49 Plantar fasciitis Introduction Anatomy. OrthopaedicsOne Articles. Contents
|
|
|
- Brian Lamb
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 49 Plantar fasciitis Contents Introduction Anatomy Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Physical Examination Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Controversy References 49.1 Introduction Plantar heel pain is a common presenting condition. There are many causes of this malady, but one of the most common is plantar fasciitis. Unfortunately, plantar fasciitis is poorly understood and is frequently labeled and misdiagnosed as heel spur syndrome. Although heel spurs can occur with heel pain, recent research has found that they are not usually considered the cause. 19 The actual source of pain is still under debate. Some feel the pain is caused by trauma around the plantar calcaneal tuberosity from traction and shear forces from the plantar fascia, while others feel it is from a compressive neuropathy. Plantar fasciitis can be a painful and debilitating condition, which often frustrates not only the patient but also the treating physician because of its recalcitrant nature. The clinical presentation is well recognized, but there are no gold standard diagnostic tests to verify the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. Typical findings of the condition include: Pain and palpable tenderness in the area of the medial calcaneal tuberosity Significant start up pain when taking the first few steps in the morning Worsening pain with prolonged weight-bearing In a small proportion of patients, the pain can radiate to the medial border of the heel, which is thought to be attributed to entrapment of the medial calcaneal branch of the posterior tibial nerve. No universally accepted treatment algorithm exists for this condition, but fortunately more than 90% of cases resolve with non-surgical conservative care Anatomy 255 of 372
2 The plantar fascia is a multilayered, fibrous aponeurosis located at the sole of the foot that originates from the plantar aspect of the calcaneus. It spreads broadly from the central third of the foot at the medial tuberosity of the calcaneus, then divides into five digital bands at the metatarsalphalangeal joints. Each band inserts into the base of the proximal phalanges, and fibers merge with the dermis, transverse-metatarsal ligaments, and flexor tendon sheaths. Three distinct compartments of intrinsic plantar muscles are also formed through strong vertical septa that divide the medial, central, and lateral portions of the plantar fascia. The terminal branches of the posterior tibial nerve and artery and the medial calcaneal, medial plantar, and lateral plantar supply cutaneous branches through the plantar aponeurosis. The plantar fascia can be said to be an anatomic extension of the Achilles tendon. It is essentially an inelastic structure with minimal elongation. 8 During the toe-off phase of gait, the metatarsalphalangeal joints are dorsiflexed, which results in high tensile forces at the calcaneal origin of the plantar fascia. This has been referred to as the windlass effect of the plantar fascia. 14 The plantar heel fat pad is a complex structure of multiple fibrous septa enclosed by adipose tissue that function as a shock absorber. This protects the underlying bone and soft tissue structures even with the heel absorbing 110% of body weight at heel strike and up to 200% while running Clinical Presentation Obtaining a thorough history is extremely important in diagnosing plantar fasciitis and will often preclude the need for further imaging or diagnostic studies. A typical history of the condition begins with the patient describing the insidious onset of a sharp, stabbing inferior heel pain that localizes to the plantar medial aspect of the heel. The pain is at its greatest intensity when the patient takes the first few steps in the morning when arising from bed or from a chair after sitting for an extended period of time. The pain tends to lessen with activity, but worsens by the end of the day, especially after prolonged periods of weight-bearing. 10,22 The symptomatic patient will deny radiation of pain and will not usually have any associated parasthesia. Plantar fasciitis is primarily unilateral, accounting for 70% of all cases of the condition. 3 Bilateral heel pain however, in conjunction with multiple sites of enthesopathy and joint pain, suggests a systemic rheumatologic disorder. The patient population between the ages of 40 and 60 is at the highest risk, along with those who describe themselves as running athletes or have occupations that require them to engage in prolonged periods of standing. Sudden increases in activity or training should lead the clinician to further investigate the possibility of a calcaneal stress fracture. Infection or neoplasm are the most likely cause of plantar heel pain when described as unrelenting or nocturnal pain or when accompanied by constitutional symptoms such as unplanned weight loss, fevers or chills Pathogenesis 256 of 372
