Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation
|
|
|
- Linda Atkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 94 The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, 3, Open Access Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation Pooja Mittal, Vivien Pan and Deborah A. Wing * Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of California, Irvine Medical Center, 101 The City Drive South, Building 56, Suite 800, Orange, CA 92868, USA Abstract: Objective: To compare 3-day vs 7-day antimicrobial treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women in a pilot study. Methods: Pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria (100,000 cfu/ml) were randomized to 3-day or 7-day nitrofurantoin treatment. Exclusion criteria included symptomatic bacteriuria at enrollment, previously treated bacteriuria in the current pregnancy, underlying renal disorders, antibiotic use within one week prior to initial culture or treatment, bacterial resistance to nitrofurantoin, or other contraindications to nitrofurantoin. Urine test of cure (TOC) was performed 2-4 weeks after initiation of treatment. Subjects with persistent bacteriuria received an additional 7-day treatment course with an antimicrobial agent based on uropathogen sensitivities and selected at the physician s discretion. Following delivery, antenatal, perinatal, and neonatal data were reviewed. Statistical analyses were performed using t-test, Chisquare, and Fisher exact where appropriate. Analysis was based on intent-to-treat. Results: Forty-four of 60 patients had complete prenatal and delivery records. Twenty-four patients (54.5%) were randomized to 3-day treatment and 20 patients (45.5%) to 7-day treatment. Six (25%) patients in the 3-day group had persistent bacteriuria at TOC, compared to 2 (10%) patients in the 7-day group (p=0.19). There were no statistical differences between the groups in maternal age, gestational age at enrollment, mode of delivery, birth weight, NICU admissions, or the incidence of recurrent urinary tract infections or pyelonephritis. Conclusion: Based on our small sample group, 3-day nitrofurantoin treatment had statistically comparable outcomes to 7- day treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant patients, yet 3-day-treated women were 2.5 times more likely to have persistent bacteriuria than 7-day-treated women. The possibility of a beta error exists. In light of recent data which indicates that 1-day nitrofurantoin therapy is less effective than 7-day treatment in pregnant women, we recommend 7-day treatment for ASB. INTRODUCTION Asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB) affects 2-14% of pregnancies annually in the United States [1, 2]. This translates to 80, ,000 cases a year [3]. The traditional diagnostic criteria of significant bacteriuria included cultures of 10 colony forming units (cfu)/ml of a single uropathogen on two consecutive clean catch urine specimens [4, 5]. However, recent evidence suggests that lower colony counts (>10) demonstrate infection that will predispose to the development of pyelonephritis in pregnancy [1, 6, 7]. In pregnancy, the presence of ASB has been found to increase the risk of preterm delivery, infants of low birth weight [8] and other adverse perinatal outcomes [9]. Antibiotic treatment of ASB in pregnancy has been shown to significantly lower the risk of preterm labor when compared to untreated counterparts [10]. Furthermore, pregnant women are at an increased risk for the development of symptomatic urinary tract infections resulting from ASB than their non-- pregnant counterparts. It is estimated that 30-50% of women *Address correspondence to this author at the Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of California, Irvine Medical Center, 101 The City Drive South, Building 56, Suite 800, Orange, CA 92868, USA; Tel: (714) ; Fax: (714) ; mfm@uci.edu with a diagnosis of ASB in pregnancy will progress to a symptomatic infection [11]. Routine screening and treatment for ASB in pregnancy to prevent progression to pyelonephritis has been shown to be both beneficial and cost-effective [12]. Appropriate treatment of ASB in pregnancy decreases the progression rate of pyelonephritis down to 3% [13], emphasizing the importance of insuring adequate treatment. Pyelonephritis in pregnancy is associated with an increase in both maternal and fetal morbidities [13-15]. The current prevailing practice for treatment of ASB in pregnancy is a 7-day course of an oral antimicrobial agent [4, 5, 16-18]. There is no consensus on the appropriate first-line therapy for ASB in pregnancy [19]. If bacteriuria persists, a repeat 7 or 14 day course is prescribed. In non-pregnant women, short course antibiotics have become routine in the treatment of even symptomatic bacteriuria, or cystitis [20-22]. After a meta-analysis of the literature, the Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA) issued committee guidelines supporting the efficacy of a 3-day course of an appropriate antimicrobial for treatment of cystitis in nonpregnant women [23]. Short course therapy carries with it the benefits of decreased healthcare costs, fewer side effects, and increased patient compliance [24]. We undertook this / Bentham Open
