Taking Out a Tooth. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! CHAPTER11
|
|
|
- Jeremy Jennings
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal treatment for a tooth with an abscess, or wiring for a loose tooth require the skills of an experienced dental worker. Even if you cannot treat every person, a more experienced worker can help you by taking care of the more difficult tooth problems. Remove a tooth only when it is necessary. Here are three reasons to take out a tooth: It hurts all the time or hurts enough to wake the person at night. It is loose and hurts when you move it. It has a broken root (p. 96) or a broken top with an exposed nerve. It is important to learn from another person, not just from a book. Find an experienced dental worker who can show you how to take out a tooth and who can then watch you as you try it yourself. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! Before you take out a tooth, you need to learn about the person s health. Tell the person what to expect, and then ask: Do you bleed a lot when your skin is cut? (If so, you may bleed a lot when your tooth comes out.) Do you have swollen feet and difficulty breathing? (You may have heart disease.) Do you have any allergies? (You may be allergic to some medicines we give when we take out a tooth.) Are you a diabetic? (If you have diabetes, your wound will take a long time to heal.) Are you pregnant? (Some problems can be treated during pregnancy, but sometimes it is better to wait. See pages 15 16, 77, 102, and 160.) If the person answers yes to any of these questions, you must take special precautions. See the next page. 159
2 160 Where There Is No Dentist 2012 five PROBLEMS TO WATCH FOR 1. A person who bleeds a lot must know how to prevent bleeding afterward. Explain very carefully the steps given on page 167. You may also want to place a suture (pages ) to hold the gums tightly together. 2. Persons with heart disease often take aspirin or medicines called anticoagulants that do not allow the blood to clot normally. Ask what medicine the person takes. Heparin and warfarin are examples of anticoagulants. Another heart medicine, digitalis, is not an anticoagulant. If the medicine is not an anticoagulant, you can take out the tooth. But do not use more than 2 cartridges of local anesthetic. The epinephrine inside the anesthetic can harm a weak heart. (See page 137, #2). 3. A person with allergies may be allergic to aspirin, penicillin, erythromycin, or other medicines you often use. Find out which medicine has caused problems and give a different medicine, one that will not cause a reaction. 4. A diabetic s wound may become infected. Watch carefully the place where you took out the tooth and give antibiotics (page 94) if an infection begins. 5. During the last month of pregnancy, a woman may be too uncomfortable to have a tooth taken out. Control the infection with a 5-day course of penicillin (page 94), and take out the tooth after the baby is born. It is also better to wait if the woman has high blood pressure, because she may bleed too much when you take out the tooth. For more information about treating pregnant women, see page 77, and the story on pages 15 to 16. Be Patient, Careful, and Considerate Inject local anesthetic slowly in the right place, so the tooth becomes numb and you do not hurt the person when you remove it. If the person says the tooth still hurts, it is probably true! Inject again. Use the correct instrument in the correct way. If you are careful you can avoid breaking the tooth. When you take out a baby tooth, be extra careful not to hurt the new tooth growing under it. Explain everything to the person. Tell the person if something is going to hurt, even a little. When you take out the tooth, you can explain, for example, that there will be a feeling of pressure. Press on the person s arm to demonstrate what it will be like. When you finish taking out the tooth, explain what you have done and what the person can do at home to help the mouth heal. THE INSTRUMENTS YOU NEED Buying instruments can be confusing, because there are so many. Only a few of them are really necessary. You can take out most teeth with the 4 basic instruments on page 161.
3 The Four Basic Instruments You can take out most teeth with these 4 instruments: Where There Is No Dentist When you order, use the proper name. Many companies use numbers to describe the instruments, but a different company may use a different number. If you use the proper name along with the number given here, most companies will understand what you want. (See page 213.) A spoon or probe an elevator and two forceps 150 upper universal forcep 151 lower universal forcep Use this to separate the gum from the tooth. An elevator will loosen a tooth, or lift out a broken root. Use forceps to pull out the tooth. There is one for upper teeth and one for lower teeth. Other forceps can be useful, especially for taking out a strong back tooth. They have pointed beaks that are made to fit between the roots of a back molar. As a result, you can hold onto the larger tooth better. 87 cowhorn forcep 73 lower molar hawk s bill forcep 18R right upper molar forcep 18L left upper molar forcep
4 162 Where There Is No Dentist 2012 Curved elevators are good for taking out broken roots. You can force their pointed ends more easily between the root and the bone that is holding it Cryers elevators Unfortunately, forceps and elevators are expensive. If you want to order more than the 4 basic instruments (page 161), remember the cost. WHERE YOU WORK IS IMPORTANT Work wherever it is light and bright. You must be able to see what needs to be done. Sunlight or light from a lamp is usually enough. Use a dental mirror (page 145) to direct more light into the mouth. Use a chair that has a back high enough to support the person s head. Think about how you can stand and work the most easily. To take out a lower tooth, you need to push down and then pull up. So the person should be sitting down low. To take out an upper tooth, you need to push up and then pull down. So the person should be sitting up high. If you stand on a box, he will be lower. If he sits on cushions, he will be higher.
