How to Obtain an OPC License--5. Creating a System Code 5 Entering an Authorization Code 6. Getting Started with SNMP Editor--7
|
|
|
- Cori Lucas
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents Introduction--1 Product definition 1 Implementing SNMP 2 Integrating SNMP into the user interface 3 Components of OPC SNMP Gateway 4 How to Obtain an OPC License--5 Creating a System Code 5 Entering an Authorization Code 6 Getting Started with SNMP Editor--7 Auto-discovery of Network Devices Before using the Auto-discovery feature of SNMP OPC Gateway 8 Using Auto-discovery in SNMP Editor 8 Setup for Auto-Discovered Unmanaged Devices Device tab 11 Advanced tab 11 Setup for Auto-Discovered SNMP-Managed Devices Device tab 13 Advanced tab 15 Manual Network Device Configuration--17 Manual Network Device Setup Unmanaged Basic setup 18 Advanced tab unmanaged device 18 Manual Network Device Setup Managed Managed device advanced tab 21 I
2 Tag Configuration--22 Polled Tag Configuration 22 Creating Trap tags within SNMP 25 Finding tags 28 Filtering tags 29 Importing Templates--30 SNMP Traps and Event Notification--32 Advanced SNMP Settings--37 User-Defined Tag Setup--40 SNMP Communicator--42 Browsing an Existing Database 43 Reading SNMP Data 48 Writing SNMP Data 48 Spot-Checking SNMP Data 48 SNMP Dataviewer--51 Reading Data 51 Writing Data 54 Saving and retrieving Dataview windows 55 Advanced settings 56 OPC Server Interface--57 II
3 Introduction Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) device management is one of the tools available from modern Ethernet devices such as APC uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs). It offers the industrial user remote access to real-time performance and troubleshooting data. Implementing an SNMP-based network management system to monitor critical network infrastructure can help to ensure that Ethernet network-based control systems perform reliably. Product definition SNMP provides remote management access to an Ethernet network device. A microprocessor-based management agent in the manageable device gathers diagnostic and device configuration data from the device and stores this information in memory locations, similar to data registers in a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). The data can be accessed by polling the SNMP agent in the network device from a remote computer, using the SNMP communication protocol. The database within the manageable device is called a Management Information Base (MIB). There are two types of MIBs, public and private. Public MIBs contain information common among most network devices. Private MIBs contain information unique to a manufacturer s products. 1
4 Currently, network administrators can use a variety of stand-alone network management software tools which allow them to display and historically record network status information. Information provided by an SNMPmanageable APC UPS includes online/battery status, battery maintenance notification, power conditioning, and more. In addition to providing information, SNMP allows an administrator to configure devices remotely and perform management functions, such as setting a device name. Implementing SNMP Implementing SNMP device management into your network requires the following: The use of a TCP/IP-based Ethernet network. Manageable network devices. APC offers an optional slide-in UPS Network Management Card for many of its UPS products to convert the unmanaged UPS into a networked SNMP-manageable device. A network management software package. Implementing the network management software in a industrial control network is commonly accomplished by using a dedicated network administrator computer. Unfortunately, this method leads to a total control system that has two dashboards. One dashboard displays the SNMP management information. The other dashboard is the Human-Machine Interface (HMI) package, which displays real-time PLC and control system parameters. 2
5 Integrating SNMP into the user interface Using the OPC Server within, you can integrate APC UPS management data into any OPC-client control system. SNMP MIB data can be converted to user interface tags using this tool. This merging of the network and control system data into the same interface ensures that analysis of control system problems includes network status at the time the problem occurred. Operating two dashboards is no longer necessary. The historical data logging, trending, and graphical user interface tools that are part of modern user interface software can now be used to track UPS infrastructure as well. 3
6 Components of OPC SNMP Gateway SNMP Editor. Use the Editor to configure the SNMP database. Communicator. Use the Communicator to verify data directly from the Network Management Card. Dataviewer. Use the Dataviewer to verify that the SNMP OPC Server is collecting and sharing data properly. OPC Server Interface. Use the Server Interface to view the event log. 4
7 How to Obtain an OPC License There are two steps to obtaining an OPC SNMP Gateway software license first, create a system code and submit that code to APC, and second, enter the authorization code in the License Utility. Creating a System Code To create a system code for the computer that will be running the licensed software: 1. Open the License Utility using the following path: Start > Programs > American Power Conversion > > License Utility. 2. Choose Step 1 Generate System Code, then click Next. 3. Type in the product serial number and click Next. The product serial number is located on the card enclosed with your SNMP OPC Gateway software CD. This serial number generates your unique system code. 4. Call the APC Enterprise Account Team at , or them at [email protected], and APC will generate your license code. 5. When you receive your license code from APC, enter an authorization code using the procedure on the following page. 5
8 Entering an Authorization Code To complete the licensing process: 1. Open the License Utility using the following path: Start > Programs > American Power Conversion > > License Utility. 2. Choose Step 2 Enter Authorization Code and click Next. 3. Enter the license code you received from APC and click Next. 4. When the confirmation page appears, showing that licensing is complete, click Finish. 6
9 Getting Started with SNMP Editor Before you can monitor your network devices, the Simple Network Management Protocol () must first be made aware of the network devices to monitor. To quickly set up a database of network data: 1. Auto-discover or manually define your network devices. 2. Define the data points you want to read from the network devices. 3. Do one of the following: a. Monitor the configured devices in the SNMP Dataviewer. b. Set up your user interface to read the OPC tags from the SNMP Server. To define the UPSs or other APC devices in your network, either autodiscover the network devices (recommended), or define the network devices manually (advanced). 7
10 Auto-discovery of Network Devices Before using the Auto-discovery feature of SNMP OPC Gateway Ensure that the IP address(es) of your APC devices are already assigned and the devices are on to the network. See also For help configuring your network devices, see the device s network management manual, or contact your supplier for the hardware. For an APC UPS, see the Network Management Card Installation and Quick-Start manual, provided with network-manageable UPSs, with any separately ordered Network Management Card, and on the APC Web site, Most Windows 2000 and Windows XP Professional operating systems have SNMP services enabled by default, but to monitor SNMP data from Windows NT workstations, you may have to install SNMP services. Detailed instructions are available from the Microsoft help files. Using Auto-discovery in SNMP Editor Use the following path to open SNMP Editor: Start > Programs > American Power Conversion > > SNMP Editor. 1. Make sure that the SNMP computer is connected to the Ethernet network on which you want to auto-discover network devices. 2. Click the green eye on the SNMP Editor taskbar, or select Auto-discover from the Operations menu. 3. In the Search Network dialog box, enter the first and last IP address for the range of the Ethernet devices in your network, and click Begin. 8
11 4. After searches the network, the Discovered Devices dialog box displays a list of both SNMP-manageable and currently unmanaged devices. If you defined or auto-discovered a device previously, the Current Devices dialog box lists it below Discovered Devices. To add devices identified by the auto-discovery tool to SNMP Editor, double-click the device s IP address in the Discovered Devices dialog box. If the device is unmanaged, see Setup for Auto-Discovered Unmanaged Devices. If the device is SNMP-manageable, see Setup for Auto-Discovered SNMP-Managed Devices. 9
12 Setup for Auto-Discovered Unmanaged Devices If an unmanaged device is auto-discovered, SNMP assigns it the following default device name: (Unmanaged Device) - xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. Use the Device Wizard to define the device s name, description, and advanced settings. To access the Device Wizard (shown below), select the New Item icon ( ) from the toolbar, then select Managed (SNMP). 10
13 Device tab 1. Replace the default device name with a brief, logical Name (such as SNMP product 1). 2. Leave the Device field as (Unmanaged Device). 3. Leave the IP address field unchanged. 4. If desired, type a brief description of the device in the Description field. Advanced tab The following Advanced tab settings define how the reacts if a field device is not responding promptly. For APC devices, leave these settings at the default values unless an APC Enterprise Account Support technician asks you to make changes. If you have problems communicating with an APC field device, contact APC Enterprise Account Support. 11
14 Device Time Out (ms): The amount of time allowed to complete an SNMP GET. In situations where there is heavy network traffic, the customer support technician may ask you to set a longer timeout before SNMP assumes a communication failure has occurred. The default setting of 500 ms is suitable for most applications. Device Retries: The number of times that SNMP attempts to retrieve data before assuming that the device has failed. Skip Count: The amount of time that SNMP waits before attempting another GET from a device that has failed. For example, an 800 ms device timeout with a skip count setting of 30 will result in a ms delay before a new GET attempt. 12
15 Setup for Auto-Discovered SNMP-Managed Devices SNMP-manageable devices can provide much detailed network data. In addition, for APC network devices, SNMP can provide auto-discovered device data to monitor the communication status of the network devices during periods of inactivity. Use the SNMP Editor Device Wizard. To open the Device Wizard, select the New Item icon ( ), then select Managed (SNMP). Device tab If recognizes the managed device from its pre-defined list of supported network devices, much of the required information is already displayed. 13
16 Complete the device configuration as follows: 1. By default, creates a device name by merging the type of network device that it discovered with the device s IP address. Since the device name often is used as part of an OPC address string in your user interface, change the Device Name to a shorter, unique string. 2. If the network device that you are configuring is one of the devices has in its pre-defined device list, select it in the drop-down Device menu. The type of network device that SNMP detected will already be displayed. If the network device that you are setting up is not part of the pre-defined list, leave the Device field blank. You will have to create each SNMP data tag individually. 3. Do not change the address in the IP Address field. This address follows standard IP addressing format (for example: ). 4. Community is the control access level you will use when communicating with the network device. In an SNMP-manageable device, you can limit the access that an SNMP manager application (such as SNMP itself) can have, based on the manager software s password level. There are generally two default password (community) levels Read-only and Read/Write. In most SNMP devices, including APC devices, the default community for Read-only privileges is Public, and the default community for Read/Write privileges is Private. Some SNMP-manageable devices can be configured to have custom levels of access. To limit access for only a few SNMP tags, select the highest access level for the device, and then limit the access level for specific SNMP tags within Editor. See the Tag Configuration help for more information on how to limit access on a tag-by-tag basis. 5. Specifying a value in the Description field is optional, but helps you recognize a device in the Editor. 14
17 Advanced tab The following Advanced tab settings define how the reacts if a field device is not responding promptly. For APC devices, leave these settings at the default values unless an APC Enterprise Account Support technician asks you to make changes. If you have problems communicating with an APC device, contact APC Enterprise Account Support. Device Time Out (ms): The amount of time allowed to complete an SNMP GET. In situations where there is heavy network traffic, the customer support technician may ask you to set a longer timeout before SNMP assumes a communication failure has occurred. The default setting of 800 ms is suitable for most applications. 15
