ROBATIC, ROBA -quick ROBA -takt
|
|
|
- Melvyn Hudson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROBATIC, ROBA -quick ROBA -takt Electromagnetic Clutches and Brakes, Clutch Brake Units High torque capacity Low wear Compact construction Easy assembly and maintenance K.500.V09.GB your reliable partner
2 Largest variety in selection of standard products Market leader s competence arising from decades of experience in the development, production and application of power transmission products Optimum product selection due to our expertise in design and calculation Reliable component dimensioning Intelligent platform (modular construction) High flexibility for individual requests and customer-tailored solutions Quality-inspected suppliers Modern, highly robust materials In-house production 00 % quality control your reliable partner What is your definition of reliability? We define reliability as the highest product quality and competent service from the initial contact right up to the after-sale service Certified according to DIN EN ISO 900:2000 Personal supervision from the first contact right up to the after-sale service Worldwide local service network CAD-files available online to save time and costs during construction 24-hour delivery service for preferred products Short delivery times and on-time delivery Unlimited replacement part availability worldwide
3 Your advantages when using electromagnetic ROBATIC -clutches, ROBA -quick brakes and ROBA -takt clutch brake units Easy integration into your machine: The optimised magnetic circuit minimises the magnetic leakage flux. The high power density and torque security based on it allow compact dimensions and an easy integration in your construction. High reliability and operational safety: The switching behaviour is constant during the entire service lifetime. Therefore, the positioning accuracy and reliability of the clutches or brakes respectively and herewith the operational security of your machine are increased. Less operating expenses and maintenance charges: The large friction surface and the smooth switching behaviour increase the wear resistance. Therefore, the clutches and brakes are maintenance-free until the friction surfaces are worn down. There is no re-adjustment work and the resulting operational interruptions. Therefore, the operating expenses and maintenance charges are very low. Increase of productivity: Short switching times allow high switching frequencies and increase the productivity of your machine. Total Quality Management Product Quality Every delivery which leaves our firm has been subjected to a careful quality inspection, meaning that you are able to rely 00 % on mayr products. If required, we pre-adjust our clutches and brakes accurately to the requested values and confirm the product characteristics with an Inspection Report. Quality Management mayr uses the term quality to describe its products and services. Certification of our quality management confirms the qualityconsciousness of our colleagues at every level of the company. Our integrated management system is certified according to DIN EN ISO 900:2000 (Quality) and DIN EN ISO 400 (Environment) and complies with the OHSAS 800/OHRIS (Occupational Health and Safety) demands. All products are subject to comprehensive inspections and tests regarding loads. Only after having passed the strongest long-time tests and when they fully meet all the technical requirements and proof their reliability they are included in our delivery programme. Please Observe: According to german notation, decimal points in this document are represented with a comma (e.g. 0,5 instead of 0.5).
4 Electromagnetic Clutches and Brakes Guidelines Description and Operating Conditions. The catalogue values, in particular the values for the nominal torque, are reference values and may deviate in individual cases. 2. During dimensioning, please contact the manufacturers for consultation on installation conditions, torque fluctuations, permitted friction work, run-in behaviour, wear and ambient conditions. 3. The clutches and brakes are designed for dry running. If the friction surfaces come into contact with oil, grease or similar substances, there may be a severe decrease in torque. 4. When the devices are switched off, voltage peaks may occur due to the counter-induction on the magnetic coils, causing in extreme cases damage to the magnetic coil and therefore to the components. For this reason, excess voltage must be damped using a suitable protective circuit (e.g. using a varistor). 5. The surfaces on the clutches and the brakes are corrosionprotected except for the friction surfaces. However, in operation in extreme ambient conditions or in outdoor conditions with direct weather influences, additional protective measures are necessary. 6. The connection cable or connection strands on the clutches and brakes have a surface coating which is not resistant against all influences. After contact with chemical substances, please check compatibility. 7. The clutches and brakes are designed for a relative duty cycle of 00 %. Torque Characteristics In new condition, c. 50 % of the catalogue nominal torque (M 2 ) is transmitted. The components reach the catalogue nominal torque when the friction surfaces are run in. As a rough guideline value, c switchings in dynamic operation, a typical speed (c. 50 to 000 rpm) and a medium friction work (see Table ) can be given. Longer slipping of the clutch or brake is to be avoided, especially at low speeds, as this can cause scoring formation and therefore damage to the friction surfaces. Clutches or brakes used in static or virtually static operation do not reach the nominal torque (M 2 ). If requested, the clutches or brakes can also be run in at the place of manufacture. This is most expedient for Type with complete bearing. However, Types 500. and 520. can also be run in under certain conditions. For this, please ensure exact installation customer-side according to the regulations in order to reproduce the friction conditions as precisely as possible. At the same time, the friction carbon produced must not be rubbed off. If the clutch is run in to the nominal torque at the place of manufacture and then operated in static or virtually static mode, please allow for a drop to c % of the nominal torque. This is the case if the clutch or brake falls below the speed or friction work (Q a ) stated in Table. For static and virtually static applications, we therefore recommend our double-flow designs construction series (see pages 2/3). Friction work Q a [J] Clutch or brake speed n min. [rpm] Run-in Conditions For running in, different procedures can be used according to the Type design. An artificial run-in is to be carried out if a run-in procedure is not possible in the machine due to the type of application (see section Torque Characteristics ), e.g. due to insufficient friction work, speed or switching frequencies. For the run-in conditions of the individual clutch and brake types, please see the respective Installation and Operational Instructions on our website Electrical Connection and Wiring DC current is necessary for the operation of the brake. The coil voltage is indicated on the Type tag as well as on the brake body and is designed according to the DIN IEC (± 0 % tolerance). Operation is possible both via alternating voltage in connection with a rectifier or with another suitable DC supply. Dependent on the brake equipment, the connection possibilities can vary. Please follow the exact connections according to the Wiring Diagram. The manufacturer and the user must observe the applicable directives and standards (e.g. DIN EN and DIN VDE 0580). Their observance must be guaranteed and double-checked. Electrical Wiring 24 VDC and 04 VDC can be selected as standard voltages. 24 VDC: Operation with a power supply unit of 24 VDC 04 VDC: Half-wave recifier with 230 VAC mains voltages Earthing Connection The brake is designed for Protection Class I. This protection covers not only the basic insulation but also the connection of all conductive parts to the PE conductor on the fixed installation. If the basic insulation fails, no contact voltage will remain. Please carry out a standardized inspection of the PE conductor connections to all contactable metal parts. Device Fuses To protect against damage from short circuits, please add suitable device fuses to the mains cable. Protection Circuit When using DC-side switching, the coil must be protected by a suitable protective circuit according to VDE This is achieved by using a sufficiently dimensioned varistor, which has already been integrated into the mayr rectifier. To protect the switching contact from consumption when using DCside switching, additional protective measures may be necessary (e.g. series connection of switching contacts). The switching contacts used should have a minimum contact opening of 3 mm and should be suitable for inductive load switching. Please make sure on selection that the rated voltage and the rated operation current are sufficient. Depending on the application, the switching contact can also be protected by other protective circuits (e.g. mayr spark quenching units), although this may of course then alter the switching times. 4 Table
5 Electromagnetic Clutches and Brakes Table of Contents Page ROBATIC Electromagnetic, energise to engage pole face clutches ROBA -quick Electromagnetic, energise to engage pole face brakes ROBATIC Description 6 Summary of structural designs 7 Data sheets ROBATIC -standard s ROBATIC -standard s ROBATIC double-flow design s ROBATIC small mounting diameter s ROBATIC small mounting diameter s ROBATIC with bearing-supported coil carrier s ROBATIC with bearing-supported flange s Technical explanations Electronic accessories ROBA -quick Description 28 Summary of structural designs 29 Data sheets ROBA -quick standard s ROBA -quick standard s ROBA -quick small mounting diameter s Technical explanations Electronic accessories 40 4 ROBA -takt clutch brake module Clutch-brake unit ROBA -takt clutch brake module Description 42 Summary of structural designs 43 Data sheets ROBA -takt 44 5 Technical explanations Electronic accessories
6 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Constant switching performance throughout the entire service lifetime High torque security due to an optimised magnetic circuit and the new design of the ROBATIC -clutch. Therefore, higher capacities due to less magnetic leakage flux. Half the wear due to large friction surfaces and smooth switching behaviour, the ROBATIC -clutch has a higher wear resistance (approx. 00 %). Large internal diameters of the magnetic coil bodies therefore large permitted shaft diameters Low noise Short switching times/high switching frequencies Correct function up to wear limit wear, air gap max. adjusting interval conventional electromagnetic clutches number of switchings Functional principle ROBATIC -clutches are energise to engage, electromagnetic pole face units. When DC voltage is applied to the magnetic coil (), a magnetic field is build up, the armature disk (3) is attracted to the rotor (2) and the friction lining (4). The torque is transmitted via friction locking. The torque is transmitted from the drive element (6) via the armature disk (3) and the rotor (2) to the output shaft (7). After having de-energised the coil, the membrane spring (5) draws back the armature disk (3) to the drive element (e.g. belt pulley), and the torque transmission is then disconnected. wear, air gap max. ROBATIC adjusting interval number of switchings
7 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Summary of structural designs ROBATIC ROBATIC -standard s 3 to 9 Type 500. _._ s 3 to 7 Type _.0 s 8 to 9 Type 500. without accessories Type flange hub Type without accessories Type 500.0_ flange hub Type 500._ Pages 8 ROBATIC double-flow design s 3 to 7 Type _ without accessories Type flange hub Type Pages 2 3 ROBATIC small mounting diameter s 3 to 7 Type 500.2_.0 s 8 to 9 Type 580._0 with small bolt circle without accessories Type flange hub Type without accessories Type flange hub Type Pages 4 7 ROBATIC with bearing-supported coil carrier s 3 to 9 Type 540. without accessories Type 540.0_ flange hub Type 540._ Pages 8 9 ROBATIC with bearing-supported flange s 3 to 9 Type 540.4_ Type 540.4_ Pages
8 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Standard s 3 7 Type _.0 L O l L a L 2 l2 ØH ØM ØZ Øs l køk Ød ØG ØM ØD ØD W Ød Øg ØD 2 z Øs V V strand length: 400 mm; 45 offset to screw-on bores b t t Type Standard Type Standard with flange hub Order Number / / / / / s 3 to 7 without accessories flange hub 0 Coil voltage [VDC] Rotor bore Ø d H7 Flange hub bore Ø d H7 Keyway acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 Example: 6 / / 24 / 35 / 40 / DIN 6885/ 8
9 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Standard s 3 7 Type _.0 Technical Data Nominal torque ) Type _.0 M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0,68 2,5 3,48 6,6 with flange hub m [kg] 0,75,3 2,35 4,03 7,5 Rotor 2) I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 2 5,4 3,25 29,85 86,75 Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,76,92 6,86 7,56 52,86 Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ],02 2,75 8,63 24,66 70,63 ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores Ød H7 min. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 0; 5 7; 20 20; 25; 30 25; 30; 35 30; 40; 50 Ød H7 max. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 7; 20 20; 25 25; 30 30; 40 40; 50 3) Up to Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/, above Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/3 min. [mm] max. [mm] ) [mm] a 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 b 4,5 4 5,5 5,5 7,5 D 73, D D G , g 29, H h K 3 x 4,6 3 x 6,4 3 x 7,0 3 x 0,4 3 x 0,2 k,7,7 2,5 2,8 2,7 L 28, 3,2 36,0 40,8 46, L 24 26, ,5 37,5 L l 20, ,5 3,5 [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset l 3,5 4,3 5,2 6 7 l M M O 48, 53,2 64, 72,9 82,2 s 4 x 4,8 4 x 5,7 4 x 6,8 4 x 6,8 4 x 9,2 s 3 x M4 3 x M5 3 x M6 3 x M8 3 x M8 t 3,9 4,5 5,8 7,0 8,3 t 5,2 7,2 8,7 8,0 9,7 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, V 0, 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,2 W Z H z 3,5 4, We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 9
10 L l b a t Øs z l ØH ØM ØZ ØN ØF Ød ØG ØM ØD ØD 90 º Øs Øs ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Standard s 8 9 Type 500. strand length: 400 mm; 45 offset to screw-on bores O L 2 l2 W Ød Øg ØD 2 V 45 º ØK V V l 4 Øs k i t Type Standard with connection strand ØM Type Standard with flange hub with connection strand 45 º Øs Ød ØK ØG ØM ØD ØD 90 º Type 500._2 Standard with connecting terminal ØM Order Number without accessories flange hub 0 / / / / / 8 9 connection strand connecting terminal 0 2 Coil voltage [VDC] Rotor bore 3) Ø d H7 Flange hub bore Ø d H7 Keyway acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 0 Example: 8 / / 24 / 40 / DIN 6885/
11 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Standard s 8 9 Type 500. Technical Data 8 9 Nominal torque ) Type 500. M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] 6 82 Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0, 20,5 with flange hub m [kg] 3 25 Rotor 2) I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 8 35 Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores 8 9 Ød H7 min. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 40; 50; 60 50; 60; 70 Ød H7 max. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 40; 50 50; 60 min. [mm] max. [mm] [mm] 8 9 a 0,5 0,5 b 8 9 D D D F 3) - - G 9 g H h i 8 9,5 K 3 x 4 x 20 k 2 4,2 L 55, 63,9 L 2 45,3 53,9 l 44 5 l ) Turning for RS-ball bearing according to order regulations no turning is allowed for in the standard range. [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset 8 9 l 2 36,3 42,9 l M M N 93,9 6,8 O 00,4 7,8 s 4 x 9 4 x s 3 x M0 4 x M2 t 0,6 2,4 t 8,5,8 V 0, 0, V 0,2 0,25 W 5 20 Z H z 4 4 We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations.
