Understanding and Configuring the ip unnumbered Command
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Pope
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Understanding and onfiguring the ip unnumbered ommand Document D: ontents ntroduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions What is an Unnumbered nterface? P and P Unnumbered onfiguration Examples Same Major Net, Different Subnets Different Major Nets, No Subnets Major Net with Subnet, Major Net with No Subnet Two Different Major Nets and Their Respective Subnets Related nformation ntroduction This document explains the concept of P unnumbered, and provides several configuration examples for reference. The ip unnumbered configuration command allows you to enable P processing on a serial interface without assigning it an explicit P address. The ip unnumbered interface can "borrow" the P address of another interface already configured on the router, which conserves network and address space. Prerequisites Requirements There are no specific requirements for this document. omponents Used This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. onventions For more information on document conventions, refer to isco Technical Tips onventions. What is an Unnumbered nterface? onsider the network shown below. Router A has a serial interface S0 and an Ethernet interface E0.
2 Router A's Ethernet 0 interface can be configured with an P address as shown below: ip address Logically, to enable P on interface S0, you would need to configure a unique P address on it. However, it is also possible to enable P on the Serial interface and bring it up without assigning a unique P address to it. This is done by borrowing an P address already configured on one of the router's other interfaces. To do this, the ip unnumbered interface mode command is used as shown below. ip unnumbered Ethernet 0 The ip unnumbered <type> <number> interface mode command borrows the P address from the specified interface to the interface on which the command has been configured. Use of the ip unnumbered command results in the P address being shared by two interfaces. Thus, in our example, the P address which was configured on the Ethernet interface is also assigned to the Serial interface, and both interfaces involved function normally. This can be verified using the output of the show ip interface brief command, as shown below: RouterA# show ip interface brief nterface P Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet YES manual up up Serial YES manual up up As you can see from the output of the show ip interface brief command above, the serial interface has an P address identical to that of the Ethernet interface, and both interfaces are fully functional. The interface that borrows its address from one of the router's other functional interfaces is called the "unnumbered interface". n our example, Serial 0 is the unnumbered interface. The only real disadvantage that the unnumbered interface suffers from is that it is unavailable for remote testing and management. You should also remember that the unnumbered interface should borrow its address from an interface that is up and running. f the unnumbered interface is pointing to an interface that is not functional (that is, which does not show "nterface status UP", "Protocol UP"), the unnumbered interface does not work. This is precisely why it is recommended that the unnumbered interface point to a loopback interface since loopbacks do not fail. Finally, remember that the ip unnumbered command works on point to point interfaces only. When you configure the command on the Multiaccess interface (that is, Ethernet) or the loopback interface, the following messages are displayed: RouterA(config)# int e0 RouterA(config if)# ip unnumbered serial 0 Point to point (non multi access) interfaces only RouterA(config if)# ip unnumbered loopback 0 Point to point (non multi access) interfaces only
3 P and P Unnumbered On a isco router, every interface connecting to a network segment must belong to a unique subnet. Directly connected routers have interfaces connecting to the same network segment and are assigned P addresses from the same subnet. f a router needs to send data to a network that is not directly connected, it looks in its routing table and forwards the packet to the next directly connected hop toward the destination. f there is no route in the routing table, the router forwards the packet to its gateway of last resort. When a router that is directly connected to the final destination receives the packet, it delivers the packet directly to the end host. The P routing table contains either subnet routes or major network routes. Each route has one or more directly attached next hop address(es). Subnet routes are aggregated or summarized by default at major network boundaries in order to reduce the size of the routing table. Note: The aggregation scheme discussed above assumes a traditional distance vector routing protocol such as Routing nformation Protocol (RP) or nterior Gateway Routing Protocol (GRP). Let's consider assigning P addresses to the interfaces of a router using a class B network that has been subnetted using eight bits of subnetting. Every interface requires a unique subnet. Although each point to point serial connection has only two end points to address, if we assign an entire subnet to each serial interface, we use 254 available addresses for each interface where only two addresses are needed. f we use P unnumbered on each serial interface, we save address