18 Device Retries: The number of times that SNMP attempts to retrieve data before assuming that the device has failed. Skip Count: The amount of time that SNMP waits before attempting another GET from a device that has failed. For example, defining an 800 ms device timeout with a skip count setting of 30 will result in a ms delay before a new GET attempt. No. of Items/Message: The software requests data in groups of Object Identifiers (OIDs). Number of Items/Messages refers to the number of OIDs requested in one SNMP GET. For most networks, 25 items is the ideal message size for the best performance. When you finish configuring the field definitions, select OK. If you selected a pre-defined tag database from the drop-down menu, prompts you to auto-import the tag database for the defined network device. Click OK. SNMP will automatically populate the tag list for the device and will automatically populate your tag database with all the SNMP data that can be accessed from the device. In some cases many tags may be imported, and in other cases only a few tags may be imported. If you have a pre-defined device tag database, this device is completely configured. You can either add additional network devices, or save your configuration and exit the SNMP Editor. To define the MIB data for the device, see Tag Configuration. 16
19 Manual Network Device Configuration To define a device that has not yet been installed on the network or to list and set up a device without using Auto-Discovery, use the following procedure. 1. Place the mouse pointer over the Network Devices tab in SNMP Editor, and right-click the mouse. 2. Select New Device. Select either a managed device or an unmanaged device. To set up an unmanaged device, see Manual Network Device Setup Unmanaged. To set up an SNMP-manageable device, see Manual Network Device Setup Managed. 17
20 Manual Network Device Setup Unmanaged Basic setup 1. Open the Device Wizard. Select the New Item icon ( ), then select Managed (SNMP). 2. In the Device Wizard Name field, type a brief, logical alias for the device. 3. In the Device Field, use the drop-down menu to select (Unmanaged Device). 4. Type the IP address of the unmanaged device into the IP Address field. 5. Optionally, type a brief description of the device in the Description field. Advanced tab unmanaged device The following Advanced tab settings define how the reacts if a field device is not responding promptly. For APC devices, leave these settings at the default values unless an APC Enterprise Account Support technician asks you to make changes. If you have problems communicating with an APC device, contact APC Enterprise Account Support. The following list defines the Advanced tab fields: Device Time Out (ms): The amount of time allowed to complete an SNMP GET. In situations where there is heavy network traffic, the customer support technician may ask you to set a longer timeout before SNMP assumes a communication failure has occurred. The default setting of 500 ms is suitable for most applications. Device Retries: The number of times that SNMP attempts to retrieve data before assuming that the device has failed. 18
21 Skip Count: The amount of time that SNMP waits before attempting another GET from a device that has failed. For example, defining an 800 ms device timeout with a skip count setting of 30 will result in a ms delay before a new GET attempt. 19
22 Manual Network Device Setup Managed If recognizes the managed device from its predefined list of supported network devices, much of the required information is already displayed. Complete the device configuration as follows: 1. By default, creates a device name by merging the type of network device that it discovered with the device s IP address. Since the device name often is used as part of an OPC address string in your user interface, change the device name to a shorter, unique string. 2. If the network device that you are configuring is one of the devices has in its pre-defined device list, select it from the drop-down Device menu. The type of network device that SNMP detected will already be displayed. If the network device that you are setting up is not part of the pre-defined list, leave the Device field blank. You will have to create each SNMP data tag individually. 3. Do not change the address in the IP Address field. This address follows standard IP addressing format (for example: ). 4. Community is the control access level you will use when communicating to the network device. In an SNMP-manageable device, you can limit the access that an SNMP manager application (such as SNMP itself) can have, based on the manager software s password level. There are generally two default password (community) levels Read-only and Read/Write. In most SNMP devices, including APC devices, the default community for Read-only privileges is Public, and the default community for Read/Write privileges is Private. Some SNMP-manageable devices can be configured to have custom levels of access. To limit access for only a few SNMP tags, you can select the 20
23 highest access level for the device, and then limit the access level for specific SNMP tags within Editor. See the Tag Configuration help for more information on how to limit access on a tag-by-tag basis. 5. Specifying a value in the Description field is optional, but in larger networks, it may help you recognize the device you are looking at in the Editor. Managed device advanced tab The following Advanced tab settings define how the reacts if a field device is not responding promptly. For APC devices, leave these settings at the default values unless an APC Enterprise Account Support technician asks you to make changes. If you have problems communicating with an APC device, contact APC Enterprise Account Support. Device Time Out (ms): The amount of time allowed to complete an SNMP GET. In situations where there is heavy network traffic, the customer support technician may ask you to set a longer timeout before SNMP assumes a communication failure has occurred. The default setting of 500 ms is suitable for most applications. Device Retries: The number of times that SNMP attempts to retrieve data before assuming that the device has failed. Skip Count: The amount of time that SNMP waits before attempting another GET from a device that has failed. For example, defining an 800 ms device timeout with a skip count setting of 30 will result in a ms delay before a new GET attempt. 21
24 Tag Configuration You can create two major types of tags within SNMP. Polled tags are tags that SNMP uses to retrieve data from network devices on a regular basis. Traps are tags that SNMP uses to retrieve data from devices that are not polled, and broadcast alarm messages. Polled Tag Configuration To define polled tags manually (if you are not auto-discovering your network devices or if auto-discovery did not find an OID that you need): Open SNMP Editor by selecting Programs from your computer s Start menu, then American Power Conversion, then OPC Gateway. Select Editor, then Device, and right click in the Description field. Highlight the network device to which you want to add an SNMP tag in the SNMP Editor s left screen frame. In the right screen frame, right-click, and select New Item. 22
25 In the dialog box for creating a new SNMP database tag: 1. In the Name field, enter a logical and brief description of the MIB object data being read. (For example, if the MIB data represents the current link status for Port Number 1 on a network switch, a brief tag name might be PortLink1.) 2. In the ObjectID field, enter the specific data address for the information you are requesting from the SNMP agent. Most MIB addresses use an Object ID nomenclature of a leading period, followed by a series of whole numbers separated by periods (for example: ). See also For MIB information, see the APC MIB Guide supplied with your SNMP-manageable device. 23
26 If the Object ID for the tag does not reference a table, the offset is 0. In those cases where the Object ID references a table, the offset is the number of SNMP GET calls needed to access all the data of the table. For information on the structure of MIB, see the documentation provided by the manufacturer of the device you are monitoring, or for APC devices, see the APC MIB Reference Guide. 3. In the Data Type drop-down list, select the data type for the MIB data you are requesting. For APC device Object ID addresses and descriptions, see the APC PowerNet MIB. 4. In the Description field, the tag description is optional, but helps identify the tag in the SNMP Editor. 5. As the Access selection for the tag, you can choose to limit communication to the tag to allow only reading of the data. Some MIB data can be set, such as a System Contact field. Leaving this box unchecked will allow write commands to be sent to the MIB data point. The SNMP agent on the network device might only support read-only access for all or some tags, and selecting write privileges from within does not guarantee that write commands will be executed. See the network management manual for your network device to determine the access it supports. The SNMP agent on APC devices supports different access for different tags. For APC devices, view the OIDs in the APC MIB through your MIB browser to determine access on a tag-by-tag basis. 6. You can create additional OPC tags that can help in network History applications. Selecting the Previous Value box creates an OPC tag that retains the previous SNMP GET value. The Delta time box creates a tag based on the difference in time between the values of the 24
27 current and last SNMP Object ID. The Moving Average section creates an OPC tag for a moving average of a particular SNMP value. In most applications, selecting any of the History options is unnecessary. For APC devices, consult APC Enterprise Account Support for assistance with these tags. After you finish the field definitions, click OK. The tag that you just created appears on the first line on the right frame of the interface. To add additional tags for this device, right-click on the right frame of the SNMP Editor interface and follow the preceding procedure (Polled Tag Configuration) again. After you create all the tags for the network device, you can either add another network device or close the SNMP Editor and begin to view the SNMP data from your OPC client program by using SNMP Dataviewer. You can use this tool to view the SNMP data in your configured system. For more information on using SNMP Dataviewer, see SNMP Dataviewer Creating Trap tags within SNMP If a network agent has been configured to generate traps, the network agent broadcasts a string of data to all configured SNMP manager applications whenever specified trap conditions occur. The trap string includes the unique SNMP object identifier (OID) address of the trap condition. When SNMP receives a trap from a field device, it compares the incoming trap string to the defined Trap tags for that field device. For traps 25
28 that have been defined within SNMP Editor, the incoming OID string is converted from the raw x.x.x.x.x.x format into the associated OPC tag name for the trap. SNMP makes the trap name available as part of the Event string to be displayed within your user interface. If a matching OID address for an incoming trap cannot be found, SNMP displays the raw OID in the trap string alongside the time stamp and trap condition value. If you do not want to receive a raw OID in the Event string from a trap, and want a Tag name instead, define the Trap tag manually. 1. Open SNMP Editor by selecting Programs from your computer s Start menu, then American Power Conversion, then OPC Gateway. Select Editor, then Device, and right click in the Description field. 2. First highlight the network device to which you want to add an SNMP Trap tag to in the SNMP Editor left screen frame. With the correct device highlighted, move your mouse to the right screen frame, rightclick, and select New Item. 3. The dialog box for creating a new SNMP database tag will appear. To configure the trap, you must do the following: 1. Give the trap a Name. The tag name should be a logical and brief description of the trap condition. ( For example, if the MIB data represents an overheat sensor, a simple name could be Overheat.) 2. Enter the value for the ObjectID field for the tag. The ObjectID is the specific data address for the information that you are requesting from the SNMP agent. Trap addresses follow an OID nomenclature that has a series of whole numbers separated by periods. APC traps follow this data address:
29 You can find the Object ID addresses and descriptions in the network management manual supplied with your SNMPmanageable device. Be aware that some network component vendors have two product manuals one for installing and operating the network device, the other detailing network management information. If the Object ID for the tag does not reference a table, the offset is 0. In those cases where the Object ID references a table, the offset is the number of SNMP GET calls needed to access all the data of the table. For information on the structure of MIB, see the documentation provided by the manufacturer of the device you are monitoring, or for APC devices, see the APC MIB Reference Guide. 3. In the Data Type field, select the data type for the MIB data you are going to be requesting. Select Trap/Notification. 4. The fourth field is the Description field. Specifying a value in the Description field is optional, but it helps you recognize the device in the Editor. 5. Make the Access selection for the tag. If you click in this box, you can limit any communication to this tag to allow read-only access of the data. Some MIB data can be set, such as resetting a counter in the SNMP agent. The SNMP agent residing on the network device may support Read-Only access for all tags, or may support Read-Only access for some tags. Selecting write privileges from within SNMP OPC Gateway does not guarantee that write commands will be executed. Consult the network management manual for your network device to be sure of the functionality supported. Leaving this box unchecked will allow write commands to be sent to the MIB data point. 27
