. Palpebrae (Eyelids) 1. Protect the eye anteriorly 2. Lacrimal caruncle a. Contains glands that secrete a whitish, oily secretion (Sandman s eye sand) D. Eyelashes 1. Project from the free margin of each eyelid 2. Initiate reflex blinking 3. Lubricating glands associated with the eyelids E. Conjunctiva 1. Transparent membrane that: a. Lines the eyelids as the palpebral conjunctiva b. Covers the whites of the eyes as the ocular conjunctiva c. Lubricates and protects the eye F. Lacrimal Apparatus 1. Consists of the lacrimal gland and associated ducts 2. Lacrimal glands secrete tears 3. Tears a. Contain mucus, antibodies, and lysozyme b. Enter the eye via superolateral excretory ducts c. Exit the eye medially via the lacrimal punctum d. Drain into the nasolacrimal duct G. Structure of the Eyeball 1. A slightly irregular hollow sphere with anterior and posterior poles 2. The wall is composed of three tunics a. Fibrous b. Vascular c. Sensory 3. The internal cavity is filled with fluids called humors 4. The lens separates the internal cavity into anterior and posterior segments 5. Fibrous Tunic 2
3 a. Forms the outermost coat of the eye and is composed of: 1) Opaque sclera (posteriorly) a) The sclera protects the eye and anchors extrinsic muscles 2) Clear cornea (anteriorly) a) The cornea lets light enter the eye 6. Vascular Tunic (Uvea): Choroid Region a. Has three regions 1) Choroid a) Supplies blood to all eye tunics 2) Ciliary body a) A thickened ring of tissue surrounding the lens b) Composed of smooth muscle bundles (ciliary muscles) c) Anchors the suspensory ligament that holds the lens in place 3) Iris a) The colored part of the eye b) Pupil i. Central opening of the iris c) Regulates the amount of light entering the eye during: i. Close vision and bright light pupils constrict ii. Distant vision and dim light pupils dilate 7. Sensory Tunic: Retina a. A delicate two-layered membrane 1) Pigmented layer a) Outer layer that absorbs light and prevents its scattering 2) Neural layer, which contains: a) Photoreceptors that transduce light energy b. Ganglion cell axons: 1) Run along the inner surface of the retina 2) Leave the eye as the optic nerve c. The optic disc: 1) Is the site where the optic nerve leaves the eye 2) Lacks photoreceptors (the blind spot) d. Photoreceptors 1) Rods: a) Respond to dim light b) Are used for peripheral vision 2) Cones: 3
4 a) Respond to bright light b) Have high-acuity color vision c) Are found in the macula lutea d) Are concentrated in the fovea centralis H. Inner Chambers and Fluids 1. The lens separates the internal eye into anterior and posterior segments 2. The posterior segment is filled with a clear gel called vitreous humor that: a. Transmits light b. Supports the posterior surface of the lens c.holds the neural retina firmly against the pigmented layer 3. Anterior Segment a. Composed of two chambers 1) Anterior a) Between the cornea and the iris 2) Posterior a) Between the iris and the lens 4. Aqueous humor a. A plasmalike fluid that fills the anterior segment b. Supports, nourishes, and removes wastes 5. Lens a. A biconvex, transparent, flexible, avascular structure that: 1) Allows precise focusing of light onto the retina 2) With age, the lens becomes more compact and dense and loses its elasticity I. Light 1. Our eyes respond to a small portion of light called the visible spectrum 2. Different cones in the retina respond to different wavelengths of the visible spectrum 3. Refraction and Lenses a. When light passes from one transparent medium to another its speed changes and it refracts (bends) b. Light passing through a convex lens (as in the eye) is bent so that the rays converge to a focal point c. When a convex lens forms an image, the image is upside down and reversed right to left 4. Focusing for Distant Vision 4
5 a. Light from a distance needs little adjustment for proper focusing b. Far point of vision 1) Distance beyond which the lens does not need to change shape to focus (20 ft.) 5. Close vision requires: a. Accommodation 1) Changing the lens shape by ciliary muscles to increase refractory power b. Constriction 1) Pupillary reflex constricts the pupils to prevent divergent light rays from entering the eye c. Convergence 1) Medial rotation of the eyeballs toward the object being viewed 6. Problems of Refraction a. Emmetropic eye 1) Normal eye with light focused properly b. Myopic eye (nearsighted) 1) Focal point is in front of the retina 2) Corrected with a concave lens c. Hyperopic eye (farsighted) 1) Focal point is behind the retina 2) Corrected with a convex lens J. Adaptation 1. Adaptation to bright light (going from dark to light) involves: a. Dramatic decreases in retinal sensitivity 1) Rod function is lost b. Switching from the rod to the cone system 1) Visual acuity is gained 2. Adaptation to dark is the reverse a. Cones stop functioning in low light K. Depth Perception 1. Achieved by both eyes viewing the same image from slightly different angles 2. Three-dimensional vision results from cortical fusion of the slightly different images 3. If only one eye is used, depth perception is lost and the observer must rely on learned clues to determine depth 5