12 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Double-flow design s 3 7 Type _.0 strand length: 400 mm; 45º offset to screw-on bores l L b a t k O L 2 l 2 ØH ØM ØZ Øs ØF l z Ød ØG ØK ØM ØD ØD W Ød Øg ØD 2 V Øs V L t Type Double-flow design Type Double-flow design with flange hub Performance Characteristics Preferred for static or virtually static applications High torque security with low friction work No organic friction lining installed (environmentally friendly) Order Number / / / / / s 3 to 7 without accessories flange hub 0 Coil voltage [VDC] Rotor bore Ø d H7 Flange hub bore Ø d H7 Keyway acc. DIN 6885/ Example: 6 / / 24 / 35 / 40 / DIN 6885/ 2
13 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Double-flow design s 3 7 Type _.0 Technical Data Nominal torque ) 2) (+50% /-2%) Type _.0 M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed 3) n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0,65,6 2,02 3,3 6,22 with flange hub m [kg] 0,76,5 2,53 4,46 8,09 Rotor 4) I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 2,02 5,56 4,08 32,26 06,36 Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ],08 2,69 7,34 9,92 6,57 Flange hub 4) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ],46 3,98 0,26 30,43 89,0 ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) During permanent synchronisation without friction work, the torque may drop to 50 % - 60 % of the nominal torque. 3) Max. switching speed is dependent on friction work and switching frequency - if necessary, please contact the manufacturer. 4) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores Ød H7 min. 5) [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 5, 20 20, 25, 28 30, 35, 40 45, 50 55, 60 Ød H7 max. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 5, 7, 20 20, 25, 28 25, 30 35, 40, 45 50, 55, 60 min. 5) [mm] max. [mm] ) For torques smaller than the nominal torque M 2, bores below d min are possible on request. [mm] a 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 b 4,5 4 5,5 5,5 7,5 D , D D F 6) G g 29, H h K 3x8 3x0 3x2 3x6 3x4 k 3,2 3,8 4,3 6 4,4 L 28, 3,25 35,7 40,7 46, L 23,5 26, ,5 37,5 L I ,5 3,5 6) Turning for RS-ball bearing according to order regulations no turning is allowed for in the standard range. [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset I 3,5 4,3 5,2 6 7 I M M O 48, 53,25 63,7 72,7 82,2 s 4x4,8 4x5,7 4x6,8 4x6,8 4x9,2 s 3xM4 3xM5 3xM6 3xM8 3xM8 t 4,3 4,45 5,5 6,9 8,3 t 5 7,2 8,7 4 3,7 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, V 0, 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,2 W Z H z 3,5 4, We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. For detailed information, please see our brochure P.500.V._GB 3
14 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Small mounting diameter s 3 7 Type 500.2_.0 L O l L a L 2 l2 ØH ØM ØZ Øs z l køk Ød ØG ØM ØD ØD W Ød Øg ØD 2 V Øs V strand length: 400 mm; 45 offset to screw-on bores b t t Type Small mounting diameter Type Small mounting diameter with flange hub Order Number / / / / / s 3 to 7 without accessories flange hub 0 Coil voltage [VDC] Rotor bore Ø d H7 Flange hub bore Ø d H7 Keyway acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 Example: 6 / / 24 / 40 / 30 / DIN 6885/ 4
15 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Small mounting diameter s 3 7 Type 500.2_.0 Technical Data Nominal torque ) Type 500.2_.0 M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0,65, 2, 3,4 6,4 with flange hub m [kg] 0,7,6 2,25 3,6 6,95 Rotor 2) I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 2,2 5,3 3,47 32,3 90,3 Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,7,79 6,28 5,77 48, Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,8,97 7,9 7,45 55,2 ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores Ød H7 min. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 0; 5 7; 20 20; 25; 30 25; 30; 35 30; 40; 50 Ød H7 max. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 0; 5 7; 20 20; 25 25; 30 30; 40 3) Up to Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/, above Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/3 min. [mm] max. [mm] ) 45 [mm] a 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 b 4,5 4 5,5 5,5 7,5 D 73, D D G , g 27 29, H h K 3 x 4,3 3 x 4,6 3 x 6,4 3 x 7 3 x 0,4 k,5,7,5 2,2 2,7 L 28, 3, 36,0 40,4 45,8 L 24 26, ,5 37,5 L l [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset l 3,5 4,3 5,2 6 7 l 2, M M O 43, 5, 58, 68,8 77,9 s 4 x 4,5 4 x 5,7 4 x 6,8 4 x 6,8 4 x 9,2 s 3 x M3 3 x M4 3 x M5 3 x M6 3 x M8 t 3,9 4,4 5,8 6,6 8,0 t 4, 5,2 6,7 8,7 8,0 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, V 0, 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,2 W Z H z 2 2,5 3 3,5 3,5 We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 5
16 l L t O a L 2 l2 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Small mounting diameter s 8 9 Øs W Type 580._0 L L t t O ØM 2 ØZ ØN ØF z l l a l Ød a ØG ØM ØD ØD Ød L 2 l2 Øg ØD 2 strand length: 400 mm ØS ØS ØK Øs Øs V W B k ØM 2 ØZ V ØN ØM 2 ØF ØZ z l z l t ØN ØF Ød ØG ØM Ød ØD ØG ØD ØM ØD ØD Ød Øg ØD 2 ØS ØS ØS ØS ØK ØK V B B k k V V t t Type Coil carrier with small bolt circle Type Coil carrier with small bolt circle and flange hub Bore for screws DIN 692, 7984 with spring ring DIN 7980 Order Number / / / / / 8 9 without accessories flange hub 0 Coil voltage [VDC] Rotor bore Ø d H7 Flange hub bore Ø d H7 Keyway acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 Example: 8 / / 24 / 40 / 40 / DIN 6885/ 6
17 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Small mounting diameter s 8 9 Type 580._0 Technical Data 8 9 Nominal torque ) Type 580._0 M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0, 20,5 with flange hub m [kg] 3 23,5 Rotor 2) I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 8 35 Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores 8 9 Ød H7 min. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 40; 50; 60 50; 60; 70 Ød H7 max. [mm] Preferred bores [mm] 40; 50 50; 60 min. [mm] max. [mm] [mm] 8 9 a 0,5 0,5 B 3 3 D D D F 3) - - G 9 g H h i 8 9,5 K 3 x 4 x 20 k 2 4,2 L 55, 63,9 L 2 45,3 53,9 l 44 5 l ) Turning for RS-ball bearing according to order regulations no turning is allowed for in the standard range. [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset 8 9 t 0,6 2,4 l 2 36,3 42,9 M M N 93,9 6,8 O 00,4 7,8 S 3,5 3,5 S 3 x 8,4 3 x 8,4 s 3 x M0 4 x M2 t 8,5,8 V 0, 0, V 0,2 0,25 W 5 20 Z H z 4 4 We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 7
18 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch With bearing-supported coil carrier s 3 9 Type 540. strand length: 400 mm; 45º offset to screw-on bores n O L a k O L 2 l2 W l 6 Øs ØP Øp Ød 2 ØG ØM ØD ØD Ød Øg ØD 2 ØK V t t Type With bearing-supported coil carrier Type With bearing-supported coil carrier and flange hub O n L a k 5 Y Y 3 U u Keyway for friction support ØK l 6 Øp Ød 2 ØG ØM ØD ØD Type 540._2 With connecting terminal Order Number Øs without accessories flange hub 0 V t t / / / / / s 3 to 9 connecting strand connecting terminal 0 2 Coil voltage [VDC] Rotor bore Ø d 2 Keyway acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 Flange hub bore Ø d 8 Example: 5 / / 24 / 20 / DIN 6885/
19 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch With bearing-supported coil carrier s 3 9 Type 540. Technical Data 8 9 Nominal torque ) Type 540. M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0,73,22,85 3,6 5,54,6 22,2 with flange hub m [kg] 0,78,29 2,0 3,38 6, 2,86 23,93 Rotor 2) I own [0-4 kgm 2 ],37 3,35 9,36 20,8 54, Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,35,05 2,97 7, Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,5,5 4,5 0,9 37, ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores 8 9 Preferred bores [mm] 0; 5 7; 20 20; 25; 30 20; 25; 30 25; 30; 40 40; 45; 50 40; 50; 60 Ød H7 2 min. [mm] Ød H7 max. [mm] 20 3) 25 3) Preferred bores [mm] 0; 5 7; 20 20; 25 25; 30 30; 40 40; 50 50; 60 3) With max. bore keyway to DIN 6885/3 4) Up to Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/, above Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/3 min. [mm] max. [mm] ) [mm] 8 9 a 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 0,5 0,5 D 64,5 8, D D G 29,5 30,5 45, g 27 29, K 3 x 4,3 3 x 4,6 3 x 5,8 3 x 7 3 x 9,4 3 x,5 4 x 20 k 0,8,7,0,0 2,0 2,0 4,2 L ,9 40,5 46,5 55,4 63,9 L , ,3 53,9 l 2, ,5 3 36,3 42,9 l , , M n , ,5 [mm] 8 9 O ,9 9,5 08,5 30,4 47,8 O ,9 62,0 70,5 85, 93,9 P 70 79,7 98,2 5,4 50,4 89,4 235,8 p s Permitted shaft misalignment 3 x M3 3 x M4 3 x M5 3 x M6 3 x M8 3 x M0 3 x M2 t 3,8 4,3 5,7 6,7 8,7 0,6 2,4 t 4, 5,0 6,9 6,7 8,2 8,5,8 U u 2 2,5 2,5 2,5 3 4,5 6 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, 0, 0, W Y [ ] Y [ ] ,5 22, We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 9
20 With bearing-supported flange ) s 3 9 Y 2 n 3 n L a L 7 l 8 W ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Type 540.4_ ØD ØP O 5 n Ln n 3 L a L 7 L 7 l 8 W W ØD ØP ØD Øp ØP Ød 3 Øp Ød 3 AS O 5 AÜ Øs 2 Øs 2 x x 3x20º Y 2 Øp strand length: 400 mm; 45º offset to screw-on l bores 3 Ød 3 n 3 a l 8 Ød 4 Øe ØM 3 ØD 3 Keyway for key x O 5 Ød 4 Øe Ød ØM 4 3 Øe ØD 3 ØM 3 ØD 3 l 3 l 3 Øs 2 x 3x20º Keyway for friction support Y Type With bearing-supported flange U u Y U u Order Number / / / / / s 3 to 9 connecting strand connecting terminal 0 2 Coil voltage [VDC] Hub bore Ø d 4 Keyway acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 AS AÜ Counterbore: coil carrier side transmission flange side Example: 5 / / 24 / 24 / 6885/ / AS 20
21 ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch With bearing-supported flange ) s 3 9 Type 540.4_ Technical Data *) 8 *) 9 *) Nominal torque 2) Type 540.4_ M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight with max. bore m [kg],2,85 2,95 4,7 8,25 6,6 29,2 Mass moment of inertia Rotor (max. bore) I own [0-4 kgm 2 ],59 3,82 0,24 23,22 52,05 97, Armature disk + driver flange I own [0-4 kgm 2 ],97 4,06 9,95 22,93 50,53 47,83 533,7 ) 2-shaft connection on request 2) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). *) From 7 on, the installation of a key in the driver flange is necessary in order to ensure torque transmission. Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores 8 9 Ød 4 maximum [mm] 5 9 3) Ød 3 [mm] ) ) ) / 5) _ 8) 37 6) 47 7) 59 8) 47 9) 67 8) _ 0) 3) Above Ø 8 keyway to DIN 6885/3 with d 4 max depth of hub keyway,2 +0, 4) above Ø d 4 to 9 5) above Ø d 4 over 9 6) above Ø d 4 to 28 7) above Ø d 4 over 28 8) above Ø d 4 over 38 9) above Ø d 4 to 38 0) above Ø d 4 over 55 [mm] 8 9 a 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 0,5 0,5 D D G 29,5 30,5 45, e h L ,9 40,5 46,5 55,4 63,9 L 7 25,8 29,7 38,7 43,5 48,9 53,9 57, l ) ) 50 4) ) 40 5) 5) 20 7) 55 6) 35 7) _ 8) 75 6) 55 7) 25 8) 70 9) 40 8) _ 0) l 8 2, M n , ,5 n , ) above Ø d 4 to 4 2) above Ø d 4 over 4 3) From 7 on, the installation of a key in the driver flange is necessary in order to ensure torque transmission. [mm] 8 9 O P 70 79,7 98,2 5,4 50,4 89,4 235,8 p s 2 3 x M4 3 x M5 3 x M5 3 x M6 3 x M8 3 x M8 3 x M8 U u 2 2,5 2,5 2,5 3 4,5 6 W 7,5 9 24, Key X 3) 6x6 x6 6x6 x8 8x7 x22 0x8 x25 0x8 x28 4x9 x32 6x0 x36 x 3,5 3, ,5 6 Y [ ] ,5 52, Y 2 [ ] We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 2
22 e Technical Explanations ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Installation Guidelines a e V Fig. Fig a 0,2 +0, -0,05 0,2 +0,5-0,05 0,2 +0,5-0,05 0,3 +0,5-0,05 0,3 +0,5-0,05 0,5 +0,5-0, 0,5 +0,5-0, e 0,25 0,3 0,2 0,35 0,5 0,55 0,6 8 9 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, 0, 0, Table 2 Permitted shaft misalignments Table Adjustment of the air gaps The dimension a (Fig. ) must be adjusted according to Table. Please ensure that the shaft is fastened axially, since otherwise the dimension a will change and cause the rotor to brush against the armature disk or the coil carrier. The air gap e is selected so that a brushing of the rotor against the coil carrier is not possible when keeping to the permitted centre offsets V and V (see Table ). 22 Design: ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutches are manufactured according to the electric protection IP 54 specification and the insulation material class F up to 55 C for coil, moulding compound and connection strands as well as insulation class B +30 C for the magnetic coil plastic-coated. The friction linings are asbestos-free, the surfaces of coil carrier, rotor and flange hub are phosphated. The armature disk is gas nitro-carburized and the transmission spring is made of stainless steel. The drive elements should be made of magnetically poorly transmitting material to avoid magnetic leakage flux and subsequent power reduction. ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutches are used for dry running. The torque is transmitted via the connection of the armature disk on the iron poles and the friction lining of the rotor (except the double-flow ROBATIC clutch without friction lining, Type _.0). When coupling two shafts, the eccentricity V of the shafts according to Table 2 must not be exceeded. The larger the misalignment V the more the torque decreases and the hotter the friction surface becomes. In the case of this arrangement care must be taken that both shafts have no axial backlash since, otherwise, a brushing of the rotor would also be possible. The flange hub is kept axially by means of a set screw (on set 90 to the key). The V -values are indicated again in the Technical Data of the individual clutches. Please observe: The run-in conditions or the minimum speed must be observed (see page 4). The friction surfaces have to be absolutely free of oil and grease, as otherwise, the torque drops significantly. The air gap a (Fig. ) has to be checked periodically. The clutch does not function correctly, if the max. working air gap is exceeded (see Table 4, page 25). Assembly and maintenance should be carried out by well trained specialists.
23 Technical Explanations ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Clutch size calculation Formulas. Drive torque M A 9550 x P A [Nm] n 2. Required torque M req. K x M A [Nm] 3. Switchable torque of the clutch (acc. to diagram, page 24) M S M req. [Nm] 4. Mass moment of inertia I I own + I add. [kgm 2 ] 5. Acceleration torque of the clutch M a M S M L [Nm] 6. Acceleration time t a I x n 9,55 x M a + t [sec] 7. Max. switching frequency per hour (dependent on time) S h max t vm + (t a + t 2 ) x,2 x 3600 [h - ] Key: P A [kw] drive power M A [Nm] drive torque M a [Nm] acceleration torque of the clutch M req. [Nm] required torque M L [Nm] load torque (+ drop load) (- lift load) M S [Nm] switchable torque of the clutch (diagram, page 24) n [rpm] drive speed K safety factor > 2 I [kgm 2 ] mass moment of inertia I own [kgm 2 ] own mass moment of inertia ( Technical data ) I add. [kgm 2 ] additional mass moment of inertia t a [sec] acceleration time t vm [sec] braking time of the machine t [sec] switch-on time of the clutch Table 3, t 2 [sec] switch-off time of the clutch page 25 S h max [h - ] max. switching frequency per hour (dependent on time) Q tot. [J] total friction work (acc. Table 4, page 25) Q a [J] total friction work per acceleration Q E [J] perm. friction work for single switching Table 4, Q [J/mm] friction work until mm wear page 25 Z n Z number of switchings until re-adjustment number of switchings until wear limit a [mm] nominal air gap Table 4, a n [mm] max. working air gap page Friction work per acceleration I x n 2 M s Q a x 82,4 M a [J] 9. Examination of the selected clutch size in diagram 2 (page 24 friction power diagram). Intersection friction work / switching frequency must be below the friction power curve! If it is above, the next size has to be selected and re-calculated from point 3 on. Q a < Q E [J] 0. Number of switchings until re-adjustment Z n Q x (a - a) [-] n Q a. Number of switchings until wear limit Z Q tot. [-] Q a 23
24 Technical Explanations ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Calculation example Data: Input power P A 3 kw Input speed n 400 rpm Load torque output M L 5 Nm Additional mass moment of inertia I add. 0,5 kgm² Braking time of the machine t vm,5 [sec] 80 switchings per hour 000 Switchable torque Drive torque 9550 x P A 9550 x 3 M A 20,5 [Nm] n 400 Required torque M req. K x M A 2 x 20,5 4 [Nm] Determined clutch size (acc. to diagram ) 6 M S M req. 47 [Nm] Selected clutch 6, type ** Switchable torque M s [Nm] 00 0 Mass moment of inertia I I own + I add. 0, ,5 0,5756 [kgm²] Acceleration torque of the clutch M a M S - M L [Nm] Acceleration time of the clutch t a I x n + t * 0,5756 x ,5 0,845 [sec] 9,55 x M a 9,55 x 32 * Switching times t and t 2 from Table 3, page 25 without overexcitation Max. switching frequency per hour S h max S h max t vm + (t a + t 2 *) x,2,5 + (0, ,060) x,2 Friction work per acceleration Q a Q a I x n 2 M S x 82,4 M a 0,5756 x x 82,4 32 x 3600 x [h - ] 2395 [J] Q E The point of intersection determined in diagram 2 must be located in or under the characteristic curve of the selected clutch. Switching frequency: 80 switchings per hour permitted Number of switchings until adjustment Z n Q Q a x (a n - a) Speed n [rpm] Diagram (not valid for Type _) Q a Switching work [J] Friction power diagram valid for speed 500 rpm ** Friction surfaces have been run in Calculation example 24 Z n 57 x 07 x (,2-0,3) 2496 switchings 2395 Number of switchings until wear limit Z Q tot. 00 x switchings Q a Switching frequency S h [h - ] Diagram 2 (not valid for Type _)
25 Technical Explanations ROBATIC -electromagnetic clutch Switching times The switching times stated in Table 3 have been determined by comprehensive series of tests. They are valid for switching DC-side with nominal air gap and warm coil. Deviations depend on the respective installation situation, ambient temperatures, release path and the type of rectification with which the corresponding clutch is operated. Switching times 8 9 t [sec] 0,00 0,05 0,020 0,030 0,045 0,050 0,060 Without Type 500. _._ t overexcitation [sec] 0,045 0,065 0,080 0,50 0,200 0,350 0,400 t 2 [sec] 0,02 0,020 0,045 0,060 0,090 0,095 0,30 With Type 500. _._ t [sec] 0,003 0,005 0,007 0,00 0,05 0,020 0,035 overexcitation t [sec] 0,025 0,035 0,040 0,075 0,00 0,70 0,235 t [sec] 0,00 0,02 0,02 0,020 0,025 0,050 0,060 Without Type 540. _._ t overexcitation [sec] 0,050 0,072 0,2 0,60 0,200 0,350 0,460 t 2 [sec] 0,04 0,020 0,030 0,050 0,075 0,095 0,30 With overexcitation Without overexcitation With overexcitation Table 3 Type 540. _._ t [sec] 0,004 0,005 0,006 0,00 0,03 0,020 0,035 t [sec] 0,024 0,035 0,056 0,080 0,00 0,70 0,235 t [sec] 0,07 0,026 0,035 0,052 0, Type _ t [sec] 0,079 0,3 0,40 0,262 0, t 2 [sec] 0,00 0,06 0,036 0,048 0, Type _ t [sec] 0,005 0,009 0,02 0,07 0, t [sec] 0,044 0,06 0,070 0,3 0, M Key: P ON M 2 M L t t 3 t t 2 t a 0, M 2 t M 2 M L P t a t t t 2 t 3 Nominal torque of the clutch Load torque of the drive Electrical power Acceleration time Connection time Response delay on connection Disconnection time Slip time OFF t Diagram 3: Torque-time Friction work ) and air gap Friction work up to mm wear Total friction work 8 9 Type 500. _._ Q [0 7 J/mm] 2, Type 540. _._ Q [0 7 J/mm] 8,8 3, Type 500. _._ Q tot. [0 7 J] 2, Type 540. _._ Q tot. [0 7 J] Permitted friction work with a single switching Q E [0 3 J] 3,8 6, Nominal air gap a [mm] 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 0,5 0,5 Max. working air gap a n [mm] 0,6 0,8,0,2,5,8 2,0 Table 4 ) The friction work data are not valid for Type _.0 double-flow design. Please Observe! Wear values can only be recommended values due to operating parameters, such as sliding speed, pressing or temperature. 25
26 Application Rectifiers are used to connect DC consumers to alternating voltage supplies, for example electromagnetic brakes and clutches (ROBA-stop, ROBA-quick, ROBATIC ), electromagnets, electrovalves, contactors, switch-on safe DC motors, etc. Function The AC input voltage (VAC) is rectified (VDC) in order to operate DC voltage units. Also, voltage peaks, which occur when switching off inductive loads and which may cause damage to insulation and contacts, are limited and the contact load reduced. Half-wave Rectifiers and Bridge Rectifiers Type 02_ Electrical Connection (Terminals) + 2 Input voltage Connection for an external switch for DC-side switching Coil 7-0 Free nc terminals (only for 2) (mm) ØD A C E 9 5 Order Number B / up to Half-wave rectifier Bridge rectifier A B C ØD E ,5 4, ,5 5,0 3/ ,5 5,0 Accessories: Mounting bracket set for 35 mm rail acc. EN 6075: Article-No Technical Data Bridge rectifier Half-wave rectifier Calculation output voltage VDC VAC x 0,9 VDC VAC x 0,45 Type /025 2/025 /024 2/024 3/024 4/024 Max. input voltage ± 0 % U AC [VAC] Max. output voltage U DC [VDC] Output current at 50 C I RMS [A] 2,5 2,5 3,0 4,0 4,0 4,0 max. 85 C I RMS [A],7,7,8 2,4 2,4 2,4 Max. coil nominal capacity at U AC 5 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 230 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 400 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 500 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 600 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] Peak reverse voltage [V] Rated insulation voltage U RMS [V RMS] Pollution degree (insulation coordination) Device fuses To be included in the input voltage line. Recommended microfuse switching capacity H The microfuse corresponds to the max. possible connection capacity. If fuses are used corresponding to the actual capacities, FF 3,5 A FF 3,5 A FF 4 A FF 5 A FF 5 A FF 5 A the permitted limit integral I²t must be observed on selection. Permitted limit integral l 2 t [A 2 s] Protection IP65 components, encapsulated / IP20 terminals Terminals Cross-section 0,4 -,5 mm 2 (AWG 26-4) Ambient temperature [ C] - 25 up to + 85 Storage temperature [ C] - 25 up to + 05 Conformity markings UL, CE UL, CE UL, CE UL, CE UL, CE CE The installation position can be user-defined. Please ensure sufficient Installation conditions heat dissipation and air convection! Do not install near to sources of intense heat!