30 6. The last section allows you to create some additional OPC tags that can help in network History applications. The History section is not applicable to SNMP Traps. After you have filled out the field definitions, click the OK button. To add additional traps for this device, right click on the right frame of the SNMP Editor interface and repeat the preceding procedure. Finding tags To quickly locate an OID in the complete list of tags for that device, use the FIND tag feature. Press the Find Tag button, as shown below: Type all or part of the OID name in the dialog box and click Find Next. The find feature will display the next instance of the string of characters typed in the dialog box. 28
31 Filtering tags To quickly locate a group of OIDs which include a specific string of characters, select the Filter Tags feature by clicking the Filter Tags button on the interface. Type all or part of the string in the dialog box and click OK. will return all tags for that device that include the string of characters you have defined. 29
32 Importing Templates SNMP Editor enables you to import additional templates for devices into. In SNMP Editor, select Operations, then Import Templates. Click Add to select the.csv file for the template you want to add. 30
33 The Import Templates tool allows you to select three options when adding templates: Prompt If an imported template has the same name as an existing template in the template library, the system will prompt you to either overwrite the existing template with the imported template or leave the existing template in place (this is referred to as skipping the existing template). Overwrite If an imported template has the same name as an existing template in the template library, the system will automatically overwrite the existing template. Skip If an imported template has the same name as an existing template in the template library, the system will automatically skip the imported template. 31
34 SNMP Traps and Event Notification SNMP supports both active polling of SNMP agents and the receipt of unsolicited event messages from SNMP agents. Unsolicited event messages sent by network agents to network manager applications are commonly called traps. A network agent transmits traps whenever a configured event, such as a link up/down change occurs. APC network devices can be configured to send traps to more than one network agent, so if you are sharing network hardware with your IT department, traps can be sent to both SNMP and the IT network management application simultaneously. See the device s manual for detailed instructions. To configure an SNMP Agent, and receive SNMP traps from it within SNMP, complete the following steps: 1. Configure the SNMP agents on the network manager(s) to send SNMP traps to the network manager application. The network device should be receiving power. Access the device s management menu. All devices are configured slightly differently, but the example on the next page shows a UPS being configured through its Web browser interface to send traps to an SNMP application running on a PC with an IP address of
35 2. Verify that the network device and SNMP server are connected to the same network. Launch SNMP Editor and run the auto-discovery tool. (If you cannot run the auto-discovery tool, skip to step 3.) If the network device has been correctly configured with an IP address, it will appear in the Discovered Devices window. If the device has a pre-defined SNMP MIB template, SNMP will recognize it and prebuild the tag database, including trap data. If the device is not supported as a pre-defined SNMP device, you will have to manually define the traps you wish to receive, and verify them as described in step 3, below. 33
36 For a description of the manual trap definition procedure, see Creating Trap tags within SNMP. 3. Verify that SNMP is receiving the trap data from the target device. If you still have the SNMP Editor Application open, save and close it now. Launch the SNMP Dataviewer application using the following path: Start > Programs > American Power Conversion > SNMP OPC Gateway > Tools > SNMP Dataviewer. Open the tree next to the device you wish to test, and scroll down until you see the Events group. There are often many tags; SNMP Dataviewer lists the tags and groups alphabetically. Select and move the Events Count and Event_xxx tags over to the active monitoring portion of the screen (the right frame). 34
37 Initially, you may not have any values in the trap tags to view. Begin to create trap conditions. For example, if the network device is a switch, and it is configured to send Link Up and Link Down traps, then you can connect and disconnect devices from the switch to create trap conditions. As trap conditions occur, you should see the trap counter increment, and the traps string sent by the network agent will be displayed in the value column of the Events detail tags. As SNMP traps are received from the network, SNMP places the most current trap in the Events_001 field, and moves the previous traps down by one on the range. This process enables a first-in/first-out alarm log history easily displayed in your user interface. 35
38 The default number of Event strings is 10. If you wish to increase or decrease the number of Event strings available, open SNMP Editor, right click on the Events tab under the target device, and enter the number of notifications you need in the Notification box that appears. 4. If you are receiving traps, you can now repeat the process for any other network devices from which you wish to receive traps. 36
39 Advanced SNMP Settings To set advanced polling features: 1. Click Edit, then OPC Server Settings. 2. The OPC Server Settings page will appear (as pictured on the next page). Warning Do not change the default settings on the OPC Server Settings page unless you are experiencing problems with polling devices on your network. 37
40 38
41 Setting Trace Level Trace File Path COM Call Tracing Base UDP Port Minimum SNMP Scan Rate (ms) Run Server as Windows Service Run Server as Application Disable Auto Shutdown Enable Initial Polling Description Select the level of communication fault reporting, if you wish to maintain a file detailing COM problems. Default is None. Select the destination where the COM tracing file will be stored. Turn communication fault tracing on or off. Default is Off. First port in the multi-threaded polling sequence. The default setting uses this port and up to 100 ports above it to execute the multi-threaded polling of network devices. Base rate for network polling; all devices are a multiple of this number. Default is 1000 ms. SNMP runs continuously as a Windows service, rather than starting when an OPC client requests information. Default setting; SNMP runs when an OPC client requests data, and shuts down if there is no demand for several seconds. If SNMP is running as an application, the OPC server will not shutdown once it is started, even if no OPC clients are requesting data. The SNMP OPC Server will not display a value to an OPC client application until a verified value has been returned; this can increase server startup time significantly. Default setting is Off. 39
42 User-Defined Tag Setup SNMP User-Defined SNMP tags are derived OPC tags that require the user to define a new tag by manipulating the value of existing SNMP tags. Use the following steps to add a user-defined tag. 1. Expand the device detail view of the target device, in the left-hand window of SNMP Editor. 2. Highlight the User-Defined icon, move your mouse to the right screen frame, right-click, and select New Item. 3. The dialog box for creating a new SNMP database derived tag will appear, as seen below: 40
43 SNMP uses Microsoft JScript as the syntax for derived tags. This syntax offers tremendous flexibility for creating derived tag equations. SNMP has added an extension to Jscript in order to use the current values of certain OPC tags in the Jscript equations. To use the SNMP Jscript extension: The Val ( ) function takes the name of an SNMP OPC tag and returns the value of that tag into the equation variable. Example: x = val(ifoutucastpkts.01); If the input to the Val ( ) variable is a valid OPC tag name, Val ( ) returns the current value of that OPC tag into the equation. If the equation that is created in the derived tag includes tags from multiple devices, the full OPC tag name (< device>.< tag name>) will bring in the current values from multiple devices. See also For information on the syntax for Jscript, visit the Microsoft Web site and search for Jscript. 41
44 SNMP Communicator During system troubleshooting, you may wish to communicate with your SNMP-manageable network devices without having to start the SNMP Server. One advantage of the Communicator is that you do not have to configure your SNMP database using the SNMP Editor. This allows you to retrieve and verify SNMP data directly from the field device, bypassing an HMI and the OPC server. If you have an existing SNMP Editor configuration set up, then you will be able to browse the tag database you have already set up. To open SNMP Communicator, select Programs from your computer s Start menu. Select American Power Conversion, then OPC SNMP Gateway, then Tools, then SNMP Communicator. When you start SNMP Communicator, the SNMP Server screen does not open. SNMP Communicator is a stand-alone SNMP communication product, and it accesses the field device directly over the network. There are two ways to use Communicator. You may browse a network that has already been configured using SNMP Editor. Alternately, you may manually fill in the required SNMP MIB data fields. To browse an existing configuration, see Browsing an Existing Database. To use SNMP Communicator without browsing, see Spot-Checking SNMP Data. 42
45 Browsing an Existing Database The Communicator screen is split into two major parts. The left screen is the device browser area; it shows a list of the available network devices and the tags that you have configured in SNMP Editor. The right side of the screen displays real-time data from any of the configured tags or from any tag for which you have the correct MIB address data. To begin, browse the SNMP tree in the left screen. Click the mouse over the + sign to the left of the words APC in the device browser area of the OPC Data Tree screen to display the configured devices on your network. 43
46 If there is no + or sign to the left of the tree, then you probably have not configured any devices from within SNMP Editor. Exit SNMP Communicator and first configure the devices in your network, or skip ahead to the Spot-Checking SNMP Data section of this Help manual. Click on the + sign to the left of a configured network device to view a list of all the tags configured for that device. 44
47 When all the tags that have been configured are displayed, it is possible to add individual tags to the Communicator real-time view area. To view any tag, first highlight the individual tag by clicking on it in the SNMP OPC Gateway window (the left frame of the screen). The MIB data for that tag will be automatically entered into the data fields in the right frame of the screen. SNMP Communicator allows access to one tag at a time; it is primarily meant as a troubleshooting tool. If you need to view multiple tags concurrently, use the SNMP Dataviewer utility. 45
48 Six items of information are displayed about each tag within the SNMP Communicator display windows. 1. The first window is the IP address of the SNMP agent that is being polled. To communicate with a manageable network device, you must first configure an SNMP address for it. If you are unsure whether this has been done, refer to the management manual for your network device. 2. The second text box is the Community field. The Community field is essentially a password field. The community setting in this field must match the community that is set in the UPS or other APC network device. Many device manufacturers will have a default community setting of Private for full access privileges to their network device. Often there is also a default Public community, which will allow read-only privileges from the SNMP agent. Many network devices will allow you to create a number of communities, all of which have varying levels of access to that device s MIB data. If an IT group maintains the network device that you are communicating to, you should coordinate with them to determine the correct community to use. 3. The third field is the SNMP Object Identifier for the tag. The SNMP Object Identifier is the specific data address for the information you are requesting from the SNMP agent embedded in your UPS or other APC network device. Most MIB addresses follow an Object ID nomenclature that has a series of whole numbers separated by periods (for example: ). 46
49 See also You can find the MIB Object ID addresses and descriptions in the network management manual supplied with your SNMPmanageable device. Be aware that some network component vendors have two product manuals one for installing and operating the network device, the other detailing network management information. 4. The fourth field is the Data Type for the MIB data you are going to be requesting. MIB data is stored in a number of formats various types of integers, strings, etc. Press the drop-down arrow on the right side of this dialog box to choose the data type from a pre-defined list. The Data Type for your specific MIB data can be found in the management manual or in the MIB definition file for your network device. 5. The fifth field of data is the Current Value of the tag. SNMP Communicator only retrieves data from the manageable network device when you press the Get Next or Set button. It is normal to see a line of question marks until the Trigger button is pressed. 6. The sixth field is the Description field. This field will be populated with the text that was set in the Description field of SNMP Editor. If there is no text, SNMP Communicator will still work. 47
