RISK FACTORS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS IN THE RURAL POPULATION OF NORTH KERALA, INDIA: A CASE CONTROL STUDY
|
|
|
- Christina Lindsey
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Academy of Medical Sciences, Pariayaram, Kannur, Kerala, India; 2 Research Division, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates Original Research Article RISK FACTORS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS IN THE RURAL POPULATION OF NORTH KERALA, INDIA: A CASE CONTROL STUDY Balakrishnan Valliyot 1, Jayadevan Sreedharan 2, Jayakumary Muttappallymyalil 2, Sudha Balakrishnan Valliyot 1 Key words: diabetes mellitus, risk factors, rural population, North Kerala, India SUMMARY The aim of the study was to assess the risk factors associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in rural population of North Kerala, India. The study included 100 T2DM cases randomly selected among patients with diabetes admitted to medicine ward and 200 controls without DM recruited from visitors and patient attendants at a tertiary care centre in the northern part of Kerala, India. A questionnaire that contained sociodemographic characteristics and risk factors was used for data collection. ANOVA was performed to find the significance of more than two means. Simple binary logistic regression and multiple binary logistic regression were performed to find the crude and adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated to find the significance of the observed OR. A p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Study results showed those above 50 years of age to have five times more chance to get diabetes when compared with Corresponding author: Dr. Jayadevan Sreedharan, Assistant Director & Professor, Research Division, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates drjayadevans@gmail.com those in the age group. Gender and religion did not show any statistically significant association with diabetes. Physical activity was observed as a protective factor for the development of DM. Hypertension, especially systolic hypertension, emerged as a strong risk factor for T2DM in this study. Subjects with systolic hypertension had 4.6-fold chance to develop T2DM, making it mandatory to screen all patients with hypertension above 25 years of age for T2DM irrespective of the presence of other risk factors. In conclusion, results of the present study will be of use in planning primordial, primary and secondary measures of prevention at the community level. INTRODUCTION Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is the commonest form of diabetes affecting more than 90% of the diabetic population worldwide. There is a rapid upsurge in the number of diabetic patients and this explosive growth is noted in both urban and rural areas. Wild et al. estimated the number of T2DM patients in the year 2000 at 174 million and predicted it to increase to 366 million in 2030 (1). Diabetologia Croatica 42-1,
2 The majority of the patients with diabetes in developed countries are above age 64. It is predicted that by 2030, the number of people aged above 64 with diabetes will be around 82 million, of which about 48 million in developing countries. India has the largest diabetic population and it is expected to increase to 174 million in the year 2025 (2). In developing countries, the majority of people with diabetes are in the age group (3). Seventy percent of the Indian population live in rural areas. It is a well-known fact that urban and rural populations have different lifestyles, work patterns, and environmental and sociocultural factors. The presentation of T2DM is not uniform throughout the world and there are geographical and ethnic variations in the presentation of T2DM across the world. Most studies from western countries (4-6) and urban studies from India point to lifestyle changes (7), sedentary life (5), diet and related epidemiological transition (8) as the major factors in the development of DM. The risk factors hitherto specified in the development of T2DM in the western and urban population cannot fully apply to a rural setting. So, when there is a rapid upsurge of T2DM in both urban and rural areas, it is an imperative to identify the factors predisposing to the development of the disease, which affects one out of every five Indians. There are only limited studies on the subject from India; of them, the most acclaimed studies are from Chennai and other metropolitan cities in India. The majority of the studies from India are prevalence studies on DM and only very few studies have focused on the profile and risk factors of T2DM. The North Malabar areas of Kerala state include Kannur, Kasargod and Wayanad districts and most of the population in this area have a traditional rural lifestyle. Hence, this study was undertaken to determine the risk factors of T2DM among rural population of North Kerala, India. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study was conducted at the Academy of Medical Sciences, Pariyaram, which is a Research Centre and Postgraduate Institute situated in the Kannur District of North Malabar area in Kerala, India. One hundred cases with T2DM and 200 unmatched controls without DM were recruited for the study. Cases were randomly selected among patients with diabetes admitted to the medicine ward and 200 controls among visitors and patient attendants. A case control ratio of 1:2 was adopted in this study. A pretested structured interviewer administered questionnaire was used for data collection. The questionnaire contained data pertaining to sociodemographic characteristics and various risk factors associated with the occurrence of DM. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS 13 version (IBM, Illinois, Chicago). Frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation were calculated and associations between variables were assessed using chi-square test. Also, t-test was used to find significant differences of two means and ANOVA was employed to find the significance of more than two means. In addition to the above statistical tools, simple binary logistic regression analysis and multiple binary logistic regression were performed to find crude and adjusted odds ratio (OR). The 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated to find the significance of observed OR. In all cases, p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS Gender wise distribution of subjects showed that 71.0% of cases and 59.0% of control subjects were males. A statistically significant association was found between cases and controls with regard to gender (p<0.05). With regard to age, 83.0% of the case group subjects and more than 56.0% of control group subjects were above age 40. A highly significant association was observed between cases and controls with regard to age (p<0.001). The majority of study subjects from both case and control groups belonged to Hindu religious groups. There was no statistically significant association between diabetes status and religion. When the participants were compared according to occupation, it was found that 29% of control subjects and 25% of cases were homemakers, whereas 8% of control subjects and 7% of cases were manual laborers. Other occupational groups included 34
3 professionals, mechanics, etc. A highly significant statistical association was observed between diabetes status and occupation (p<0.001). Dietary pattern showed that among controls 93% were having mixed diet and 7% were vegetarians, whereas among cases 89% were mixed diet consumers and 11% were on vegetarian food. When further analyzed with chi-square test, dietary pattern did not show any significant association. It was observed that 38% of the cases and 18.5% of the controls were tobacco users. When tested with chi-square test, tobacco use showed a statistically significant association (p<0.001). Assessment of self-reported physical activity showed that 42% of cases and 14.5% of control group subjects were involved in heavy work. Among cases and controls, 39% and 18% were involved in moderate physical activity, respectively, whereas 19% of cases and 67.5% of controls were involved in sedentary activity. The association between physical activity with regard to diabetes status was found to be statistically significant (p<0.01). With regard to family history of DM, 55.0% of cases and 37.5% of controls had a family history of DM. The association observed was high (p <0.001). A detailed study of the family history of DM showed that in 24% of cases and 11.5% of controls mothers were diabetic, whereas fathers were diabetic in 10.5% of controls and 7% of cases. When compared according to body mass index (BMI) less than 18.5 kg/m 2, both cases and controls were equally distributed, whereas 67% of cases and 62% of controls had BMI in the range of kg/m 2.Overweight was recorded in 25% of cases and 29% of control subjects. BMI greater than 30 kg/m 2 was found in only 3% of cases and 4.5% of controls. There was no statistically significant association between BMI and diabetic status. Systolic blood pressure of less than 140 mm Hg was measured in 93.5% of control subjects and 61% of cases. When this observation was tested with Pearson chi-square test, systolic blood pressure was found to be a significant factor associated with diabetes status (p<0.001). With regard to diastolic blood pressure, 88.5% of control group subjects and 82% of case group subjects had a diastolic blood pressure of less than 90 mm Hg. There was no statistically significant association between diastolic blood pressure and diabetic status. Details are given in Table 1. Table 2 shows that the mean age was lower in the case group than in the control group. The mean height in both cases and controls was found to be equal. Difference in the mean weight was not statistically significant. Age, gender, occupation, physical activity, family history, diet, tobacco use, and systolic blood pressure showed statistically significant correlation with diabetic status level. The above parameters that revealed significance were included in the simple binary logistic regression model and then in the multiple logistic regression model. The OR and its confidence interval are shown in Table 3. Age was found to be a significant factor. In comparison with the age group, the age group had a 4.7-fold and age group 5.5-fold likelihood of developing DM. On adjustment for all other factors, gender was not found to yield statistically significance. Physical activity was measured according to their type of work and was divided into minimal, moderate and hard physical activity. For those involved in doing hard activity, the chance of getting diabetic was by 89% less when compared to those doing minimal activity, which was statistically significant. Family history was found to be an important risk factor with a p value of Multiple logistic regression analysis showed an adjusted OR of Those with a family history of DM had 3.09-fold greater chance of getting the disease as compared to those without a family history of DM. Tobacco use appeared as a significant risk factor for the occurrence of DM. The adjusted OR was 2.49, which was statistically significant. Systolic blood pressure was another risk factor for the development of DM. After adjusting for all other factors, the OR observed was 4.69 with a CI of So, age, family history, physical activity, tobacco use and systolic hypertension emerged as significant independent risk factors for the occurrence of DM. Diabetologia Croatica 42-1,
