Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases Boston University School of Medicine
|
|
|
- Oscar Wells
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2010 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases Boston University School of Medicine
2 Clinical Practice Guidelines, CID 2011; 52:e103-20
3 Co-Sponsoring Organizations: Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases - Canada American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Society of Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) American Urological Association (AUA) European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) Specialties represented: infectious diseases, microbiology, internal medicine, family medicine (primary care), urology, OB-GYN, emergency med
4 Update the 1999 IDSA uncomplicated UTI guideline Time period examined: Population addressed: healthy, premenopausal, nonpregnant women with uncomplicated cystitis or pyelonephritis The guidelines do not address complicated UTI (including those with anatomical or voiding abnormalities, or co-morbidities), recurrent UTI, or UTI in men or children
5 Uncomplicated UTI cystitis and pyelonephritis Scope Major Recommendations Controversies/Limitations
6 Study Inclusion Criteria: Randomized clinical trial involving women with acute cystitis or pyelo by symptoms published in English since Exclusion Criteria: mixed populations (>10% men/complicated UTI) Outcomes Evaluated: Clinical and Bacterial Early (first visit post-treatment, typically occurring at 0-7 days after the last dose of the antimicrobial) Late (last visit post-treatment, typically occurring at days after the last dose of the antimicrobial) Adverse side effects
7 A 35-yo woman who presents with 2 days of burning on urination and today noticed some blood in her urine married; monogamous no h/o STDs; contracepts with OCP had a UTI last year
8 a. Ask her if symptoms are similar to previous episode b. Ask her if she has vaginal discharge c. You need a urine culture to make the diagnosis d. All the above are needed e. Only 1 and 2 are needed
9 Bent et al women with symptoms of UTI, no vaginal discharge, had > 90% probability of acute cystitis Do not need to do a urinalysis Do not need a urine culture Bent S, et al. JAMA. 2002;287(20):
10 Woman with symptoms of UTI (acute onset dysuria, frequency, or urgency) No complicating conditions (if pregnant, known voiding abnormalities, co-morbid conditions -> complicated UTI) No back pain (if present -> consider pyelonephritis) No vaginal discharge (if present -> consider STD) then > 90% probability of acute cystitis If hx not clear dipstick positive 80% cystitis (consider tx for UTI) negative 20% cystitis (dipstick not very specific so 1/5th of these cases might still have real UTI consider urine cx, close f/u, other diagnoses) Bent S, et al. JAMA. 2002;287(20):
11 Complicated UTI: Anatomic, functional or metabolic abnormality of the urinary tract Women pregnant, bladder outlet obstruction Men eg, voiding dysfunction due to prostatic disorders Diabetes, immunocompromised, post-menopausal, elderly Catheter, calculi, neurogenic bladder h/o Multi-drug resistance Pyelonephritis (even if uncomplicated) Get a urine culture; start empiric antibiotics; tailor therapy based on culture
12 a. Ciprofloxacin b. Nitrofurantoin c. Ampicillin d. Cephalexin
13 Cystitis: Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (T-S) is standard choice (A1) Fluoroquinolones (A1) Nitrofurantoin, Fosfomycin (B1) β lactams, including pivmecillinam1 (E1) Pyelonephritis: oral FQ x 14 days (A1) T-S, if known to be susceptible Amox/clav if Gram Stain shows gram postive cocci Pivmecillinam is not available in the United States
14 Increasing antimicrobial resistance rates Increased reporting of clinical outcomes Inclusion in of uropathogens resistant to the study drugs in clinical trials (previously excluded) New antibiotics and disappearance of others from market Increased appreciation of the importance of collateral damage
15 Collateral damage is a term used to refer to ecological adverse effects of antibiotic therapy; the selection of drug-resistant organisms unwanted development of colonization or infection with multidrug-resistant organisms Paterson DL. 2004; 38 Suppl 4:S341-S345.
