Immunodeficiency. Introduction
|
|
|
- Blaze King
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Immunodeficiency Laura Carceles Campbell Lawson Liam Edward O'Hara Chiho Okada Maureen Elizabeth Esme Roach Andrew Forbes Robertson Emma Clare Rogers Introduction Immunodeficiency results from the absence or failure of normal function of one or more elements of the immune system. Primary Immunodeficiency Secondary Immunodeficiency 1
2 Primary Immunodeficiency B cell immunodeficiency X-linked agammaglobulinemia IgA deficiency Ig subclass deficiencies Common variable immunodeficiency BLNK deficiency Severe Combined Immunodeficiency IL-2 receptor gamma chain deficiency Adenosine deaminase deficiency Purine nucleoside phosphate deficiency JAK3 deficiency Recombination activating gene (RAG) 1 and 2 deficiencies Omenn Syndrome Hyper IgM syndrome Zap 70 deficiencies CD3 sub unit deficiencies X linked lyphoproliferative disease Interferon gamma receptor deficiencies Major Histocompatibility complex class I and class II deficiencies B cell development 2
3 X- Linked agammaglobulinemia XLA Congenital defect 1 in 100,000 male newborns. No B cells No IgA, IgM,IgD, IgE, small amount of IgG for 1st 6-12 months via maternal placenta. Recurrent pyogenic infections Have to be infused with large amounts of immunoglobulin to remain healthy. Btk gene missense mutation Bruton s Tyrosine Kinase Signalling molecule B-cell development into anti-body producing plasma cells 5 domains all of which can be affected by disease causing alterations. 3
4 XLA - summary Btk gene mutation Loss of functional tyrosine kinase Blocked B cell maturation No antibodies produced Severe Combined Immunodeficiencies (SCIDs) SCID a hetergenous group of monogenic disorders Characterised by: Early on-set (1 in 75,000 births) Severe infections by a full range of pathogens 20 genetic defects identified Genetic defect: Lies in T-cell differentiation Indirect impairment of B-cell function & development 4
5 SCIDs Types SCID Defect in: Cytokine signalling T-cell receptor signalling Receptor gene recombination Nucleotide salvage pathway MHC-I expression MHC-II expression Other Genetic Lesions IL2RG, IL2RA, IL7RA, JAK3 PTPRC, CD3G, CD3E, ZAP70 RAG1, RAG2 ADA, NP TAP1, TAP2 MHC2TA, RFXANK, RFX5, RFAXAP WASP Source: Bonilla, F.A. & Geha, R.F., (2003), Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases J Allergy Clin Immol Vol. 111(2) pp X-Linked SCID Most common form: 3:1 male:female Defect in IL2RG gene Defect in Cytokine receptor (γ c ) affecting: Receptors of IL-2, IL- 4 IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 & IL-21 Absent T-cells, normal / raised B-cells: IgM IL-7 cytokine important for T-cell maturation 5
6 γ c dependent cytokines in T-cell Development Malek, T.R., Porter, B. & You-Wen, H., (1999) Multiple γc-dependent cytokines regulate T-cell development Immunology Today, Vol. 20(2) pp71-76 SCID ADAD Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency Autosomally recessive 15% of SCIDs Defect in salvage pathway Accumulation of toxic datp and dgtp Inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase Impaired development and lifespan of: T-cells & B-cells 6
7 ADAD & PNPD Mechanism SCID Impaired Ca 2+ flux Defect in nuclear translocation of nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) T-cell development normal Impaired proliferation in response to activation Defective Ca 2+ influx via calcium regulated activated calcium (CRAC) channels Defect in ORAI1- essential CRAC component 7
8 Mechanism of impaired NFAT T-cell receptor crosslinking Activation of T-cell Activation of phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ) Inositol-1,4,5 trisphosphate release Defect in essential ORAI1 subunit of CRAC channel Ca 2+ released from ER T-cell proliferation Activation of CRAC channels Ca 2+ influx NFAT Mutations in genes required for T-cell development 8
9 Secondary Immunodeficiency Acquired immune deficiency caused by: Malnutrition Malignancy Drugs Trauma Infections Ageing: thymus deterioration no new T cells also affects antibody production Malnutrition Most common cause of 2 o immune deficiency Protein-Calorie malnutrition can lead to abnormalities of T cells, B cells and phagocytes Atrophic and fibrotic thymus Reduced lymphocyte proliferation in response to antigens hiakorchild.jpg 9