50 Reading SNMP Data To initiate a poll of the SNMP MIB data, click on the Get button to poll the SNMP agent in the selected device. The Get Next button will increment through the MIB and retrieve the data. The Current Value text box will reflect the state of the requested SNMP MIB Object Identifier. The read function is only activated once, at the moment that the Get or Get Next button is pressed. To update the data, you must press the Get or Get Next button again. Writing SNMP Data To initiate a write to the SNMP MIB database, use the Set button on the bottom of the screen. You can change the value of an Object ID only if it is permitted by the configuration of the SNMP agent in the device you are interrogating. You also have to configure the tag for write ability in the SNMP Editor. You can view the status of the tag in the SNMP OPC Gateway Information section of the Communicator. When attempting to set a value in the SNMP MIB, you must be at the proper community setting (either Read/Write or Write only). This community setting is configured when setting up the device. Spot-Checking SNMP Data It is not necessary to set up a device in SNMP Editor to be able to communicate with any SNMP-manageable device using SNMP Communicator. To spot-check SNMP MIB data on a network, you will need four pieces of information from the SNMP agent about the MIB data item that you want to read: 1. The IP address of the SNMP agent that is being polled. Enter this data in the SNMP Agent field on the right side of the Communicator 48
51 interface. There are four boxes in this field, one for each of the four sections of the SNMP agent IP address. You must configure an SNMP address in the manageable network device to communicate to it. If you are unsure whether this configuration has been done, refer to the network manual for the device and configure it before attempting to use SNMP Communicator. 2. The Community for which that the managed network device is configured. The Community is essentially a password field. The community setting in this field must match the community that is set in the SNMP manageable switch. Many device manufacturers will have a default community setting of Private for full access privileges to their network device. Often there is also a default Public community, which will allow read-only privileges from the SNMP agent. Many network devices will allow you to create a number of communities, all of which have varying levels of access to the device s MIB data. If the network device that you are communicating to is maintained by an IT group, you should coordinate with that group to determine the correct community to use. 3. The SNMP Object Identifier for the tag. The SNMP Object Identifier is the specific data address for the information you are requesting from the SNMP agent embedded in your manageable network device. Most MIB addresses follow an Object ID nomenclature that has a series of whole numbers separated by periods (for example: ). 49
52 See also You can find the MIB Object ID addresses and descriptions in the network management manual supplied with your SNMPmanageable device. Be aware that some network component vendors have two product manuals one for installing and operating the network device, the other detailing network management information. 4. The Data Type for the MIB data you are going to be requesting. MIB data is stored in a number of formats various types of integers, strings, etc. Press the drop-down arrow on the right side of this dialog box to choose the data type from a pre-defined list. The Data Type for your specific MIB data can be found in the management manual or in the MIB definition file for your network device. See also 50
53 SNMP Dataviewer SNMP Dataviewer is an OPC client application designed to help SNMP users verify that the SNMP OPC Server is collecting and sharing data properly. SNMP Dataviewer can be a useful tool in troubleshooting potential problems with OPC communication. When you first start SNMP Dataviewer, the SNMP Server screen will flash open and then will minimize to run as a service on your computer. To open SNMP Dataviewer, select Programs from your computer s Start menu. Select American Power Conversion, then, then Tools, then Dataviewer. Reading Data Before using SNMP Dataviewer, you must configure your SNMP database using the SNMP Editor. Refer to SNMP Editor in the Help menu for instructions. The Dataviewer screen is split into two windows. The left screen is the device browser area. This area will show a list of the available network devices and the tags that you have configured in SNMP Editor. The right side of the screen allows you to view real-time data from any of the configured tags. To begin, you must browse the SNMP data tree in the left screen. Click the mouse over the + sign to the left of the phrase APC on the OPC Data Tree screen; you will see a list of the configured devices on the network. 51
54 If there is no + or sign to the left of the phrase APC SNMP OPC Gateway, you probably have not configured any devices from within SNMP Editor. Exit SNMP Dataviewer and launch SNMP Editor to configure the devices in your network first. Click on the + sign to the left of the network device you wish to receive data from. A list of all the tags configured for that device will appear, and you can add individual tags into the Dataviewer real-time view area. To view any tag, first click on the individual tag in the OPC Data Tree window, then press the -> in the taskbar. (Double-clicking on the tag will also move the tag into the real-time viewing area.) 52
55 To give the OPC Data tree window a more organized appearance, you can press the button to the left of any device s icon. This will hide the list of tags from this device, and help you navigate to other network devices more easily. You will note that there are four items of information displayed about each tag within the real-time display window: 1. First is the tag Name of the data. The tag name from within the real-time window is displayed in OPC naming format, which is <Device>.<Tag name>. 2. The second column is the Read/Write column. This column displays whether the tag is configured for read-only or for read/write privileges. If the device has read/write privileges, then you can actually set the tag value from within SNMP Dataviewer. See Writing Data for details. 3. The third column of data is the current value of the tag. This column displays the data in real-time as often as it is updated by the SNMP driver. If you are receiving values of 0 or *, the Dataviewer probably has a problem communicating to your SNMP manageable network devices. Verify that you are attached to the network and then verify that the network device you have configured is powered. 4. The fourth column shows the time stamp for the last update time the data was retrieved from the SNMP manageable device. To increase or decrease the frequency of the data update, see Advanced settings. 53
56 Now that you have begun to gather real-time data, you can easily change the data points that you are monitoring. To add a tag from another device, simply open the tag listing for that device by clicking on the + sign to the left of the device name as you did for the first device, highlight the tag that you want to monitor, and press the -> button on the taskbar above the Dataview windows. To remove a tag from the real-time window, highlight it by clicking on it and then press the <- button on the taskbar. If you want to remove multiple tags, you can hold down the Ctrl key on your keyboard, and then click to select each desired tag. When you press the <- button on the taskbar, all highlighted tags will be moved out of the real-time Dataview window. Writing Data To write data to a manageable network device from within SNMP Dataviewer, first ensure that the point is read/writeable. You can do this by looking at the R/W column in Dataviewer. If the column has a R/W by the tag, then the tag was configured with Read/Write properties in SNMP Editor. The SNMP agent residing on the network device may only support read-only for all or some tags, and selecting write privileges from within SNMP Editor does not guarantee that write commands will be executed. Another factor that affects read/write privileges is the community password that you defined during the Network Device setup. Consult the network management manual for your network device to be sure of the functionality supported. Assuming that you have configured the tag to be writeable, you can write a value by simply double clicking on the tag from within the real-time Dataviewer window. When you double click on the point, a Write Value pop-up window will appear. 54
57 Type the new value that you want in the New Item Value text box, and click the OK button. Once you have done this, the new value should appear on the next scan of that tag. Saving and retrieving Dataview windows After you have selected the tags that you want to monitor, you may want to save the list, so that you do not have to re-browse and select the tags every time you restart SNMP Dataviewer. To save your list, press the Save Dataview button (which looks like a floppy disk) located above the real-time Dataviewer window. A Save As window will appear. Type a file name for the Dataview that you want to be able to recall and then click the Save button. At this point the Dataview that you have created will be available any time you restart SNMP Dataviewer. To recall a Dataview after restarting SNMP Dataviewer, press the Open button, located above the real-time Dataviewer window, or select Open from the File menu. An Open window will appear. Select the Dataview you want from the list and press the Open button. Your pre-selected tag database will automatically be loaded. 55
58 Advanced settings SNMP Dataviewer allows you to make changes to the base SNMP OPC Gateway poll rate, as well as the SNMP Dataviewer OPC update rate. The difference between these two poll rates is as follows: The Base SNMP Poll rate is the frequency with which the SNMP OPC Gateway driver will make requests of the network device for data. For example, a base SNMP poll rate of 1000 ms will ensure that the SNMP OPC Gateway driver will attempt to poll the network devices that have been configured no more than once every 1000 milliseconds. The Sync Poll rate is the rate at which SNMP Dataviewer requests information from the SNMP polling engine. There are two selections within the Sync poll rate. The default is the Cache setting. In most circumstances, the Cache is the preferred polling method. This allows the SNMP Dataviewer to display a cached value if the SNMP polling engine does not have a refreshed value from the manageable network device. Selecting the device polling selection will make Dataviewer wait for a refreshed SNMP data value. This action can sometimes slow the performance of the application. Do not change the base SNMP poll rate below 1000 ms, unless you have discussed your application with SNMP tech support. 56
59 OPC Server Interface The OPC driver will be started by any OPC client that requests data from it. If there is not an OPC client requesting information, the SNMP Server will be inactive. You can verify that the SNMP Server is running by looking for a small SNMP icon in the lower right hand taskbar of your operating system. This icon shows that the OPC driver is running. If you minimize the OPC client software application (and any other software windows you may have opened), you will see the OPC Engine interface. This interface has a few important tools, as well as an event log that can assist you in troubleshooting your application. In the window, you will be told how many OPC clients are currently connected to the SNMP Server. Multiple OPC clients can connect to the SNMP Server, so it is possible to have both SNMP Dataviewer and a user interface package communicating simultaneously to the SNMPmanageable device. If any polling errors occur, they will be listed in the event log screen, with a date and time stamp for the event. You can easily view a history of the last 100 errors. The log will begin to overwrite the oldest error after reaching 100 events, to ensure that the event log does not become too large. If you wish, you can save the event log at any time by pressing the Save button on the left side of the interface. This action will save the log file as a text file, which can be helpful to tech support staff, in the event you are having communication problems. 57
60 You can also print the event log out to a printer. Press the Print button on the left side of the interface, and follow the instructions to print to one of your pre-configured printers. 58
61 APC Enterprise Account Support Customer support for this APC product is available at no charge when you contact an APC Enterprise Account Support center by telephone or . Telephone: (888) Contact the APC representative or other distributor from whom you purchased your APC product for information on how to obtain local customer support. 59
62 Copyright Entire contents 2005 American Power Conversion. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited. APC and the APC logo are trademarks of American Power Conversion Corporation and may be registered in some jurisdictions. All other trademarks, product names, and corporate names are the property of their respective owners and are used for informational purposes only /
Legal Notes. Regarding Trademarks. 2012 KYOCERA Document Solutions Inc.
 Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held liable for any problems arising from
Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held liable for any problems arising from
NETWORK PRINT MONITOR User Guide
 NETWORK PRINT MONITOR User Guide Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held liable
NETWORK PRINT MONITOR User Guide Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held liable
Moxa EDS-SNMP OPC Server Pro User s Manual. www.moxa.com/product
 Moxa EDS-SNMP OPC Server Pro User s Manual www.moxa.com/product Second Edition, June 2008 2008 Moxa Inc., all rights reserved. Reproduction without permission is prohibited. Moxa EDS-SNMP OPC Server Pro
Moxa EDS-SNMP OPC Server Pro User s Manual www.moxa.com/product Second Edition, June 2008 2008 Moxa Inc., all rights reserved. Reproduction without permission is prohibited. Moxa EDS-SNMP OPC Server Pro
How To Use Senior Systems Cloud Services
 Senior Systems Cloud Services In this guide... Senior Systems Cloud Services 1 Cloud Services User Guide 2 Working In Your Cloud Environment 3 Cloud Profile Management Tool 6 How To Save Files 8 How To
Senior Systems Cloud Services In this guide... Senior Systems Cloud Services 1 Cloud Services User Guide 2 Working In Your Cloud Environment 3 Cloud Profile Management Tool 6 How To Save Files 8 How To
Rapid Assessment Key User Manual
 Rapid Assessment Key User Manual Table of Contents Getting Started with the Rapid Assessment Key... 1 Welcome to the Print Audit Rapid Assessment Key...1 System Requirements...1 Network Requirements...1
Rapid Assessment Key User Manual Table of Contents Getting Started with the Rapid Assessment Key... 1 Welcome to the Print Audit Rapid Assessment Key...1 System Requirements...1 Network Requirements...1
Dell SupportAssist Version 2.0 for Dell OpenManage Essentials Quick Start Guide
 Dell SupportAssist Version 2.0 for Dell OpenManage Essentials Quick Start Guide Notes, Cautions, and Warnings NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
Dell SupportAssist Version 2.0 for Dell OpenManage Essentials Quick Start Guide Notes, Cautions, and Warnings NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
User Manual. Onsight Management Suite Version 5.1. Another Innovation by Librestream
 User Manual Onsight Management Suite Version 5.1 Another Innovation by Librestream Doc #: 400075-06 May 2012 Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Reproduction in any manner
User Manual Onsight Management Suite Version 5.1 Another Innovation by Librestream Doc #: 400075-06 May 2012 Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Reproduction in any manner
Network FAX Driver. Operation Guide
 Network FAX Driver Operation Guide About this Operation Guide This Operation Guide explains the settings for the Network FAX driver as well as the procedures that are required in order to use the Network
Network FAX Driver Operation Guide About this Operation Guide This Operation Guide explains the settings for the Network FAX driver as well as the procedures that are required in order to use the Network
There are numerous ways to access monitors:
 Remote Monitors REMOTE MONITORS... 1 Overview... 1 Accessing Monitors... 1 Creating Monitors... 2 Monitor Wizard Options... 11 Editing the Monitor Configuration... 14 Status... 15 Location... 17 Alerting...
Remote Monitors REMOTE MONITORS... 1 Overview... 1 Accessing Monitors... 1 Creating Monitors... 2 Monitor Wizard Options... 11 Editing the Monitor Configuration... 14 Status... 15 Location... 17 Alerting...
XStream Remote Control: Configuring DCOM Connectivity
 XStream Remote Control: Configuring DCOM Connectivity APPLICATION BRIEF March 2009 Summary The application running the graphical user interface of LeCroy Windows-based oscilloscopes is a COM Automation
XStream Remote Control: Configuring DCOM Connectivity APPLICATION BRIEF March 2009 Summary The application running the graphical user interface of LeCroy Windows-based oscilloscopes is a COM Automation
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions
 HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Applications Notes Best Practices for Using SolarWinds' ORION to Monitor SANiQ Performance Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Applications Notes Best Practices for Using SolarWinds' ORION to Monitor SANiQ Performance Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services
Liebert Nform Infrastructure Monitoring Software. User Manual - Version 4
 Liebert Nform Infrastructure Monitoring Software User Manual - Version 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 ABOUT LIEBERT NFORM................................................1 1.1 How Do You Contact Emerson Network
Liebert Nform Infrastructure Monitoring Software User Manual - Version 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 ABOUT LIEBERT NFORM................................................1 1.1 How Do You Contact Emerson Network
PREFACE http://www.okiprintingsolutions.com 07108001 iss.01 -
 Network Guide PREFACE Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document is complete, accurate, and up-to-date. The manufacturer assumes no responsibility for the results of errors
Network Guide PREFACE Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document is complete, accurate, and up-to-date. The manufacturer assumes no responsibility for the results of errors
Nortel Networks Call Center Reporting Set Up and Operation Guide
 Nortel Networks Call Center Reporting Set Up and Operation Guide www.nortelnetworks.com 2001 Nortel Networks P0919439 Issue 07 (24) Table of contents How to use this guide... 5 Introduction...5 How this
Nortel Networks Call Center Reporting Set Up and Operation Guide www.nortelnetworks.com 2001 Nortel Networks P0919439 Issue 07 (24) Table of contents How to use this guide... 5 Introduction...5 How this
Advantech WebAccess Device Driver Guide. BwSNMP Advantech WebAccess to SNMP Agent (Simple Network Management Protocol) Device Driver Guide
 BwSNMP Advantech WebAccess to SNMP Agent (Simple Network Management Protocol) Device Driver Guide Version 5.0 rev 1 Advantech Corp., Ltd. Table of Contents BwSNMP Advantech WebAccess to SNMP Agent (Simple
BwSNMP Advantech WebAccess to SNMP Agent (Simple Network Management Protocol) Device Driver Guide Version 5.0 rev 1 Advantech Corp., Ltd. Table of Contents BwSNMP Advantech WebAccess to SNMP Agent (Simple
3 Setting up Databases on a Microsoft SQL 7.0 Server
 3 Setting up Databases on a Microsoft SQL 7.0 Server Overview of the Installation Process To set up GoldMine properly, you must follow a sequence of steps to install GoldMine s program files, and the other
3 Setting up Databases on a Microsoft SQL 7.0 Server Overview of the Installation Process To set up GoldMine properly, you must follow a sequence of steps to install GoldMine s program files, and the other
ODBC Client Driver Help. 2015 Kepware, Inc.
 2015 Kepware, Inc. 2 Table of Contents Table of Contents 2 4 Overview 4 External Dependencies 4 Driver Setup 5 Data Source Settings 5 Data Source Setup 6 Data Source Access Methods 13 Fixed Table 14 Table
2015 Kepware, Inc. 2 Table of Contents Table of Contents 2 4 Overview 4 External Dependencies 4 Driver Setup 5 Data Source Settings 5 Data Source Setup 6 Data Source Access Methods 13 Fixed Table 14 Table
Launch Create Store. Import Orders Enter Orders Manually Process Orders. Note: Ctrl+click on a number to jump to that topic.
 Order Manager Version 5 QUICK START GUIDE Updated 1/6/11 About the Quick Start Guide This Quick Start Guide is designed to help users get started with the Order Manager as rapidly as possible. Although
Order Manager Version 5 QUICK START GUIDE Updated 1/6/11 About the Quick Start Guide This Quick Start Guide is designed to help users get started with the Order Manager as rapidly as possible. Although
File Management Utility User Guide
 File Management Utility User Guide Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held
File Management Utility User Guide Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held
OPC Server Machine Configuration
 OPC Server Machine Configuration General Information For remote OPC Server operation, server must be running under Windows XP Pro, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista (Business & Ultimate), Windows 7 (Professional
OPC Server Machine Configuration General Information For remote OPC Server operation, server must be running under Windows XP Pro, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista (Business & Ultimate), Windows 7 (Professional
Administrator s Guide
 Administrator s Guide Citrix Network Manager for MetaFrame XPe Version 1.0 Citrix Systems, Inc. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in examples
Administrator s Guide Citrix Network Manager for MetaFrame XPe Version 1.0 Citrix Systems, Inc. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in examples
Network Scanner Tool R3.1. User s Guide Version 3.0.04
 Network Scanner Tool R3.1 User s Guide Version 3.0.04 Copyright 2000-2004 by Sharp Corporation. All rights reserved. Reproduction, adaptation or translation without prior written permission is prohibited,
Network Scanner Tool R3.1 User s Guide Version 3.0.04 Copyright 2000-2004 by Sharp Corporation. All rights reserved. Reproduction, adaptation or translation without prior written permission is prohibited,
DocuPrint C3290 FS Features Setup Guide
 DocuPrint C3290 FS Features Setup Guide Adobe and PostScript are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/or other countries. Apple, Bonjour, ColorSync, EtherTalk, Macintosh, and
DocuPrint C3290 FS Features Setup Guide Adobe and PostScript are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/or other countries. Apple, Bonjour, ColorSync, EtherTalk, Macintosh, and
RSView 32 ACTIVE DISPLAY SYSTEM GETTING RESULTS GUIDE. PUBLICATION VW32AD-GR001E-EN-E July 2011 Supersedes Publication VW32AD-GR001D-EN-E
 RSView 32 ACTIVE DISPLAY SYSTEM GETTING RESULTS GUIDE PUBLICATION VW32AD-GR001E-EN-E July 2011 Supersedes Publication VW32AD-GR001D-EN-E Contact Rockwell Copyright Notice Trademark Notices Customer Support
RSView 32 ACTIVE DISPLAY SYSTEM GETTING RESULTS GUIDE PUBLICATION VW32AD-GR001E-EN-E July 2011 Supersedes Publication VW32AD-GR001D-EN-E Contact Rockwell Copyright Notice Trademark Notices Customer Support
USER GUIDE WEB-BASED SYSTEM CONTROL APPLICATION. www.pesa.com August 2014 Phone: 256.726.9200. Publication: 81-9059-0703-0, Rev. C
 USER GUIDE WEB-BASED SYSTEM CONTROL APPLICATION Publication: 81-9059-0703-0, Rev. C www.pesa.com Phone: 256.726.9200 Thank You for Choosing PESA!! We appreciate your confidence in our products. PESA produces
USER GUIDE WEB-BASED SYSTEM CONTROL APPLICATION Publication: 81-9059-0703-0, Rev. C www.pesa.com Phone: 256.726.9200 Thank You for Choosing PESA!! We appreciate your confidence in our products. PESA produces
Server Manager Performance Monitor. Server Manager Diagnostics Page. . Information. . Audit Success. . Audit Failure
 Server Manager Diagnostics Page 653. Information. Audit Success. Audit Failure The view shows the total number of events in the last hour, 24 hours, 7 days, and the total. Each of these nodes can be expanded
Server Manager Diagnostics Page 653. Information. Audit Success. Audit Failure The view shows the total number of events in the last hour, 24 hours, 7 days, and the total. Each of these nodes can be expanded
Kaseya 2. Quick Start Guide. for Network Monitor 4.1
 Kaseya 2 Syslog Monitor Quick Start Guide for Network Monitor 4.1 June 5, 2012 About Kaseya Kaseya is a global provider of IT automation software for IT Solution Providers and Public and Private Sector
Kaseya 2 Syslog Monitor Quick Start Guide for Network Monitor 4.1 June 5, 2012 About Kaseya Kaseya is a global provider of IT automation software for IT Solution Providers and Public and Private Sector
Getting Started with Vision 6
 Getting Started with Vision 6 Version 6.9 Notice Copyright 1981-2009 Netop Business Solutions A/S. All Rights Reserved. Portions used under license from third parties. Please send any comments to: Netop
Getting Started with Vision 6 Version 6.9 Notice Copyright 1981-2009 Netop Business Solutions A/S. All Rights Reserved. Portions used under license from third parties. Please send any comments to: Netop
Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing User s Guide. Citrx EdgeSight for Load Testing 2.7
 Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing User s Guide Citrx EdgeSight for Load Testing 2.7 Copyright Use of the product documented in this guide is subject to your prior acceptance of the End User License Agreement.
Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing User s Guide Citrx EdgeSight for Load Testing 2.7 Copyright Use of the product documented in this guide is subject to your prior acceptance of the End User License Agreement.
Network Monitoring. SAN Discovery and Topology Mapping. Device Discovery. Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.
 CHAPTER 57 The primary purpose of Fabric Manager is to manage the network. In particular, SAN discovery and network monitoring are two of its key network management capabilities. This chapter contains
CHAPTER 57 The primary purpose of Fabric Manager is to manage the network. In particular, SAN discovery and network monitoring are two of its key network management capabilities. This chapter contains
Legal Notes. Regarding Trademarks. 2011 KYOCERA MITA Corporation
 Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held liable for any problems arising from
Legal Notes Unauthorized reproduction of all or part of this guide is prohibited. The information in this guide is subject to change without notice. We cannot be held liable for any problems arising from
ViewPower. User s Manual. Management Software for Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems
 ViewPower User s Manual Management Software for Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Table of Contents 1. ViewPower Overview... 2 1.1. Introduction...2 1.2. Structure...2 1.3. Applications...2 1.4. Features...2
ViewPower User s Manual Management Software for Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Table of Contents 1. ViewPower Overview... 2 1.1. Introduction...2 1.2. Structure...2 1.3. Applications...2 1.4. Features...2
FactoryTalk Gateway Getting Results Guide
 Performance and Visibility FactoryTalk Gateway Getting Results Guide Getting Results Guide Table of contents Chapter 1 Introduction Intended audience... 7 Where to find additional information... 7 Help...
Performance and Visibility FactoryTalk Gateway Getting Results Guide Getting Results Guide Table of contents Chapter 1 Introduction Intended audience... 7 Where to find additional information... 7 Help...
Software Version 5.1 November, 2014. Xerox Device Agent User Guide
 Software Version 5.1 November, 2014 Xerox Device Agent User Guide 2014 Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Xerox and Xerox and Design are trademarks of Xerox Corporation in the United States and/or
Software Version 5.1 November, 2014 Xerox Device Agent User Guide 2014 Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Xerox and Xerox and Design are trademarks of Xerox Corporation in the United States and/or
TAMUS Terminal Server Setup BPP SQL/Alva
 We have a new method of connecting to the databases that does not involve using the Texas A&M campus VPN. The new way of gaining access is via Remote Desktop software to a terminal server running here
We have a new method of connecting to the databases that does not involve using the Texas A&M campus VPN. The new way of gaining access is via Remote Desktop software to a terminal server running here
Device Installer User Guide
 Device Installer User Guide Part Number 900-325 Revision B 12/08 Table Of Contents 1. Overview... 1 2. Devices... 2 Choose the Network Adapter for Communication... 2 Search for All Devices on the Network...
Device Installer User Guide Part Number 900-325 Revision B 12/08 Table Of Contents 1. Overview... 1 2. Devices... 2 Choose the Network Adapter for Communication... 2 Search for All Devices on the Network...
Chapter 5 - Ethernet Setup
 Chapter 5 - Ethernet Setup Chapter Overview Introduction... 5-3 EtherTalk Network Configuration... 5-3 Select the EtherTalk Phase 2 Driver...5-3 Change the EtherTalk Zone Name...5-4 Novell NetWare Configuration...
Chapter 5 - Ethernet Setup Chapter Overview Introduction... 5-3 EtherTalk Network Configuration... 5-3 Select the EtherTalk Phase 2 Driver...5-3 Change the EtherTalk Zone Name...5-4 Novell NetWare Configuration...
Context-sensitive Help Guide
 MadCap Software Context-sensitive Help Guide Flare 11 Copyright 2015 MadCap Software. All rights reserved. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described in this
MadCap Software Context-sensitive Help Guide Flare 11 Copyright 2015 MadCap Software. All rights reserved. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described in this
TSM Studio Server User Guide 2.9.0.0
 TSM Studio Server User Guide 2.9.0.0 1 Table of Contents Disclaimer... 4 What is TSM Studio Server?... 5 System Requirements... 6 Database Requirements... 6 Installing TSM Studio Server... 7 TSM Studio
TSM Studio Server User Guide 2.9.0.0 1 Table of Contents Disclaimer... 4 What is TSM Studio Server?... 5 System Requirements... 6 Database Requirements... 6 Installing TSM Studio Server... 7 TSM Studio
SNMP Web card. User s Manual. Management Software for Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems
 SNMP Web card User s Manual Management Software for Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Table of Contents 1. Overview... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Features... 3 1.3 Overlook... 3 1.4 Installation and
SNMP Web card User s Manual Management Software for Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Table of Contents 1. Overview... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Features... 3 1.3 Overlook... 3 1.4 Installation and
Andover Continuum Remote Communication Configuration Guide
 Andover Continuum Remote Communication Configuration Guide 2010, Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced, read or stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted,
Andover Continuum Remote Communication Configuration Guide 2010, Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced, read or stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted,
Using DC Agent for Transparent User Identification
 Using DC Agent for Transparent User Identification Using DC Agent Web Security Solutions v7.7, 7.8 If your organization uses Microsoft Windows Active Directory, you can use Websense DC Agent to identify
Using DC Agent for Transparent User Identification Using DC Agent Web Security Solutions v7.7, 7.8 If your organization uses Microsoft Windows Active Directory, you can use Websense DC Agent to identify
2X ApplicationServer & LoadBalancer Manual
 2X ApplicationServer & LoadBalancer Manual 2X ApplicationServer & LoadBalancer Contents 1 URL: www.2x.com E-mail: [email protected] Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies,
2X ApplicationServer & LoadBalancer Manual 2X ApplicationServer & LoadBalancer Contents 1 URL: www.2x.com E-mail: [email protected] Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies,
Novell ZENworks Asset Management 7.5
 Novell ZENworks Asset Management 7.5 w w w. n o v e l l. c o m October 2006 USING THE WEB CONSOLE Table Of Contents Getting Started with ZENworks Asset Management Web Console... 1 How to Get Started...
Novell ZENworks Asset Management 7.5 w w w. n o v e l l. c o m October 2006 USING THE WEB CONSOLE Table Of Contents Getting Started with ZENworks Asset Management Web Console... 1 How to Get Started...
Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing User s Guide. Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing 3.8
 Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing User s Guide Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing 3.8 Copyright Use of the product documented in this guide is subject to your prior acceptance of the End User License Agreement.
Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing User s Guide Citrix EdgeSight for Load Testing 3.8 Copyright Use of the product documented in this guide is subject to your prior acceptance of the End User License Agreement.
12 NETWORK MANAGEMENT
 12 NETWORK MANAGEMENT PROJECTS Project 12.1 Project 12.2 Project 12.3 Project 12.4 Understanding Key Concepts Backing Up and Restoring Data Monitoring Computer Activity Configuring SNMP Support 276 Networking
12 NETWORK MANAGEMENT PROJECTS Project 12.1 Project 12.2 Project 12.3 Project 12.4 Understanding Key Concepts Backing Up and Restoring Data Monitoring Computer Activity Configuring SNMP Support 276 Networking
Monitoring the Network
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how the DCNM-SAN manages the network. In particular, SAN discovery and network monitoring are two of its key network management capabilities. This chapter contains the
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how the DCNM-SAN manages the network. In particular, SAN discovery and network monitoring are two of its key network management capabilities. This chapter contains the
SHARP Digital Signage Software Pro PN-SS05 OPERATION MANUAL
 SHARP Digital Signage Software Pro PN-SS05 Version 4.1 OPERATION MANUAL Contents Introduction... 2 Precautions on Use...2 Trademarks...2 How to Read this Manual...3 Definitions...3 Installing/Launching...
SHARP Digital Signage Software Pro PN-SS05 Version 4.1 OPERATION MANUAL Contents Introduction... 2 Precautions on Use...2 Trademarks...2 How to Read this Manual...3 Definitions...3 Installing/Launching...
Network Setup Guide. Introduction. Setting up for use over LAN
 Network Setup Guide This manual contains the setup information required to use the machine over wired LAN. If you use the machine with USB connection, refer to your setup sheet. Introduction To use the
Network Setup Guide This manual contains the setup information required to use the machine over wired LAN. If you use the machine with USB connection, refer to your setup sheet. Introduction To use the
SNMP Adapter Installation and Configuration Guide
 SNMP Adapter Installation and Configuration Guide vcenter Operations Manager 1.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
SNMP Adapter Installation and Configuration Guide vcenter Operations Manager 1.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
rev. 31 (applies to CyBro OPC Server v3.0.4 and later)
 CyBro OPC Server User Manual rev. 31 (applies to CyBro OPC Server v3.0.4 and later) 2003-2013 Cybrotech Ltd www.cybrotech.co.uk Index Index... 1 General... 2 Installation... 2 Activation code... 2 Configuration...
CyBro OPC Server User Manual rev. 31 (applies to CyBro OPC Server v3.0.4 and later) 2003-2013 Cybrotech Ltd www.cybrotech.co.uk Index Index... 1 General... 2 Installation... 2 Activation code... 2 Configuration...
