WHAT S WRONG WITH MY LIVER? HEMANGIOMA
|
|
|
- Brian Baldwin
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY LIVER? HEMANGIOMA
2 This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about hepatic hemangioma in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient & his or her family with useful information on this particular liver problem, the procedures and tests you may need to undergo, treatment approaches, risks involved, duration, expenses and helpful advice on coping successfully with the problem. If you require more information, Dr. D.R.Kulkarni or your doctor will be able to provide more information.
3 WHAT IS LIVER? The human liver is a reddish brown organ normally weighing approximately 1.5% of body weight. It is the largest internal organ. It is located in the right upper part of the abdominal cavity, resting just below the diaphragm under the protection of rib cage. Liver is broadly divided into a large right and a relatively small left lobe. Additionally there is a small lobe called caudate lobe. The right and left lobes are further subdivided into segments. These subdivisions help in planning liver surgery when a patient
4 needs removal of a portion of liver. Apart from a patch where it connects to the diaphragm the liver is covered entirely by peritoneum, a thin, double-layered membrane that reduces friction against other organs. The peritoneum folds back on itself to form the falciform ligament and the right and left triangular ligaments. These "ligaments" are in no way related to the true anatomic ligaments in joints, and have essentially no functional
5 importance. An exception to this is the falciform ligament, which attaches the liver to the anterior body wall from within. Liver is supplied by two large blood vessels, one called the hepatic artery and one called the portal vein. The hepatic artery carries blood from the aorta, whereas the portal vein carries blood containing digested nutrients from the entire gastrointestinal tract and also from the spleen and pancreas. The hepatic portal vein supplies approximately 75% of the liver's blood supply, the hepatic artery accounting for the remainder of its blood flow. Oxygen is provided from both sources. Before entering the liver the portal vein and hepatic artery divide into right and left branch for each of the lobes. They further subdivide within the liver tissue to supply each segment in total 9 in number. Blood flows through channels called sinusoids and empties into the central vein of each lobule. (Each lobule is made up of millions
6 of hepatic cells, which are the basic metabolic cells.). The central veins coalesce into hepatic veins, which leave the liver. There are 3 main hepatic veins that drain blood from liver into a large vein (inferior vena cava), which carries blood from lower portion of body to heart. Apart from the 3 main Hepatic Veins there are many smaller draining veins, which enlarge if any or all of the 3 veins are blocked due to diseases like cirrhosis or hepatic vein thrombosis or venoocclusive disorders. The caudate lobe is a separate structure, which receives blood flow from both the right- and leftsided vascular branches and then drains through small veins directly into the vena cava. The bile produced in the liver is collected in bile canaliculi, which merge to form bile ducts. Bile ducts are tube like structures carrying bile produced within liver to the intestine. Within the liver, these ducts are called intrahepatic (within
7 the liver) bile ducts, and once they exit the liver they are considered extrahepatic (outside the liver). The intrahepatic ducts eventually drain into the right and left hepatic ducts, which merge to form the common hepatic duct. The term biliary tree is derived from the arboreal branches of the bile ducts. The cystic duct draining the gallbladder joins with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct. Bile can either drain directly into the duodenum via the common bile duct, or be temporarily stored in the gallbladder via the cystic duct. The common bile duct and the pancreatic duct enter the second part of the duodenum together at the ampulla of Vater. The liver has a "capsule" around it, which contains nerve endings, accounting for pain when the liver enlarges and stretches its capsule. The damaged liver has an amazing ability to regenerate itself. The body needs only about 20% of the liver to live, and if a piece is cut out
