IP Telephony v1.0 Scope and Sequence. Cisco Networking Academy Program
|
|
|
- Berniece Gillian Osborne
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IP Telephony v1.0 Scope and Sequence Cisco Networking Academy Program
2 Table of Content COURSE OVERVIEW...4 Course Description...4 Course Objectives...4 Target Audience...5 Prerequisites...5 Lab Requirements...5 Certification Information...5 Course Duration...5 IP TELEPHONY V1.0 OUTLINES...6 IP Telephony Lab Outlines...6 Introduction to Packet Voice Technologies... 6 Introduction to VoIP... 6 Configuring Cisco CallManager Express... 6 Voice Dial Plans, Configuring Voice Interfaces and Dial Peers... 6 Configuring CME Additional Features... 6 VoIP Signaling and Call Control... 7 Improving and Maintaining Voice Quality... 7 Job Aids... 7 IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines...8 Introduction to Packet Voice Technologies... 8 Traditional Telephony... 8 Packetized Telephony Networks... 8 IP Telephony Applications... 8 Analog Voice Basics... 8 Analog-to-Digital Voice Encoding... 8 Signaling Systems... 9 Introduction to VoIP Requirements of Voice in an IP Internetwork Gateway and Their Roles Encapsulating Voice in IP Packets Calculating Bandwidth Requirements Configuring Cisco CallManager Express (CME) Overview of Cisco CME Differences between Traditional Telephony and VoIP Challenges and Solutions in VoIP Cisco CME Features and Functionality Cisco CME Network Parameters IP Phone Registration Ephone-dn and Ephone CallManager Express Files Initial Phone Setup Voice Dial Plans, Configuring Voice Interfaces and Dial Peers Call Establishment Principles Configuring Dial Peers Special-Purpose Connections Building a Scalable Numbering Plan Configuring Voice Ports Adjusting Voice Quality Analog and Digital Voice Interfaces Configuring Analog and Digital Voice Interfaces Dial Peers Call Setup and Digit Manipulation Class of Restriction Configuring CME Additional Features Cisco CME GUI Features Configuring Phone Features VoIP Signaling and Call Control Need for Signaling and Call Control Configuring H Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > Table of Content 2
3 Configuring MGCP Improving and Maintaining Voice Quality IP QoS Mechanisms Implementing AutoQoS Comparing Voice Quality Measurement Standards VoIP Challenges QoS and Good Design Jitter Delay Apply QoS in the Campus QoS Tools in the WAN Configuring QoS in the WAN Configuring CAC Voice Bandwidth Engineering Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > Table of Content 3
4 Course Overview IP Telephony is the most requested new course offering within the Academy community. To meet the demand, Cisco has created an R&D course built on suggestions from Academy Instructors. Course content will focus on lab activities surrounding voice and data convergence, but does NOT include traditional on-line curriculum or assessment. IP Telephony will focus on entry level skills required to implement IP Telephony in a SOHO environment. Course Description The Cisco IP Telephony version 1.0 course provides an introduction to converged voice and data networks as well as the challenges faced by its various technologies. The course presents Cisco solutions and implementation considerations to address those challenges. In this course, students will learn about Cisco CallManager Express (CME) architecture, components, functionality and features. They will also learn some Voice over IP (VoIP) and Quality of Service (QoS) technologies and apply them to Cisco CME environment. The focus of the course is: Course Objectives Call Manager Express (Windows-based call manager is not taught at this time) Connecting to a PSTN network Connecting from one router across a WAN to another router running CME Connecting from one CME enabled router to another CME enabled router Upon completing this course, the learner will be able to meet these overall objectives: Determine the relevant critical business and technical needs in order to develop a Cisco IP Telephony design framework in a SOHO environment, including the choice of signaling type and encoding methods. Select the appropriate hardware and software components to support a proposed SOHO IP telephony design Determine which high availability issues would influence the selection of network hardware and software for an SOHO environment. Design the appropriate dial plan to support SOHO design requirements Describe the similarities and differences between PSTN and VoIP including call transport, call signaling and bandwidth requirements Describe the technologies used in Voice over IP and how they differ from PSTN technologies. Determine how PSTN connectivity issues influence SOHO hardware and software selection. Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > Course Overview 4
5 Target Audience Understand and be able to configure various connection types to the PSTN. Explain the benefits of hierarchical and scalable dial and numbering plans Install an IP Telephony solution in a SOHO environment using CME Configure Cisco Call Manager Express to support IP Phones Secure an IP Communications network Describe effective troubleshooting methods to resolve issues in SOHO IP Telephony networks Use appropriate troubleshooting methods to determine and solve QoS issues in an SOHO IP Telephony networks The target audience is individuals desiring to continue their post-ccna preparation in designing, maintaining and troubleshooting an SMB IP telephony network. Prerequisites Prior to taking this course, students should have completed CCNA 1 through 4 or the equivalent. The following prerequisites are beneficial, but not required: CCNA certification Work experience Lab Requirements Please refer to the IP Telephony Equipment Bundle Spreadsheets on Cisco Academy Connection (CAC). Certification Information IP Telephony version 1.0 does not align to any one Cisco certification. Course Duration The course is designed to be delivered in a 40 contact hour time frame. Approximately 30 hours will be devoted to lab activities and a hands-on skills exam and 10 hours will be spent on curriculum content. Case studies on IP telephony are recommended, but format and timing are to be determined by the Local Academy. Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > Course Overview 5
6 IP Telephony v1.0 Outlines IP Telephony Lab Outlines Introduction to Packet Voice Technologies There is no lab in this module. Introduction to VoIP Basic Setup for the CME Router with Switch Module Basic Setup for the CME Router and Switch Installing Cisco CME Software Connecting the IP Phone to a Switch Resetting a 7900 Series Cisco IP Phone to Factory Defaults Configuring Cisco CallManager Express CME Automated Phone Setup CME Manual Phone Setup CME Partially Automated Phone Setup Voice Dial Plans, Configuring Voice Interfaces and Dial Peers Configuring a FXS Port Configuring a FXO Port Configuring PRI Interface and DID Configuring VoIP Dial-Peers Across a WAN Link Configuring Class of Restriction Configuring CME Additional Features Configure GUI for System Administrator Configure GUI for Customer Administrator Configure GUI for Phone User Configuring Call Transfer and Call Forwarding Configuring Call Park Customize the IP Phone Display Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Lab Outlines 6
7 Configure the Intercom Feature Configuring a Dialable Intercom Configure Paging Group VoIP Signaling and Call Control There is no lab in this module. Improving and Maintaining Voice Quality Configuring AutoQoS Job Aids Table 1 IP Telephony Addressing Scheme Table 2 IP Telephony Dial Plan TCP and UDP Port Numbers Adtran Atlas 550 Configuration Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Lab Outlines 7