16 There is no single best agent for treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis (AUC)
17 Recommended antimicrobials Nitrofurantoin 100 mg bid X 5 days (AI) Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 160/800 mg (one DS tablet) bid X 3 days (avoid if resistance prevalence is known to exceed 20% or if used for UTI in previous 3 months) (AI) Fosfomycin2 3 gm single dose (lower efficacy than some other recommended agents; avoid if pyelonephritis suspected) (AI) Pivmecillinam3 400 mg bid x 5 days (lower efficacy than some other recommended agents; avoid if pyelonephritis suspected) (AI) Absence of fever, flank pain, or other suspicion for pyelonephritis; able to take po, 2. Only approved for E coli; 3. Not available in the US
18 Strength of recommendation A Good evidence to support a recommendation for or against use B Moderate evidence to support a recommendation for or against use C Poor evidence to support a recommendation Quality of evidence I Evidence from 1 properly randomized, controlled trial II Evidence from 1 well-designed clinical trial, without randomization; from cohort or case-controlled analytic studies (preferably from > 1 center); from multiple time-series; or from dramatic results from uncontrolled experiments III Evidence from opinions of respected authorities; based on clinical experience, descriptive studies, or reports of expert committees. Source: The periodic health examination. Canadian Task Force on the Periodic Health Examination. Health Canada, Adapted and reproduced with the permission of the Minister of Public Works and Government Services, Canada, 2009
19 Quality of evidence scale Most choices are a level I (Evidence from >1 RCT) Strength of recommendation Efficacy Safety/tolerability Prevalence of resistance Promotion of resistance/collateral damage
20 Antibiotic Efficacy Safety Resistant Prevalence Collateral Damage NTF 93% (84-95%) Good Low Low T-S 93% (90-100%) Good Intermed. (varies) Poss Fosfomycin 91% Good Low Low
21 Gupta K et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:e103-e120
22 a. Ciprofloxacin b. Nitrofurantoin c. Ampicillin d. Cephalexin
23 No longer available: Gatifloxacin and Sparfloxacin: Henry, Naber, Richards New Formulation: Ciprofloxacin XR vs. ciprofloxaicn bid: Henry, Fourcroy Differing doses, durations: Ciprofloxacin bid x 3 days vs. 7 days: Vogel Norfloxacin 400 vs. 800: Pimentel Ciprofloxacin vs. Norfloxacin: Auguer FQ vs. other: Ciprofloxacin vs. Amox/clav: Hooton Norfloxacin vs. Pivmecillinam: Nicolle Ciprofloxacin vs. NTF vs. T-S: Iravani
24
25 Antibiotic Efficacy Safety Resistant Prevalence Collateral Damage NTF 93% (84-95%) Good Low Low T-S 93% (90-100%) Good Intermed. (varies) Poss Fosfomycin 91% Good Low Low Pivmecillinam 55-82% Good Low Low FQs 90% (85-98%) Good Intermed. (varies) Prob. B-lactams 89% (79-98%) Fair Intermed. (varies) Prob.
26 The fluoroquinolones, ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin, in 3-day regimens are highly efficacious (A-I) but have a propensity for collateral damage and should be reserved for important uses other than acute cystitis, and thus should be considered alternative antimicrobials for acute cystitis (A-III). β-lactam agents including amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefdinir, cefaclor, and cefpodoxime-proxetil in 3- to 7-day regimens are appropriate choices for therapy when other recommended agents cannot be used (B-I). Other β-lactams, such as cephalexin, are less well studied but may also be appropriate in certain settings (B-III). The β-lactams generally have inferior efficacy and more adverse effects compared to other UTI antimicrobials (B- I).
27 What IDSA fails to recognize in their new UTI guidelines is that nitrofurantoin is about 40x more costly than TMP/SMX
28 We (IDSA) do in fact recognize that cost plays an important role in decision making about antimicrobials, and it is one of several factors that we think should go into a decision about choice. T/S is not right for everyone due to allergy or concern about resistance; cipro is not right for everyone due to concerns about collateral damage; and NF, while more expensive, is effective and has very little collateral damage. Fosfomycin also has little collateral damage, but it is not as effective and is also an expensive agent.