2 Short-Course Antibiotic Therapy for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, Volume 3 95 pilot study to determine the feasibility of the 3-day short course antimicrobial treatment to the pregnant population diagnosed with ASB. MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY The single institution study was conducted at the Women s and Children s Hospital of the Los Angeles County + University of Southern California Hospital system as well as at Good Samaritan Hospital, both located in Los Angeles, CA. Our intent was to conduct a pilot trial given that at the time of study initiation, there are no previous reports in the literature for short-course treatment of ASB in pregnancy. Approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of both institutions and written informed consent obtained from all participants. Subjects were recruited from the prenatal clinics at both hospitals for this prospective randomized controlled trial from 2000 to Routine urine dipstick, performed at every prenatal visit, was sent for urine culture if suspicious for bacteriuria (positive nitrate, leukocyte esterase, and/or protein). Prior to obtaining urine culture sample, patients underwent education for use of disinfectant wipes and midstream clean-catch collection. Patients, at any gestational age, with a urine culture exhibiting bacterial growth >100,000 cfu/ml of a uropathogen and no symptoms of cystitis (dysuria, urgency, frequency, pyrexia) were enrolled. Additional inclusion criteria included pregnant women with a documented intrauterine pregnancy greater than 18 years of age, and the ability to provide informed consent. Exclusion criteria included the following: symptomatic bacteriuria at the time of enrollment, previously treated bacteriuria in the current pregnancy, congenital or acquired urinary tract anomaly, antibiotic use in the week prior to enrollment, glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, allergy to nitrofurantoin, and pathogen insensitive to nitrofurantoin. At the time of enrollment, initial data collection included maternal demographics (age, gravidity, parity, ethnicity, medical problems), and bacterial species isolated. Subjects were then randomized via a computer generated randomization algorithm to either a 3-day or 7-day antimicrobial course. Assignments were placed in sealed, opaque envelopes until which time a subject was enrolled, and the next envelope opened to make the assignment. The dosing regimens were not blinded due to financial resource limitations. The first line antimicrobial agent used was nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin 100mg QID or Macrobid 100mg BID), chosen for the minimal uropathogen resistance to the drug in our institutions, as well as its high urinary concentration. The choice between one and the other formulation of nitrofurantoin was made at the discretion of the managing physician. At the subsequent prenatal visit, two to four weeks after initiating treatment, a second midstream urine specimen was collected for repeat urine culture. This served as a test of cure (TOC). Patients with urine cultures that demonstrated persistent bacteriuria (urine culture demonstrating any growth of the same uropathogen) were considered failed treatment and received an additional 7-day course of antimicrobial therapy based on bacterial sensitivities. Secondary outcome measures included comparison of the two treatment groups for persistent or recurrent asymptomatic bacteriuria (after treatment, incidence of symptomatic bacteriuria (cystitis or pyelonephritis), gestational age at delivery, infant birth weight, neonatal intensive care admissions, and incidence of preterm delivery. We diagnosed acute pyelonephritis based on the presence of fever (temperature of degrees Fahrenheit), costovertebral angle tenderness, and urinalysis suggestive of infection (positive leukocyte esterase and nitrites). Uropathogens from these cultures were tabulated. Statistical analyses were performed with the SPSS 13.0 statistical software pack (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). Student t test, Chi-square, and Fisher exact test were used where appropriate. A probability value of <.05 was considered significant. RESULTS A total of 60 gravid women were enrolled (Fig. 1). Thirty-five subjects were randomized to 3-day treatment, while 25 were randomized to 7-day treatment. Forty-four women completed the trial so that full datasets were available on 24 women in the 3-day arm, and 20 women in the 7-day arm. As can be seen in Table 1, the two groups did not significantly differ in respect to demographic characteristics, [gravidity, parity, gestational age at enrollment, race/ethnicity (data not shown)] with the exception of maternal age where a significant difference was noted between the 3-day and 7-day groups. The distribution of specific uropathogens and their specific colony counts did not differ between the two groups. E. coli was the most prevalent causative organism, cultured in 63.6% of all initial cultures, followed by E. faecalis (13.6%), S. agalactiae (7%), S. aureus (7%). 11 subjects lost to follow-up 35 subjects randomized to 3D treatment 24 (68.6%) completed study 60 subjects enrolled 25 subjects randomized to 7D treatment 20 (80%) completed study 5 subjects lost to follow-up Fig. (1). Participant flow chart for comparison of 3-day vs 7-day nitrofurantoin treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. For the primary outcome measure, persistent bacteriuria on TOC, no statistically significant difference was found between 3-day and 7-day treatment groups; however, those women receiving the 3-day regimen were 2.5 times more likely to demonstrate persistent bacteriuria than those treated with the 7-day regimen. No difference was noted between the two groups in the number of recurrent infections (p=0.57) or the development of pyelonephritis. For those subjects who developed pyelonephritis, the length of hospital stay (in days) was similar between treatment groups (Table 2). The vast majority of these pyelonephritis cases were due to Escherichia coli (10/11, 90.9%) which was pan-sensitive to standardly administered antibiotics. Of the women who