8 IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines Introduction to Packet Voice Technologies Traditional Telephony Basic Components of a Telephony Network CO Switches Private Switching Systems Call Signaling Multiplexing Techniques Packetized Telephony Networks Benefits of Packet Telephony Networks Call Control Distributed vs. Centralized Call Control Packet Telephony Components Best-Effort Delivery of Real-Time Traffic IP Telephony Applications Analog Interfaces Digital Interfaces IP Phones Analog Voice Basics Local-Loop Connections Types of Local-Loop Signaling Supervisory Signaling Address Signaling Informational Signaling Trunk Connections Types of Trunk Signaling E&M Signaling Types Trunk Signal Types Used by E&M Line Quality Management of Echo Analog-to-Digital Voice Encoding Basic Voice Encoding: Converting Analog to Digital Basic Voice Encoding: Converting Digital to Analog Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 8
9 The Nyquist Theorem Voice Compression and Codec Standards Compression Bandwidth Requirements Voice Quality Measurement Signaling Systems CAS Systems: T1 CAS Systems: E1 CCS Systems ISDN Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 9
10 Introduction to VoIP Requirements of Voice in an IP Internetwork Real-Time Voice in a Best-Effort IP Internetwork Packet Loss, Delay, and Jitter Consistent Throughput Reordering of Voice Packets Reliability and Availability Gateway and Their Roles Understanding Gateways Guidelines for Selecting the Correct Gateway Determining Gateway Interconnection Requirements in an Enterprise Environment, Central and Remote Site Determining Gateway Interconnection Requirements in a Service Provider Environment Encapsulating Voice in IP Packets Major VoIP Protocols RTP and RTCP Reducing Header Overhead with CRTP When to Use RTP Header Compression Calculating Bandwidth Requirements Codec Bandwidths Impact of Voice Samples and Packet Size on Bandwidth Data Link Overhead Security and Tunneling Overhead Specialized Encapsulations Calculating the Total Bandwidth for a VoIP Call Effects of VAD on Bandwidth Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 10
11 Configuring Cisco CallManager Express (CME) Overview of Cisco CME What is Cisco CallManager Express? How Does Cisco CallManager Express Work? Licensing Differences between Traditional Telephony and VoIP Traditional Telephony PCM Theory Basic Voice Encoding: Converting Digital to Analog PCM Theory Coder-Decoder Encapsulating Voice in IP Packets Challenges and Solutions in VoIP Challenges in VoIP Bandwidth Requirements in VoIP Cisco CME Features and Functionality Supported Protocols and Integration Options Cisco CallManager Express Requirements Cisco CallManager Express Restrictions Cisco CME Network Parameters Auxiliary VLANs Configuring Auxiliary VLANs DHCP Service Setup IP Phone Registration Files IP Phone Information Download and Registration Ephone-dn and Ephone Ephone-dn Ephone Type of Ephone-dns Number of Ephone-dns Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 11
12 CallManager Express Files Cisco CME File Bundled Cisco CME File Individual Cisco CME Files GUI Files Cisco CME - TAPI Integration Additional Files Initial Phone Setup Setting Up Phones in a Cisco CME System Automated Phone Setup Partially Automated Phone Setup Manual Phone Setup Setup Tips Optional Parameters Router Configuration: Two Commands Optional Parameters Locale Parameters Rebooting Cisco CallManager Express Phones Setup Troubleshooting Verifying Cisco CallManager Express Phone Configuration Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 12
13 Voice Dial Plans, Configuring Voice Interfaces and Dial Peers Call Establishment Principles What Are Call Legs? End-to-End Calls Configuring Dial Peers Understanding Dial Peers Configuring POTS Dial Peers Configuring VoIP Dial Peers Configuring Destination-Pattern Options Default Dial Peer Matching Inbound Dial Peers Matching Outbound Dial Peers Hunt-Group Commands Configuring Hunt Groups Digit Collection and Consumption Understanding Digit Manipulation Practice Item Answer Key Special-Purpose Connections Connection Commands PLAR and PLAR-OPX Configuring Trunk Connections Tie-Line Connections Building a Scalable Numbering Plan Scalable Numbering Plan Scalable Numbering Plan Attributes Hierarchical Numbering Plans Internal Numbering and Public Numbering Plan Integration Enhancing and Extending an Existing Plan to Accommodate VoIP Configuring Voice Ports Voice Port Applications FXS Ports FXO Ports E&M Ports Timers and Timing Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 13
14 Digital Voice Ports ISDN CCS Options Monitoring and Troubleshooting Adjusting Voice Quality Electrical Characteristics Voice Quality Tuning Echo Cancellation Commands Analog and Digital Voice Interfaces Local-Loop Connections Analog Voice Interfaces Channel Associated Signaling Systems: T1 Channel Associated Signaling Systems: E1 Common Channel Signaling Systems PRI/BRI Configuring Analog and Digital Voice Interfaces Foreign Exchange Station Ports (FXS) Foreign Exchange Office Ports (FXO) Ear and Mouth Ports (E&M) Common Channel Signaling (CCS): ISDN BRI Timers and Timing Digital Voice Ports Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) Common Channel Signaling (CCS): ISDN Primary Rate Interface (PRI) Dial Peers What is Dial Peer? Plain Old Telephone Service Dial Peers VoIP Dial Peers Destination-Pattern Options What is the Default Dial Peer? Call Setup and Digit Manipulation End-to-End Calls Matching Inbound Dial Peers Matching Outbound Dial Peers Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 14
15 Digit Collection and Consumption What Is Digit Manipulation? PLAR Class of Restriction Class of Restriction (COR) Steps to Configure Class of Restriction Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 15
16 Configuring CME Additional Features Cisco CME GUI Features User Classes Cisco CallManager Express GUI Prerequisites Accessing the GUI Configuring Administrative User Classes Configuring Phone Features Call Transfer Call Forwarding IP Phone Display Calling and Directory Features Productivity Tools Custom IP Phone Rings Music on Hold Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 16
17 VoIP Signaling and Call Control Need for Signaling and Call Control VoIP Signaling Call Control Models Translation between Signaling and Call Control Models Call Setup Call Administration and Accounting Call Status and Call Detail Records Address Management Admission Control Centralized Call Control Distributed Call Control Centralized Call Control vs. Distributed Call Control Configuring H.323 H.323 and Associated Recommendations Functional Components of H.323 H.323 Call Establishment and Maintenance Call Flows without a Gatekeeper Call Flows with a Gatekeeper Multipoint Conferences Call Flows with Multiple Gatekeepers Survivability Strategies H.323 Proxy Server Cisco Implementation of H.323 Configuring H.323 Gateways Configuring H.323 Gatekeepers Monitoring and Troubleshooting Configuring MGCP MGCP and Its Associated Standards Basic MGCP Components MGCP Endpoints MGCP Gateways MGCP Call Agents Basic MGCP Concepts Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 17
18 MGCP Calls and Connections MGCP Events and Signals MGCP Packages MGCP Digit Maps MGCP Control Commands Call Flows Survivability Strategies Cisco Implementation of MGCP Understanding Basics of Cisco CallManager Configuring MGCP Monitoring and Troubleshooting MGCP Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 18
19 Improving and Maintaining Voice Quality IP QoS Mechanisms QoS Mechanisms Classification Marking Trust Boundaries Congestion Management Traffic Shaping Compression Link Fragmentation and Interleaving Implementing AutoQoS AutoQoS AutoQoS: Router Platforms AutoQoS: Switch Platforms AutoQoS Prerequisites Configuring AutoQoS Monitoring AutoQoS Automation with Cisco AutoQoS Comparing Voice Quality Measurement Standards Audio Clarity VoIP Challenges IP Networking Overview Jitter Delay QoS and Good Design Need for QoS Mechanisms Objectives of QoS Applying QoS for End-to-End Improvement of Voice Quality Jitter Understanding Jitter Overcoming Jitter Adjusting Playout Delay Parameters Symptoms of Jitter on a Network Dynamic Jitter Buffer Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 19