6 II. Chemical Senses A. Gustation (taste) B. Olfaction (smell) C. Their chemoreceptors respond to chemicals in aqueous solution 1. Taste a. Substances dissolved in saliva 2. Smell a. Substances dissolved in fluids of the nasal membranes C. Sense of Smell 1. The organ of smell is the olfactory epithelium, which covers the superior nasal concha 2. Olfactory receptor cells are bipolar neurons with radiating olfactory cilia 3. Physiology of Smell a. Olfactory receptors respond to several different odor-causing chemicals D. Taste Buds 1. Taste buds are found in papillae of the tongue mucosa 2. Taste Sensations a. There are five basic taste sensations 1) Sweet a) Sugars, saccharin, alcohol, and some amino acids 2) Salt a) Metal ions 3) Sour a) Hydrogen ions 4) Bitter a) Alkaloids such as quinine and nicotine 5) Umami a) Elicited by the amino acid glutamate 3. Physiology of Taste a. In order to be tasted, a chemical: 1) Must be dissolved in saliva 2) Must contact gustatory hairs 4. Influence of Other Sensations on Taste a. Taste is 80% smell b. Thermoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, nociceptors also influence tastes c. Temperature and texture enhance or detract from taste 6
7 III. The Ear: Hearing and Balance A. The three parts of the ear are the inner, outer, and middle ear B. The outer and middle ear are involved with hearing C. The inner ear functions in both hearing and equilibrium D. Receptors for hearing and balance: 1. Respond to separate stimuli 2. Are activated independently E. Outer Ear 1. The auricle (pinna) is composed of: a. The helix (rim) b. The lobule (earlobe) 2. External auditory canal 3. Tympanic membrane (eardrum) a. Thin connective tissue membrane that vibrates in response to sound b. Transfers sound energy to the middle ear ossicles c. Boundary between outer and middle ears F. Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) 1. Pharyngotympanic tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx a. Equalizes pressure in the middle ear cavity with the external air pressure G. Ear Ossicles 1. The tympanic cavity contains three small bones a. Malleus b. Incus c. Stapes d. Transmit vibratory motion of the eardrum to the oval window H. Inner Ear 1. Bony labyrinth a. Contains 1) Vestibule 2) Cochlea 3) Semicircular canals b. Filled with perilymph 2. Membranous labyrinth a. Series of membranous sacs within the bony labyrinth b. Filled with a potassium-rich fluid 3. The Vestibule a. The central egg-shaped cavity of the bony labyrinth 7
8 b. Suspended in its perilymph are two sacs: 1) Saccule a) Extends into the cochlea 2) Utricle a) Extends into the semicircular canals 3) House equilibrium receptors called maculae a) Respond to gravity and changes in the position of the head 4. The Semicircular Canals a. Three canals that each define two-thirds of a circle and lie in the three planes of space b. Membranous semicircular ducts line each canal and communicate with the utricle c. The ampulla is the swollen end of each canal and it houses equilibrium receptors in a region called the crista ampullaris 1) These receptors respond to angular movements of the head 5. The Cochlea a. A spiral, conical, bony chamber that: b. Extends from the anterior vestibule c. Contains the cochlear duct, which ends at the cochlear apex d. Contains the organ of Corti (hearing receptor) I. Sound and Mechanisms of Hearing 1. Sound vibrations beat against the eardrum 2. The eardrum pushes against the ossicles, which presses fluid in the inner ear against the oval and round windows 3. This movement sets up shearing forces that pull on hair cells 4. Moving hair cells stimulates the cochlear nerve that sends impulses to the brain 4. Properties of Sound a. Sound is: 1) A pressure disturbance (alternating areas of high and low pressure) originating from a vibrating object b. Frequency 1) Number of waves that pass a given point in a given time c. Pitch 1) Perception of different frequencies (we hear from 20 20,000 Hz) 8
