Diagnosis and Management of Plantar Fasciitis. John V. Thompson, DO; Sundeep S. Saini, OMS IV; Christopher W. Reb, DO; and Joseph N.
|
|
|
- Shawn Carson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diagnosis and Management of Plantar Fasciitis John V. Thompson, DO; Sundeep S. Saini, OMS IV; Christopher W. Reb, DO; and Joseph N. Daniel, DO From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery at Memorial Hospital in York, Pennsylvania (Dr Thompson); the Rowan University School of Osteopathic Medicine (RowanSOM) in Stratford, New Jersey (Student Doctor Saini); the Department of Orthopedics at RowanSOM in Stratford, New Jersey (Dr Reb); and the Department of Surgery at Jefferson Medical College in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (Dr Daniel). Dr Thompson is in his second year of residency training, and Dr Reb is in his fifth year of residency training. Financial Disclosures: None reported. Support: None reported. Address correspondence to Joseph N. Daniel, DO, Rothman Institute, 2500 English Creek Ave, Building 1300, Egg Harbor Township, NJ rothmaninstitute.com Submitted February 20, 2014; final revision received July 23, 2014; accepted August 7, Plantar fasciitis, a chronic degenerative process that causes medial plantar heel pain, is responsible for approximately 1 million physician visits each year. Individuals with plantar fasciitis experience pain that is most intense during their first few steps of the day or after prolonged standing. The authors provide an overview of the diagnosis and management of a common problem encountered in the primary care setting. Routine imaging is not initially recommended for the evaluation of plantar fasciitis but may be required to rule out other pathologic conditions. Overall, plantar fasciitis carries a good prognosis when patients use a combination of several conservative treatment modalities. Occasionally, referral to a specialist may be necessary. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2014;114(12): doi: /jaoa The initial evaluation of plantar fasciitis often occurs in the primary care setting. 1 Although the diagnosis is often straightforward, an extensive list of alternative diagnoses may need to be ruled out. Effective treatment is predicated on the modification of risk factors and the implementation of an evidencebased treatment approach. 2 Ultimately, a good prognosis is expected. The aim of the present article is to provide the reader with an overview of the diagnosis and management of plantar fasciitis, a problem commonly encountered in the primary care setting. To identify current best practices, we conducted a thorough search of the English language literature for articles containing information pertaining to the diagnosis and management of plantar fasciitis. Only peer-reviewed articles were included, and preference was given to studies with higher levels of evidence. Current clinical practice guidelines for plantar fasciitis were also reviewed, and recommendations are incorporated herein. Anatomy The plantar fascia comprises 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate at the medial tubercle of the calcaneus and fan distally to insert into the base of each proximal phalanx (Figure 1). 3 First described by Hicks 4 in 1954 as the windlass mechanism, the plantar fascia tenses during the terminal stance to toe-off phases of gait. 3,4 This tension elevates and reinforces the medial longitudinal arch, which in turn allows the foot to function as a rigid lever for forward propulsion. 5 Pathophysiology Plantar fasciitis is a chronic degenerative process involving the plantar aponeurosis of the foot, most commonly at its insertion into the medial tubercle of the calcaneus. The process involves repetitive strain that seems to cause microtearing, which induces a repair response. 4,6 Histologic analysis demonstrates marked thickening and fibrosis of the plantar fascia along with collagen necrosis, chondroid metaplasia, and calcification. 6,7 Although plantar fasciitis has historically been assumed to be primarily an inflammatory process, these findings suggest a principally degenerative mechanism, leading some authors to suggest that plantar fasciosis may be a more histologically accurate term. 6,8 Epidemiology Each year approximately 1 million office-based physician visits result in a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. 1 Most Each year approximately 1 million office-based physician visits result in a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. patients initially seek care from their primary care physician. 1 The peak incidence of plantar fasciitis occurs in persons aged between 45 and 64 years, and it is more common among women. 1,9 Other at-risk populations 900