4 Table 1. Sociodemographic characteristics and other correlates between cases and controls Variable Gender Age group (yrs) Religion Occupation Physical activity Family history Body mass index Pattern of diet Tobacco use Group Cases Controls Total n % n % n % Male Female Hindu Christian Muslim Home maker Laborer Farmer Teacher Others Heavy Moderate Minimal Yes No < > Mixed Vegetarian Yes No p value p<0.05 p<0.001 p<0.05 p<0.001 p<0.01 p<0.001 p<0.05 p<0.05 p<0.001 Systolic blood pressure Normal p<0.001 Hypertension Diastolic blood pressure Normal p<0.05 Hypertension Table 2. Distribution of cases and controls according to age, height, weight, body mass index (BMI) and blood pressure (mean ± standard deviation, SD) Factor Cases Control Mean SD Mean SD p value Age (yrs) p<0.001 Height (cm) NS Weight (kg) NS BMI (kg/m 2 ) NS Systolic blood pressure p<0.001 Diastolic blood pressure NS 36
5 Table 3. Distribution of significant variables: binary logistic regression analysis Variable Group Crude OR CI Adjusted OR CI Age (yrs) Gender Male Female Minimal Physical activity Moderate Heavy Family history No Yes Tobacco use No Yes Hypertension No Yes DISCUSSION Type 2 diabetes mellitus is one of the most important public health problems in the developed and developing countries. Age, gender, occupation, physical activity, obesity, family history, diet, tobacco use and hypertension were investigated in this study. It was observed that those above 50 years of age had a fivefold chance to get diabetes when compared to those of the age group. In a study of T2DM risk factors in southeast Anatolia, Turkey, Acemoglu et al. (9) found OR of 3.99 for age group, 4.3 for age group and 6.16 for those above 60 years of age. In our study, OR was 4.7 for those in the age group, which is consistent with the findings reported by Acemoglu et al. (9). The findings of the present study were in conformity with King et al. (10), the NUDS (11) and CUPS (12) studies, and the significance of this finding is that it will help greatly in planning the screening and preventive measures in diabetes. The screening should preferably be undertaken before 35 years of age and early intervention should start at an earlier age in this region. In the present study, gender was not found to be a statistically significant risk factor. Our results showed that physical activity is a protective factor for the development of DM. Acemoglu et al. (9) report that physical activity alone is not a factor, but leisure time activity is also as important in the development of T2DM. Kokiwar et al. (13) found the prevalence of diabetes among hard working group to be lower as compared with sedentary workers. Gill and Cooper also support the fact that physical activity has a protective role in the development of T2DM (14). Karter et al. (15) report that in the North California study conducted in 1999, the majority of patients had a maternal history of DM. Shashank and Rakesh (16) suggest that pedigree analysis is an excellent tool to study the genetic factor in diabetes. The finding of this study is very important in planning preventive strategy and will help identify the potential candidates who have a high chance to develop diabetes (16). Earlier, Kawakami et al. (17) have reported a 3.27 times higher risk for development of T2DM in those smokers who use cigarette per day when compared to non-smokers. The present finding is also similar to this finding. In various studies conducted in the United States, where women were followed up for 8 years, 2333 cases of T2DM were confirmed, with a 1.42-fold risk reported (18,19). Rimm et al. (20) showed that tobacco use may increase the risk of developing diabetes and the relative risk for men was 1.94-fold. The findings of the present study were higher than those reported by Rimm et al. (20). Diabetologia Croatica 42-1,
6 Hypertension, especially systolic hypertension, emerged as a strong risk factor for T2DM in the present study. Subjects with systolic hypertension had a 4.6-fold chance to develop T2DM, making it mandatory to screen for T2DM all patients with hypertension above 25 years of age, irrespective of the presence of other risk factors. Anderson and Mark noticed in their study that 57.4% of diabetics had hypertension (21). According to the Health Survey, 51% of diabetics had hypertension and a 2.5-fold risk of diabetes in hypertension, less than that noticed in the present study. According to a recent JNC VII report, hypertension is twice as common among diabetics (22). Acemoglu et al. (9), who studied the risk factors of T2DM in a region of Turkey, found that hypertension increased the risk of diabetes and recorded a 2.05-fold risk. Subtle autonomic dysfunction, decreased baroreceptor sensitivity, associated nephropathy, endothelial dysfunction due to hyperglycemia, and many other factors contribute to the development of hypertension in diabetes. Age is associated with a progressive rise in systolic blood pressure and aging vessels become stiffer due to the loss of elasticity, increased collagen cross-linking, fibrosis of vessel wall, and reduced vascular compliance (9). Isolated systolic hypertension occurs earlier in people with diabetes when compared to nondiabetics. The exact mechanism that leads to the development of diabetes in hypertension is not known. T2DM was associated with insulin resistance and long standing T2DM leading to endothelial changes. CONCLUSION The risk factors of T2DM have regional and ethnic variations. The results of the present study suggested a positive relationship of age with the incidence of diabetes, however, with no gender difference in the development of DM. Manual laborers are less affected compared to other occupations. Those engaged in hard work have a less chance to develop diabetes than those with sedentary habits. This also proves the protective effect of physical activity in the prevention of T2DM. Those with a family history of diabetes have three times greater chance to get T2DM compared to those without it. Dietary factors were not found to be a statistically significant risk factor in the development of T2DM. Hypertension is a significant risk factor in the development of T2DM. Many factors like obesity, diet, stress, occupation, which are considered more important in the western and urban studies, were not found to be significant in this rural area, whereas strong genetic factors, tobacco use, less physical activity and systolic hypertension emerged as strong risk factors. 38