20 Static Jitter Buffer Delay Need for a Delay Budget Guidelines for Acceptable Delay Sources of Delay Effects of Coders and Voice Sampling on Delay Managing Serialization Delay Managing Queuing Delay Verifying End-to-End Delay Apply QoS in the Campus Need for QoS in the Campus Marking Control and Management Traffic QoS Tools in the WAN Need for QoS on WAN Links Recommendations for Generic QoS in the WAN Bandwidth Provisioning Optimized Queuing Link Efficiency Link Fragmentation and Interleaving CAC Configuring QoS in the WAN Configuring AutoQoS Configuring CAC Need for CAC CAC as Part of Call Control Services RSVP Understanding CAC Tools H.323 CAC Voice Bandwidth Engineering Erlangs Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. Scope and Sequence > IP Telephony Content Resource Outlines 20
Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS
 Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS Course CVOICE v8.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS (CVOICE) v8.0 teaches learners about voice
Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS Course CVOICE v8.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS (CVOICE) v8.0 teaches learners about voice
CVOICE - Cisco Voice Over IP
 CVOICE - Cisco Voice Over IP Table of Contents Introduction Audience At Course Completion Prerequisites Applicable Products Program Contents Course Outline Introduction This five-day course covers the
CVOICE - Cisco Voice Over IP Table of Contents Introduction Audience At Course Completion Prerequisites Applicable Products Program Contents Course Outline Introduction This five-day course covers the
640-460 - Implementing Cisco IOS Unified Communications (IIUC)
 640-460 - Implementing Cisco IOS Unified Communications (IIUC) Course Introduction Course Introduction Module 1 - Cisco Unified Communications System Introduction Cisco Unified Communications System Introduction
640-460 - Implementing Cisco IOS Unified Communications (IIUC) Course Introduction Course Introduction Module 1 - Cisco Unified Communications System Introduction Cisco Unified Communications System Introduction
IMPLEMENTING CISCO VOICE COMMUNICATIONS AND QOS Volume 1
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO VOICE COMMUNICATIONS AND QOS Volume 1 Course Introduction Overview Learner Skills and Knowledge Course Goal and Course Flow Additional References Cisco Glossary of Terms Your Training
IMPLEMENTING CISCO VOICE COMMUNICATIONS AND QOS Volume 1 Course Introduction Overview Learner Skills and Knowledge Course Goal and Course Flow Additional References Cisco Glossary of Terms Your Training
CCNP: Optimizing Converged Networks
 CCNP: Optimizing Converged Networks Cisco Networking Academy Program Version 5.0 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for noncommercial
CCNP: Optimizing Converged Networks Cisco Networking Academy Program Version 5.0 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for noncommercial
Introduction to Packet Voice Technologies and VoIP
 Introduction to Packet Voice Technologies and VoIP Cisco Networking Academy Program Halmstad University Olga Torstensson 035-167575 [email protected] IP Telephony 1 Traditional Telephony 2 Basic
Introduction to Packet Voice Technologies and VoIP Cisco Networking Academy Program Halmstad University Olga Torstensson 035-167575 [email protected] IP Telephony 1 Traditional Telephony 2 Basic
CVOICE Exam Topics Cisco Voice over IP Exam #642-432 7/14/2005
 CVOICE Exam Topics Cisco Voice over IP Exam #642-432 7/14/2005 From the Cisco CVOICE 642-432 Exam Topics Voice over IP Technologies Describe the similarities and differences between PSTN and VoIP including
CVOICE Exam Topics Cisco Voice over IP Exam #642-432 7/14/2005 From the Cisco CVOICE 642-432 Exam Topics Voice over IP Technologies Describe the similarities and differences between PSTN and VoIP including
Implementing Cisco IOS Telephony and Unified Communications Express (IITUCX)
 Implementing Cisco IOS Telephony and Unified Communications Express (IITUCX) Who should attend The primary audience for this course is as follows: Network administrators Network engineers Systems engineers
Implementing Cisco IOS Telephony and Unified Communications Express (IITUCX) Who should attend The primary audience for this course is as follows: Network administrators Network engineers Systems engineers
Implementing Cisco IOS Telephony and Unified Communications Express (IITUCX)
 Implementing Cisco IOS Telephony and Unified Communications Express (IITUCX) Course Objectives Explain the benefits and components of a Cisco Unified Communications system Describe how traditional telephony
Implementing Cisco IOS Telephony and Unified Communications Express (IITUCX) Course Objectives Explain the benefits and components of a Cisco Unified Communications system Describe how traditional telephony
Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT)
 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Module 2: Cisco VoIP Implementations (Deploy) Calculating Bandwidth Requirements for VoIP Objectives Describe factors influencing encapsulation overhead and bandwidth
Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Module 2: Cisco VoIP Implementations (Deploy) Calculating Bandwidth Requirements for VoIP Objectives Describe factors influencing encapsulation overhead and bandwidth
Voice Dial Plans, Configuring Voice Interfaces and Dial Peers
 Voice Dial Plans, Configuring Voice Interfaces and Dial Peers Cisco Networking Academy Program 1 Call Establishment Principles 2 Dial-Peer Call Legs 3 End-to-End Calls 4 Configuring Dial Peers 5 Understanding
Voice Dial Plans, Configuring Voice Interfaces and Dial Peers Cisco Networking Academy Program 1 Call Establishment Principles 2 Dial-Peer Call Legs 3 End-to-End Calls 4 Configuring Dial Peers 5 Understanding
IMPLEMENTING CISCO IOS TELEPHONY AND UNIFIED COMMUNICATIONS EXPRESS (IITUCX)
 Temario IMPLEMENTING CISCO IOS TELEPHONY AND UNIFIED COMMUNICATIONS EXPRESS (IITUCX) This course is designed to be the primary training for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express and Cisco Unity
Temario IMPLEMENTING CISCO IOS TELEPHONY AND UNIFIED COMMUNICATIONS EXPRESS (IITUCX) This course is designed to be the primary training for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express and Cisco Unity
Need for Signaling and Call Control
 Need for Signaling and Call Control VoIP Signaling In a traditional voice network, call establishment, progress, and termination are managed by interpreting and propagating signals. Transporting voice
Need for Signaling and Call Control VoIP Signaling In a traditional voice network, call establishment, progress, and termination are managed by interpreting and propagating signals. Transporting voice
- Basic Voice over IP -
 1 Voice over IP (VoIP) - Basic Voice over IP - Voice over IP (VoIP) is a digital form of transport for voice transmissions, replacing analog phone systems. The benefits of VoIP are considerable: Better
1 Voice over IP (VoIP) - Basic Voice over IP - Voice over IP (VoIP) is a digital form of transport for voice transmissions, replacing analog phone systems. The benefits of VoIP are considerable: Better
"Charting the Course... Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 v1.0 ( CIPTV1 ) Course Summary
 Description Course Summary Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day course that prepares the learner for implementing a Cisco Collaboration solution at a single-site
Description Course Summary Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day course that prepares the learner for implementing a Cisco Collaboration solution at a single-site
642-436 Q&A. DEMO Version
 Cisco Voice over IP (CVOICE) Q&A DEMO Version Copyright (c) 2010 Chinatag LLC. All rights reserved. Important Note Please Read Carefully For demonstration purpose only, this free version Chinatag study
Cisco Voice over IP (CVOICE) Q&A DEMO Version Copyright (c) 2010 Chinatag LLC. All rights reserved. Important Note Please Read Carefully For demonstration purpose only, this free version Chinatag study
This topic describes dial peers and their applications.