9 d. Amplitude 1) Intensity of a sound measured in decibels (db) e. Loudness 1) Subjective interpretation of sound intensity 5. Transmission of Sound to the Inner Ear a. The route of sound to the inner ear follows this pathway: 1) Pinna 2) Auditory canal 3) Eardrum 4) Malleus 5) Incus 6) Stapes 7) Oval window 8) Stimulation of the organ of Corti 9) Generation of impulses in the cochlear nerve 6. Deafness a. Conduction deafness 1) Something hampers sound conduction to the fluids of the inner ear 2) e.g., impacted earwax, perforated eardrum, osteosclerosis of the ossicles b. Sensorineural deafness 1) Results from damage to the neural structures at any point from the cochlear hair cells to the auditory cortical cells c. Tinnitus 1) Ringing or clicking sound in the ears in the absence of auditory stimuli J. Mechanisms of Equilibrium and Orientation 1. Vestibular apparatus a. Equilibrium receptors in the semicircular canals and vestibule b. Maintains our orientation and balance in space c. Vestibular receptors monitor static equilibrium d. Semicircular canal receptors monitor dynamic equilibrium 2. Anatomy of Maculae a. Maculae are the sensory receptors for static equilibrium b. Contain supporting cells and hair cells c. Each hair cell has stereocilia and kinocilium embedded in the otolithic membrane d. Otolithic membrane 9
10 1) Jellylike mass studded with tiny CaCO 3 stones called otoliths 2) Utricular hairs respond to horizontal movement 3) Saccular hairs respond to vertical movement e. Crista Ampullaris and Dynamic Equilibrium 1) The crista ampullaris (or crista): a) Is the receptor for dynamic equilibrium b) Is located in the ampulla of each semicircular canal c) Responds to angular movements IV. Developmental Aspects A. All special senses are functional at birth B. Chemical senses 1. Few problems occur until the fourth decade, when these senses begin to decline C. Vision 1. Vision is not fully functional at birth 2. Babies are hyperopic, see only gray tones, and eye movements are uncoordinated 3. Depth perception and color vision is well developed by age five 4. With age the lens loses clarity, dilator muscles are less efficient, and visual acuity is drastically decreased by age 70 10
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology. Sensory Adaptation. Four Steps to Sensation. Types of Sensors Structural Design
 Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
SPECIAL SENSES. Introduction: Activity 1: Observation of the Human Eye Model
 SPECIAL SENSES Introduction: The special senses include vision, hearing, equilibrium (balance), taste and smell. In these activities you will be performing a series of physiological tests for each of these
SPECIAL SENSES Introduction: The special senses include vision, hearing, equilibrium (balance), taste and smell. In these activities you will be performing a series of physiological tests for each of these
The Eye ACCESSORY STRUCTURES
 The Eye The eye forms a visual image and projects it onto the sensory receptors (photoreceptors) of the retina. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport,
The Eye The eye forms a visual image and projects it onto the sensory receptors (photoreceptors) of the retina. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport,
Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline
 Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline Five special senses Olfaction = smell Gustation = taste Vision = sight Hearing Equilibrium Special sensory receptors: 1. Distinct cells 2. Complex organ /
Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline Five special senses Olfaction = smell Gustation = taste Vision = sight Hearing Equilibrium Special sensory receptors: 1. Distinct cells 2. Complex organ /
4/17/2012. General Senses
 General Senses The general senses are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. Receptors for those sensations are distributed throughout the body. A sensory receptor is a specialized
General Senses The general senses are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. Receptors for those sensations are distributed throughout the body. A sensory receptor is a specialized
Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES
 SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Senses 3. The optics of the eye Accommodation of the eye Ammetropias The eyeground Visual field
 Senses 3 The optics of the eye Accommodation of the eye Ammetropias The eyeground Visual field Practical tasks Purkinje s images Keratoscopy Ophthalmoscopy Purkinje s flash figure Determination of the
Senses 3 The optics of the eye Accommodation of the eye Ammetropias The eyeground Visual field Practical tasks Purkinje s images Keratoscopy Ophthalmoscopy Purkinje s flash figure Determination of the
The light. Light (normally spreads out straight... ... and into all directions. Refraction of light
 The light Light (normally spreads out straight...... and into all directions. Refraction of light But when a light ray passes from air into glas or water (or another transparent medium), it gets refracted