7 REFERENCES 1. Wild SH, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimate for year 2000 and projections for Diabetes Care 2004;27(5): Diabetes atlas, Executive summary, World Diabetes Foundation, second Edition, Sicree R, Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ. Global burden of diabetes. Diabetes atlas, 2 nd edn. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2003: Ziv E, Shaffir E. Psammomys obesus: nutritionally induced NIDDM-like syndrome on thrifty gene background. In: Shafrir E, ed. Lessons from animal diabetes. London: Smith-Gordon, 1995; Heimlich SP, Ragland DR, Lecins RQW. Physical activity and reduced occurrence of non insulin dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med 1991;325: Mooy JM, DeVries H, Grootenhuis PA, Bouter LM, Hein Major RJ. Stressful life events in relation to prevalence and undetected type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;15(3): Arunachalam S, Guneshekharan S. Diabetes research in India and China today. From literature based mapping to health care policy. Curr Sci 2002;82: Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Latha F. Rising prevalence of NIDDM in an urban population in India. Diabetologia 1997;40: Acemoglu H, Ceylan A, Saka G, Plalanci Y, Erten M, Turgut S, et al. Risk factors for diabetes in South Eastern Anatolia of Turkey. Int J Epidemiol 2001;3(1): King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes Prevalence, numerical estimate and projections. Diabetes Care 1998;21: Ramachandran C, Snehalatha, Kapur A, Vijay V, Mohan V, Das AK, et al. High prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in India: National Urban Diabetes Survey (NUDS). Diabetologia 2001;44(9): Mohan V, Santhirani CS, Deepa R. Prevalence of diabetes and IGT in selected south Indian population with special reference to family history, obesity and lifestyle factor Chennai Urban Population Study [CUPS-14]. J Assoc Physicians India 2003;51: Kokiwar PR, Gupta S, Durge PM. Prevalence of diabetes in a rural area of central India. Int J Diabetes Dev Countries 2007;27(1): Gill JMR, Cooper AR. Physical activity and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Sports Med 2008;38(10): Karter AJ, Rowell SE, Ackerson LM, Mitchell BD, Ferrara A, Selby JV, et al. Excess maternal transmission of type 2 diabetes. The Northern California Kaisser Permanent Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care 1999;22: Shashank RJ, Rakesh MP. Family history and pedigree charting a simple genetic tool for Indian diabetes. JAPI 2006;54: Kawakami N, Takatwuka N, Shimizu H, Ishibarshi H. Effect of smoking on the incidence of NIDDM. Replication and extension in a Japanese cohort of male employee. Am J Epidemiol 1997;145: Vanderpump MP, Tunbridge WM, French JM, Appleton D, Bates D, Rodgers H, et al. The incidence of diabetes mellitus in an English community a 20-year follow up of the Wickham survey. Diabetes Med 1996;13: Giannini C, Dyck PJ. Basement membrane reduplication and pericyte degeneration precede development of diabetic polyneuropathy and are associated with its severity. Ann Neurol 1995;37: Diabetologia Croatica 42-1,
8 20. Rimm EB, Chan J, Stampfer MJ. Prospective study of cigarette smoking, alcohol use and the risk of diabetes in men. Br Med J 1995;310: Anderson EA, Mark AL. The vasodilator actions of insulin. Implication for the insulin hypothesis of hypertension revisited. Cardiovasc Risk Factors 1993;3: National High Blood Pressure Education programme working group report on HTN in Diabetes. Hypertension 1994;23:
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined
 Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Medical College in South India: A Pilot Study K Sreekanthan*, A Belicita, K Rajendran, Anil Vijayakumar Abstract Background: The prevalence of diabetes
Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Medical College in South India: A Pilot Study K Sreekanthan*, A Belicita, K Rajendran, Anil Vijayakumar Abstract Background: The prevalence of diabetes
THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION. normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications
 CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
How To Determine The Prevalence Of Microalbuminuria
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Family History and Diabetes. Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional
 Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]
![Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]](/thumbs/28/12601472.jpg) Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613
 Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613 1 Definition Hypertension is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. 2 Primary
Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613 1 Definition Hypertension is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. 2 Primary
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults
 The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme
 International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS
 THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS Alshammari S., *Al-Jameel N., Al-Johani H, Al-Qahtani A., Al-Hakbani A., Khan A. and Alfaraj S.
THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS Alshammari S., *Al-Jameel N., Al-Johani H, Al-Qahtani A., Al-Hakbani A., Khan A. and Alfaraj S.