 Dial Peers What is Dial Peer? This topic describes dial peers and their applications. What is a Dial Peer? A dial peer is an addressable call endpoint. Dial peers establish logical connections, called
Dial Peers What is Dial Peer? This topic describes dial peers and their applications. What is a Dial Peer? A dial peer is an addressable call endpoint. Dial peers establish logical connections, called
Cisco Networks (ONT) 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) reserved. Lesson 2.4: Calculating Bandwidth Requirements for VoIP reserved. Objectives Describe factors influencing encapsulation overhead and bandwidth requirements
Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) reserved. Lesson 2.4: Calculating Bandwidth Requirements for VoIP reserved. Objectives Describe factors influencing encapsulation overhead and bandwidth requirements
Voice over IP Fundamentals
 Voice over IP Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days Course Code: GK3277 Overview: The aim of this course is for delegates to gain essential data networking and Voice over IP (VoIP) knowledge in a single, week-long
Voice over IP Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days Course Code: GK3277 Overview: The aim of this course is for delegates to gain essential data networking and Voice over IP (VoIP) knowledge in a single, week-long
Gateways and Their Roles
 Gateways and Their Roles Understanding Gateways This topic describes the role of voice gateways and their application when connecting VoIP to traditional PSTN and telephony equipment. Analog vs. Digital
Gateways and Their Roles Understanding Gateways This topic describes the role of voice gateways and their application when connecting VoIP to traditional PSTN and telephony equipment. Analog vs. Digital
Version dated 25/11/2014. 1.Course Title. NATO Voice over IP Foundation Course. 2.Identification Number (ID) 3. Purpose of the Course
 1.Course Title Version dated 25/11/2014 NATO Voice over IP Foundation Course 2.Identification Number (ID) 095 3. Purpose of the Course There are a number of new technologies (to NATO) that are encompassed
1.Course Title Version dated 25/11/2014 NATO Voice over IP Foundation Course 2.Identification Number (ID) 095 3. Purpose of the Course There are a number of new technologies (to NATO) that are encompassed
Encapsulating Voice in IP Packets
 Encapsulating Voice in IP Packets Major VoIP Protocols This topic defines the major VoIP protocols and matches them with the seven layers of the OSI model. Major VoIP Protocols 15 The major VoIP protocols
Encapsulating Voice in IP Packets Major VoIP Protocols This topic defines the major VoIP protocols and matches them with the seven layers of the OSI model. Major VoIP Protocols 15 The major VoIP protocols
Cisco CCNP 642 845 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT)
 Cisco CCNP 642 845 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Course Number: 642 845 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: Cisco CCNP Exam 642 845:
Cisco CCNP 642 845 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Course Number: 642 845 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: Cisco CCNP Exam 642 845:
640-461: Introducing Cisco Voice and Unified Communications Administration (ICOMM) v8.0 Course Introduction
 640-461: Introducing Cisco Voice and Unified Communications Administration (ICOMM) v8.0 Course Introduction Course Introduction Module 01 - Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Solutions Understanding
640-461: Introducing Cisco Voice and Unified Communications Administration (ICOMM) v8.0 Course Introduction Course Introduction Module 01 - Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Solutions Understanding
Introducing Cisco Voice and Unified Communications Administration Volume 1
 Introducing Cisco Voice and Unified Communications Administration Volume 1 Course Introduction Overview Learner Skills and Knowledge Course Goal and Course Flow Additional Cisco Glossary of Terms Your
Introducing Cisco Voice and Unified Communications Administration Volume 1 Course Introduction Overview Learner Skills and Knowledge Course Goal and Course Flow Additional Cisco Glossary of Terms Your
Requirements of Voice in an IP Internetwork
 Requirements of Voice in an IP Internetwork Real-Time Voice in a Best-Effort IP Internetwork This topic lists problems associated with implementation of real-time voice traffic in a best-effort IP internetwork.
Requirements of Voice in an IP Internetwork Real-Time Voice in a Best-Effort IP Internetwork This topic lists problems associated with implementation of real-time voice traffic in a best-effort IP internetwork.
Table of Contents. Cisco Mapping Outbound VoIP Calls to Specific Digital Voice Ports
 Table of Contents Mapping Outbound VoIP Calls to Specific Digital Voice Ports...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 Configure...2 Network Diagram...2
Table of Contents Mapping Outbound VoIP Calls to Specific Digital Voice Ports...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 Configure...2 Network Diagram...2
Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 CIPTV1 v1.0; 5 Days; Instructor-led
 Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 CIPTV1 v1.0; 5 Days; Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day course that prepares the
Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 CIPTV1 v1.0; 5 Days; Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day course that prepares the
Dial Peer. Example: Dial-Peer Configuration
 Configuring Dial Peers Understanding Dial Peers This topic describes dial peers and their applications. Understanding Dial Peers A dial peer is an addressable call endpoint. Dial peers establish logical
Configuring Dial Peers Understanding Dial Peers This topic describes dial peers and their applications. Understanding Dial Peers A dial peer is an addressable call endpoint. Dial peers establish logical
Clearing the Way for VoIP
 Gen2 Ventures White Paper Clearing the Way for VoIP An Alternative to Expensive WAN Upgrades Executive Overview Enterprises have traditionally maintained separate networks for their voice and data traffic.
Gen2 Ventures White Paper Clearing the Way for VoIP An Alternative to Expensive WAN Upgrades Executive Overview Enterprises have traditionally maintained separate networks for their voice and data traffic.
Cisco CME Features and Functionality
 Cisco CME Features and Functionality Supported Protocols and Integration Options This topic describes the supported protocols and integration options of Cisco CME. Supported Protocols and Integration FAX
Cisco CME Features and Functionality Supported Protocols and Integration Options This topic describes the supported protocols and integration options of Cisco CME. Supported Protocols and Integration FAX
How To Use Cisco Cucm For A Test Drive
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP TELEPHONY & VIDEO, PART 1 V1.0 (CIPTV1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day course that prepares the learner for implementing
IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP TELEPHONY & VIDEO, PART 1 V1.0 (CIPTV1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day course that prepares the learner for implementing
Special-Purpose Connections
 Special-Purpose Connections Connection Commands This topic identifies different special-purpose connection commands. Special-Purpose Connection Commands connection plar Associates a voice port directly
Special-Purpose Connections Connection Commands This topic identifies different special-purpose connection commands. Special-Purpose Connection Commands connection plar Associates a voice port directly
Packetized Telephony Networks
 Packetized Telephony Networks Benefits of Packet Telephony Networks Traditionally, the potential savings on long-distance costs was the driving force behind the migration to converged voice and data networks.