space; the address of a LAN interface is "borrowed" and used as the source address for routing updates and packets sourced from the serial interface. n this way, address space is conserved. P unnumbered only makes sense for point to point links. A router receiving a routing update installs the source address of the update as the next hop in its routing table. Normally, the next hop is a directly connected network node. This is no longer the case if we use P unnumbered because each serial interface "borrows" their P address from a different LAN interface, each in a different subnet and possibly in a different major network. When P unnumbered is configured, routes learned through the P unnumbered interface have the interface as the next hop instead of the source address of the routing update. Thus we avoid an invalid next hop address problem due to the source of the routing update coming from a next hop that is not directly connected. onfiguration Examples Note: The information in these configuration examples is based on isco OS Software version 12.2(10b) and was tested on isco 2500 series routers. Let us look at four different sample configurations for P unnumbered. Note: We could have used loopback interfaces instead of ethernet interfaces. Same Major Net, Different Subnets Figure 1 shows that on either side of the serial link we have the same major net with different subnets. Figure 1 Network Diagram
4 Router ip address network ip address Router # show ip route /26 is subnetted, 3 subnets network [100/8976] via , 00:00:02, Serial is directly connected, Ethernet [100/8976] via , 00:00:02, Serial0 Router # ping Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 28/30/32 ms # show ip route /26 is subnetted, 3 subnets is directly connected, Ethernet [100/8976] via , 00:00:02, Serial [100/8976] via , 00:00:02, Serial0 Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 32/32/32 ms The route information about subnets is correctly maintained in this scenario. Different Major Nets, No Subnets Figure 2 shows that on either side of the serial link we have different major nets and no subnets. Figure 2 Network Diagram Router
5 ip address network Router # show ip route ip address /16 is directly connected, Ethernet0 network /16 [100/8976] via , 00:01:26, Serial0 Router # ping Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 28/28/28 ms # show ip route /16 [100/8976] via , 00:00:21, Serial /16 is directly connected, Ethernet0 Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 28/29/32 ms Major Net with Subnet, Major Net with No Subnet Figure 3 shows that on one side of the serial link we have a major net with a subnet, and on the other side a major net with no subnet. Figure 3 Network Diagram Router ip address network ip address
6 Router # show ip route /26 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Ethernet /16 [100/8976] via , 00:00:03, Serial0 Router # ping Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 28/31/32 ms # show ip route /16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /32 [100/8976] via , 00:00:48, Serial /16 [100/8976] via , 00:00:48, Serial /16 is directly connected, Ethernet0 Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 28/29/32 ms Note: Prior to isco OS software version 11.0(2), you are required to put a static route for the majornet /16 in. n this scenario, the subnet information gets lost since it's treated as a host route. n isco OS software version 11.0(2) and higher, nterior Gateway Routing Protocol (GRP) and Routing nformation Protocol (RP) fix this problem by sending the summary route for the majornet across the unnumbered point to point links. Two Different Major Nets and Their Respective Subnets Figure 4 shows that on both sides of the serial link we have two different major nets with respective subnets. Figure 4 Network Diagram Router ip address ip address
7 network network Router # show ip route /26 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Ethernet /16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /16 [100/8976] via , 00:00:02, Serial /32 [100/8976] via , 00:00:02, Serial0 Router # ping Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 32/81/280 ms # show ip route /16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /32 [100/8976] via , 00:00:22, Serial /16 [100/8976] via , 00:00:22, Serial /26 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Ethernet0 Sending 5, 100 byte MP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 28/31/32 ms Note: n isco OS software versions earlier than 11.0(2), you are required to put a static route for the majornet /16 in and /16 in Router n this scenario, the subnet information gets lost since it's treated as a host route. n isco OS software version 11.0(2) and later, GRP and RP fix this problem by sending the summary route for the majornet across the unnumbered point to point links. Related nformation P Routed Protocols Support Page P Routing Support Page Technical Support isco Systems ontacts & Feedback Help Site Map isco Systems, nc. All rights reserved. Terms & onditions Privacy Statement ookie Policy Trademarks of isco Systems, nc. Updated: Oct 26, 2005 Document D: 13786
- IGRP - IGRP v1.22 Aaron Balchunas
 1 - GRP - GRP (nterior Gateway Routing Protocol) GRP is a isco-proprietary Distance-Vector protocol, designed to be more scalable than RP, its standardized counterpart. GRP adheres to the following Distance-Vector
1 - GRP - GRP (nterior Gateway Routing Protocol) GRP is a isco-proprietary Distance-Vector protocol, designed to be more scalable than RP, its standardized counterpart. GRP adheres to the following Distance-Vector