8 or injured, it can grow back. Sometimes, however, the liver gets chronic diseases, which impair its ability to regenerate. It can become infiltrated with fat ("steatosis"), shrink from chronic alcohol or viral exposure ("cirrhosis") or grow large from infection or a blocked blood drainage ("hepatomegly"). Any inflammation of the liver, whether caused by germs, drugs, or radiation, is called hepatitis. A damaged liver may heal, or may slowly fail and require liver transplant to save the patient's life. WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF LIVER? The liver is an astounding laboratory sustaining metabolism. Liver's main job is to filter the blood coming from the digestive tract, before passing it to the rest of the body. The liver detoxifies chemicals and metabolizes drugs. As it does so, the liver also secretes bile that ends up back in the intestines. Bile contains bile salts, which are responsible for digestion and absorption of food material. The liver is responsible for
9 carbohydrate, fats & protein metabolism and also makes albumin, proteins important for blood clotting and other functions. It also produces various clotting factors, stores glucose, fats, vitamins like A, D3, B12 & minerals like iron & copper. This myriad of functions makes clear why the liver is essential to life. WHAT ARE THE TESTS TO CHECK LIVER FUNCTION? The diagnosis of liver function is made by blood tests. Liver function tests can readily pinpoint the extent of liver damage. Usually in liver diseases patient can have a combination of raised bilirubin, increase in liver enzymes, and drop in blood albumin levels, alteration in clotting test results, depending on the type of liver disease. If liver function is altered then other tests are asked depending on clinical picture and lab results. If hepatitis is suspected, then tests to detect cause of hepatitis are done. Sometimes,
10 one may require an ultrasound or a CT scan or MRI to produce images of the liver and diagnose liver tumors, abscess, and other pathologies. Physical examination of the liver is not accurate in determining the extent of liver damage. It can only reveal presence of tenderness or the size of liver, but in most cases, some type of radiological study is required to examine it. In patients with chronic liver disease noninvasive tests like Phytate liver scan (nuclear scan) and Ultrasound elastography of liver (Fibroscan) are done to assess the liver status. However, the ideal way to determine damage to the liver is with a biopsy. A biopsy is not required in all cases, but may be necessary when the cause or extent of damage is unknown. A needle is inserted into the skin just below the rib cage and a biopsy is obtained. The tissue is sent to the laboratory, where it is analyzed under a microscope. Sometimes, a radiologist may assist the physician performing a liver biopsy by
11 providing ultrasound guidance. LLLLLL WHAT IS HEMANGIOMA? A hemangioma is a noncancerous tumor made of widened (dilated) blood vessels that are atypical or irregular in arrangement and size. These vascular spaces may contain thrombin, calcifications, or prominent scarring (sclerosed hemangioma). Phleboliths are rare. Grossly, these lesions often appear as having a flat surface or as bulging subcapsular lesions. Lesions are reddishblue and well demarcated from surrounding tissue. Large tumors may become pedunculated. HOW COMMON IS LIVER HEMANGIOMA? Hemangioma is the most common benign tumor affecting the liver. The widespread use of noninvasive abdominal imaging modalities has led to increased detection of it even when it is asymptomatic. WHAT IS A GIANT HEMANGIOMA?
12 Giant hemangiomas are large hemangiomas and the size definition actually varies in the books but commonly anything more than 5cms is considered giant hemngioma. WHAT CAUSES A HEMANGIOMA IN LIVER? It's not clear what causes a liver hemangioma to form. It is probably congenital meaning that you're born with it. It is certainly not familial or genetically inherited. Some associations are observed regarding occurrence and growth of a hemangioma like age, sex, hormonal influence, drugs etcetera. Women, especially with a history of multiparity, are affected more often than men. Women who have been pregnant are more likely to be diagnosed with a liver hemangioma than women who have never been pregnant. Women who used hormone replacement therapy for menopausal symptoms may be more likely to be diagnosed with liver hemangioma than women who did not.
13 Several pharmacologic agents have been postulated to promote its growth. Steroid therapy, estrogen therapy, and pregnancy can increase the size of an already existing hemangioma. Hepatic hemangiomas can occur at all ages. Most hepatic hemangiomas are diagnosed in individuals aged years. Female patients often present at a younger age and with larger tumors. Hepatic hemangiomas may be seen in infancy. They have also been detected prenatally in a growing fetus. Babies may develop a type of hepatic hemangioma called benign infantile hemangioendothelioma. This rare, noncancerous tumor has been linked to high rates of heart failure and death in infants. Infants are usually diagnosed by the time they are 6 months old. Hepatic hemangiomas may be seen in 5-10% of children aged 1 year. They typically regress during childhood.