5 Where There Is No Dentist HOW TO TAKE OUT THE TOOTH Once you are certain which tooth must come out, decide which instruments you will need. Lay them out ahead of time on a clean cloth: a syringe, needle, and local anesthetic forceps an elevator spoon instrument cotton gauze Before you touch your instruments, be sure your hands are clean. Wash with soap and water, and put on clean plastic or rubber gloves. See pages 85 and 86. Be sure, also, that your instruments are clean. See pages 87 to 90. Prevent infection keep clean! To take out a tooth, follow these 8 steps (pages ): 1. Explain what you are going to do. 2. Inject local anesthetic. 3. Separate the gum from the tooth. 4. Loosen the tooth. 5. Take out the tooth. 6. Stop the bleeding. 7. Explain to the person what to do at home to look after the wound. 8. Help the person to replace the tooth with a false tooth. 1. Always begin by talking to the person. Explain why you must take out a tooth (or teeth) and tell how many teeth you will take out. Begin working only when the person understands and agrees. 2. Inject some local anesthetic slowly, in the right place. Remember from Chapter 9 that the injection for a lower tooth is different from the injection for an upper tooth. Wait 5 minutes for the anesthetic to work, and then test to be sure the tooth is numb. Be kind always test before you start. If the person still feels pain, give another injection.
6 164 Where There Is No Dentist Separate the gum from the tooth. The gum is attached to the tooth inside the gum pocket. Separate the gum and tooth before you take out the tooth. If you do not, the gum may tear when the tooth comes out. Torn gums bleed more and take longer to heal. Use this or this Slide the end of the instrument along the side of the tooth into the gum pocket. At the deepest part of the pocket, you can feel the Front Side place where the gum attaches to the tooth. Push the instrument between this attached part and the tooth. Then separate the tooth from the gum by moving the instrument back and forth. Do this on both the cheek side (outside) Back Side and the tongue side (inside) of the tooth. The attached gum is strong, but it is also thin. Control your instrument carefully so that it only cuts through the part that is attached to the tooth. Do not go any deeper. 4. Loosen the tooth. A loose tooth is less likely to break when you take it out. Before you take out a strong tooth, always loosen it first with a straight elevator. Caution: if you do not use it properly, a straight elevator can cause more harm than good. The blade goes between the bad tooth and the good one in front of it. Put the curved face of the blade against the tooth you are removing. Slide the blade down the side of the tooth, as far as possible under the gum. Turn the handle so that the blade moves the top of the bad tooth backward. It is important to hold a straight elevator properly. Place your first finger against the next tooth while you turn the handle. This will control it. Remember that the sharp blade can slip and hurt the gums or tongue. Put pressure on the bone, not the tooth beside it. Do not loosen the good tooth!
7 Where There Is No Dentist Now, take out the tooth. Push your forceps as far up the tooth as possible. The beaks of the forceps must hold onto the root under the gum. YES NO Use your other hand to support the bone around the tooth. Your fingers will feel the bone expanding a little at a time as the tooth comes free. With practice, you will be able to decide how much movement the tooth can take without breaking. To decide which way to move a tooth, think about how many roots it has. If a tooth has 1 root, you can turn it. If a tooth has 2 or 3 roots, you need to tip it back and forth. Take your time. If you hurry and squeeze your forceps too tightly, you can break a tooth. Removing a tooth is like pulling a post out of the ground. When you move it back and forth a little more each time, it soon becomes loose enough to come out.
