EDGE-BASED PARTITION CODING FOR FRACTAL IMAGE COMPRESSION
|
|
|
- Brook Summers
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EDGE-BASED PARTITION CODING FOR FRACTAL IMAGE COMPRESSION Tilo Ohotta and Dietmar Saupe Department of Computer and Information Siene University of Konstanz, Germany ABSTRACT This paper presents an approah for fratal image ompression that yields the best performane ompared to fratal methods that do not rely on hybrid transform oding. The ahievement is obtained using the standard algorithm in whih the image is partitioned into non-overlapping range bloks whih are approximated by orresponding larger domain bloks with image intensities that are affinely similar to those of the range bloks. The partiular feature of our approah is the adaptive spatial partition, that proeeds in a split/merge fashion. In previous split/merge partitions for fratal image oding the merging started from a uniform partition onsisting of square bloks of equal size. In this paper we base the blok merging on an adaptive quadtree partitioning. An effiient enoding method for the quadtree-based split/merge partitions is proposed whih generalizes the oding of region edge maps and whih inludes speial ontext modeling. The enoding method may be used for other appliations that rely on image partitions. Key words: Fratal Image Compression, Partition Coding, Region Edge Maps, Image Segmentation. 1
2 EDGE-BASED PARTITION CODING FOR FRACTAL IMAGE COMPRESSION 1 INTRODUCTION Fratal image ompression was oneived by Barnsley and Sloan [1, 2], and the first fully automated fratal image ompression algorithm was published by Jaquin in 1989 [3, 4]. Given an image, the enoder finds a ontrative affine image transformation (fratal transform) T suh that the fixed point of T is lose to the given image in a suitable metri. The deoding is by iteration of the fratal transform starting from an arbitrary image. Due to the ontration mapping priniple, the sequene of iterates onverges to the fixed point of T. Jaquin s original sheme showed promising results. Sine then, many researhers have improved the original algorithm outperforming standard JPEG image ompression. However, the rate-distortion performane of urrent stateof-the-art odes based on wavelet transform oding as, e.g., in JPEG2000 annot yet be reahed even by the best fratal oders that work in the spatial domain. For surveys, detailed disussions, omputer ode, and bibliography see [5, 6, 7]. The fratal transform in its ommon form has two essential omponents, namely first, an image partition and seond, for eah blok of the partition (alled range blok) an address for a similar image blok, alled domain, and a small set of real quantized transform parameters. These parameters determine an affine mapping of the intensity values of the domain blok that is shaped like the range blok. These mappings are hosen suh that the intensities in eah range blok are approximated by the transformed intensities of the orresponding domain blok. The fratal transform T operates on an arbitrary image by mapping domains to ranges as speified in the fratal ode. Contrativity of the transform may be provided by a simple ondition on one of the parameters of the affine mappings. Uniform image partitions do not yield satisfying rate-distortion performane for fratal oding. Thus, already the first papers on fratal ompression suggested adaptive image partitions. Jaquin used image squares that were subdivided into smaller regions onsisting of one to three subsquares of half the size [4]. In [5] adaptive quadtrees were used. These partitions are built with square bloks whih are reursively subdivided into four subbloks of equal size until some approximation quality is reahed or the blok size falls below a given threshold. Other hierarhial image partitions an be based on retangles [8, 9] and polygons [10]. Delaunay triangulations have also been used [11, 12]. Highly adaptive partitions an be generated by a split/merge sheme [13] in two phases. First, the image is partitioned into suessively smaller bloks until a termination riterion is fulfilled. Then neighboring regions may be merged again as long as some oherene riterion is satisfied. In the methods in [14, 15, 16] the splitting is simple and results in uniform square bloks. These small squares are merged again to form irregularly shaped range bloks that adapt well to the struture of the underlying image and provide some of the best fratal oders [16]. Uniform and quadtree partitions are easy to enode omprising just a small fration of the total rate in a fratal image ode. However, more adaptive partitions suh as those based on a split/merge proess are harder to enode effiiently. There are two main approahes. One may either enode the boundaries of the image regions, or one an enode onnetivity of the basi bloks that make up the image regions. Chain oding [17] belongs to the first ategory, while region edge maps [18] are an example for the seond kind. Our work extends and improves the methods in [16] in two ways. 1. In 1976 Horowitz and Pavlidis [19] suggested a split/merge sheme for effiient image representation in whih the splitting provided a quadtree partition whose bloks are then merged to form adaptive image regions. Suh image partitions an also be generated when splitting all the way down to equal sized squares. However, due to the ourrene of larger oherent bloks in the underlying quadtree partition a 2
3 more effiient ode of the partition may be expeted without signifiantly reduing the adaptivity of the final partition. Thus, we propose to use this approah in the ontext of fratal oding. We note that this has already been tried in [20, 21]. 2. Our main ontribution is an effiient method to enode the orresponding split/merge partition, i.e., an image partition in whih eah blok is the union of some neighboring square bloks from a given quadtree partition, whih must also be enoded effiiently. For this purpose we generalize the region edge maps proposed in [18] and provide omprehensive ontext modelling for effiient arithmeti enoding. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In setion 2 we briefly review the basis about fratal image oding and give a short survey of previous work in the field of lossless partition oding that is relevant with respet to our approah. In partiular, we revisit region edge maps whih provide the basis of our new method for quadtree-based region edge maps. In setion 3 we define a ompression sheme for quadtree odes and introdue quadtree-based region edge maps and their effiient enoding with ontext modelling. In setion 4 we apply the proposed sheme to region-based fratal image ompression providing effiient partition oding. Experimental results are presented in setion 5. 