14 WHY IS IT NECESSARY TO INVESTIGATE A PATIENT WITH HEMANGIOMA OF LIVER? Hemangiomas can be mistaken for hypervascular malignancies of the liver or vice versa and can coexist with (and occasionally mimic) other benign and malignant hepatic lesions, including focal nodular hyperplasia, hepatic adenoma, hepatic cysts, hemangioendothelioma, hepatic metastasis, and primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Additionally liver hemangioma could be one feature of a larger disease complex or a welldefined clinical syndrome. In Klippel-Trenaunay- Weber syndrome, hepatic hemangiomas occur in association with congenital hemiatrophy and nevus flammeus, with or without hemimeganencephaly. In Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, giant hepatic hemangiomas are associated with thrombocytopenia and intravascular coagulation. Osler-Rendu-Weber disease is characterized by numerous small
15 hemangiomas of the face, nares, lips, tongue, oral mucosa, gastrointestinal tract, and liver. Von Hippel-Lindau disease is marked by cerebellar and retinal angiomas, with lesions also in the liver and pancreas. Multiple hepatic hemangiomas have been reported in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS? Hemangiomas of the liver are usually small and hence asymptomatic. However, even large hemangiomas remain asymptomatic most often. Most cases of liver hemangioma are discovered during a test or procedure for some other condition. Most people who have a liver hemangioma never experience symptoms, never show signs and most hemangiomas don t grow even over long periods or have complications and hence may never need treatment. But in a small number of people, liver
16 hemangioma will grow, may cause symptoms or complications and require treatment. It's not clear why this happens. Larger, especially more than 10cms and multiple lesions may produce symptoms. Dull pain, vague discomfort, which cannot be explained in words or fullness in the right upper abdomen, is the most common complaint especially when it is located in the right lobe of liver. Hepatic hemangiomas are more common in the right lobe of the liver than in the left lobe. Early satiety (feeling full after eating even small amount of food), nausea, and vomiting may occur when large lesions compress the stomach, producing obstruction. This is more common with lesions located in the left side or those hanging form liver like bunch of grapes. Rarely, hemangiomas may present as a large abdominal mass. Other atypical presentations
17 include jaundice from compression of the bile ducts, gastrointestinal bleeding, fever of unknown origin or cardiac failure. In some cases, acute abdominal pain occurs due to various complications like clot formation inside the hemangioma (called thrombosis), hemorrhage into the lesion or free intraabdominal cavity, twisting or torsion if there is a stalk for hanging hemangioma or compression of adjacent tissues or organs. Consumption of coagulation factors causes an illness that resembles a systematic inflammatory process with findings of fever, weight loss, anemia, thrombocytosis, increased fibrinogen level, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Babies with benign infantile hemangioendothelioma may have a growth in the abdomen, failure to survive or grow, anemia, and heart failure
18 The only findings upon physical examination are, infrequently, an enlarged liver, a palpable abdominal mass or the presence of an arterial bruit over the right upper quadrant. CAN IT CAUSE CANCER? It may be unsettling to know you have a mass in your liver, even if it's a benign mass. However, there's no evidence that an untreated liver hemangioma can lead to liver cancer. Problem comes when one cannot differentiate between a hemangioma from a cancer. It is usually solitary, but 10% patients can have multiple hemangiomas in their liver. WILL THERE BE COMPLICATIONS IF LEFT UNTREATED? Complications are rare with hemangiomas even when they are large in size. They include rupture with resultant hemoperitoneum, intratumoral
19 bleeding, compression of bile ducts and nearby arteries and veins, gastric compression, bleeding inside the bile ducts & heart failure. Complications depend on the size and location of the tumor. Women who have been diagnosed with liver hemangioma face a risk of complications if they become pregnant. The female hormone estrogen, which increases during pregnancy, is believed to cause some liver hemangiomas to grow larger. A growing hemangioma can cause signs and symptoms and may require treatment. Having a liver hemangioma doesn't mean you can't become pregnant. However, discussing the possible complications with your doctor can help you make a more informed choice. Medications that affect hormone levels in your body, such as birth control pills, could cause complications if you have been diagnosed with liver hemangioma. But this is controversial. If