10 Malignancy Immunodeficiency caused by lymphoid tumours e.g. leukaemia, lymphoma, plasma cell dyscrasias Hodgkin s lymphoma: causes classic example of T-cell deficiency Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: causes classic example of B-cell deficiency Lymphocyte Depletion Hodgkin's Lymphoma H/000p044k.jpg Drugs and Trauma Cytotoxic drugs e.g. azathioprine and cyclophosphamide kill tumour cells but also lymphocytes Corticosteroids Downregulate lymphocytic genes Mimic action of glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids released naturally in response to trauma (burns/surgery) induce immunodeficiency 10
11 Infections Bacterial e.g. Mycobacterium leprae Tuberculoid leprosy: antibody deficiency Lepromatous leprosy: severe T-cell deficiency Viral Measles transient suppression of NK, T & B cells Herpes (Epstein Barr, HSV, cytomegalovirus) Influenza HIV Ultrastructural appearance of a single virion of measles virus. HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Human retrovirus RNA genome Enveloped (gp41, gp120) Strains M, O, N Targets host cell immune system itself abnormalities in every arm of the immune system 11
12 REPLICATION OVERVIEW Enters lymphocytes and monocytes. Gp120 recognises CD4 and chemokine receptor (CXR4 or CCR5) Gp 41 binds to heparan sulphate on cell surface, triggering envelope fusion capsid released into cytoplasm 2 types of cell tropism: M-tropic- R5 viruses CCR5 coreceptor T-tropic- X4 viruses CXCR4 coreceptor Viral cdna randomly integrates with host genome. Viral proteins are expressed 12
13 IMMUNOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES HIV infection induces: Dysfunction and deficiency of B cells Dysfunction and deficiency of T cells Decreased phagocytosis and intracellular killing by monocytes and neutrophils Decreased cell-mediated cytotoxicity by natural killer cells ultimately leading to severe secondary IMMUNODEFICIENCY HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE B-CELL DYSFUNCTION B-cell hyperplasia depletion Polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia Autoantibodies Specific antibody response 13
14 CELLULAR IMMUNE RESPONSE IMMUNE EVASION: Provirus latency, reservoirs, strain switch, MHC downregulation, viral epitope mutation Lymphopenia CD4+ & CD8+ T cells Cytokines T Cell CYTOKINES Switch T H 1 T H 2 cytokine response enables efficient evolution of HIV tropism phenotype R5 X4 T H 1 more CCR5 R5 strain proliferates T H 2 more CXCR4 X4 strain proliferates Alters cytokine secretion (IL1/ 2/ 6/ 7/ 10/ 12, IFNs) E.g. IL-7 favours HIV persistence 14
15 Summary of Immunodeficiency Immunodeficiency is split into two main categories: primary and secondary. Each has a variety of causes and immunological effects XLA (Primary) Blocked B-cell development: antibody deficiencies. SCIDs (Primary) directly compromises the normal development and function of T-cells and therefore indirectly, B-cells. HIV is an excellent example of a secondary immunodeficiency, affecting every aspect of the human immune system to devastating effect. References 1) Ballow, M., (2002) 'Primary immunodeficiency disorders: Antibody deficiency', Current reviews of allergy and clinical immunology Vol. 109(4): pp [doi: /mai ] 2) Maródi, L., & Notarangelo, L.D., (2007) 'Immunological and genetic bases of new primary immunodeficiencies' Nature Reviews - Immunology Vol. 7, November 2007 pp [doi: /nr2195] 3) Gupta, S., & Fernades, G., (2001) 'Immunodeficiency: Secondary' Encyclopedia of Life Sciences 4) Chinen, J., & Shearer, W.T., (2002) 'Molecular virology and immunology of HIV infection' Current reviews of allergy and clinical immunology Vol. 110(2): pp [doi: /mai ] 15
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity CHAPTER 4 04/05/15. Different Immunoglobulins
 Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
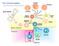 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Core Topic 2. The immune system and how vaccines work
 Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Antibody Function & Structure
 Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS.
 TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID)
 Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID) ASCIA EDUCATION RESOURCES (AER) PATIENT INFORMATION Severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) is the most serious form of primary immune deficiency and is usually
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID) ASCIA EDUCATION RESOURCES (AER) PATIENT INFORMATION Severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) is the most serious form of primary immune deficiency and is usually
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy. Chapter 7
 Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Why use passive immunity?
 Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Disclosures Outline Starting with the Immune System The Innate Immune System The Adaptive Immune System
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
Viral Replication. Viral Replication: Basic Concepts
 Viral Replication Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Viral Replication: Basic Concepts Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites Viruses carry their genome (RNA or DNA) and sometimes functional proteins required
Viral Replication Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Viral Replication: Basic Concepts Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites Viruses carry their genome (RNA or DNA) and sometimes functional proteins required
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Gene Therapy. The use of DNA as a drug. Edited by Gavin Brooks. BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press
 Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation. B cell maturation
 B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Viral Infection: Receptors
 Viral Infection: Receptors Receptors: Identification of receptors has come from expressing the gene for the receptor in a cell to which a virus does not normally bind -OR- By blocking virus attachment
Viral Infection: Receptors Receptors: Identification of receptors has come from expressing the gene for the receptor in a cell to which a virus does not normally bind -OR- By blocking virus attachment
The Case of Baby Joe by Kristen L.W. Walton Page 1
 The Case of Baby Joe: Chronic Infections in an Infant by Kristen L.W. Walton SPIRE Postdoctoral Fellowship Program University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Part I Background At birth, Baby Joe appeared
The Case of Baby Joe: Chronic Infections in an Infant by Kristen L.W. Walton SPIRE Postdoctoral Fellowship Program University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Part I Background At birth, Baby Joe appeared
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute
 Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication. Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic
 Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Why do Waldenstrom s cells need to communicate? Waldenstrom s cells need activating signals to stay alive. WM cells
Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Why do Waldenstrom s cells need to communicate? Waldenstrom s cells need activating signals to stay alive. WM cells
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
BioMmune Technologies Inc. Corporate Presentation 2015
 BioMmune Technologies Inc Corporate Presentation 2015 * Harnessing the body s own immune system to fight cancer & other autoimmune diseases BioMmune Technologies Inc. (IMU) ABOUT A public biopharmaceutical
BioMmune Technologies Inc Corporate Presentation 2015 * Harnessing the body s own immune system to fight cancer & other autoimmune diseases BioMmune Technologies Inc. (IMU) ABOUT A public biopharmaceutical
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014)
 Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
Immunity and how vaccines work
 1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells. Effector T cells. After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells
 After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Final Review. Aptamers. Making Aptamers: SELEX 6/3/2011. sirna and mirna. Central Dogma. RNAi: A translation regulation mechanism.
 Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease
 Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease Jing Shen, MD Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation February 2005
Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease Jing Shen, MD Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation February 2005
TABLE OF CONTENT. Page ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. iii ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT. vii LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES. xvi ABBREVIATIONS.
 x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated 14 September 1999 Pre- Transformed Ig Surface Surface Secreted Myeloma Major malignant counterpart
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Principles of Vaccination
 Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Chapter 5: Organization and Expression of Immunoglobulin Genes
 Chapter 5: Organization and Expression of Immunoglobulin Genes I. Genetic Model Compatible with Ig Structure A. Two models for Ab structure diversity 1. Germ-line theory: maintained that the genome contributed
Chapter 5: Organization and Expression of Immunoglobulin Genes I. Genetic Model Compatible with Ig Structure A. Two models for Ab structure diversity 1. Germ-line theory: maintained that the genome contributed
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer
 Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
7.012 Quiz 3 practice
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.012 Quiz 3 practice Quiz 3 on Friday, November 12th
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.012 Quiz 3 practice Quiz 3 on Friday, November 12th
Mechanical barriers are a crucial first line of defence. It would be impossible to provide an exhaustive list. Two examples are:
 Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity
 Immunologie II für Naturwissenschaftler Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity Beda M. Stadler Institute of Immunology Inselspital Bern, Switzerland http://www.immunology.unibe.ch/teaching/imm2/immuno2.htm
Immunologie II für Naturwissenschaftler Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity Beda M. Stadler Institute of Immunology Inselspital Bern, Switzerland http://www.immunology.unibe.ch/teaching/imm2/immuno2.htm
What is HIV? What is AIDS? The HIV pandemic HIV transmission Window period Stages of HIV infection
 Module 1 Overview of HIV Infection Purpose Pre-requisite Modules Learning Objectives To provide you with the basic terms and concepts related to HIV infection. None At the end of this module, you will
Module 1 Overview of HIV Infection Purpose Pre-requisite Modules Learning Objectives To provide you with the basic terms and concepts related to HIV infection. None At the end of this module, you will
MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Dr Malkit S Riyat. MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
LYMPHOMA. BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons
 LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
Immunosuppressive drugs
 Immunosuppressive drugs RJM ten Berge Afd. Inw. Geneeskunde AMC contents overview targets mechanism of action Effects on immune capacity measured by responses to vaccination Immune response 1 calcineurin
Immunosuppressive drugs RJM ten Berge Afd. Inw. Geneeskunde AMC contents overview targets mechanism of action Effects on immune capacity measured by responses to vaccination Immune response 1 calcineurin
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies. Mark Holguin
 Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies Mark Holguin 25 years ago Why I chose oncology People How to help people with possibly the most difficult thing they may have to deal with Science Turning
Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies Mark Holguin 25 years ago Why I chose oncology People How to help people with possibly the most difficult thing they may have to deal with Science Turning
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
Viruses. Viral components: Capsid. Chapter 10: Viruses. Viral components: Nucleic Acid. Viral components: Envelope
 Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
Comparative Drug Ranking for Clinical Decision Support in HIV Treatment
 Comparative Drug Ranking for Clinical Decision Support in HIV Treatment Emiliano Mancini University of Amsterdam 1 Prevalence of HIV 2 Global Overview HIV Infection People living with HIV: 34 million (2010
Comparative Drug Ranking for Clinical Decision Support in HIV Treatment Emiliano Mancini University of Amsterdam 1 Prevalence of HIV 2 Global Overview HIV Infection People living with HIV: 34 million (2010
Immunology. B lymphocytes & Antibodies. 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected]
 Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected] What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected] What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) [email protected] 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org
 Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) [email protected] 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) [email protected] 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins that compete with animal A) Antibodies. B) Red blood cells. C) Transferrin. D) White blood cells. E) Receptors.
 Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
OKT3. ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody. used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~
 g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
Special report. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Genomic Biology 3020 April 20, 2006
 Special report Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Genomic Biology 3020 April 20, 2006 Gene And Protein The gene that causes the mutation is CCND1 and the protein NP_444284 The mutation deals with the cell
Special report Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Genomic Biology 3020 April 20, 2006 Gene And Protein The gene that causes the mutation is CCND1 and the protein NP_444284 The mutation deals with the cell
I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin
 (English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
(English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
CHAPTER 9 IMMUNOGLOBULIN BIOSYNTHESIS
 CHAPTER 9 IMMUNOGLOBULIN BIOSYNTHESIS Although the process by which a functional gene for immunoglobulin HEAVY and LIGHT CHAINS is formed is highly unusual, the SYNTHESIS, POST- TRANSLATIONAL PROCESSING
CHAPTER 9 IMMUNOGLOBULIN BIOSYNTHESIS Although the process by which a functional gene for immunoglobulin HEAVY and LIGHT CHAINS is formed is highly unusual, the SYNTHESIS, POST- TRANSLATIONAL PROCESSING
treatments) worked by killing cancerous cells using chemo or radiotherapy. While these techniques can
 Shristi Pandey Genomics and Medicine Winter 2011 Prof. Doug Brutlag Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A look into how genomics is changing the way we treat Cancer. Until the late 1990s, nearly all treatment methods
Shristi Pandey Genomics and Medicine Winter 2011 Prof. Doug Brutlag Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A look into how genomics is changing the way we treat Cancer. Until the late 1990s, nearly all treatment methods
Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 2
 Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 2 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Cancer Therapies 3. Adjunctive Therapies On completion of this module the RN will State the difference between a normal
Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 2 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Cancer Therapies 3. Adjunctive Therapies On completion of this module the RN will State the difference between a normal
Overview. Transcriptional cascades. Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity. Conventional (B2) B cell development
 Overview B cell development Transcriptional cascades Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity Conventional (B2) B cell development What happens to an autoreactive B cell? B1 vs B2 cells Key anatomical sites
Overview B cell development Transcriptional cascades Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity Conventional (B2) B cell development What happens to an autoreactive B cell? B1 vs B2 cells Key anatomical sites
Practice parameter. PREFACE The purpose of this Practice Parameter for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Immunodeficiency is to provide the
 Practice parameter Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency Francisco A. Bonilla, MD, PhD*; I. Leonard Bernstein, MD ; David A. Khan, MD ; Zuhair K. Ballas, MD ;
Practice parameter Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency Francisco A. Bonilla, MD, PhD*; I. Leonard Bernstein, MD ; David A. Khan, MD ; Zuhair K. Ballas, MD ;
Pathophysiology of the human immunodeficiency virus
 Pathophysiology of the human immunodeficiency virus Nancy R. Calles, MSN, RN, PNP, ACRN, MPH Desiree Evans, MD, MPH DeLouis Terlonge, MD Objectives 1. Provide an overview of the healthy immune system.