29 *The choice between these agents should be individualized and based on patient allergy and compliance history, local practice patterns, local community resistance prevalence, availability, cost, and patient and provider threshold for failure
30 a. Do a Pub-med search b. Consult your local hospital antibiogram c. Ask the patient d. Get a urine culture
31 Most of us don t know our local resistance rates Hospital antibiograms often not stratified by gender/location/other clinical data Laboratory surveys based on passive surveillance biased by urine cultures obtained from women who may have been sicker, failed initial regimen, or have RF for resistance Active surveillance not done in the US
32 Sanchez et al, CID 2011; Letter to Editor in response to UTI GL
33 Passive surveillance systems have inherent selection bias Prospective, systematic, active surveillance of uncomplicated uropathogens at the local practice and/or health care system levels is essential to inform empirical antimicrobial decisions for acute cystitis Focused examination of clinical failure rates with empiric regimens for uncomplicated cystitis patients can also be informative
34 There are data to support the wide variation in rates obtained from laboratories compared with rates from patients with acute cystitis who would normally not have urine cultures performed. The difference in rates for TS: (27% higher in lab survey) FQ: (18% higher in lab survey) Cefuroxime (14% higher in lab survey) NTF: no significant difference T. Y. Ti Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2003)
35 Most data is for T-S; some for FQ Exposure in past 3 months Travel to endemic area Previous MDR Ask your patient!
36
37 Ciprofloxacin Fosfomycin Cefuroxime Hold off on antibiotics; check-in with her in 2 days
38 Phosphonic acid derivative Inhibits cell wall synthesis Oral sachet - for uncomplicated cystitis Also IV formulation (Germany, France, Spain, Italy, Japan) --- but data for use in non-uti conditions sparse
39 Active against wide spectrum of GP and GN organisms, including ESBL, VRE, Resistance is chromosomally encoded rather than plasmid little cross-reactivity with R to other agents Clinical cure 83% = cipro x 5 days (81%) for AUC in Turkey (Ceran et al, J Infect Chem, 2010) Fosfomycin Ca+ tablet 500 mg tid x 2 days = fosfomycin trometamol 1 gm sachet (Matsumoto et al, J Infect Chemo 2010 ) Meta-analysis: Fosfomycin = comparators (Falagas et al. J Antimicrob Chemo 2010)
40 Availability limited (FDA approved in US but not widely used) Inferior efficacy in some studies (medical letter) Not tested or reported in most clinical labs Breakpoints vary by study Increased use increasing resistance (Oteo et al, J Antimicrob Chemo 2010)
41 Clinical cure can be achieved in 25% 42% of women Associated with prolongation of symptoms as well as a small risk of progression to pyelonephritis (1/38; Christiaens et al)
42 Antibiotics vs. placebo in the treatment of women with uncomplicated cystitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Falagas ME, et al. J Infection 2009;58: RCT in uncomplicated cystitis reviewed: Antibiotics superior to placebo Cure: OR=4.67, 95% CI = Micro eradication: OR=10.67, 95% CI= Adverse events: OR=1.64, 95% CI=
43 Only pertains to cystitis not for more invasive or serious diseases Minimal risk of progression to tissue invasion or sepsis spontaneous resolution may attenuate differences in clinical outcomes when a drug with 80% efficacy is compared with one with 95% efficacy AUC is one of the most common indications for antimicrobial exposure in an otherwise healthy population very small increments in collateral damage repeated many times may in aggregate magnify the impact
44
45 Approach to choosing an optimal antimicrobial agent for empirical treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis. Gupta K et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:e103-e120
46 A-III B-I* A-I *amox/clav, cefdinir, cefaclor, cefpdoxime for 3-7 d B-1 A-I β-lactams generally have inferior efficacy & more adverse effects, compared with other UTI anti-microbials B-I A-I A-I Gupta K et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:e103-e120a
47 a. Ciprofloxacin for 7 days b. Fosfomycin for 7 days c. Cefpodoxime for 7 days d. Bactrim DS for 10 days
48 Oral ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice daily) for 7 days, with or without an initial 400-mg dose of intravenous ciprofloxacin, is an appropriate choice for therapy in patients not requiring hospitalization (A-I) where the prevalence of resistance of community uropathogens to fluoroquinolones is not known to exceed 10% A once-daily oral fluoroquinolone, including ciprofloxacin (1000 mg extended release for 7 days) or levofloxacin (750 mg for 5 days)(b-ii)
49 Obvious clinical criteria (Nausea/vomiting; sepsis) Initial therapy for borderline patient who is probably going home with an oral regimen Resistance to FQ and T-S An initial 1-time intravenous dose of a long-acting parenteral antimicrobial, such as 1 g of ceftriaxone (B-III) or a consolidated 24-h dose of an aminoglycoside, is recommended (B-III)