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands
 Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
- Classful vs. Classless Routing -
 lassful vs lassless outing v1.10 Aaron Balchunas 1 - lassful vs. lassless outing - lassful vs lassless routing protocols lassful routing protocols do not send subnet mask information with their routing
lassful vs lassless outing v1.10 Aaron Balchunas 1 - lassful vs. lassless outing - lassful vs lassless routing protocols lassful routing protocols do not send subnet mask information with their routing
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
- Routing Information Protocol -
 1 - Routing Information Protocol - RIP (Routing Information Protocol) RIP is a standardized Distance Vector protocol, designed for use on smaller networks. RIP was one of the first true Distance Vector
1 - Routing Information Protocol - RIP (Routing Information Protocol) RIP is a standardized Distance Vector protocol, designed for use on smaller networks. RIP was one of the first true Distance Vector
Understanding Route Aggregation in BGP
 Understanding Route Aggregation in BGP Document ID: 5441 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Aggregate Without the as set Argument Aggregate with
Understanding Route Aggregation in BGP Document ID: 5441 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Aggregate Without the as set Argument Aggregate with
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF
 OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users
 IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users Document ID: 13788 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Additional Information Conventions Understanding IP Addresses Network Masks
IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users Document ID: 13788 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Additional Information Conventions Understanding IP Addresses Network Masks
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP. Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration. VoIP Network Switch. Control Network Switch
 Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP Vocia software rev. 1.4 or higher required Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration The Vocia Message Server 1 (MS-1) has a number of roles in a Vocia Paging
Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP Vocia software rev. 1.4 or higher required Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration The Vocia Message Server 1 (MS-1) has a number of roles in a Vocia Paging
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers
 Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch
 1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch If a network is not available, or if it is desired to keep the WX64 and PC(s) completely separated from other computers, a simple network
1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch If a network is not available, or if it is desired to keep the WX64 and PC(s) completely separated from other computers, a simple network
Part A:Background/Preparation
 Lab no 1 PC Network TCP/IP Configuration In this lab we will learn about Computer Networks Configuration Introduction to IP addressing Identify tools used for discovering a computer s network configuration
Lab no 1 PC Network TCP/IP Configuration In this lab we will learn about Computer Networks Configuration Introduction to IP addressing Identify tools used for discovering a computer s network configuration
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. 1. IP address for this host computer 2. Subnet mask 3. Default gateway address
 Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
7 TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL/ INTERNET PROTOCOL (TCP/IP)
 7 TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL/ INTERNET PROTOCOL (TCP/IP) PROJECTS Project 7.1 Project 7.2 Project 7.3 Project 7.4 Project 7.5 Understanding Key Concepts Configuring TCP/IP Properties Comparing Name
7 TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL/ INTERNET PROTOCOL (TCP/IP) PROJECTS Project 7.1 Project 7.2 Project 7.3 Project 7.4 Project 7.5 Understanding Key Concepts Configuring TCP/IP Properties Comparing Name
O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1
![O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1 O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1](/thumbs/39/20242582.jpg) 1 Which two statements are true regarding the advantages of the use of static routes? (Choose increased security reduced effort in configuring routes the administrator maintains control over routing easier
1 Which two statements are true regarding the advantages of the use of static routes? (Choose increased security reduced effort in configuring routes the administrator maintains control over routing easier
Lab#2: IP Addressing and Subnetting
 IP Addressing Lab#2: IP Addressing and Subnetting Each Network Interface Card (NIC or Network card) present in a PC is assigned one Network address called as IP address. This IP address is assigned by
IP Addressing Lab#2: IP Addressing and Subnetting Each Network Interface Card (NIC or Network card) present in a PC is assigned one Network address called as IP address. This IP address is assigned by
Chapter 3: IP Addressing and VLSM
 Chapter 3: IP Addressing and VLSM QUESTION 54 What is the principle reason to use a private IP address on an internal network? A. Subnet strategy for private companies. B. Manage and scale the growth of