Packetized Telephony Networks Benefits of Packet Telephony Networks Traditionally, the potential savings on long-distance costs was the driving force behind the migration to converged voice and data networks.
Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1
 Course Code: CI-CIPTV1 Vendor: Cisco Course Overview Duration: 5 RRP: 2,320 Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 Overview Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day
Course Code: CI-CIPTV1 Vendor: Cisco Course Overview Duration: 5 RRP: 2,320 Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 Overview Implementing Cisco IP Telephony & Video, Part 1 (CIPTV1) v1.0 is a five-day
Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices CICD v1.0; 5 Days; Instructor-led
 Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices CICD v1.0; 5 Days; Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices (CICD v1.0) is an extended hours 5-day course focusing on providing
Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices CICD v1.0; 5 Days; Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices (CICD v1.0) is an extended hours 5-day course focusing on providing
Curso de Telefonía IP para el MTC. Sesión 1 Introducción. Mg. Antonio Ocampo Zúñiga
 Curso de Telefonía IP para el MTC Sesión 1 Introducción Mg. Antonio Ocampo Zúñiga Conceptos Generales VoIP Essentials Family of technologies Carries voice calls over an IP network VoIP services convert
Curso de Telefonía IP para el MTC Sesión 1 Introducción Mg. Antonio Ocampo Zúñiga Conceptos Generales VoIP Essentials Family of technologies Carries voice calls over an IP network VoIP services convert
VoIP Bandwidth Considerations - design decisions
 VoIP Bandwidth Considerations - design decisions When calculating the bandwidth requirements for a VoIP implementation the two main protocols are: a signalling protocol such as SIP, H.323, SCCP, IAX or
VoIP Bandwidth Considerations - design decisions When calculating the bandwidth requirements for a VoIP implementation the two main protocols are: a signalling protocol such as SIP, H.323, SCCP, IAX or
Network administrators must be aware that delay exists, and then design their network to bring end-to-end delay within acceptable limits.
 Delay Need for a Delay Budget The end-to-end delay in a VoIP network is known as the delay budget. Network administrators must design a network to operate within an acceptable delay budget. This topic
Delay Need for a Delay Budget The end-to-end delay in a VoIP network is known as the delay budget. Network administrators must design a network to operate within an acceptable delay budget. This topic
Convergence Technologies Professional (CTP) Course 1: Data Networking
 Convergence Technologies Professional (CTP) Course 1: Data Networking The Data Networking course teaches you the fundamentals of networking. Through hands-on training, you will learn the vendor-independent
Convergence Technologies Professional (CTP) Course 1: Data Networking The Data Networking course teaches you the fundamentals of networking. Through hands-on training, you will learn the vendor-independent
Cisco Unified Communications IP Telephony Part 1 (CIPT1) v8.0. Course Objectives. Associated Certification. Required Exam(s) Price.
 Cisco Unified Communications IP Telephony Part 1 (CIPT1) v8.0 Implementing Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Part 1 (CIPT1) v8.0 prepares you for implementing a Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Cisco Unified Communications IP Telephony Part 1 (CIPT1) v8.0 Implementing Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Part 1 (CIPT1) v8.0 prepares you for implementing a Cisco Unified Communications Manager
VoIP Configuration Examples
 APPENDIX C This section uses four different scenarios to demonstrate how to configure Voice over IP (VoIP). The actual VoIP configuration procedure depends on the topology of your voice network. The following
APPENDIX C This section uses four different scenarios to demonstrate how to configure Voice over IP (VoIP). The actual VoIP configuration procedure depends on the topology of your voice network. The following
Voice Over IP Per Call Bandwidth Consumption
 Over IP Per Call Bandwidth Consumption Interactive: This document offers customized voice bandwidth calculations with the TAC Bandwidth Calculator ( registered customers only) tool. Introduction Before
Over IP Per Call Bandwidth Consumption Interactive: This document offers customized voice bandwidth calculations with the TAC Bandwidth Calculator ( registered customers only) tool. Introduction Before
642-437- Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS
 Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS Duration: 5 Days Course Code: CVOICE Version: 8 Overview: This course will provide delegates with knowledge of voice gateways, the characteristics of VoIP
Implementing Cisco Voice Communications and QoS Duration: 5 Days Course Code: CVOICE Version: 8 Overview: This course will provide delegates with knowledge of voice gateways, the characteristics of VoIP
Implementing Cisco Quality of Service QOS v2.5; 5 days, Instructor-led
 Implementing Cisco Quality of Service QOS v2.5; 5 days, Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements,
Implementing Cisco Quality of Service QOS v2.5; 5 days, Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements,
The Basics. Configuring Campus Switches to Support Voice
 Configuring Campus Switches to Support Voice BCMSN Module 7 1 The Basics VoIP is a technology that digitizes sound, divides that sound into packets, and transmits those packets over an IP network. VoIP
Configuring Campus Switches to Support Voice BCMSN Module 7 1 The Basics VoIP is a technology that digitizes sound, divides that sound into packets, and transmits those packets over an IP network. VoIP
Operation Manual Voice Overview (Voice Volume) Table of Contents
 Operation Manual Voice Over (Voice Volume) Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Voice Over... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to VoIP... 1-1 1.1.1 VoIP System... 1-1 1.1.2 Basic VoIP Call Flow... 1-2 1.1.3
Operation Manual Voice Over (Voice Volume) Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Voice Over... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to VoIP... 1-1 1.1.1 VoIP System... 1-1 1.1.2 Basic VoIP Call Flow... 1-2 1.1.3
640-460. IIUC Implementing Cisco IOS Unified Communications (IIUC) Version: Demo. Page <<1/9>>
 640-460 IIUC Implementing Cisco IOS Unified Communications (IIUC) Version: Demo Page 1. You are CCNA VOICE associate in XXXX.com. You need configure a voice port that will allow the gateway to