8 166 Where There Is No Dentist 2012 Front teeth come straight out Back teeth usually come out toward the cheek When you remove lower molars with the lower molar cow-horn forcep, you use it in a different way: Fit the points under the gum, between the tooth s roots. Squeeze the handles gently and move them up and down, then side to side. This will force the points of the forcep further between the roots and lift the tooth up and out. Note: some lower molars come out toward the tongue. Warning: Do not use the cowhorn forcep to take out a baby molar. Its points can damage the permanent tooth growing under it. When the tooth comes out, look carefully at its roots to see if you have broken any part off and left it behind. Whenever possible, take out broken roots so that they do not cause infection Iater inside the bone.
9 Where There Is No Dentist Stop the bleeding. Squeeze the sides of the socket (the hole that is left after you take out the tooth) back into place. Then cover the socket with cotton gauze and ask the person to bite firmly against it for 30 minutes. A child should bite firmly on the gauze for 2 hours. See page 142. Whenever the gums are loose, join them together. To stop the bleeding and heal the wound, you must hold the gums tightly against the bone under them. HOW TO PLACE A SUTURE When you remove 2 or more teeth in a row, it is a good idea to join the gums with a suture (needle and thread). If you need more than one suture, place the first one nearest the front of the mouth and work toward the back. The needle and thread you use must be sterile. Boil both for 30 minutes. See page 88. You will need an instrument to hold the needle firmly (hemostat) and scissors to cut the thread. a) Pass the needle through the loose gum the one you can move most easily. Then pass it through the more firmly attached gum. If the looser gum is on the outside, you will bring the needle toward the tongue. Protect the tongue with a tongue blade or your dental mirror. You must suture both the upper and the lower gums in this way. After this you must tie 2 knots and cut the thread. See the next page.
10 168 Where There Is No Dentist 2012 b) Pull the thread until about 4 cm of thread is left loose on the starting side. Wrap the longer end of thread 2 times around the beaks of the needle holder. Then grab the shorter free end of the thread with the tip of the needle holder. With the needle in your fingers, pull the needle holder in the opposite direction. The thread will slide off the beaks and form the first knot. Tighten the knot onto the side of the wound, not on top of it. c) Tie a second knot, to keep the first one tight. Wrap the thread once around the beaks of the needle holder. Grab the free end with the tip of the needle holder as you did before. Pull the 2 ends in opposite directions. The second knot will form over the first knot. d) Cut the threads so that about.5 cm is left free. If the ends are too long, they will bother the person s tongue. If they are too short, the knot may come open. Then cover the area with cotton gauze. Tell the person to: bite against the cotton for 1 hour to stop the bleeding, and return in 1 week for you to remove the thread. There is a special kind of suture material that disappears by itself, which is good to use because the person does not have to return for you to remove sutures. Unfortunately, it is expensive. If you cannot afford it, use sewing thread and remove it 1 week later.
11 Where There Is No Dentist Explain to the person what you have done, and what to do at home to look after the wound. Remember that her mouth is numb, so she cannot feel what is happening. Taking out a tooth is like a small operation. There will be bleeding and later some pain and swelling. This is normal and should be expected. Tell the person this. Then give the following advice: Bite firmly on cotton gauze for an hour, and again later if blood comes from the socket. Always give the person some extra cotton gauze to carry home, in case bleeding starts again later. Show her how to use the cotton gauze. Take aspirin or acetominophen for pain as soon as you need it, and then every 3 to 4 hours (pages 94-95). Keep your head up when you rest. This reduces bleeding because it is harder for blood to flow uphill. It also hurts less. Do not rinse your mouth. In some places people believe they should immediately rinse with salt water and spit a lot after a tooth comes out, but this is harmful! It is important for the blood clot to stay inside the socket and not wash away. Do not drink hot Iiquids like tea or coffee, because they encourage bleeding. However, cool Iiquids are good for you. Drink a lot of water. Continue to eat, but be sure the food is soft and easy to chew. Try to chew food on the side opposite the wound. Keep your mouth clean. Start on the second day and continue until the socket is well. To do this, rinse your mouth with warm salt water (page 7) and keep your teeth clean (pages 69 72), especially the teeth near the socket. False Teeth After a tooth comes out, it is a good idea to replace it with a false tooth. If you do not, the other teeth soon start to shift into the open space. This weakens the bone around their roots. After some years, they too become loose and sore, and they have to be taken out.