2 TERMINOLOGY AND RELATED WORK 2.1 Fratal Image Compression We onsider an image F of size N N as a funtion that maps a set of N 2 pixel oordinates (x, y), x, y = 0,...,N 1, to the set of grey values v {0,...,255}. The funtion F may be represented as a orresponding set of 3-tuples (x, y, v). A base blok b is an n n subset of F, b = {(x, y, v) F x = x min,...,x max, y = y min,..., y max } where x max x min = y max y min = n 1. The base blok size n is a fixed parameter of our method and may be hosen as small as n = 1 amounting to base bloks being single pixels. For our image partition we need to onsider groups of onneted base bloks as range bloks for the fratal oder. We all two base bloks b 1, b 2, b 1 b 2 = adjaent, if and only if there are two pixels p 1 = (x 1, y 1, v 1 ) b 1, p 2 = (x 2, y 2, v 2 ) b 2 suh that x 2 x 1 + y 2 y 1 = 1. We define a region as a onneted set of base bloks. A set of regions P = {r i i = 0,...,n R 1} with r i r j and r i r j = for i j whih overs the image F, i.e., r P r = F, is alled a partition of F. The image F in a range blok is approximated by an intensity transformed opy of a larger blok, alled domain blok. Let us denote by D F the domain image of size N/2 N/2 obtained by downsampling the original N N image F. Usually, downsampling proeeds by averaging intensity values of pixels in 2 2 bloks. For a given range blok r parameters x d, y d {0,...,N/2 1} and s r, o r R are sought suh that v ˆv = s r D F ((x + x d ) mod N/2, (y + y d ) mod N/2) + o r, (x, y, v) r, (2.1) The region that is addressed with (x d, y d ) in the domain image D and the same shape as the range blok is the domain blok for the range r. The parameters s r and o r allow saling and adjustment of brightness of the grey values of the domain. Saling fators are hosen with the onstraint s r < 1. Moreover, saling fators s r and offsets o r are quantized for the purpose of enoding. We also onsider an approximation error for mapping (2.1): E(r) = (v ˆv) 2. (2.2) (x,y,v) r The approximation error E(r) should be as small as possible. Typially, least squares optimization is used to determine the best saling fator and offset for a given domain address (x d, y d ), and a searh through a 3
4 0 1 NW N NE NW N NE 2 3 W X W X (a) (b) () Figure 1: Region edge maps with ontext modeling: (a) a blok is represented by a symbol from {0, 1, 2, 3} whih enodes the presene resp. absene of region edges at the Northern and Western boundary of the blok; (b) the symbols of four preeding bloks (West, North West, North, and North East) are used to define a ontext; () the symbol ombination N = 1, W = 2, X = 2 annot our in a partition. pool of domains determines the domain whih yields the least approximation error. We also onsider a global approximation error for the image F whih is alled ollage error: E = E(F, P) = r P E(r). (2.3) The fratal ode must uniquely desribe the image partition and for eah range blok in the partition the domain blok used together with the saling fator and the offset. This ode essentially amounts to the definition of an image operator T. Given an image I k, the transformed image I k+1 = T(I k ) is obtained by applying all range blok transformations in (2.1), where the domain bloks are taken from the image I k in plae of F. This image operator T is a ontration and, hene, iterating T starting with an arbitrary initial image I 0 onverges to a unique image I, the fixed point of the fratal transform T. The fixed point I an be onstruted by the deoder and serves as the image reonstrution. The reonstrution quality depends on the ollage error 2.3, whih is due to the so-alled ollage theorem. For further details, bakground material, and proofs we refer to the large body of literature, see, e.g., [5, 22, 23]. 2.2 Lossless Partition Coding There are two lasses for lossless partition oding. The first one is hain oding in whih sequenes of symbols for diretions represent region boundaries [17]. A naive hain oding for image partitions enodes the losed boundary of eah region as a starting position and a sequene of steps in the diretions North, East, South, and West. This approah is not satisfying. The reason is that boundary segments are enoded twie beause an edge is shared by two neighboring regions exept at the image boundary. Furthermore, the enoding of the start positions an beome expensive in bits even when the absolute address for a region is enoded relative to another one. Several optimizations have been introdued, e.g., in [24], where three symbols are used to represent a hain (go straight, left, or right). In [25] the partition is not oded as a set of losed region boundaries but as set of line sequenes. Eah sequene desribes a number of onneted lines for whih a relative starting point, the length of eah line, and the relative diretions of the line segments are enoded. Eah region edge is visited only one and long straight lines an be enoded by a small number of symbols. Other, more sophistiated, methods for hain oding (in the ontext of fratal image oding) are in our previous paper [26]. The seond lass of methods to represent region shapes is related to enoding binary images. A fundamental method for ompressing blak-and-white images has been proposed in [27]. The binary intensities are enoded individually in line-by-line order using an arithmeti oder [28] with ontext modelling. In [18], this approah was extended to enode grid-based partitions in whih the onnetivity of a base blok is enoded with one out of four symbols eah. For a given base blok it suffies to indiate whether its Northern and Western borders are part of a region boundary, whih requires two bits per base blok (see figure 1a). The resulting 4-nary image is alled a region edge map. In [18] the symbols of a region edge map are enoded line-by-line with an adaptive arithmeti oder and 4
5 W NE N NW X 0 * 0 * 1 0 * 0 * 2 0 * 1 * 1 0 * 1 * 2 0 * 2 * 0 0 * 3 * 0 1 * 0 * 0 1 * 1 * 0 W NE N NW X 2 * 0 * 1 2 * 0 * 2 2 * 1 * 1 2 * 1 * 2 2 * 2 * 0 2 * 3 * 0 3 * 0 * 0 3 * 1 * 0 Table 1: Impossible symbol ombinations. The asterisks orrespond to any symbol {0,..., 3}. All in all 768 out of 4 5 = 1024 ombinations may our. ontext modelling similar to [27]. The ontext modelling (figure 1b) uses four previously enoded/deoded symbols (symbols for bloks in West, North West, North and North East diretion). Due to elementary geometri fats some symbol ombinations annot our (figure 1, table 1). Taking this into aount the following formula is proposed to update the probability p for a symbol z, that may appear in ontext : p(z ) = λ ount(z ) + 1 λ ount() + A, (2.4) where ount(z ) is the number of symbols z enoded in ontext, ount() is the total number of ourrenes of ontext, and A 4 is the number of symbols that are possible in ontext. Probabilities p(z ) for symbols z that are not possible in ontext as indiated in table 1 are set to zero. Following experimental results in [18], the weight fator λ should be set to of 4 or 5 for best ompression results. In our empirial studies we used λ = 4. 3 PARTITION CODING METHOD 3.1 Quadtree Deomposition Our partition method is based on a split/merge approah as introdued by Horowitz and Pavlidis in [19]. In our ase, the splitting phase onsists of a quadtree segmentation. Tate s edge-based oding sheme [18] uses a uniform grid of equally sized square base bloks. In this setion we extend the oding to partitions in whih regions are unions of square base bloks from a quadtree segmentation. A quadtree is a hierarhial data struture [29] amounting to an ordered tree with inner nodes of degree four. In image proessing appliations a node orresponds to a retangular (or square) image area, whih is reursively split into four equal size subretangles (or subsquares) orresponding to the four hildren of the node. A split rule evaluated for a given node, respetively the orresponding retangle (square), determines termination of the reursion in whih ase the node ends up as a leaf node of the quadtree. The bloks belonging to the leaf nodes of the tree omprise the quadtree partition. By means of the split riterion the quadtree may adapt to image ontent. For example, large bloks in low frequeny areas and small bloks in high frequeny areas an be generated, respetively. Pseudo ode for the proedure is given in algorithm 1. After quadtree segmentation, an iterative merging phase follows where in eah iteration two adjaent bloks are merged, whih may be further merged with other bloks in a sueeding iteration. An appliation speifi merge riterion, evaluated for eah pair of adjaent bloks to be merged, determines two bloks that are merged in an iteration step. Pseudo ode for the proedure is given in algorithm 2. 5
