Appraisal of risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 in central Indian population: a case control study
|
|
|
- Barbara Goodwin
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physical Anthropology Appraisal of risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 in central Indian population: a case control study Rama Lakshmi G. 1, Bandyopadhyay S.S. 1, Bhaskar L.V.K.S. 2, Sharma Madhubala 1, Rao Raghavendra V. 1,3 * Abstract Background: Diabetes mellitus is characterized by high levels of blood glucose, late onset of disease and associated with serious complications. Genetic and environmental risk factors are known to exist and the importance of elucidating these risk factors in different populations will be of importance in view of the ultimate goal of personalized medicine. The objective was to assess the impact of risk factors such as Body Mass Index (BMI), Waist Circumference (WC), and Waist to Hip Ratio (WHR) on diabetic and control subjects using statistical tools in a specific geographical category of Indian population. Methods: 92 diabetic patients and 123 controls living in urban areas of Nagpur city, Maharashtra, India, were selected for a case control study. BMI, WC, WHR, fasting glucose, blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) and skinfold thickness at four points were assessed. For logical interpretation, the data have been subjected to statistical analysis such as risk ratio, odds ratio and chi square. Multivariate regression analysis was carried out to adjust for age and sex. Results: The plasma glucose, HDL cholesterol and Waist to hip ratio are significant in between control and diabetes subjects even after adjusting to age and sex. Conclusion: Comparison of diabetic and control showed that the central obesity (WHR) and HDL were most important risk factors for type 2 diabetes in the studied population. Key Words Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Waist to Hip Ratio, diabetes mellitus type 2. Introduction Diabetes Mellitus is a major global health problem (Wild et al 2004). Based on the Diabetes atlas 2009 published by the International Diabetic Federation, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Indian population is estimated to be around 51 million and India is regarded as the diabetic capital of the world (Unwin et al 2010). Type 2 diabetes is a complex metabolic disease, primarily characterised by insulin resistance, relative insulin deficiency and hyperglycemia (Kraegen et al 2008) and leading to micro vascular diseases, blindness, nerve damage, 1 Anthropological Survey of India, Central Regional Centre, S. Hills, Nagpur, India 2 Department of Biomedical Sciences, Sri Ramachandra University, Chennai. India 3 Formerly, Director In-Charge, Anthropological Survey of India. Presently Professor, Department of Anthropology, Delhi University, North campus. Delhi, India * Corresponding Address: Prof. V. R. Rao, Department of Anthropology, Delhi University, North Campus Delhi Tel: ; Fax: ; Mobile: ; e.mail: drraovr@yahoo.com 103
2 arthrosclerosis and renal complications (McAlpine et al 2005, van Dieren et al 2010). The cause of Diabetes Mellitus is poorly understood. Changes in diet and life style due to rapid economic development are fore most among the principle drives of diabetes in developing and developed countries. Barring the environmental impact, genetic component plays a vital role for the development of diabetes (Mohan 2004). Though, obesity is a leading risk factor for late onset of diabetes, life style habits play a vital role to become obese (Gupta and Agrawal 2009). Obesity results from an imbalance between energy expenditure and intake which is modulated by genetic predisposition. International Diabetes Congress in Helsinki, Finland reported that obesity is the most preventable and important risk factor for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (WCPD 2008). Almost four out of five people who are newly diagnosed with diabetes are obese (Kissebah et al 1989). The risk for diabetes has been reported to be about 2-folds in the mildly obese, 5 fold in the moderately obese and 10 folds in morbidly obese persons (Scheen and Lefebvre 1998). Increasing general obesity or central obesity is known to predispose individuals for insulin resistance. The prevalence of diabetes is 2.9 times higher in over weight (BMI 27.8 in males and 27.3 in women) than in normal weight subjects of 20 to 75 years of age (Burton et al 1985). Abdominal fat deposition is hormonally controlled by secretion of adipokinase which may impair glucose tolerance. Abdominal obesity, measured by an elevated WHR is shown to be a strong risk factor for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Bray et al 2008, Lahti-Koski et al 2000, Miljkovic-Gacic et al 2008). It has also been noted that for a given BMI, Asian Indian have higher fat percentage compared with Caucasian subjects (Banerji et al 1999). High proportion of upper-body fat or abdominal fat independent of overall obesity is recognized as an important component in the insulin resistance linked to obesity and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Goodpaster et al 2000). Few studies have suggested less influence of fat distribution on carbohydrate and fat metabolism for African Americans where as other studies observed differences in the association among white people (Karter et al 1996). Asian Indians (living in the United States) are more susceptible of developing abdominal adiposity and insulin resistance, which might account for the excessive morbidity and mortality from diabetes in this population (Chandalia et al 1999). But studies on adiposity and hyperglycemic condition from Indian population are scanty. World Health Organization report predicted 79.4 million diabetic patients by the year 2030 (Wild et al 2004). Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 differs in Indians from that of Europeans in three aspects namely onset is at early age (Mohan et al 2007), obesity is less common (Joshi 2003) and genetic factors appears to be stronger (Ramprasad et al 2007, Rema and Pradeepa 2007). The standard epidemiological translations of BMI, WC and WHR have been shown to be associated with Type 2 Diabetes. From clinical perspective, central obesity (approximated by waist circumference or waist/hip ratio) is known to provide more information than general Body Mass Index (Vazquez et al 2007). The standard epidemiological translation of BMI, WC and WHR are important tools used for anthropometric measures. Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio have been used as measures of central obesity, whereas BMI has been used as a measure of general obesity (Molarius and Seidell 1998). Taking into consideration some of the said facts, this research study was planned to evaluate the influence of various socio biological parameters for the development of Diabetes, through a case control study.our objective is to test the hypothesis that increase of BMI, WHR and WC values enhance the chance of occurrence of diabetes in these subjects. To evaluate this hypothesis, we attempted to throw light on the role of distribution of fat measured through skin fold thickness at four sites and circumferences at two sites. Subjects and Method Subjects The criteria of world health organization (WHO 1999) (fasting plasma glucose 126 mg/dl) was followed to differentiate diabetic and control subjects. A total of 92 Diabetes Mellitus subjects (48 males and 44 females) and 123 controls (74 males and 49 females) were the subjects of the study. The diabetic patients were selected from the outpatient department of Central government polyclinic, Nagpur city, Maharashtra, India. The age, sex, ethnic group matched individuals who are willingly opted to become subjects of the study with normal fasting glucose values were considered as controls. The case history of diabetes was verified from the record of diabetic patients. The persons with communicable as well as non communicable diseases were excluded from the control 104
3 subjects. Methods Anthropometric measurements were taken without heavy outdoor clothing. Stature was measured to the nearest millimeter using an Anthropometric rod. Weight was measured on a pre-standardized body weighing machine. Skinfold measurements were taken from subjects using Harpendent skinfold caliper with a jaw pressure of 10 gm/sq.mm. BMI was calculated using the formula, weight (kg) divided by height (meter square). The hip circumference was measured at the maximum circumference around the hips and the waist circumference was obtained at the level of the umbilicus using a steel tape. The general obesity was defined based on the revised standards for adult obesity in Asia and India, proposed by International ObesityTask Force (Low et al 2009). The cut off values for WHR and WC for men are 0.9 and 85cm and that for female 0.8 and 80 cm are considered as normal (Snehalatha et al 2003). Blood pressure was recorded in the sitting position in the right arm to the nearest 2 mm/ Hg with a mercury sphygmomanometer (Diamond Deluxe, Industrial Electronic products, Electronic Co. Pune, India). Two readings were taken at 5 minutes apart and the mean of the two was recorded as the final blood pressure reading of the individual. The blood sugar was determined by finger pricking method using a one touch glucose meter (Life Scan, Johnson and Johnson glucometer) after an overnight fast. Means± SD and proportions of baseline characteristics were compared using t-tests. Multivariate regression analysis was carried out to adjust for age and sex. Age and sex adjusted means of p-glucose, blood pressure, and lipids and skinfold thickness by category of diabetes, BMI, and waist circumference were calculated in general linear models. Diabetes status and obesity measurements (diabetes, waist circumference and BMI) were analysed as independent variables in general linear models with each of the metabolic risk factors as dependent variables. All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS statistical software version 16.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) for Windows. p 0.05 (two-tailed) was considered statistically significant. Results The basic demographic information of these subjects was summarised in Table 1. The mean age and standard deviation (SD) was 55.22±8.12yrs for the diabetes cases, 56.59±9.35yrs for the control subjects (p = 0.260). The age at onset of diabetes is ± 9.30 years for males and ± 7.64 years for females. Our study revealed that percent diabetic patients were non vegetarian. The enquiry of disease profile from diabetic patients showed that percent have Neuro and cardiopathic problems followed by percent who suffered from arthritis and spondylitis. In the present study there are no differences in age, SBP, DBP, fasting glucose, waist circumference and different forms cholesterol in between male and female subjects (Table 1). The BMI, waisthip ratio and skinfold variable have shown significant differences between male and female subjects. The plasma glucose, HDL cholesterol and Waist to hip ratio are significant in between control and diabetes subjects even after adjusting to age and sex. The mean values of the other parameters have not shown any significant difference between diabetes and control groups (Table 2). General obese and non-obese groups that defined by BMI were showing statistically significant differences in SBP, DBP, BMI, waist circumference and Skinfold thickness at triceps, biceps and Scapular even after adjusting to age and sex. LDL cholesterol in obese and non obese is statically significant, but the significance vanished after adjusting to age and sex. The mean waist circumference between the male (88.15±12.46) and females (87.28±9.08) is not statistically significant (p=0.555). Similarly the WC is not significant in between diabetics and control subjects (p= 0.741). The central obesity that defined by the WC has revealed statistically significant differences in the mean values of BMI, WC, waist to hip ratio and all skinfold thickness parameters (Triceps, biceps, abdomen and scapular) among obese and non-obese groups (Table 3). After categorization of BMI (>25 and <25), WHR (<.9 and >.9 for males, <.8 and >.8 females), WC (<85cm and >85 cm males, <80 cm and >80 cm females) in control and diabetics the risk ratio and odds ratios were also not supported the association of these variables with diabetes. For BMI the risk ratio is (95% CI is ) and odds ratio is 1.211(95% CI is ). The chi-square statistic indicates no significant relationship between general obesity and diabetes (χ2=0.48; p=0.488). For central obesity the risk ratio is (95% CI is ) and odds ratio is (95% CI is ) with chi-square of 0.09 demonstrated no significant relationship between central obesity and diabetes (p=0.764). Waist to hip ratio also has shown similar relationship with diabetes (χ2=2.26; p=0.133). The risk ratio and odds ratios are (95% CI is ) 105
4 and (95% CI is ) respectively. Discussion The present study demonstrated that the plasma glucose, HDL cholesterol and Waist to hip ratio are significant in between control and diabetes subjects even after adjusting to age and sex. The other parameters such as general obesity, central obesity and skinfold variables have not shown any significant difference between diabetes and control groups. Even though we tried to test for the effect obesity and other risk components in causing diabetes, we still failed to demonstrate such an association. Table 1 Demographic characteristics of study Subjects by sex. Total Subjects Female Male P value Number of samples Age (years) 56± ± ±9.05 <0.001 Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Fasting plasma glucose ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± Cholesterol ± ± HDL cholesterol LDL cholesterol ± ± ± ± ± ± ± Triglycerides (mg/dl) ± ± ± ± BMI (kg/m 2 ) 25.69± ± ±3.41 <0.001 Waist circumference (cm) 87.65± ± ± Waist/hip (ratio) 0.92± ±.09.93± Skin fold Triceps 12.04± ± ±3.42 <0.001 Skin fold biceps 7.91± ± ±2.60 <0.001 Skin fold abdomen 16.53± ± ± Skin fold scapular 17.97± ± ± Values are mean ±SD Body mass index, WC, WHR, hypertension, ethnicity, sedentary life style, genetic predisposition are the most easily detectable risk factors for Diabetes Mellitus. Adiposity leads to worsening of the metabolic syndrome namely insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and hypertension (McAlpine et al 2005). In the present study comparison of diabetic and control showed that the general obesity (BMI) was not effective; however, central obesity (WHR) was most important risk factor for type 2 diabetes. In recent times abdominal obesity has been correlated to 106
5 various metabolic disturbances (DeNino et al 2001) and increased metabolic risk vis a vis diabetic and cardiovascular risk are in appraisal these days (Feller et al 2010). Metabolic profile worsens with the increase in BMI and WHR, however, abdominal obesity (WHR) causes more hazardous influence on the metabolic status of type 2 diabetic patients (Parikh et al 2002). As predicted earlier that by 2030, India s diabetic population will be increased to 79.4 million (Wild et al 2004). Preventive measures should be taken by identifying the risk factors for diabetes and accordingly modifying the life style activities through counseling. Early detection of risk factors of diabetes can be possible by screening of asymptomatic individuals and follow up counseling programmes as it not only helps in delaying the onset but also can reduce the burden of severity of the secondary complications such as stroke, heart diseases, micro vascular diseases, neuropathy, retinopathy and nephropathy. These in turn will help in reducing the morbid condition of health and economic burden on society. Table 2: Distribution of different risk components in diabetes and controls. Number of samples Control Diabetic p value P value a Age (years) 56.59± ±8.12 Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Fasting plasma glucose Cholesterol HDL cholesterol LDL cholesterol Triglycerides (mg/dl) ± ± ± ± ± ± < ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± BMI (kg/m 2 ) 25.71± ± Waist circumference (cm) 87.42± ± Waist/hip (ratio) 0.91± ± Skin fold Triceps Skin fold biceps Skin fold abdomen Skin fold scapular 11.84± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±
6 a p values adjusted for age and sex Table 3: Distribution of different risk components in central obesity and controls defined by the waist circumference. Number of samples Age (years) 56.42± ±8.02 Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Fasting plasma glucose Control Obese p value P value a ± ± ± ± ± ± Cholesterol ± ± HDL cholesterol LDL cholesterol 42.28± ± ± ± Triglycerides (mg/dl) ± ± BMI (kg/m2) 23.00± ±3.34 <0.001 <0.001 Waist/hip (ratio) 0.89± ±0.09 <0.001 <0.001 Skin fold Triceps Skin fold biceps Skin fold abdomen Skin fold scapular 10.33± ±5.23 < ± ±4.07 <0.001 < ± ± ± ±7.57 <0.001 <0.001 a p values adjusted for age and sex While comparing differences between obesity indicators we found that the present study had several limitations for its meager sample size. Span length of BMI, WC and WHR character need to be evaluated in narrow range value for the assessment of relative risk for the causation of diabetes for subset of different variables. Further comparative studies on diabetes in varied ecozones through case control and identification of determinants of genetic and environmental factors of diabetic complications in different ethnic groups are the need of the hour of this vast country like India. The dissemination of knowledge acquired so through these processes if implemented, can diminish the burden on society to a great extent. 108
7 Acknowledgements: This research work was supported by the Anthropological Survey of India, Ministry of Culture, Government of India. References Banerji MA, Faridi N, Atluri R, Chaiken RL, Lebovitz HE (1999). Body composition, visceral fat, leptin, and insulin resistance in Asian Indian men; in J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84: Bray GA, Jablonski KA, Fujimoto WY, Barrett-Connor E, Haffner S, Hanson RL et al (2008). Relation of central adiposity and body mass index to the development of diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program; in Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 87: Burton BT, Foster WR, Hirsch J, Van Itallie TB (1985). Health implications of obesity: an NIH Consensus Development Conference; in Int. J. Obes. 9: Chandalia M, Abate N, Garg A, Stray-Gundersen J, Grundy SM (1999). Relationship between generalized and upper body obesity to insulin resistance in Asian Indian men; in J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84: DeNino WF, Tchernof A, Dionne IJ, Toth MJ, Ades PA, Sites CK et al (2001). Contribution of abdominal adiposity to age-related differences in insulin sensitivity and plasma lipids in healthy nonobese women; in Diabetes Care 24: Feller S, Boeing H, Pischon T (2010). Body mass index, waist circumference, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: implications for routine clinical practice; in Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 107: Goodpaster BH, Thaete FL, Kelley DE (2000). Thigh adipose tissue distribution is associated with insulin resistance in obesity and in type 2 diabetes mellitus; in Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71: Gupta R, Agrawal M (2009). High cardiovascular risks in a North Indian Agarwal community: a case series; in Cases J. 2: Joshi SR (2003). Metabolic syndrome--emerging clusters of the Indian phenotype; in J. Assoc. Physicians. India. 51: Karter AJ, Mayer-Davis EJ, Selby JV, D'Agostino RB, Jr., Haffner SM, Sholinsky P et al (1996). Insulin sensitivity and abdominal obesity in African-American, Hispanic, and non-hispanic white men and women. The Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis Study; in Diabetes 45: Kissebah AH, Freedman DS, Peiris AN (1989). Health risks of obesity; in Med. Clin. North Am. 73: Kraegen EW, Cooney GJ, Turner N (2008). Muscle insulin resistance: a case of fat overconsumption, not mitochondrial dysfunction; in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 105: Lahti-Koski M, Pietinen P, Mannisto S, Vartiainen E (2000). Trends in waist-to-hip ratio and its determinants in adults in Finland from 1987 to 1997; in Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 72: Low S, Chin MC, Ma S, Heng D, Deurenberg-Yap M (2009). Rationale for redefining obesity in Asians; in Ann. Acad. Med. Singapore 38: McAlpine RR, Morris AD, Emslie-Smith A, James P, Evans JM (2005). The annual incidence of diabetic complications in a population of patients with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes; in Diabet. Med. 22:
8 Miljkovic-Gacic I, Gordon CL, Goodpaster BH, Bunker CH, Patrick AL, Kuller LH et al (2008). Adipose tissue infiltration in skeletal muscle: age patterns and association with diabetes among men of African ancestry; in Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 87: Mohan V (2004). Why are Indians more prone to diabetes?, in J. Assoc Physicians India 52: Mohan V, Jaydip R, Deepa R (2007). Type 2 diabetes in Asian Indian Youth; in Pediatr. Diabetes 8 Suppl 9: Molarius A, Seidell JC (1998). Selection of anthropometric indicators for classification of abdominal fatness--a critical review, in Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 22: Parikh P, Mani U, Iyer U (2002). Abdominal Adiposity and Metabolic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; in Int. J. Diab. Dev. Ctries 22: Ramprasad S, Radha V, Mathias RA, Majumder PP, Rao MR, Rema M (2007). Rage gene promoter polymorphisms and diabetic retinopathy in a clinic-based population from South India; in Eye (Lond) 21: Rema M, Pradeepa R (2007). Diabetic retinopathy: an Indian perspective; in Indian J. Med. Res. 125: Scheen AJ, Lefebvre PJ (1998). Oral antidiabetic agents. A guide to selection; in Drugs 55: Snehalatha C, Viswanathan V, Ramachandran A (2003). Cutoff values for normal anthropometric variables in asian Indian adults; in Diabetes Care 26: Unwin N, Gan D, Whiting D (2010). The IDF Diabetes Atlas: providing evidence, raising awareness and promoting action; in Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 87: 2-3. van Dieren S, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, Grobbee DE, Neal B (2010). The global burden of diabetes and its complications: an emerging pandemic; in Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 17 Suppl 1: S3-8. Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR, Jr., Silventoinen K (2007). Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: a meta-analysis; in Epidemiol. Rev. 29: WCPD (2008). International Diabetes Congress in Helsinki, Finland WHO (1999). Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications: Report of a WHO Consultation. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva, World Health Org. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004). Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030; in Diabetes Care 27:
Prevalence of Obesity among Type-2 Diabetics
 Kamla-Raj 2009 J Hum Ecol, 25(1): 31-35 (2009) Prevalence of Obesity among Type-2 Diabetics Shilpi Sharma and Shashi Jain College of Home Science, Department of Foods and Nutrition, MPUAT, Udaipur, Rajasthan,
Kamla-Raj 2009 J Hum Ecol, 25(1): 31-35 (2009) Prevalence of Obesity among Type-2 Diabetics Shilpi Sharma and Shashi Jain College of Home Science, Department of Foods and Nutrition, MPUAT, Udaipur, Rajasthan,
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION. Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D.
 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
Body Composition & Longevity. Ohan Karatoprak, MD, AAFP Clinical Assistant Professor, UMDNJ
 Body Composition & Longevity Ohan Karatoprak, MD, AAFP Clinical Assistant Professor, UMDNJ LONGEVITY Genetic 25% Environmental Lifestyle Stress 75% BMI >30 OBESE 25-30 OVERWEIGHT 18-25 NORMAL WEIGHT 18
Body Composition & Longevity Ohan Karatoprak, MD, AAFP Clinical Assistant Professor, UMDNJ LONGEVITY Genetic 25% Environmental Lifestyle Stress 75% BMI >30 OBESE 25-30 OVERWEIGHT 18-25 NORMAL WEIGHT 18
Role of Body Weight Reduction in Obesity-Associated Co-Morbidities
 Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
Treatment of diabetes In order to survive, people with type 1 diabetes must have insulin delivered by a pump or injections.
 National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition:
 Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest. Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007
 Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME
 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness
 Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075
 Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Family History and Diabetes. Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional
 Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Obesity in the United States Workforce. Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
Diabetes and Heart Disease
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Mortality Associated with Diabetes
 Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
 International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
How To Determine The Prevalence Of Microalbuminuria
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION. normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications
 CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
How To Know If You Have Microalbuminuria
 3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN?
 ! WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN? Dysmetabolic syndrome (also referred to as syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome, and metabolic syndrome ) is a condition in which a group of risk factors for
! WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN? Dysmetabolic syndrome (also referred to as syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome, and metabolic syndrome ) is a condition in which a group of risk factors for
Nutrition. Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT
 1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
DIABETES YOUR GUIDE TO
 YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
Do You Know the Health Risks of Being Overweight?
 Do You Know the Health Risks of Being Overweight? U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH WIN Weight-control Information Network What are the risks to my health from
Do You Know the Health Risks of Being Overweight? U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH WIN Weight-control Information Network What are the risks to my health from
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Overview of Diabetes Management. By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health
 Overview of Diabetes Management By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health Objectives: Describe the pathophysiology of diabetes. From a multiorgan systems viewpoint. Identify the types of diabetes.
Overview of Diabetes Management By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health Objectives: Describe the pathophysiology of diabetes. From a multiorgan systems viewpoint. Identify the types of diabetes.
MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS
 BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin resistance syndrome in Children
 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin resistance syndrome in Children Anil R Kumar MD Pediatric Endocrinology MCV/VCU, Richmond VA Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM) has increased in children
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin resistance syndrome in Children Anil R Kumar MD Pediatric Endocrinology MCV/VCU, Richmond VA Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM) has increased in children
Diabetes mellitus. Lecture Outline
 Diabetes mellitus Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis II. Epidemiology III. Causes of diabetes IV. Health Problems and Diabetes V. Treating Diabetes VI. Physical activity and diabetes 1 Diabetes Disorder characterized
Diabetes mellitus Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis II. Epidemiology III. Causes of diabetes IV. Health Problems and Diabetes V. Treating Diabetes VI. Physical activity and diabetes 1 Diabetes Disorder characterized
Examining the Validity of the Body Mass Index Cut-Off Score for Obesity of Different Ethnicities
 Volume 2, Issue 1, 2008 Examining the Validity of the Body Mass Index Cut-Off Score for Obesity of Different Ethnicities Liette B. Ocker, Assistant Professor, Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi, liette.ocker@tamucc.edu
Volume 2, Issue 1, 2008 Examining the Validity of the Body Mass Index Cut-Off Score for Obesity of Different Ethnicities Liette B. Ocker, Assistant Professor, Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi, liette.ocker@tamucc.edu
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults
 The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE
 DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY. 12a. FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
Diabetes and Stroke. Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke
 Diabetes and Stroke Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke Make the Connection Almost 26 million people in the U.S. roughly 8 percent of the population have diabetes.
Diabetes and Stroke Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke Make the Connection Almost 26 million people in the U.S. roughly 8 percent of the population have diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes ( Juvenile Diabetes)
 Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus
 Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
Original Article. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes
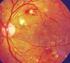 Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI Measurement Laboratory (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area
 CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
Diabetes: The Numbers
 Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes
 MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires
 Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders. Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness
 Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness Dr. med. J. Cordes LVR- Klinikum Düsseldorf Kliniken der Heinrich-Heine-Universität
Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness Dr. med. J. Cordes LVR- Klinikum Düsseldorf Kliniken der Heinrich-Heine-Universität
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Markham Stouffville Hospital
 Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Diabetes, Type 2. RelayClinical Patient Education Sample Topic Diabetes, Type 2. What is type 2 diabetes? How does it occur?
 What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
Diabetes and Obesity in Children. Janie Berquist, RN, BSN, MPH, CDE Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Kansas City, MO
 Diabetes and Obesity in Children Janie Berquist, RN, BSN, MPH, CDE Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Kansas City, MO Diabetes and Obesity in Children What is Diabetes? How are Diabetes and Obesity
Diabetes and Obesity in Children Janie Berquist, RN, BSN, MPH, CDE Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Kansas City, MO Diabetes and Obesity in Children What is Diabetes? How are Diabetes and Obesity
How Do You Recognize the BMI Diagnosis of Obesity?
 Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics April 2010, Volume 12, Number 4: 292-298. CLINICAL PEARL Diagnosing Obesity: Beyond BMI Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, MD, MSc, and William R. Miranda,
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics April 2010, Volume 12, Number 4: 292-298. CLINICAL PEARL Diagnosing Obesity: Beyond BMI Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, MD, MSc, and William R. Miranda,
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
Plasma Testosterone Level in Male Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, June: 351-357, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Plasma Testosterone Level in Male Patients with Metabolic Syndrome NASHWA EL-SARRAF, M.D. and AMR EL-HADIDY,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, June: 351-357, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Plasma Testosterone Level in Male Patients with Metabolic Syndrome NASHWA EL-SARRAF, M.D. and AMR EL-HADIDY,
Losing Weight in Singapore - Public Perception of Obesity
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Diabetes, hypertension and a lot more `in the elderly` JORIS SCHAKEL INTERNIST- CLINICAL GERIATRICIAN JGSCHAKEL@SEHOS.CW
 Diabetes, hypertension and a lot more `in the elderly` JORIS SCHAKEL INTERNIST- CLINICAL GERIATRICIAN JGSCHAKEL@SEHOS.CW IT`S HARD TO GIVE GENERAL ADVICE! ``The Elderly`` Heterogeneous group ;widely varying
Diabetes, hypertension and a lot more `in the elderly` JORIS SCHAKEL INTERNIST- CLINICAL GERIATRICIAN JGSCHAKEL@SEHOS.CW IT`S HARD TO GIVE GENERAL ADVICE! ``The Elderly`` Heterogeneous group ;widely varying
Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India
 Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
1.0 Introduction. 1.1 Diabetes mellitus (DM)
 1.0 Introduction Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is a complex disorder which involves complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors and it is characterised by dysfunction in insulin secretion combined
1.0 Introduction Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is a complex disorder which involves complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors and it is characterised by dysfunction in insulin secretion combined
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY. Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know
 Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes
 ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes
 Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
How To Treat Dyslipidemia
 An International Atherosclerosis Society Position Paper: Global Recommendations for the Management of Dyslipidemia Introduction Executive Summary The International Atherosclerosis Society (IAS) here updates
An International Atherosclerosis Society Position Paper: Global Recommendations for the Management of Dyslipidemia Introduction Executive Summary The International Atherosclerosis Society (IAS) here updates
Multiple comorbidities: additive and predictive of cardiovascular risk. Peter M. Nilsson Lund University University Hospital Malmö, Sweden
 Multiple comorbidities: additive and predictive of cardiovascular risk Peter M. Nilsson Lund University University Hospital Malmö, Sweden Clinical outcomes: major complications of CVD Heart Attack/ACS
Multiple comorbidities: additive and predictive of cardiovascular risk Peter M. Nilsson Lund University University Hospital Malmö, Sweden Clinical outcomes: major complications of CVD Heart Attack/ACS
Dietary Composition for Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance
 Dietary Composition for Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance Bridget M. Hron, MD Instructor in Pediatrics, Harvard Medical School Staff Physician in Gastroenterology & Nutrition and New Balance Foundation
Dietary Composition for Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance Bridget M. Hron, MD Instructor in Pediatrics, Harvard Medical School Staff Physician in Gastroenterology & Nutrition and New Balance Foundation
Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]
![Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]](/thumbs/28/12601472.jpg) Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe
 Deutsches Institut für Ernährungsforschung Potsdam-Rehbrücke General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe Tobias Pischon Department of Epidemiology German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke
Deutsches Institut für Ernährungsforschung Potsdam-Rehbrücke General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe Tobias Pischon Department of Epidemiology German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke
Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme
 International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
Risk factors and complications of type 2 diabetes in Asians
 Risk factors and complications of type 2 diabetes in Asians Rajbharan Yadav, Pramil Tiwari* and Ethiraj Dhanaraj Department of Pharmacy Practice National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research
Risk factors and complications of type 2 diabetes in Asians Rajbharan Yadav, Pramil Tiwari* and Ethiraj Dhanaraj Department of Pharmacy Practice National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research
Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE
 NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
Diabetes Mellitus. Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes Mellitus
 Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
Men Sexual Dysfunction Associated with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
 Men Sexual Dysfunction Associated with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome By Aly A. Abbassy, MD, FACE Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Alexandria University My Talk will include: 1-Types of Men sexual
Men Sexual Dysfunction Associated with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome By Aly A. Abbassy, MD, FACE Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Alexandria University My Talk will include: 1-Types of Men sexual
RISK FACTORS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS IN THE RURAL POPULATION OF NORTH KERALA, INDIA: A CASE CONTROL STUDY
 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Academy of Medical Sciences, Pariayaram, Kannur, Kerala, India; 2 Research Division, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates Original Research Article RISK
1 Department of Internal Medicine, Academy of Medical Sciences, Pariayaram, Kannur, Kerala, India; 2 Research Division, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates Original Research Article RISK
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health?
 Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention.
 Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention. Professor Paolo Pozzilli University Campus Bio-Medico, Rome Institute of Cell & Molecular Science, Queen Mary, University of
Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention. Professor Paolo Pozzilli University Campus Bio-Medico, Rome Institute of Cell & Molecular Science, Queen Mary, University of
Diabetes and Hypertension Care For Adults in Primary Care Settings
 and Hypertension Care For Adults in Primary Care Settings What is Type 2? The carbohydrates including sugar and starch which we take become glucose after digestion. It will then be absorbed by the small
and Hypertension Care For Adults in Primary Care Settings What is Type 2? The carbohydrates including sugar and starch which we take become glucose after digestion. It will then be absorbed by the small
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group. Learning Objectives. Background. CAPA 2015 Annual Conference
 Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting
 Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes
 DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME
 HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
Published Quarterly Mangalore, South India ISSN 0972-5997 Volume 4, Issue 1; January-March 2005
 Published Quarterly Mangalore, South India ISSN 0972-5997 Volume 4, Issue 1; January-March 2005 Original Article Genetic Association Between Insulin Resistance And Total Cholesterol In Type 2 Diabetes
Published Quarterly Mangalore, South India ISSN 0972-5997 Volume 4, Issue 1; January-March 2005 Original Article Genetic Association Between Insulin Resistance And Total Cholesterol In Type 2 Diabetes
Family history of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians
 JCDR Original Article Family history of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians Mithun Das, Susil Pal 1, Arnab Ghosh 2 Department of Anthropology, Sree Chaitanya College,
JCDR Original Article Family history of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians Mithun Das, Susil Pal 1, Arnab Ghosh 2 Department of Anthropology, Sree Chaitanya College,
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Cardiovascular disease physiology. Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 14, 2011
 Cardiovascular disease physiology Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 14, 2011 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics Recommendations The disease process
Cardiovascular disease physiology Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 14, 2011 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics Recommendations The disease process
DR. Trinh Thi Kim Hue
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE CHILD AND ADOLESCENT DR. Trinh Thi Kim Hue CONTENTS Definition Diagnosis Treatment Comorbidities and Complications Comorbidities and Complications Screening for T2D References DEFINITION
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE CHILD AND ADOLESCENT DR. Trinh Thi Kim Hue CONTENTS Definition Diagnosis Treatment Comorbidities and Complications Comorbidities and Complications Screening for T2D References DEFINITION
Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2
 IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
Adult Weight Management Training Summary
 Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
Diabetes. C:\Documents and Settings\wiscs\Local Settings\Temp\Diabetes May02revised.doc Page 1 of 12
 Diabetes Introduction The attached paper is adapted from the initial background paper on Diabetes presented to the Capital and Coast District Health Board Community and Public Health Advisory Committee
Diabetes Introduction The attached paper is adapted from the initial background paper on Diabetes presented to the Capital and Coast District Health Board Community and Public Health Advisory Committee
High Blood Cholesterol
 National Cholesterol Education Program ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference 1 Step 1 2 Step 2 3 Step 3 Determine lipoprotein levels obtain complete lipoprotein profile after 9- to 12-hour
National Cholesterol Education Program ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference 1 Step 1 2 Step 2 3 Step 3 Determine lipoprotein levels obtain complete lipoprotein profile after 9- to 12-hour
Racial and ethnic disparities in type 2 diabetes
 Racial and ethnic disparities in type 2 diabetes Nisa M. Maruthur, MD, MHS Assistant Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology Welch Center for Prevention, Epidemiology, & Clinical Research The Johns Hopkins
Racial and ethnic disparities in type 2 diabetes Nisa M. Maruthur, MD, MHS Assistant Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology Welch Center for Prevention, Epidemiology, & Clinical Research The Johns Hopkins
TERMS FOR UNDERSTANDING YOUR TYPE 2 DIABETES. Definitions for Common Terms Related to Type 2 Diabetes
 TERMS FOR UNDERSTANDING YOUR TYPE 2 DIABETES Definitions for Common Terms Related to Type 2 Diabetes TYPE 2 DIABETES AND BLOOD SUGAR 1-3 This list of terms may help you beter understand type 2 diabetes,
TERMS FOR UNDERSTANDING YOUR TYPE 2 DIABETES Definitions for Common Terms Related to Type 2 Diabetes TYPE 2 DIABETES AND BLOOD SUGAR 1-3 This list of terms may help you beter understand type 2 diabetes,
INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME
 1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN
1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN
EUROPEAN JOURNAL EPIDEMIOLOGY
 Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study
 Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Elizabeth J Mayer-Davis, PhD University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill For the SEARCH Study Group, May 2014
Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Elizabeth J Mayer-Davis, PhD University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill For the SEARCH Study Group, May 2014
Alzheimer s disease and diabetes
 1007029 CM1053CS Alzheimer s disease and diabetes Nearly 21 million Americans in the United States have diabetes, a disease that makes the body less able to convert sugar to energy. More than 6 million
1007029 CM1053CS Alzheimer s disease and diabetes Nearly 21 million Americans in the United States have diabetes, a disease that makes the body less able to convert sugar to energy. More than 6 million
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined
 Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Medical College in South India: A Pilot Study K Sreekanthan*, A Belicita, K Rajendran, Anil Vijayakumar Abstract Background: The prevalence of diabetes
Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Medical College in South India: A Pilot Study K Sreekanthan*, A Belicita, K Rajendran, Anil Vijayakumar Abstract Background: The prevalence of diabetes
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients
 Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer Is Diabetic
 European Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (5): 196-202, 2012 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2012.4.5.2027 A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer
European Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (5): 196-202, 2012 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2012.4.5.2027 A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer
6.4 Diabetes. 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion. Background. Developments since 2004. See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.
 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium. HCV Beyond the Liver
 Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1. used confidence intervals to answer questions such as...
 HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1 PREVIOUSLY used confidence intervals to answer questions such as... You know that 0.25% of women have red/green color blindness. You conduct a study of men
HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1 PREVIOUSLY used confidence intervals to answer questions such as... You know that 0.25% of women have red/green color blindness. You conduct a study of men