12 170 Where There Is No Dentist 2012 WHY FALSE TEETH ARE HELPFUL When you take out a tooth, it is like removing a brick from the center of a wall. The area around the space becomes weaker and begins to crumble. To prevent this, a plastic tooth can fit into the space. This tooth is not for chewing food but to hold the remaining teeth in their normal, healthy position. A full set of teeth allows a person to chew the foods needed to stay healthy and feel good. Moreover, teeth help you look good! A person without many teeth looks old. With a new set of plastic false teeth, the same person looks and feels much younger. If possible, after you take out a tooth, encourage the person to replace the tooth with a plastic tooth. Find out where they are made and how much they cost. Then explain: how to clean the remaining teeth to prevent them from going bad (pages 69 72), and how it is possible to get a replacement plastic tooth.
13 Where There Is No Dentist PROBLEMS THAT CAN OCCUR Sometimes a problem develops even though you have tried to be careful. Give help whenever you can. If you are not able to help, refer the person to a doctor or dentist as soon as possible. Broken Roots If you can see the root, try to remove it. If you leave a broken root inside the bone, it can start an infection. Removing a broken UPPER root. Use your straight elevator. Slide the blade along the wall of the socket until it meets the broken root. 1. Force the blade between the root and the socket. 2. Move the root away from the socket wall. 3. Move the root further until it is loose. 4. Grab the loose root and pull it out. Removing a broken LOWER root. Use a straight elevator (or a curved elevator if you have one). If the broken root is from a molar tooth, slide the blade into the socket beside the broken root. 1. Break away the bone between the root and the blade. 2. Force the blade between the root and the socket. 3. Move the root away from the socket wall. 4. Grab the loose root and pull it out. Warning: It is better to leave a small broken root inside the socket. In a week or so, it will loosen itself and be easier to remove.
14 172 Where There Is No Dentist 2012 Root Pushed Into the Sinus An upper root that seems to disappear may have gone into the sinus (page 95). Do not try to find it. Instead, cover the socket with cotton gauze and send the person to the hospital. A special operation is needed to open the sinus, find the root, and take it out. Ask the person not to blow his nose. That forces air through the opening and prevents it from healing. Bone Chips and Tags of Flesh Small pieces of bone that lie loose inside the socket can cause bleeding and delay healing. Gently reach into the socket with the end of an elevator or spoon instrument. Feel for the piece of bone and carefully lift it out. Give local anesthetic if needed. When you are finished, ask the person to bite on cotton gauze until the bleeding stops. Small tags of flesh are not serious, but they bother the person. Hold the tag steady with cotton tweezers and use sterile scissors carefully to cut the bit of flesh free. Rinsing with warm water makes gums tough and helps them heal. But do not rinse for the first 24 hours. See page 169. Bleeding If the first cotton gauze (page 161) does not stop the bleeding in the socket, place more cotton gauze. Wait 5 minutes to see if the bleeding stops. If this does not work, follow the steps on pages for placing a suture. Swelling Hold a cloth wet with cold water against the face. This helps to prevent swelling. This is a good thing to do if the tooth was hard to take out, or if it took a long time. If there already is swelling, heat against the face will help to reduce swelling. Hold a cloth wet with hot water against the swollen area, 30 minutes on and 30 minutes off. Be careful not to burn the skin! A large swelling usually means there is an infection. The person needs additional treatment. See page 116.
15 Painful Socket Where There Is No Dentist The socket area often hurts for a day or so after the tooth has been removed. Aspirin or acetominophen (page 94) is usually enough to relieve the pain. A strong, steady pain that lasts for several days is a sign that the person is having a problem called dry socket. The treatment for this special kind of problem is given on page 117. Dislocated Jaw When you press against a person s jaw while taking out a tooth you can sometimes dislocate it. The jaw has been pushed out of position and it is not able to go back again. We describe the care for a dislocated jaw on page 113. Most important: Be sure to tell each person you treat, If your problem gets worse, you can come back to see me immediately! CLEAN YOUR INSTRUMENTS AFTER YOU FINISH If your instruments are dirty, they can pass on germs that cause tetanus (page 118) or hepatitis (see page 172 in Where There Is No Doctor). Germs on dirty instruments can also go into the socket and start an infection. Dental instruments must be not only clean, but also sterile. This means they need to be both scrubbed and then boiled before they can be used again. See pages 86 to 89. Use a brush and clean each instrument with soap and water. Be careful to scrub away all bits of old dried blood. Then kill the germs by placing the instruments into a covered pot of boiling water for 30 minutes.