6 During the merging proess it is possible that a group of four bloks belonging to four hild nodes of the same parent node in the quadtree are merged into one region. In suh a ase it is possible to simplify the quadtree by pruning it at the parent node. We all the resulting quadtree a fitted quadtree and expet to be able to enode the fitted quadtree as well as the quadtree-based regions of the final image partition with a smaller rate. Algorithm 1 split(n) Input: quadtree leaf node n with orresponding image blok r(n). Output: quadtree root node n with orresponding quadtree partition of r(n). split riterion is given by boolean funtion SC( ). if SC(r(n)) then expand the node n using four hild nodes n i, i = 0,..., 3 for i=0,...,3 do n i = split(n i ) end for end if return node n. Algorithm 2 merge(p,n R ) Input: quadtree partition P, target region number n R < P. Output: partition P with P = n R regions. Set P =. for all q P do initialize q as region r insert r into P end for while P > n R do find the region pair (r i, r j ), r i, r j neighbors in P minimizing an error riterion insert r i r j into P remove r i and r j from P end while return P. 3.2 Quadtree Coding In this subsetion we desribe the enoding of the quadtree partition. The following subsetion overs the enoding of the image partition derived from merging quadtree bloks. The (ordered) quadtree (figure 2a,b) is traversed in depth-first order proessing eah node by outputting a binary symbol 1 for an inner node and 0 for a leaf node. Sine we also enode the smallest and largest depth of a leaf node as side information, we may delete the symbols 1 for inner nodes above the minimal leaf depth and the symbols 0 for leaf nodes at the maximal depth. Context-based arithmeti oding is ruial for obtaining ompat odes for quadtrees. For example, ontext modelling an exploit the fat that situations given by one large quadtree blok adjaent to many small quadtree bloks (figure 2) seldomly our. For a given blok q we onsider the number of neighboring leaves in North and West (z N and z W respetively). These numbers are known also at the deoder due to the depth-first traversal of the quadtree. These ounts are bounded, 0 z N, z W z max, where z max is determined by the side information (minimal and maximal depth of leaf nodes). For example, z max = 8 for a 4-32-quadtree, i.e., a quadtree segmentation in whih the minimal and maximal blok sizes are 4 4 and 32 32, respetively. We propose the following three heuristi shemes to build up a ontext for the given blok q. In the last subsetion we empirially ompare the performane of these three ontext models for quadtree partitions of 6
7 (b) (a) q () Figure 2: Quadtree deomposition after the top down sheme: (a) stepwise split up of the bloks; (b) enoding order; () situation with low probability of ourrene: one blok q has many neighbor bloks. varying omplexity for test images. Full Context Two symbols are defined to be in the same ontext lass if and only if the orresponding tuples (z N, z W ) of neighbor leaf numbers are equal. If we number the ontext lasses by = 0,..., max 1, we may write = (z max + 1)z N + z W and max = (z max + 1) 2. Sum Context Two symbols are in the same ontext lass if and only if the orresponding ombined neighbor leaf numbers, i.e., z N + z W, are equal. Thus, = z N + z W and max = 2 (z max + 1). Redued Context Four ontext lasses are defined by heking whether there are several neighboring leaf nodes in the North and in the West. More preisely, 0 for z N 1 and z W 1 1 for z N 1 and z W 2 = 2 for z N 2 and z W 1 3 for z N 2 and z W 2 and max = Quadtree-based Region Edge Maps In this subsetion we generalize the region edge map (REM) enoding sheme desribed in subsetion 2.2 to the ase where the bloks used in the merging phase are from a quadtree image partition. We assume that the enoding of the split/merge partition ours after enoding the quadtree partition as given in the last subsetion 3.2. Thus, we may use the quadtree partition in the ontext modelling. We first note that the split/merge partition based on merging bloks of the quadtree partition an easily be enoded using the previous method for REM enoding when we define the region edge map in terms of a uniform image partition onsisting of atomi bloks of the size that is given by the smallest bloks that our in the quadtree partition. In other words, we imagine expanding the quadtree so that it beomes a full quadtree (all leaves have the same depth) and define a symbol z {0, 1, 2, 3} for eah leaf blok depending on the presene of a region boundary along its Western and Northern edges as before (figure 1a). We again enode the resulting symbol sequene line by line from top to bottom and from left to right. Let us all this symbol sequene the quadtree-based region edge map (QBREM). This sequene typially has many more symbols than there are bloks in the initial quadtree partition. However, sine the quadtree is available at the oder and the deoder we may use it in order to design the ontext modelling to take advantage of this knowledge. For example, in this way the deoder is able to ompletely determine many symbols from their ontext alone without any additional information. 7
8 h n h n v t i v n i h n h n h n h t v n i v t i i i v n i i i v n i i i Figure 3: Types of atomi bloks in quadtree-based region edge maps: orner bloks (), interior bloks (i), trivial horizontal boundary bloks (h t ), nontrivial horizontal boundary blok (h n ), trivial vertial boundary bloks (v t ), and nontrivial vertial boundary bloks (v n ). With the ontext modelling for region edge maps of subsetion?? the oder maintains a table of up to four probabilities for eah of 256 ontexts. With the quadtree in the bakground we an differentiate between six types of atomi bloks (figure 3), for eah of whih we propose to maintain a separate probability table. Some of these tables are trivial, however, and need not be expliitly implemented in a omputer program. In the following paragraphs we desribe the six ases and the fats that determine the struture of the orresponding probability tables. Case 1 (orner blok) The neighboring atomi blok in the West and the blok in the North do not belong to the quadtree blok that ontains the given orner blok, see the bloks marked by in figure 3. In this ase the quadtree partition does not lead to a simplifiation of the probability table. Thus, for orner bloks the same ontext model is used as in usual REM oding (subsetion 2.2). Case 2 (interior blok) The neighboring atomi bloks in the West and in the North both belong to the quadtree blok that ontains the given interior blok, see the bloks marked by i in figure 3. For suh an interior blok it is lear that neither the Northern nor the Western edge is a region edge. Thus, the symbol for any interior atomi blok in a QBREM must be equal to 0. Formally, we may set the probability for symbol 0 equal to 1 for all of the 256 ontexts, while all other probabilities are zero. Enoding the symbol 0 for an interior blok does not require any rate. Case 3 (horizontal boundary blok) The neighboring atomi blok in the West belongs to the quadtree blok that ontains the given horizontal boundary blok, while the neighboring atomi blok in the North does not, see the bloks marked by h t and h n in figure 3. In this ase we further differentiate between a trivial and a nontrivial subase. Case 3a (trivial horizontal boundary blok) The neighboring atomi bloks in the North and in the North- West both belong to the same quadtree blok, see the bloks marked by h t in figure 3. This ase is trivial beause the symbol for the atomi blok is already determined by that of the preeding blok in the West. The atomi blok has a region edge at its Northern edge if and only if the same holds for the neighboring blok in the West. In terms of the probability table, it an be seen that the probability for symbol X = 1 must be set to 1 if W = 1 or W = 3, and the probability for symbol X = 0 must be set to 1 if W = 0 or W = 2. As for interior bloks, these trivial horizontal boundary bloks do not require any rate for enoding. Case 3b (nontrivial horizontal boundary blok) The neighboring atomi bloks in the North and in the North-West belong to different quadtree bloks, see the blok marked by h n in figure 3. For these bloks 8