20 you're considering this type of medication, discuss the benefits and risks with your doctor. HOW IS A PATIENT WITH HEMANGIOMA OF LIVER INVESTIGATED? Most patients with liver hemangioma come with the diagnosis on a routine ultrasonography as said before & rarely other form of imaging like CT or MRI. Rarely a diagnosis is made before investiagations because the tumor is large. The modalities used to aid in the diagnosis of hepatic hemangiomas include ultrasonography, dynamic contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scanning, nuclear medicine studies using technetium-99m ( 99m Tc) labeled RBCs, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), hepatic arteriography, and digital subtraction angiography. Ultrasonography is the most commonly used initial diagnostic tool. Serial ultrasonographic examinations are done to monitor any increase in
21 size of the hemangioma over time. Microbubble contrast -enhanced ultrasonography helps in differentiating from a hepatocellular cancer. However, difficulty occurs in large lesions where central thrombosis or scarring may be present. Unfortunately, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography is available at relatively few medical centers. The finding on ultrasonography of a suspected hemangioma should be diagnostically correlated with CT scan or MRI to ensure a correct diagnosis. Dynamic contrast-enhanced CT scanning is preferred to routine CT scanning. When requesting a CT scan to investigate a liver mass, the hepatobiliary specialist insists on nonenhanced, arterial, portal venous, and delayed imaging (the so-called triple phase CT with delayed imaging). First, the liver is imaged by CT before the
22 administration of intravenous contrast. The next series of images is obtained about 30 seconds after the injection of contrast, at the time that contrast is entering the liver via the hepatic artery. Portal venous imaging occurs 60 seconds later, as contrast is returning to the liver from the mesenteric veins via the portal vein. Finally, delayed images are obtained several minutes later. If you have already done a CT scan but it is suboptimal & improperly done it is advisable to repeat it properly or do an MRI with proper technique MRI is highly sensitive and specific in the diagnosis of & differentiating liver tumors especially hepatic hemangioma. When gadolinium is used as an intravenous contrast agent, hemangiomas enhance in a fashion similar to that seen on dynamic CT. The sensitivity for detection of hepatic hemangioma is upwards of 90%. Therefore often patient has to go through these 3 forms of imaging sequentially. In spite of
23 all this diagnosis may still be unsure especially since it is matter of differentiating a benign lesion from a malignant tumor. Scintigraphic studies using Tc-99m pertechnetate-labeled red blood cells were used for many years to help in diagnosing hepatic hemangiomas. Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) using Tc- 99m pertechnetate-labeled RBCs is more accurate. However, it is not available at all medical centers and with availability of CT & MRI these are now used very infrequently. WILL I REQUIRE AN ANGIOGRAPHY? The diagnostic accuracy of noninvasive tests has obviated the need for hepatic arteriography also in most cases. However, this invasive modality still may be useful in helping to diagnose some hepatic hemangiomas. IS IT POSSIBLE TO DIAGNOSE A SMALL HEMANGIOMA CONVINCINGLY?
24 Diagnostic accuracy diminishes for all imaging modalities when assessing a liver lesion that is less than 2 cm in diameter. MRI is the most accurate radiologic study to establish the diagnosis of a small hepatic tumor. MRI used to confirm the diagnosis when a probable hemangioma is detected on ultrasonography. Nuclear medicine studies will be used when nature of a lesion when the diagnosis is equivocal on CT or MRI. WILL I REQUIRE A BIOPSY? Percutaneous biopsy is frequently used for liver tumors whose pathology cannot be established on CT scan or MRI. But biopsy of a suspected hepatic hemangioma carries an increased risk of hemorrhage. Liver biopsy is not done in most circumstances where a hemangioma is high in the differential diagnosis of a hepatic mass. Liver biopsy is only used when radiologic study results and alpha-fetoprotein testing are equivocal.
25 WILL THERE BE MORE TESTS? Tumor markers like Alpha-FetoProtein (AFP), CA 19-9, and CarcinoEmbryonicAntigen (CEA) are done and normal levels bolster clinical suspicion of a benign hepatic mass. Blood investigations like CBC or LFT are not done routinely as they do not contribute to diagnosis and are required only if a surgery is planned. DO ALL LIVER HEMANGIOMAS REQUIRE TREATMENT? Most hepatic hemangiomas are small and asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis, and they are likely to remain that way. In addition, malignant transformation has not been reported in hepatic hemangiomas. Even large hemangiomas have very little risk of complications. For these reasons, most asymptomatic hepatic hemangiomas are left safely alone. HOW IS THE PATIENT FOLLOWED UP?