3 96 The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, Volume 3 Mittal et al. developed pyelonephritis, three were found to have persistent bacteriuria after undergoing their initial treatment. These were two from the 3-day group and one from the 7- day group. Table 1. Maternal Characteristics (n=35) (n=25) Maternal age (years) ± ± Gravidity 2.97 ± ± Parity 1.23 ± ± Gestational age at enrollment (weeks) Table 2. Treatment Results Persistent bacteriuria (positive test of cure) 16.8 ± ± (n=24) (n=20) 6 (25%) 2 (10%) 0.19 Recurrent UTI 2 (8%) 1 (5%) 0.57 Pyelonephritis 5 (21%) 6 (30%) 0.48 Days in hospital for those subjects diagnosed with pyelonephritis (range) 2.80 ± 0.84 (2-4) 2.83 ± 1.16 (2-5) 0.40 Obstetrical and neonatal outcome measures of both groups did not differ significantly (Table 3). Both groups delivered at a similar gestational age, with a similar birth weight. One preterm birth occurred in the 7-day treatment group; an intrauterine fetal demise occurred at 23.6 weeks due to multiple congenital anomalies. It is unlikely that this occurrence was related to infectious causes or to the duration of treatment. In addition, the subject had successfully cleared the initial bacterium with treatment and did not experience any further infection during her pregnancy. Admissions to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) also did not differ between the two groups. The vast majority of these admissions were for suspected sepsis. Table 3. Neonatal Outcomes Gestational age at delivery (weeks) Delivery < 34 weeks (range) Birth weight (grams) (n=24) (n=20) 38.6 ± ± ( ) 1 ( ) ± ± NICU admission DISCUSSION The key finding of our limited data indicates that 3-day treatment of ASB in pregnancy is statistically equivalent to 7-day treatment; however, the clinical implications of a 25% chance of persistence compared to a 10% chance are marked and would suggest that this regimen is inferior to a longer duration of treatment. No significant difference was noted in the occurrence of persistent bacteriuria, recurrence, or in progression to pyelonephritis. Neonatal morbidities were also similar, including gestational age at delivery, birth weight and NICU admissions. Our results should further be considered in light of the recent published World Health Organization trial evaluation 1-day vs 7-day nitrofurantoin treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. In that investigation, 778 women were recruited for participation in this international, multicenter trial. Three hundred eighty-six women were randomly assigned to 1-day treatment, and 392 women were assigned to 7-day treatment. Bacteriologic cure rates at treatment day 14 were 75.7% and 86.2% for 1-day and 7-day regimens, respectively. The cure rate difference was -10.5% (95% CI % to -4.9%). Interestingly, there were also differences in neonatal outcomes such that mean birth weight and mean gestational age at delivery were significantly lower in the 1- day regimen group. The authors concluded that pregnant women with ASB should be treated with 7-days of nitrofurantoin [18]. Earlier studies examining short course therapy for ASB in pregnancy focused on single dose regimens [25], which have been associated with higher rates of early recurrence by the original uropathogen [26, 27]. This is postulated to be secondary to incomplete eradication of the bacteria from the urinary tract, and potentially high colony counts from enteric repositories. Other short course treatment regimes include four- and five-day antimicrobial courses which were hypothesized to be more effective at complete eradication of bacteria from the urinary tract than the single dose regimen [26]. While randomized trials conclude that these regimens are effective, the studies, like this one, are limited by small sample sizes. We acknowledge the limitations of this investigation. Although the results support prior studies indicating the usefulness of short-course antimicrobial therapy in ASB in pregnancy, by its nature as a pilot investigation, the current study was underpowered to exclude the role of chance influencing the results; comparability or lack thereof of the treatment groups was not fully proven [28]. Based on the results of our pilot investigation, using an alpha-error of 0.05, for 90% power, a total of 146 women in either treatment arm would be needed. Our choice of antibiotics was also based on institutional history; a different antibiotic may have demonstrated greater efficacy [19]. Our diagnostic criterion for ASB was based on a single culture. We acknowledge that the recommendation of the IDSA [29] for the diagnosis of ASB is two urine cultures with colony counts which exceed 100,000/mL. Because of logistical difficulties that would require subjects to return to the clinic for repeat cultures, we based our diagnosis on a single sample. This may have led to over diagnosis of ASB and also led to the atypical assortment of uropathogens identified. Because the repeat urine cultures were not obtained in some subjects for up to four weeks after diagnosis of ASB, it is possible that some of these cases represented colonization, rather than persistence or lack of
4 Short-Course Antibiotic Therapy for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, Volume 3 97 clinical effect of the prescribed antibiotic. Most TOCs, however, were obtained within two weeks of diagnosis. Some of the organisms may have been skin contaminants because of our urine collection methods. But, given randomization, we would expect equal distribution between the groups. Other collection methods such as urinary catheterization would not have been practical. Lastly, more than 25% of the subjects dropped out of the investigation, with proportionately more from the 3-day group than the 7- day group. Ideally, this would have not occurred. Nonetheless, we believe our study has merit as the only description of its kind for the treatment of ASB in pregnancy, and provides the basis for larger trials in the future. Proven short-course therapy might prove beneficial in decreasing overall healthcare costs as well as improving patient compliance [30]. Currently, the annual direct cost of urinary tract infections in the United States approximates $1 billion, emphasizing the healthcare burden incurred by the 8 million women annually seeking healthcare for evaluation of urinary tract infections [31-33]. In light of the compelling results from the WHO trial of 1-day vs 7-day nitrofurantoin treatment for ASB which favor the longer course, future investigations may focus on differing choices of antibiotics rather than on the duration of antimicrobial treatment for ASB in pregnancy. CONCLUSION Based on this limited investigation, 3-day antimicrobial therapy appears inferior to 7-day treatment for ASB in pregnancy. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Contribution P. Mittal V. Pan D.A. Wing Concept X X Design X X Data Acquisition X X Data Analysis and Interpretation X X X Manuscript Draft X X X Manuscript Review X X X REFERENCES [1] Whalley PJ. Significance of asymptomatic bacteriuria detected during pregnancy. JAMA 1965; 193: [2] Krcmery S, Hromec J, Demesova D. Treatment of lower urinary tract infection in pregnancy. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2001; 17: [3] Millar LK, Cox SM. Urinary tract infections complicating pregnancy. Infect Dis Clin North Am 1997; 11: [4] Connolly A, Thorp JM. Urinary tract infections in pregnancy. Urol Clin North Am 1999; 26: [5] Christensen F. Which antibiotics are appropriate for treating bacteriuria in pregnancy? J Antimicrob Chemother 2000; 46(Suppl 1): [6] Le J, Briggs FF, McKeown A, Bustillo G. Urinary tract infections during pregnancy. Ann Pharmacother 2004; 38: [7] Lenke RR, VanDorsten JP, Schifrin BS. Pyelonephritis in pregnancy: A prospective randomized trial to prevent recurrent disease evaluating suppressive therapy with nitrofurantoin and close surveillance. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983; 146: [8] Romero R, Oyarzun E, Mazor M, Sirtori M, Hobbins JC, Bracken M. Meta-analysis of the relationship between asymptomatic bacteriuria and preterm delivery/low birth weight. Obstet Gynecol 1989; 73: [9] Mazor-Draz E, Levy A, Schlaeffer F, Sheiner E. Maternal urinary tract infection: Is it independently associated with adverse pregnancy outcome? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2009; 22: [10] Villar J, Gulmezoglu AM, de Onis M. Nutritional and antimicrobial interventions to prevent preterm birth: An overview of randomized controlled trials. Obstet Gynecol Survey 1998; 53: [11] Kass EH. Bacteriuria and pyelonephritis of pregnancy. Arch Intern Med 1960; 105: [12] Rouse DJ, Andrews WW, Goldenberg RL, Owen J. Screening and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria of pregnancy to prevent pyelonephritis: A cost-effectiveness and cost-benefit analysis. Obstet Gynecol 1995; 86: [13] Smaill F. Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001; 2: CD [14] Wing DA. Pyelonephritis. Clin Obstet Gynecol 1998; 41: [15] Mabie WC, Barton JR, Sibai B. Septic shock in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1997; 90(4 Pt 1): [16] Graves CR. Acute pulmonary complications during pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2002; 45: [17] Gilstrap LC, Ramin SM. Urinary tract infections during pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2001; 28: [18] Lumbiganon P, Villar J, Laopaiboon M, et al. World Health Organization Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Trial Group. One-day compared with 7-day nitrofurantoin for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2009; 113: [19] Smaill F, Vasquez JC. Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007; (2): CD [20] Ovalle A, Levancini M. Urinary tract infections in pregnancy. Curr Opin Urol 2001; 11: [21] Hooton TM. Fluoroquinolones and resistance in the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2003; 22(Suppl 2): [22] Nicolle LE. Short-term therapy for urinary tract infection: Success and failure. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2008; Suppl 1: S40-5. [23] Warren JW, Abrutyn E, Hebel JR, Johnson JR, Schaeffer AJ, Stamm WE. Guidelines for antimicrobial treatment of uncomplicated acute bacterial cystitis and acute pyelonephritis in women. Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA). Clin Infect Dis 1999; 29: [24] Tan JS, File TM Jr. Treatment of bacteriuria in pregnancy. Drugs 1992; 44: [25] Jakobi P, Neiger R, Merzbach D, Paldi E. Single-dose antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1987; 156: [26] Villar J, Lydon-Rochelle MT, Gulmezoglu AM, Roganti A. Duration of treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000; 2: CD [27] Rubin RH, Shapiro DS, Andriole VT, Davis RJ, Stamm WE. Evaluation of new anti-infective drugs for the treatment of urinary tract infection. Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Food and Drug Administration. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 15(Suppl 1): S [28] Jones B, Jarvis P, Lewis JA, Ebbutt AF. Trials to assess equivalence: The importance of rigorous methods. BMJ 1996; 313: [29] Nicolle LE, Bradley S, Colgan R, Rice JC, Schaeffer A, Hooton TM. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in adults. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40:
5 98 The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, Volume 3 Mittal et al. [30] Grob PR. Antibiotic prescribing practices and patient compliance in the community. Scand J Infect Dis 1992; Suppl 83: [31] Foxman B, Barlow R, D Arcy H, Gillespie B, Sobel JD. Urinary tract infection: Self-reported incidence and associated costs. Ann Epidemiol 2000; 10: [32] Foxman B. Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Dis Mon 2003; 49: [33] Schappert S. National ambulatory medical care survey: 1994 summary. Adv Data 1996; 10: Received: September 18, 2009 Revised: October 7, 2009 Accepted: October 16, 2009 Mittal et al.; Licensee Bentham Open. This is an open access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted, non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the work is properly cited.