27 Spark Quenching Unit Type Application Reduces spark production on the switching contacts occurring during DC-side switching-off of inductive loads. Voltage limitation according to VDE , Item 4.6. Reduction of EMC-disturbance by voltage rise limitation, suppression of switching sparks. Reduction of brake engagement times by a factor of 2-4 compared to free-wheeling diodes. Function The spark quenching unit will absorb voltage peaks resulting from inductive load switching, which can cause damage to insulation and contacts. It limits these to 70 V and reduces the contact load. Switching products with a contact opening distance of > 3 mm are suitable for this purpose. Electrical Connection (Terminals) (mm) (+) Input voltage 2 ( ) Input voltage 3 ( ) Coil 4 (+) Coil 5 Free nc terminal 6 Free nc terminal Ø3, ,5 9 5 Technical Data 30 Input voltage max. 300 VDC, max. 65 V peak (rectified voltage 400 VAC, 50 / 60 Hz) Switch-off energy max. 9 J / 2 ms Power dissipation max. 0, Watt Max. voltage nc terminals 250 V Protection IP65 / IP20 terminals Ambient temperature -25 C up to +85 C Storage temperature -25 C up to +05 C Max. conductor connection diameter 2,5 mm 2 / AWG 26-2 Max. terminal tightening torque 0,5 Nm Accessories Mounting bracket set for 35 mm rail acc. EN 6075: Article-No Order Number /
28 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Exact positioning over the entire service lifetime High torque security due to an optimised magnetic circuit and new design of the ROBA -quick. Therefore higher capacities due to less magnetic leakage flux. Exact positioning until wear limit ideal for positioning operations Large internal diameters of the magnetic coil bodies Therefore large permitted shaft diameters and few magnetic field losses Low noise Short switching times/high switching frequency wear, air gap max. adjusting interval wear, air gap max. adjusting interval conventional electromagnetic brakes number of switchings ROBA -quick number of switchings Functional principle ROBA -quick are energise to engage, electromagnetic pole face brakes. When DC voltage is applied to the magnetic coil (), a magnetic field is built up. The armature disk (3) is attracted to the brake coil carrier with friction lining (4). The brake torque runs from the coil carrier (2) via friction lining (4), armature disk (3) and membrane transmission spring (5) to the flange (6) and the shaft. If the magnetic coil is de-energised, the membrane transmission spring (5) draws the armature disk (3) back to the flange (6). The brake is released and the shaft (7) can run freely
29 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Summary of structural designs ROBA -quick ROBA -quick standard s 3 to 7 Type _.0 without accessories Type flange hub Type internal hub Type Pages 30 3 ROBA -quick standard s 8 to 9 Type 520._0 without accessories Type flange hub Type internal hub Type Pages ROBA -quick small mounting diameter s 3 to 7 Type 520.2_.0 without accessories Type flange hub Type internal hub Type Pages
30 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Standard s 3 7 Type _.0 L O ØH ØM ØZ Øs l z a t ØG Øs ØM ØD L2 W l 2 O 2 Ød Øg ØD 2 Øg n 2 L 2 Ød ØK ØD 2 V V strand length: 400 mm; 45º offset to screw-on bores b t k Type Standard Type Standard with flange hub Type Standard with internal hub Order Number / / / / s 3 to 7 without accessories flange hub internal hub 0 2 Coil voltage [VDC] Hub * bore Ø d H7 Keyway * acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 Example: 5 / / 24 / 30 / DIN 6885/ * Indication only with flange hub design or internal hub design. 30
31 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Standard s 3 7 Type _.0 Technical Data Nominal torque ) Type _.0 M 2 [Nm] 8, Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0,38 0,55,25,88 3,5 with flange hub m [kg] 0,42 0,86,40 2,35 7,5 Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,76,92 6,86 7,56 52,86 Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ],02 2,75 8,63 24,66 70,63 ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores Ød H7 Preferred bores [mm] 7; 20 20; 25 25; 30 30; 40 40; 50 min. [mm] max. [mm] ) ) Up to Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/, above Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/3 [mm] a 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 b 4,5 4 5,5 5,5 7,5 D 73, D G , g 29, H h K 3 x 4,5 3 x 5,5 3 x 6,6 3 x 8,7 3 x 8,8 k,6,7,7 2,2 2,2 L 22, 24,7 28, 3,4 34,7 L l 3,5 4,3 5,2 6 7 l M [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset M n 2 2,6 3,2, 0,3,7 O 42, 46,7 56, 63,4 70,7 O 2 26, 29,7 34, 38,3 43,7 s 4 x 4,8 4 x 5,7 4 x 6,8 4 x 6,8 4 x 9,2 s 3 x M4 3 x M5 3 x M6 3 x M8 3 x M8 t 3,9 4,5 5,8 7, 8,3 t 5,2 7,2 8,7 8,0 9,7 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, V 0, 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,2 W Z H z 3,5 4, We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 3
32 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Standard s 8 9 Type 520._0 strand length: 400 mm; 45º offset to screw-on bores b l 7 L 6 a O 2 O 3 k ØK W L 2 ØH ØM ØZ Øf ØG ØM ØD V Øs Ød Øg ØD 2 Øg Ød ØD 2 n 2 l 2 V Øs l 4 t L 2 V Type Standard Type Standard with flange hub Type Standard with internal hub Order Number / / / 8 9 without accessories flange hub internal hub 0 2 Coil voltage [VDC] Hub * bore Ø d H7 Example: 8 / / 24 / 40 * Indication only with flange hub design or internal hub design. 32
33 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Standard s 8 9 Type 520._0 Technical Data 8 9 Nominal torque ) Type 520. _0 M 2 [Nm] Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 5,64 6,90 with flange hub m [kg] 3,9 5,63 Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 8 35 Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores Ød H7 8 9 Preferred bores [mm] 40; 50 50; 60 min. [mm] max. [mm] [mm] 8 9 a 0,5 0,5 b 6 6 D D f 92 2 G 9 g H h K 3 x,5 4 x 20 k 2 4,2 L 2 45,3 53,9 L 6 40, 47,9 l 2 36,3 42,9 l [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset 8 9 l M M n 2 0,8,0 O 2 86,4 0,8 O 3 50, 58,9 s 4 x 9 4 x s 3 x M0 4 x M2 t 8,5,8 V 0, 0, V 0,2 0,25 W 5 20 Z H z 4 4 We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 33
34 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Small mounting diameter s 3 7 Type 520.2_.0 L O l a L 2 l2 O 2 L2 t ØH ØM ØZ Øs ØG Øs ØM ØD W Ød Øg ØD 2 Øg Ød ØD 2 z n 2 V ØK V strand length: b t 400 mm; 45º offset to screw-on bores k Type Small mounting diameter Type Small mounting diameter and flange hub Type Small mounting diameter and internal hub Order Number / / / / s 3 to 7 without accessories flange hub internal hub 0 2 Coil voltage [VDC] Hub * bore Ø d H7 Keyway * acc. DIN 6885/ or DIN 6885/3 Example: 6 / / 24 / 35 / DIN 6885/3 * Indication only with flange hub design or internal hub design. 34
35 ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Small mounting diameter s 3 7 Type 520.2_.0 Technical Data Nominal torque ) Type 520.2_.0 M 2 [Nm] 8, Electrical power P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Mass moment of inertia without accessories m [kg] 0,35 0,58,2,8 3,3 with flange hub m [kg] 0,4 0,65,35 2 3,85 Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,7,79 6,28 5,77 48, Flange hub 2) + Armature disk I own [0-4 kgm 2 ] 0,8,97 7,9 7,54 55,2 ) Please observe run-in regulations or minimum speed (see page 4). 2) With max. bore Standard voltages 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. Bores Ød H7 Preferred bores [mm] 0; 5 7; 20 20; 25 25; 30 30; 40 min. [mm] max. [mm] ) 45 3) Up to Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/, above Ø 32 keyway acc. DIN 6885/3 [mm] a 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 b 4,5 4 5,5 5,5 7,5 D 73, D G , g 27 29, H h K 3 x 3,5 3 x 4,5 3 x 5,5 3 x 6,6 3 x 8,8 k,6,7 2,3 2,7 2,7 L 22, 24,6 28, 30,9 34,4 L l 3,5 4,3 5,2 6 7 l 2, M [mm] Permitted shaft misalignm. and centre offset M n 2 8,5 6, 7,9 5,5 5,7 O 37, 44,6 50, 58,9 66,4 O 2 25,6 28,6 33, 36,9 4,4 s 4 x 4,8 4 x 5,7 4 x 6,8 4 x 6,8 4 x 9,2 s 3 x M3 3 x M4 3 x M5 3 x M6 3 x M8 t 3,9 4,4 5,9 6,6 8, t 4,0 5,2 6,7 8,7 8,2 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, V 0, 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,2 W Z H z 2 2,5 3 3,5 3,5 We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 35
36 Technical Explanations ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Installation Guidelines a V Fig. Fig. 2 Table Adjustment of the air gaps 8 9 a 0,2 +0, -0,05 0,2 +0,5-0,05 0,2 +0,5-0,05 0,3 +0,5-0,05 0,3 +0,5-0,05 0,5 +0,5-0, 0,5 +0,5-0, 8 9 V 0,05 0,05 0,05 0,05 0, 0, 0, Table 2 Permitted shaft misalignments The dimension a (Fig. ) must be adjusted according to Table. Please ensure that the shaft is fastened axially, since otherwise the dimension a will change and cause the armature disk to band against coil carrier. Design: ROBA -quick electromagnetic brakes are manufactured according to the electric protection IP 54 specification and the insulation material class F up to 55 C for coil, moulding compound and connection strands as well as insulation class B +30 C for the magnetic coil plastic-coated. The friction linings are asbestos-free, the surfaces of coil carrier and flange hub are phosphated. The armature disk is gas nitro-carburized and the transmission spring is made of stainless steel. ROBA -quick electromagnetic brakes are used for dry running. The torque is transmitted by friction between armature disk and the iron poles and the friction lining surfaces of the coil carrier. When braking the eccentricity V according to Table must not be exceeded. The larger the displacement V the more the torque decreases and the hotter the friction surface becomes. In the case of arrangement according to table care must be taken that the coil carrier and shaft have no axial backlash since otherwise a brushing of the coil carrier would be possible. The flange hub is kept axially by means of a set screw (on set 90 to the key). The V -values are indicated again in the Technical Data of the individual brakes. Please observe: The run-in conditions or the min. speed must be observed (see page 4). The friction surfaces have to be absolutely free of oil and grease as otherwise, the torque drops significantly. The air gap a (Fig. ) has to be checked periodically. The brake does not function correctly if the max. working air gap (see Table 4, page 39) is exceeded. Assembly and maintenance have to be carried out by well-trained specialists. 36
37 Technical Explanations ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Brake size calculation Formulas. Drive torque M A 9550 x P A [Nm] n 2. Required torque M req. K x M A [Nm] 3. Switchable torque of the brake (acc. to diagram, page 38) M S M req. [Nm] 4. Mass moment of inertia I I own + I add. [kgm 2 ] 5. Deceleration torque of the brake M v M S M L [Nm] 6. Deceleration time t v I x n 9,55 x M v + t [sec] 7. Max. switching frequency per hour (dependent on time) S h max t am + (t v + t 2 ) x,2 x 3600 [h - ] Key: P A [kw] drive power M A [Nm] drive torque M v [Nm] deceleration torque of the brake M req. [Nm] required torque M L [Nm] load torque (+ drop load) (- lift load) M S [Nm] switchable torque of the brake (diagram, page 38) n [rpm] drive speed K safety factor > 2 I [kgm 2 ] mass moment of inertia I own [kgm 2 ] own mass moment of inertia ( Technical data ) I add. [kgm 2 ] additional mass moment of inertia t v [sec] deceleration time t am [sec] acceleration time of the machine t [sec] switch-on time of the brake Table 3, t 2 [sec] switch-off time of the brake page 39 S h max [h - ] max. switching frequency per hour (dependent on time) Q tot. [J] total friction work (acc. Table 4, page 39) Q v [J] friction work per deceleration Q E [J] perm. friction work for single switching Table 4, Q [J/mm] friction work until mm wear page 39 Z n Z number of switchings until re-adjustment number of switchings until wear limit a [mm] nominal air gap Table 4, a n [mm] max. working air gap page Friction work per deceleration I x n 2 M s Q v x 82,4 M v [J] 9. Examination of the selected brake size in diagram 2 (page 38 friction power diagram). Intersection friction work / switching frequency must be below the friction power curve! If it is above, the next size has to be selected and re-calculated from point 3 on. Q v < Q E [J] 0. Number of switchings until re-adjustment Z n Q x (a - a) [-] n Q v. Number of switchings until wear limit Z Q tot. [-] Q v 37
38 Technical Explanations ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Calculation example Data: Input power P A 3 kw Input speed n 400 rpm Load torque output M L 5 Nm Additional mass moment of inertia I add. 0,5 kgm² Acceleration time of the machine t am,5 [sec] 350 switchings per hour 000 Switchable torque Drive torque M A Required torque 9550 x P A 9550 x 3 n ,5 [Nm] M req. K x M A 2 x 20,5 4 [Nm] Determined brake size (acc. to diagram ) 6 M S M req. 47 [Nm] selected brake 6, Type Mass moment of inertia I I own + I add. 0, ,5 0,5756 [kgm²] Deceleration torque of the brake M v M S + M L [Nm] ** Switchable torque M s [Nm] 00 0 Deceleration time of the brake t v I x n + t * 0,5756 x ,0 0,46 [sec] 9,55 x M v 9,55 x 62 * Switching times t and t 2 from Table 3, page 25 without overexcitation Max. switching frequency per hour S h max S h max t am + (t v + t 2 *) x,2 Friction work per deceleration Q v,5 + (0,46 + 0,060) x,2 I x n 2 M S x 82,4 M v x 3600 x [h - ] Diagram Speed n [rpm] ** Friction surfaces have been run in Friction power diagram valid for speed 500 rpm Calculation example Q v 0,5756 x x 82, [J] Q E The point of intersection determined in diagram 2 must be located in or under the characteristic curve of the selected brake. Switching frequency: 350 switchings per hour permitted Number of switchings until adjustment Z n Q Q v x (a n - a) Q v Switching work [J] Z n 57 x 07 x (,2-0,3) switchings 236 Number of switchings until wear limit Z Q tot. 00 x switchings Q v 236 Diagram Switching frequency S h [h - ]
39 Technical Explanations ROBA -quick electromagnetic brake Switching times The switching times stated in Table 3 have been determined by comprehensive series of tests. They are valid for switching DC-side with nominal air gap and warm coil. Deviations depend on the respective installation situation, ambient temperatures, release path and the type of rectification with which the corresponding brake is operated. Switching times Without overexcitation Type 520. _._ 8 9 t [sec] 0,006 0,008 0,00 0,05 0,025 0,027 0,030 t [sec] 0,035 0,040 0,055 0,00 0,50 0,245 0,330 t 2 [sec] 0,00 0,08 0,030 0,060 0,090 0,00 0,40 With overexcitation Type 520. _._ t [sec] 0,002 0,003 0,004 0,006 0,008 0,00 0,05 t [sec] 0,020 0,022 0,030 0,050 0,075 0,20 0,65 Table 3 M Key: P EINON M 2 M L t t v t 3 t t 2 0, M 2 t M 2 M L P t v t t t 2 t 3 Nominal torque of the brake Load torque of the drive Electrical power Deceleration time Connection time Response delay on connection Disconnection time Slip time AUS OFF t Diagram 3: Torque-time Friction work and air gap Friction work up to mm wear 8 9 Type 520. _._ Q [0 7 J/mm] 2, Total friction work Type 520. _._ Q tot. [0 7 J] 2, Permitted friction work with a single switching Q E [0 3 J] 3,8 6, Nominal air gap a [mm] 0,2 0,2 0,2 0,3 0,3 0,5 0,5 Max. working air gap a n [mm] 0,6 0,8,0,2,5,8 2,0 Table 4 Please Observe! Wear values can only be recommended values due to operating parameters, such as sliding speed, pressing or temperature. 39