The light Light (normally spreads out straight...... and into all directions. Refraction of light But when a light ray passes from air into glas or water (or another transparent medium), it gets refracted
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system
 Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
Light and Sound. Pupil Booklet
 Duncanrig Secondary School East Kilbride S2 Physics Elective Light and Sound Name: Pupil Booklet Class: SCN 3-11a - By exploring the refraction of light when passed through different materials, lenses
Duncanrig Secondary School East Kilbride S2 Physics Elective Light and Sound Name: Pupil Booklet Class: SCN 3-11a - By exploring the refraction of light when passed through different materials, lenses
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE SENSORY SYSTEM SUBCOURSE MD0582 EDITION 100
 U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE SENSORY SYSTEM SUBCOURSE MD0582 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE SENSORY SYSTEM SUBCOURSE MD0582 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates in the labyrinth.... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates in the labyrinth.... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
MODERN CLINICAL OPTOMETRY BILLING & CODING THE MEDICAL EYE EXAMINATION. Definitions of Eye Examinations. Federal Government Definition
 MODERN CLINICAL OPTOMETRY BILLING & CODING THE MEDICAL EYE EXAMINATION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 [email protected] Definitions of Eye Examinations Optometry
MODERN CLINICAL OPTOMETRY BILLING & CODING THE MEDICAL EYE EXAMINATION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 [email protected] Definitions of Eye Examinations Optometry
An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye
 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye Changes in the eyelid fissure A, Graves disease stare. B, Myathenia gravis. C, Congenital ptosis of right eye. D, Levator disinsertion. E, Horner syndrome
An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye Changes in the eyelid fissure A, Graves disease stare. B, Myathenia gravis. C, Congenital ptosis of right eye. D, Levator disinsertion. E, Horner syndrome
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Optical Illusion Eye Tricks. This one will make you dizzy. Try focusing on just the center circle while moving your head.
 Optical Illusion Eye Tricks This one will make you dizzy. Try focusing on just the center circle while moving your head. Photocopy from original for best quality. H A N D O U T The Visual System The properly,
Optical Illusion Eye Tricks This one will make you dizzy. Try focusing on just the center circle while moving your head. Photocopy from original for best quality. H A N D O U T The Visual System The properly,
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Eye Injuries. The Eyes The eyes are sophisticated organs. They collect light and focus it on the back of the eye, allowing us to see.
 Eye Injuries Introduction The design of your face helps protect your eyes from injury. But injuries can still damage your eyes. Sometimes injuries are severe enough that you could lose your vision. Most
Eye Injuries Introduction The design of your face helps protect your eyes from injury. But injuries can still damage your eyes. Sometimes injuries are severe enough that you could lose your vision. Most
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
IMAGE ASSISTANT: OPHTHALMOLOGY
 IMAGE ASSISTANT: OPHTHALMOLOGY Summary: The Image Assistant has been developed to provide medical doctors with a software tool to search, display, edit and use medical illustrations of their own specialty,
IMAGE ASSISTANT: OPHTHALMOLOGY Summary: The Image Assistant has been developed to provide medical doctors with a software tool to search, display, edit and use medical illustrations of their own specialty,
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Keeping Your Eyes Healthy after Treatment for Childhood Cancer
 Keeping Your Eyes Healthy after Treatment for Childhood Cancer High doses of radiation to the brain, eye, or eye socket (orbit) during treatment for childhood cancer can have a long-lasting affect on the
Keeping Your Eyes Healthy after Treatment for Childhood Cancer High doses of radiation to the brain, eye, or eye socket (orbit) during treatment for childhood cancer can have a long-lasting affect on the
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
Science In Action 8 Unit C - Light and Optical Systems. 1.1 The Challenge of light
 1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06)
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
COW S EYE dissection. Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions. Safety first!