2 fascia, and intrinsic muscles of the foot has also been deminclude persons with flat (planus) or high-arched (cavus) feet, long-distance runners, military personnel, persons with occupations requiring prolonged standing, and persons who are obese or sedentary Up to one-third of patients may present with bilateral plantar fasciitis. 6 Diagnosis Clinical Evaluation Plantar fasciitis is primarily a clinical diagnosis. Patients classically describe medial plantar heel pain on weight bearing, which is often most intense during their first few steps in the morning but tends to improve with rest. 3,12 This pain may progress over the course of the day, especially after prolonged standing. Acute exacerbations may occur at any time when rising from a seated position. 3,12 Physicians should look for other risk factors for plantar fasciitis and assess the appropriateness of the patients footwear choices for their customary activities. A thorough musculoskeletal examination of both lower extremities should be performed. Classic physical examination findings suggestive of plantar fasciitis include reproducible pain with palpation of the plantar medial aspect of the heel and pain with passive dorsiflexion of the ankle and toes (windlass test). 12 A contributing planus or cavus foot deformity may be noted. 3,12 Ankle range of motion should also be assessed. Active dorsiflexion less than 10 beyond neutral is indicative of an equinus contracture. 13 The Table summarizes the distinguishing historical and physical examination findings of other items in the differential diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. Imaging Diagnostic imaging is not recommended for the initial evaluation of plantar fasciitis. 21 However, magnetic resonance images, triple-phase bone scans, or other imaging results may be required to rule out other considerations in the differential diagnosis, particularly when 4 to 6 months of nonsurgical treatment has failed or when the patient presents with atypical heel pain (Table). 12 KEY POINTS Plantar fasciitis is primarily a clinical diagnosis that requires a thorough history and physical examination because of the breadth of the differential diagnosis. Female patients, middle-aged patients, long-distance runners, military personnel, obese patients, and individuals with a cavus or planus foot deformity are at an increased risk for developing plantar fasciitis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, focused stretching, footwear modifications, and over-thecounter orthotics are recommended for the initial management of plantar fasciitis. There is limited evidence supporting the efficacy of osteopathic manipulative treatment for patients with plantar fasciitis. The risks associated with corticosteroid injection of the plantar fascia include skin and fat pad atrophy, infection, and plantar fascia rupture. Treatment Nonsurgical Approximately 85% to 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis can be successfully treated without surgery. 6 Methods include rest, over-the-counter (OTC) nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), stretching, counterstrain technique, orthoses, corticosteroid injections, extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), and ultrasound therapy. Although treatment may be required for 6 months or longer, 80% of patients treated conservatively have no long-term recurrence of pain. 1,16 Current recommendations for the conservative management of plantar fasciitis call for a multimodal, evidence-based approach. 2 Initial treatment should include sufficient foot rest with conservative analgesic use. Over-the-counter NSAIDs have been shown to be an adequate means of pain control when used in combination with other forms of treatment. 22,23 Focused stretching of the Achilles tendon, plantar 901
3 Medial View Plantar View Bones of the medial longitudinal arch 1. calcaneus 2. talus 3. navicular 4. cuneiforms 5. first, second, and third metatarsals Base of the proximal phalanx Plantar fascia 1 Medial tubercle of the calcaneus Achilles tendon Lateral plantar fascia Plantar aponeurosis Medial plantar fascia Calcaneus Figure 1. The plantar fascia supports the medial longitudinal arch by transmitting forces between the heel and forefoot during the late stance to toe-off phases of gait. benefit ratio for patients with plantar fasciitis. In a ranonstrated to improve pain. 24,25 The intermittent application of ice seems to provide some benefit to patients with plantar fasciitis when compared with heat application. 23 The osteopathic manipulative treatment technique of counterstrain may provide immediate improvement of plantar fasciitis symptoms; however, maintenance of these results has not been documented, to the authors knowledge. 26,27 The plantar fascia should be placed in a position of least resistance with passive flexion of the knee and plantar flexion of the ankle and toes. 27 This position should be maintained for approximately 90 seconds while monitoring the tenderpoint, which is most commonly located at the plantar fascial insertion on the medial calcaneus. 27 The foot should then be returned to a neutral position and reassesed. 27 A wide variety of orthosis options are available for the management of plantar fasciitis. The use of shoe inserts (eg, silicone heel pads, felt pads, and rubber heel cups) in combination with stretching exercises has been shown to provide superior short-term improvement in heel pain compared with stretching alone. 