40 Application Rectifiers are used to connect DC consumers to alternating voltage supplies, for example electromagnetic brakes and clutches (ROBA-stop, ROBA-quick, ROBATIC ), electromagnets, electrovalves, contactors, switch-on safe DC motors, etc. Function The AC input voltage (VAC) is rectified (VDC) in order to operate DC voltage units. Also, voltage peaks, which occur when switching off inductive loads and which may cause damage to insulation and contacts, are limited and the contact load reduced. Half-wave Rectifiers and Bridge Rectifiers Type 02_ Electrical Connection (Terminals) + 2 Input voltage Connection for an external switch for DC-side switching Coil 7-0 Free nc terminals (only for 2) (mm) ØD A C E 9 5 Order Number B / up to Half-wave rectifier Bridge rectifier A B C ØD E ,5 4, ,5 5,0 3/ ,5 5,0 Accessories: Mounting bracket set for 35 mm rail acc. EN 6075: Article-No Technical Data Bridge rectifier Half-wave rectifier Calculation output voltage VDC VAC x 0,9 VDC VAC x 0,45 Type /025 2/025 /024 2/024 3/024 4/024 Max. input voltage ± 0 % U AC [VAC] Max. output voltage U DC [VDC] Output current at 50 C I RMS [A] 2,5 2,5 3,0 4,0 4,0 4,0 max. 85 C I RMS [A],7,7,8 2,4 2,4 2,4 Max. coil nominal capacity at U AC 5 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 230 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 400 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 500 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] U AC 600 VAC 50 C P nom [W] up to 85 C P nom [W] Peak reverse voltage [V] Rated insulation voltage U RMS [V RMS] Pollution degree (insulation coordination) Device fuses To be included in the input voltage line. Recommended microfuse switching capacity H The microfuse corresponds to the max. possible connection capacity. If fuses are used corresponding to the actual capacities, FF 3,5 A FF 3,5 A FF 4 A FF 5 A FF 5 A FF 5 A the permitted limit integral I²t must be observed on selection. Permitted limit integral l 2 t [A 2 s] Protection IP65 components, encapsulated / IP20 terminals Terminals Cross-section 0,4 -,5 mm 2 (AWG 26-4) Ambient temperature [ C] - 25 up to + 85 Storage temperature [ C] - 25 up to + 05 Conformity markings UL, CE UL, CE UL, CE UL, CE UL, CE CE The installation position can be user-defined. Please ensure sufficient Installation conditions heat dissipation and air convection! Do not install near to sources of intense heat!
41 Spark Quenching Unit Type Application Reduces spark production on the switching contacts occurring during DC-side switching-off of inductive loads. Voltage limitation according to VDE , Item 4.6. Reduction of EMC-disturbance by voltage rise limitation, suppression of switching sparks. Reduction of brake engagement times by a factor of 2-4 compared to free-wheeling diodes. Function The spark quenching unit will absorb voltage peaks resulting from inductive load switching, which can cause damage to insulation and contacts. It limits these to 70 V and reduces the contact load. Switching products with a contact opening distance of > 3 mm are suitable for this purpose. Electrical Connection (Terminals) (mm) (+) Input voltage 2 ( ) Input voltage 3 ( ) Coil 4 (+) Coil 5 Free nc terminal 6 Free nc terminal Ø3, ,5 9 5 Technical Data 30 Input voltage max. 300 VDC, max. 65 V peak (rectified voltage 400 VAC, 50 / 60 Hz) Switch-off energy max. 9 J / 2 ms Power dissipation max. 0, Watt Max. voltage nc terminals 250 V Protection IP65 / IP20 terminals Ambient temperature -25 C up to +85 C Storage temperature -25 C up to +05 C Max. conductor connection diameter 2,5 mm 2 / AWG 26-2 Max. terminal tightening torque 0,5 Nm Accessories Mounting bracket set for 35 mm rail acc. EN 6075: Article-No Order Number /
42 ROBA -takt clutch brake module The clutch brake module for positioning and synchronising Energy-saving and environmentally-friendly Positioning accuracy for the entire service lifetime High switching frequency Maintenance-free during the entire service lifetime Low-noise Sealed Individual variants - without flange - with cast IEC-flange - with hollow shaft Maintenance-free/ no manual readjustment Constant switching behaviour, i.e. high positioning accuracy and freedom maintenance over the entire service lifetime No downtime due to re-adjustment Low leakage flux/ high friction power Larger magnetic and friction surfaces (asbestos free) with the same dimensions due to the new technology of the clutches and brakes Optimised electromagnetic effect, i.e. low leakage flux, faster switching behaviour, less heat build-up and, therefore, constant holding accuracy High radial shaft end loads Strengthened bearings High radial loads of the input and output shafts permitted Heat dissipation Optimized heat dissipation and large cooling ribs operational Optimum operation temperature due to dissipation of the frictional heat Constant characteristic operating data Functional Principle Sturdy housing Consists of en bloc cast two part ribbed housing, in a flanged design with cast flanges Large housing rigidity guarantees dimensional stability, even with loads not caused under regular conditions (for example weight load by people) The ROBA -takt clutch brake module is an electromagnetic clutch brake unit. Whilst the drive machine runs through continuously, it generates cycle operation via alternating coupling and braking actions. ROBA -takt clutch brake modules guarantee high cycle times. Due to the completely enclosed construction (Protection IP55), conceived acc. VDE/IEC directives, the ROBA -takt clutch brake module is ideal for all standardized motors and gearboxes. This means that many different installation positions are possible. Due to the patented principle of self-readjustment, the ROBA -takt clutch brake module is accurately positioned and maintenance-free over the entire service lifetime. 42
43 ROBA -takt clutch brake module Summary of structural designs ROBA -takt ROBA -takt s 3 to 7 Type 674.0_4.0 without feet Type with feet Type without flange/shaft without flange/shaft Pages ROBA -takt s 3 to 7 Type without feet IEC-flange small Type IEC-flange large Type with feet IEC-flange small Type IEC-flange large Type without flange/shaft ROBA -takt IEC-flange/hollow shaft Pages s 3 to 7 Type 67_.0_4.0 without feet IEC-flange small Type IEC-flange large Type with feet IEC-flange small Type IEC-flange large Type IEC-flange/shaft ROBA -takt without flange/shaft Pages s 3 to 7 Type 67_.0.0 without feet IEC-flange small/small Type IEC-flange small/large Type IEC-flange large/small Type IEC-flange large/large Type with feet IEC-flange small/small Type IEC-flange small/large Type IEC-flange large/small Type IEC-flange large/large Type IEC-flange/shaft IEC-flange/hollow shaft Pages 50 5 Additional designs are available on request. 43
44 i L L k H Ød i ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type 674.0_4.0 output side brake side input side clutch side B 2 M6x,5 f f l l u Ød H k A c Ør c c B B f l Order Number / / / W / W with control unit s 3 to 7 without feet with feet 0 Coil voltage [VDC] output * shaft Ø d k6 input * shaft Ø d k6 see pages Example: 5 / / 24 / W24 / W24 * Special dimensions on request 44
45 ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type 674.0_4.0 Technical Data Nominal torque Electrical power Clutch M 2 [Nm] Brake M 2 [Nm] 8, Clutch P 20 [W] Brake P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Type m [kg] 3,9 6,8 9,9 5,3 27,7 Mass moment of inertia Output Type I [0-4 kgm 2 ] 2,5 6,37 2,5 60,5 38 Standard voltage 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. [mm] A B B B c c 37 46, d k f H [mm] H i M5 M6 M8 M0 M2 k 2, L L l r 6,6 9 4 u We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 45
46 i ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type L L I 45 Øs f M6x,5 f 90 (4x) Ød k l Ød Øb Øe ØD H H H 2 u Ør B c A c c p B output side brake side input side clutch side l f Order Number Clutch side IEC-flange small IEC-flange large 5 6 / / / W / B with control unit s 3 to 7 without feet with feet 0 Coil voltage [VDC] output shaft * Ø d k6 input hollow shaft bore * Ø d F8 see pages Example: 4 / / 24 / W9 / B24 * Special dimensions on request
47 ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type Technical Data Nominal torque Electrical power Clutch M 2 [Nm] Brake M 2 [Nm] 8, Clutch P 20 [W] Brake P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Type m [kg] 3,9 6,8 9,9 5,3 27,7 Mass moment of inertia Output Type I [0-4 kgm 2 ] 2,5 6,37 2,5 60,5 38 Standard voltage 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. IEC [mm] optionally with small or large IEC-flange IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large D d F b +0,5 +0, e f 3, ,5 4,5 4,5 H ) l s [mm] A B B c c 3, d k f H H 2 ) [mm] i M5 M6 M8 M0 M2 k 2, L L l p r 6,6 9 4 u We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. ) Please observe the difference in height of the feet input side and output side. 47
48 i ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type 67_.0_4.0 output side brake side input side clutch side L M6x,5 Øs L 45 H m l l f H H 2 ØD Øe Øb Ød Ød i 90º (4x) k k u Ør B B f p c c A c l m Order Number Brake side IEC-flange small IEC-flange large 5 6 / / / W / W with control unit s 3 to 7 without feet with feet 0 Coil voltage [VDC] output shaft * Ø d k6 input shaft * Ø d k6 see pages Example: 4 / / 24 / W4 / W9 * Special dimensions on request
49 ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type 67_.0.0 Technical Data Nominal torque Electrical power Clutch M 2 [Nm] Brake M 2 [Nm] 8, Clutch P 20 [W] Brake P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Type m [kg] 3,9 6,8 9,9 5,3 27,7 Mass moment of inertia Output Type I [0-4 kgm 2 ] 2,5 6,37 2,5 60,5 38 Standard voltage 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. IEC [mm] optionally with small or large IEC-flange IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large D d k b j e f 3 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3, H ) i M4 M5 M5 M6 M6 M8 M8 M0 M0 M2 k 0 2,5 2, L l m 3 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3, s [mm] A B B c c 3, d k f H ) Please observe the difference in height of the feet input side and output side. [mm] H 2 ) i M5 M6 M8 M0 M2 k 2, L l p r 6,6 9 4 u 2, We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 49
50 i ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type 67_.0.0 output side brake side input side clutch side L L l f M6x,5 m 90º (4x) ØD Øe Øb Ød Ød Øb Øe ØD H k u H Øs Øs l Ør B f p c c A c p 45º B l m Order Number Brake side IEC-flange small IEC-flange large 5 6 Clutch side IEC-flange small IEC-flange large 5 6 / / / W / B with control unit s 3 to 7 without feet with feet 0 Coil voltage [VDC] output shaft * Ø d k6 input hollow shaft bore * Ø d F8 see pages Example: 7 / / 24 / W28 / B28 * Special dimensions on request
51 ROBA -takt clutch brake module s 3 7 Type 67_.0.0 Technical Data Nominal torque Electrical power Clutch M 2 [Nm] Brake M 2 [Nm] 8, Clutch P 20 [W] Brake P 20 [W] Maximum speed n max [rpm] Weight Type m [kg] 3,9 6,8 9,9 5,3 27,7 Mass moment of inertia Output Type I [0-4 kgm 2 ] 2,5 6,37 2,5 60,5 38 Standard voltage 24 VDC; 04 VDC. Permitted voltage tolerances acc. IEC 38 +/-0 %. IEC [mm] optionally with small or large IEC-flange IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large IEC-small IEC-large D d k d F b j b +0,5 +0, e f 3 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3, f 3, ,5 4,5 4,5 H ) i M4 M5 M5 M6 M6 M8 M8 M0 M0 M2 k 0 2,5 2, L l l m 3 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3, s ) The difference in height of feet depends on the flange diameter [mm] A B B c c 3, ) Please observe the difference in height of the feet input side and output side. [mm] H L p r 6,6 9 4 u We reserve the right to make dimensional and constructional alterations. 5
52 Technical Explanations ROBA -takt clutch brake module Installation Clutch Brake Unit with flange: The shafts, centring, screw-on pitch circles and diameters of the flanges are designed according to IEC-standard. Input and output sides can be fitted with the corresponding flanges of motor, gearbox or other units without problems, as shown in Fig.. Permitted shaft loads The drive elements located on the shafts exert a radial load during operation which has to be absorbed by the bearings of the unit. The load is limited by the required life of the bearings and strength of the shaft (Table ). Fig. 3 Fig. Installation of the transmission elements: The drive elements are mounted onto the respective shafts and secured axially via a press cover and a screw screwed into the threaded centre hole of the shaft, see Fig. 2. For the combination motor shaft - ROBA -takt hollow shaft, the motor shaft must be greased slightly to prevent frictional corrosion. Extensive force or hammer blows can damage the bearings. Radial loads acting on the shaft via the drive elements must not exceed the maximum allowable values (see heading permissible shaft load ). Should both radial and axial loads be present on the shaft, the permissible loads must be determined - please contact our engineers. ROBA -takt max. permitted radial force F max [N] Input shaft without IEC-flange Output shaft without IEC-flange Output shaft small IEC-flange Output shaft large IEC-flange Table : Max. permitted radial force F max limited due to the strength of the shaft, application of load midway along shaft. The application of load is assumed to be midway along the shaft, determining the acceptable radial load. In case of additional axial loads, an extensive calculation is necessary (please contact the manufacturer). The permitted radial forces stated in Table 2 refer to a speed of n 500 rpm and a bearing service life L h hours. ROBA -takt Radial force F N [N] Input shaft without IEC-flange Output shaft without IEC-flange Output shaft small IEC-flange Output shaft large IEC-flange Fig. 2 Table 2: Permitted radial force F N with speed n 500 rpm, bearing service life L h hours assuming load applied midway along shaft. The permitted force F can be calculated with factor k for other speeds or bearing lifetimes. The factor k is determined from diagram. Correction factor k [-] bearing service life in hours L h [h] F k F N F max [N] F in N Permitted radial force k Correction factor (diagram ) F N in N Permitted radial force at n 500 rpm and bearing service life L h hours (Table 2) 52 Diagram Speed n [rpm] F max in N Max. permitted radial force, limited due to shaft strength (Table )
53 Technical Explanations ROBA -takt clutch brake module Clutch brake modul size calculation Formulas. Drive torque M A 9550 x P A [Nm] n 2. Required torque M req. K x M A [Nm] 3. Pre-selection of the unit size acc. diagram page 54 M S M req. [Nm] 4. Mass moment of inertia I I own + I add. [kgm 2 ] 5. Acceleration time input side (M A M S ) I x n ) t a + t [sec] 9,55 x (M S M L ) 6. Braking time output side t v Basis: M L constant M S constant I x n 2) + t [sec] 9,55 x (M S M L ) Key: P A [kw] drive power M A [Nm] drive torque M req. [Nm] required torque M L [Nm] load torque ( / drop load) In case of a load reduce the value in the bracket M S [Nm] switchable torque (diagram, page 54) n [rpm] drive speed K safety factor > 2 I [kgm 2 ] mass moment of inertia I own [kgm 2 ] own mass moment of inertia ( Technical data ) I add. [kgm 2 ] additional mass moment of inertia t a [sec] acceleration time (input side) t v [sec] braking time (output side) ) t [sec] switching time of the clutch Table 3, 2) t [sec] switching time of the brake page 55 S h max [h - ] max. switching frequency per hour (dependent on time) Q tot. [J] total friction work (acc. to Table 4, page 55) Q a [J] friction work per acceleration Q E [J] perm. friction work with single switching Table 4, Q v [J] friction work per deceleration page 55 t S [s] delay times Z number of switchings until wear limit 7. Max. switching frequency per hour (dependent on time) S h max x 3600 [h - ] (t v + t a ) x,2 8. Friction work per acceleration I x n 2 M s Q a x 82,4 M S M L [J] Q a < Q E [J] 9. Friction work per delay I x n 2 M s Q v x 82,4 M S M L [J] Q v < Q E [J] 0. Check the selected unit size in diagram 2 (page 54 friction power diagram). The point of intersection of friction work (switching work)/ cycling frequency must be below the friction power curve! If it is above, the next size has to be selected and re-calculated from point 3 on.. Number of switchings until wear limit Z Q tot. [-] * Qa (Q v ) x 2 * Q a /Q v - put in higher value 53