Chapter 3: IP Addressing and VLSM QUESTION 54 What is the principle reason to use a private IP address on an internal network? A. Subnet strategy for private companies. B. Manage and scale the growth of
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme
 Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Finding Feature Information Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: August 15, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Finding Feature Information Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: August 15, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice
 BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
One of the most important topics in any discussion of TCP/IP is IP. IP Addressing
 IP Addressing 125 machine, called a RARP server, responds with the answer, and the identity crisis is over. RARP uses the information it does know about the machine s MAC address to learn its IP address
IP Addressing 125 machine, called a RARP server, responds with the answer, and the identity crisis is over. RARP uses the information it does know about the machine s MAC address to learn its IP address
Expert Reference Series of White Papers. Basics of IP Address Subnetting
 Expert Reference Series of White Papers Basics of IP Address Subnetting 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com Basics of IP Address Subnetting Norbert Gregorio, Global Knowledge Instructor Introduction
Expert Reference Series of White Papers Basics of IP Address Subnetting 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com Basics of IP Address Subnetting Norbert Gregorio, Global Knowledge Instructor Introduction
Table of Contents. Cisco IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users
 Table of Contents IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 Additional Information...1 Understanding IP
Table of Contents IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 Additional Information...1 Understanding IP
Networking Basics for Automation Engineers
 Networking Basics for Automation Engineers Page 1 of 10 mac-solutions.co.uk v1.0 Oct 2014 1. What is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)------------------------------------------------------------
Networking Basics for Automation Engineers Page 1 of 10 mac-solutions.co.uk v1.0 Oct 2014 1. What is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)------------------------------------------------------------
DG Forwarding Algorithm
 DG Forwarding Algorithm Host or Router first check if destination on same Network Router multiple interfaces Match found deliver to that Network If not found default router for every router a default router
DG Forwarding Algorithm Host or Router first check if destination on same Network Router multiple interfaces Match found deliver to that Network If not found default router for every router a default router
Troubleshooting IP Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Table of Contents. Cisco How Does Load Balancing Work?
 Table of Contents How Does Load Balancing Work?...1 Document ID: 5212...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Load Balancing...1 Per Destination and
Table of Contents How Does Load Balancing Work?...1 Document ID: 5212...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Load Balancing...1 Per Destination and
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Zarząd (7 osób) F inanse (13 osób) M arketing (7 osób) S przedaż (16 osób) K adry (15 osób)
 QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
Module 10 Subnetting Class A, B and C addresses. Solutions to the Lab Exercises 10.3.5a, 10.3.5b, 10.3.5c and 10.3.5d
 Module 10 Subnetting Class A, B and C addresses Solutions to the Lab Exercises 10.3.5a, 10.3.5b, 10.3.5c and 10.3.5d 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Use the following information and answer the following subnet
Module 10 Subnetting Class A, B and C addresses Solutions to the Lab Exercises 10.3.5a, 10.3.5b, 10.3.5c and 10.3.5d 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Use the following information and answer the following subnet
USER GUIDE. Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6
 KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. USER GUIDE Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6 Contents 1 Connecting to the Kramer Device via the Ethernet Port 1 1.1 Connecting the Ethernet Port Directly
KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. USER GUIDE Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6 Contents 1 Connecting to the Kramer Device via the Ethernet Port 1 1.1 Connecting the Ethernet Port Directly
ASA/PIX: Allow Split Tunneling for VPN Clients on the ASA Configuration Example
 ASA/PIX: Allow Split Tunneling for VPN Clients on the ASA Configuration Example Document ID: 70917 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram Related Products Conventions
ASA/PIX: Allow Split Tunneling for VPN Clients on the ASA Configuration Example Document ID: 70917 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram Related Products Conventions
IP Addressing and Subnetting. 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
IP-6600 Router Configuration Quickstart Backing Up a Broadband Connection with Dialup
 Configuration Quickstart Backing Up a Broadband Connection with Dialup Introduction Broadband network service is becoming a desirable alternative to dialup or leased line service for access to remote networks.