 COW S EYE dissection Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions One way to figure out how something works is to look inside it. To learn about how your eyes work, you can dissect, or take apart,
COW S EYE dissection Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions One way to figure out how something works is to look inside it. To learn about how your eyes work, you can dissect, or take apart,
Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions
 Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions What is a Vitreo-Retinal specialist? Retinal specialists are eye physicians and surgeons who focus on diseases in the back of the eye
Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions What is a Vitreo-Retinal specialist? Retinal specialists are eye physicians and surgeons who focus on diseases in the back of the eye
Sound Perception. Sensitivity to Sound. Sensitivity to Sound 1/9/11. Not physically sensitive to all possible sound frequencies Range
 Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
THE EYES IN MARFAN SYNDROME
 THE EYES IN MARFAN SYNDROME Marfan syndrome and some related disorders can affect the eyes in many ways, causing dislocated lenses and other eye problems that can affect your sight. Except for dislocated
THE EYES IN MARFAN SYNDROME Marfan syndrome and some related disorders can affect the eyes in many ways, causing dislocated lenses and other eye problems that can affect your sight. Except for dislocated
Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation
 Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation 1. When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it is A. absorbed. B. bent away from the normal. C. bent towards from the normal. D. continues in the
Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation 1. When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it is A. absorbed. B. bent away from the normal. C. bent towards from the normal. D. continues in the
A concise guide to Safety Glasses, the different standards and the effects of light on the eye. Contents. Links. Year of publication: 2010
 A concise guide to Safety Glasses, the different standards and the effects of light on the eye Year of publication: 2010 Produced by the leading supplier of Safety Glasses in the UK. All Rights Reserved.
A concise guide to Safety Glasses, the different standards and the effects of light on the eye Year of publication: 2010 Produced by the leading supplier of Safety Glasses in the UK. All Rights Reserved.
MAZAHERI LASIK METHOD FOR VISUAL ENHANCEMENT TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION. [0001] The present invention is directed, in general, to
![MAZAHERI LASIK METHOD FOR VISUAL ENHANCEMENT TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION. [0001] The present invention is directed, in general, to MAZAHERI LASIK METHOD FOR VISUAL ENHANCEMENT TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION. [0001] The present invention is directed, in general, to](/thumbs/26/8162223.jpg) MAZAHERI LASIK METHOD FOR VISUAL ENHANCEMENT TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION [0001] The present invention is directed, in general, to a surgical procedure and, more particularly, to surgical procedure
MAZAHERI LASIK METHOD FOR VISUAL ENHANCEMENT TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION [0001] The present invention is directed, in general, to a surgical procedure and, more particularly, to surgical procedure
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video. IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
 Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
LASIK. Cornea. Iris. Vitreous
 LASIK Introduction LASIK surgery is a procedure that improves vision and can decrease or eliminate the need for eyeglasses or contact lenses. If you and your doctor decide that LASIK surgery is right for
LASIK Introduction LASIK surgery is a procedure that improves vision and can decrease or eliminate the need for eyeglasses or contact lenses. If you and your doctor decide that LASIK surgery is right for
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
HEALTHY EYES. Type 2 diabetes. Information for patients. Disease Management Programme
 HEALTHY EYES Information for patients Type 2 diabetes Disease Management Programme WHAT CAN I DO FOR HEALTHY EYES DESPITE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES? More and more people suffer from type 2 diabetes; among them,
HEALTHY EYES Information for patients Type 2 diabetes Disease Management Programme WHAT CAN I DO FOR HEALTHY EYES DESPITE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES? More and more people suffer from type 2 diabetes; among them,
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Review Vocabulary spectrum: a range of values or properties
 Standards 7.3.19: Explain that human eyes respond to a narrow range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. 7.3.20: Describe that something can be seen when light waves emitted or reflected by
Standards 7.3.19: Explain that human eyes respond to a narrow range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. 7.3.20: Describe that something can be seen when light waves emitted or reflected by
Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
 Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Patient Information Content
 KORNMEHL LASER EYE ASSOCIATES Patient Information Content Near Vision Loss Understanding Near Vision Loss Why is My Near Vision Changing? In our 40 s and 50 s, we begin to experience the naturally frustrating
KORNMEHL LASER EYE ASSOCIATES Patient Information Content Near Vision Loss Understanding Near Vision Loss Why is My Near Vision Changing? In our 40 s and 50 s, we begin to experience the naturally frustrating
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION. Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology
 PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
iocutouchtm for ipad Contents of Videos and Still Images Anatomy 906. Normal Eye and Orbit - no labels 907. Normal Eye and Orbit - with labels
 iocutouchtm for ipad Contents of Videos and Still Images Anatomy 906. Normal Eye and Orbit - no labels 907. Normal Eye and Orbit - with labels Normal Eye 474. Normal Eye overview 476. Cornea - overview
iocutouchtm for ipad Contents of Videos and Still Images Anatomy 906. Normal Eye and Orbit - no labels 907. Normal Eye and Orbit - with labels Normal Eye 474. Normal Eye overview 476. Cornea - overview
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Eye Diseases. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com otf30101 Last reviewed: 05/21/2014 1
 Eye Diseases Introduction Some eye problems are minor and fleeting. But some lead to a permanent loss of vision. There are many diseases that can affect the eyes. The symptoms of eye diseases vary widely,
Eye Diseases Introduction Some eye problems are minor and fleeting. But some lead to a permanent loss of vision. There are many diseases that can affect the eyes. The symptoms of eye diseases vary widely,
LASIK. What is LASIK? Eye Words to Know. Who is a good candidate for LASIK?
