CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION. Airway must be open so oxygen can enter the body.
|
|
|
- Nancy Flowers
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent worsening of the condition. Promote the casualty s recovery. Emergency Aid Emergency aid depends on the ABC of life: Airway must be open so oxygen can enter the body. Breathing must take place so oxygen can enter the bloodstream via the lungs. Circulation heart must beat to ensure blood travels around the body and is not lost through the result of injury. The initial assessment of the casualty consists of: DANGER RESPONSE AIRWAY BREATHING CIRCULATION Remember this as Dr ABC! Recovery Position All unconscious casualties must be placed in the recovery position. This is to: Stop the tongue from blocking the throat. Allow fluid to drain from the mouth and reduce the risk of inhaling stomach contents. The aim is to keep head, neck and back aligned, while bent limbs keep the body propped in a comfortable and secure position. If you are forced to leave the casualty, the recovery position will minimise the risks. Beware of neck or spinal injury. Take more care and use extra help if this is suspected. CASAID Page 1 of FA01-08HO
2 RESUSCITATION Mouth to Mouth Ventilation Air breathed in contains 21% oxygen and air breathed out contains 16% oxygen. This is sufficient to ensure that the cells of the body, especially the brain, obtain sufficient oxygen to stay alive when air is blown into the casualty s lungs. 1. Carry out initial assessment as far as breathing check. 2. Close the casualty s nose by pinching it, and seal around casualty s mouth with your lips. 3. Blow into casualty s mouth for two seconds until chest rises, maintaining jaw lift/head tilt and nose seal. Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation If there is no pulse this indicates that the heart is not beating. Oxygen which is air breathed into the lungs cannot be circulated around the body and to the brain cells in particular unless the heart is able to pump the oxygenated blood around the body. You will have to provide an artificial circulation by means of chest compressions. Chest compressions must be combined with mouth to mouth ventilation to maintain both the circulation and the supply of oxygen to the brain. 1. If no pulse, locate one of the lower ribs with two fingers, move fingers to where the ribs meet the breastbone. 2. Place fingers on the lower breastbone with the heel of the other hand immediately above the two fingers and in the centre of the chest ( landmark the exact position for next time). 3. Place the heel of the first hand over the other hand with fingers of both hands interlocked. 4. Lean well over the casualty, arms straight and elbows locked, and press down 4 5 cms. 5. Without removing your hands compress the chest 15 times at the rate of 100 compressions per minute for 8 9 seconds. 6. Give two breaths of mouth to mouth ventilation Getting Help The rules for deciding when to leave your casualty and get help depend on whether you have someone to help or are alone, and whether the absence of breathing is due to injury or drowning, or some other condition such as a heart attack. If breathing/pulse fails as a result of a heart attack the one single factor which will save the casualty is the early arrival of an ambulance with a defibrillator preferably within eight minutes. In these circumstances get help on the way as soon as it is detected that there is no breathing. CASAID Page 2 of FA01-08HO
3 STOPPING BLEEDING, HOW TO APPLY A DRESSING AND TREATMENT FOR SHOCK, CUTS AND GRAZES Severe Bleeding 1. Apply direct pressure to control the bleeding by pressing with fingers or the palm of the hand on the wound. Press over a clean dressing if one is immediately available. 2. Raise and support the injured part if the wound is on a limb and you do not suspect a fracture. 3. Place a sterile or clean dressing over the wound. Ensure that it is large enough to extend well beyond the edges of the wound. Press down firmly and secure with the bandage attached to the dressing or with a separate bandage. 4. Tie the bandage firmly enough to control the bleeding, but not so tight as to cut off circulation. 5. Raise and support the injured part put an injured arm into an elevation sling, or improvise. 6. If bleeding continues, apply up to two more dressings on top of the original one and bandage firmly. Do not remove dressings once applied. 7. Treat for shock. If no sterile dressing is available, improvise with any suitable material. Indirect Pressure Indirect pressure must be applied only in the very exceptional case of an injury to a limb where direct pressure is not possible or effective. It is applied to the main artery which supplies the limb and should be attempted only when the technique has been properly taught. Do not apply indirect pressure for more than 10 minutes. Do not apply a tourniquet. Embedded Foreign Body Never attempt to remove a large foreign body embedded in a wound. The treatment is modified as follows: 1. Apply direct pressure by squeezing the sides of the wound together alongside the foreign body. 2. Raise and support the affected limb. 3. Place a piece of gauze or other dressing over and around the foreign body. 4. Place pads of cotton wool or other material around the foreign body until high enough to prevent any pressure on it. CASAID Page 3 of FA01-08HO