3 There is no widely accepted agreement as to the cause of plantar fasciitis, but mechanical derangements and restriction of motion are at the least contributory causes of both classic proximal fasciitis and the less-common distal plantar fasciitis. This is contrary to the popular belief that the presence of a heel spur is the causative factor in the development of plantar fasciitis. Recent studies, in fact, have suggested that only 50% of patients with heel pain will have heel spurs. 7 Further, cadaveric dissections have revealed the presence of the spur within the flexor digitorum brevis as well as the abductor hallucis, rather than the plantar fascia itself. 9 Thus, although heel spurs do indeed occur with heel pain, they are generally not considered the cause. The condition of plantar fasciitis denotes an inflammatory process, but histologic evidence is not in agreement with this notion. Findings demonstrate microtears in the fascia, myxoid degeneration, angiofibroblastic hyperplasia, and collagen necrosis. 13 Such changes would suggest a non-inflammatory state of degenerative fasciosis secondary to chronic repetitive microtrauma of the plantar fascia. An inflammatory model of the development of symptomatic plantar fasciitis does, however, gain support in the concept that the inflamed plantar fascia tightens when the patient is at rest, especially as the foot and ankle assume an equinus position at night. Upon ambulation, with the foot and ankle in a now neutral and dorsiflexed position, the tissue contracts, producing heel pain typically at the origin of the plantar fascia with the first few steps in the morning or after prolonged rest Physical Examination The foot and ankle physical exam should be thorough and include inspection of the patient s stance and gait. A pes planus or pes cavus foot deformity can increase loading through the plantar fascia. Obesity and limited ankle dorsiflexion are also risk factors for the development of the condition. A neurologic examination of the lower extremity and back should be done to explain paresthesias or abnormal sensation accompanying pain. The location of the pain is important in making the correct diagnosis. Pain associated with plantar fasciitis is most commonly linked with the origin of the plantar fascia in the area of the medial tubercle of the calcaneus. However, patients may experience pain more distal to the origin as the plantar fascia extends into the medial arch or branches into the five digital bands. Although possible, variations of the typical clinical finding of plantar medial heel pain should warrant further investigation of another diagnosis. Lastly, the diagnosis can be further identified through dorsiflexion of the toes, which typically exacerbates the pain in patients with symptomatic plantar fasciitis Imaging 257 of 372
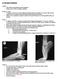
4 Imaging plays a limited role for the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis, as a thorough history and physical exam usually leads to the cause of the plantar heel pain. Although conventional radiographs are rarely needed for the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis, standing AP and lateral radiographs of the heel provide information about the osseous structures of the foot, as well as specific details of the calcaneus. A triple-phase bone scan may be warranted as an imaging study of choice when trying to differentiate plantar fasciitis from other plantar heel etiologies. This test can provide objective evidence of predictable increased uptake in the heel (medial calcaneal tubercle) that can differentiate the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis from calcaneal stress fracture. 17 Symptomatic improvement of the condition is also correlated with decrease in uptake over time. 18 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is seldom used for the confirmation of plantar fasciitis due to its low specificity. It will typically show increased signal intensity, thickening of the plantar fascia, and edema of surrounding structures. An MRI is useful, however, in excluding other causes of heel pain such as tumors and infection. 20 Ultrasound is less expensive than an MRI and has been shown to be equally as effective as using a triple-phase bone scan in the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. 12 Ultrasound is also very quick and provides no radiation exposure, but is unfortunately user dependent. Typical findings include a thickened, hypoechoic plantar fascia with soft-tissue edema. Laboratory, electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies can provide additional information for the clinician but are not routinely ordered. Laboratory studies are usually normal in the patient with plantar heel pain, but serum hematologic and immunologic testing can detect other systemic causes. HLA-B27, complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibodies, and uric acid can be considered in patients with bilateral or atypical heel pain. 8 EMG/NCV studies are effective in identifying a spinal radiculopathy, peripheral neuropathy as well as local nerve entrapment Conservative Treatment Non-surgical treatment is the mainstay of treating plantar fasciitis, with an array of conservative strategies available to treat the condition. Non-surgical treatment is very effective, at a reported success rate of 85-90%. 6,23 Common non-surgical treatments include: Achilles and plantar fascia stretching Activity modification Orthotic devices Short-term non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) therapy Night splint use Formal physical therapy Immobilization via cast or boot Steroid injections Extracorporeal shock wave therapy A daily home stretching program focusing on Achilles and plantar fascia stretching exercises and eccentric Achilles strengthening exercises should be the initial treatment offered for the patient with plantar fasciitis (Figures 1-4) The patient should also be advised to modify his/her activities and minimize overuse by cross-training and losing weight. 258 of 372