54 Technical Explanations ROBA -takt clutch brake module Calculation example Data: Input power P A 0,75 kw Input speed n 400 rpm Load torque output M L 3,0 Nm Additional mass moment of inertia I add. 0,0042 kgm² 3000 cycles per hour Drive torque M A Required torque 9550 x P A 9550 x 0,75 5, [Nm] n 400 M req. K x M A 2 x 5, 0,2 [Nm] Determined unit size acc. diagram 4 M S M req. [Nm] Mass moment of inertia I I own + I add. 0, ,0042 0,00484 [kgm2 ] Acceleration time input side (lift load) (M A M S ) t a t a I x n 9,55 x (M S M L ) 0,00484 x 400 9,55 x ( - 3) + *t ) (clutch) + 0,065 0,53 [sec] ** Switchable torque M s [Nm] Switchable torque Speed n [rpm] 7 4 Clutch 6 4 Brake 5 3 Clutch Calculation example 3 Brake Braking time output side (drop load) t v I x n 9,55 x (M S M L ) 2) + *t (brake) t v 0,00484 x 400 9,55 x ( - 3) + 0,040 0,29 [sec] ) 2) * switching times t and t from Table 3, page 55 without overexcitation Max. switching frequency per hour S h max (t v + t a ) x,2 x 3600 S h max (0,29 + 0,53) x,2 x [h - ] Diagram ** Friction surfaces have been run Friction power diagram valid for speed 500 rpm Calculation example Friction work per acceleration Q a I x n 2 M x S 82,4 M S - M L Q a 0,00484 x x 82,4-3 Friction work per deceleration Q v I x n 2 M x S 82,4 M S + M L 7,5 [J] Q E Q a /Q v Switching work [J] Q v 0,00484 x x 82, ,9 [J] Q E Check the selected unit size in the friction power diagram (determine point of intersection Q a or Q v to S h ). (The point of intersection determined in diagram 2 must be located in or under the characteristic curve of the selected unit). Number of switchings until wear limit Z Q tot. 44 x 0 7 3,08 x 0 6 switchings Q a x 2 7,5 x Switching frequency S h [h - ] Diagram 2
55 Technical Explanations ROBA -takt clutch brake module Switching Times The switching times stated in Table 3 have been determined by comprehensive series of tests. They are valid for switching DC-side with nominal air gap and warm coil. Deviations depend on the respective installation situation, ambient temperatures, release path and the type of rectification with which the corresponding clutch is operated. Switching times t Clutch [sec] 0,00 0,05 0,020 0,030 0,045 t Clutch [sec] 0,045 0,065 0,080 0,50 0,200 Without t Brake [sec] 0,006 0,008 0,00 0,05 0,025 overexcitation t Brake [sec] 0,035 0,040 0,055 0,00 0,50 t 2 Clutch [sec] 0,02 0,020 0,045 0,060 0,090 t 2 Brake [sec] 0,00 0,08 0,030 0,060 0,090 t Clutch [sec] 0,003 0,005 0,007 0,00 0,05 With t Clutch [sec] 0,025 0,035 0,040 0,075 0,00 overexcitation t (only switch-on time) Brake [sec] 0,002 0,003 0,004 0,006 0,008 t Brake [sec] 0,020 0,022 0,030 0,050 0,075 Recommended duration of overexcitation [sec] 0,00 ) 0,00 ) 0,00 0,05 0,020 Minimal necessary slope with overexcitation [sec] 0,020 0,025 0,030 0,080 0,20 separation without overexcitation [sec] 0 0 0,05 0,050 0,080 Height of the overexcitation approx. 0 x nominal voltage (current limited) Table 3 ) In case of operation with overexcitation and high switching frequency (80-00 % of the diagram value), the recommended period of the overexcitation acc. Table 3 must not be exceeded. M M 2 M L t t Clutch t 3 t a Brake t 2 t 2 t t 3 t t v 0, M 2 t Key: M 2 M L P t a t v t t t 2 t 3 Nominal torque of the brake or clutch Load torque of the drive Electrical power Acceleration time Deceleration time Connection time Response delay on connection Disconnection time Slip time P Clutch ON OFF Brake ON Slope separation Slope separation t Diagram 3: Torque-time Friction work Permitted friction work for single switching Q E [0 3 J] 3,8 6, Total friction work Q tot. [0 7 J] 22, Table 4 Please Observe! Wear values can only be recommended values due to operating parameters, such as sliding speed, pressing or temperature. 55
56 ROBA -takt control unit Type Application This unit is used to start, stop and to position by switching and controlling the mayr ROBA -takt clutch brake modules. Function The ROBA -takt control unit operates according to the principle of a clocked switching controller with a frequency of 8 khz. Its coil is energised by actuating the sensor for clutch and brake. A temperature monitor protects the unit from overheating. Should the temperature exceed >80 C, the coil voltage is switched off. The LED excess temperature unit lights up red. A slope separation avoids simultaneous occurrence of clutch and brake torques. On overexcitation, the coil attraction time is reduced, allowing exact switching and positioning. Electrical Connection (mm) 2 7 Coil connection for clutch Ku / Ku2 2 Coil connection for brake Br / Br2 3 Sensor connection for clutch +2 V / Ku / Gnd 4 Sensor connection for brake +2 V / Br / Gnd2 5 Connection input voltage PE, L, N 6 Temperature monitoring Option (bare) 7 Signalling relay Option 2 (bare) Technical Data Input voltage 230 VAC ±0 %, Hz Power input max. 4 Ampere /00 % duty cycle No-load supply power < 7 Watt Coil Nom -Voltage 24 VDC Coil Nom -power maximal 96 Watt Coil Nom -current Manufacturer-side setting to mayr ROBA -takt-size Coil overexcitation maximal 325 VDC current limitation is adapted to the respective coil size Overexcitation time 2-50 ms ( 30 % to +60 %), externally adjustable (only applicable with coding overexcitation ON ) Slope separation 2-50 ms ( 25 % to +30 %), externally adjustable Protection IP20 Ambient temperature 0 C to +50 C Storage temperature -20 C to +70 C Clamping conductor cross section 2,5 mm 2 Weight,5 kg / 3,3 lb Protection fuse Input-side: G-microfuse F/F2, (M) 4 A, 5x20mm Protection fuse Coil-side: G-microfuse F3, the current is adapted to the ROBA -takt sizes. Always use the same replacement fuses Overvoltage category two; one for connection to PELV/SELV PELV/SELV (control wires) Overvoltage protection For installation in overvoltage category III, a suitable overvoltage protection unit is required between the incoming voltage and the ROBA -takt control unit. Order Number / s 3-7 ROBA -takt control unit 56 Control unit temperature monitoring A fitted temperature switch prevents the control unit from overheating.
57 ROBA -takt control unit Type Functional Sequence Brake Voltage Brake Current Clutch Voltage Clutch Current Clutch Slope separation Clutch Overexcitation Brake Slope separation Brake Overexcitation 325 VDC overexcitation Voltage with current limitation 24 VDC coil voltage Limited current with overexcitation Current with 24 VDC coil voltage 325 VDC overexcitation Voltage with current limitation 24 VDC coil voltage Limited current with overexcitation Current with 24 VDC coil voltage LED LED LED Mains Clutch Brake Mains OFF ON Clutch Start ON Brake Start ON Connection Example Control elements / control function Control sensor for start and stop Connection example -sensor operation Connection example 2-sensor operation Brake (Br) Clutch (Ku) 2V Ku Gnd 2V Br Gnd 2 2V Ku Gnd 2V Br Gnd 2 Application Function (condition-controlled) Function (slope-controlled) Contact potential-free (NO-Contact) 2V Ku Gnd 2V Br Gnd 2 Close contact Clutch ON Close contact clutch or Clutch ON Open contact Brake ON Close contact brake Brake ON SPS - Control (0-30 VDC) (-) (0-30 VDC) (+) 2V Ku Gnd 2V Br Gnd VDC signal Clutch ON 0 VDC signal Brake ON + 24 VDC signal to clutch or + 24 VDC signal to brake Clutch ON Brake ON External voltage (0-30 VDC) (-) (0-30 VDC) (+) 2V Ku Gnd 2V Br Gnd VDC signal Clutch ON 0 VDC signal Brake ON VDC signal to clutch or VDC signal to brake Clutch ON Brake ON NAMUR Proximity switch (0-30 VDC) sw bl 2V Ku Gnd 2V Br Gnd 2 Sensor undamped Sensor damped Clutch ON Brake ON Sensor clutch undamped or Sensor brake undamped Clutch ON Brake ON PNP - NC contact Proximity switch (0-30 VDC) br sw bl 2V Ku Gnd 2V Br Gnd 2 Sensor undamped Sensor damped Clutch ON Brake ON Geber Kupplung undamped or Sensor brake undamped Clutch ON Brake ON 57
58 Application This device is used to start and stop mayr ROBA -takt clutch brake modules. It can be used for alternating 24 VDC coil switching, if a 24 VDC power supply is available. ROBA -takt circuit module Type _ Function -sensor operation: activated deactivated clutch is energised brake is energised The respective control of the clutch or brake is indicated via LED. The ROBA -takt circuit module has no over excitation function. The brake has priority: The brake is energised independently of the sensor position when the 24 VDC power supply is switched on. The coil is energised with the 24 VDC power supply. Slope separation: To avoid simultaneous clutch and braking torques, a slope separation of 0-00 ms between clutch and brake can be set, which acts according to the respective rise time and drop-out time of the coils (see switching time table). This adjustment is carried out via the potentiometers Ku clutch (P2) and Br brake (P). The factory default setting is 0 ms. Brake Clutch ON OFF ON OFF Slope separation clutch max. 00 ms Slope separation brake max. 00 ms Electrical Connection (Terminals) Input voltage 24 VDC 2 Input voltage GND Brake Clutch 7 Control voltage for switches or sensors 2 VDC Control inputs Technical Data Input voltage 24 VDC SELV/PELV ripple content 5% Recommended fuse T 4A Output voltage 24 VDC Output power maximal 79 W Slope separation 0 00 ms (factory default setting is 0 ms) Ambient temperature 0 C to +70 C Storage temperature -20 C to +85 C Conductor cross section 0,4 -,5 mm² / AWG 26-4 Protection IP00 Design Printed board with screw-on attachment part or a mounting frame for 35 mm standard mounting rails Maximal cycle frequencies 45 C 70 C up to A / sizes cycles / min approx. 2 A / sizes cycles / min approx. 3 A / size 7 cycles / min (mm) with mounting frame Component assembly only shown partially Order Number 77 67,5 63 / _ 58 Please Observe! Higher cycle frequencies will lead to ROBA -takt circuit module overload and failure. only printed board without frame printed board with mounting frame 0
59 Headquarters Chr. Mayr GmbH + Co. KG Eichenstrasse, D Mauerstetten Tel.: /8 04-0, Fax: / [email protected] Service Germany Baden-Württemberg Esslinger Straße Leinfelden-Echterdingen Tel.: 07 / Fax: 07 / Bavaria Eichenstrasse Mauerstetten Tel.: / Fax: / Chemnitz Bornaer Straße Chemnitz Tel.: 03 7/ Fax: 03 7/ Franken Unterer Markt Hersbruck Tel.: 0 9 5/ Fax: 0 9 5/ Hagen Im Langenstück Hagen Tel.: / Fax: / Kamen Lünener Strasse Kamen Tel.: / Fax: / North Schiefer Brink Extertal Tel.: / Fax: / Rhine-Main Hans-Böckler-Straße Groß-Umstadt Tel.: / Fax: / Branch office China Mayr Zhangjiagang Power Transmission Co., Ltd. Changxing Road No. 6, Zhangjiagang Tel.: 05 2/ Fax: 05 2/ [email protected] Great Britain Mayr Transmissions Ltd. Valley Road, Business Park Keighley, BD2 4LZ West Yorkshire Tel.: / Fax: / [email protected] France Mayr France S.A. Z.A.L. du Minopole BP Bully-Les-Mines Tel.: Fax: [email protected] Italy Mayr Italia S.r.l. Viale Veneto, Saonara (PD) Tel.: 0 49/ Fax: 0 49/ [email protected] Singapore Mayr Transmission (S) PTE Ltd. No. 8 Boon Lay Way Unit 03-06, TradeHub 2 Singapore Tel.: 00 65/ Fax: 00 65/ [email protected] Switzerland Mayr Kupplungen AG Tobeläckerstrasse 822 Neuhausen am Rheinfall Tel.: 0 52/ Fax: 0 52/ [email protected] USA Mayr Corporation 4 North Street Waldwick NJ Tel.: 2 0/ Fax: 2 0/ [email protected] Representatives Australia Transmission Australia Pty. Ltd. 22 Corporate Ave, 378 Rowville, Victoria Australien Tel.: 0 39/ Fax: 0 39/ [email protected] China Mayr Power Transmission Co., Ltd. Shanghai Representative Office Room 2206, No. 888 Yishan Road Shanghai, VR China Tel.: 0 2/ Fax: 0 2/ [email protected] India National Engineering Company (NENCO) J-225, M.I.D.C. Bhosari Pune 4026 Tel.: 0 20/ Fax: 0 20/ [email protected] Japan MATSUI Corporation Azabudai Minato-ku Tokyo Tel.: 03/ Fax: 03/ [email protected] South Africa Torque Transfer Private Bag 9 Elandsfonstein 406 Tel.: 0 / Fax: 0 / [email protected] South Korea Mayr Korea Co. Ltd. Room No.002, 0th floor, Nex Zone, SK TECHNOPARK, 77-, SungSan-Dong, SungSan-Gu, Changwon, Korea Tel.: 0 55/ Fax: 0 55/ [email protected] Taiwan German Tech Auto Co., Ltd. No. 28, Fenggong Zhong Road, Shengang Dist., Taichung City 429, Taiwan R.O.C. Tel.: 04/ Fax: 04/ [email protected] Machine tools Applications in China Dynamic Power Transmission Co., Ltd. Block 5th, No. 699, Songze Road, Xujing Industrial Zone Shanghai, China Tel.: 02/ Fax: 02/ [email protected] More representatives: Austria, Benelux States, Brazil, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, Greece, Hongkong, Hungary, Indonesia, Israel, Malaysia, New Zealand, Norway, Philippines, Poland, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Thailand, Turkey You can find the complete address for the representative responsible for your area under in the internet. your reliable partner 59
60 Product Summary Safety Clutches/Overload Clutches EAS -Compact /EAS -NC Positive locking and completely backlash-free torque limiting clutches EAS -smartic Cost-effective torque limiting clutches, quick installation EAS -element clutch/eas -elements Load-disconnecting protection against high torques EAS -axial Exact limitation of tensile and compressive forces EAS -Sp/EAS -Sm/EAS -Zr Load-disconnecting torque limiting clutches with switching function ROBA -slip hub Load-holding, frictionally locked torque limiting clutches ROBA -contitorque Magnetic continuous slip clutches Shaft Couplings smartflex Perfect precision couplings for servo and stepping motors ROBA -ES Backlash-free and damping for vibration-sensitive drives ROBA -DS/ROBA -D Backlash-free, torsionally rigid all-steel couplings EAS -control-ds Cost-effective torque-measuring couplings Electromagnetic Brakes/Clutches ROBA-stop standard Multifunctional all-round safety brakes ROBA-stop -M motor brakes Robust, cost-effective motor brakes ROBA-stop -S Water-proof, robust monoblock brakes ROBA-stop -Z/ROBA-stop -silenzio Doubly safe elevator brakes ROBA -diskstop Compact, very quiet disk brakes ROBA -topstop Brake systems for gravity loaded axes ROBA -linearstop Backlash-free brake systems for linear motor axes ROBATIC /ROBA -quick/roba -takt Electromagnetic clutches and brakes, clutch brake units DC Drives tendo -PM Permanent magnet-excited DC motors tendo -SC quadrant and 4 quadrant transistor controllers 5/05/202 GF/SC
Installation and Operating Instructions for ROBA -takt Control Unit Type 014.000.2
 Manufacturer s Declaration This product is intended f installation in a machine system, based on the machine directive 006/4/EC. It is fbidden to start use of the product until the machine system into
Manufacturer s Declaration This product is intended f installation in a machine system, based on the machine directive 006/4/EC. It is fbidden to start use of the product until the machine system into
Mounting Instructions. Torque Transducer. A0329 3.2 en
 Mounting Instructions Torque Transducer T5 T5 Contents 3 Page Safety instructions.............................................. 4 1 Measuring characteristics..................................... 7 2 Mounting.....................................................