26 Once the diagnosis of hepatic hemangioma is confirmed by radiologic studies, there will not be any further follow up if it is a small hemangioma. If there is any doubt about diagnosis you will be asked to follow up after I month again to repeat the investigations. For larger hemangioma you will be advised to undergo ultrasonography at 6 months and at 12 months after the initial diagnosis. Providing that no change in hemangioma size has occurred, long-term follow-up radiologic studies are probably not necessary. However if you continue to do USG every 6 months and follow up with your surgeon it is always better. Certainly, patients with a new onset of abdominal pain deserve a follow-up imaging study. The same is true for patients who are undergoing treatment with estrogens or have become pregnant. Finally, patients with large hemangiomas (i.e., >10 cm) may deserve long-
27 term follow-up radiologic studies, perhaps annually, because of their probable increased risk of complications however it is not mandatory. IS THERE ANY NONSURGICAL THERAPY AVAILABLE? Until recently, no medical therapy capable of convincingly & permanently reducing the size of hepatic hemangiomas has been described. Modalities like radiation or drugs like thalidomide are used occasionally with unconvincing effect. WHEN DOES A PATIENT WITH LIVER HEMANGIOMA WARRANT SURGERY? Hepatic hemangiomas warrant therapy only if they are causing significant symptoms and the cause of pain is proved to be hemangioma beyond doubt. Therefore all tests must be performed to rule out other causes for pain like peptic ulcer disease, colitis, gastroduodenitis, gallstones & irritable bowel syndrome. Upper GI endoscopy, colonoscopy, imaging studies should
28 be performed to rule out other causes. Unfortunately, in some individuals, determining if the symptoms are caused by a hemangioma or by another process (e.g., irritable bowel syndrome) is difficult. Surgical treatment may be appropriate in cases of rapidly growing tumors. Surgery may also be warranted in cases where a hepatic hemangioma cannot be differentiated from hepatic malignancy on imaging studies. Obviously for patients coming with hemangioma complications surgery is mandatory. SO SIZE OF HEMANGIOMA DOES NOT MATTER? Size actually does not matter in most cases and as said above it is the symptoms that decide the requirement of treatment. The management of very large (>10 cm) hepatic hemangioma is controversial. Resection is advocated for such lesions because of the potential risk of complications.
29 WHAT IS THE NATURE OF SURGERY? Surgical resection and surgical enucleation are the treatments of choice. In resection, a hemangioma-containing portion of liver with surrounding normal liver tissue is removed. In enucleation, hemangioma is removed without removing any of the surrounding liver tissue. The size and location of a lesion will influence the surgeon's decision to perform either a formal segmental resection of the hemangioma or an enucleation of the hemangioma. Typically, these procedures are performed using an open approach, but laparoscopic surgery can be performed in some cases. Hepatic lobectomy may be necessary in the case of large lesions. Very rarely (large and / or multiple lesions) liver may have to be replaced (transplantation) In general, both surgical resection and enucleation are safe and are well tolerated by patients. Typically, postoperative complications are less and the average length of hospital stay is
30 6 days. Surgery is technically more demanding in resection. WILL IT RECUR AFTER SURGERY? In the absence of tumor-promoting factors, such as estrogen therapy, hemangiomas rarely recur after successful resection. WHAT IS DONE IF HEMANGIOMA RUPTURES? Spontaneously ruptured hemangioma is an emergency life-threatening situation. These patients are usually admitted with acute abdominal pain & shock state. Patients are immediately taken to ICU and top priority will be given to hemodynamic stabilization. Patient will require various accesses for rapid fluid and blood transfusion (called central or jugular or subclavian or femoral line). Patient may require support for breathing too (ventilator). After patient is stabilized investigations are done to find the cause of shock including USG & CT
31 scan, which confirm that patients critical condition is due to a ruptured hemangioma. The patient will be then immediately shifted to radiology department where interventional radiologist does an urgent Arterial embolization. Branches of the hepatic artery feeding the hemangioma are embolized with polyvinyl alcohol, metal coils and other substances. Embolization results in stopping the bleeding. It also shrinks the tumor, thereby minimizing the risk of complications. Patient may get pain & fever after this procedure. If this facility is not available then patient will certainly require a surgery with due risk to life. During surgery, resection or enucleation is usually not attempted unless patient is stable since there is risk of more bleeding and usually a surgical ligation of the hepatic artery is performed. Selective ligation of large feeding vessels used to be performed in the days when
32 embolization was not available or is not available. It has the same effect like embolization provided all feeders are ligated, but this is difficult and therefore results are not assured. Once the patient is stabilized, formal surgical resection of the hepatic hemangioma can be performed. ARE THERE ALTERNATIVE TREATMENTS IF I DON T WANT SURGERY OR I AM UNFIT? Surgical resection may not be possible in certain cases because of the massive or diffuse nature of the lesion, its proximity to vascular structures, or the patient's comorbidities. Minimally invasive therapies for hepatic hemangioma include arterial embolization, radiofrequency ablation, and hepatic irradiation can be tried in such patients. However the long-term success rate of embolization (without subsequent surgical resection) is not known. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation may be used to improve abdominal pain in patient with symptomatic
33 hepatic hemangiomas. But this would be useful only in small tumor which otherwise also do not need therapy. Hepatic irradiation over several weeks may cause tumor regression and symptom relief with minimal morbidity but no assurance. WHAT IS THE TREATMENT IN INFANTS? Treatment for infantile hemangioendothelioma depends on the child's growth and development. The following treatments may be needed: Embolization Tying off (ligation) a liver artery Medications for heart failure Surgery to remove the tumor In infants whose tumor is only in one lobe of the liver, surgery is a cure, even if the child has heart failure. ARE THERE ANY DIETARY & PHYSICAL ACTIVITY RESTRICTIONS? No special dietary management is required.