4 5. Secure with a firm bandage. 6. Treat for shock. Treatment for Shock Shock is a serious condition which may prove fatal. It is caused when the pressure or volume of circulating blood falls. This happens when the heart pump fails so that the pressure of the circulating blood becomes weak. It also happens when the volume of circulating blood falls, as in all cases of external or internal bleeding, or burns. The treatment for shock is: 1. Treat the cause, e.g., stop bleeding. 2. Keep the casualty still. Lay him down with his head low and turned to one side. 3. Reassure the casualty. 4. Raise and support the casualty s legs. 5. Loosen any tight or restrictive clothing. 6. Shelter from the cold and keep comfortable. Do not overheat. 7. Check breathing rate, pulse and level of response at ten minute intervals. 8. If breathing becomes difficult or vomiting occurs, place in the Recovery position. 9. If the casualty becomes unconscious, follow the ABC rule. Do not move the casualty unnecessarily Do not give anything to eat or drink (moisten his lips with water if necessary) Do not use hot water bottles Do not allow the casualty to smoke Treatment for Cuts and Grazes Trivial cuts and grazes which involve only slight bleeding should be treated as follows: 1. If possible, wash hands before dealing with the wound. 2. Lightly rinse the wound with running water, if available, until it is clean. 3. Temporarily protect the wound with a sterile swab. Clean the surrounding area with water and soap, if available. Wipe away from the wound using each swab once only. 4. Take care not to wipe off any blood clots. 5. Dab gently to dry. CASAID Page 4 of FA01-08HO
5 6. If bleeding persists, apply direct pressure. 7. Cover with an adhesive dressing or appropriate dressing. 8. If in any doubt about the injury, seek medical aid. Tetanus Infection Every wound carries the risk of tetanus infection. Any casualty with a wound who has not had an anti-tetanus injection or whose last injection was more than five years ago should be referred for medical advice. CASAID Page 5 of FA01-08HO
6 FRACTURES AND HOW TO TREAT THEM AND OTHER INJURIES Fractures A fracture is a broken or cracked bone, they may be either: Closed. This is where there is no external injury. Open. The bone may protrude through the skin. Signs and Symptoms of Fractures Not all the signs and symptoms will be present. Some may develop later. Those which may be se or described by the casualty are: The casualty may have felt or heard the bone snap. Pain, increased by movement. Inability to move the injured part normally. en Closed Open Tenderness on gentle pressure at or near the fracture site, with swelling and/or bruising in that area. Deformity, such as a limb at an unusual angle or other abnormality, especially when comparing one side of the body with the other. Signs and symptoms of shock, particularly in the case of closed fractures. Treating Fractures The injured part should be steadied and supported whilst dealing with the more important priorities, if this is possible without hindering the immediate treatment. This applies particularly to putting the casualty into the Recovery position which should be done with regard for the other injuries. Open wounds with severe bleeding must be immobilised and then treated as a bleed, treating a bone protruding outside the wound as for an embedded foreign body. Immobilising Fractures If it is essential for first aiders to move the casualty or the ambulance is likely to be delayed, immobilise the injured part by fixing it to another part of the body with padding and bandages. Blisters and Stings Blisters Blisters are caused by friction or heat. Unless a blister breaks or is likely to be further damaged it requires no treatment. If it does break or is likely to be further damaged apply a dressing large enough to extend well beyond the blistered area do not break a blister. Stings Insect stings may be painful but do not usually require first aid treatment. They may cause a problem in people who are allergic to the poison in the sting, in the case of multiple stings from a swarm of insects or where stings in the mouth have caused swelling. The general treatment is to: CASAID Page 6 of FA01-08HO