Mounting Instructions Torque Transducer T5 T5 Contents 3 Page Safety instructions.............................................. 4 1 Measuring characteristics..................................... 7 2 Mounting.....................................................
Type: DILM115(RAC240) Article No.: 239548 Sales text Contactor,55kW/400V,AC operated. Ordering information
 Type: DILM115(RAC240) Article No.: 239548 Sales text Contactor,55kW/400V,AC operated Ordering information Connection technique Description Description Rated operational current Screw terminals 3 pole AC
Type: DILM115(RAC240) Article No.: 239548 Sales text Contactor,55kW/400V,AC operated Ordering information Connection technique Description Description Rated operational current Screw terminals 3 pole AC
Data Sheet. Electro-mechanical counters Hengstler 800 series
 Data Pack D Issued March 00 504897 Data Sheet Electro-mechanical counters Hengstler 800 series The 800 series totalising and predetermining batch counters, manufactured by Hengstler, is available from
Data Pack D Issued March 00 504897 Data Sheet Electro-mechanical counters Hengstler 800 series The 800 series totalising and predetermining batch counters, manufactured by Hengstler, is available from
Cable Plug acc. to DIN EN 175301-803, Form A
 Cable Plug acc. to DIN EN 175301-803, Form A Complete program Contact form 18 mm Also available with LED indicator Optional 4-pin version for pressure switch or impulse valves respectively Versions with
Cable Plug acc. to DIN EN 175301-803, Form A Complete program Contact form 18 mm Also available with LED indicator Optional 4-pin version for pressure switch or impulse valves respectively Versions with
Series 8146/5-V37 and Series 8150/5-V37
 www.stahl.de > Clear assignment safe technology easy installation > Intelligent structure only one rotary actuator for frequency-controlled drives ) 20 ms leading auxiliary contact for safe motor disconnection
www.stahl.de > Clear assignment safe technology easy installation > Intelligent structure only one rotary actuator for frequency-controlled drives ) 20 ms leading auxiliary contact for safe motor disconnection
Electronic timer CT-VBS.17+18 OFF-delayed without auxiliary voltage, for DC contactors Data sheet
 Characteristics Single-function OFF-delay timer for DC contactors, without auxiliary voltage Width.5 mm CDC 5 6 F3 Approvals A culus E CCC CT-VBS a Circuit diagram b Marker label Marks a CE b C-Tick Order
Characteristics Single-function OFF-delay timer for DC contactors, without auxiliary voltage Width.5 mm CDC 5 6 F3 Approvals A culus E CCC CT-VBS a Circuit diagram b Marker label Marks a CE b C-Tick Order
industrial drive systems AC LINE Spring-applied single-disc brake 73 341..A00 73 431..H00 73 241..E00 / 73 245..E00
 industrial drive systems AC LINE Spring-applied single-disc brake 73 341..A00 73 431..H00 73 241..E00 / 73 245..E00 AC LINE Kendrion (Aerzen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion (Villingen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion Magnetic
industrial drive systems AC LINE Spring-applied single-disc brake 73 341..A00 73 431..H00 73 241..E00 / 73 245..E00 AC LINE Kendrion (Aerzen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion (Villingen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion Magnetic
Technical Description. Transistor D.C. Chopper Controller Type GS 24 S
 Technical Description Transistor D.C. Chopper Controller Type GS 24 S Table of contents 1. Getting started guide 2. General information 2.1. Characteristics 2.2. Accessories 3. Information about the Machine
Technical Description Transistor D.C. Chopper Controller Type GS 24 S Table of contents 1. Getting started guide 2. General information 2.1. Characteristics 2.2. Accessories 3. Information about the Machine
Single-Phase AC Synchronous Generator
 ST Series Single-Phase AC Synchronous Generator Instructions for Operation and Maintenance English to English translation by R.G. Keen, May 2004. ST Series of Single-Phase AC Synchronous Generators Description
ST Series Single-Phase AC Synchronous Generator Instructions for Operation and Maintenance English to English translation by R.G. Keen, May 2004. ST Series of Single-Phase AC Synchronous Generators Description
48.12. 2 pole, 8 A Safety relay. Screw terminal. 35 mm rail (EN 60715) mounting. 2 CO (DPDT) 8/15 250/400 2,000 500 0.37 8/0.65/0.
 48 Series - Relay interface modules 8 A Features 48.12 2 Pole Safety relay interface modules, 15.8 mm wide 48.12-2 Pole 8 A (screw terminal) DC sensitive coils Relay with forcibly guided contacts according
48 Series - Relay interface modules 8 A Features 48.12 2 Pole Safety relay interface modules, 15.8 mm wide 48.12-2 Pole 8 A (screw terminal) DC sensitive coils Relay with forcibly guided contacts according
ABB i-bus EIB / KNX Analogue Input AE/S 4.2
 Product Manual ABB i-bus EIB / KNX Analogue Input AE/S 4.2 Intelligent Installation Systems This manual describes the functionality of Analogue Input AE/S 4.2. Subject to changes and errors excepted. Exclusion
Product Manual ABB i-bus EIB / KNX Analogue Input AE/S 4.2 Intelligent Installation Systems This manual describes the functionality of Analogue Input AE/S 4.2. Subject to changes and errors excepted. Exclusion
38 Series - Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 - 16 A
 38 Series - Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 - 16 A 38 SERIES Common features Instant ejection of relay by plastic retaining clip Integral coil indication and protection circuit EMR Electromechanical
38 Series - Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 - 16 A 38 SERIES Common features Instant ejection of relay by plastic retaining clip Integral coil indication and protection circuit EMR Electromechanical
Series 6000 Torque measured metal bellow coupling
 Properties Free of float metal bellow coupling with integrated torque measurement Non-contact measurement system, high robustness High torsional stiffness Limited torque of inertia Performance Measurement
Properties Free of float metal bellow coupling with integrated torque measurement Non-contact measurement system, high robustness High torsional stiffness Limited torque of inertia Performance Measurement
38 SERIES. Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 - 16 A. EMR Electromechanical Relays. Common features. SSR Solid State Relays. 6.
 38 Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 - 16 A 38 Common features Instant ejection of relay by plastic retaining clip Integral coil indication and protection circuit 6.2 mm wide EMR - DC, AC or AC/DC
38 Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 - 16 A 38 Common features Instant ejection of relay by plastic retaining clip Integral coil indication and protection circuit 6.2 mm wide EMR - DC, AC or AC/DC
Torque motors. direct drive technology
 Torque motors direct drive technology Why Direct Drive Motors? Fast and effective Direct-drive technology in mechanical engineering is defined as the use of actuators which transfer their power directly
Torque motors direct drive technology Why Direct Drive Motors? Fast and effective Direct-drive technology in mechanical engineering is defined as the use of actuators which transfer their power directly
Vario Line. Spring pressure single-disc brake 76 431..H00
 Vario Line Spring pressure single-disc brake 76 431..H00 Vario Line Industrial Drive Systems Die Welt von Kendrion Industrial Drive Systems Kendrion the brake experts As a solution provider, Kendrion develops,
Vario Line Spring pressure single-disc brake 76 431..H00 Vario Line Industrial Drive Systems Die Welt von Kendrion Industrial Drive Systems Kendrion the brake experts As a solution provider, Kendrion develops,
RM4TG20 three-phase network control relay RM4-T - range 200..500 V
 Characteristics three-phase network control relay RM4-T - range 200..500 V Complementary [Us] rated supply voltage Output contacts Setting accuracy of time delay Delay at power up Measuring cycle Marking
Characteristics three-phase network control relay RM4-T - range 200..500 V Complementary [Us] rated supply voltage Output contacts Setting accuracy of time delay Delay at power up Measuring cycle Marking
Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFE
 Data sheet Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFE The CM-PFE is a three-phase monitoring relay that monitors the phase parameter phase sequence and phase failure in three-phase mains. 2CDC 251 005 S0012 Characteristics
Data sheet Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFE The CM-PFE is a three-phase monitoring relay that monitors the phase parameter phase sequence and phase failure in three-phase mains. 2CDC 251 005 S0012 Characteristics
38 Series - Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 A
 38 Series - Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 A Common features Instant ejection of relay by plastic retaining clip Integral coil indication and protection circuit EMR Electromechanical Relays
38 Series - Relay interface modules 0.1-2 - 3-5 - 6-8 A Common features Instant ejection of relay by plastic retaining clip Integral coil indication and protection circuit EMR Electromechanical Relays
Your Advantages For safety application up to PL e / Cat. 4 e.g. SIL 3 Manual or automatic start 0225592. * see variants. Applications.
 Safety Technique SAFEMASTER Emergency Stop Module BG 5924, IP 5924 Your Advantages For safety application up to PL e / Cat. 4 e.g. SIL 3 Manual or automatic start 0225592 BG 5924 IP 5924 Product Description
Safety Technique SAFEMASTER Emergency Stop Module BG 5924, IP 5924 Your Advantages For safety application up to PL e / Cat. 4 e.g. SIL 3 Manual or automatic start 0225592 BG 5924 IP 5924 Product Description
49 Series - Relay interface modules 8-10 - 16 A. Features
 Features 1 & 2 Pole relay interface modules 5 µm Gold plate contacts for low level switching capability 49.31-50x0-1 Pole 10 A (screw terminal) 49.52-50x0-2 Pole 8 A (screw terminal) 49.72-50x0-2 Pole
Features 1 & 2 Pole relay interface modules 5 µm Gold plate contacts for low level switching capability 49.31-50x0-1 Pole 10 A (screw terminal) 49.52-50x0-2 Pole 8 A (screw terminal) 49.72-50x0-2 Pole
48 SERIES Relay interface modules 10 A
 48 Relay interface modules 10 A 1 CO relay interface modules, mm wide Ideal interface for PLC and electronic systems Type 48.P3 1 CO 10 A s Type 48.31 1 CO 10 A s AC coils or DC sensitive coils Supply
48 Relay interface modules 10 A 1 CO relay interface modules, mm wide Ideal interface for PLC and electronic systems Type 48.P3 1 CO 10 A s Type 48.31 1 CO 10 A s AC coils or DC sensitive coils Supply
MINEX -S. Magnetic coupling. You will find continuously updated data in our online catalogue at www.ktr.com
 MINEX - 171 Table of contents NEW MINEX - 171 Coupling description 173 Technical description 174 s A 22/4 to B 60/8 with containment shroud made of stainless steel 175 s A 75/10 to F 250/38 with containment
MINEX - 171 Table of contents NEW MINEX - 171 Coupling description 173 Technical description 174 s A 22/4 to B 60/8 with containment shroud made of stainless steel 175 s A 75/10 to F 250/38 with containment
Relés e Contatores de Estado Sólido SIRIUS
 Relés e Contatores de Estado Sólido SIRIUS Coletânea de dados técnicos ( product data sheet ) Agosto/212 SSR - 3RF21 22,5 mm Ponto Zero SSR - 3RF2 45 mm Ponto Zero SSR - 3RF22 45 mm Ponto Zero Trifásico
Relés e Contatores de Estado Sólido SIRIUS Coletânea de dados técnicos ( product data sheet ) Agosto/212 SSR - 3RF21 22,5 mm Ponto Zero SSR - 3RF2 45 mm Ponto Zero SSR - 3RF22 45 mm Ponto Zero Trifásico
INDUSTRIAL DRIVE SYSTEMS ELEVATION LINE. Spring-applied single-disc/double-disc brake 76 461..A00 76 451..A00
 INDUSTRIAL DRIVE SYSTEMS ELEVATION LINE Spring-applied single-disc/double-disc brake 76 461..A00 76 451..A00 ELEVATION LINE Kendrion (Aerzen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion (Villingen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion Magnetic
INDUSTRIAL DRIVE SYSTEMS ELEVATION LINE Spring-applied single-disc/double-disc brake 76 461..A00 76 451..A00 ELEVATION LINE Kendrion (Aerzen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion (Villingen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion Magnetic
Positive-guided relay outputs: 3 safety contacts (N/O), instantaneous. 1 auxiliary contact (N/C), instantaneous
 Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons. Approvals Unit features Positive-guided relay outputs: 3 safety contacts (N/O), instantaneous 1 auxiliary contact (N/C), instantaneous Safe separation of
Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons. Approvals Unit features Positive-guided relay outputs: 3 safety contacts (N/O), instantaneous 1 auxiliary contact (N/C), instantaneous Safe separation of
Single-phase (220...240 V) voltage monitoring: Undervoltage Overvoltage Window mode (overvoltage + undervoltage) Voltage fault memory selectable
 Features 70.11 70.31 70.41 Electronic voltage monitoring relays for single and three-phase applications Multifunctional types, providing the flexibility of monitoring Undervoltage, Overvoltage, Window
Features 70.11 70.31 70.41 Electronic voltage monitoring relays for single and three-phase applications Multifunctional types, providing the flexibility of monitoring Undervoltage, Overvoltage, Window
Harmonic Drive acutator P r e c i s i o n G e a r i n g & M o t i o n C o n t r o l
 D C S e r v o S y s t e m s RH Mini Series Total Motion Control Harmonic Drive acutator P r e c i s i o n G e a r i n g & M o t i o n C o n t r o l Precision Gearing & Motion Control DC SERVO ACTUATORS
D C S e r v o S y s t e m s RH Mini Series Total Motion Control Harmonic Drive acutator P r e c i s i o n G e a r i n g & M o t i o n C o n t r o l Precision Gearing & Motion Control DC SERVO ACTUATORS
UM Series UniModule. Pre-assembled, C-face Clutches and Brakes. Original Design Sizes 210 & 215. GEN 2 Design Sizes 50, 100 & 180
 re-assembled, C-face Clutches and Brakes UniModules offer the ultimate in Clutch/ Brake performance and convenience. UniModules offer the same performance as EM s without the assembly required. Completely
re-assembled, C-face Clutches and Brakes UniModules offer the ultimate in Clutch/ Brake performance and convenience. UniModules offer the same performance as EM s without the assembly required. Completely
BETA Switching. Switching Devices. 5TT5 8 Insta contactors, AC technology. Overview
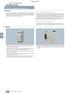 BETA Switching Siemens AG 200 5TT5 Insta contactors, AC technology Overview The 5TT5 Insta contactors are equipped with an AC magnetic system and are ideal for use under harsh conditions. The auxiliary