34 Also no restriction of physical activity is indicated for most patients with hepatic hemangiomas. Patients with large hemangiomas may need to be instructed to avoid trauma to the right upper abdominal quadrant. IS THERE ANY MEDICAL MANAGEMENT? No medications are useful to shrink or eradicate hepatic hemangiomas. WHAT IS THE PROGNOSIS? Overall, a patient with a hepatic hemangioma has an excellent prognosis. Malignant transformation has not been described. Above information will help you to make an informed decision but it cannot replace the professional advice and expertise of a doctor who is familiar with your condition. You may have questions that are not covered; you should discuss these with your surgeon. You must remember every individual is different.
35 DOCTORS DEALING WITH LIVER DISEASE THAT YOU MAY MEET Endoscopist: This may be a gastroenterologist or a surgeon who is able to undertake endoscopy (examination of the stomach or bowel using a flexible telescope). A few endoscopists can also perform ERCP and EUS, which are special forms of endoscopy that examine the biliary and pancreatic ducts and the pancreas Gastroenterologist: A physician who is highly specialized in gut problems. General physician: A consultant medical doctor who works in a hospital and who is broadly specialized including gut problems. General surgeon: A consultant surgeon who works in a hospital and who is broadly specialized including gut problems.
36 HepatoPancreatoBiliary surgeon: A surgeon who is highly specialized in pancreato-biliary & liver operations. GLOSSARY MRI -- Magnetic Resonance Imaging A type of scanning performed to diagnose problems not picked up by regular investigations CT SCAN Computerized Tomography A type of scanning performed to diagnose problems not picked up by regular investigations ERCP Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiography.
37 An endoscopic procedure performed to visualize bile & pancreatic ducts & treat the disease endoscopically whenever possible EUS -- Endoscopic UltraSound. An endoscopic procedure performed to visualize pancreas & biliary tract from very close, diagnose problems, obtain biopsies and at times treat the disease too. MRCP Magnetic Resonance Cholangio- Pancreatography
38
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Biliary Stone Disease
 Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A multidisciplinary approach to the prevention and early detection of invasive pancreatic cancer.