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest. Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007
 Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
High Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Metabolic Disorders in Rural Central Kerala
 Original Article High Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Metabolic Disorders in Rural Central Kerala G Vijayakumar *, R Arun **, VR Kutty *** Abstract Background: Within India, inter-regional
Original Article High Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Metabolic Disorders in Rural Central Kerala G Vijayakumar *, R Arun **, VR Kutty *** Abstract Background: Within India, inter-regional
How To Know If You Have Microalbuminuria
 3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia. Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN)
 NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition:
 Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
Original Research Paper
 1 of 6 Original Research Paper Age at diagnosis and family history in Type II diabetes: implications for office screening Ching-Ye Hong MBBS, MCGP, FAFP, FRACGP Kee-Seng Chia MBBS, MSc (OM), MD Ching-Ye
1 of 6 Original Research Paper Age at diagnosis and family history in Type II diabetes: implications for office screening Ching-Ye Hong MBBS, MCGP, FAFP, FRACGP Kee-Seng Chia MBBS, MSc (OM), MD Ching-Ye
Mortality Associated with Diabetes
 Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Prevalence of Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes and its Associated Risk Factors in Rural Population of Tamil Nadu
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 11 (2): 222-227, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.11.2.84252 Prevalence of Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes and its Associated Risk
World Journal of Medical Sciences 11 (2): 222-227, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.11.2.84252 Prevalence of Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes and its Associated Risk
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness
 Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
 International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
Use of antihypertensive medications in patients with diabetes in Ajman, UAE
 Use of antihypertensive medications in patients with diabetes in Ajman, UAE Mohammed Arifulla 1*, Lisha J John 1, Jayadevan Sreedharan 2, Jayakumary Muttappallymyalil 2, Jenny Cheriathu 3, Sheikh Altaf
Use of antihypertensive medications in patients with diabetes in Ajman, UAE Mohammed Arifulla 1*, Lisha J John 1, Jayadevan Sreedharan 2, Jayakumary Muttappallymyalil 2, Jenny Cheriathu 3, Sheikh Altaf
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis. Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy.
 Running head: SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS AND HEALTHY BEHAVIORS The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy Hanover College Prior research
Running head: SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS AND HEALTHY BEHAVIORS The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy Hanover College Prior research
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients
 Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION. Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D.
 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
Deakin Research Online
 Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Cameron, Adrian J., Shaw, J.E. and Zimmet, P.Z. 2003, Diabetes, in Diabetes and kidney disease : time to act, nternational Diabetes Federation, Brussels,
Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Cameron, Adrian J., Shaw, J.E. and Zimmet, P.Z. 2003, Diabetes, in Diabetes and kidney disease : time to act, nternational Diabetes Federation, Brussels,
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Physical Activity, Obesity, and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in a High-Risk Population
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 158, No. 7 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwg191 Physical Activity, Obesity,
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 158, No. 7 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwg191 Physical Activity, Obesity,
Hypertension and Diabetes Status. 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey
 Hypertension and Diabetes Status 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey Methodology and Sampling Total 18,000 households were selected nationwide (207 in urban and 393 in rural areas) One-third
Hypertension and Diabetes Status 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey Methodology and Sampling Total 18,000 households were selected nationwide (207 in urban and 393 in rural areas) One-third
The South Asian Indian Women s s Weight Loss Study. Latha Palaniappan, MD, MS BIRCWH Scholar October 20, 2005
 The South Asian Indian Women s s Weight Loss Study Latha Palaniappan, MD, MS BIRCWH Scholar October 20, 2005 South Asian Emigrants and second generation from India Bhutan Bangladesh Maldives Nepal Pakistan
The South Asian Indian Women s s Weight Loss Study Latha Palaniappan, MD, MS BIRCWH Scholar October 20, 2005 South Asian Emigrants and second generation from India Bhutan Bangladesh Maldives Nepal Pakistan
Losing Weight in Singapore - Public Perception of Obesity
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population. Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology
 Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention
 Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention Sukhpal Kaur, Indarjit Walia Abstract : Nurses are the key providers of diabetes care. However the information provided
Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention Sukhpal Kaur, Indarjit Walia Abstract : Nurses are the key providers of diabetes care. However the information provided
Original Article. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes
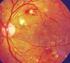 Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
6.4 Diabetes. 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion. Background. Developments since 2004. See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.
 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
Summary ID# 13614. Clinical Study Summary: Study F3Z-JE-PV06
 CT Registry ID# Page 1 Summary ID# 13614 Clinical Study Summary: Study F3Z-JE-PV06 INSIGHTS; INSulin-changing study Intending to Gain patients insights into insulin treatment with patient-reported Health
CT Registry ID# Page 1 Summary ID# 13614 Clinical Study Summary: Study F3Z-JE-PV06 INSIGHTS; INSulin-changing study Intending to Gain patients insights into insulin treatment with patient-reported Health
Socio-economic and demographic characteristics of alcohol and other substance abusers, undergoing treatment in Sikkim, a north east state of India
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2014, 6 (2):106-110 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Socio-economic
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2014, 6 (2):106-110 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Socio-economic
inflammation of the pancreas and damage to the an increased risk of hypertension, stroke and Table 7.1: Classification of alcohol consumption
 H E A LT H SURVEY Alcohol Consumption 7 Alcohol Consumption N AT I O N A L Introduction Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with inflammation of the pancreas and damage to the an increased risk
H E A LT H SURVEY Alcohol Consumption 7 Alcohol Consumption N AT I O N A L Introduction Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with inflammation of the pancreas and damage to the an increased risk
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Support Supplement
 CLINICALLY T E S T E D Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic
CLINICALLY T E S T E D Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic
EUROPEAN JOURNAL EPIDEMIOLOGY
 Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
The association between health risk status and health care costs among the membership of an Australian health plan
 HEALTH PROMOTION INTERNATIONAL Vol. 18, No. 1 Oxford University Press 2003. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain The association between health risk status and health care costs among the membership
HEALTH PROMOTION INTERNATIONAL Vol. 18, No. 1 Oxford University Press 2003. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain The association between health risk status and health care costs among the membership
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change?