Scheduling Automated Outlet Control Using FineSNMPSet with Sentry Switched Power Distribution Units
 Scheduling Automated Outlet Control Using FineSNMPSet with Sentry Switched Power Distribution Units This documents the following topics: Purpose Overview FineSNMPSet Free-Ware Utility Windows Scheduled
Scheduling Automated Outlet Control Using FineSNMPSet with Sentry Switched Power Distribution Units This documents the following topics: Purpose Overview FineSNMPSet Free-Ware Utility Windows Scheduled
RedundancyMaster Help. 2014 Kepware Technologies
 2014 Kepware Technologies 2 RedundancyMaster Help Table of Contents Table of Contents 2 Introduction 4 System Requirements 10 Accessing the Administration Menu 11 Setting Up Redundancy 11 Adding Redundancy
2014 Kepware Technologies 2 RedundancyMaster Help Table of Contents Table of Contents 2 Introduction 4 System Requirements 10 Accessing the Administration Menu 11 Setting Up Redundancy 11 Adding Redundancy
CentreWare Internet Services Setup and User Guide. Version 2.0
 CentreWare Internet Services Setup and User Guide Version 2.0 Xerox Corporation Copyright 1999 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. XEROX, The Document Company, the digital X logo, CentreWare, and
CentreWare Internet Services Setup and User Guide Version 2.0 Xerox Corporation Copyright 1999 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. XEROX, The Document Company, the digital X logo, CentreWare, and
Network/Floating License Installation Instructions
 Network/Floating License Installation Instructions Installation steps: On the Windows PC that will act as License Manager (SERVER): 1. Install HASP Run-time environment, SERVER 2. Plug in the red USB hardware
Network/Floating License Installation Instructions Installation steps: On the Windows PC that will act as License Manager (SERVER): 1. Install HASP Run-time environment, SERVER 2. Plug in the red USB hardware
Portions of this product were created using LEADTOOLS 1991-2009 LEAD Technologies, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
 Installation Guide Lenel OnGuard 2009 Installation Guide, product version 6.3. This guide is item number DOC-110, revision 1.038, May 2009 Copyright 1992-2009 Lenel Systems International, Inc. Information
Installation Guide Lenel OnGuard 2009 Installation Guide, product version 6.3. This guide is item number DOC-110, revision 1.038, May 2009 Copyright 1992-2009 Lenel Systems International, Inc. Information
Allworx Installation Course
 VPN Hello and welcome. In the VPN section we will cover the steps for enabling the VPN feature on the Allworx server and how to set up a VPN connection to the Allworx System from your PC. Page 1 VPN The
VPN Hello and welcome. In the VPN section we will cover the steps for enabling the VPN feature on the Allworx server and how to set up a VPN connection to the Allworx System from your PC. Page 1 VPN The
DiskPulse DISK CHANGE MONITOR
 DiskPulse DISK CHANGE MONITOR User Manual Version 7.9 Oct 2015 www.diskpulse.com [email protected] 1 1 DiskPulse Overview...3 2 DiskPulse Product Versions...5 3 Using Desktop Product Version...6 3.1 Product
DiskPulse DISK CHANGE MONITOR User Manual Version 7.9 Oct 2015 www.diskpulse.com [email protected] 1 1 DiskPulse Overview...3 2 DiskPulse Product Versions...5 3 Using Desktop Product Version...6 3.1 Product
Setting Up ALERE with Client/Server Data
 Setting Up ALERE with Client/Server Data TIW Technology, Inc. November 2014 ALERE is a registered trademark of TIW Technology, Inc. The following are registered trademarks or trademarks: FoxPro, SQL Server,
Setting Up ALERE with Client/Server Data TIW Technology, Inc. November 2014 ALERE is a registered trademark of TIW Technology, Inc. The following are registered trademarks or trademarks: FoxPro, SQL Server,
C-more Remote Access, Data Log, FTP File Transfer, and Email Tutorial
 C-more Remote Access, Data Log, FTP File Transfer, and Email Tutorial P a g e 2 Introduction: This script will walk you through the basic process of setting up the remote access, data logging, FTP file
C-more Remote Access, Data Log, FTP File Transfer, and Email Tutorial P a g e 2 Introduction: This script will walk you through the basic process of setting up the remote access, data logging, FTP file
User's Reference Guide for PowerAlert UPS Management Software Version 10.2 for Windows
 User's Reference Guide for PowerAlert UPS Management Software Version 10.2 for Windows 1111 W. 35th Street Chicago, IL 60609 USA (773) 869-1234 www.tripplite.com Table of Contents A QUICK GUIDE TO POWERALERT
User's Reference Guide for PowerAlert UPS Management Software Version 10.2 for Windows 1111 W. 35th Street Chicago, IL 60609 USA (773) 869-1234 www.tripplite.com Table of Contents A QUICK GUIDE TO POWERALERT
Application Notes for Configuring Dorado Software Redcell Enterprise Bundle using SNMP with Avaya Communication Manager - Issue 1.
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Dorado Software Redcell Enterprise Bundle using SNMP with Avaya Communication Manager - Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Dorado Software Redcell Enterprise Bundle using SNMP with Avaya Communication Manager - Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Citrix Access Gateway Plug-in for Windows User Guide
 Citrix Access Gateway Plug-in for Windows User Guide Access Gateway 9.2, Enterprise Edition Copyright and Trademark Notice Use of the product documented in this guide is subject to your prior acceptance
Citrix Access Gateway Plug-in for Windows User Guide Access Gateway 9.2, Enterprise Edition Copyright and Trademark Notice Use of the product documented in this guide is subject to your prior acceptance
ECView Pro Network Management System. Installation Guide. www.edge-core.com
 ECView Pro Network Management System Installation Guide www.edge-core.com INSTALLATION GUIDE ECVIEW PRO NETWORK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM SNMP-Based Network Management Software for Windows SW6102 E102010-CS-R01
ECView Pro Network Management System Installation Guide www.edge-core.com INSTALLATION GUIDE ECVIEW PRO NETWORK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM SNMP-Based Network Management Software for Windows SW6102 E102010-CS-R01
Monitor TemPageR 4E With PageR Enterprise
 Monitor TemPageR 4E With PageR Enterprise TemPageR 4E is AVTECH Software s Real-Time Temperature Monitor with Data Logging, SNMP & Unlimited Alerting. It is designed specifically to monitor 1-4 digital
Monitor TemPageR 4E With PageR Enterprise TemPageR 4E is AVTECH Software s Real-Time Temperature Monitor with Data Logging, SNMP & Unlimited Alerting. It is designed specifically to monitor 1-4 digital
WhatsUpGold. v3.0. WhatsConnected User Guide
 WhatsUpGold v3.0 WhatsConnected User Guide Contents CHAPTER 1 Welcome to WhatsConnected Finding more information and updates... 2 Sending feedback... 3 CHAPTER 2 Installing and Configuring WhatsConnected
WhatsUpGold v3.0 WhatsConnected User Guide Contents CHAPTER 1 Welcome to WhatsConnected Finding more information and updates... 2 Sending feedback... 3 CHAPTER 2 Installing and Configuring WhatsConnected
How To Sync Between Quickbooks And Act
 QSalesData User Guide Note: In addition to this User Guide, we have an extensive Online Video Library that you can access from our website: www.qsalesdata.com/onlinevideos Updated: 11/14/2014 Installing
QSalesData User Guide Note: In addition to this User Guide, we have an extensive Online Video Library that you can access from our website: www.qsalesdata.com/onlinevideos Updated: 11/14/2014 Installing
ebus Player Quick Start Guide
 ebus Player Quick Start Guide This guide provides you with the information you need to efficiently set up and start using the ebus Player software application to control your GigE Vision or USB3 Vision
ebus Player Quick Start Guide This guide provides you with the information you need to efficiently set up and start using the ebus Player software application to control your GigE Vision or USB3 Vision
Compuprint 4247 Serial Matrix Printers
 Compuprint 4247 Serial Matrix Printers Remote Printer Management Utility for Serial Matrix Printers MAN10300-00.00 First edition (October 2011) This edition applies to the Compuprint 4247 printers and
Compuprint 4247 Serial Matrix Printers Remote Printer Management Utility for Serial Matrix Printers MAN10300-00.00 First edition (October 2011) This edition applies to the Compuprint 4247 printers and
Central Management Software CV3-M1024
 Table of Contents Chapter 1. User Interface Overview...5 Chapter 2. Installation...6 2.1 Beginning Installation...6 2.2 Starting the CMS software...10 2.3 Starting it from the Start menu...10 2.4 Starting
Table of Contents Chapter 1. User Interface Overview...5 Chapter 2. Installation...6 2.1 Beginning Installation...6 2.2 Starting the CMS software...10 2.3 Starting it from the Start menu...10 2.4 Starting
ATVS. Amano Time Validation System. Installation and Operation Guide. Enterprise Edition Version 4.2
 ATVS Amano Time Validation System Installation and Operation Guide Enterprise Edition Version 4.2 Thank you for purchasing another fine product from Amano Cincinnati, Inc. Proprietary Notice This document
ATVS Amano Time Validation System Installation and Operation Guide Enterprise Edition Version 4.2 Thank you for purchasing another fine product from Amano Cincinnati, Inc. Proprietary Notice This document
P-660R-T1/T3 v2 Quick Start Guide
 P-660R-T1/T3 v2 ADSL2+ Access Router Quick Start Guide Version 3.40 Edition 1 12/2006 0 Overview P-660R-T1/T3 v2 Quick Start Guide This Quick Start Guide shows you how to: 1 Connect the Hardware 2 Set
P-660R-T1/T3 v2 ADSL2+ Access Router Quick Start Guide Version 3.40 Edition 1 12/2006 0 Overview P-660R-T1/T3 v2 Quick Start Guide This Quick Start Guide shows you how to: 1 Connect the Hardware 2 Set
DTAP3000 DTSX3000 Control Visualization Software LAS2.0 Data Conversion Guide
 User s Manual DTAP3000 DTSX3000 Control Visualization Software LAS2.0 Data Conversion Guide 1st Edition Blank Page < Introduction > i Introduction About this Manual Thank you for purchasing the DTSX3000
User s Manual DTAP3000 DTSX3000 Control Visualization Software LAS2.0 Data Conversion Guide 1st Edition Blank Page < Introduction > i Introduction About this Manual Thank you for purchasing the DTSX3000
Velocity Web Services Client 1.0 Installation Guide and Release Notes
 Velocity Web Services Client 1.0 Installation Guide and Release Notes Copyright 2014-2015, Identiv. Last updated June 24, 2015. Overview This document provides the only information about version 1.0 of
Velocity Web Services Client 1.0 Installation Guide and Release Notes Copyright 2014-2015, Identiv. Last updated June 24, 2015. Overview This document provides the only information about version 1.0 of
Configuring a Custom Load Evaluator Use the XenApp1 virtual machine, logged on as the XenApp\administrator user for this task.
 Lab 8 User name: Administrator Password: Password1 Contents Exercise 8-1: Assigning a Custom Load Evaluator... 1 Scenario... 1 Configuring a Custom Load Evaluator... 1 Assigning a Load Evaluator to a Server...
Lab 8 User name: Administrator Password: Password1 Contents Exercise 8-1: Assigning a Custom Load Evaluator... 1 Scenario... 1 Configuring a Custom Load Evaluator... 1 Assigning a Load Evaluator to a Server...