Injecting Inside the Mouth
 Injecting Inside the Mouth 135 9 CHAPTER It is possible to treat a tooth without pain. You do this with an injection of local anesthetic. You must inject near the nerve, so to give good injections, you
Injecting Inside the Mouth 135 9 CHAPTER It is possible to treat a tooth without pain. You do this with an injection of local anesthetic. You must inject near the nerve, so to give good injections, you
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
How to Fill a Cavity WHEN NOT TO PLACE A FILLING CHAPTER10
 143 How to Fill a Cavity CHAPTER10 When someone s tooth hurts, you do not always need to take it out. There may be a way to treat it and keep it. Always ask yourself whether a bad tooth really needs to
143 How to Fill a Cavity CHAPTER10 When someone s tooth hurts, you do not always need to take it out. There may be a way to treat it and keep it. Always ask yourself whether a bad tooth really needs to
What Dental Implants Can Do For You!
 What Dental Implants Can Do For You! Putting Smiles into Motion About Implants 01. What if a Tooth is Lost and the Area is Left Untreated? 02. Do You Want to Restore Confidence in Your Appearance? 03.
What Dental Implants Can Do For You! Putting Smiles into Motion About Implants 01. What if a Tooth is Lost and the Area is Left Untreated? 02. Do You Want to Restore Confidence in Your Appearance? 03.
Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery
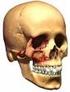 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP
 1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
Understanding Dental Implants
 Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma
 GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter
 The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
The Emily Center How to Care for your Child s Indwelling Subcutaneous Catheter Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #1054
call 811 to get advice from a nurse, or have someone drive the patient to a hospital Emergency Department. Patients should NOT drive themselves.
 Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay
 Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions
 Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions. Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes
 Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin) or Heparin
 Contents www.bcwomens.ca What is Dalteparin (Fragmin)...1 Where do I get this medication from?...1 How often do I give myself this medication?...1 Side effects...1 Steps to Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin)..1
Contents www.bcwomens.ca What is Dalteparin (Fragmin)...1 Where do I get this medication from?...1 How often do I give myself this medication?...1 Side effects...1 Steps to Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin)..1
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Orthodontics Removing wisdom teeth Information for patients
 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Orthodontics Removing wisdom teeth Information for patients The information in this leaflet will help you to understand your treatment. It contains answers
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Orthodontics Removing wisdom teeth Information for patients The information in this leaflet will help you to understand your treatment. It contains answers
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
MRC Medical Jeopardy Feud List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions
 List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count What is a low platelet count? A platelet count measures the number of platelets you have in your blood.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count What is a low platelet count? A platelet count measures the number of platelets you have in your blood.
LANAP. (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure)
 LANAP (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure) Marcus Hannah, DDS 970 N. Kalaheo Avenue, Suite A305 Kailua, HI 96734 Tel: 808.254.5454 Fax: 808.254.5427 Dental Laser ANAP Informed Consent and Authorization
LANAP (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure) Marcus Hannah, DDS 970 N. Kalaheo Avenue, Suite A305 Kailua, HI 96734 Tel: 808.254.5454 Fax: 808.254.5427 Dental Laser ANAP Informed Consent and Authorization
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter
 Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners
 USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
Going Home after Replantation Surgery
 Going Home after Replantation Surgery TWH Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: how to care for yourself what problems to look out for how to take care of your wound sites who
Going Home after Replantation Surgery TWH Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: how to care for yourself what problems to look out for how to take care of your wound sites who
Care of Your Hickman Catheter
 Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
GOING HOME AFTER YOUR TAVR PROCEDURE
 GOING HOME AFTER YOUR TAVR PROCEDURE HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE GOING HOME After your TAVR procedure, you will need help when you go home. It is hard to predict how much help
GOING HOME AFTER YOUR TAVR PROCEDURE HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE GOING HOME After your TAVR procedure, you will need help when you go home. It is hard to predict how much help
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
How To Stretch Your Body
 Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
TREATMENT 1. Control bleeding by applying pressure over wound with Gauze Pads (Surgical Supply-4). 2. Contact Surgeon for laceration repair options.
 Page 1 of 8 pages NOTE Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible.
Page 1 of 8 pages NOTE Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible.
Patient Information. Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip Code: Date of Birth: Gender:
 Patient Information: Patient Information Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: Date of Birth: Gender: Best Number to Confirm Your Appointments: Alternate Phone Number: Social
Patient Information: Patient Information Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: Date of Birth: Gender: Best Number to Confirm Your Appointments: Alternate Phone Number: Social
MRSA. Living with. Acknowledgements. (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
 How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
5420-R STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods
 STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
Tooth Decay. What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth.
 Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
How To Choose Between A Vaginal Birth Or A Cesarean Section
 Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS AIDS and other blood-borne pathogens such as Hepatitis B and C are deadly diseases that are present in today s society. All blood-borne pathogens are transmitted in blood and other
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS AIDS and other blood-borne pathogens such as Hepatitis B and C are deadly diseases that are present in today s society. All blood-borne pathogens are transmitted in blood and other
Post operative instructions and information. after a Sinus Lift procedure
 This article is written and presented by Dr. Boris Pulec MDS Dr. Pulec graduated from the University of Toronto and has been practicing privately for over 27 years. He has been a proponent of patient education
This article is written and presented by Dr. Boris Pulec MDS Dr. Pulec graduated from the University of Toronto and has been practicing privately for over 27 years. He has been a proponent of patient education
INTRODUCTION TO POSITIONING. MODULE 3: Positioning and Carrying
 MODULE 3: Positioning and Carrying Blankets, pillows and towels, sandbags, carpet on the floor, a doll with floppy limbs that can be positioned i.e. not a hard plastic doll, display materials. Icebreaker
MODULE 3: Positioning and Carrying Blankets, pillows and towels, sandbags, carpet on the floor, a doll with floppy limbs that can be positioned i.e. not a hard plastic doll, display materials. Icebreaker
Taking care of your dental Implants ( By Dr. B. Pulec )
 This article is written and presented by Dr. Boris Pulec MDS Dr. Pulec graduated from the University of Toronto and has been practicing privately for over 27 years. He has been a proponent of patient education
This article is written and presented by Dr. Boris Pulec MDS Dr. Pulec graduated from the University of Toronto and has been practicing privately for over 27 years. He has been a proponent of patient education
Skin biopsy. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Skin biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm A skin biopsy is a
Skin biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm A skin biopsy is a
Oral Health Program 4300 Cherry Creek Drive South PSD-OH-A4 Denver, CO 80246-1530 (303) 692-2470
 Oral Health Program 4300 Cherry Creek Drive South PSD-OH-A4 Denver, CO 80246-1530 (303) 692-2470 2 This flip chart is designed to aid school nurses, school office personnel, teachers and parents in the
Oral Health Program 4300 Cherry Creek Drive South PSD-OH-A4 Denver, CO 80246-1530 (303) 692-2470 2 This flip chart is designed to aid school nurses, school office personnel, teachers and parents in the
Community home-based prevention of disability due to lymphatic filariasis
 Community home-based prevention of disability due to lymphatic filariasis World Health Organization Geneva WHO/CDS/CPE/CEE/2003.35 Part 3 Figure 1 Wash your leg, or other part of the body affected by lymphoedema,
Community home-based prevention of disability due to lymphatic filariasis World Health Organization Geneva WHO/CDS/CPE/CEE/2003.35 Part 3 Figure 1 Wash your leg, or other part of the body affected by lymphoedema,
dental care every day
 dental care every day A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
dental care every day A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
Exercise and advice after breast cancer surgery
 Exercise and advice after breast cancer surgery Irving Building Physiotherapy All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. Role of the physiotherapist Exercises for the first week following
Exercise and advice after breast cancer surgery Irving Building Physiotherapy All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. Role of the physiotherapist Exercises for the first week following
TOWN CENTER ORTHOPAEDIC ASSOCIATES P.C. Labral Tears
 Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
Lateral pterygoid muscle Medial pterygoid muscle
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section. Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby.
 Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery.
 JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
JP Drain Introduction A JP Drain is a soft tube and container used to drain fluids that build up under the skin after surgery. This reference summary explains what a JP Drain is and discusses how to take
Spedding Dental Clinic. 73 Warwick Road Carlisle CA1 1EB T: 01228 521889 www.speddingdental.co.uk
 DENTAL IMPLANTS Spedding Dental Clinic 73 Warwick Road Carlisle CA1 1EB T: 01228 521889 www.speddingdental.co.uk SPEDDING DENTAL CLINIC Jack Spedding is a partner in Spedding dental clinic. He is a highly
DENTAL IMPLANTS Spedding Dental Clinic 73 Warwick Road Carlisle CA1 1EB T: 01228 521889 www.speddingdental.co.uk SPEDDING DENTAL CLINIC Jack Spedding is a partner in Spedding dental clinic. He is a highly
INFORMATION ON AFTERCARE OF DENTAL IMPLANTS
 INFORMATION ON AFTERCARE OF DENTAL IMPLANTS.132.indd 1 30.11.11 16:0 WHAT DOES AFTERCARE CONSIST OF? Straumann implants are a modern option for tooth replacement when you are missing one or more teeth.