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) makes
 Annals of Internal Medicine Clinical Guidelines Screening for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement U.S. Preventive Services Task
Annals of Internal Medicine Clinical Guidelines Screening for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement U.S. Preventive Services Task
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
 in Adults RICHARD COLGAN, M.D, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland LINDSAY E. NICOLLE, M.D., University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada ANDREW McGLONE, M.D., University of Maryland
in Adults RICHARD COLGAN, M.D, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland LINDSAY E. NICOLLE, M.D., University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada ANDREW McGLONE, M.D., University of Maryland
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers
 J Occup Health 2002; 44: 329 333 Journal of Occupational Health Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers Jian-Nan WANG 1, Shih-Bin SU 2, 3 and How-Ran GUO 3 1 Department of Family Medicine, Chie-Mei
J Occup Health 2002; 44: 329 333 Journal of Occupational Health Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers Jian-Nan WANG 1, Shih-Bin SU 2, 3 and How-Ran GUO 3 1 Department of Family Medicine, Chie-Mei
How To Find Out If A Diabetic Woman Has A Urinary Tract Infection
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections
 Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D.
 ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Urinary Tract Infection
 Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Packages of antenatal care for low-risk pregnancy
 Packages of antenatal care for low-risk pregnancy Evolution of knowledge and lessons learnt A. Metin Gülmezoglu G on behalf of Professor Pisake Lumbiganon Outline The background to the WHO antenatal care
Packages of antenatal care for low-risk pregnancy Evolution of knowledge and lessons learnt A. Metin Gülmezoglu G on behalf of Professor Pisake Lumbiganon Outline The background to the WHO antenatal care
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly
 Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
Clinical Policy Title: Home uterine activity monitoring
 Clinical Policy Title: Home uterine activity monitoring Clinical Policy Number: 12.01.01 Effective Date: August 19, 2015 Initial Review Date: July 17, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: July 15, 2015 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Home uterine activity monitoring Clinical Policy Number: 12.01.01 Effective Date: August 19, 2015 Initial Review Date: July 17, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: July 15, 2015 Next Review
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance
 Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
Laboratory confirmation requires isolation of Bordetella pertussis or detection of B. pertussis nucleic acid, preferably from a nasopharyngeal swab.
 Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
Welcome and Instructions
 Welcome and Instructions For audio, join by telephone at 877-594-8353, participant code: 56350822 Your line is OPEN. Please do not use the hold feature on your phone but do mute your line by dialing *6.
Welcome and Instructions For audio, join by telephone at 877-594-8353, participant code: 56350822 Your line is OPEN. Please do not use the hold feature on your phone but do mute your line by dialing *6.
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection
 Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes?
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
in children less than one year old. It is commonly divided into two categories, neonatal
 INTRODUCTION Infant Mortality Rate is one of the most important indicators of the general level of health or well being of a given community. It is a measure of the yearly rate of deaths in children less
INTRODUCTION Infant Mortality Rate is one of the most important indicators of the general level of health or well being of a given community. It is a measure of the yearly rate of deaths in children less
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Study Design and Statistical Analysis
 Study Design and Statistical Analysis Anny H Xiang, PhD Department of Preventive Medicine University of Southern California Outline Designing Clinical Research Studies Statistical Data Analysis Designing
Study Design and Statistical Analysis Anny H Xiang, PhD Department of Preventive Medicine University of Southern California Outline Designing Clinical Research Studies Statistical Data Analysis Designing
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Are Urinary Catheters necessary during Endovascular Procedures? A prospective randomized pilot study. Medical Student Research Project.