28 A randomized, controlled study comparing OTC shoe inserts with customized shoe inserts found no significant difference in pain relief between the 2 groups at 12-month followup. 29 Regardless, the long-term efficacy of shoe inserts for plantar fasciitis is uncertain. 30 The use of posteriortension night splints has also shown benefit in patients Approximately 85% to 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis can be successfully treated without surgery. with chronic plantar fasciitis. 16,31 The suspected therapeutic mechanism of night splinting is the maintenance of ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension, creating a constant mild stretch on the plantar fascia, presumably allowing it to heal at a functional length. 16,30 Corticosteroid injections should be considered with caution, owing to a potentially unfavorable risk-to- 902
4 Table. Differential Diagnosis of Plantar Fasciitis 2,3,12-18 Physical Examination Diagnostic Diagnosis History Findings Imaging c Skeletal Origin Acute calcaneal High-energy axial overloading through Patients often unable to ambulate; Plain radiography tuberosity/body fracture heel such as from a fall or MVA acute ecchymosis and swelling of heel Calcaneal stress Overuse injury associated with sudden Reproducible pain with simultaneous MR imaging, fracture a increase in athletic activity; deep, dull medial and lateral compression of single-phase pain in calcaneal tuberosity worsened calcaneous (squeeze test a ) bone scan by walking on hard surfaces Subtalar and Insidious lateral and medial heel pain, Pain, swelling, and stiffness worsened Plain radiography talonavicular arthritis b respectively, and relieved with rest by weight-bearing activity Soft Tissue Origin Acute plantar fascia Acute plantar pop followed by Ecchymosis and swelling in plantar Noncontrast rupture severe heel pain with foot swelling heel and midfoot; palpable mass MR imaging under medial arch may exist Fat pad atrophy Centrally located heel pain worsened Deep pain with palpation of medial MR imaging by walking on hard surfaces; most aspect of heel common in elderly patients Insertional Achilles Posterior heel pain worsened Point tenderness over posterior Noncontrast tendonitis by ascending stairs or hills tendon of foot; Achilles contracture MR imaging may be present Retrocalcaneal Pain in posterior heel near Pain with passive dorsiflexion and Noncontrast bursitis calcaneal insertion of Achilles eversion of the foot MR imaging, tendon; common in runners plain radiography Neurogenic Origin Tarsal tunnel syndrome Pain radiating from the medial Plantar parasthesias elicited by Electrodiagnostic malleolus into the foot, which may tapping the tibial nerve behind the studies, MR worsen throughout the day; improves medial malleolus (Tinel sign); imaging, US with rest of intrinsic foot muscles plantar sensory loss or atrophy LPN/MCN entrapment Plantar foot pain consistent LPN: tender over lateral plantar aspect Electrodiagnostic throughout day of foot; possible atrophy of abductor studies, MR digiti minimi. MCN: tender over plantar imaging, US aspect of medial arch; no muscle atrophy S1 radiculopathy Radiating pain traveling down Diminished ankle jerk reflex and Electrodiagnostic the posterior aspect of leg weakened plantar flexion of foot; studies, MR weakened toe walking imaging, US Peripheral neuropathy c Risk factors for peripheral Decreased sensation to vibration, Electrodiagnostic neuropathy c ; gradual onset of light touch, temperature, and pain, studies, nerve diffuse pain, numbness or hair loss, smooth skin, muscle biopsy, noncontrast tingling in foot that may atrophy, ulceration, and MR imaging, US progress to sharp, jabbing pain progressive clawing of toes a A positive squeeze test finding would not occur in patients with plantar fasciitis. 3 b Plain radiographs may reveal degenerative changes, including joint space narrowing and marginal osteophyte formation. 2 c Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that is most commonly associated with diabetes but also can result from alcohol abuse and other metabolic deficiencies. 3 The diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy is made clinically, and it infrequently requires the use of further imaging. Abbreviations: LPN, lateral plantar nerve; MCN, medial calcaneal nerve; MR, magnetic resonance; MVA, motor vehicle accident; S1, first sacral vertebra; US, ultrasonography. 903