7 1. If the sting is embedded in the skin, grasp the sting with tweezers as near as possible to the skin surface and remove. 2. Relieve pain and swelling by applying a cold compress. 3. If pain or swelling increases over the next day, seek medical aid. Stings in the Mouth or Throat The treatment for stings in the mouth or throat resulting in swelling is to: 1. Give the casualty ice to suck, or rinse the mouth with cold water. 2. If breathing is difficult place in Recovery position. 3. Arrange removal to hospital. Burns Burns are injuries to the body tissues which may be caused in the following ways: Dry Burns. Caused by contact with flames, hot objects and friction. Scalds. Caused by wet heat such as steam, hot water or fat. Cold Burns. Caused by contact with a very cold object. Chemical Burns. Caused by contact with chemicals (including some household items). Electrical Burns. Caused by electric current or lightning. Radiation Burns. Caused by rays from the sun. Most burns need medical attention, including: Any burn more than 25 mm (1 inch) square in area. All burns resulting from electrical contact. Any deep burn involving all layers of the skin. Treatment 1. If clothing is on fire, put out the flames by wrapping the casualty tightly in a coat or heavy material that will not catch 2. Cool as quickly as possible by flooding the affected area with cold water. For minor burns and scalds place the injured part under slowly running cold water or immerse in cold water for at least ten minutes, but longer if the pain persists. 3. Carefully remove any clothing soaked in boiling fluid, such as hot tea or coffee. 4. Do not remove burnt clothing or anything that is sticking to the burn. 5. Reassure the casualty. 6. Remove rings, watches etc., before the affected area begins to swell. 7. Cover the burn with a sterile dressing. 8. Immobilise a badly burnt limb. 9. Treat for shock. 10. If the casualty is conscious give frequent sips of cold water. Do not: Use plasters or adhesive materials. Use any creams or lotions. Break blisters. Remove loose skin or otherwise interfere with the injury in any way. CASAID Page 7 of FA01-08HO
8 Injury to Joints and Muscles Sprains and Strains A sprain occurs when ligaments and issues at a joint are wrenched or torn, causing pain and tenderness at the joint, increased by movement. Swelling will occur and later, bruising. A strain is the overstretching and possible tearing of a muscle, causing pain at the site of the injury with stiffness and cramp. Treatment Remember to use the mnemonic: R I C E R Rest and support the joint in the most comfortable position. I Ice bag, or cold compress, applied for 30 minutes if the sprain is recent. C Compress, by applying a firm bandage over a good layer of cotton wool. E Elevate the injured limb. Note: If in doubt, treat as a fracture. Dislocation A dislocation is the displacement of a bone at a joint, usually shoulder, elbow, thumb, finger or jaw. Symptoms and signs include severe and sickening pain at the joint with immobility of the joint. The joint will appear misshapen and swelling will occur. To treat a dislocation: Do not attempt to reduce the dislocation by moving the bones to their normal position. Support and secure the injured part in the most comfortable position using padding, bandages and slings. Remove to hospital. Note: If in doubt, treat as a fracture. Foreign Body in the Ear or Nose An insect in the ear may be removed by tilting the casualties head and flooding the ear with tepid water. Otherwise do not attempt to remove foreign bodies from the ear or nose seek medical aid or remove to hospital. CASAID Page 8 of FA01-08HO
First Aid Multiple Choice Test
 First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
MRC Medical Jeopardy Feud List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions
 List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS
 CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
Heart information. CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation
 Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
American Red Cross First Aid EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
FIRST AID TEST. 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988. www.schoolbusing.com. Revised April 21, 2008 - 1 -
 FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
5420-R STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods
 STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
2. (U4C2L3:F2) If your friend received a deep cut on her wrist, what would you do?
 Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Types of electrical injuries
 Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff
 Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Scout Skills... Simple First Aid
 Scout Skills... Simple First Aid Item Code FS315077 Aug/00 Edition no 2 (103851) 0845 300 1818 The practice of first aid is often said to be one of 'common sense' and in many ways this is true, for example,
Scout Skills... Simple First Aid Item Code FS315077 Aug/00 Edition no 2 (103851) 0845 300 1818 The practice of first aid is often said to be one of 'common sense' and in many ways this is true, for example,
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK
 CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY. Emergency Telephone Number 112
 IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
Dressing and bandage
 Dressing and bandage Mihajlo Lojpur, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION The terms dressing and bandage are often used synonymously. In fact, the term dressing refers more correctly to the primary layer in contact
Dressing and bandage Mihajlo Lojpur, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION The terms dressing and bandage are often used synonymously. In fact, the term dressing refers more correctly to the primary layer in contact
EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES
 T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
Emergency Action Plans
 Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
Upon completion of this course, the healthcare providers should be able to:
 First Aid WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed May, 2016, Expires May, 2018 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2016 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC By Wanda Lockwood,
First Aid WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed May, 2016, Expires May, 2018 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2016 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC By Wanda Lockwood,
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Injury Law Center OTHER INJURIES
 Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. OTHER INJURIES
Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. OTHER INJURIES
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
MEASURING VITAL SIGNS TRAINING CHECKLIST
 Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
12/5/2012. Introduction. Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries. Recognizing and Caring for Serious Head, Neck and Back Injuries
 Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter
 Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Taking Out a Tooth. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! CHAPTER11
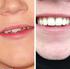 159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
THE SHIP CAPTAIN S MEDICAL GUIDE
 THE SHIP CAPTAIN S MEDICAL GUIDE 5 Introduction When a ship is in port, or near to port where hospital and other expert medical attention are available, the first aid treatment necessary aboard ship is
THE SHIP CAPTAIN S MEDICAL GUIDE 5 Introduction When a ship is in port, or near to port where hospital and other expert medical attention are available, the first aid treatment necessary aboard ship is
First aid. Priorities. Introduction. Priorities
 5 Introduction When a ship is in port, or near to port where hospital and other expert medical attention are available, the first aid treatment necessary aboard ship is similar to that practised ashore.
5 Introduction When a ship is in port, or near to port where hospital and other expert medical attention are available, the first aid treatment necessary aboard ship is similar to that practised ashore.
How to treat your injured neck
 How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
First aid guidance note
 Document control information First aid guidance note Published document name: First-aid-gn.pdf Date issued: July 2012 Version: 2.0 Previous review dates: Next review date: Related documents: Governing
Document control information First aid guidance note Published document name: First-aid-gn.pdf Date issued: July 2012 Version: 2.0 Previous review dates: Next review date: Related documents: Governing
Keeping your lungs healthy
 Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
Recent Injuries. www.physiofirst.org.uk
 Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Basic First Aid Tutorial
 Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
How To Manage A Catastrophic Injury
 Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
Getting Your Hand Moving After a Wrist Fracture
 Information for patients Getting Your Hand Moving After a Wrist Fracture Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703318 DPS ref: 06175-14(RP) Issue 1: April 2015 Review date: March 2018 The Ipswich Hospital
Information for patients Getting Your Hand Moving After a Wrist Fracture Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703318 DPS ref: 06175-14(RP) Issue 1: April 2015 Review date: March 2018 The Ipswich Hospital
CPR/First Aid. Lesson 12 Injuries to Muscles, Bones & Joints
 CPR/First Aid Lesson 12 Injuries to Muscles, Bones & Joints 1 Muscles Muscles are soft tissues. Your body has over 600 different muscles. Injuries to the brain, spinal cord or nerves can affect the muscles.
CPR/First Aid Lesson 12 Injuries to Muscles, Bones & Joints 1 Muscles Muscles are soft tissues. Your body has over 600 different muscles. Injuries to the brain, spinal cord or nerves can affect the muscles.