 2014 2015 LASIK What is LASIK? LASIK (laser in situ keratomileusis) is a type of refractive surgery. This kind of surgery uses a laser to treat vision problems caused by refractive errors. You have a refractive
2014 2015 LASIK What is LASIK? LASIK (laser in situ keratomileusis) is a type of refractive surgery. This kind of surgery uses a laser to treat vision problems caused by refractive errors. You have a refractive
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
ReLEx smile Minimally invasive vision correction Information for patients
 ReLEx smile Minimally invasive vision correction Information for patients Seeing is living Our eyes are our most important sensory organ. The human brain obtains over 80 % of its information via the sense
ReLEx smile Minimally invasive vision correction Information for patients Seeing is living Our eyes are our most important sensory organ. The human brain obtains over 80 % of its information via the sense
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments. 27.1 The Human Eye and the Camera 27.2 Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics 27.3 The Magnifying Glass
 Chapter 27 Optical Instruments 27.1 The Human Eye and the Camera 27.2 Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics 27.3 The Magnifying Glass Figure 27 1 Basic elements of the human eye! Light enters the
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments 27.1 The Human Eye and the Camera 27.2 Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics 27.3 The Magnifying Glass Figure 27 1 Basic elements of the human eye! Light enters the
The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software
 Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Middle ear conditions
 Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who has a hearing loss? How does hearing work?
 This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect
 Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
YEAR 1: The Human Body and Senses
 YEAR 1: The Human Body and Senses Contents Include: What our bodies can do Eyes and Sight Ears and Hearing Touch, Taste and Smell Understanding Sensory Impairment Please Note: The activities included in
YEAR 1: The Human Body and Senses Contents Include: What our bodies can do Eyes and Sight Ears and Hearing Touch, Taste and Smell Understanding Sensory Impairment Please Note: The activities included in
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Visual Cortex 0 http://www.tutis.ca/neuromd/index.htm 20 February 2013
 T he Visual Cortex 0 Chapter contents Contents Chapter 2... 0 T he Visual Cortex... 0 Chapter Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Optic Chiasm... 2 Where do the eye's ganglion cells project to?... 3 To where
T he Visual Cortex 0 Chapter contents Contents Chapter 2... 0 T he Visual Cortex... 0 Chapter Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Optic Chiasm... 2 Where do the eye's ganglion cells project to?... 3 To where
FIFTH GRADE TECHNOLOGY
 FIFTH GRADE TECHNOLOGY 3 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES SCIENCE AND MATH OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE SCIENCE AND MATH WEEK 1. PRE: Interpreting data from a graph. LAB: Estimating data and comparing results
FIFTH GRADE TECHNOLOGY 3 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES SCIENCE AND MATH OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE SCIENCE AND MATH WEEK 1. PRE: Interpreting data from a graph. LAB: Estimating data and comparing results
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
9.00 EXAM 1 NOTES KOSSLYN CHAPTER 3 Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind
 The processes of sensation and perception lie at the root of our experience of feeling alive, serving as the foundation for most of what we know and do. Sensation the result of neural responses that occur
The processes of sensation and perception lie at the root of our experience of feeling alive, serving as the foundation for most of what we know and do. Sensation the result of neural responses that occur
Visual Acuity, Impairments and Vision Insurance Plan Provisions. Stuart West Specialty Sales Manager Virginia CE Forum 2009 Course # 201718
 Visual Acuity, Impairments and Vision Insurance Plan Provisions Stuart West Specialty Sales Manager Virginia CE Forum 2009 Course # 201718 How Vision Works Light passes through the cornea & lens Light
Visual Acuity, Impairments and Vision Insurance Plan Provisions Stuart West Specialty Sales Manager Virginia CE Forum 2009 Course # 201718 How Vision Works Light passes through the cornea & lens Light
Vision Glossary of Terms
 Vision Glossary of Terms EYE EXAMINATION PROCEDURES Eyeglass Examinations: The standard examination procedure for a patient who wants to wear eyeglasses includes at least the following: Case history; reason
Vision Glossary of Terms EYE EXAMINATION PROCEDURES Eyeglass Examinations: The standard examination procedure for a patient who wants to wear eyeglasses includes at least the following: Case history; reason
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services
 Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED
 Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
BSM Connection elearning Course
 BSM Connection elearning Course Anatomy of the Eye 2004, BSM Consulting All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents OVERVIEW...1 THE MECHANISM OF SIGHT... 1 EXTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EYE... 1 INTERNAL STRUCTURE
BSM Connection elearning Course Anatomy of the Eye 2004, BSM Consulting All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents OVERVIEW...1 THE MECHANISM OF SIGHT... 1 EXTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EYE... 1 INTERNAL STRUCTURE
GOVERNMENT OF NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR. Department of Education
 GOVERNMENT OF NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR Department of Education Table of Contents Acknowledgments...i Introduction... 1 Section One The Structure and Function of the Eye...1.0 What are the parts of the
GOVERNMENT OF NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR Department of Education Table of Contents Acknowledgments...i Introduction... 1 Section One The Structure and Function of the Eye...1.0 What are the parts of the
The Eye: Anatomy, Histology & Histopathology. Gillian Shaw, DVM, MS September 9, 2011 [email protected]
 The Eye: Anatomy, Histology & Histopathology Gillian Shaw, DVM, MS September 9, 2011 [email protected] Overview Macroscopic Anatomy Some clinical presentations of eye disease Microscopic Anatomy Normal
The Eye: Anatomy, Histology & Histopathology Gillian Shaw, DVM, MS September 9, 2011 [email protected] Overview Macroscopic Anatomy Some clinical presentations of eye disease Microscopic Anatomy Normal
GAZE STABILIZATION SYSTEMS Vestibular Ocular Reflex (VOR) Purpose of VOR Chief function is to stabilize gaze during locomotion. Acuity declines if
 GAZE STABILIZATION SYSTEMS Vestibular Ocular Reflex (VOR) Purpose of VOR Chief function is to stabilize gaze during locomotion. Acuity declines if slip exceeds 3-5 deg/sec. Ex: Head bobbing and heel strike
GAZE STABILIZATION SYSTEMS Vestibular Ocular Reflex (VOR) Purpose of VOR Chief function is to stabilize gaze during locomotion. Acuity declines if slip exceeds 3-5 deg/sec. Ex: Head bobbing and heel strike
Vision and Care of the Eyes in Prader-Willi Syndrome
 Vision and Care of the Eyes in Prader-Willi Syndrome The chromosome abnormality that causes Prader-Willi syndrome leads to various problems in development, including a number of ocular features. Strabismus
Vision and Care of the Eyes in Prader-Willi Syndrome The chromosome abnormality that causes Prader-Willi syndrome leads to various problems in development, including a number of ocular features. Strabismus
Lecture 2, Human cognition
 Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK)
 Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) John D. Goosey, MD Introduction DSAEK is a corneal transplant technique where the unhealthy, diseased, posterior portion of a patient s cornea
Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) John D. Goosey, MD Introduction DSAEK is a corneal transplant technique where the unhealthy, diseased, posterior portion of a patient s cornea
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Cassie Schroeder Refractive Surgery Coordinator Boozman-Hof Regional Eye Clinic (479) 246-1820 (479) 531-3937
 Thank you for your interest in refractive surgery here at Boozman-Hof Regional Eye Clinic. Enclosed is a bio on Dr. Cole and articles about LASEK. There is also information on our financing company that
Thank you for your interest in refractive surgery here at Boozman-Hof Regional Eye Clinic. Enclosed is a bio on Dr. Cole and articles about LASEK. There is also information on our financing company that
14 Taste. 14 The Nature of Taste. Vocabulary conventions. Systems of taste classification. Odor Perceived through the orthonasal pathway
 Taste Taste Some definitions --- again 4 basic tastes anatomy and physiology coding of taste quality genetic variation in taste experience the pleasures of taste The Nature of Taste Vocabulary conventions
Taste Taste Some definitions --- again 4 basic tastes anatomy and physiology coding of taste quality genetic variation in taste experience the pleasures of taste The Nature of Taste Vocabulary conventions
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