 C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost
 Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting
 Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice. Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology. Psoriatic Arthritis
 Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
A Passage to India: Establishing a Cardiac Rehabilitation program in India s south-east
 A Passage to India: Establishing a Cardiac Rehabilitation program in India s south-east Kathryn Kelly Clinical Nurse Consultant, Cardiac Rehabilitation Coordinator The Royal Melbourne Hospital India 1,025,000,000
A Passage to India: Establishing a Cardiac Rehabilitation program in India s south-east Kathryn Kelly Clinical Nurse Consultant, Cardiac Rehabilitation Coordinator The Royal Melbourne Hospital India 1,025,000,000
Profiles and Data Analysis. 5.1 Introduction
 Profiles and Data Analysis PROFILES AND DATA ANALYSIS 5.1 Introduction The survey of consumers numbering 617, spread across the three geographical areas, of the state of Kerala, who have given information
Profiles and Data Analysis PROFILES AND DATA ANALYSIS 5.1 Introduction The survey of consumers numbering 617, spread across the three geographical areas, of the state of Kerala, who have given information
PREVALENCE OF VISUAL IMPAIRMENT AMONG DIABETIC PATIENTS IN THE KUMBA URBAN AREA, CAMEROON
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 4 May 2016, pp. 872-876 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ PREVALENCE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 4 May 2016, pp. 872-876 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ PREVALENCE
Southern Grampians & Glenelg Shires COMMUNITY PROFILE
 Southern Grampians & Glenelg Shires COMMUNITY PROFILE Contents: 1. Health Status 2. Health Behaviours 3. Public Health Issues 4. References This information was last updated on 14 February 2007 1. Health
Southern Grampians & Glenelg Shires COMMUNITY PROFILE Contents: 1. Health Status 2. Health Behaviours 3. Public Health Issues 4. References This information was last updated on 14 February 2007 1. Health
Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India
 Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease
 The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE
 FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE Descriptive analysis variables table shells hypotheses Measures of association methods design justify analytic assess calculate analysis problem stratify confounding statistical
FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE Descriptive analysis variables table shells hypotheses Measures of association methods design justify analytic assess calculate analysis problem stratify confounding statistical
Traditional View of Diabetes. Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? 8/9/2012. Change in Traditional View of Diabetes
 Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? Traditional View of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes ( T1DM) Onset Juvenile Lean Type 2 Diabetes ( T2DM) Onset Adult Obese QI Project Indrajit Majumdar
Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? Traditional View of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes ( T1DM) Onset Juvenile Lean Type 2 Diabetes ( T2DM) Onset Adult Obese QI Project Indrajit Majumdar
Adult Weight Management Training Summary
 Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
GEOSPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN DISEASE MAPPING, E-SURVEILLANCE AND HEALTH CARE FOR RURAL POPULATION IN SOUTH INDIA
 GEOSPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN DISEASE MAPPING, E-SURVEILLANCE AND HEALTH CARE FOR RURAL POPULATION IN SOUTH INDIA Praveenkumar BA a, Suresh Krishnamurthy a, Nikhil Agarwal b, Rohan Mahalank b, Nikhila B.S b,
GEOSPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN DISEASE MAPPING, E-SURVEILLANCE AND HEALTH CARE FOR RURAL POPULATION IN SOUTH INDIA Praveenkumar BA a, Suresh Krishnamurthy a, Nikhil Agarwal b, Rohan Mahalank b, Nikhila B.S b,
The Hong Kong Family 10-point Healthy Living Index
 The Hong Kong Family 10-point Healthy Living Index FAMILY: A Jockey Club Initiative for a Harmonious Society Cohort Study Press Conference December 21, 2011 1 Part 1 FAMILY Project: An Overview and 10-point
The Hong Kong Family 10-point Healthy Living Index FAMILY: A Jockey Club Initiative for a Harmonious Society Cohort Study Press Conference December 21, 2011 1 Part 1 FAMILY Project: An Overview and 10-point
Hai Fang, PhD Professor China Center for Health Development Studies Peking University
 Hai Fang, PhD Professor China Center for Health Development Studies Peking University Presentation for Asia Health Policy Program at Stanford University November 7th, 2014 Outline Introduction Background
Hai Fang, PhD Professor China Center for Health Development Studies Peking University Presentation for Asia Health Policy Program at Stanford University November 7th, 2014 Outline Introduction Background
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY. Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital
 Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Role of Body Weight Reduction in Obesity-Associated Co-Morbidities
 Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
 A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004
 Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004 The Children s Health Fund The Children s Health Fund (CHF), working with hospitals and
Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004 The Children s Health Fund The Children s Health Fund (CHF), working with hospitals and