640-460 IIUC Implementing Cisco IOS Unified Communications (IIUC) Version: Demo Page 1. You are CCNA VOICE associate in XXXX.com. You need configure a voice port that will allow the gateway to
Challenges and Solutions in VoIP
 Challenges and Solutions in VoIP Challenges in VoIP The traditional telephony network strives to provide 99.99 percent uptime to the user. This corresponds to 5.25 minutes per year of down time. Many data
Challenges and Solutions in VoIP Challenges in VoIP The traditional telephony network strives to provide 99.99 percent uptime to the user. This corresponds to 5.25 minutes per year of down time. Many data
IP Telephony Deployment Models
 CHAPTER 2 Sections in this chapter address the following topics: Single Site, page 2-1 Multisite Implementation with Distributed Call Processing, page 2-3 Design Considerations for Section 508 Conformance,
CHAPTER 2 Sections in this chapter address the following topics: Single Site, page 2-1 Multisite Implementation with Distributed Call Processing, page 2-3 Design Considerations for Section 508 Conformance,
GW400 VoIP Gateway. User s Guide
 GW400 VoIP Gateway User s Guide P/N: 956YD30001 Copyright 2006. All Rights Reserved. Document Version: 1.0 All trademarks and trade names are the properties of their respective owners. i Table of Contents
GW400 VoIP Gateway User s Guide P/N: 956YD30001 Copyright 2006. All Rights Reserved. Document Version: 1.0 All trademarks and trade names are the properties of their respective owners. i Table of Contents
Curso de Telefonía IP para el MTC. Sesión 2 Requerimientos principales. Mg. Antonio Ocampo Zúñiga
 Curso de Telefonía IP para el MTC Sesión 2 Requerimientos principales Mg. Antonio Ocampo Zúñiga Factors Affecting Audio Clarity Fidelity: Audio accuracy or quality Echo: Usually due to impedance mismatch
Curso de Telefonía IP para el MTC Sesión 2 Requerimientos principales Mg. Antonio Ocampo Zúñiga Factors Affecting Audio Clarity Fidelity: Audio accuracy or quality Echo: Usually due to impedance mismatch
"Charting the Course... ... to Your Success!" QOS - Implementing Cisco Quality of Service 2.5 Course Summary
 Course Summary Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such as best effort, IntServ, and DiffServ,
Course Summary Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such as best effort, IntServ, and DiffServ,
Hands on VoIP. Content. Tel +44 (0) 845 057 0176 [email protected]. Introduction
 Introduction This 4-day course offers a practical introduction to 'hands on' VoIP engineering. Voice over IP promises to reduce your telephony costs and provides unique opportunities for integrating voice
Introduction This 4-day course offers a practical introduction to 'hands on' VoIP engineering. Voice over IP promises to reduce your telephony costs and provides unique opportunities for integrating voice
EarthLink Business SIP Trunking. NEC SV8300 IP PBX Customer Configuration Guide
 EarthLink Business SIP Trunking NEC SV8300 IP PBX Customer Configuration Guide Publication History First Release: Version 1.0 May 18, 2012 CHANGE HISTORY Version Date Change Details Changed By 1.0 5/18/2012
EarthLink Business SIP Trunking NEC SV8300 IP PBX Customer Configuration Guide Publication History First Release: Version 1.0 May 18, 2012 CHANGE HISTORY Version Date Change Details Changed By 1.0 5/18/2012
Indepth Voice over IP and SIP Networking Course
 Introduction SIP is fast becoming the Voice over IP protocol of choice. During this 3-day course delegates will examine SIP technology and architecture and learn how a functioning VoIP service can be established.
Introduction SIP is fast becoming the Voice over IP protocol of choice. During this 3-day course delegates will examine SIP technology and architecture and learn how a functioning VoIP service can be established.
NetVanta 7100 Exercise Service Provider SIP Trunk
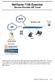 NetVanta 7100 Exercise Service Provider SIP Trunk PSTN NetVanta 7100 FXS 0/1 x2001 SIP Eth 0/0 x2004 SIP Server 172.23.102.87 Hosted by x2003 www.voxitas.com In this exercise, you will create a SIP trunk
NetVanta 7100 Exercise Service Provider SIP Trunk PSTN NetVanta 7100 FXS 0/1 x2001 SIP Eth 0/0 x2004 SIP Server 172.23.102.87 Hosted by x2003 www.voxitas.com In this exercise, you will create a SIP trunk
Troubleshooting Voice Over IP with WireShark
 Hands-On Course Description Voice over IP is being widely implemented both within companies and across the Internet. The key problems with IP voice services are maintaining the quality of the voice service
Hands-On Course Description Voice over IP is being widely implemented both within companies and across the Internet. The key problems with IP voice services are maintaining the quality of the voice service
CompTIA Convergence+ 2006 Examination Objectives
 CompTIA Convergence+ 2006 Examination Objectives Introduction The CompTIA Convergence+ examination covering the 2006 objectives certifies that the successful candidate has the necessary knowledge to perform
CompTIA Convergence+ 2006 Examination Objectives Introduction The CompTIA Convergence+ examination covering the 2006 objectives certifies that the successful candidate has the necessary knowledge to perform
4. H.323 Components. VOIP, Version 1.6e T.O.P. BusinessInteractive GmbH Page 1 of 19
 4. H.323 Components VOIP, Version 1.6e T.O.P. BusinessInteractive GmbH Page 1 of 19 4.1 H.323 Terminals (1/2)...3 4.1 H.323 Terminals (2/2)...4 4.1.1 The software IP phone (1/2)...5 4.1.1 The software
4. H.323 Components VOIP, Version 1.6e T.O.P. BusinessInteractive GmbH Page 1 of 19 4.1 H.323 Terminals (1/2)...3 4.1 H.323 Terminals (2/2)...4 4.1.1 The software IP phone (1/2)...5 4.1.1 The software
Call Setup and Digit Manipulation
 Call Setup and Digit Manipulation End-to-End Calls This topic explains how routers interpret call legs to establish end-to-end calls. End-to-End Calls IP Telephony 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Call Setup and Digit Manipulation End-to-End Calls This topic explains how routers interpret call legs to establish end-to-end calls. End-to-End Calls IP Telephony 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
IP Implementation in Private Branch Exchanges From 9:30 a.m until 4:30 p.m (7 hrs./day) 5 days / week
 Course Title: No. of Hours: IP Implementation in Private Branch Exchanges From 9:30 a.m until 4:30 p.m (7 hrs./day) 5 days / week 1 Course Duration: 3 Months (12weeks) No. Of Hours: 7 Hrs./Day- 5 days/week.
Course Title: No. of Hours: IP Implementation in Private Branch Exchanges From 9:30 a.m until 4:30 p.m (7 hrs./day) 5 days / week 1 Course Duration: 3 Months (12weeks) No. Of Hours: 7 Hrs./Day- 5 days/week.