HALO ORTHOSIS. 1. The ring and pins. 2. The vest. 3. The superstructure (uprights that connect the ring to the vest)
 UM Orthotics & Prosthetics Center UM Orthopaedics UM Neurosurgery HALO ORTHOSIS HALO Front View HALO Back View You have been placed in a halo vest. This orthosis (brace) is used to immobilize a neck fracture
UM Orthotics & Prosthetics Center UM Orthopaedics UM Neurosurgery HALO ORTHOSIS HALO Front View HALO Back View You have been placed in a halo vest. This orthosis (brace) is used to immobilize a neck fracture
How To Recover From A Surgical Wound From A Cast
 Care of Your Wounds After Amputation Surgery by Paddy Rossbach, RN Depending on the reason for your amputation and the state of your limb at the time of surgery, definitive closure of the wound may take
Care of Your Wounds After Amputation Surgery by Paddy Rossbach, RN Depending on the reason for your amputation and the state of your limb at the time of surgery, definitive closure of the wound may take
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response
 Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Arthroscopic shoulder stabilisation. Patient Information to be retained by patient
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Shoulder instability The shoulder is the most common joint in the body to dislocate.
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Shoulder instability The shoulder is the most common joint in the body to dislocate.
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
Total hip replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
THE CONDENSED GUIDE TO OUTDOOR FIRST AID
 THE CONDENSED GUIDE TO OUTDOOR FIRST AID Part 1: The Boring Basics planning & preparation Slides used in presentation to Christchurch Tramping Club by Cathy Harlow, 19 August 2010. THE 7 P S OF PLANNING:
THE CONDENSED GUIDE TO OUTDOOR FIRST AID Part 1: The Boring Basics planning & preparation Slides used in presentation to Christchurch Tramping Club by Cathy Harlow, 19 August 2010. THE 7 P S OF PLANNING:
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course
 Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Having a circumcision information for men
 Having a circumcision information for men This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a circumcision. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you
Having a circumcision information for men This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a circumcision. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients
 let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Spinal Cord Injury Education. Common Medical Problems Following Spinal Cord Injury
 Spinal Cord Injury Education Common Medical Problems Following Spinal Cord Injury Common Medical Complications After SCI, your body is vulnerable to various complications This presentation gives a brief
Spinal Cord Injury Education Common Medical Problems Following Spinal Cord Injury Common Medical Complications After SCI, your body is vulnerable to various complications This presentation gives a brief
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
CHAPTER 2 APPROACH TO THE INCIDENT
 CHAPTER 2 APPROACH TO THE INCIDENT Reassuring the casualty is very important in first aid and the best reassurance for both casualty and bystanders is a confident first aider taking decisive action. In
CHAPTER 2 APPROACH TO THE INCIDENT Reassuring the casualty is very important in first aid and the best reassurance for both casualty and bystanders is a confident first aider taking decisive action. In
Objectives. Burn Assessment and Management. Questions Regarding the Case Study. Case Study. Patient Assessment. Patient Assessment
 Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter
 Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Safety Point: Preparing Your First Aid Kit
 Safety Point: Preparing Your First Aid Kit We all have things in our home that keep us safe, healthy, and happy: Lots of food and water Clothes that keep us warm and dry Comfortable bed and pillow Toothbrush
Safety Point: Preparing Your First Aid Kit We all have things in our home that keep us safe, healthy, and happy: Lots of food and water Clothes that keep us warm and dry Comfortable bed and pillow Toothbrush
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Heat Illnesses. Common Heat Rash Sites
 Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Almond SPAMANICURE. Step-by-Step Guide INDULGENT AND RELAXING
 Step-by-Step Guide Almond SPAMANICURE INDULGENT AND RELAXING 60 MIN A journey cradled in sweet almond and jojoba oils and vitamin E. A soothing menu entrée to comfort and indulge clients time after time.
Step-by-Step Guide Almond SPAMANICURE INDULGENT AND RELAXING 60 MIN A journey cradled in sweet almond and jojoba oils and vitamin E. A soothing menu entrée to comfort and indulge clients time after time.