 Are Urinary Catheters necessary during Endovascular Procedures? A prospective randomized pilot study Medical Student Research Project Jordan Knepper Faculty advisor: Mark Langsfeld, MD Introduction Background
Are Urinary Catheters necessary during Endovascular Procedures? A prospective randomized pilot study Medical Student Research Project Jordan Knepper Faculty advisor: Mark Langsfeld, MD Introduction Background
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011
 The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
signs suggesting chlamydia:
 Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION
 PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL PROTOCOL NO. 1.03 Policy Group Infection Control Committee
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CLOSE CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS INFECTION Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL PROTOCOL NO. 1.03 Policy Group Infection Control Committee
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor
 Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
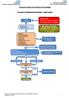 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care
 Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN paulak@parkmanorwi.com
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN paulak@parkmanorwi.com
The American Academy of Pediatrics
 Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management. March 2010
 Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon
 Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Lyme Disease in Pregnancy. Dr Sarah Chissell Consultant Obstetrician William Harvey Hospital, Kent
 Lyme Disease in Pregnancy Dr Sarah Chissell Consultant Obstetrician William Harvey Hospital, Kent Conflict of interest My son has chronic Lyme disease Infections in pregnancy Transplacental infection Perinatal
Lyme Disease in Pregnancy Dr Sarah Chissell Consultant Obstetrician William Harvey Hospital, Kent Conflict of interest My son has chronic Lyme disease Infections in pregnancy Transplacental infection Perinatal
A single center experience with 1000 consecutive cases of multifetal pregnancy reduction
 A single center experience with 1000 consecutive cases of multifetal pregnancy reduction Joanne Stone, MD, Keith Eddleman, MD, Lauren Lynch, MD, and Richard L. Berkowitz, MD New York, NY, and San Juan,
A single center experience with 1000 consecutive cases of multifetal pregnancy reduction Joanne Stone, MD, Keith Eddleman, MD, Lauren Lynch, MD, and Richard L. Berkowitz, MD New York, NY, and San Juan,
Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy
 Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Pack Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Booklet CONTENTS: THE VIRUS page 3 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS page 6 DIAGNOSIS page 8 PATIENT MANAGEMENT
Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Pack Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Booklet CONTENTS: THE VIRUS page 3 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS page 6 DIAGNOSIS page 8 PATIENT MANAGEMENT
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections
 Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis
 10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence
 Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND FACTSHEET
 AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND FACTSHEET What is Stillbirth? In Australia and New Zealand, stillbirth is the death of a baby before or during birth, from the 20 th week of pregnancy onwards, or 400 grams birthweight.
AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND FACTSHEET What is Stillbirth? In Australia and New Zealand, stillbirth is the death of a baby before or during birth, from the 20 th week of pregnancy onwards, or 400 grams birthweight.
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases Boston University School of Medicine
 2010 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department
2010 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department
Assessment of Fetal Growth
 Assessment of Fetal Growth Unit / Trust: 1. INTRODUCTION The aim of this guideline template is to outline the methods used to assess fetal growth and the referral pathways utilising customised antenatal
Assessment of Fetal Growth Unit / Trust: 1. INTRODUCTION The aim of this guideline template is to outline the methods used to assess fetal growth and the referral pathways utilising customised antenatal
A randomized controlled trial comparing amoxicillin and azithromycin for the treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis in pregnancy
 A randomized controlled trial comparing amoxicillin and azithromycin for the treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis in pregnancy Gavin F. Jacobson, MD, a Amy M. Autry, MD, b Russell S. Kirby, PhD, a Elaine
A randomized controlled trial comparing amoxicillin and azithromycin for the treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis in pregnancy Gavin F. Jacobson, MD, a Amy M. Autry, MD, b Russell S. Kirby, PhD, a Elaine
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis. Patient and Public information sheet
 Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Patient and Public information sheet Who is at risk of TB? Anyone can catch TB, but it is possible that pregnant women have a slightly higher risk of TB. Some people are more
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Patient and Public information sheet Who is at risk of TB? Anyone can catch TB, but it is possible that pregnant women have a slightly higher risk of TB. Some people are more
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA
 GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients.
 Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections
 Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections Robert L. Holley, MSc, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections Robert L. Holley, MSc, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES IN THE MEASURES OF MATERNAL MORBIDITY MORTALITY (MM 1 MM 2 ) Dr. AKO Simon
 (1) METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES IN THE MEASURES OF MATERNAL MORBIDITY MORTALITY (MM 1 MM 2 ) Dr. AKO Simon Postgraduate Research Training in Reproductive Health 2004 Faculty of Medicine, University of Yaounde
(1) METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES IN THE MEASURES OF MATERNAL MORBIDITY MORTALITY (MM 1 MM 2 ) Dr. AKO Simon Postgraduate Research Training in Reproductive Health 2004 Faculty of Medicine, University of Yaounde
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Vaccines in Pregnancy MARK H. SAWYER, MD UCSD SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RADY CHILDREN S HOSPITAL SAN DIEGO
 Vaccines in Pregnancy MARK H. SAWYER, MD UCSD SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RADY CHILDREN S HOSPITAL SAN DIEGO 1 Objectives List vaccines that should be given either during pregnancy or immediately post-partum in
Vaccines in Pregnancy MARK H. SAWYER, MD UCSD SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RADY CHILDREN S HOSPITAL SAN DIEGO 1 Objectives List vaccines that should be given either during pregnancy or immediately post-partum in
VITAMIN C AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND THE RESULTS OF A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, PROSPECTIVE STUDY OVER 8 YEARS
 39 Chapter 3 VITAMIN C AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND THE RESULTS OF A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, PROSPECTIVE STUDY OVER 8 YEARS Maxine Briggs TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Review of the
39 Chapter 3 VITAMIN C AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND THE RESULTS OF A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, PROSPECTIVE STUDY OVER 8 YEARS Maxine Briggs TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Review of the
OET: Listening Part A: Influenza
 Listening Test Part B Time allowed: 23 minutes In this part, you will hear a talk on critical illnesses due to A/H1N1 influenza in pregnant and postpartum women, given by a medical researcher. You will
Listening Test Part B Time allowed: 23 minutes In this part, you will hear a talk on critical illnesses due to A/H1N1 influenza in pregnant and postpartum women, given by a medical researcher. You will
Assisted Living - TB Risk Assessment
 Montana DPHHS Tuberculosis Program Assisted Living - TB Risk Assessment Assisted Living, Adult Day Care, Adult Foster Care & Transitional Living Centers Today s Date Facility Address Phone County Completed
Montana DPHHS Tuberculosis Program Assisted Living - TB Risk Assessment Assisted Living, Adult Day Care, Adult Foster Care & Transitional Living Centers Today s Date Facility Address Phone County Completed
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a pilot study using the mobile phone short messaging service (SMS)
 RESEARCH Original article... Q The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a pilot study using the mobile phone short messaging service (SMS) Lathy Prabhakaran*, Wai Yan Chee*, Kia Chong Chua,
RESEARCH Original article... Q The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a pilot study using the mobile phone short messaging service (SMS) Lathy Prabhakaran*, Wai Yan Chee*, Kia Chong Chua,
Study of bacteria isolated from urinary tract infections and determination of their susceptibility to antibiotics
 Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology (2009); 2(3): 118-123 118 Original article Study of bacteria isolated from urinary tract infections and determination of their susceptibility to antibiotics Mansour
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology (2009); 2(3): 118-123 118 Original article Study of bacteria isolated from urinary tract infections and determination of their susceptibility to antibiotics Mansour
Preconception Clinical Care for Women Medical Conditions
 Preconception Clinical Care for Women All women of reproductive age are candidates for preconception care; however, preconception care must be tailored to meet the needs of the individual. Given that preconception
Preconception Clinical Care for Women All women of reproductive age are candidates for preconception care; however, preconception care must be tailored to meet the needs of the individual. Given that preconception
IDSA GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
Does This Woman Have an Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection?
 THE RATIONAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION CLINICIAN S CORNER Does This Woman Have an Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection? Stephen Bent, MD Brahmajee K. Nallamothu, MD, MPH David L. Simel, MD, MHS Stephan
THE RATIONAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION CLINICIAN S CORNER Does This Woman Have an Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection? Stephen Bent, MD Brahmajee K. Nallamothu, MD, MPH David L. Simel, MD, MHS Stephan
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology
 Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis. Information for clinicians
 Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
Substance Abuse During Pregnancy: Moms on Meds. Jennifer Anderson Maddron, M.D LeConte Womens Healthcare Associates
 Substance Abuse During Pregnancy: Moms on Meds Jennifer Anderson Maddron, M.D LeConte Womens Healthcare Associates 2010 National Survey on Drug Use and Health An estimated 4.4% of pregnant women reported
Substance Abuse During Pregnancy: Moms on Meds Jennifer Anderson Maddron, M.D LeConte Womens Healthcare Associates 2010 National Survey on Drug Use and Health An estimated 4.4% of pregnant women reported
Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization
 Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization H.J. Mulder MANP 1-11-2011 Henk-Jan Mulder MANP Department of Urology Martini General Hospital Van Swietenplein 1 9700
Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization H.J. Mulder MANP 1-11-2011 Henk-Jan Mulder MANP Department of Urology Martini General Hospital Van Swietenplein 1 9700
Current Status of GBS vaccine Research and Development
 Current Statut of Group B Streptococcus Vaccine Research and Development Claire Poyart CNR-Strep, Service de Bactériologie Hôpital Cochin, Université Paris Descartes Current Status of GBS vaccine Research
Current Statut of Group B Streptococcus Vaccine Research and Development Claire Poyart CNR-Strep, Service de Bactériologie Hôpital Cochin, Université Paris Descartes Current Status of GBS vaccine Research
Cardiovascular Disease and Maternal Mortality what do we know and what are the key questions?