50 T-S: The threshold of 20% as the resistance prevalence at which the agent is no longer recommended for empirical treatment of acute cystitis is based on expert opinion derived from clinical, in vitro, and mathematical modeling studies (B-III). FQ: Data are insufficient to make a recommendation about what fluoroquinolone resistance level requires an alternative agent in conjunction with or to replace a fluoroquinolone for treatment of pyelonephritis.
51 Oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole DS twice daily for 14 days is effective for treatment of acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis if the uropathogen is known to be susceptible (AI). If susceptibility is not known and trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole is used, an initial intravenous one gram dose of ceftriaxone is recommended (BII) Oral β-lactam agents are less effective than other available agents (BIII). Initial intravenous dose of a long-acting parenteral antimicrobial is recommended (CTX BII; AG BIII)
52 Panel Members: Kalpana Gupta, MD, MPH (Chair) Richard Colgan, MD Thomas Hooton, MD Loren G. Miller, MD, MPH Gregory Moran, MD Kurt G. Naber, MD Lindsay E. Nicolle, MD Raul Raz, MD Anthony J. Schaeffer, MD David E. Soper, MD Björn Wullt, MD SPGC Liaison: Jasmine Dhindsa, MD Rick Watkins, MD IDSA Staff: Vita L. Washington, MSA Jennifer J. Padberg, MPH
53 This resource is based on an IDSA practice guideline. The practice guideline and this presentation are not intended to substitute for the independent professional judgment of the treating physician. It is important to realize that guidelines cannot always account for individual variation among patients. They are not intended to supplant physician judgment with respect to particular patients or special clinical situation. IDSA considers adherence to its guidelines to be voluntary, with the ultimate determination regarding their application to be made by the physician in the light of each patient's individual circumstances. The full practice guideline and additional resources are available at:
IDSA GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance
 Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions
 Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions CYSTITIS The growing importance of resistance to quinolones, their environmental impact and reduced
Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions CYSTITIS The growing importance of resistance to quinolones, their environmental impact and reduced
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D.
 ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
How To Find Out If A Diabetic Woman Has A Urinary Tract Infection
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
RECOMMENDATIONS. MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 PRACTICE POINT
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 GOALS Urgent primary care assessment and management of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 GOALS Urgent primary care assessment and management of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H.
 CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients.
 Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Urinary Tract Infection
 Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Guidelines on Urological Infections
 Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt European Association of Urology 2013 TABLE
Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt European Association of Urology 2013 TABLE
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection
 Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1. Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs
 Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults
 IDSA GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults Lindsay E. Nicolle, 1 Suzanne Bradley, 2 Richard Colgan, 3 James
IDSA GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults Lindsay E. Nicolle, 1 Suzanne Bradley, 2 Richard Colgan, 3 James
Chlamydia THE FACTS. How do people get Chlamydia?
 What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
California Gonorrhea Treatment Guidelines
 Califnia Gonrhea Treatment Guidelines These guidelines were developed by the Califnia Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch in conjunction with the Califnia
Califnia Gonrhea Treatment Guidelines These guidelines were developed by the Califnia Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch in conjunction with the Califnia
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS
 ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Testing for Gonorrhea Q1: What test should be completed for accurately diagnosing gonorrhea? A1: Testing is done with either a culture or a NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test).