Configuration Quickstart Backing Up a Broadband Connection with Dialup Introduction Broadband network service is becoming a desirable alternative to dialup or leased line service for access to remote networks.
APPENDIX B. Routers route based on the network number. The router that delivers the data packet to the correct destination host uses the host ID.
 APPENDIX B IP Subnetting IP Addressing Routers route based on the network number. The router that delivers the data packet to the correct destination host uses the host ID. IP Classes An IP address is
APPENDIX B IP Subnetting IP Addressing Routers route based on the network number. The router that delivers the data packet to the correct destination host uses the host ID. IP Classes An IP address is
ICS 351: Today's plan
 ICS 351: Today's plan Quiz, on overall Internet function, linux and IOS commands, network monitoring, protocols IPv4 addresses: network part and host part address masks IP interface configuration IPv6
ICS 351: Today's plan Quiz, on overall Internet function, linux and IOS commands, network monitoring, protocols IPv4 addresses: network part and host part address masks IP interface configuration IPv6
Setting up VPN Access for Remote Diagnostics Support
 Setting up VPN Access for Remote Diagnostics Support D. R. Joseph, Inc. supports both dial-up and Internet access for remote support of 3GIBC1 and LF-Sizer control systems. This document describes how
Setting up VPN Access for Remote Diagnostics Support D. R. Joseph, Inc. supports both dial-up and Internet access for remote support of 3GIBC1 and LF-Sizer control systems. This document describes how
Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing
 Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 4, 2007 Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing Akram Al-Rawi College of CS & IT, King Faisal University, Al-Hassa,
Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 4, 2007 Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing Akram Al-Rawi College of CS & IT, King Faisal University, Al-Hassa,
Configuring a Lan-to-Lan VPN with Overlapping Subnets with Juniper NetScreen/ISG/SSG Products
 Application Note Configuring a Lan-to-Lan VPN with Overlapping Subnets with Juniper NetScreen/ISG/SSG Products Version 1.0 January 2008 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089
Application Note Configuring a Lan-to-Lan VPN with Overlapping Subnets with Juniper NetScreen/ISG/SSG Products Version 1.0 January 2008 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089
RIP: Routing Information Protocol
 Laboratory 6 RIP: Routing Information Protocol A Routing Protocol Based on the Distance-Vector Algorithm Objective The objective of this lab is to configure and analyze the performance of the Routing Information
Laboratory 6 RIP: Routing Information Protocol A Routing Protocol Based on the Distance-Vector Algorithm Objective The objective of this lab is to configure and analyze the performance of the Routing Information
Laboratory guide nº 2
 Introduction to Computer Networks (IRC) Licenciatura in Electronics Engineering (LEE) Licenciatura in Communication Networks Engineering (LERC) Laboratory guide nº 2 1 Objectives To familiarize your- self
Introduction to Computer Networks (IRC) Licenciatura in Electronics Engineering (LEE) Licenciatura in Communication Networks Engineering (LERC) Laboratory guide nº 2 1 Objectives To familiarize your- self
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
04 Internet Protocol (IP)
 SE 4C03 Winter 2007 04 Internet Protocol (IP) William M. Farmer Department of Computing and Software McMaster University 29 January 2007 Internet Protocol (IP) IP provides a connectionless packet delivery
SE 4C03 Winter 2007 04 Internet Protocol (IP) William M. Farmer Department of Computing and Software McMaster University 29 January 2007 Internet Protocol (IP) IP provides a connectionless packet delivery
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
You can probably work with decimal. binary numbers needed by the. Working with binary numbers is time- consuming & error-prone.
 IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
IP Routing Features. Contents
 7 IP Routing Features Contents Overview of IP Routing.......................................... 7-3 IP Interfaces................................................ 7-3 IP Tables and Caches........................................
7 IP Routing Features Contents Overview of IP Routing.......................................... 7-3 IP Interfaces................................................ 7-3 IP Tables and Caches........................................
Configuring IP Load Sharing in AOS Quick Configuration Guide
 Configuring IP Load Sharing in AOS Quick Configuration Guide ADTRAN Operating System (AOS) includes IP Load Sharing for balancing outbound IP traffic across multiple interfaces. This feature can be used
Configuring IP Load Sharing in AOS Quick Configuration Guide ADTRAN Operating System (AOS) includes IP Load Sharing for balancing outbound IP traffic across multiple interfaces. This feature can be used
Basic ViPNet VPN Deployment Schemes. Supplement to ViPNet Documentation
 Basic ViPNet VPN Deployment Schemes Supplement to ViPNet Documentation 1991 2015 Infotecs Americas. All rights reserved. Version: 00121-04 90 01 ENU This document is included in the software distribution
Basic ViPNet VPN Deployment Schemes Supplement to ViPNet Documentation 1991 2015 Infotecs Americas. All rights reserved. Version: 00121-04 90 01 ENU This document is included in the software distribution
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
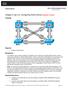 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Troubleshooting Load Balancing Over Parallel Links Using Cisco Express Forwarding
 Page 1 of 16 Troubleshooting Load Balancing Over Parallel Links Using Cisco Express Forwarding Document ID: 18285 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background
Page 1 of 16 Troubleshooting Load Balancing Over Parallel Links Using Cisco Express Forwarding Document ID: 18285 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background
Router and Routing Basics
 Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Instructor Notes for Lab 3
 Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Layer 3 Routing User s Manual
 User s Manual Second Edition, July 2011 www.moxa.com/product 2011 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
User s Manual Second Edition, July 2011 www.moxa.com/product 2011 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
Teldat Router. ARP Proxy
 Teldat Router ARP Proxy Doc. DM734-I Rev. 10.00 November, 2002 INDEX Chapter 1 Introduction...1 1. ARP Proxy... 2 Chapter 2 Configuration...4 1. ARP Proxy Configuration... 5 1.1. Enabling ARP Proxy...
Teldat Router ARP Proxy Doc. DM734-I Rev. 10.00 November, 2002 INDEX Chapter 1 Introduction...1 1. ARP Proxy... 2 Chapter 2 Configuration...4 1. ARP Proxy Configuration... 5 1.1. Enabling ARP Proxy...