INFORMATION ON AFTERCARE OF DENTAL IMPLANTS.132.indd 1 30.11.11 16:0 WHAT DOES AFTERCARE CONSIST OF? Straumann implants are a modern option for tooth replacement when you are missing one or more teeth.
Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis
 Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Home Care for Your Wound Drain
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression and rotator cuff repair
 Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Endoscopy Unit
 Manchester Royal Infirmary Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Endoscopy Unit Information For Patients 2 You have been advised to have an endoscopic mucosal resection to your oesophagus (gullet) or stomach. This
Manchester Royal Infirmary Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Endoscopy Unit Information For Patients 2 You have been advised to have an endoscopic mucosal resection to your oesophagus (gullet) or stomach. This
INFLUENZA (FLU) Flu and You
 Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Removal of impacted wisdom teeth
 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Removal of impacted wisdom teeth Information for patients This leaflet aims to help you understand the treatment you are going to have and contains answers to many commonly
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Removal of impacted wisdom teeth Information for patients This leaflet aims to help you understand the treatment you are going to have and contains answers to many commonly
Dental Emergencies and Oral Sports Injuries. What to Do When Minutes Count
 Dental Emergencies and Oral Sports Injuries What to Do When Minutes Count Table of Contents Dental Emergencies and Oral Sports Injuries Introduction 3 Is it a Dental Emergency 3 Dental Emergency Prevention
Dental Emergencies and Oral Sports Injuries What to Do When Minutes Count Table of Contents Dental Emergencies and Oral Sports Injuries Introduction 3 Is it a Dental Emergency 3 Dental Emergency Prevention
Information for patients Exercise and advice after breast cancer surgery
 Information for patients Exercise and advice after breast cancer surgery Physiotherapy Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust Stott Lane, Salford, M6 8HD Telephone: 0161 206 5328 Page 1 of 5 Role of the physiotherapist
Information for patients Exercise and advice after breast cancer surgery Physiotherapy Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust Stott Lane, Salford, M6 8HD Telephone: 0161 206 5328 Page 1 of 5 Role of the physiotherapist
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES
 HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
INTRODUCTION TO OSTEO-TI IMPLANTS; A NURSES MANUAL
 INTRODUCTION TO OSTEO-TI IMPLANTS; A NURSES MANUAL Osteo-Ti INTRODUCTION This handbook has been designed to give you a basic understanding of dental implants and related surgery procedures. As with all
INTRODUCTION TO OSTEO-TI IMPLANTS; A NURSES MANUAL Osteo-Ti INTRODUCTION This handbook has been designed to give you a basic understanding of dental implants and related surgery procedures. As with all
Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips
 Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet
 Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital. If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life.
 Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life. Easy read This booklet is about a germ called MRSA. It is an Easy
Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life. Easy read This booklet is about a germ called MRSA. It is an Easy
Throughout this reference summary, you will find out what massage therapy is, its benefits, risks, and what to expect during and after a massage.
 Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Managing Mouth Sores
 Managing Mouth Sores The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Managing Mouth Sores The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Changes in the Jaw Bones, Teeth and Face after Tooth Loss
 Changes in the Jaw Bones, Teeth and Face after Tooth Loss The loss of teeth create many problems from the dissolving away of bone structure, loss of support for the face giving an increased appearance
Changes in the Jaw Bones, Teeth and Face after Tooth Loss The loss of teeth create many problems from the dissolving away of bone structure, loss of support for the face giving an increased appearance
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know. Patient information Leaflet
 Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
PROTECT YOURSELF PROTECT YOUR FAMILY PROTECT YOUR COMMUNITY from Ebola
 PROTECT YOURSELF PROTECT YOUR FAMILY PROTECT YOUR COMMUNITY from Ebola Things Everyone Should Know and Do gchv flipbook for Interpersonal Communication And Partners What are the signs and symptoms of Ebola?
PROTECT YOURSELF PROTECT YOUR FAMILY PROTECT YOUR COMMUNITY from Ebola Things Everyone Should Know and Do gchv flipbook for Interpersonal Communication And Partners What are the signs and symptoms of Ebola?