EarthLink Business SIP Trunking. NEC SV8100 IP PBX Customer Configuration Guide
 EarthLink Business SIP Trunking NEC SV8100 IP PBX Customer Configuration Guide Publication History First Release: Version 1.0 August 30, 2011 CHANGE HISTORY Version Date Change Details Changed By 1.0 8/30/2011
EarthLink Business SIP Trunking NEC SV8100 IP PBX Customer Configuration Guide Publication History First Release: Version 1.0 August 30, 2011 CHANGE HISTORY Version Date Change Details Changed By 1.0 8/30/2011
IMPLEMENTING CISCO QUALITY OF SERVICE V2.5 (QOS)
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO QUALITY OF SERVICE V2.5 (QOS) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such
IMPLEMENTING CISCO QUALITY OF SERVICE V2.5 (QOS) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such
210-060. Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices v1.0. Version: Demo. Page <<1/10>>
 210-060 Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices v1.0 Version: Demo Page 1. Which two technologies comprise a Cisco Presence deployment? (Choose two.) A. Cisco Unified Presence Server B. Cisco
210-060 Implementing Cisco Collaboration Devices v1.0 Version: Demo Page 1. Which two technologies comprise a Cisco Presence deployment? (Choose two.) A. Cisco Unified Presence Server B. Cisco
Voice Over Internet Protocol(VoIP)
 Voice Over Internet Protocol(VoIP) By Asad Niazi Last Revised on: March 29 th, 2004 SFWR 4C03 Major Project Instructor: Dr. Kartik Krishnan 1. Introduction The telecommunications companies around the world
Voice Over Internet Protocol(VoIP) By Asad Niazi Last Revised on: March 29 th, 2004 SFWR 4C03 Major Project Instructor: Dr. Kartik Krishnan 1. Introduction The telecommunications companies around the world
Online course syllabus. MAB: Voice over IP
 Illuminating Technology Course aim: Online course syllabus MAB: Voice over IP This course introduces the principles and operation of telephony services that operate over Internet Protocol (IP) networks
Illuminating Technology Course aim: Online course syllabus MAB: Voice over IP This course introduces the principles and operation of telephony services that operate over Internet Protocol (IP) networks
Network Connection Considerations for Microsoft Response Point 1.0 Service Pack 2
 Network Connection Considerations for Microsoft Response Point 1.0 Service Pack 2 Updated: February 2009 Microsoft Response Point is a small-business phone solution that is designed to be easy to use and
Network Connection Considerations for Microsoft Response Point 1.0 Service Pack 2 Updated: February 2009 Microsoft Response Point is a small-business phone solution that is designed to be easy to use and
D. No calling search space has been configured on the line. E. An incorrect device pool has been configured on the phone
 1. An end user reports that they are unable to control their Cisco IP phone using Cisco Unified Personal Communicator and cannot make any calls. Which situation can cause this issue? A. The Cisco Unified
1. An end user reports that they are unable to control their Cisco IP phone using Cisco Unified Personal Communicator and cannot make any calls. Which situation can cause this issue? A. The Cisco Unified
Dial Peer Configuration Examples
 Dial Peer Configuration Examples This appendix contains a series of configuration examples featuring the minimum required components and critical Cisco IOS command lines extracted from voice gateway configuration
Dial Peer Configuration Examples This appendix contains a series of configuration examples featuring the minimum required components and critical Cisco IOS command lines extracted from voice gateway configuration
H.323 and Associated Recommendations. This topic describes H.323 and its protocols and explains how H.323 is used in the IP internetwork environment.
 Configuring H.323 H.323 and Associated Recommendations This topic describes H.323 and its protocols and explains how H.323 is used in the IP internetwork environment. H.323 and Associated Recommendations
Configuring H.323 H.323 and Associated Recommendations This topic describes H.323 and its protocols and explains how H.323 is used in the IP internetwork environment. H.323 and Associated Recommendations
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME. Scenario
 Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Enterprise VoIP. Silvano Gai. ftp://ftpeng.cisco.com/sgai/t2000voip.pdf. Cisco Systems, USA Politecnico di Torino, IT [email protected].
 Enterprise Vo Terena 2000 ftp://ftpeng.cisco.com/sgai/t2000voip.pdf Silvano Gai Cisco Systems, USA Politecnico di Torino, IT [email protected] Terena 2000 1 Compass Motivation for Vo Voice over in the Enterprise
Enterprise Vo Terena 2000 ftp://ftpeng.cisco.com/sgai/t2000voip.pdf Silvano Gai Cisco Systems, USA Politecnico di Torino, IT [email protected] Terena 2000 1 Compass Motivation for Vo Voice over in the Enterprise
Case in Point. Voice Quality Parameter Tuning
 Case in Point To continue our efforts to help you with your network needs, we will be making several real-world network troubleshooting case studies available to you. The attached case study,, discusses
Case in Point To continue our efforts to help you with your network needs, we will be making several real-world network troubleshooting case studies available to you. The attached case study,, discusses
642-436 - Cisco Voice over IP
 642-436 - Cisco Voice over IP Number: 642-436 Passing Score: 825 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 2.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ This material is copy from pass4sure 642-436. All answers was collected
642-436 - Cisco Voice over IP Number: 642-436 Passing Score: 825 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 2.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ This material is copy from pass4sure 642-436. All answers was collected
IPNext 50 NGN IP-PBX High-performance Next Generation IP-PBX Solution
 IPNext 50 NGN IP-PBX High-performance Next Generation IP-PBX Solution IP-PBX Features www.addpac.com AddPac Technology 2008, Sales and Marketing Contents IP-PBX Features Smart Multimedia Manager VoIP Gateway
IPNext 50 NGN IP-PBX High-performance Next Generation IP-PBX Solution IP-PBX Features www.addpac.com AddPac Technology 2008, Sales and Marketing Contents IP-PBX Features Smart Multimedia Manager VoIP Gateway
2- Technical Training (9 weeks) 3- Applied Project (3 weeks) 4- On Job Training (OJT) (4 weeks)
 Course Title: Prerequisites: Training Program (5 months) IP Implementation in Private Branch Exchanges Must fresh graduates Communication/Electronics Engineers" 1- Soft Skills Training (4 weeks) 1. Communication
Course Title: Prerequisites: Training Program (5 months) IP Implementation in Private Branch Exchanges Must fresh graduates Communication/Electronics Engineers" 1- Soft Skills Training (4 weeks) 1. Communication
Voice over IP Basics for IT Technicians
 Voice over IP Basics for IT Technicians White Paper Executive summary The IP phone is coming or has arrived on desk near you. The IP phone is not a PC, but does have a number of hardware and software elements
Voice over IP Basics for IT Technicians White Paper Executive summary The IP phone is coming or has arrived on desk near you. The IP phone is not a PC, but does have a number of hardware and software elements
SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for Time Warner Cable Business Class
 SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for Time Warner Cable Business Class NDA-31669 Issue 1.0 NEC Corporation of America reserves the right to change the specifications, functions, or features at
SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for Time Warner Cable Business Class NDA-31669 Issue 1.0 NEC Corporation of America reserves the right to change the specifications, functions, or features at
Bandwidth Security and QoS Considerations
 This chapter presents some design considerations for provisioning network bandwidth, providing security and access to corporate data stores, and ensuring Quality of Service (QoS) for Unified CCX applications.
This chapter presents some design considerations for provisioning network bandwidth, providing security and access to corporate data stores, and ensuring Quality of Service (QoS) for Unified CCX applications.
SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for MegaPath
 Notice Note that when converting this document from its original format to a.pdf file, some minor font and format changes may occur. When viewing and printing this document, we cannot guarantee that your
Notice Note that when converting this document from its original format to a.pdf file, some minor font and format changes may occur. When viewing and printing this document, we cannot guarantee that your
ACD: Average Call Duration is the average duration of the calls routed bya a VoIP provider. It is a quality parameter given by the VoIP providers.