BETA Switching Siemens AG 200 5TT5 Insta contactors, AC technology Overview The 5TT5 Insta contactors are equipped with an AC magnetic system and are ideal for use under harsh conditions. The auxiliary
Electric Rotary Actuator - On/Off or programmable control actuator
 Electric Rotary Actuator - On/Off or programmable control actuator Direct mounting on quarter-turn valves Manual override standard Corrosion resistant Adjustable limit switches Multi-voltage version Type
Electric Rotary Actuator - On/Off or programmable control actuator Direct mounting on quarter-turn valves Manual override standard Corrosion resistant Adjustable limit switches Multi-voltage version Type
0.8 U N /0.5 U N 0.8 U N /0.5 U N 0.8 U N /0.5 U N 0.2 U N /0.1 U N 0.2 U N /0.1 U N 0.2 U N /0.1 U N
 55 Series - General purpose relays 7-10 A Features 55.12 55.13 55.14 Printed circuit mount, general purpose 2, 3 & 4 Pole relays 55.12-2 Pole 10 A 55.13-3 Pole 10 A 55.14-4 Pole 7 A AC coils & DC coils
55 Series - General purpose relays 7-10 A Features 55.12 55.13 55.14 Printed circuit mount, general purpose 2, 3 & 4 Pole relays 55.12-2 Pole 10 A 55.13-3 Pole 10 A 55.14-4 Pole 7 A AC coils & DC coils
Contact expander modules
 Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Kontakterweiterungen Contact expansion module for increasing the number of available contacts Approvals Zulassungen Unit features Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs:
Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Kontakterweiterungen Contact expansion module for increasing the number of available contacts Approvals Zulassungen Unit features Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs:
Permanent Magnetic Couplings and Brakes for Drive Technology
 Tridelta Magnetsysteme A Tridelta Group Company Permanent Magnetic Couplings and Brakes for Drive Technology Raw Materials Magnets Systems and Components Magnet N1 Soft iron N2 Resin Introduction and principals
Tridelta Magnetsysteme A Tridelta Group Company Permanent Magnetic Couplings and Brakes for Drive Technology Raw Materials Magnets Systems and Components Magnet N1 Soft iron N2 Resin Introduction and principals
AF09-30-22-.. / AF09Z-30-22-.. 2-stack 3-pole Contactors AC / DC Operated - with Screw Terminals
 Technical Datasheet 1SBC101403D0201 24/03/11 AF09-30-22-.. / AF09Z-30-22-.. 2-stack 3-pole Contactors AC / DC Operated - with Screw Terminals AF09(Z) contactors are used for controlling power circuits
Technical Datasheet 1SBC101403D0201 24/03/11 AF09-30-22-.. / AF09Z-30-22-.. 2-stack 3-pole Contactors AC / DC Operated - with Screw Terminals AF09(Z) contactors are used for controlling power circuits
BoWex SD, SD1 and SD2 Operating-/Assembly Instructions
 D-807 Rheine 0111 E 1 curved-tooth gear couplings are flexible shaft connections. They are able to compensate for shaft displacement caused by, as an example, inaccuracies in production, heat expansion,
D-807 Rheine 0111 E 1 curved-tooth gear couplings are flexible shaft connections. They are able to compensate for shaft displacement caused by, as an example, inaccuracies in production, heat expansion,
STEP-PS/1AC/12DC/1.5. Extract from the online catalog. Order No.: 2868567. DIN rail power supply unit 12 V DC/1.5 A, primary switched-mode, 1- phase
 Extract from the online catalog STEP-PS/1AC/12DC/1.5 Order No.: 2868567 DIN rail power supply unit 12 V DC/1.5 A, primary switched-mode, 1- phase Commercial data EAN 4046356292924 Pack 1 pcs. Customs tariff
Extract from the online catalog STEP-PS/1AC/12DC/1.5 Order No.: 2868567 DIN rail power supply unit 12 V DC/1.5 A, primary switched-mode, 1- phase Commercial data EAN 4046356292924 Pack 1 pcs. Customs tariff
Type: DILM50(230V50HZ,240V60HZ) Article No.: 277830
 Type: DILM50(230V50HZ,240V60HZ) Article No.: 277830 Ordering information Rated operational current AC 3 400 V I e A 50 Max. rating for three phase motors, 50 60 Hz AC 3 230 V Max. rating for three phase
Type: DILM50(230V50HZ,240V60HZ) Article No.: 277830 Ordering information Rated operational current AC 3 400 V I e A 50 Max. rating for three phase motors, 50 60 Hz AC 3 230 V Max. rating for three phase
3/2- and 2/2-way cartridge valve type BVE
 3/2- and 2/2-way cartridge valve type BVE for any flow direction, zero leakage, all ports pressure resistant Flow Q max = 70 lpm Perm. pressure p max = 400 bar Additional valves with same function: ' Type
3/2- and 2/2-way cartridge valve type BVE for any flow direction, zero leakage, all ports pressure resistant Flow Q max = 70 lpm Perm. pressure p max = 400 bar Additional valves with same function: ' Type
RY2 miniature industrial relays
 6 RY2 Relays of general application For plug-in sockets, 35 mm rail mount acc. to PN-EN 60715 or on panel mounting Flat insert connectors - faston x 0,5 mm Recognitions, certifications, directives: RoHS,
6 RY2 Relays of general application For plug-in sockets, 35 mm rail mount acc. to PN-EN 60715 or on panel mounting Flat insert connectors - faston x 0,5 mm Recognitions, certifications, directives: RoHS,
Technical Manual Functional Description for S800-RSU-H / S800W-RSU 2CCC413022M0205. 8201 Schaffhausen 1 / 10
 ABB ABB Schweiz AG Technical Manual Functional Description for S800-RSU-H / S800W-RSU 2CCC413022M0205 09.04.2014 Page: 8201 Schaffhausen 1 / 10 Please use also the assembly instruction S800-RSU-H Remote
ABB ABB Schweiz AG Technical Manual Functional Description for S800-RSU-H / S800W-RSU 2CCC413022M0205 09.04.2014 Page: 8201 Schaffhausen 1 / 10 Please use also the assembly instruction S800-RSU-H Remote
Emergency stop As an emergency switching off/emergency stop device. Standards According to IEC/EN 60204-1, VDE 0113 Part 1
 MainswitchSurfacemounting Partno. P3-63/I4/SVB Articleno. 207343 CatalogNo. SP3-063-I4CRQ IP65 Deliveryprogramme Product range Switch-disconnectors Basic function Main switches Maintenance switches Manual
MainswitchSurfacemounting Partno. P3-63/I4/SVB Articleno. 207343 CatalogNo. SP3-063-I4CRQ IP65 Deliveryprogramme Product range Switch-disconnectors Basic function Main switches Maintenance switches Manual
Type: DILM32 10(24V50HZ) Article No.: 277247
 Type: DILM32 10(24V50HZ) Article No.: 277247 Ordering information Rated operational current AC 3 400 V I e A 32 Max. rating for three phase motors, 50 60 Hz AC 3 230 V Max. rating for three phase motors,
Type: DILM32 10(24V50HZ) Article No.: 277247 Ordering information Rated operational current AC 3 400 V I e A 32 Max. rating for three phase motors, 50 60 Hz AC 3 230 V Max. rating for three phase motors,
Current valve. for AC 24 V pulse/pause control of electrical loads up to 30 kw
 4 937 DESIO Current valve for AC 24 V pulse/pause control of electrical loads up to 30 kw SEA45.1 Use The current valve is used for the control of electric heating elements in heating, ventilation and
4 937 DESIO Current valve for AC 24 V pulse/pause control of electrical loads up to 30 kw SEA45.1 Use The current valve is used for the control of electric heating elements in heating, ventilation and
CONNECTOR AMPLIFIER FOR PROPORTIONAL VALVES (4-20 ma Input Version)
 TECHNICAL DATASHEET #TD1102AX CONNECTOR AMPLIFIER FOR PROPORTIONAL VALVES (4-20 ma Input Version) Part Number: Connector Amplifier CAPV-H-4-20MA-x complete with cable CAPV-4C-yM Where: x = current output
TECHNICAL DATASHEET #TD1102AX CONNECTOR AMPLIFIER FOR PROPORTIONAL VALVES (4-20 ma Input Version) Part Number: Connector Amplifier CAPV-H-4-20MA-x complete with cable CAPV-4C-yM Where: x = current output
Siemens AG 2011 SINAMICS V60. The perfect solution for basic servo applications. Brochure May 2011 SINAMICS. Answers for industry.
 The perfect solution for basic servo applications Brochure May 2011 SINAMICS Answers for industry. with 1FL5 servomotors The solution for basic servo applications There is a requirement to automate motion
The perfect solution for basic servo applications Brochure May 2011 SINAMICS Answers for industry. with 1FL5 servomotors The solution for basic servo applications There is a requirement to automate motion
Contactless Encoder RI360P0-QR24M0-INCRX2-H1181
 Compact, rugged housing Many mounting possibilities Status displayed via LED Immune to electromagnetic interference 1024 pulses per revolution (default) 360, 512, 1000, 1024, 2048, 2500, 3600, 4096, parametr.
Compact, rugged housing Many mounting possibilities Status displayed via LED Immune to electromagnetic interference 1024 pulses per revolution (default) 360, 512, 1000, 1024, 2048, 2500, 3600, 4096, parametr.
HERZ-Thermal Actuators
 HERZ-Thermal Actuators Data Sheet 7708-7990, Issue 1011 Dimensions in mm 1 7710 00 1 7710 01 1 7711 18 1 7710 80 1 7710 81 1 7711 80 1 7711 81 1 7990 00 1 7980 00 1 7708 11 1 7708 10 1 7708 23 1 7709 01
HERZ-Thermal Actuators Data Sheet 7708-7990, Issue 1011 Dimensions in mm 1 7710 00 1 7710 01 1 7711 18 1 7710 80 1 7710 81 1 7711 80 1 7711 81 1 7990 00 1 7980 00 1 7708 11 1 7708 10 1 7708 23 1 7709 01
Contact expansion modules
 Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Kontakterweiterungen Contact for increasing the number of available contacts Approvals Zulassungen Unit features Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs: 4 safety contacts
Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Kontakterweiterungen Contact for increasing the number of available contacts Approvals Zulassungen Unit features Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs: 4 safety contacts
OLI. Oil level indicator
 OLI Oil level indicator Oil level indicator Unexpected or accidental oil leakages may occur randomly along transformer s lifetime. Clear indication of oil level inside transformer tank and on load tap
OLI Oil level indicator Oil level indicator Unexpected or accidental oil leakages may occur randomly along transformer s lifetime. Clear indication of oil level inside transformer tank and on load tap
3RT1015-1BB41 CONTACTOR, AC-3 3 KW/400 V,
 Automation Technology > Industrial Controls > Switching Devices > Contactors and Contactor Assemblies > Power Contactors for Switching Motors > Contactors SIRIUS 3RT10, 3-pole, 3... 250 kw 3RT1015-1BB41
Automation Technology > Industrial Controls > Switching Devices > Contactors and Contactor Assemblies > Power Contactors for Switching Motors > Contactors SIRIUS 3RT10, 3-pole, 3... 250 kw 3RT1015-1BB41
Ferrostat Speed Sensor Series DSF Explosion Proof Versions EEx
 Ferrostat Speed Sensor Series DSF Explosion Proof Versions EEx DSF..10.**.HV Ex ATEX Operating Instructions 374E-64368 Valid from lot nr. 0103 General Function Use in potentially explosive environment
Ferrostat Speed Sensor Series DSF Explosion Proof Versions EEx DSF..10.**.HV Ex ATEX Operating Instructions 374E-64368 Valid from lot nr. 0103 General Function Use in potentially explosive environment
Pressure monitoring equipment for oil-sf 6. bushings, type GOEK
 Pressure monitoring equipment for oil-sf 6 bushings, type GOEK Installation and maintenance guide 5693 827-6 en, Rev. 3, 2002-01-30 This document must not be copied without our written permission, and
Pressure monitoring equipment for oil-sf 6 bushings, type GOEK Installation and maintenance guide 5693 827-6 en, Rev. 3, 2002-01-30 This document must not be copied without our written permission, and
BETA Protecting SITOR Semiconductor Fuses
 BETA Protecting SITOR Semiconductor Fuses /2 Product overview /3 /17 SITOR, cylindrical fuse design /22 SILIZED, NEOZED and DIAZED design Siemens ET B1 /2008 Product overview Overview Devices Page Field
BETA Protecting SITOR Semiconductor Fuses /2 Product overview /3 /17 SITOR, cylindrical fuse design /22 SILIZED, NEOZED and DIAZED design Siemens ET B1 /2008 Product overview Overview Devices Page Field
D.C. Motors. Products and specifications subject to change without notice.
 D.C. Motors Order/Technical Support - Tel: (8) 677-5 / FAX: (8) 677-865 / www.crouzet-usa.com / DC Motors Selection guide Gearbox Speed Torque max (Nm).5. Type of Gearbox 8 8 8. Power usable (w) Torque
D.C. Motors Order/Technical Support - Tel: (8) 677-5 / FAX: (8) 677-865 / www.crouzet-usa.com / DC Motors Selection guide Gearbox Speed Torque max (Nm).5. Type of Gearbox 8 8 8. Power usable (w) Torque
Product and Applications Description. Application Programs. Example of Operation. GAMMA instabus Technical Product-Information.
 Product and Applications Description The power supply units N 125/x2 can supply DC 24 V power from an additional pair of terminals (yellowwhite). This DC 24 V output voltage can be used to power e.g. an
Product and Applications Description The power supply units N 125/x2 can supply DC 24 V power from an additional pair of terminals (yellowwhite). This DC 24 V output voltage can be used to power e.g. an
Highly flexible couplings
 Construction and operation 8.03.00 Instructions for installation 8.03.00 Types of stress 8.04.00 Diagrams for static deformation of the coupling ring 8.05.00 Coupling size 8.07.00 Examples of combinations
Construction and operation 8.03.00 Instructions for installation 8.03.00 Types of stress 8.04.00 Diagrams for static deformation of the coupling ring 8.05.00 Coupling size 8.07.00 Examples of combinations
TECHNICAL DATASHEET #TD1404AX PWM CONTROLLED SOLENOID DRIVER
 TECHNICAL DATASHEET #TD1404AX PWM CONTROLLED SOLENOID DRIVER (PWM Input, 1.2A or 2A Output, Metal Box or PCB) PCB Board - P/N: PWMC-PCB-2A, PWMC-PCB-1.2A Packaged Driver (metal box with 1.5 m (5 ft.) cable)
TECHNICAL DATASHEET #TD1404AX PWM CONTROLLED SOLENOID DRIVER (PWM Input, 1.2A or 2A Output, Metal Box or PCB) PCB Board - P/N: PWMC-PCB-2A, PWMC-PCB-1.2A Packaged Driver (metal box with 1.5 m (5 ft.) cable)
Type: DILM9 10(24VDC) Article No.: 276705
 Type: DILM9 10(24VDC) Article No.: 276705 Ordering information Rated operational current AC 3 400 V I e A 9 Max. rating for three phase motors, 50 60 Hz AC 3 230 V Max. rating for three phase motors, 50
Type: DILM9 10(24VDC) Article No.: 276705 Ordering information Rated operational current AC 3 400 V I e A 9 Max. rating for three phase motors, 50 60 Hz AC 3 230 V Max. rating for three phase motors, 50
Thyristor-controlled power supplies and battery chargers
 Thyristor-controlled power supplies and battery chargers Input voltage: 115 / 230 VAC, single phase, 50 / 60 Hz or 208 / 400 / 480 VAC, three phases, 50 / 60 Hz Output voltage: 12 / 24 / 48 / 60 / 72 /
Thyristor-controlled power supplies and battery chargers Input voltage: 115 / 230 VAC, single phase, 50 / 60 Hz or 208 / 400 / 480 VAC, three phases, 50 / 60 Hz Output voltage: 12 / 24 / 48 / 60 / 72 /
ABB 1. Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFS. Data sheet. Features. Approvals. Marks. Order data. Order data - Accessories. Application.