5 Figure 1. Gastroch stretch. Note that the back knee is straight and the back foot is internally rotated. Figure 2. Plantar fascia deep tissue massage Figure 3. Soleous stretch. Note that the back knee is bent and the back foot is internally rotated. 259 of 372
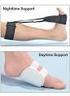
6 Figure 4. Step stretch Concurrent NSAID therapy is often appropriate as studies have shown successful outcomes with its use, 1 although no study has specifically examined the effectiveness of this treatment alone. Steroid injections are commonly given for the symptomatic patient; evidence shows that injections give temporary relief but provide minimal long-term beneficial effect in most patients. 15 In addition, complications of long-term use of steroid injections include plantar fascia rupture and fat pad atrophy, but these complications can be minimized by limited use and by placing the needle superior to the fascia on the medial side. Shoe inserts may also serve as an adjunctive therapy in helping to relieve symptomatic pain associated with plantar fasciitis. Orthotic devises such as a heel pad or cup, custom arch supports, and UCBL orthoses can optimize biomechanical loading of the foot and off-load the plantar fascia at its origin, as well as recreate the shape of the heel pad. Formal physical therapy can guide the patient with Achilles and plantar fascia stretching, as well as provide other therapies such as icing, heat, massage, iontophoresis, and taping. The use of a night splint offers symptomatic benefit and can alleviate morning start-up pain by managing fascia stretching during sleep. In the small percentage of patients with continued symptoms despite the therapies discussed above, casting and extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) can be beneficial. Application of a short leg walking cast or boot for 4-6 weeks may minimize repetitive microtrauma by unloading the heel and immobilizing the plantar fascia. The efficacy of immobilization in relieving plantar fasciitis has been supported in several retrospective studies. 4,10 ESWT is a new treatment for recalcitrant plantar fasciitis and is based on lithotripsy technology to utilize powerful shock waves in breaking up scar tissue to enable the inflamed fascia to heal. That being said, ESWT is indicated only after the failure of three conservative therapies as well as recalcitrant proximal plantar heel pain for at least 6 months. ESWT therapy is well tolerated by most patients but should not be a treatment choice for patients with coagulopathies, hemophilia, malignancy, or open physes Operative Treatment 260 of 372
7 All conservative options should be offered and tried for 6 months to 1 year before surgical intervention is considered. An open or endoscopic release of the plantar fascia remains a common method of surgical correction for patients with severe recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. Decompression of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve can be done along with partial plantar fascia release if suspicion of entrapment of the calcaneal branches of the tibial nerve exists. The success of partial plantar fascia release remains a topic of debate, as some studies show an acceptable success rate, 5,7 whereas others show a long-term patient satisfaction rate after plantar fasciotomy of less than 50%. 11 Because of the high incidence of lateral foot pain and detrimental effects to the stability of the arch, it is recommended that less than 40% of the plantar fascia be released. 2 Complications from release of the plantar fascia include prolonged healing and rehabilitation times, alteration of the biomechanics of the foot leading to a decrease in arch height, increased strain of the plantar ligaments cuboid attachment areas, and increased stress to the midfoot and metatarsal bones. Postoperatively, patients may experience acute plantar fasciitis, heel numbness, neuroma formation and infection. A new, less-invasive surgical technique has been described that utilizes bipolar radiofrequency microtenotomy (Topaz Procedure) to treat recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. 16 Studies indicate that the radiofrequency in wound healing could lead to increased angiogenesis. Patients have reported a rapid recovery with pain relief though 24 months. Unfortunately, this technique has not been subject to prospective, randomized trials and further studies need to be undertaken to solidify its efficacy Controversy Controversy surrounds the effectiveness of a new treatment technique of utilizing platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections to increase the concentration of growth factors at the site of injury and augment the natural healing process of chronic plantar fasciitis. The evidence for the use of this technique is limited; however, it does show compelling promise for clinical use if deemed successful by future clinical studies. Surgical intervention, especially endoscopic surgery, is also controversial due to the inherent risks of surgery as well as the relatively low long-term satisfaction rate of those that undergo this mode of treatment. This reality further necessitates the need to have the patient with plantar fasciitis undertake all non-surgical intervention for a period of 6 months to 1 year before entertaining the option of surgical correction References 1. Baxter DE, Pfeffer GB: Treatment of chronic heel pain by surgical release of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1992; 279: Berkowitz JF, Kier R, Rudicel S: Plantar fasciitis: MR imaging. Radiology 1991; 179: Buchbinder R: Clinical practice: Plantar fasciitis. N Engl J Med 2004;350: Chen HS, Chen LM, Huang TW: Treatment of painful heel syndrome with shock waves. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001; 387: Conflitti JM, Tarquinio TA: Operative outcome of partial plantar fasciectomy and neurolysis to the nerve of the abductor digiti minimi muscle for recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int 2004; 25: of 372
8 6. Crawford F, Atkins D, Young P, et al: Steroid injections for heel pain: Evidence of short-term effectiveness. A randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology 1999; 38: Davies MS, Weiss GA, Saxby TS: Plantar fasciitis: How successful is surgical intervention? Foot Ankle Int 1999; 20: Donley BG, Moore T, Sferra J, et al: The efficacy of oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAID) in the treatment of plantar fasciitis: A randomized, prospective, placebo controlled study. Foot Ankle Int 2007; 28: Forman WM, Green MA: The role of intrinsic musculature in the formation of inferior calcaneal exostoses. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 7(2): , Gill LH: Plantar fasciitis: Diagnosis and conservative treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 1997; 5: Hicks JH: The mechanics of the foot: II. The plantar aponeurosis and the arch. J Anat 1954; 88: Kenzora JE: The painful heel syndrome: An entrapment neuropathy. Bull Hosp J Dis Orthop Inst 47: , Landorf KB, Keenan A, Herbert RD: Effectiveness of foot orthoses to treat plantar fasciitis: A randomized trial. Arch Intern Med 2006; 166: Levy JC, Mizel MS, Clifford PD, et al: Value of radiographs in the initial evaluation of nontraumatic adult heel pain. Foot Ankle Int 2006; 27: Mizel MS, Marymont JV, Trepman E: Treatment of plantar fasciitis with a night splint and shoe modification consisting of a steel shank and anterior rocker bottom. Foot Ankle Int 16. Ogden JA, Alvarez R, Levitt R, et al: Shock wave therapy for chronic proximal plantar fasciitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001; 387: Saxena A, Fullem B: Plantar fascia ruptures in athletes. Am J Sports Med 2004; 32: Sewell JR, Black CM, Chapman AH, et al: Quantitative scintigraphy in diagnosis and management of plantar fasciitis (calcaneal periostitis): Concise communication. J Nucl Med 21(7): , Shmokler RL, Bravo AA, Lynch FR, et al: A new use of instrumentation in fluoroscopy controlled heel spur surgery. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 78: , Snook GA, Chrisman OD: The management of subcalcaneal pain. Clin Orthop 82: , Tisdel CL: Heel pain, in Orthopaedic Knowledge Update: Foot and Ankle 22. Vohra PK, Giorgini RJ, Sobel E, et al: Long-term follow-up of heel spur surgery: A 10-year retrospective study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 1999;89: Wolgin M, Cook C, Graham C, et al: Conservative treatment of plantar heel pain: Long-term follow-up. Foot Ankle Int 1994;15: of 372
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis. Heel Pain - common causes. Plantar Fasciitis 1/16/2012. Robert A Erdin III, MD
 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Using Might Splints in the Treatment
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain)
 Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN
 PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
How To Treat Heel Pain
 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Chapter 140 Heel Pain
 Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People
 The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Plantar Heel Pain. Papers. Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla
 Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla Abstract Plantar Heel pain is one of the most commonly encountered problems of foot pain in active adults over the age of 40. One in ten people will experience
Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla Abstract Plantar Heel pain is one of the most commonly encountered problems of foot pain in active adults over the age of 40. One in ten people will experience
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar fasciitis - suspected
 Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN. Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
Plantar Fasciitis: Nonsurgical & Surgical Options for Chronic Heel Pain. Mathew M. John, DPM, FACFAS Atlanta, GA
 Plantar Fasciitis: Nonsurgical & Surgical Options for Chronic Heel Pain Mathew M. John, DPM, FACFAS Atlanta, GA Heel Pain:Plantar fasciitis Over 2 million Americans suffer from heel pain Most common cause
Plantar Fasciitis: Nonsurgical & Surgical Options for Chronic Heel Pain Mathew M. John, DPM, FACFAS Atlanta, GA Heel Pain:Plantar fasciitis Over 2 million Americans suffer from heel pain Most common cause
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus)
 The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Key Contents. Learning Objectives. Indep Rev Oct-Dec 2013;15(10-12) 476-480. IR-276. Dr. Farhad Alam