Pathophysiology of the human immunodeficiency virus Nancy R. Calles, MSN, RN, PNP, ACRN, MPH Desiree Evans, MD, MPH DeLouis Terlonge, MD Objectives 1. Provide an overview of the healthy immune system.
The immune system and HIV
 The immune system and HIV How HIV damages the immune system Source: Aidsmap: http://www.aidsmap.com A patient oriented educational website Adapted by Luc Kestens for SCART 2005 students Recommended reading
The immune system and HIV How HIV damages the immune system Source: Aidsmap: http://www.aidsmap.com A patient oriented educational website Adapted by Luc Kestens for SCART 2005 students Recommended reading
Principles of Vaccination
 Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
SYMPOSIUM. June 15, 2013. Photonics Center Colloquium Room (906) 8 Saint Mary's St., Boston, MA 02215 Boston University
 SYMPOSIUM June 15, 2013 Photonics Center Colloquium Room (906) 8 Saint Mary's St., Boston, MA 02215 Bette Korber Los Alamos National Labs HIV evolution and the neutralizing antibody response We have recently
SYMPOSIUM June 15, 2013 Photonics Center Colloquium Room (906) 8 Saint Mary's St., Boston, MA 02215 Bette Korber Los Alamos National Labs HIV evolution and the neutralizing antibody response We have recently
Applications of Ab Molecules. Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128)
 Applications of Ab Molecules Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128) Monoclonal Antibodies Clonal Selection of B Lymphocytes Hybridoma Köhler and Milsten (1975) - continuous
Applications of Ab Molecules Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128) Monoclonal Antibodies Clonal Selection of B Lymphocytes Hybridoma Köhler and Milsten (1975) - continuous
The Human Immune System
 The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
Chapter 36. Media Directory. Characteristics of Viruses. Primitive Structure of Viruses. Therapy for Viral Infections. Drugs for Viral Infections
 Chapter 36 Media Directory Drugs for Viral Infections Slide 23 Slide 27 Slide 29 Zidovudine Animation Saquinavir Mesylate Animation Acyclovir Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Chapter 36 Media Directory Drugs for Viral Infections Slide 23 Slide 27 Slide 29 Zidovudine Animation Saquinavir Mesylate Animation Acyclovir Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Hypersensitivity. TYPE I Hypersensitivity Classic allergy. Allergens. Characteristics of allergens. Allergens. Mediated by IgE attached to Mast cells.
 Gel and Coombs classification of hypersensitivities. Hypersensitivity Robert Beatty Type I Type II Type III Type IV MCB150 IgE Mediated IgG/IgM Mediated IgG Mediated T cell Classic Allergy rbc lysis Immune
Gel and Coombs classification of hypersensitivities. Hypersensitivity Robert Beatty Type I Type II Type III Type IV MCB150 IgE Mediated IgG/IgM Mediated IgG Mediated T cell Classic Allergy rbc lysis Immune
Lymphomas after organ transplantation
 Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
Structure and Function of DNA
 Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Disclosures. I have no disclosures.
 Not Your Own Marrow Jenni Krajewski, MD Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School Attending Physician, Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplantation The Institute for Pediatric Cancer
Not Your Own Marrow Jenni Krajewski, MD Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School Attending Physician, Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplantation The Institute for Pediatric Cancer
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences / Clinical Microbiology, Immunology or
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences / Clinical Microbiology, Immunology or
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer
 Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells
 Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of General Medicine, CUMC September 16, 2009 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared purpose:
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of General Medicine, CUMC September 16, 2009 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared purpose:
Some terms: An antigen is a molecule or pathogen capable of eliciting an immune response
 Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY. Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds
 NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small
 The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