9 we an exploit only the fat that the neighbor in the West belongs to the same quadtree blok and, thus, the Western edge of a nontrivial horizontal boundary blok annot be a part of a region boundary. For the probability table this implies that in addition to the simplifiation due to the impossible ases listed in table 1 we have that the probabilities for the symbols X = 2 and X = 3 must both be zero for all ontext ases. For many of the ontexts this lead to trivial ases. For example, suppose W = 0 and N = 0. Then X = 1 and X = 2 are ruled out, see table 1. Sine also X = 3 annot our for nontrivial horizontal boundary bloks we onlude that only X = 0 is possible. Case 4 (vertial boundary blok) The neighboring atomi blok in the North belongs to the quadtree blok that ontains the given vertial boundary blok, while the neighboring atomi blok in the West does not, see the bloks marked by v n and v t in figure 3. Naturally, this ase is similar to that of a horizontal boundary blok disussed above. To omplete the list of ases we just state the trivial and the nontrivial subases below omitting the details whih are idential to ases 3a and 3b exept for an appropriate and straightforward adaptation. Case 4a (trivial vertial boundary blok) Case 4b (nontrivial vertial boundary blok) Consider the ase of nontrivial horizontal and vertial boundary bloks from ases 3b and 4b above. We may ask whih of the 256 ontexts for either ase leads to a nontrivial list of probabilities for the symbols X = 0, 1 (ase 3b) or X = 0, 2 (ase 4b). Taking into aount table 1 we dedue that the only ontexts in whih the symbol X is not already uniquely determined is given by W = 1 or W = 2 and N = 2 or N = 3. This holds for nontrivial horizontal as well as vertial boundary bloks. Together with NW, NE = 0, 1, 2, 3 we obtain 64 ontexts in whih X {0, 1} for horizontal boundary bloks and X {0, 2} for vertial boundary bloks. For simpliity and in order to avoid ontext dilution due to an insuffiient number of ourrenes of nontrivial boundary bloks we have joined the probability tables in our implementation for the horizontal and vertial ases, listing probabilities only for X = 0 and X 0. Speial ases should also be onsidered for bloks at the Western and Northern image border, whih is known to form region boundaries throughout. We omit these details. Alternatively, one may allow range bloks to wrap around image boundaries [16]. The proposed ontext modelling above yields larger probability tables than for the ase of region edge maps without quadtree struture. For small images or for oarse quadtree partitions smaller ontext models may be preferable in order to avoid the ontext dilution problem. Therefore we also onsider redued ontext models in whih some of the tables are merged. In a first step we may ignore the dependene on the symbol for the North East neighbor. Then we may drop the neighbors in the North West, North, and finally also the West. Table 2 shows how the number of non-redundant probabilities in the tables is redued aordingly. The resulting different ontext models are alled QBREM{num}, where num=0,...,4 is the number of neighboring bloks used Type neighbor bloks used in ontext probs. ase 1 probs. ase 3b/4b (QB)REM0 4 2 (QB)REM1 West 16 4 (QB)REM2 West, North 64 8 (QB)REM3 West, North West, North (QB)REM4 West, North West, North, North East Table 2: (QB)REM with different ontext models. The right olumns list the number of (nontrivial) probabilities that need to be maintained in the tables of the ontext model. 9
10 in the ontext model. In the same way we define REM{0,1,2,3,4} in whih ase only one table of probabilities is needed whose size is the same as that for ase 1 of QBREM. 3.4 Results for partition oding We used our fratal image oder to produe a sequene of quadtree-based image partitions with varying numbers of regions. Here we onsider only the performane of the enoding of the otrees alone and the partitions inluding the otrees. In figure 4 we show the rates (ost in bits) for QBREM{2,3,4} ompared to REM*. Here by REM* we mean that eah of REM{0,1,2,3,4} has been tried and the ontext template with the lowest osts was taken at eah point. In (a) the enoding of the quadtree alone is studied. For the omplete quadtree (with leaves) the osts vanish. Regarding the different proposed ontext models we observed that the sum ontext is least effiient, whereas the sum ontext and the redued ontext have a better and omparable performane. Thus, in all further experiments we use the redued ontext for enoding quadtrees. Figures (b-f) show the osts of the entire partition oding based on 4-32-quadtrees with various numbers of bloks. Generally the partition oding with quadtree-based region edge maps is superior to that using plain region edge maps whih in turn is better than hain oding given by [21]. The advantage of QBREM is espeially large when the partition is based on quadtrees with relatively few bloks. If the number of quadtree bloks is very large ompared to the number of regions formed by merging (see (b) and (e)), then oding the REMs is more eonomial than oding QBREMs. However, this drawbak an be eliminated by using the quadtree fitting proedure explained in subsetion 3.1, see (e). 4 FRACTAL IMAGE CODING In this setion we present implementation details of our fratal oding method. In partiular we explain the parameters that must be hosen in the method. 4.1 Domain Pool and Coeffiients As usual, [4], we onsider domain bloks that are twie as large as range bloks. In [30, 21] it has been shown, that domains with small ollage error may be found near the range blok. We make use of this observation by defining a square array of L 2 domains whih is entered over the orresponding range. Two neighboring domains are offset horizontally or vertially by a fixed step size d (figure 5). Domain bloks may wrap around image boundaries. The domain oordinates (x d, y d ) in (2.1) an be enoded by an integer index i d = 0,...,L 2 1 sine the deoder an reonstrut the domain pool from a given range blok. The transform parameters s, o are quantized with the method in [5], using representations of n s and n o bits, respetively. The quantized parameters and the domain address index i d are enoded using adaptive arithmeti oding [28]. 4.2 Quadtree Partitioning in the Splitting Phase The quadtree partition proeeds along algorithm 1. We restrit the blok sizes in the partition to a minimum and maximum size, qmin 2 and q2 max, respetively (see subsetion 3.2). The split riterion is given by a threshold T on the mean square ollage error E(r)/ r of a blok r orresponding to a node of the tree. The node is expanded and the blok is subdivided into four subbloks, if E(r)/ r > T. As in [31, 21], we use an adaptive threshold T, whih is multiplied by a fator k for bloks of the next deeper quadtree level. For the bloks of maximum size qmax 2, an initial threshold T = T 1 is used. 10