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD
 THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet
 Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
call 811 to get advice from a nurse, or have someone drive the patient to a hospital Emergency Department. Patients should NOT drive themselves.
 Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Infant CPR. What You Need to Know. How to Do Infant CPR
 Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Preparing for the Unexpected www.redcross.org
 Terrorism Preparing for the Unexpected www.redcross.org A1366 Oct. 2001 An American Red Cross mobile service center stationed at the Pentagon Sept. 18 shows one small part of the ongoing response you can
Terrorism Preparing for the Unexpected www.redcross.org A1366 Oct. 2001 An American Red Cross mobile service center stationed at the Pentagon Sept. 18 shows one small part of the ongoing response you can
Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis
 Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan
 Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Sterile Dressing Change - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Sterile Dressing Change - The James A dressing protects your catheter site and helps reduce the risk of infection. You will need
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Sterile Dressing Change - The James A dressing protects your catheter site and helps reduce the risk of infection. You will need
PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL DAY OF SURGERY
 PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL DAY OF SURGERY PREPARING YOUR SKIN BEFORE SURGERY PRE-OP HIBICLENS BATHING INSTRUCTIONS: General Information: Because the skin is not sterile, it is important to make sure
PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL DAY OF SURGERY PREPARING YOUR SKIN BEFORE SURGERY PRE-OP HIBICLENS BATHING INSTRUCTIONS: General Information: Because the skin is not sterile, it is important to make sure
A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca
 www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
Bone and Joint Injuries
 Bone and Joint Injuries Lesson Length 2 hours, 15 minutes Materials, Equipment and Supplies n Newsprint and markers n Wilderness and Remote First Aid Emergency Reference Guide (one for each participant)
Bone and Joint Injuries Lesson Length 2 hours, 15 minutes Materials, Equipment and Supplies n Newsprint and markers n Wilderness and Remote First Aid Emergency Reference Guide (one for each participant)
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES
 RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
Lymphedema of the Head and Neck After Surgery or Radiation
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lymphedema of the Head and Neck After Surgery or Radiation The lymph system helps to get rid of waste products from your cells and helps your body fight infection.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lymphedema of the Head and Neck After Surgery or Radiation The lymph system helps to get rid of waste products from your cells and helps your body fight infection.
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes
 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes UHN People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to keep your feet healthy. Please visit the UHN Patient
Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes UHN People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to keep your feet healthy. Please visit the UHN Patient
MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES
 Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Part 4. Emergencies and Crashes
 83 Part 4 Emergencies and Crashes 84 The previous chapters have provided advice that can help avoid emergencies. It is vital that you study and learn that information and apply it whenever you are driving
83 Part 4 Emergencies and Crashes 84 The previous chapters have provided advice that can help avoid emergencies. It is vital that you study and learn that information and apply it whenever you are driving
Exercise After Breast Surgery. Post Mastectomy Therapy
 Exercise After Breast Surgery Post Mastectomy Therapy Dear Patient, Breast cancer is a journey and you have made it this far successfully. This booklet will help you continue your journey to recovery.
Exercise After Breast Surgery Post Mastectomy Therapy Dear Patient, Breast cancer is a journey and you have made it this far successfully. This booklet will help you continue your journey to recovery.
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
Chapter 6. Hemorrhage Control UNDER FIRE KEEP YOUR HEAD DOWN
 Hemorrhage Control Chapter 6 Hemorrhage Control The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel
Hemorrhage Control Chapter 6 Hemorrhage Control The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Collarbone (Clavicle) Fractures: A Guide to Recovery After Surgery
 The collarbone or 'clavicle' is a bone that connects the shoulder blade to the chest bone. Fractures or breaks of the clavicle are common injuries during childhood and with falls onto the shoulder. The
The collarbone or 'clavicle' is a bone that connects the shoulder blade to the chest bone. Fractures or breaks of the clavicle are common injuries during childhood and with falls onto the shoulder. The
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
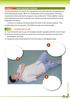 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