 1SR 430 824 F9300 Features Monitoring of three-phase mains for phase sequence and failure Powered by the measuring circuit 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts 1 LED for status indication Approvals R: yellow LED - relay
1SR 430 824 F9300 Features Monitoring of three-phase mains for phase sequence and failure Powered by the measuring circuit 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts 1 LED for status indication Approvals R: yellow LED - relay
Thermistor motor protection relays CM-MSS.22 and CM-MSS.23
 Data sheet Thermistor motor protection relays CM-MSS.22 and CM-MSS.23 The thermistor motor protection relays CM-MSS.22 and CM-MSS.23 monitor the winding temperature of motors and protect them from overheating,
Data sheet Thermistor motor protection relays CM-MSS.22 and CM-MSS.23 The thermistor motor protection relays CM-MSS.22 and CM-MSS.23 monitor the winding temperature of motors and protect them from overheating,
System 8. ü www.nassmagnet.com ( +49 511 6746-0. System 8
 System 8 ü www.nassmagnet.com ( +9 11 7-0 System 8 The name System 8 stands for a modular system of solenoid coils, armature systems, solenoid operators and solenoid valves. The diameter of the armatures
System 8 ü www.nassmagnet.com ( +9 11 7-0 System 8 The name System 8 stands for a modular system of solenoid coils, armature systems, solenoid operators and solenoid valves. The diameter of the armatures
Directional seated valves type VP 1
 Directional seated valves type VP 1 zero leakage, intended for general hydraulic applications and grease lubing systems Flow Q max Operation pressure p max = 15 lpm = 400 bar Individual valve Individual
Directional seated valves type VP 1 zero leakage, intended for general hydraulic applications and grease lubing systems Flow Q max Operation pressure p max = 15 lpm = 400 bar Individual valve Individual
E-STOP relays, safety gate monitors
 Unit features Safety features Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons and safety gates. Approvals Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs: 3 safety contacts (N/O),
Unit features Safety features Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons and safety gates. Approvals Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs: 3 safety contacts (N/O),
Electronic overload relay EF19 and EF45
 Data sheet Electronic overload relay EF19 and EF45 Electronic overload relays offer reliable protection in case of overload and phase-failure. They are the alternative to thermal overload relays. Motor
Data sheet Electronic overload relay EF19 and EF45 Electronic overload relays offer reliable protection in case of overload and phase-failure. They are the alternative to thermal overload relays. Motor
RM17TE 183...528 V AC. Main. Product or component type. Product specific application. Relay monitored parameters 250 V DC 5 A DC
 Characteristics multifunction control relay RM17-TE - range 183..528 V AC Complementary Reset time Maximum switching voltage Minimum switching current Maximum switching current [Us] rated supply voltage
Characteristics multifunction control relay RM17-TE - range 183..528 V AC Complementary Reset time Maximum switching voltage Minimum switching current Maximum switching current [Us] rated supply voltage
E-STOP relays, safety gate monitors
 Unit features Safety features gang engertebild ][Bildunterschrift_NOT_Sch.tuer_Licht Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons, safety gates and light beam devices Approvals Gertemerkmale Positive-guided
Unit features Safety features gang engertebild ][Bildunterschrift_NOT_Sch.tuer_Licht Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons, safety gates and light beam devices Approvals Gertemerkmale Positive-guided
Assisted lift operated 2/2-way solenoid valves Type EV250B
 MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Data sheet Assisted lift operated 2/2-way solenoid valves Type EV250B EV250B with assisted lift can operate from zero and up to 10 bar differential pressure. This 2/2-way
MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Data sheet Assisted lift operated 2/2-way solenoid valves Type EV250B EV250B with assisted lift can operate from zero and up to 10 bar differential pressure. This 2/2-way
LC1D65AM7 TeSys D contactor - 3P(3 NO) - AC-3 - <= 440 V 65 A - 220 V AC coil
 Product data sheet Characteristics LC1D65AM7 TeSys D contactor - 3P(3 NO) - AC-3 -
Product data sheet Characteristics LC1D65AM7 TeSys D contactor - 3P(3 NO) - AC-3 -
Example of use: Fuse for a solenoid valve. If the fuse is defective, no information is sent to the electronic component.
 Overview Switch and button modules The dimensions of the switch and button modules are adapted to the electronic components in the integral housing. The modules are equipped with the universal clip-on
Overview Switch and button modules The dimensions of the switch and button modules are adapted to the electronic components in the integral housing. The modules are equipped with the universal clip-on
Description. Dimensions. Features. www.pwb-encoders.com. precision works better
 Description The MEC22 is a high resolution optical hollow shaft encoder that can be fixed quickly and easily on different sizes of motor shafts. The encoder provides two square wave outputs in quadrature
Description The MEC22 is a high resolution optical hollow shaft encoder that can be fixed quickly and easily on different sizes of motor shafts. The encoder provides two square wave outputs in quadrature
E-STOP relays, safety gate monitors
 Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons and safety gates. Approvals Unit features Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs: 2 safety contacts (N/O), instantaneous
Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons and safety gates. Approvals Unit features Gertemerkmale Positive-guided relay outputs: 2 safety contacts (N/O), instantaneous
Linear modules Lifting units Rotary modules Grip modules Inductive proximity switches Plug connectors
 20000 Linear modules Lifting units Rotary modules Grip modules Inductive proximity switches Plug connectors 23000 22000 21000 20000 09000 08000 07000 06000 05000 04000 03000 02000 01000 823 Notes 824 Technical
20000 Linear modules Lifting units Rotary modules Grip modules Inductive proximity switches Plug connectors 23000 22000 21000 20000 09000 08000 07000 06000 05000 04000 03000 02000 01000 823 Notes 824 Technical
Plug and Socket Devices CES 63 A Series 8579
 www.stahl.de > Switch socket / plug 63 A > Large switch handle with clear switch position indication padlockable in 0- and I-position > Low insertion and withdrawal forces through individually encapsulated
www.stahl.de > Switch socket / plug 63 A > Large switch handle with clear switch position indication padlockable in 0- and I-position > Low insertion and withdrawal forces through individually encapsulated
HB Hysteresis Brakes and MHB Matched Brakes
 Data Sheet HB s and MHB s Features Torque up to 3500 oz in/26 N m Speed up to 20,000 rpm Power up to 2400 W Available in Metric or English dimensions Torque independent of speed Long, maintenance-free
Data Sheet HB s and MHB s Features Torque up to 3500 oz in/26 N m Speed up to 20,000 rpm Power up to 2400 W Available in Metric or English dimensions Torque independent of speed Long, maintenance-free
MasterINTERFACE 39 Series - Relay interface modules
 MasterINTERFACE 39 Series - Relay interface modules Common features Space saving 6.2 mm wide Connections for 16-way jumper link Integral coil indication and protection circuit Secure retention and easy
MasterINTERFACE 39 Series - Relay interface modules Common features Space saving 6.2 mm wide Connections for 16-way jumper link Integral coil indication and protection circuit Secure retention and easy
industrial drive systems PM LINE Permanent magnet single-surface brake 86 611..H00 86 621..H00
 industrial drive systems PM LINE Permanent magnet single-surface brake 86 611..H00 86 621..H00 PM LINE Kendrion (Aerzen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion (Villingen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion Magnetic (Suzhou) Co.
industrial drive systems PM LINE Permanent magnet single-surface brake 86 611..H00 86 621..H00 PM LINE Kendrion (Aerzen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion (Villingen) GmbH, Germany Kendrion Magnetic (Suzhou) Co.
Power Supply Unit, Primary Switched, Narrow Design MINI-PS-12-24DC/24DC/1
 Power Supply Unit, Primary Switched, Narrow Design MINI POWER provides: Extra narrow design with widths of 22.5 mm, 45 mm, and 67.5 mm (0.886, 1.772, and 2.657 in.) Global use due to a wide-range input
Power Supply Unit, Primary Switched, Narrow Design MINI POWER provides: Extra narrow design with widths of 22.5 mm, 45 mm, and 67.5 mm (0.886, 1.772, and 2.657 in.) Global use due to a wide-range input
Linear Luminaire with LED Series EXLUX 6402/2
 > Latest LED technology with a high luminous efficacy and a long service life > As pendant light fitting or side entry lamp > Central locking > All-pole disconnection by means of an N/C switch when the
> Latest LED technology with a high luminous efficacy and a long service life > As pendant light fitting or side entry lamp > Central locking > All-pole disconnection by means of an N/C switch when the
Inductive sensor NI10-M18-Y1X-H1141
 ATEX category II 1 G, Ex zone 0 ATEX category II 1 D, Ex zone 20 SIL2 as per IEC 61508 Threaded barrel, M18 x 1 Chrome-plated brass DC 2-wire, nom. 8.2 VDC Output acc. to DIN EN 60947-5-6 (NA- MUR) M12
ATEX category II 1 G, Ex zone 0 ATEX category II 1 D, Ex zone 20 SIL2 as per IEC 61508 Threaded barrel, M18 x 1 Chrome-plated brass DC 2-wire, nom. 8.2 VDC Output acc. to DIN EN 60947-5-6 (NA- MUR) M12
Application Information
 Moog Components Group manufactures a comprehensive line of brush-type and brushless motors, as well as brushless controllers. The purpose of this document is to provide a guide for the selection and application
Moog Components Group manufactures a comprehensive line of brush-type and brushless motors, as well as brushless controllers. The purpose of this document is to provide a guide for the selection and application
E-STOP relays, safety gate monitors
 Unit features Safety features Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift_NOT_Sch.tuer_Licht Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons, safety gates and light beam devices Approvals Gertemerkmale Positive-guided
Unit features Safety features Gertebild ][Bildunterschrift_NOT_Sch.tuer_Licht Safety relay for monitoring E-STOP pushbuttons, safety gates and light beam devices Approvals Gertemerkmale Positive-guided
5SV Residual Current Protective Devices
 s Siemens AG 2013 SENTRON 5SV Residual Current Protective Devices New portfolio for reliable personnel, material and fire protection Safe protection against residual currents Residual current protective
s Siemens AG 2013 SENTRON 5SV Residual Current Protective Devices New portfolio for reliable personnel, material and fire protection Safe protection against residual currents Residual current protective
RM35UA13MW. range 15..600 V. Main. Product or component type. Relay monitored parameters
 Characteristics multifunction voltage control relay RM35-U - range 15..600 V Complementary Reset time Maximum switching voltage [Us] rated supply voltage Supply voltage limits Power consumption in W Main
Characteristics multifunction voltage control relay RM35-U - range 15..600 V Complementary Reset time Maximum switching voltage [Us] rated supply voltage Supply voltage limits Power consumption in W Main
Safety Manual BT50(T) Safety relay / Expansion relay
 Safety Manual BT50(T) Safety relay / Expansion relay ABB Jokab Safety Varlabergsvägen 11, SE-434 39, Sweden www.abb.com/jokabsafety Read and understand this document Please read and understand this document
Safety Manual BT50(T) Safety relay / Expansion relay ABB Jokab Safety Varlabergsvägen 11, SE-434 39, Sweden www.abb.com/jokabsafety Read and understand this document Please read and understand this document
SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mat Product information
 SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mat Product information SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mats Safety mats are used for the protection of man on machinery and plants with hazardous movements. Typical fields of application are,
SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mat Product information SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mats Safety mats are used for the protection of man on machinery and plants with hazardous movements. Typical fields of application are,
Electronic timer CT-AHD.12 OFF-delayed with 1 c/o (SPDT) contact
 Data sheet Electronic timer CT-AHD.12 OFF-delayed with 1 c/o (SPDT) contact The CT-AHD.12 is an electronic time relay with OFF-delay. It is from the CT-D range. With their MDRC profile and a width of only
Data sheet Electronic timer CT-AHD.12 OFF-delayed with 1 c/o (SPDT) contact The CT-AHD.12 is an electronic time relay with OFF-delay. It is from the CT-D range. With their MDRC profile and a width of only
Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breaker 3120-...-M1-..
 Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breaker -...-M-.. Description Single or two pole rocker switch/thermal-magnetic circuit breaker with trip-free mechanism (S-type TM CBE to EN 34). The addition of a magnetic tripping
Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breaker -...-M-.. Description Single or two pole rocker switch/thermal-magnetic circuit breaker with trip-free mechanism (S-type TM CBE to EN 34). The addition of a magnetic tripping
Safety technique. Emergency stop module BO 5988 safemaster
 Safety technique Emergency stop module BO 5988 safemaster 0221562 Function diagram Pushbutton on Mains or emergencystop () K1 According to EC Directive for machines 98/37/EG According to IEC/E 60204-1
Safety technique Emergency stop module BO 5988 safemaster 0221562 Function diagram Pushbutton on Mains or emergencystop () K1 According to EC Directive for machines 98/37/EG According to IEC/E 60204-1
Housing diameter Shaft diameter 1. Flange (Mounting of housing) Protection class shaft input (EN 60529) Protection class housing (EN 60529)
 Direct mounting without coupling Flexible hollow shaft design up to diameter 4 mm Through hollow shaft or as end shaft (blind shaft) Easy installation by means of clamping shaft or blind shaft Short overall
Direct mounting without coupling Flexible hollow shaft design up to diameter 4 mm Through hollow shaft or as end shaft (blind shaft) Easy installation by means of clamping shaft or blind shaft Short overall
CompactLogix Power Supplies Specifications
 Technical Data CompactLogix Power Supplies Specifications 1768 CompactLogix Power Supplies Catalog Numbers 1768-PA3, 1768-PB3 1769 Compact I/O Power Supplies Catalog Numbers 1769-PA2, 1769-PB2, 1769-PA4,
Technical Data CompactLogix Power Supplies Specifications 1768 CompactLogix Power Supplies Catalog Numbers 1768-PA3, 1768-PB3 1769 Compact I/O Power Supplies Catalog Numbers 1769-PA2, 1769-PB2, 1769-PA4,
BMD. Permanent Magnet AC Synchronous Motors
 BMD Permanent Magnet AC Synchronous Motors Power, control and green solutions About us 3 Bonfiglioli, one name for a large international group. It was back in 1956 that Clementino Bonfiglioli established
BMD Permanent Magnet AC Synchronous Motors Power, control and green solutions About us 3 Bonfiglioli, one name for a large international group. It was back in 1956 that Clementino Bonfiglioli established
Operating Manual UWAPS-TINY Series
 Operating Manual UWAPS-TINY Series Powecon Oy WWW.POWECON.FI 1/9 Table of content 1 Warranty...3 2 Safety information...3 3 Abbreviations and terminology...3 4 List of appendices...4 5 Introduction...4
Operating Manual UWAPS-TINY Series Powecon Oy WWW.POWECON.FI 1/9 Table of content 1 Warranty...3 2 Safety information...3 3 Abbreviations and terminology...3 4 List of appendices...4 5 Introduction...4
Technical data UNIBLOCK UBSF 180 625
 Data TECHNICL DT Technical data UNIBLOCK UBSF 80 6 Output data Type UBSF 80 UBSF 0 UBSF 00 UBSF 6 Output power 80 kv 0 kv 00 kv 6 kv Output voltage 80/77 V 0/ V 0/ V 0/ V Output current 7 8 66 80 Power
Data TECHNICL DT Technical data UNIBLOCK UBSF 80 6 Output data Type UBSF 80 UBSF 0 UBSF 00 UBSF 6 Output power 80 kv 0 kv 00 kv 6 kv Output voltage 80/77 V 0/ V 0/ V 0/ V Output current 7 8 66 80 Power
34 Series - Slim electromechanical PCB relays 6 A. Features SERIES 34.51
 34 Series - Slim electromechanical PCB relays 6 34 SERIES Features 34.51 Ultra-slim 1 Pole - 6 relay Printed circuit mount - direct or via PCB socket 35 mm rail mount - via screw, screwless or push-in
34 Series - Slim electromechanical PCB relays 6 34 SERIES Features 34.51 Ultra-slim 1 Pole - 6 relay Printed circuit mount - direct or via PCB socket 35 mm rail mount - via screw, screwless or push-in
1150 hp motor design, electromagnetic and thermal analysis
 115 hp motor design, electromagnetic and thermal analysis Qasim Al Akayshee 1, and David A Staton 2 1 Mawdsley s Ltd., The Perry Centre, Davey Close, Waterwells, Gloucester GL2 4AD phone: +44 1452 888311
115 hp motor design, electromagnetic and thermal analysis Qasim Al Akayshee 1, and David A Staton 2 1 Mawdsley s Ltd., The Perry Centre, Davey Close, Waterwells, Gloucester GL2 4AD phone: +44 1452 888311
MILLENIUM INSTALLATION MANUAL NTR 735 A. Simple Automation Control Module (MAS)
 MILLENIUM Table of contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1 2. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION 2 3. INSTALLATION 5 4. CONNECTION 6 5. USER SAFETY AND PROTECTION OF EQUIPMENT 8 1. Introduction The MILLENIUM series has been designed
MILLENIUM Table of contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1 2. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION 2 3. INSTALLATION 5 4. CONNECTION 6 5. USER SAFETY AND PROTECTION OF EQUIPMENT 8 1. Introduction The MILLENIUM series has been designed
1 pole, 16 A Screw terminal connection 35 mm rail (EN 60715) mounting. 2 pole, 8 A Screw terminal connection 35 mm rail (EN 60715) mounting
 Series - Relay interface modules 8-10 - 16 A Features.01.02 1 & 2 pole relay interface modules, screw terminal socket, mm wide. Ideal interface for PL and electronic systems.01-1 Pole 16 A.02-2 Pole 8
Series - Relay interface modules 8-10 - 16 A Features.01.02 1 & 2 pole relay interface modules, screw terminal socket, mm wide. Ideal interface for PL and electronic systems.01-1 Pole 16 A.02-2 Pole 8