11 Costs [bits] sum ontext full ontext 4 ontext Quadtree Bloks (a) Costs [bits] quadtree bloks Regions (b) REM* QBREM4 QBREM3 QBREM2 Costs [bits] quadtree bloks REM* QBREM4 QBREM3 QBREM2 Costs [bits] quadtree bloks REM* QBREM4 QBREM3 QBREM Regions Regions () (d) Costs [bits] quadtree bloks Regions (e) REM* QBREM4 QBREM3 QBREM2 Costs [bits] quadtree bloks Regions (f) REM* QBREM4 QBREM3 QBREM2 Costs [bits] quadtree bloks REM* QBREM* fit QBREM* Costs [bits] quadtree bloks Chain Codes REM* QBREM* Regions Regions (g) (h) Figure 4: Coding performane for quadtree-based region edge maps (QBREM) ompared to plain region edge maps (REM) for partitions of the Lenna image based on split/merge using 4-32-quadtrees. (a) ompares the osts of different ontext models for quadtree oding. (b)-(f) ompare the performane of enoding QBREMs based on quadtrees of differing omplexities. (g) shows the benefits of additional quadtree fitting, and (h) ompares enoding methods for QBREMs and REMs with the hain oding method in [21]. 11
12 domain domain L domains d d domain L domains range domain area with L 2 domains Figure 5: The domain pool for a given range is formed by domains that are twie as large as the range. L 2 domains are arranged around the range blok with horizontal and vertial offsets of d pixels. 4.3 Region Growing in the Merging Phase After the splitting phase, the quadtree partition P onsists of a number of range bloks that depends on the image and on the parameters q 2 min, q2 max, T 1, and k. In the subsequent merging phase an iteration takes plae (algorithm 2). In eah iteration step neighboring pairs (r i, r j ) of bloks are managed in a priority list struture L P. From this list of andidate pairs an optimal pair (r i, r j ) is merged to form a new larger blok r i r j until the desired number of bloks, n R, is reahed. The pair that is atually merged is defined by minimizing the inrease in ollage error due to the merging, i.e., by the minimal value of E(r i, r j ) = E(r i r j ) E(r i ) E(r j ). After a merging step the number of range bloks in the partition P has dereased by 1. Then the list L P of pairs of adjaents bloks and their assoiated ollage error inreases, E, requires an update for the next iteration. Pairs involving r i or r j must be removed and new pairs with r i r j must be inserted. This proedure is omputationally omplex. Moreover, many ollage errors are omputed in vain, namely for those range blok pairs that will never be merged. To overome this problem, a lazy evaluation strategy was proposed in [16]. The update of the priority list is not performed. Instead in eah iteration the top pair (r i, r j ) on the list L P is proessed as follows. If it is still a valid pair, i.e., if both bloks r i and r j are still members of the urrent partition P, merging takes plae and the iteration step is omplete. If one of the two bloks, either r i or r j, is obsolete due to a previous merger, then the ollage error for the enlarged blok must be reomputed and the blok pair is moved to the orresponding position in the priority list. If both of the bloks, r i and r j, have already been merged in previous steps, a new ollage error needs to be omputed only when the larger bloks that r i and r j belong to are disjoint (and thus form a new legal andidate pair for a merger). This approah yields savings of more than 50% of the omputation time ompared to the omplete updating. The proedure delivers the same result as the one using omplete updating in eah iteration step if E(a b, ) E(b, ) holds for any given neighboring regions a, b and. Unfortunately, this ondition is not guaranteed. However, in pratie of fratal image oding disussed here only at very high ompression ratios there is a small loss of about 0.05 db in PSNR quality of the reonstruted image with respet to the merging method using a full update in eah iteration step. For details see [32]. 12
13 image parameters partition osts [bits] oeffiient ompression PSNR q min, q max T 1 n R total quadtree osts [bits] ratio [db] Lenna 4, , , Boat 4, , , Peppers 3, , , Barbara 3, , , Table 3: Coding results for images Lenna, Boat, Peppers and Barbara. k = 2, L = 256, d = 2, n s = 4, n o = Partition Coding For the enoding of the quadtree-based split/merge partition P we use our quadtree-based region edge maps as proposed in setion 3. We also try the different ontext models from table 2 and hoose the model that works best. 5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In this setion we present results for the proposed fratal image oder using quadtree-based region edge maps. For the experiments we hose the images Lenna, Boat, Peppers, and Barbara from the Waterloo BragZone [33]. We used the following settings for the parameters of the fratal oder introdued in the last setion. Minimum and maximum allowed blok size for the quadtree bloks ((q min, q max ), see subsetion 3.2). For eah bit rate the setting from (4, 32), (4, 64), (5, 40), (5, 80), (6, 24), (6, 48), (7, 28), (7, 56), (8, 32) that led to the lowest distortion was seleted. Threshold and threshold fator for quadtree segmentation (T 1, k, see subsetion 4.2). Experiments showed that a value of k = 2 leads to good results in most ases. However, the differenes in PSNR of the reonstruted images were very small ompared to other values for k. The best value for the threshold T 1 {0, 5,..., 100} was determined experimentally for eah bit rate. Number of rows/olumns of the domain arrays and step length (L, d, subsetion 4.1). Values of L = 256 and d = 2 spread the domains uniformly over the entire image and led to best rate-distortion performane. Number of bits for quantization of fratal parameters (n s and n o, subsetion 4.1). We set n s = 4 and n o = 6. These values led to best rate-distortion performane at ompression ratios larger than 30. Number of regions in the split/merge partition (n R, subsetion 4.3). The parameter varies and ontrols the bit rate and the distortion. 13
14 PSNR [db] PSNR [db] Lenna Compression ratio (a) Lenna QBREM REM quadtree only (rd optimized) Compression ratio () Costs [bits] PSNR [db] oeffiients REM QBREM Lenna Regions (b) Boat QBREM REM quadtree only (rd optimized) Compression ratio (d) PSNR [db] Peppers QBREM REM quadtree only (rd optimized) Compression ratio (e) PSNR [db] Barbara QBREM REM quadtree only (rd optimized) Compression ratio (f) Figure 6: (a) Comparison of different base blok sizes for region merging (Lenna); (b) osts for fratal oeffiients and domain addresses ompared to partition oding osts for REM and QBREM (Lenna); (-f) rate-distortion performane for four test images: quadtree-based split/merge approah versus merging of bloks from a uniform partition and fratal enoding with rate-distortion optimized quadtree (without blok merging). 14