5 domized, prospective clinical trial, corticosteroid injections provided better relief of plantar fasciitis symptoms at 1 month but not at 6 months when compared with control groups. 32 The risks associated with corticosteroid injection include skin and fat pad atrophy, infection, and plantar fascia rupture. 32,33 In a retrospective study, corticosteroid injections were associated with a 10% incidence of plantar fascia rupture. 33 This complication can be serious, possibly leading to problems associated with the loss of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. 34 There are limited data available regarding ESWT for the management of plantar fasciitis. Its therapeutic mechanism is unknown. Nonetheless, in a randomized, double-blinded clinical trial, the addition of 1 application of 3800 high-energy shock waves to standard therapies demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in symptoms at 3 months compared with standard therapies without ESWT. 35 Ultrasound therapy has recently been investigated for the management of refractory plantar fasciitis. 36,37 Although there is presently insufficient evidence to support its efficaciousness, studies suggest it is relatively safe. History and Physical Examination Findings Medial plantar heel pain with weight bearing Pain is most intense during first few steps in the morning Pain improves with rest Reproducible pain with palpation of the plantar medial aspect of the heel Pain with passive dorsiflexion of the ankles and toes Nonoperative Management NSAIDs, focused stretching, footwear modification, and orthotics are recommended for the initial management of plantar fasciitis OMT, corticosteroid injections, ESWT, and ultrasound therapy may provide pain relief Operative Management Plantar fasciotomy is indicated only after failed conservative treatment for at least 6 to 12 months Figure 2. Take home points: diagnosis and management of plantar fasciitis. Abbreviations: ESWT, extracorporeal shock wave therapy; NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; OMT, osteopathic manipulative treatment. Surgical Partial or complete plantar fasciotomy is indicated only after at least 6 to 12 months of conservative treatment has failed. 2 Before proceeding with surgery, the differential diagnosis must be revisited to consider other causes of subcalcaneal pain (Table). Surgical release of greater than 40% of the plantar fascia may have detrimental effects on other ligamentous and bony structures in the foot. 38 Nevertheless, Davies and colleagues 39 reported that 75% of patients who underwent surgical intervention after failed conservative treatment reported substantial or complete reduction in heel pain. Suggested Treatment Plan Conservative treatment should first be initiated (Figure 2). Patients should limit activity by level of tolerance and modify footwear (eg, avoid flip-flops and sandals, use OTC shoe inserts). Also, a plantar fascial stretching regimen should be initiated, as follows: Wall push: With the heel on the ground and ball of foot on the base of a wall, the patient leans into the wall to stretch the plantar fascia for at least 2 minutes at 10-second intervals on the affected side at least 2 times daily. (The condition will improve much more rapidly if the patient can do 3 sets of wall pushes every hour on the hour.) Towel pick-up: With the toes of the affected foot, the patient picks up a dry paper towel, drops it, and repeats for 2 minutes once daily in the evening. Ice roll: The patient rolls the foot over the top of a frozen water bottle for 2 minutes once daily in the evening. 904
6 Outcomes with home stretching alone are excellent after treatment for half the amount of time that symptoms have been present. For example, symptoms present for 1 year would get good results after 6 months of treatment. If conservative treatment is not effective, moderate treatment consisting of custom orthoses, night splints, and judicious use of injection therapy should be tried. If moderate measures fail, if the symptoms have lasted more than 1 year, and if the patient has been fully compliant with the multiple daily stretching routine, surgery may be required. Summary The plantar fascia is subject to chronic repetitive stress at its origin, and plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. The diagnosis is often made clinically based on the location of pain at the medial calcaneal tubercle. Risk factors include age, female sex, obesity, prolonged weight bearing, and repetitive activities that cause strain on the plantar fascia. Imaging may be necessary to rule out other causes of heel pain in the differential diagnosis after nonsurgical treatment has failed or after the patient presents with atypical pain. A combination of conservative treatments is successful in most cases and should include NSAIDs, a proper stretching regimen, night splints, and, if there is no relief after 6 to 12 months, referral to a specialist. Short-term relief may be provided by OMT and foot orthoses, but there is no evidence of these modalities providing long-term improvement. Surgical treatment should only be considered if all other methods fail. Author Contributions Dr Thompson, Student Doctor Saini, and Drs Reb and Daniel provided substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; drafted the article or revised it critically for important intellectual content; and gave final approval of the version of the article to be published. References 1. Riddle DL, Schappert SM. Volume of ambulatory care visits and patterns of care for patients diagnosed with plantar fasciitis: a national study of medical