 Cardiovascular Disease and Maternal Mortality what do we know and what are the key questions? AFSHAN HAMEED, MD, FACOG, FACC Associate Clinical Professor Maternal Fetal Medicine and Cardiology University
Cardiovascular Disease and Maternal Mortality what do we know and what are the key questions? AFSHAN HAMEED, MD, FACOG, FACC Associate Clinical Professor Maternal Fetal Medicine and Cardiology University
Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit
 Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit Lori A. Kestenbaum, Jessica L. Ebberson, Joseph J. Zorc, Caitlin LaRussa, Richard L. Hodinka
Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit Lori A. Kestenbaum, Jessica L. Ebberson, Joseph J. Zorc, Caitlin LaRussa, Richard L. Hodinka
Vitamin A Deficiency: Counting the Cost in Women s Lives
 TECHNICAL BRIEF Vitamin A Deficiency: Counting the Cost in Women s Lives Amy L. Rice, PhD INTRODUCTION Over half a million women around the world die each year from conditions related to pregnancy and
TECHNICAL BRIEF Vitamin A Deficiency: Counting the Cost in Women s Lives Amy L. Rice, PhD INTRODUCTION Over half a million women around the world die each year from conditions related to pregnancy and
Nosocomial Urinary Tract Infection
 Nosocomial Urinary Tract Infection Michael F. Ksycki, DO, Nicholas Namias, MD, MBA* KEYWORDS Nosocomial infection Urinary tract infection Urinary catheter Nosocomial urinary tract infection is a major
Nosocomial Urinary Tract Infection Michael F. Ksycki, DO, Nicholas Namias, MD, MBA* KEYWORDS Nosocomial infection Urinary tract infection Urinary catheter Nosocomial urinary tract infection is a major
University of Hawai i Human Studies Program. Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol
 University of Hawai i Human Studies Program Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol Following are guidelines for writing a clinical research protocol for submission to the University of
University of Hawai i Human Studies Program Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol Following are guidelines for writing a clinical research protocol for submission to the University of
Viral hepatitis. Report by the Secretariat
 SIXTY-THIRD WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A63/15 Provisional agenda item 11.12 25 March 2010 Viral hepatitis Report by the Secretariat THE DISEASES AND BURDEN 1. The group of viruses (hepatitis A, B, C, D and
SIXTY-THIRD WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A63/15 Provisional agenda item 11.12 25 March 2010 Viral hepatitis Report by the Secretariat THE DISEASES AND BURDEN 1. The group of viruses (hepatitis A, B, C, D and
Epidemiology 521. Epidemiology of Maternal and Child Health Problems. Winter / Spring, 2010
 Extended MPH Degree Program School of Public Health Department of Epidemiology University of Washington Epidemiology 521 Epidemiology of Maternal and Child Health Problems Winter / Spring, 2010 Instructor:
Extended MPH Degree Program School of Public Health Department of Epidemiology University of Washington Epidemiology 521 Epidemiology of Maternal and Child Health Problems Winter / Spring, 2010 Instructor:
URINE CULTURES GENERAL PROCEDURE
 University of Nebraska Medical Center Division of Laboratory Science Clinical Laboratory Science Program CLS 418/CLS 419 URINE CULTURES GENERAL PROCEDURE I. Principle Urine cultures are performed to detect
University of Nebraska Medical Center Division of Laboratory Science Clinical Laboratory Science Program CLS 418/CLS 419 URINE CULTURES GENERAL PROCEDURE I. Principle Urine cultures are performed to detect
Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department. 24/06/2013 Beryl Navti, Clinical Pharmacist, SEPT
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore
 Research Article Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore HS. Shekar 1*, HR. Chandrashekhar 2, M. Govindaraju 3, P. Venugopalreddy 1, Chikkalingiah
Research Article Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore HS. Shekar 1*, HR. Chandrashekhar 2, M. Govindaraju 3, P. Venugopalreddy 1, Chikkalingiah
California Guidelines for STD Screening and Treatment in Pregnancy
 California Guidelines for STD Screening and Treatment in Pregnancy These guidelines were developed by the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch
California Guidelines for STD Screening and Treatment in Pregnancy These guidelines were developed by the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch
Prevention of CAUTI is discussed in the CDC/HICPAC document, Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection 4.
 Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [UTI]) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [UTI]) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Uterus myomatosus. 10-May-15. Clinical presentation. Incidence. Causes? 3 out of 4 women. Growth rate vary. Most common solid pelvic tumor in women
 Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Vanderbilt University Medical Center Policy Manual
 Key Words: OB, Obstetric, L&D, Labor and Delivery, Triage Applicable to VUH Children s VMG VMG Off-site locations VPH VUSN VUSM Sandra Smith, RN Manager, Labor and Delivery Approved by Robin Mutz, RNC,
Key Words: OB, Obstetric, L&D, Labor and Delivery, Triage Applicable to VUH Children s VMG VMG Off-site locations VPH VUSN VUSM Sandra Smith, RN Manager, Labor and Delivery Approved by Robin Mutz, RNC,