 Indep Rev Oct-Dec 2013;15(10-12) IR-276 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Dr. Farhad Alam Key Contents Pathophysiology Causes and risk factor Diagnostic feature Treatment Options Prognosis and prevention Learning Objectives
Indep Rev Oct-Dec 2013;15(10-12) IR-276 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Dr. Farhad Alam Key Contents Pathophysiology Causes and risk factor Diagnostic feature Treatment Options Prognosis and prevention Learning Objectives
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study
 Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Plantar Fascitis
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE
 C H A P T E R 8 COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Heel pain is one of the most common disorders that foot and ankle surgeons treat. Investigators have stated
C H A P T E R 8 COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Heel pain is one of the most common disorders that foot and ankle surgeons treat. Investigators have stated
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Foot and Ankle Complaints
 Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Plantar fasciitis in a Professional Boxer:
 Plantar fasciitis in a Professional Boxer: Clinical Case Report for The Trevor Silver Memorial Essay Prize Gurjit Bhogal MBChB (Hons) MSc MRCGP July 2012 Total Word Count (excluding References) 2976 words
Plantar fasciitis in a Professional Boxer: Clinical Case Report for The Trevor Silver Memorial Essay Prize Gurjit Bhogal MBChB (Hons) MSc MRCGP July 2012 Total Word Count (excluding References) 2976 words
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults
 Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults AUTHOR TRACY ALDRIDGE, NAME, Location M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, Illinois Heel pain is a common condition in adults that may
Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults AUTHOR TRACY ALDRIDGE, NAME, Location M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, Illinois Heel pain is a common condition in adults that may
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol
 Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
.org. Rotator Cuff Tears. Anatomy. Description
 Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Platelet-Rich Plasma Rehabilitation Guidelines
 UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Platelet-Rich Plasma Rehabilitation Guidelines What is Tendinopathy? Tendons are strong bands of connective tissue comprised primarily of a substance called collagen. Mechanically,
UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Platelet-Rich Plasma Rehabilitation Guidelines What is Tendinopathy? Tendons are strong bands of connective tissue comprised primarily of a substance called collagen. Mechanically,
Plantar Fasciitis - Ayurvedic Strain
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: (diagnosis specific, impairment/ dysfunction specific) ICD9-728.71 plantar fibromatosis Plantar
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: (diagnosis specific, impairment/ dysfunction specific) ICD9-728.71 plantar fibromatosis Plantar
July 2012 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move
 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
By: Jerry Ryan, M.D., University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, Wisconsin
 UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME. Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4.
 OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
Chronic Low Back Pain
 Chronic Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What is Chronic Pain? Low back pain is considered to be chronic if it has been present for longer than three months. Chronic low
Chronic Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What is Chronic Pain? Low back pain is considered to be chronic if it has been present for longer than three months. Chronic low
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Common Foot Pathologies
 Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
New York State Workers' Comp Board. Mid and Lower Back Treatment Guidelines. Summary From 1st Edition, June 30, 2010. Effective December 1, 2010
 New York State Workers' Comp Board Mid and Lower Back Treatment Guidelines Summary From 1st Edition, June 30, 2010 Effective December 1, 2010 General Principles Treatment should be focused on restoring
New York State Workers' Comp Board Mid and Lower Back Treatment Guidelines Summary From 1st Edition, June 30, 2010 Effective December 1, 2010 General Principles Treatment should be focused on restoring
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC. Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program
 J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient
 C H A P T E R 4 5 MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient M. Jay Groves, IV, DPM Gastrosoleal equinus is a common deforming force on the foot and ankle.
C H A P T E R 4 5 MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient M. Jay Groves, IV, DPM Gastrosoleal equinus is a common deforming force on the foot and ankle.
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body. It attaches the calf muscles (soleus and gastrocnemius)
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body. It attaches the calf muscles (soleus and gastrocnemius)