doctors. Foot Ankle Int. 2004;25(5): Thomas JL, Christensen JC, Kravitz SR, et al; American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons Heel Pain Committee. The diagnosis and treatment of heel pain: a clinical practice guideline revision J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010;49(3 suppl):s1-s19. doi: /j.jfas Gill LH. Plantar fasciitis: diagnosis and conservative management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1997;5(2): Hicks JH. The mechanics of the foot, II: the plantar aponeurosis and the arch. J Anat. 1954;88(1): /pdf/janat pdf. Accessed September 30, Flanigan RM, Nawoczenski DA, Chen L, Wu H, Digiovanni BF. The influence of foot position on stretching of the plantar fascia. Foot Ankle Int. 2007;28(7): Schepsis AA, Leach RE, Gorzyca J. Plantar fasciitis: etiology, treatment, surgical results, and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;266: Snider MP, Clancy WG, McBeath AA. Plantar fascia release for chronic plantar fasciitis in runners. Am J Sports Med. 1983;11(4): Lemont H, Ammirati KM, Usen N. Plantar fasciitis: a degenerative process (fasciosis) without inflammation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2003;93(3): Owens BD, Wolf JM, Seelig AD. Risk factors for lower extremity tendinopathies in military personnel. Orthop J Sports Med. 2013;1(1). doi: / Riddle DL, Pulisic M, Pidcoe P, Johnson RE. Risk factors for plantar fasciitis: a matched case-control study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(5): Ballas MT, Tytko J, Cookson D. Common overuse running injuries: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 1997;55(7): Neufeld SK, Cerrato R. Plantar fasciitis: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(6): Pfeffer G, Easley M, Frey C, Hintermann B, Sands A. Operative Techniques: Foot and Ankle Surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2010; Hunt KJ, Anderson RB. Heel pain in the athlete. Sports Health. 2009;1(5): /PMC /. Accessed September 30, Lawrence DA, Rolen MF, Morshed KA, Moukaddam H. MRI of heel pain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200(4): doi: /ajr Banerjee R, Chao JC, Taylor R, Siddiqui A. Management of calcaneal tuberosity fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(4): doi: /jaaos
7 17. Alshami AM, Souvlis T, Coppieters MW. A review of plantar heel pain of neural origin: differential diagnosis and management. Man Ther. 2008;13(2): Buchbinder R. Clinical practice: plantar fasciitis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21): Dixit S, Maiya A. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and its evaluation in a clinical scenario: a review. J Postgrad Med. 2014;60(1): D Ambrogi E, Giurato L, D Agostino MA, et al. Contribution of plantar fascia to the increased forefoot pressures in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(5): Levy JC, Mizel MS, Clifford PD, Temple HT. Value of radiographs in the initial evaluation of nontraumatic adult heel pain. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(6): Wolgin M, Cook C, Graham C, et al. Conservative treatment of plantar heel pain: long-term follow-up. Foot Ankle Int. 1994;15(3): Gill LH, Kiebzak GM. Outcome of nonsurgical treatment for plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 1996;17(9): DiGiovanni BF, Nawoczenski DA, Malay DP, et al. Plantar fascia-specific stretching exercise improves outcomes in patients with chronic plantar fasciitis: a prospective clinical trial with two-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(8): Hyland MR, Webber-Gaffney A, Cohen L, Lichtman PT. Randomized controlled trial of calcaneal taping, sham taping, and plantar fascia stretching for the short-term management of plantar heel pain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36(6): Wynne M, Burns JM, Eland DC, Conatser RR, Howell JN. Effect of counterstrain on stretch reflexes, Hoffmann reflexes, and clinical outcomes in subjects with plantar fasciitis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2006;106(9): Accessed September 30, Nelson KE, Glonek T. Somatic Dysfunction in Osteopathic Family Medicine. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007:147, Pfeffer G, Bacchetti P, Deland J, et al. Comparison of custom and prefabricated orthoses in the initial treatment of proximal plantar fascitis. Foot Ankle Int. 1999;20(4): Landorf KB, Keenan AM, Herbert RD. Effectiveness of foot orthoses to treat plantar fasciitis: a randomized trial. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(12): Hawke F, Burns J, Radford JA, du toit V. Custom-made foot orthoses for the treatment of foot pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(3):CD doi: / cd pub Roos E, Engström M, Söderberg B. Foot orthoses for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(8): Kalaci A, Cakici H, Hapa O, Yanat AN, Dogramaci Y, Sevinç TT. Treatment of plantar fasciitis using four different local injection modalities: a randomized prospective clinical trial. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2009;99(2): Acevedo JI, Beskin JL. Complications of plantar fascia rupture associated with corticosteroid injection. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19(2): Kim C, Cashdollar MR, Mendicino RW, Catanzariti AR, Fuge L. Incidence of plantar fascia ruptures following corticosteroid injection. Foot Ankle Spec. 2010;3(6); doi: / Kudo P, Dainty K, Clarfield M, Coughlin L, Lavoie P, Lebrun C. Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial evaluating the treatment of plantar fasciitis with an extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) device: a North American confirmatory study. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(2): doi/ /jor.20008/pdf. 36. Grecco MV, Brech GC, Greve JM. One-year treatment follow-up of plantar fasciitis: radial shockwaves vs. conventional physiotherapy. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013;68(8): doi: /clinics/2013(08) Crawford F, Snaith M. How effective is therapeutic ultrasound in the treatment of heel pain? Ann Rheum Dis. 1996;55(4): /annrheumd pdf. Accessed September 30, Cheung JT, An K, Zhang M. Consequences of partial and total plantar fascia release: a finite element study. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(2): Davies MS, Weiss GA, Saxby TS. Plantar fasciitis: how successful is surgical intervention? Foot Ankle Int. 1999;20(12): American Osteopathic Association 906
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis. Heel Pain - common causes. Plantar Fasciitis 1/16/2012. Robert A Erdin III, MD
 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Chapter 140 Heel Pain
 Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
How To Treat Heel Pain
 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study
 Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Using Might Splints in the Treatment
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN
 PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Key Contents. Learning Objectives. Indep Rev Oct-Dec 2013;15(10-12) 476-480. IR-276. Dr. Farhad Alam
 Indep Rev Oct-Dec 2013;15(10-12) IR-276 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Dr. Farhad Alam Key Contents Pathophysiology Causes and risk factor Diagnostic feature Treatment Options Prognosis and prevention Learning Objectives
Indep Rev Oct-Dec 2013;15(10-12) IR-276 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Dr. Farhad Alam Key Contents Pathophysiology Causes and risk factor Diagnostic feature Treatment Options Prognosis and prevention Learning Objectives
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF JOGGER S HEEL
 Art & science The foot acute synthesis injuries care of art and science is lived by the nurse in the nursing act JOSEPHINE G PATERSON DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF JOGGER S HEEL Laura Horobin outlines how
Art & science The foot acute synthesis injuries care of art and science is lived by the nurse in the nursing act JOSEPHINE G PATERSON DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF JOGGER S HEEL Laura Horobin outlines how
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Plantar Heel Pain. Papers. Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla
 Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla Abstract Plantar Heel pain is one of the most commonly encountered problems of foot pain in active adults over the age of 40. One in ten people will experience
Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla Abstract Plantar Heel pain is one of the most commonly encountered problems of foot pain in active adults over the age of 40. One in ten people will experience
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
Foot and Ankle Complaints
 Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
49 Plantar fasciitis. 49.1 Introduction. 49.2 Anatomy. OrthopaedicsOne Articles. Contents
 49 Plantar fasciitis Contents Introduction Anatomy Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Physical Examination Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Controversy References 49.1 Introduction Plantar
49 Plantar fasciitis Contents Introduction Anatomy Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Physical Examination Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Controversy References 49.1 Introduction Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain)
 Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Plantar fasciitis - suspected
 Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
By: Jerry Ryan, M.D., University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, Wisconsin
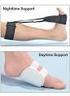
 UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People
 The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Plantar fasciitis in a Professional Boxer:
 Plantar fasciitis in a Professional Boxer: Clinical Case Report for The Trevor Silver Memorial Essay Prize Gurjit Bhogal MBChB (Hons) MSc MRCGP July 2012 Total Word Count (excluding References) 2976 words
Plantar fasciitis in a Professional Boxer: Clinical Case Report for The Trevor Silver Memorial Essay Prize Gurjit Bhogal MBChB (Hons) MSc MRCGP July 2012 Total Word Count (excluding References) 2976 words