 ACD: Average Call Duration is the average duration of the calls routed bya a VoIP provider. It is a quality parameter given by the VoIP providers. API: An application programming interface (API) is a source
ACD: Average Call Duration is the average duration of the calls routed bya a VoIP provider. It is a quality parameter given by the VoIP providers. API: An application programming interface (API) is a source
Voice over IP (VoIP) for Telephony. Advantages of VoIP Migration for SMBs BLACK BOX. 724-746-5500 blackbox.com
 Voice over IP (VoIP) for Telephony Advantages of VoIP Migration for SMBs BLACK BOX Hybrid PBX VoIP Gateways SIP Phones Headsets 724-746-5500 blackbox.com Table of Contents Introduction...3 About Voice
Voice over IP (VoIP) for Telephony Advantages of VoIP Migration for SMBs BLACK BOX Hybrid PBX VoIP Gateways SIP Phones Headsets 724-746-5500 blackbox.com Table of Contents Introduction...3 About Voice
Building a Scalable Numbering Plan
 Building a Scalable Numbering Plan Scalable Numbering Plan This topic describes the need for a scalable numbering plan in a VoIP network. Dial Plans Dial plans contain specific dialing patterns for a user
Building a Scalable Numbering Plan Scalable Numbering Plan This topic describes the need for a scalable numbering plan in a VoIP network. Dial Plans Dial plans contain specific dialing patterns for a user
Voice Over IP. Priscilla Oppenheimer www.priscilla.com
 Voice Over IP Priscilla Oppenheimer www.priscilla.com Objectives A technical overview of the devices and protocols that enable Voice over IP (VoIP) Demo Packet8 and Skype Discuss network administrator
Voice Over IP Priscilla Oppenheimer www.priscilla.com Objectives A technical overview of the devices and protocols that enable Voice over IP (VoIP) Demo Packet8 and Skype Discuss network administrator
VoIP Application Note:
 VoIP Application Note: Configure NEC UX5000 w/ BroadVox SIP Trunking Service P/N 0913226 Date: 8/12/09 Table of Contents: GOAL... 3 PREREQUISITES... 3 SIP TRUNKING INFORMATION PROVIDED BY BROADVOX:...
VoIP Application Note: Configure NEC UX5000 w/ BroadVox SIP Trunking Service P/N 0913226 Date: 8/12/09 Table of Contents: GOAL... 3 PREREQUISITES... 3 SIP TRUNKING INFORMATION PROVIDED BY BROADVOX:...
ehealth and VoIP Overview
 ehealth and VoIP Overview Voice over IP (VoIP) configurations can be very complex. Your network could contain a variety of devices, applications, and configuration capabilities to support voice traffic.
ehealth and VoIP Overview Voice over IP (VoIP) configurations can be very complex. Your network could contain a variety of devices, applications, and configuration capabilities to support voice traffic.
Description: To participate in the hands-on labs in this class, you need to bring a laptop computer with the following:
 Course: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service Duration: 5 Day Hands-On Lab & Lecture Course Price: $ 3,395.00 Learning Credits: 34 Description: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides
Course: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service Duration: 5 Day Hands-On Lab & Lecture Course Price: $ 3,395.00 Learning Credits: 34 Description: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides
VoIP Signaling and Call Control
 VoIP Signaling and Call Control Cisco Networking Academy Program 1 Need for Signaling and Call Control 2 Model for VoIP Signaling and Call Control VoIP signaling components Endpoints Common control Common
VoIP Signaling and Call Control Cisco Networking Academy Program 1 Need for Signaling and Call Control 2 Model for VoIP Signaling and Call Control VoIP signaling components Endpoints Common control Common
VIDEOCONFERENCING. Video class
 VIDEOCONFERENCING Video class Introduction What is videoconferencing? Real time voice and video communications among multiple participants The past Channelized, Expensive H.320 suite and earlier schemes
VIDEOCONFERENCING Video class Introduction What is videoconferencing? Real time voice and video communications among multiple participants The past Channelized, Expensive H.320 suite and earlier schemes
Course Overview: Learn the essential skills needed to set up, configure, support, and troubleshoot your TCP/IP-based network.
 Course Name: TCP/IP Networking Course Overview: Learn the essential skills needed to set up, configure, support, and troubleshoot your TCP/IP-based network. TCP/IP is the globally accepted group of protocols
Course Name: TCP/IP Networking Course Overview: Learn the essential skills needed to set up, configure, support, and troubleshoot your TCP/IP-based network. TCP/IP is the globally accepted group of protocols
Voice over IP (VoIP) Basics for IT Technicians
 Voice over IP (VoIP) Basics for IT Technicians VoIP brings a new environment to the network technician that requires expanded knowledge and tools to deploy and troubleshoot IP phones. This paper provides
Voice over IP (VoIP) Basics for IT Technicians VoIP brings a new environment to the network technician that requires expanded knowledge and tools to deploy and troubleshoot IP phones. This paper provides
SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for Skype
 SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for Skype NDA-31154 Issue 1.0 NEC Corporation of America reserves the right to change the specifications, functions, or features at any time without notice. NEC
SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for Skype NDA-31154 Issue 1.0 NEC Corporation of America reserves the right to change the specifications, functions, or features at any time without notice. NEC
EdgeMarc 4508T4/4508T4W Converged Networking Router
 Introduction The EdgeMarc 4508T4W combines multiple voice and data features into a single, easy to use converged networking router. It includes models that have up to 4 T1 WAN interfaces or a single Ethernet
Introduction The EdgeMarc 4508T4W combines multiple voice and data features into a single, easy to use converged networking router. It includes models that have up to 4 T1 WAN interfaces or a single Ethernet
SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for Broadvox Fusion
 Notice Note that when converting this document from its original format to a.pdf file, some minor font and format changes may occur. When viewing and printing this document, we cannot guarantee that your
Notice Note that when converting this document from its original format to a.pdf file, some minor font and format changes may occur. When viewing and printing this document, we cannot guarantee that your
This topic lists the key mechanisms use to implement QoS in an IP network.
 IP QoS Mechanisms QoS Mechanisms This topic lists the key mechanisms use to implement QoS in an IP network. QoS Mechanisms Classification: Each class-oriented QoS mechanism has to support some type of
IP QoS Mechanisms QoS Mechanisms This topic lists the key mechanisms use to implement QoS in an IP network. QoS Mechanisms Classification: Each class-oriented QoS mechanism has to support some type of
Multimedia Communications Voice over IP
 Multimedia Communications Voice over IP Anandi Giridharan Electrical Communication Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India Voice over IP (Real time protocols) Internet Telephony
Multimedia Communications Voice over IP Anandi Giridharan Electrical Communication Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India Voice over IP (Real time protocols) Internet Telephony
MINIMUM NETWORK REQUIREMENTS 1. REQUIREMENTS SUMMARY... 1
 Table of Contents 1. REQUIREMENTS SUMMARY... 1 2. REQUIREMENTS DETAIL... 2 2.1 DHCP SERVER... 2 2.2 DNS SERVER... 2 2.3 FIREWALLS... 3 2.4 NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION... 4 2.5 APPLICATION LAYER GATEWAY...
Table of Contents 1. REQUIREMENTS SUMMARY... 1 2. REQUIREMENTS DETAIL... 2 2.1 DHCP SERVER... 2 2.2 DNS SERVER... 2 2.3 FIREWALLS... 3 2.4 NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION... 4 2.5 APPLICATION LAYER GATEWAY...
SIP Trunking Service Configuration Guide for PAETEC (Broadsoft Platform)
 Notice Note that when converting this document from its original format to a.pdf file, some minor font and format changes may occur. When viewing and printing this document, we cannot guarantee that your
Notice Note that when converting this document from its original format to a.pdf file, some minor font and format changes may occur. When viewing and printing this document, we cannot guarantee that your