BGP Best Path Selection Algorithm
 BGP Best Path Selection Algorithm Document ID: 13753 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Why Routers Ignore Paths How the Best Path Algorithm Works Example: BGP
BGP Best Path Selection Algorithm Document ID: 13753 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Why Routers Ignore Paths How the Best Path Algorithm Works Example: BGP
RIP: Routing Information Protocol
 Laboratory 6 RIP: Routing Information Protocol A Routing Protocol Based on the Distance-Vector Algorithm Objective The objective of this lab is to configure and analyze the performance of the Routing Information
Laboratory 6 RIP: Routing Information Protocol A Routing Protocol Based on the Distance-Vector Algorithm Objective The objective of this lab is to configure and analyze the performance of the Routing Information
IT 3202 Internet Working (New)
 [All Rights Reserved] SLIATE SRI LANKA INSTITUTE OF ADVANCED TECHNOLOGICAL EDUCATION (Established in the Ministry of Higher Education, vide in Act No. 29 of 1995) Instructions for Candidates: Answer any
[All Rights Reserved] SLIATE SRI LANKA INSTITUTE OF ADVANCED TECHNOLOGICAL EDUCATION (Established in the Ministry of Higher Education, vide in Act No. 29 of 1995) Instructions for Candidates: Answer any
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Homework 3 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management
 Homework 3 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw3 Assigned on 2013/9/13, Due 2013/9/24 Hand In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw3_WebSys.docx) using the ECET Lab report
Homework 3 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw3 Assigned on 2013/9/13, Due 2013/9/24 Hand In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw3_WebSys.docx) using the ECET Lab report
Lab 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting
 Lab 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Objective How to identify reasons to use a subnet mask How to distinguish between a default subnet mask and a custom subnet mask What given requirements determine the subnet
Lab 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Objective How to identify reasons to use a subnet mask How to distinguish between a default subnet mask and a custom subnet mask What given requirements determine the subnet
Quick Note 53. Ethernet to W-WAN failover with logical Ethernet interface.
 Quick Note 53 Ethernet to W-WAN failover with logical Ethernet interface. Digi Support August 2015 1 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Introduction... 2 1.2 Assumptions... 3 1.3 Corrections... 3 2 Version...
Quick Note 53 Ethernet to W-WAN failover with logical Ethernet interface. Digi Support August 2015 1 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Introduction... 2 1.2 Assumptions... 3 1.3 Corrections... 3 2 Version...
ASA 8.3 and Later: Mail (SMTP) Server Access on Inside Network Configuration Example
 ASA 8.3 and Later: Mail (SMTP) Server Access on Inside Network Configuration Example Document ID: 113336 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
ASA 8.3 and Later: Mail (SMTP) Server Access on Inside Network Configuration Example Document ID: 113336 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
Cisco Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs
 Table of Contents Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...2 Hardware and Software Versions...3 Configuration Examples...3 Allow a Select Host to Access the Network...3 Allow
Table of Contents Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...2 Hardware and Software Versions...3 Configuration Examples...3 Allow a Select Host to Access the Network...3 Allow
Lecture 15. IP address space managed by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
 Lecture 15 IP Address Each host and router on the Internet has an IP address, which consist of a combination of network number and host number. The combination is unique; no two machines have the same
Lecture 15 IP Address Each host and router on the Internet has an IP address, which consist of a combination of network number and host number. The combination is unique; no two machines have the same
Administrative Distance
 RIP is a distance vector routing protocol. It shares routing information through the local broadcast in every 30 seconds. In this tutorial we will explain RIP routing fundamentals with examples such as
RIP is a distance vector routing protocol. It shares routing information through the local broadcast in every 30 seconds. In this tutorial we will explain RIP routing fundamentals with examples such as
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN
 Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
PIX/ASA: Allow Remote Desktop Protocol Connection through the Security Appliance Configuration Example
 PIX/ASA: Allow Remote Desktop Protocol Connection through the Security Appliance Configuration Example Document ID: 77869 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products
PIX/ASA: Allow Remote Desktop Protocol Connection through the Security Appliance Configuration Example Document ID: 77869 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products
Troubleshooting Tools
 Troubleshooting Tools An overview of the main tools for verifying network operation from a host Fulvio Risso Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Turin) see page 2 Notes n The commands/programs
Troubleshooting Tools An overview of the main tools for verifying network operation from a host Fulvio Risso Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Turin) see page 2 Notes n The commands/programs
How To Understand Bg
 Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
How To Lower Data Rate On A Network On A 2Ghz Network On An Ipnet 2 (Net 2) On A Pnet 2 On A Router On A Gbnet 2.5 (Net 1) On An Uniden Network On
 Lab 8.1.10.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Lab 8.1.10.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3
 Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3 ARP - RFC 826, STD 37 DHCP - RFC 2131 ICMP - RFC 0792, STD 05 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Bootstrapping an end host Learning its own configuration parameters
Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3 ARP - RFC 826, STD 37 DHCP - RFC 2131 ICMP - RFC 0792, STD 05 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Bootstrapping an end host Learning its own configuration parameters
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting
 Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter provides troubleshooting tips and information for your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. After each problem description, instructions are provided
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter provides troubleshooting tips and information for your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. After each problem description, instructions are provided
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Configuring IP Monitoring on an SRX Series Device for the Branch Published: 2014-01-10 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Network Configuration Example Configuring IP Monitoring on an SRX Series Device for the Branch Published: 2014-01-10 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Networking Guide Redwood Manager 3.0 August 2013
 Networking Guide Redwood Manager 3.0 August 2013 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 IP Addresses... 3 1.1.1 Static vs. DHCP... 3 1.2 Required Ports... 4 2 Adding the Redwood Engine to the Network...