15 Figure 6 summarizes the results of our experiments. In part (a) we show that the hoie of the minimal and maximal blok sizes in the quadtree partition that provides the base bloks for the merging phase is ruial for the rate-distortion performane of the fratal ode. Espeially for low ompression ratios (below 40) we observed that a small minimal blok size of 3 3 pixels provided muh better results than larger sizes. For high ompression ratios (above 80) larger bloks sizes gave better PSNR performane, however, only by a very small amount. Part (b) of figure 6 displays how muh of the bit rate was spent on the adaptive split/merge partition in omparison to the rest of the ode onsisting of domain addresses and oeffiients. It also demonstrates the advantage of our oding sheme exploiting the underlying quadtree struture opposed to enoding plain region edge maps. The differene was as large as about 2000 bits for medium ompression ratios. Parts (-f) of figure 6 shows omplete rate-distortion urves of our fratal oder with quadtree-based region edge maps, with plain region edge maps, and with a quadtree partition without subsequent blok merging. Eah of the plots is for one of the four test images. The plain quadtree oder is superior to that of Fisher [5]. We implemented a rate-distortion optimization that is guaranteed to selet the subtree of the omplete quadtree that yields minimum ollage error using optimization methods given in [34, 35]. Moreover, for the quadtree enoding we used arithmeti oding with ontext modelling as proposed in this paper. Our results indiate that fratal oders that use an adaptive split/merge image partition may outperform optimized fratal quadtree oders by about 0.5 to 1 db in PSNR. Using a quadtree as a base partition in the split/merge partitions provided gains of about 0.2 db in PSNR. Table 3 lists detailed numerial oding results obtained with the proposed method. In figures 7 and 8 we present reonstrutions of enoded Lenna and Peppers images at ompression ratios about 70. Parts (a) show the original image for referene, parts (b) show the reonstruted images (detailed parameters are given in the aptions). Parts () show images deoded from JPEG2000 enoded originals. For the JPEG2000 enodings we used the kakadu enoder [36]. Parts (d) and (e) show the inverted differene images between deoded and original images. The differene images were obtained from the absolute differenes between grey values of orresponding pixels, saled by a fator of 5 and lamped at 255. The rate distortion performane of our oder is omparable to that of the JPEG2000 oder with an advantage of JPEG2000 of about 0.3 to 0.5 db PSNR. The deoded images and the differene images, however, show muh more notieable differenes in terms of typial artifats. While the images obtained from JPEG2000 odes look defoussed espeially around edges, here the fratally deoded images learly have sharper edges. This impression is onfirmed by the differene images whih show broader edge artifats for the wavelet oded images of JPEG2000. On the other hand there are bloking artifats in smooth image regions of the fratally deoded images. We remark that there are postproessing tehniques that may improve the sharpness of the JPEG2000 reonstrutions [37] and redue the bloking artifats of fratally enoded images [38, 21]. Finally, in figure 9 we display quadtree partitions for two test images that provided the base bloks for the merging phase. The resulting adaptive split/merge partitions are also shown. The survey in [6] showed a omparison of the performane of published pure fratal oding methods that are working in the spatial domain ([6, figure 6]). This omparison inludes methods based on various types of adaptive image partitions, suh as quadtrees [5], HV-partitions [5], Delaunay-triangulations [11, 12], and irregular partitions [14, 15, 20]. The rate-distortion performane of our oder is learly superior to all of these. Fratal image oding with quadtree-based split/merge partitions was first proposed in [20, 21], where the hain oding method of [25] was adapted. Our reimplementation of the hain oder showed that our QBREM oding algorithm ompressed partitions with only half the rate, see figure 4h. 15
16 (a) (b) () (d) (e) Figure 7: Coding example for image Lenna with parameters q min = 6, q max =48, T 1 = 15, k = 2, L = 256, d = 2, n s = 4, n o = 6 and n R = 990. (a) Original image; (b) deoded image with proposed fratal oder, PSNR = db, ompression ratio = 70.29; () deoded image from enoding with JPEG2000 (kakadu enoder), PSNR = db, ompression ratio = 71.02; (d) differene between fratal reonstrution and original; (e) differene between JPEG2000 reonstrution and original. 16
17 (a) (b) () (d) (e) Figure 8: Coding example for Peppers with parameters q min = 4, q max = 32, T 1 = 40, k = 2, L = 256, d = 2, n s = 4, n o = 6 and n R = 990. (a) Original image; (b) deoded image with proposed fratal image oder, PSNR = db, ompression ratio = 70.30; (e) deoded image from enoding with JPEG2000 (kakadu enoder), PSNR = db, ompression ratio = 69.46; (d) differene between fratal reonstrution and original; (e) differene between JPEG2000 reonstrution and original. 17
18 (a) (b) () (d) Figure 9: Partitions for the enodings in figures 7 and 8. (a) Lenna image, quadtree partition with 1345 bloks before merging; (b) partition with 990 regions after merging quadtree bloks; () Peppers, quadtree partition with 1698 bloks before merging; (d) partition with 990 regions after merging quadtree bloks. 6 CONCLUSIONS We proposed a fratal image ompression method based on split/merge image partitions. In the splitting phase an image adaptive quadtree partition is generated. Neighboring bloks are iteratively merged using an appropriate error riterion. We provided an algorithm for lossless arithmeti ompression of the resulting image partition with suitable ontext modelling that exploits the struture of the underlying quadtree. Experimental results show that our method an save up to 30% of the total rate for the partition in omparison to enoding with region edge maps based on uniform base partitions. When applied to fratal image oding we obtained ratedistortion performanes that exeed the best known results for pure, non-hybrid fratal image oders. Compared to state of the art wavelet oders in industry, given by the JPEG2000 standard, our fratal ompression method is omparable in terms of rate-distortion performane up to less than 0.5 db PSNR. Subjetively, fratally reonstruted images have sharper edges and more ontrast than JPEG2000 reonstrutions but suffer from mild bloking artifats. Our oding method for quadtree-based region edge maps an also be used in onnetion with other image 18
19 oding systems that rely on adaptive partitions. For example, similar partitions have been used with dynami oding [39], or one may modify the segmentation-based image oding method in [40] to make use of quadtreebased split/merge partitions. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by grant Sa449/8-2 of the Deutshe Forshungsgemeinshaft. 19
20 REFERENCES [1] M. F. Barnsley, A. D. Sloan, Chaoti ompression, Computer Graphis World, [2] M. F. Barnsley, A. D. Sloan, A better way to ompress images, Byte, 1988, pp [3] A. E. Jaquin, A fratal theory of iterated markov operators with appliation to digital image oding, Ph.D. Dissertation, Georgia Institute of Tehnology, [4] A. E. Jaquin, Image oding based on fratal theory of iterated ontrative image transformations, IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 1(1) (1992), pp [5] Y. Fisher, Fratal Image Compression Theory and Appliation, Springer Verlag, New York, [6] B. Wohlberg, G. de Jager, A review of the fratal image oding literature, IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 8(12) (1999), pp [7] D. Saupe, R. Hamzaoui, A. Zerbst, The Paper Colletion on Fratal Image Compression, [8] Y. Fisher, S. Menlove, Fratal enoding with HV partitions, in Fratal Image Compression Theory and Appliation, pp Springer-Verlag, [9] D. Saupe, M. Ruhl, R. Hamzaoui, L. Grandi, D. Marini, Optimal hierarhial partitions for fratal image ompression, Proeedings IEEE International Conferene on Image Proessing, [10] E. Reusens, Partitioning omplexity issue for iterated funtion systems based image oding, Proeedings VIIth European Signal Proessing Conferene, I (1994), pp [11] F. Davoine, J.-M. Chassery, Adaptive Delaunay triangulation for attrator image oding, Proeedings 12th International Conferene on Pattern Reognition, 1994, pp [12] F. Davoine, J. Svensson J.-M. Chassery, A mixed triangular and quadrilateral partition for fratal image oding, Proeedings IEEE International Conferene on Image Proessing, [13] R. C. Gonzales, R. E. Woods, Digital Image Proessing, Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massahusetts, [14] L. Thomas, F. Deravi, Region-based fratal image ompression using heuristi searh, IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 4(6) (1995), pp [15] M. Ruhl, H. Hartenstein, D. Saupe, Adaptive partitionings for fratal image ompression, Proeedings IEEE International Conferene on Image Proessing, [16] H. Hartenstein, M. Ruhl, D. Saupe, Region-based fratal image ompression, IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 9(7) (2000), pp [17] H. Freeman, On the enoding of arbitrary geometri onfigurations, IRE Transations on Eletroni Computers, EC-10 (1961), pp [18] S. R. Tate, Lossless ompression of region edge maps, Tehnial Report DUKE TR , Duke University, Durham, [19] S. L. Horowitz, T. Pavlidis, Piture segmentation by a tree traversal, Journal of the ACM, 23 (2) (1976), pp [20] Y. C. Chang, B. K. Shyu, J. S. Wang, Region-based fratal image ompression with quadtree segmentation, Proeedings IEEE International Conferene on Aoustis, Speeh and Signal Proessing, 4 (1997), pp [21] Y. C. Chang, B. K. Shyu, J. S. Wang, Region-based fratal ompression for still image, Proeedings 8-th Internations Conferene in Central Europe on Computer Graphis, Visualization and Interative Digital Media, [22] M. Barnsley, Fratals Everywhere, Aademi Press, San Diego, [23] M. Barnsley, L. Hurd, Fratal Image Compression, AK Peters Ltd, [24] M. Eden, M. Koher, On the performane of a ontour oding algorithm in the ontext of image oding. Part I: ontour segment oding, Proeedings IEEE Internations Conferene on Aoustis, Speeh and Signal Proessing, 8 (1985), pp [25] T. Ebrahimi, A new tehnique for motion field segmentation and oding for very low bitrate video oding appliations, Proeedings IEEE International Conferene on Image Proessing, 2 (1994), pp [26] D. Saupe, M. Ruhl, Evolutionary fratal image ompression, Proeedings IEEE International Conferene on Image Proessing, [27] G. G. Langdon, J., Rissanen, Compression of blak-white images with arithmeti oding, IEEE Transations on Communiations, 29(6) (1981), pp
21 [28] I. H. Witten, R. M. Neal, J. G. Cleary, Arithmeti oding for data ompression, Communiations of the ACM, 30(6) (1987), pp [29] H. Samet, The quadtree and related hierarhial data struture, ACM Computing Surveys, 16(2) (1984), pp [30] K. U. Barthel, T. Voyé, P. Woll, Improved Fratal Image Coding, Proeedings International Piture Coding Symposium, [31] E. Shusterman, M. Feder, Image ompression via improved quadtree deomposition algorithms, IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 3(2) (1994), pp [32] T. Ohotta, Regionenbasierte Partitionierung bei fraktaler Bildkompression mit Quadtrees, Diplomarbeit, Institut für Informatik, Universität Leipzig, Germany, [33] J. Kominek, Waterloo BragZone, University of Waterloo, Canada, [34] G. Sullivan, R. Baker, Effiient quadtree oding of images and video, IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 3(3) (1994), pp [35] R. Hamzaoui, D. Saupe, Combining fratal image ompression and vetor quantization, IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 9(2) (2000), pp [36] D. Taubman, The sporty new JPEG model, SPIE s oemagazine, 2002, pp kakadu software [37] G. Fan, W. K. Cham, Post-proessing of low bit-rate wavelet-based image oding using multisale edge haraterization, IEEE Transations on Ciruits and Systems for Video Tehnology, 11(12) (2001), pp [38] K. G. Nguyen, D. Saupe, Adaptive postproessing for fratal image ompression, Proeedings IEEE International Conferene on Image Proessing, [39] E. Reusens, T. Ebrahimi, C. Le Buhan, R. Castagno, V. Vaerman, L. Piron, C. de Solà Fàbregas, S. Bhattaharjee, F. Bossen, M. Kunt, Dynami approah to visual data ompression, IEEE Transations on Ciruits and Systems for Video Tehnology, 7(1) (1997), pp [40] X. Wu, Image oding by adaptive tree-strutured segmentation, IEEE Transations on Information Theory, 38(6) (1992), pp
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
5.2 The Master Theorem
 170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
A Context-Aware Preference Database System
 J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I
 DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Pre-Experience Postgraduate Programmes Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
Improved Vehicle Classification in Long Traffic Video by Cooperating Tracker and Classifier Modules
 Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
3 Game Theory: Basic Concepts
 3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Asymmetric Error Correction and Flash-Memory Rewriting using Polar Codes
 1 Asymmetri Error Corretion and Flash-Memory Rewriting using Polar Codes Eyal En Gad, Yue Li, Joerg Kliewer, Mihael Langberg, Anxiao (Andrew) Jiang and Jehoshua Bruk Abstrat We propose effiient oding shemes
1 Asymmetri Error Corretion and Flash-Memory Rewriting using Polar Codes Eyal En Gad, Yue Li, Joerg Kliewer, Mihael Langberg, Anxiao (Andrew) Jiang and Jehoshua Bruk Abstrat We propose effiient oding shemes
Robust Classification and Tracking of Vehicles in Traffic Video Streams
 Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Pattern Recognition Techniques in Microarray Data Analysis
 Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA faramarz@sienes.sdsu.edu
Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA faramarz@sienes.sdsu.edu
Region-Based Fractal Image Compression
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 9, NO. 7, JULY 2000 1171 Region-Based Fractal Image Compression Hannes Hartenstein, Associate Member, IEEE, Matthias Ruhl, and Dietmar Saupe Abstract A fractal
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 9, NO. 7, JULY 2000 1171 Region-Based Fractal Image Compression Hannes Hartenstein, Associate Member, IEEE, Matthias Ruhl, and Dietmar Saupe Abstract A fractal
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objective Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms
 Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
cos t sin t sin t cos t
 Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
Isaac Newton. Translated into English by
 THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
In this chapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use directed graphs.
 Chapter 19 State Diagrams In this hapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use direted graphs. 19.1 Introdution State diagrams are a type of direted graph, in whih the graph nodes
Chapter 19 State Diagrams In this hapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use direted graphs. 19.1 Introdution State diagrams are a type of direted graph, in whih the graph nodes
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
Procurement auctions are sometimes plagued with a chosen supplier s failing to accomplish a project successfully.
 Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES
 The 9 th International Days of Statistis and Eonomis, Prague, September 10-1, 015 NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES Zdeněk Šul Hana Řezanková
The 9 th International Days of Statistis and Eonomis, Prague, September 10-1, 015 NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES Zdeněk Šul Hana Řezanková
i_~f e 1 then e 2 else e 3
 A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
Deduplication with Block-Level Content-Aware Chunking for Solid State Drives (SSDs)
 23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
USA Mathematical Talent Search. PROBLEMS / SOLUTIONS / COMMENTS Round 3 - Year 12 - Academic Year 2000-2001
 USA Mathematial Talent Searh PROBLEMS / SOLUTIONS / COMMENTS Round 3 - Year - Aademi Year 000-00 Gene A. Berg, Editor /3/. Find the smallest positive integer with the property that it has divisors ending
USA Mathematial Talent Searh PROBLEMS / SOLUTIONS / COMMENTS Round 3 - Year - Aademi Year 000-00 Gene A. Berg, Editor /3/. Find the smallest positive integer with the property that it has divisors ending
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Recommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model
 WWW 2008 / Refereed Trak: Data Mining - Learning April 2-25, 2008 Beijing, China Reommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model Yunbo Cao,2, Huizhong Duan, Chin-Yew Lin 2, Yong Yu, and Hsiao-Wuen
WWW 2008 / Refereed Trak: Data Mining - Learning April 2-25, 2008 Beijing, China Reommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model Yunbo Cao,2, Huizhong Duan, Chin-Yew Lin 2, Yong Yu, and Hsiao-Wuen
Programming Basics - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physics.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
Scalable Hierarchical Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising
 Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google amra@google.om Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh abhidas@mirosoft.om Alexander J. Smola
Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google amra@google.om Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh abhidas@mirosoft.om Alexander J. Smola
Discovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks
 Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Chapter 1: Introduction
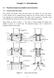 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
SLA-based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments
 2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Optimal Sales Force Compensation
 Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Optimal Online Buffer Scheduling for Block Devices *
 Optimal Online Buffer Sheduling for Blok Devies * ABSTRACT Anna Adamaszek Department of Computer Siene and Centre for Disrete Mathematis and its Appliations (DIMAP) University of Warwik, Coventry, UK A.M.Adamaszek@warwik.a.uk
Optimal Online Buffer Sheduling for Blok Devies * ABSTRACT Anna Adamaszek Department of Computer Siene and Centre for Disrete Mathematis and its Appliations (DIMAP) University of Warwik, Coventry, UK A.M.Adamaszek@warwik.a.uk
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
CIS570 Lecture 4 Introduction to Data-flow Analysis 3
 Introdution to Data-flow Analysis Last Time Control flow analysis BT disussion Today Introdue iterative data-flow analysis Liveness analysis Introdue other useful onepts CIS570 Leture 4 Introdution to
Introdution to Data-flow Analysis Last Time Control flow analysis BT disussion Today Introdue iterative data-flow analysis Liveness analysis Introdue other useful onepts CIS570 Leture 4 Introdution to
10Gbps Transmission over Standard Category-5 Copper Cable
 0Gbps Transmission oer Standard Category-5 Copper Cable Dr. Mohsen Kaehrad, Dr. John F. Doherty, Jun-Ho Jeong, Arnab Roy, Gaura Malhotra The Pennsylania State Uniersity Center for Information and Communiations
0Gbps Transmission oer Standard Category-5 Copper Cable Dr. Mohsen Kaehrad, Dr. John F. Doherty, Jun-Ho Jeong, Arnab Roy, Gaura Malhotra The Pennsylania State Uniersity Center for Information and Communiations
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
A Game Theoretical Approach to Gateway Selections in Multi-domain Wireless Networks
 1 A Game Theoretial Approah to Gateway Seletions in Multi-domain Wireless Networks Yang Song, Starsky H.Y. Wong and Kang-Won Lee IBM Researh, Hawthorne, NY Email: {yangsong, hwong, kangwon}@us.ibm.om Abstrat
1 A Game Theoretial Approah to Gateway Seletions in Multi-domain Wireless Networks Yang Song, Starsky H.Y. Wong and Kang-Won Lee IBM Researh, Hawthorne, NY Email: {yangsong, hwong, kangwon}@us.ibm.om Abstrat
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
GABOR AND WEBER LOCAL DESCRIPTORS PERFORMANCE IN MULTISPECTRAL EARTH OBSERVATION IMAGE DATA ANALYSIS
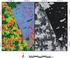 HENRI COANDA AIR FORCE ACADEMY ROMANIA INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE of SCIENTIFIC PAPER AFASES 015 Brasov, 8-30 May 015 GENERAL M.R. STEFANIK ARMED FORCES ACADEMY SLOVAK REPUBLIC GABOR AND WEBER LOCAL DESCRIPTORS
HENRI COANDA AIR FORCE ACADEMY ROMANIA INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE of SCIENTIFIC PAPER AFASES 015 Brasov, 8-30 May 015 GENERAL M.R. STEFANIK ARMED FORCES ACADEMY SLOVAK REPUBLIC GABOR AND WEBER LOCAL DESCRIPTORS
Nodal domains on graphs - How to count them and why?
 Proeedings of Symposia in Pure Mathematis Nodal domains on graphs - How to ount them and why? Ram Band, Idan Oren and Uzy Smilansky, Abstrat. The purpose of the present manusript is to ollet known results
Proeedings of Symposia in Pure Mathematis Nodal domains on graphs - How to ount them and why? Ram Band, Idan Oren and Uzy Smilansky, Abstrat. The purpose of the present manusript is to ollet known results
Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image
 Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Software Ecosystems: From Software Product Management to Software Platform Management
 Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
Design Implications for Enterprise Storage Systems via Multi-Dimensional Trace Analysis
 Design Impliations for Enterprise Storage Systems via Multi-Dimensional Trae Analysis Yanpei Chen, Kiran Srinivasan, Garth Goodson, Randy Katz University of California, Berkeley, NetApp In. {yhen2, randy}@ees.berkeley.edu,
Design Impliations for Enterprise Storage Systems via Multi-Dimensional Trae Analysis Yanpei Chen, Kiran Srinivasan, Garth Goodson, Randy Katz University of California, Berkeley, NetApp In. {yhen2, randy}@ees.berkeley.edu,
Parametric model of IP-networks in the form of colored Petri net
 Parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net Shmeleva T.R. Abstrat A parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net was developed; it onsists of a fixed number of Petri
Parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net Shmeleva T.R. Abstrat A parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net was developed; it onsists of a fixed number of Petri
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
The Advantages of Using Aountable Care Organizations ( ACOs)
 JLEO, V3 S i77 Struturing Inentives within Aountable Care Organizations Brigham Frandsen Brigham Young University James B. Rebitzer* Boston University Shool of Management and ational Bureau of Eonomi Researh
JLEO, V3 S i77 Struturing Inentives within Aountable Care Organizations Brigham Frandsen Brigham Young University James B. Rebitzer* Boston University Shool of Management and ational Bureau of Eonomi Researh
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
OpenScape 4000 CSTA V7 Connectivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1. Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76D1
 OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
A Comparison of Default and Reduced Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T
 9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
Implementation of PIC Based LED Displays
 International Journal of Eletronis and Computer Siene Engineering Available Online at www.ijese.org ISSN- - Implementation of PIC Based LED Displays Htet Htet Thit San, Chaw Myat Nwe and Hla Myo Tun Department
International Journal of Eletronis and Computer Siene Engineering Available Online at www.ijese.org ISSN- - Implementation of PIC Based LED Displays Htet Htet Thit San, Chaw Myat Nwe and Hla Myo Tun Department
Draft Notes ME 608 Numerical Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer
 Draft Notes ME 608 Numerial Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer Instrutor: Jayathi Y. Murthy Shool of Mehanial Engineering Purdue University Spring 2002 1998 J.Y. Murthy and S.R. Mathur. All Rights
Draft Notes ME 608 Numerial Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer Instrutor: Jayathi Y. Murthy Shool of Mehanial Engineering Purdue University Spring 2002 1998 J.Y. Murthy and S.R. Mathur. All Rights