AXIS Camera Station Quick Installation Guide
 AXIS Camera Station Quick Installation Guide Copyright Axis Communications AB April 2005 Rev. 3.5 Part Number 23997 1 Table of Contents Regulatory Information.................................. 3 AXIS Camera
AXIS Camera Station Quick Installation Guide Copyright Axis Communications AB April 2005 Rev. 3.5 Part Number 23997 1 Table of Contents Regulatory Information.................................. 3 AXIS Camera
Does the GC have an online document management solution?
 This FAQ contains: Web File Services definition Access web file services Create a WFS folder Upload a document Email a link to a document folder Create WFS subscription Cancel existing subscription Create
This FAQ contains: Web File Services definition Access web file services Create a WFS folder Upload a document Email a link to a document folder Create WFS subscription Cancel existing subscription Create
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions
 HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Application Notes Best Practices for Using PRTG Traffic Grapher to Monitor SANiQ Performance Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Application Notes Best Practices for Using PRTG Traffic Grapher to Monitor SANiQ Performance Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services
SevOne NMS Download Installation and Implementation Guide
 SevOne NMS Download Installation and Implementation Guide 5.3.X 530 V0002 Contents 1. Get Started... 3 2. SevOne Download Installation... 6 3. Appliance Network Configuration... 9 4. Install License and
SevOne NMS Download Installation and Implementation Guide 5.3.X 530 V0002 Contents 1. Get Started... 3 2. SevOne Download Installation... 6 3. Appliance Network Configuration... 9 4. Install License and
Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP
 Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP Mouse Desktop Windows Applications File handling Introduction to MS Windows XP 2 Table of Contents What is Windows XP?... 3 Windows within Windows... 3 The Desktop... 3 The
Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP Mouse Desktop Windows Applications File handling Introduction to MS Windows XP 2 Table of Contents What is Windows XP?... 3 Windows within Windows... 3 The Desktop... 3 The
Kaseya 2. Quick Start Guide. for Network Monitor 4.1
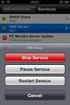 Kaseya 2 VMware Performance Monitor Quick Start Guide for Network Monitor 4.1 June 7, 2012 About Kaseya Kaseya is a global provider of IT automation software for IT Solution Providers and Public and Private
Kaseya 2 VMware Performance Monitor Quick Start Guide for Network Monitor 4.1 June 7, 2012 About Kaseya Kaseya is a global provider of IT automation software for IT Solution Providers and Public and Private
WhatsUp Event Alarm v10.x Listener Console User Guide
 WhatsUp Event Alarm v10.x Listener Console User Guide Contents WhatsUp Event Alarm Listener Console Overview Firewall Considerations... 6 Using the WhatsUp Event Alarm Listener Console... 7 Event Alarm
WhatsUp Event Alarm v10.x Listener Console User Guide Contents WhatsUp Event Alarm Listener Console Overview Firewall Considerations... 6 Using the WhatsUp Event Alarm Listener Console... 7 Event Alarm
Empowered by Innovation. Setting Up and Using Fax Mail. P/N 1770087 July 2006 Printed in U.S.A.
 Empowered by Innovation Setting Up and Using Fax Mail P/N 1770087 July 2006 Printed in U.S.A. This manual has been developed by NEC Unified Solutions, Inc. It is intended for the use of its customers and
Empowered by Innovation Setting Up and Using Fax Mail P/N 1770087 July 2006 Printed in U.S.A. This manual has been developed by NEC Unified Solutions, Inc. It is intended for the use of its customers and
NetBrain Discovery Appliance Manual
 NetBrain Discovery Appliance Manual NetBrain Technologies, Inc. 2009-07-20-1 - Table of Contents 1. Overview... 4 2. Installation... 5 2.1 Installation Software... 5 2.1.1 Install ActivePerl... 5 2.1.2
NetBrain Discovery Appliance Manual NetBrain Technologies, Inc. 2009-07-20-1 - Table of Contents 1. Overview... 4 2. Installation... 5 2.1 Installation Software... 5 2.1.1 Install ActivePerl... 5 2.1.2
Partner. Sage Pastel. Accounting. Installation Guide
 Sage Pastel Accounting Partner Installation Guide Sage Pastel: +27 11 304 3000 Sage Pastel Intl: +27 11 304 3400 www.pastel.co.za www.sagepastel.com [email protected] [email protected] Sage Pastel Accounting
Sage Pastel Accounting Partner Installation Guide Sage Pastel: +27 11 304 3000 Sage Pastel Intl: +27 11 304 3400 www.pastel.co.za www.sagepastel.com [email protected] [email protected] Sage Pastel Accounting
SA-9600 Surface Area Software Manual
 SA-9600 Surface Area Software Manual Version 4.0 Introduction The operation and data Presentation of the SA-9600 Surface Area analyzer is performed using a Microsoft Windows based software package. The
SA-9600 Surface Area Software Manual Version 4.0 Introduction The operation and data Presentation of the SA-9600 Surface Area analyzer is performed using a Microsoft Windows based software package. The
How to connect to VUWiFi
 Wireless Registration Instructions Windows XP How to connect to VUWiFi 1. The first step in setting up your wireless card for VUWiFi is to open your Network Connections window. You can find this by going
Wireless Registration Instructions Windows XP How to connect to VUWiFi 1. The first step in setting up your wireless card for VUWiFi is to open your Network Connections window. You can find this by going
Aspera Connect User Guide
 Aspera Connect User Guide Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008/7 Browser: Firefox 2+, IE 6+ Version 2.3.1 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Introduction Setting Up 2.1 Installation 2.2 Configure the Network Environment 2.3 Connect
Aspera Connect User Guide Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008/7 Browser: Firefox 2+, IE 6+ Version 2.3.1 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Introduction Setting Up 2.1 Installation 2.2 Configure the Network Environment 2.3 Connect
NEC Express5800 Series NEC ESMPRO AlertManager User's Guide
 NEC Express5800 Series NEC ESMPRO AlertManager User's Guide 7-2006 ONL-4152aN-COMMON-128-99-0606 PROPRIETARY NOTICE AND LIABILITY DISCLAIMER The information disclosed in this document, including all designs
NEC Express5800 Series NEC ESMPRO AlertManager User's Guide 7-2006 ONL-4152aN-COMMON-128-99-0606 PROPRIETARY NOTICE AND LIABILITY DISCLAIMER The information disclosed in this document, including all designs
TimeValue Software Due Date Tracking and Task Management Software
 User s Guide TM TimeValue Software Due Date Tracking and Task Management Software File In Time Software User s Guide Copyright TimeValue Software, Inc. (a California Corporation) 1992-2010. All rights
User s Guide TM TimeValue Software Due Date Tracking and Task Management Software File In Time Software User s Guide Copyright TimeValue Software, Inc. (a California Corporation) 1992-2010. All rights
Software Version 5.2 June 2015. Xerox Device Agent User Guide
 Software Version 5.2 June 2015 Xerox Device Agent User Guide 2015 Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Xerox, Xerox and Design and Phaser are trademarks of Xerox Corporation in the United States and/or
Software Version 5.2 June 2015 Xerox Device Agent User Guide 2015 Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Xerox, Xerox and Design and Phaser are trademarks of Xerox Corporation in the United States and/or
NDA-30141 ISSUE 1 STOCK # 200893. CallCenterWorX-Enterprise IMX MAT Quick Reference Guide MAY, 2000. NEC America, Inc.
 NDA-30141 ISSUE 1 STOCK # 200893 CallCenterWorX-Enterprise IMX MAT Quick Reference Guide MAY, 2000 NEC America, Inc. LIABILITY DISCLAIMER NEC America, Inc. reserves the right to change the specifications,
NDA-30141 ISSUE 1 STOCK # 200893 CallCenterWorX-Enterprise IMX MAT Quick Reference Guide MAY, 2000 NEC America, Inc. LIABILITY DISCLAIMER NEC America, Inc. reserves the right to change the specifications,
HP LaserJet MFP Analog Fax Accessory 300 Send Fax Driver Guide
 HP LaserJet MFP Analog Fax Accessory 300 Send Fax Driver Guide Copyright and License 2008 Copyright Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without prior written
HP LaserJet MFP Analog Fax Accessory 300 Send Fax Driver Guide Copyright and License 2008 Copyright Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without prior written
Microsoft Access Basics
 Microsoft Access Basics 2006 ipic Development Group, LLC Authored by James D Ballotti Microsoft, Access, Excel, Word, and Office are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation Version 1 - Revision
Microsoft Access Basics 2006 ipic Development Group, LLC Authored by James D Ballotti Microsoft, Access, Excel, Word, and Office are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation Version 1 - Revision
USER GUIDE. Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6
 KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. USER GUIDE Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6 Contents 1 Connecting to the Kramer Device via the Ethernet Port 1 1.1 Connecting the Ethernet Port Directly
KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. USER GUIDE Ethernet Configuration Guide (Lantronix) P/N: 2900-300321 Rev 6 Contents 1 Connecting to the Kramer Device via the Ethernet Port 1 1.1 Connecting the Ethernet Port Directly
NMS300 Network Management System
 NMS300 Network Management System User Manual June 2013 202-11289-01 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. After installing your device, locate
NMS300 Network Management System User Manual June 2013 202-11289-01 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. After installing your device, locate
Signature Center Getting Started Guide
 Signature Center Getting Started Guide 1113710 PRODUCED IN IRELAND Copyright 2010 McKesson Corporation and/or one of its subsidiaries. All Rights Reserved. This documentation is an unpublished work of
Signature Center Getting Started Guide 1113710 PRODUCED IN IRELAND Copyright 2010 McKesson Corporation and/or one of its subsidiaries. All Rights Reserved. This documentation is an unpublished work of
Gigabyte Management Console User s Guide (For ASPEED AST 2400 Chipset)
 Gigabyte Management Console User s Guide (For ASPEED AST 2400 Chipset) Version: 1.4 Table of Contents Using Your Gigabyte Management Console... 3 Gigabyte Management Console Key Features and Functions...
Gigabyte Management Console User s Guide (For ASPEED AST 2400 Chipset) Version: 1.4 Table of Contents Using Your Gigabyte Management Console... 3 Gigabyte Management Console Key Features and Functions...
Network Probe User Guide
 Network Probe User Guide Network Probe User Guide Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. Installation...2 Windows installation...2 Linux installation...3 Mac installation...4 License key...5 Deployment...5
Network Probe User Guide Network Probe User Guide Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. Installation...2 Windows installation...2 Linux installation...3 Mac installation...4 License key...5 Deployment...5
Integrating LANGuardian with Active Directory
 Integrating LANGuardian with Active Directory 01 February 2012 This document describes how to integrate LANGuardian with Microsoft Windows Server and Active Directory. Overview With the optional Identity
Integrating LANGuardian with Active Directory 01 February 2012 This document describes how to integrate LANGuardian with Microsoft Windows Server and Active Directory. Overview With the optional Identity