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
 SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine
 For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant NP = Navelbine (vinorelbine), cisplatin ABOUT THIS
For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant NP = Navelbine (vinorelbine), cisplatin ABOUT THIS
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks
 Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Surface Decoration. Design techniques used to put on the surface of the pottery. Slip Oxides Glaze Embossed Incised Wax on wet Altered from the wheel
 Surface Decoration Design techniques used to put on the surface of the pottery. Slip Oxides Glaze Embossed Incised Wax on wet Altered from the wheel Slip How to apply slip Colored slip is intended to add
Surface Decoration Design techniques used to put on the surface of the pottery. Slip Oxides Glaze Embossed Incised Wax on wet Altered from the wheel Slip How to apply slip Colored slip is intended to add
Dental Health in Teens DENTAL INJURIES & USING MOUTH GUARDS
 Dental Health in Teens DENTAL INJURIES & USING MOUTH GUARDS S h a r e t h e C a r e San Diego County Health and Human Services Agency Statistics on Dental Injuries from Sports More than 5 million teeth
Dental Health in Teens DENTAL INJURIES & USING MOUTH GUARDS S h a r e t h e C a r e San Diego County Health and Human Services Agency Statistics on Dental Injuries from Sports More than 5 million teeth
Ancillary Staff Training
 Ancillary Staff Training Goals of Infection Prevention Protect the patients Protect the staff Prevent spread of diseases How Does The Virus Spread Between People? Direct contact through broken skin, mouth,
Ancillary Staff Training Goals of Infection Prevention Protect the patients Protect the staff Prevent spread of diseases How Does The Virus Spread Between People? Direct contact through broken skin, mouth,
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Melbourne Children s Eye Clinic. Strabismus Surgery for Children
 Melbourne Children s Eye Clinic Strabismus Surgery for Children Why operate on turned eyes? Surgery for turned eyes aims to improve the alignment of the eyes, that is, to make the eyes look straight. The
Melbourne Children s Eye Clinic Strabismus Surgery for Children Why operate on turned eyes? Surgery for turned eyes aims to improve the alignment of the eyes, that is, to make the eyes look straight. The
Minor Lid Surgery. Information for patients
 Minor Lid Surgery Information for patients This leaflet has been produced to give you information about the problems you have been having with your eyelid. If you have any questions or require further
Minor Lid Surgery Information for patients This leaflet has been produced to give you information about the problems you have been having with your eyelid. If you have any questions or require further
How To Care For A Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
Medication Information. (a pix a ban)
 Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
Off to the best start. Important information about feeding your baby
 Off to the best start Important information about feeding your baby mum s milk the best start for your baby What happens in your baby s first years has a big effect on how healthy he or she will be in
Off to the best start Important information about feeding your baby mum s milk the best start for your baby What happens in your baby s first years has a big effect on how healthy he or she will be in
Medication Information. (Ri va rox xa - ban)
 Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication are: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication are: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
DID YOU KNOW? A SORE THROAT CAN KILL YOUR STUDENT
 DID YOU KNOW? A SORE THROAT CAN KILL YOUR STUDENT Each year, more than 60 Fijians die of Rheumatic Heart Disease and it all starts with an untreated sore throat. TEACHING PROGRAM FOR SCHOOLS ACROSS FIJI
DID YOU KNOW? A SORE THROAT CAN KILL YOUR STUDENT Each year, more than 60 Fijians die of Rheumatic Heart Disease and it all starts with an untreated sore throat. TEACHING PROGRAM FOR SCHOOLS ACROSS FIJI
Anyone who has difficulty moving can get a pressure sore. But you are more likely to get one if you:
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Pressure sores Anyone can get a pressure sore if they sit or lie still for too long without moving. People who are old or very ill are most likely to get them. Careful
Patient information from the BMJ Group Pressure sores Anyone can get a pressure sore if they sit or lie still for too long without moving. People who are old or very ill are most likely to get them. Careful
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Staying on Track with TUBERCULOSIS. Medicine
 Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Tobacco Addiction. Why does it seem so hard to stop smoking? What's in cigarettes? What if I smoke just a few cigarettes a day?
 Tobacco Addiction Why does it seem so hard to stop smoking? Smoking causes changes in your body and in the way you act. The changes in your body are caused by an addiction to nicotine. The changes in the
Tobacco Addiction Why does it seem so hard to stop smoking? Smoking causes changes in your body and in the way you act. The changes in your body are caused by an addiction to nicotine. The changes in the