Networking Guide Redwood Manager 3.0 August 2013 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 IP Addresses... 3 1.1.1 Static vs. DHCP... 3 1.2 Required Ports... 4 2 Adding the Redwood Engine to the Network...
VPN 3000 Concentrator Bandwidth Management Configuration Example
 VPN 3000 Concentrator Bandwidth Management Configuration Example Document ID: 60329 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram Conventions Configure a Default Bandwidth
VPN 3000 Concentrator Bandwidth Management Configuration Example Document ID: 60329 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram Conventions Configure a Default Bandwidth
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR
 Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Expert Reference Series of White Papers. The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address Translation
 Expert Reference Series of White Papers The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address Translation 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address
Expert Reference Series of White Papers The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address Translation 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address
Classful IP Addressing (cont.)
 Classful IP Addressing (cont.) 1 Address Prefix aka Net ID defines the network Address Suffix aka Host ID defines the node In Classful addressing, prefix is of fixed length (1, 2, or 3 bytes)! Classful
Classful IP Addressing (cont.) 1 Address Prefix aka Net ID defines the network Address Suffix aka Host ID defines the node In Classful addressing, prefix is of fixed length (1, 2, or 3 bytes)! Classful
What is VLAN Routing?
 Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
SUBNETTING SCENARIO S
 SUBNETTING SCENARIO S This white paper provides several in-depth scenario s dealing with a very confusing topic, subnetting. Many networking engineers need extra practice to completely understand the intricacies
SUBNETTING SCENARIO S This white paper provides several in-depth scenario s dealing with a very confusing topic, subnetting. Many networking engineers need extra practice to completely understand the intricacies
Transport and Network Layer
 Transport and Network Layer 1 Introduction Responsible for moving messages from end-to-end in a network Closely tied together TCP/IP: most commonly used protocol o Used in Internet o Compatible with a
Transport and Network Layer 1 Introduction Responsible for moving messages from end-to-end in a network Closely tied together TCP/IP: most commonly used protocol o Used in Internet o Compatible with a
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
How Subnets Work in Practice. Fred Marshall Coastal Computers & Networks
 How Subnets Work in Practice Fred Marshall Coastal Computers & Networks Background There's lots of literature available on how the bit structure of an address can be split up using the subnet mask. Generally,
How Subnets Work in Practice Fred Marshall Coastal Computers & Networks Background There's lots of literature available on how the bit structure of an address can be split up using the subnet mask. Generally,
Configuration of Cisco Routers. Mario Baldi
 Configuration of Cisco Routers Basics Static Routing Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino mario.baldi[at]polito.it http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi ConfRoutEn - 1 M. Baldi: see page 2 Copyright Notice This
Configuration of Cisco Routers Basics Static Routing Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino mario.baldi[at]polito.it http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi ConfRoutEn - 1 M. Baldi: see page 2 Copyright Notice This