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better. By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the
 The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Plantar Fasciitis - Ayurvedic Strain
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: (diagnosis specific, impairment/ dysfunction specific) ICD9-728.71 plantar fibromatosis Plantar
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: (diagnosis specific, impairment/ dysfunction specific) ICD9-728.71 plantar fibromatosis Plantar
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Plantar Fascitis
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
.org. Rotator Cuff Tears. Anatomy. Description
 Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
PRISCILLA TU, DO, and JEFFREY R. BYTOMSKI, DO, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina
 Diagnosis of Heel Pain PRISCILLA TU, DO, and JEFFREY R. BYTOMSKI, DO, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina Heel pain is a common presenting symptom in ambulatory clinics. There are many causes, but
Diagnosis of Heel Pain PRISCILLA TU, DO, and JEFFREY R. BYTOMSKI, DO, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina Heel pain is a common presenting symptom in ambulatory clinics. There are many causes, but
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Large L5 S1 Disc Protrusion Treated Successfully With Cox Technic
 Cox Technic Email Case #77 October 2009 by Dr. Greenwood 1 Large L5 S1 Disc Protrusion Treated Successfully With Cox Technic A case study presented to the Part III Hospital Based Training Course for Cox
Cox Technic Email Case #77 October 2009 by Dr. Greenwood 1 Large L5 S1 Disc Protrusion Treated Successfully With Cox Technic A case study presented to the Part III Hospital Based Training Course for Cox
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
July 2012 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move
 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Physician Labeling. ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.)
 Physician Labeling ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.) CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Physician Labeling ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.) CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults
 Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults AUTHOR TRACY ALDRIDGE, NAME, Location M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, Illinois Heel pain is a common condition in adults that may
Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults AUTHOR TRACY ALDRIDGE, NAME, Location M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, Illinois Heel pain is a common condition in adults that may
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Heel Steroid Injection
 Heel Steroid Injection Evidence of effectiveness 2 systematic reviews (2 included) ~/ ~ 2 experimental studies (2 included) ~/ -/~ 1 observational (1 included) 2.5/3 Evidence of safety and harm Generic
Heel Steroid Injection Evidence of effectiveness 2 systematic reviews (2 included) ~/ ~ 2 experimental studies (2 included) ~/ -/~ 1 observational (1 included) 2.5/3 Evidence of safety and harm Generic
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM
 1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY
 George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ
 Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ 6 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Your wrist hurts when you bend
Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ 6 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Your wrist hurts when you bend
Most Common Running Injuries
 Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar
 EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
Arches. Foot Injuries. Medial Longitudinal Arch. Lateral Longitudinal Arch. Transverse Arch. Arch Strains
 Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Plantar Fasciitis: Nonsurgical & Surgical Options for Chronic Heel Pain. Mathew M. John, DPM, FACFAS Atlanta, GA
 Plantar Fasciitis: Nonsurgical & Surgical Options for Chronic Heel Pain Mathew M. John, DPM, FACFAS Atlanta, GA Heel Pain:Plantar fasciitis Over 2 million Americans suffer from heel pain Most common cause
Plantar Fasciitis: Nonsurgical & Surgical Options for Chronic Heel Pain Mathew M. John, DPM, FACFAS Atlanta, GA Heel Pain:Plantar fasciitis Over 2 million Americans suffer from heel pain Most common cause
Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot (in-shoe) orthotics are reimbursable under Plans administered by QualCare, Inc.
 Subject: Foot Orthotics and Diabetic Shoes* Effective Date: October 1, 1999 Department(s): Utilization Management Policy: Objective: Procedure: Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot
Subject: Foot Orthotics and Diabetic Shoes* Effective Date: October 1, 1999 Department(s): Utilization Management Policy: Objective: Procedure: Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot
