Boy Scouts of America (BSA) & American Red Cross (ARC)
|
|
|
- Jeffry Ryan
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Boy Scouts of America (BSA) & American Red Cross (ARC) Notes prepared by James Clegern (BSA merit badge counselor, GSWC and ARC instructor) ARC class manuals are available for free down-load and printing at Scouts are still expected to read their Scout Handbook & First Aid Merit badge book Goals of First-Aid: 1) Be aware of risks and take steps to reduce or manage it (prevention and situational awareness) 2) When an accident occurs, know how to handle it a. Check the scene & approach safely b. Call for help if more than a minor injury c. Ask for victim s consent to be treated (if victim is unconscious or disoriented, assume yes) d. Treat immediate, life-threatening medical emergencies first (breathing & bleeding) e. Protect a person who is injured or ill from further harm f. Treat for shock g. Make a thorough examination h. Plan a course of action 3) Get the person under professional medical care if needed Requirement 2 Explain how you would obtain emergency medical assistance from your house, on a wilderness camping trip, and during an activity on open water. At home: Keep emergency numbers posted at the phone along with your address. 911 service is available in most areas. If phones are not working, go to a neighbor that has emergency training. Wilderness: Cell phone, radio, messenger, or evacuate. Signal fires and sounds are a last resort if you cannot evacuate. Be sure to leave a map and schedule at home to trigger an automatic rescue response. Open Water: Powered craft should be equipped with a marine band radio tuned to the emergency channel (#16). Flares and smoke bombs can be carried on any boat but must be used with caution. A distress flag (orange with a black dot and a black square) or signal mirror may be useful over short distances. Explain the term triage. Triage: the process of sorting victims, as of a battle or disaster, to determine medical priority in order to increase the number of survivors; the determination of priorities for action in an emergency. Explain the standard precautions as applied to blood borne pathogens. Treat all blood as if it were contaminated with blood borne pathogens. Thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water before and after treating a sick or injured person. Never use your bare hands to stop bleeding. Use a protective barrier, preferably nonlatex disposable gloves (a new, unused plastic food storage bag will work in a pinch). Safely discard all soiled bandages, dressings, and other used first aid items by putting them in a double plastic bag until they can be disposed of properly in a receptacle for bio-hazards. Prepare a first aid kit for your home. Display and discuss its contents with your counselor. Suggested items Roller bandage, 2 (1); Roller bandage, 1 (2); Triangular bandages (2); Elastic bandages, 3 wide (2)
2 Adhesive bandages, assorted sizes (24); Sterile gaze pads, 3-by-3 (12); Adhesive tape, 1 (1 roll); Moleskin, 3-by-6-inch (2); Soap (1 small bar) or alcohol-based hand sanitizing gel (1 travel sized bottle); Triple antibiotic ointment (1 small tube); Gel pads for blisters/burns (2 packages), Alcohol swabs (24); Scissors (1 pair); tweezers (1 pair); Non-latex disposable gloves (6 pairs); CPR breathing barrier (1);protective goggles/safety glasses (1); 1 gallon sized sealable plastic bags (4); pencil & paper Requirement 3 Explain what action you should take for someone who shows signs of a heart attack. Lay the victim down and elevate legs. Call 911. Keep warm, calm and comfortable. Monitor breathing as CPR may be required before help arrives. Transport only if no EMS is available. Under no circumstances should the patient attempt to drive to the hospital. Identify the conditions that must exist before performing CPR on a person. Rescue breathing is used if the victim does not begin breathing when the airway is opened. It also helps warm a severely hypothermic person who is breathing very slowly. Chest compressions should only be used when there are no signs of responsiveness: coughing, moving, breathing, reaction to touch or voice. Demonstrate proper technique in performing CPR using a training device approved by your counselor. (In-Class) Show the steps that need to be taken for someone suffering from a severe cut on the leg and on the wrist. Tell the dangers in the use of a tourniquet and the conditions under which its use is justified. The steps for first-aid of severe bleeding are: 1. Utilize personal protective devices (non-latex gloves, protective goggles) 2. Direct pressure with a clean cloth or sterile pad, place a hand firmly over the wound and press hard. After bleeding has stopped, hold pad in place with a sterile bandage. If blood soaks through the first pad, place another pad on top of it & continue applying pressure. 3. Elevation -- if on an extremity, lift the limb over the person's heart 4. Pressure point -- place directed pressure at one of the "pressure points" t reduce bleeding. On the arm, this is between the bicep and tricep on the upper arm (a pulse is normally palpable) and on the leg midway down the thigh and between the two leg muscles. 5. Tourniquet -- (For use in emergencies only) tie a cravat, rope or belt above the wound as tight as possible, in order to completely cut off circulation to the injured area. The most typical method of tying it is a simple overhand knot, held tight while a pencil or stick is placed on top of the middle of the knot. Another overhand knot is tied, and the pencil or stick can be twisted to tighten the knot. Cutting off circulation for extended periods can lead to the amputation of the limb, so this must not be used unless all other methods have been tried and there is no hope for help in the near future. The time should be noted when the tourniquet is applied, as this will be helpful for the doctors. Explain when a bee sting could be life threatening and what action should be taken for prevention and for first aid. Bee stings can cause a fatal reaction called anaphylaxis in people who have a severe allergy to bee venom. It is possible to have the same reaction to foods and medicines (peanuts and shellfish are also common causes of anaphylatic reactions). The effects are nearly immediate -- swelling of the neck and face, sweating, difficulty breathing and hives are among the most common signs. Many people with severe allergies, especially bee stings, carry a device called an Epi-Pen. An Epi-Pen is a dosage of a powerful drug, epinephrine, which
3 counteracts an anaphylactic reaction. To use it, remove the safety cap and simply press the needle end firmly against the victim's thigh, about midway between the knee and hip. The spring-loaded needle will automatically extend, delivering the epinephrine into the muscle where it will be rapidly transferred into the bloodstream. The effect of the epi-pen is temporary, however, and the person must still get medical attention quickly. Explain the symptoms of heat stroke and what action needs to be taken for first aid and for prevention. Heatstroke occurs in two steps: 1) Heat Exhaustion: occurs by a combination of dehydration and warm weather. Symptoms include severe lack of energy, weakness, headache, nausea, faintness and sweating; cool, pale moist skin and a rapid pulse. Treatment involves 2-3 hrs of cooling the victim in the shade or air-conditioning, encourage them to drink cool water or sports drinks to rehydrate. 2) Heatstroke: occurs when the core body temperature rises too high (105 F+) for the body's natural cooling mechanisms to function efficiently and can lead to death if not treated immediately. Key symptoms include those of heat exhaustion plus confusion, hot/flushed skin, and excessive or non-existent sweating. Treatment includes calling for medical assistance and working to lower the victim s body temperature. A victim should be places in a shady or cooled environment, have tight clothing loosened, fanned and applying wet towels to exposed skin. If ice packs are available, wrap in a thin towel and place under the armpits and around the neck/groin. If the victim is able, give them cool water to drink in small amounts. Requirement 4 Describe the signals of a broken bone. Show first-aid procedures for handling fractures, including open (compound) fractures of the forearm, wrist, upper leg, and lower leg using improvised materials. Definition: If more pressure is put on a bone than it can stand, it will split or break. A break of any size that does not cut through the skin it is called a closed fracture (or simple fracture). If the broken bone punctures the skin creating an open wound, it is called an open fracture (compound fracture). Signs of a broken bone (if yes ): Did you feel or hear a bone snap? Do you feel pain when you press on the skin over the suspected fracture? Are you unable to move the injured limb? Treatment of a bone fracture (splints): Can be made of any material, soft or hard, that can be bound to the fractures limb Is used to stabilize the injured area and prevent further damage Make the splint long enough to immobilize the joints above and below the fracture Provide padding to increase victim comfort and secure with neckerchiefs, bandaged or other strips of cloth Broken Bone Don'ts: DO NOT move the person unless the broken bone is firmly secured with a splint or sling. DO NOT try to reposition or move a bone that is sticking out DO NOT try to clean the wound of an open fracture
4 DO NOT move a person with an injured hip, pelvis, or upper leg unless it is absolutely necessary. If you must move the person, pull the person to safety by his clothes (such as by the shoulders of a shirt, a belt, or pant-legs). DO NOT move a person who has a possible spine injury. DO NOT try to reposition a suspected spine injury. Use of slings: help support an injured hand, arm, collarbone, or shoulder. Describe the symptoms and possible complications and demonstrate proper procedures for treating suspected injuries to the back, neck, and head. Explain what measures can be taken to reduce the possibility of further complicating these injuries. Anybody that has fallen, been in a car crash, or hit their head should be suspected of having a back or neck injury. Symptoms may include the person is complaining of any pain in their head, neck, or back, or they have numbness in any of their extremities. However, the person may not be complaining of any pain at all and still have an injury. The problem with these injuries is that any damage to the back and especially the neck can lead to paralysis or even death. A head injury can lead to brain damage, blood loss, or death. The most important thing to remember about spinal injuries is not to move the person unless absolutely necessary. Moving the person can make a bad injury worse. The only times when you should move such a person is if: You must move them to get to a more seriously injured person. The person is in a dangerous position and you are able to move them to a safer place You need to perform CPR and need to place the person on a hard surface The best thing that you can do is to tell the person not to move. If needed, hold their head in place. Medical professionals call this "holding C-Spine," or the inline neutral position. Make sure that the person can breathe and they have a pulse, and then wait for help to arrive. If the victim must be moved, ask for other scouts or bystanders to help so that the victim s body can be turned or lifted all at once without causing any twists or turns of the spine. If the person is bleeding from the head, try to stop the bleeding. Direct pressure is important here, but do not press too hard as you might further injure the skull. Requirement 5 Hypothermia: Hypothermia occurs when a person s body is losing more heat than it can generate and the core body temperature becomes too low. Ordinarily, the body begins shivering to regain lost heat. When the heat loss becomes severe, hypothermia begins and the victim may shiver uncontrollably and experience numbness, fatigue, confusion, poor judgment or unconscious. Treat a hypothermia victim by preventing the person from getting colder and help bring the body temperature back to normal. Get the victim under shelter and begin warming the victim's body with extra clothing (or the replacement of wet clothing), towel wrapped heat packs, body heat, and/or giving the victim warm drinks if they are able to swallow. Re-warming should occur over time rather than suddenly. Rapid re-warming of a chronic hypothermia patient can lead to an irregular and dangerous heartbeat. Monitor the victim closely for any changes in condition.
5 Convulsions/Seizures: Convulsions are involuntary muscle spasms that can be caused by a variety of diseases and injuries. There is no emergency treatment, but it is important to not hold the victim down or otherwise restrain him, and to give nothing by mouth (contrary to widely-held opinion, the victim will not "choke on his tongue"). These seizures are not uncommon in people afflicted with epilepsy, and these convulsions are generally not dangerous (though a doctor should still be consulted if the seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes). You should also remove all loose furniture that the victim could injure themselves by flailing a body part into it. Try to reassure the person and be sure that they can breath. Once the seizure is over, place the victim in the recovery position and monitor. If the person does not regularly have seizures, medical help should be call for. Medical professionals will want to know how long the seizure lasted and if the person injured themselves in any way, especially their head, neck, or back. Frostbite: Frostbite occurs when an extremity, often fingers or toes, are exposed to cold, freezing temperatures so that ice crystals form in the tissues. The top layer of skin will first appear with grayish-white patches (called frostnip) and feel painful or numb. As the exposure continues, the freezing extends deeper into the tissue and muscles, turning the affected area blue, then white, and finally black, leading to gangrene or tissue death. Treatment involves first getting the victim under shelter and removing the wet or covering clothing. If the injury is frostnip, place the affected area against bare skin to warm up (palm of hand, armpit, or belly). If you suspect deeper frostbite, wrap the area in a warm, dry towel and get to a physician as soon as possible. If there is no chance of refreezing, warm the injured area slowly in warm water ( F), until normal color appears and it feels warm, and bandage the area loosely with dry sterile gauze between toes or fingers. Dehydration: Dehydration occurs when there is insufficient amount of water for the normal functioning of the body (i.e. we expel more than we take in). Initial symptoms include severe thirst, dry mouth, dark, yellow urine. A severely dehydrated victim can experience weakness, dizziness, confusion, nausea, fainting, decreased sweating and urination. Treating mild dehydration involves replenishing the body with fluids and minerals with water or sports drinks. Severe dehydrations requires emergency medical attention. Bruises, strains, sprains: Black and blue marks are common bruises. Keep cold, wet towel over the bruise for minutes to help prevent more blood from leaking into the tissues. Next day apply a warm wet cloth. A Strain is an injury to a muscle due to overstretching. Apply ice pack to reduce swelling and pain. Wrap firmly with an elastic bandage to limit the swelling and to protect the injury. Stay off the injury. Good physical conditioning and proper warmup before exercise help to prevent strained muscles and tendons. A sprain is caused by twisting, wrenching, or lifting movements that tear or stretch ligament tissues around a joint. Take the weight off the injured joint and do not attempt to straighten, apply cold compresses, and treat as a fracture or broken bone. Burns: o A typical first-degree burn is a sunburn (mild pain + reddening of the affected skin). o A second-degree burn is a burn that raises blisters (painful). o Severe or third-degree burns char layers of skin & flesh (may not feel any pain) o Chemical burns: remove chemicals from victim s skin (don t get any on you!) flood area with cool, clean water 20 min to remove chemicals, call for emergency medical help and provide burn first-aid
6 o Electrical burns: remove victim from electrical source (don t endanger yourself!), call for emergency medical aide, perform CPR if needed & provide burn first-aid First aid for mild burns, hold burn under cold running water or apply damp, cold cloths until pain eases. If there is blistering, do not break blisters! Let the injured area dry and cover it with a loose bandage. For serious burns, leave the clothing in place and cool the burn. Protect the burn area with a dry, sterile dressing, treat for shock and seek medical attention. Do not treat burns with oil based jellies, creams, greases, or sprays since they are difficult to remove and can slow the healing process. Abdominal pain: A stomachache is usually nothing more than a pain caused by overeating, eating too fast, or eating an odd mixture of strange or unusual foods. In rare cases, the pain could be a sign of appendicitis. Watch the person closely for increasing pain or changes in the level of consciousness. If the victim s temperature goes over 102 F or if there is signs of blood in the urine, vomit or stool, call medical emergency services. If the pain starts in the lower right quarter of the abdomen and gets worse over several hours, combined with a loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, there is a good chance of appendicitis. If you suspect appendicitis, call emergency services immediately and don t give the person anything eat or drink. Broken, chipped, or loosened tooth: Gently clean. Place cold compress on face, to minimize swelling. Go to the dentist immediately with any recovered tooth pieces. Knocked-out tooth: Pick up tooth carefully by the crown, not by the roots. Rinse tooth gently under cold running water or milk. Do NOT scrub, scrape or allow the tooth to dry-out. Flush the wound with water or saline solution & apply pressure with a sterile gauze pad to control the bleeding. Place the tooth in a container of milk or cool water and go immediately to a dentist or emergency room within 30 minutes for treatment. Muscle cramps: Muscle cramps occur when a muscle contracts on its own. They usually happen when the body is fatigued or dehydrated, and muscles have not been stretched well. Muscle cramps can be minor or painful. Stretch and apply firm pressure or gently massage to help relieve the muscle spasms. Drink water or sports drink with electrolytes to help prevent future cramps. Requirement 6 Do TWO of the following: If a sick or injured person must be moved, tell how you would determine the best method. o Single-Rescuer Assists (walking, ankle, drag, blanket, lifts, carries) o Multiple person (2-4 hand seats, chair, walk-assist, hammock carry) With helpers under your supervision, improvise a stretcher and move a presumably unconscious person. o Shirt, blanket & board stretchers With your counselor's approval, arrange a visit with your patrol or troop to an emergency medical facility or through an American Red Cross Chapter for a demonstration of how an AED is used.
7 Requirement 7 Teach another Scout a first-aid skill selected by your counselor. Use the EDGE system if needed.
First Aid Multiple Choice Test
 First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS
 HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
MRC Medical Jeopardy Feud List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions
 List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
American Red Cross First Aid EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
First Aid Merit Badge Workbook
 First Aid Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge
First Aid Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge
FIRST AID TEST. 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988. www.schoolbusing.com. Revised April 21, 2008 - 1 -
 FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
Heat Illnesses. Common Heat Rash Sites
 Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
EXTREME HEAT OR COLD
 Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency. Warning Signs and Symptoms
Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency. Warning Signs and Symptoms
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION. Airway must be open so oxygen can enter the body.
 CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
5420-R STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods
 STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
Dressing and bandage
 Dressing and bandage Mihajlo Lojpur, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION The terms dressing and bandage are often used synonymously. In fact, the term dressing refers more correctly to the primary layer in contact
Dressing and bandage Mihajlo Lojpur, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION The terms dressing and bandage are often used synonymously. In fact, the term dressing refers more correctly to the primary layer in contact
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector
 OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
Types of electrical injuries
 Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector
 Lesson Guide Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 45 minutes Guidance for the Instructor To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Welcome participants and explain
Lesson Guide Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 45 minutes Guidance for the Instructor To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Welcome participants and explain
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
How to Handle First Aid Caring For Ill Person
 FIRST AID How to Use This Pamphlet The secret to successfully earning a merit badge is for you to use both the pamphlet and the suggestions of your counselor. Your counselor can be as important to you
FIRST AID How to Use This Pamphlet The secret to successfully earning a merit badge is for you to use both the pamphlet and the suggestions of your counselor. Your counselor can be as important to you
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel
 Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES
 FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES. Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator
 HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS Objectives: Factors that create HRI Stages of HRI Care Basic First Aid Protecting
HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS Objectives: Factors that create HRI Stages of HRI Care Basic First Aid Protecting
CPR/First Aid. Lesson 12 Injuries to Muscles, Bones & Joints
 CPR/First Aid Lesson 12 Injuries to Muscles, Bones & Joints 1 Muscles Muscles are soft tissues. Your body has over 600 different muscles. Injuries to the brain, spinal cord or nerves can affect the muscles.
CPR/First Aid Lesson 12 Injuries to Muscles, Bones & Joints 1 Muscles Muscles are soft tissues. Your body has over 600 different muscles. Injuries to the brain, spinal cord or nerves can affect the muscles.
LEGAL PROTECTION. Good Samaritan Law RCW 4.24.300
 GOALS This course is designed to instruct coach very basic first aid techniques to protect the players under your guidance. This presentation only provides a brief overview of the issues that you may face
GOALS This course is designed to instruct coach very basic first aid techniques to protect the players under your guidance. This presentation only provides a brief overview of the issues that you may face
Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace
 A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress.
 Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Recent Injuries. www.physiofirst.org.uk
 Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan
 Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS AIDS and other blood-borne pathogens such as Hepatitis B and C are deadly diseases that are present in today s society. All blood-borne pathogens are transmitted in blood and other
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS AIDS and other blood-borne pathogens such as Hepatitis B and C are deadly diseases that are present in today s society. All blood-borne pathogens are transmitted in blood and other
Emergency Action Plans
 Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
Basic First Aid Tutorial
 Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR
 I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
Heat Stress/Flag Condition Training
 Heat Stress/Flag Condition Training Heat stress Heat stress is the buildup of heat to the point where the body s thermostat has difficulty maintaining normal internal body temperature. When the body is
Heat Stress/Flag Condition Training Heat stress Heat stress is the buildup of heat to the point where the body s thermostat has difficulty maintaining normal internal body temperature. When the body is
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
too hot! Heat Related Illness
 too hot! Heat Related Illness Participating in recreation and sport activities provides many benefits for children and can be a fun and enjoyable way to be physically active. However, when the temperature
too hot! Heat Related Illness Participating in recreation and sport activities provides many benefits for children and can be a fun and enjoyable way to be physically active. However, when the temperature
Heat Production and Loss. Environmental Emergencies. Heat Regulation. Body Temperature Ranges. Focused Assessment: Your Patient: Heat Production
 Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet
 Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
2. (U4C2L3:F2) If your friend received a deep cut on her wrist, what would you do?
 Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
2. When temperature and wind chill falls below 35 degrees including the wind chill, students, are kept indoors.
 Weather /Environmental Guidelines Time spent outdoors is an important part of the school day. It is difficult to set guidelines that fit every circumstance and condition in regards to outside activities.
Weather /Environmental Guidelines Time spent outdoors is an important part of the school day. It is difficult to set guidelines that fit every circumstance and condition in regards to outside activities.
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter
 Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter
 Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD
 THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response
 Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
call 811 to get advice from a nurse, or have someone drive the patient to a hospital Emergency Department. Patients should NOT drive themselves.
 Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Shift Commander: The senior ranking uniformed line officer at the DOC facility, most commonly a Sergeant, Lieutenant or Captain.
 I Index: Date Signed: 04/18/2015 Replaces : N/A Supersedes Dated: 05/21/2014 Affected Units: Adult Institutions Effective Date: 04/20/2015 Scheduled Revision Date: March 2016 Revision Number: 12 Office
I Index: Date Signed: 04/18/2015 Replaces : N/A Supersedes Dated: 05/21/2014 Affected Units: Adult Institutions Effective Date: 04/20/2015 Scheduled Revision Date: March 2016 Revision Number: 12 Office
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
SCRIPT NUMBER 123 HEATSTROKE - 2 (ONE SPEAKER)
 SCRIPT NUMBER 123 HEATSTROKE - 2 (ONE SPEAKER) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: HEATSTROKE - 2 PROGRAM NUMBER: 123 SUBJECT: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, COMPLICATIONS, TREATMENT OF HEAT-RELATED CONDITIONS
SCRIPT NUMBER 123 HEATSTROKE - 2 (ONE SPEAKER) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: HEATSTROKE - 2 PROGRAM NUMBER: 123 SUBJECT: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, COMPLICATIONS, TREATMENT OF HEAT-RELATED CONDITIONS
TakE Care in Hot & Cold Weather
 www.coned.com TakE Care in Hot & Cold Weather Preventing Hyperthermia and Hypothermia When it s Too Hot! Beating the heat is as much a part of summer as baseball and hot dogs. City residents are particularly
www.coned.com TakE Care in Hot & Cold Weather Preventing Hyperthermia and Hypothermia When it s Too Hot! Beating the heat is as much a part of summer as baseball and hot dogs. City residents are particularly
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Bone and Joint Injuries
 Bone and Joint Injuries Lesson Length 2 hours, 15 minutes Materials, Equipment and Supplies n Newsprint and markers n Wilderness and Remote First Aid Emergency Reference Guide (one for each participant)
Bone and Joint Injuries Lesson Length 2 hours, 15 minutes Materials, Equipment and Supplies n Newsprint and markers n Wilderness and Remote First Aid Emergency Reference Guide (one for each participant)
SCRIPT NUMBER 82 SPRAINED ANKLE (TWO SPEAKERS)
 SCRIPT NUMBER 82 SPRAINED ANKLE (TWO SPEAKERS) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: SPRAINED ANKLE PROGRAM NUMBER: 82 SUBJECT: PATHOLOGY, CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF SPRAINED ANKLES
SCRIPT NUMBER 82 SPRAINED ANKLE (TWO SPEAKERS) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: SPRAINED ANKLE PROGRAM NUMBER: 82 SUBJECT: PATHOLOGY, CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF SPRAINED ANKLES
How to treat your injured neck
 How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
Chapter 18 THERMAL INJURIES
 Chapter 18 THERMAL INJURIES Because of the range of environmental condition within which sports take place, various temperature-related health emergencies occur each year, some result in death. Most, if
Chapter 18 THERMAL INJURIES Because of the range of environmental condition within which sports take place, various temperature-related health emergencies occur each year, some result in death. Most, if
Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin integrity.
 Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Emergency Preparedness
 Emergency Preparedness Our Scout motto, Be Prepared, is never more important than in dealing with emergency situations. The ability to make correct decisions under pressure really tests a Scout. As Scouts
Emergency Preparedness Our Scout motto, Be Prepared, is never more important than in dealing with emergency situations. The ability to make correct decisions under pressure really tests a Scout. As Scouts
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES
 RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
Play it Safe in the Heat Tips for Coaches and Parents
 Play it Safe in the Heat Tips for Coaches and Parents Heat is the number one weather related killer in the United States. Heat illness is the leading cause of preventable death in high school athletics
Play it Safe in the Heat Tips for Coaches and Parents Heat is the number one weather related killer in the United States. Heat illness is the leading cause of preventable death in high school athletics
Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery.
 JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
3/24/2014. Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014. Why do we need a First Aid Program?
 Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
12/5/2012. Introduction. Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries. Recognizing and Caring for Serious Head, Neck and Back Injuries
 Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
To protect your health when temperatures are extremely high, remember to keep cool and use common sense. The following tips are important:
 What Is Extreme Heat? Temperatures that hover 10 degrees or more above the average high temperature for the region and last for several weeks are defined as extreme heat. Humid or muggy conditions, which
What Is Extreme Heat? Temperatures that hover 10 degrees or more above the average high temperature for the region and last for several weeks are defined as extreme heat. Humid or muggy conditions, which
American Red Cross Advisory Council on First Aid, Aquatics, Safety and Preparedness
 Copyright 2008 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced; stored in a retrieval system; or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
Copyright 2008 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced; stored in a retrieval system; or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
Okolona Fire Department Standard Operating Procedure
 Page 1 of 6 October 1, 2011 New Operational Purpose: This policy will govern the type of training, the environment, gear to be used for training, and outside non-emergency activities for the Okolona Fire
Page 1 of 6 October 1, 2011 New Operational Purpose: This policy will govern the type of training, the environment, gear to be used for training, and outside non-emergency activities for the Okolona Fire
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Extreme Heat: A Prevention Guide to Promote Your Personal Health and Safety
 Extreme Heat: A Prevention Guide to Promote Your Personal Health and Safety Heat-related deaths and illness are preventable yet annually many people succumb to extreme heat. Historically, from 1979-2003,
Extreme Heat: A Prevention Guide to Promote Your Personal Health and Safety Heat-related deaths and illness are preventable yet annually many people succumb to extreme heat. Historically, from 1979-2003,
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Taking Out a Tooth. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! CHAPTER11
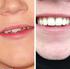 159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION
 JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
Understanding Diabetes
 Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes
 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes UHN People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to keep your feet healthy. Please visit the UHN Patient
Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes UHN People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to keep your feet healthy. Please visit the UHN Patient
CAMPSITE RISK ASSESSMENT. Risk mitigation and control measures: a practical guide for group leaders to manage general risk and hazards on tour
 CAMPSITE RISK ASSESSMENT mitigation and control measures: a practical guide for group leaders to manage general risk and hazards on tour CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2-3 2. Climbing Wall 4 3. Rock Climbing
CAMPSITE RISK ASSESSMENT mitigation and control measures: a practical guide for group leaders to manage general risk and hazards on tour CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2-3 2. Climbing Wall 4 3. Rock Climbing
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Paclitaxel and Carboplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
Raynaud s Disease. What is Raynaud s Disease? Raynaud s disease is also sometimes known as Raynaud s phenomenon or Raynaud s syndrome.
 Raynaud s Disease Introduction Raynaud s disease is a rare disorder of the blood vessels. It usually affects the fingers and toes. This disorder causes the blood vessels to narrow which turns the affected
Raynaud s Disease Introduction Raynaud s disease is a rare disorder of the blood vessels. It usually affects the fingers and toes. This disorder causes the blood vessels to narrow which turns the affected
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff
 Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
How To Recover From A Surgical Wound From A Cast
 Care of Your Wounds After Amputation Surgery by Paddy Rossbach, RN Depending on the reason for your amputation and the state of your limb at the time of surgery, definitive closure of the wound may take
Care of Your Wounds After Amputation Surgery by Paddy Rossbach, RN Depending on the reason for your amputation and the state of your limb at the time of surgery, definitive closure of the wound may take
Preparing for the Unexpected www.redcross.org
 Terrorism Preparing for the Unexpected www.redcross.org A1366 Oct. 2001 An American Red Cross mobile service center stationed at the Pentagon Sept. 18 shows one small part of the ongoing response you can
Terrorism Preparing for the Unexpected www.redcross.org A1366 Oct. 2001 An American Red Cross mobile service center stationed at the Pentagon Sept. 18 shows one small part of the ongoing response you can
Sports Injury Treatment
 Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions
 Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Dizziness and Vertigo
 Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness. and pain
 TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
1. Dosing Schedule: your customized schedule of your weekly injections as provided by the center.
 Home Immunotherapy Raza Pasha, MD Congratulations. You are now on the path to better control of your allergies. The following is your instruction guide to allow you to become more familiar with proper
Home Immunotherapy Raza Pasha, MD Congratulations. You are now on the path to better control of your allergies. The following is your instruction guide to allow you to become more familiar with proper
How To Care For A Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
Gemcitabine and Cisplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
MRSA. Living with. Acknowledgements. (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
 How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
FOLFOX Chemotherapy. This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy.
 FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