Frequently Asked Questions Testing for Gonorrhea Q1: What test should be completed for accurately diagnosing gonorrhea? A1: Testing is done with either a culture or a NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test).
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative (MUSIC) Prostate Biopsy Toolkit MUSIC
 Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative (MUSIC) Prostate Biopsy Toolkit MUSIC October 2015 Contents Executive Summary I Prostate Biopsy Infection Bundle 1. What is a bundle? 1.1. MUSIC Prostate
Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative (MUSIC) Prostate Biopsy Toolkit MUSIC October 2015 Contents Executive Summary I Prostate Biopsy Infection Bundle 1. What is a bundle? 1.1. MUSIC Prostate
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis
 10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care
 Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN paulak@parkmanorwi.com
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN paulak@parkmanorwi.com
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative treatment
 STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
GONORRHOEA. Use of lidocaine as a diluent when using ceftriaxone (see Appendix 1)
 Key practice notes: 1 st line therapy GONORRHOEA Decreasing sensitivity of gonorrhoea to cephalosporins is now a real threat: CEFTRIAXONE 500mg IM stat first-line for all gonococcal infections AZITHROMYCIN
Key practice notes: 1 st line therapy GONORRHOEA Decreasing sensitivity of gonorrhoea to cephalosporins is now a real threat: CEFTRIAXONE 500mg IM stat first-line for all gonococcal infections AZITHROMYCIN
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
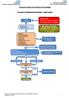 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
2/21/2016. Prolapse Surgery after Transvaginal Mesh: The Evolving Landscape. Disclosures. Objectives. No Relevant Disclosures
 Prolapse Surgery after Transvaginal Mesh: The Evolving Landscape David R. Ellington, MD, FACOG Assistant Professor Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures No Relevant Disclosures
Prolapse Surgery after Transvaginal Mesh: The Evolving Landscape David R. Ellington, MD, FACOG Assistant Professor Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures No Relevant Disclosures
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) makes
 Annals of Internal Medicine Clinical Guidelines Screening for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement U.S. Preventive Services Task
Annals of Internal Medicine Clinical Guidelines Screening for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement U.S. Preventive Services Task
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology
 Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department. 24/06/2013 Beryl Navti, Clinical Pharmacist, SEPT
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon
 Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View.
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan
 Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011
 The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Screening and preventive therapy for MDR/XDR-TB exposed/infected children (and adults)
 Screening and preventive therapy for MDR/XDR-TB exposed/infected children (and adults) H S Schaaf Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, and Desmond Tutu TB Centre Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg
Screening and preventive therapy for MDR/XDR-TB exposed/infected children (and adults) H S Schaaf Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, and Desmond Tutu TB Centre Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg
SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization
 WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR RESEARCH IN HUMAN REPRODUCTION Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization Dr SALONEY NAZEER Department of Gynaecology
WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR RESEARCH IN HUMAN REPRODUCTION Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization Dr SALONEY NAZEER Department of Gynaecology
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings
 Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections
 Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Optimizing Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Reporting
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2011, p. S15 S19 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00712-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. VOL. 49, NO. 9 SUPPL. Optimizing
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2011, p. S15 S19 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00712-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. VOL. 49, NO. 9 SUPPL. Optimizing
Develop an understanding of the differential diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Reading and Analyzing Scientific Articles. Wednesday, October 20, 2010
 Reading and Analyzing Scientific Articles Wednesday, October 20, 2010 Zuber D. Mulla, Ph.D. Associate Professor & Director of Epidemiologic Research Department of OB/GYN and Affiliate Associate Professor
Reading and Analyzing Scientific Articles Wednesday, October 20, 2010 Zuber D. Mulla, Ph.D. Associate Professor & Director of Epidemiologic Research Department of OB/GYN and Affiliate Associate Professor
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections
 Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infections are a very common medical problem. The term urinary tract infection is frequently used to refer to an infection of the bladder. However, although
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infections are a very common medical problem. The term urinary tract infection is frequently used to refer to an infection of the bladder. However, although
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections
 Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence
 Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Urinary Tract Infections - How to Identify, Treat and Prevent Them
 1 of 12 4/29/2016 1:49 PM Library Home Find A Physician Find A Practice Request An Appointment Search Clinical Studies Classes and Support Groups Ask A Health Librarian Subscribe to enewsletters Bone and
1 of 12 4/29/2016 1:49 PM Library Home Find A Physician Find A Practice Request An Appointment Search Clinical Studies Classes and Support Groups Ask A Health Librarian Subscribe to enewsletters Bone and
HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS
 HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS Professor Dr. Michael FRASS Medical University of Vienna, Department Medicine I Doctor s Asscociation for Classical Homeopathy www.aekh.at President, Umbrella
HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS Professor Dr. Michael FRASS Medical University of Vienna, Department Medicine I Doctor s Asscociation for Classical Homeopathy www.aekh.at President, Umbrella
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
Clinical Indicator Ages 19-29 Ages 30-39 Ages 40-49 Ages 50-64 Ages 65+ Frequency of visit as recommended by PCP
 SCREENING EXAMINATION & COUNSELING UPMC Health Plan Clinical Indicator Ages 19-29 Ages 30-39 Ages 40-49 Ages 50-64 Ages 65+ Annually Physical Exam and Counseling 1 Blood Pressure 2 At each visit. At least
SCREENING EXAMINATION & COUNSELING UPMC Health Plan Clinical Indicator Ages 19-29 Ages 30-39 Ages 40-49 Ages 50-64 Ages 65+ Annually Physical Exam and Counseling 1 Blood Pressure 2 At each visit. At least
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services. 18/07/2008 Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust
 Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Acne. Objectives. Conflicts of Interest. Acne 05/18/2015
 Objectives Acne Jonathan A. Dyer, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Child Health University of Missouri Discuss acne pathogenesis Recognize common acne subtypes Implement a treatment plan based
Objectives Acne Jonathan A. Dyer, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Child Health University of Missouri Discuss acne pathogenesis Recognize common acne subtypes Implement a treatment plan based
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care
 COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care In this issue: Page Introduction, Background & Diagnostic Tests 1 UTI in non-pregnant women 3 UTI in pregnant
COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care In this issue: Page Introduction, Background & Diagnostic Tests 1 UTI in non-pregnant women 3 UTI in pregnant
GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America Guidelines for Developing an Institutional Program to Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship Timothy
GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America Guidelines for Developing an Institutional Program to Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship Timothy
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey
 2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
The Treatment ofnon-gonococcal Urethritis with Single Dose Oral Azithromycin
 The Journal of International Medical Research 1995; 23: 386-393 The Treatment ofnon-gonococcal Urethritis with Single Dose Oral Azithromycin T ERDOGRU\ A AGA9FIDAff, M ONELz,S BADUR z, 0 ANG 2 AND S TELALLOGLU
The Journal of International Medical Research 1995; 23: 386-393 The Treatment ofnon-gonococcal Urethritis with Single Dose Oral Azithromycin T ERDOGRU\ A AGA9FIDAff, M ONELz,S BADUR z, 0 ANG 2 AND S TELALLOGLU
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Contact centred strategies to reduce transmission of M. leprae
 Contact centred strategies to reduce transmission of M. leprae Jan Hendrik Richardus, MD, PhD Department of Public Health Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands Outline lecture
Contact centred strategies to reduce transmission of M. leprae Jan Hendrik Richardus, MD, PhD Department of Public Health Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands Outline lecture
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly
 Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
WHO Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza and other Influenza Viruses
 WHO Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza and other Influenza Viruses 20 August 2009 Table of contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... i Other recommendations...iii 1. INTRODUCTION...
WHO Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza and other Influenza Viruses 20 August 2009 Table of contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... i Other recommendations...iii 1. INTRODUCTION...
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
signs suggesting chlamydia:
 Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