 This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery
 Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery Summary Gallstones are small stones made from cholesterol, bile pigment and calcium salts, which form in a person s gall bladder. Medical treatment isn t necessary
Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery Summary Gallstones are small stones made from cholesterol, bile pigment and calcium salts, which form in a person s gall bladder. Medical treatment isn t necessary
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 SMALL BOWEL BLEEDING: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA 1. What is the small
SMALL BOWEL BLEEDING: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA 1. What is the small
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
 CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
Catheter Embolization and YOU
 Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET
 LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
Consent for Treatment/Procedure Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
 Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
CEU Update. Pancreatic Cancer
 CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
Liver Resection. Patient Information Booklet. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Liver Resection Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Liver Resection Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
The Whipple Procedure. Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain
 The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD
 Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD Biliary Injuries during Cholecystectomy In the 1990s, high rate of biliary injury was due in part to learning
Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD Biliary Injuries during Cholecystectomy In the 1990s, high rate of biliary injury was due in part to learning
Benign Liver Tumors. Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013
 Benign Liver Tumors Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013 Outline Benign Liver Tumors are, in general. Asymptomatic Diagnosed: imaging Treatment: Do no harm Unless Malignant potential Causing symptoms Differential
Benign Liver Tumors Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013 Outline Benign Liver Tumors are, in general. Asymptomatic Diagnosed: imaging Treatment: Do no harm Unless Malignant potential Causing symptoms Differential
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES What are the Adrenal Glands? The adrenal glands are two small organs, one located above each kidney. They are triangular
Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES What are the Adrenal Glands? The adrenal glands are two small organs, one located above each kidney. They are triangular
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA. Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005
 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
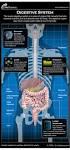 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
UCLA Asian Liver Program
 CLA Program Update Program Faculty Myron J. Tong, PhD, MD Professor of Medicine Hepatology Director, Asian Liver Program Surgery Ronald W. Busuttil, MD, PhD Executive Chair Department of Surgery Director,
CLA Program Update Program Faculty Myron J. Tong, PhD, MD Professor of Medicine Hepatology Director, Asian Liver Program Surgery Ronald W. Busuttil, MD, PhD Executive Chair Department of Surgery Director,
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent
 A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Gary M. Annuniziata, D.O., F.A.C.P. Anh T. Duong, M.D. Jonathan C. Lin, M.D., MPH. Preparation for EGD, ERCP, Peg Placement.
 Gary M. Annuniziata, D.O., F.A.C.P. Anh T. Duong, M.D. Jonathan C. Lin, M.D., MPH Phone- (760) 321-2500 Fax- (760) 321-5720 Preparation for EGD, ERCP, Peg Placement Patient Name- Procedure Date and Time-
Gary M. Annuniziata, D.O., F.A.C.P. Anh T. Duong, M.D. Jonathan C. Lin, M.D., MPH Phone- (760) 321-2500 Fax- (760) 321-5720 Preparation for EGD, ERCP, Peg Placement Patient Name- Procedure Date and Time-
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
Chemoembolization for Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours
 Chemoembolization for Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours What is this cancer? Pancreatic Endocrine Tumours are also called Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours. This cancer is rare and it starts
Chemoembolization for Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours What is this cancer? Pancreatic Endocrine Tumours are also called Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours. This cancer is rare and it starts
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015
 Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS)
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
The Anorexic Cat For this reason, any cat that stops eating for any reason is considered an emergency situation.
 The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS
 YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations. Chapter. Grade. CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
Facing Pancreatic Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Pancreatic Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Pancreatitis/Pancreatic Cancer The pancreas is an organ that produces enzymes and hormones to help your body digest
Facing Pancreatic Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Pancreatitis/Pancreatic Cancer The pancreas is an organ that produces enzymes and hormones to help your body digest
Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer
 Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer Guest Expert: Sukru, MD Professor of Transplant Surgery Mario Strazzabosco, MD Professor of Internal Medicine www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer Guest Expert: Sukru, MD Professor of Transplant Surgery Mario Strazzabosco, MD Professor of Internal Medicine www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
Tumour Markers. What are Tumour Markers? How Are Tumour Markers Used?
 Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Risk Management Plan
 Risk Management Plan Active substance: Drospirenone/ethinylestradiol Version number: 4.0 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Oral contraception Effective control
Risk Management Plan Active substance: Drospirenone/ethinylestradiol Version number: 4.0 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Oral contraception Effective control
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Diseases of peritoneum Lect. Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32
 Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy. Patient Name
 Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Whipple Procedure: A guide for patients and families UHN
 Whipple Procedure: A guide for patients and families UHN Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca 2014 University Health Network. All rights
Whipple Procedure: A guide for patients and families UHN Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca 2014 University Health Network. All rights
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
 Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Summary Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn s disease can appear in any part of a person s digestive
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Summary Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn s disease can appear in any part of a person s digestive
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis affects various systems in children and young adults, including the following:
 Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Viral Liver Disease. The Liver and Its Functions
 Viral Liver Disease The Liver and Its Functions The liver, the body's largest organ weighing about three pounds, is located on the right side of the abdomen, protected by the lower rib cage. It is responsible
Viral Liver Disease The Liver and Its Functions The liver, the body's largest organ weighing about three pounds, is located on the right side of the abdomen, protected by the lower rib cage. It is responsible
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
How common is bowel cancer?
 information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder)
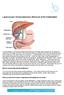 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors
 Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Uterine Fibroids. More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth.
 Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
Mesenteric Angiography
 Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