How To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
 Introduction The Primary Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes AADE Practice Synopsis Issued December 1, 2014 The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is reaching epidemic proportions with more than 9.3% of adults in
Introduction The Primary Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes AADE Practice Synopsis Issued December 1, 2014 The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is reaching epidemic proportions with more than 9.3% of adults in
Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2006 Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Majeda Fikree* Baderuldeen Hanafi** Zahra Ali Hussain** Emad M Masuadi*** Objective: To determine the
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2006 Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Majeda Fikree* Baderuldeen Hanafi** Zahra Ali Hussain** Emad M Masuadi*** Objective: To determine the
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium. HCV Beyond the Liver
 Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2009; 11(1): 34-38 Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal MR Chhetri 1,2 and RS Chapman 1 1 College of Public
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2009; 11(1): 34-38 Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal MR Chhetri 1,2 and RS Chapman 1 1 College of Public
Exercise Prescription Case Studies
 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies 14 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies Case 1 Risk Stratification CY CHAN is a 43-year-old man with known history of hypertension on medication under good control.
14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies 14 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies Case 1 Risk Stratification CY CHAN is a 43-year-old man with known history of hypertension on medication under good control.
Using the Concept of Being Safe as a Positive Motivator In Diabetes Education
 Inova Health System Using the Concept of Being Safe as a Positive Motivator In Diabetes Education Ann Carnes MN RN CDE Sally Guise RD CDE AADE Annual Meeting August 6, 2009 Why Safety? 67% of Americans
Inova Health System Using the Concept of Being Safe as a Positive Motivator In Diabetes Education Ann Carnes MN RN CDE Sally Guise RD CDE AADE Annual Meeting August 6, 2009 Why Safety? 67% of Americans
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes
 Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
IMPACT OF DIABETES ON QUALITY OF LIFE OF ELDERLY
 1 Panacea Journal of Health Science IMPACT OF DIABETES ON QUALITY OF LIFE OF ELDERLY Shama Begum, Research Scholar, Roopa K.S. Associate Professor, Department of Human Development and Research Centre,
1 Panacea Journal of Health Science IMPACT OF DIABETES ON QUALITY OF LIFE OF ELDERLY Shama Begum, Research Scholar, Roopa K.S. Associate Professor, Department of Human Development and Research Centre,
Effect of Nutrition Education Program on Dietary Eating Patterns of Adolescent Girls (16-19 Years)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (2): 427-431 (2015) Research Article Effect of Nutrition Education Program
Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (2): 427-431 (2015) Research Article Effect of Nutrition Education Program
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS BIOSTATISTICS DESCRIBING DATA, THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION 1. The duration of time from first exposure to HIV infection to AIDS diagnosis is called the incubation period.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS BIOSTATISTICS DESCRIBING DATA, THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION 1. The duration of time from first exposure to HIV infection to AIDS diagnosis is called the incubation period.
College of Nursing Degree: PhD
 College of Nursing No Name Title Degree year 1 Kareem fatah Aziz Impact of a health education program on PhD 2009 knowledge of female nursing staff and students regarding breast cancer prevention and early
College of Nursing No Name Title Degree year 1 Kareem fatah Aziz Impact of a health education program on PhD 2009 knowledge of female nursing staff and students regarding breast cancer prevention and early
1) The table lists the smoking habits of a group of college students. Answer: 0.218
 FINAL EXAM REVIEW Name ) The table lists the smoking habits of a group of college students. Sex Non-smoker Regular Smoker Heavy Smoker Total Man 5 52 5 92 Woman 8 2 2 220 Total 22 2 If a student is chosen
FINAL EXAM REVIEW Name ) The table lists the smoking habits of a group of college students. Sex Non-smoker Regular Smoker Heavy Smoker Total Man 5 52 5 92 Woman 8 2 2 220 Total 22 2 If a student is chosen
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH
 HENK SWINKELS (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) BRUCE JONAS (US NATIONAL CENTER FOR HEALTH STATISTICS) JAAP VAN DEN BERG (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH IN THE
HENK SWINKELS (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) BRUCE JONAS (US NATIONAL CENTER FOR HEALTH STATISTICS) JAAP VAN DEN BERG (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH IN THE
The Cross-Sectional Study:
 The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
A prospective study on drug utilization pattern of anti-diabetic drugs in rural areas of Islampur, India
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):33-37 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):33-37 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME
 HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY
 ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY This fact sheet highlights the prevalence and health-consequences of physical inactivity and summarises some of the key facts and figures on the economic costs of
ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY This fact sheet highlights the prevalence and health-consequences of physical inactivity and summarises some of the key facts and figures on the economic costs of
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI Measurement Laboratory (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area
 CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
What women can do to optimise their health during pregnancy and that of their baby Claire Roberts
 Periconception Planning to Protect Pregnancy and Infant Health 2015 What women can do to optimise their health during pregnancy and that of their baby Claire Roberts Pregnancy Complications Preterm Birth
Periconception Planning to Protect Pregnancy and Infant Health 2015 What women can do to optimise their health during pregnancy and that of their baby Claire Roberts Pregnancy Complications Preterm Birth
Type 2 diabetes and prostate cancer risk: a population-based case-control study in Montreal, Canada
 Type 2 diabetes and prostate cancer risk: a population-based case-control study in Montreal, Canada Audrey Blanc-Lapierre, Pierre I. Karakiewicz, Armen Aprikian, Fred Saad, Marie-Élise Parent June 2 nd
Type 2 diabetes and prostate cancer risk: a population-based case-control study in Montreal, Canada Audrey Blanc-Lapierre, Pierre I. Karakiewicz, Armen Aprikian, Fred Saad, Marie-Élise Parent June 2 nd
Protocol: Alcohol consumption and diabetes risk factors: a meta-analysis of interventional studies
 Protocol: Alcohol consumption and diabetes risk factors: a meta-analysis of interventional studies Version: 1 Date: Study team: C Mary Schooling, CUNY School of Public Health at Hunter College, 2180 Third
Protocol: Alcohol consumption and diabetes risk factors: a meta-analysis of interventional studies Version: 1 Date: Study team: C Mary Schooling, CUNY School of Public Health at Hunter College, 2180 Third
survival, morality, & causes of death Chapter Nine introduction 152 mortality in high- & low-risk patients 154 predictors of mortality 156
 introduction 152 < mortality in high- & low-risk patients 154 < predictors of mortality 156 < impact of anemia & dialysis therapy on mortality 158 < mortality in esrd patients with rare s 16 < expected
introduction 152 < mortality in high- & low-risk patients 154 < predictors of mortality 156 < impact of anemia & dialysis therapy on mortality 158 < mortality in esrd patients with rare s 16 < expected
Type 2 Diabetes: Making Prevention a Priority The IGT Care Call Project
 Type 2 Diabetes: Making Prevention a Priority The IGT Care Call Project Katherine Grady, Care Call Development Manager, SRFT. Linda Savas, Knowledge Transfer Associate, NIHR CLAHRC Greater Manchester.
Type 2 Diabetes: Making Prevention a Priority The IGT Care Call Project Katherine Grady, Care Call Development Manager, SRFT. Linda Savas, Knowledge Transfer Associate, NIHR CLAHRC Greater Manchester.
The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China. White Paper
 White Paper Catalysts driving successful decisions in life sciences. The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China by Marco DiBonaventura, Ph.D. Director, Health Economics and Outcomes
White Paper Catalysts driving successful decisions in life sciences. The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China by Marco DiBonaventura, Ph.D. Director, Health Economics and Outcomes
Obesity in the United States Workforce. Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
Fewer people with coronary heart disease are being diagnosed as compared to the expected figures.
 JSNA Coronary heart disease 1) Key points 2) Introduction 3) National picture 4) Local picture of CHD prevalence 5) Mortality from coronary heart disease in Suffolk County 6) Trends in mortality rates
JSNA Coronary heart disease 1) Key points 2) Introduction 3) National picture 4) Local picture of CHD prevalence 5) Mortality from coronary heart disease in Suffolk County 6) Trends in mortality rates
Using Family History to Improve Your Health Web Quest Abstract
 Web Quest Abstract Students explore the Using Family History to Improve Your Health module on the Genetic Science Learning Center website to complete a web quest. Learning Objectives Chronic diseases such
Web Quest Abstract Students explore the Using Family History to Improve Your Health module on the Genetic Science Learning Center website to complete a web quest. Learning Objectives Chronic diseases such
AusDiab 2005. The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study. Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes
 AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking
AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking
Blood donation awareness and beliefs among medical and nursing students
 Research Article Blood donation awareness and beliefs among medical and nursing students Suchetha Singh, Muninarayana Chandrappa, Mahesh Venkatesha, Anil NS Department of Community Medicine, Sri Devaraj
Research Article Blood donation awareness and beliefs among medical and nursing students Suchetha Singh, Muninarayana Chandrappa, Mahesh Venkatesha, Anil NS Department of Community Medicine, Sri Devaraj
Attending Director, Division of Psychosomatic Medicine, Miyagi Chuou Hospital
 Stress-related Diseases Diabetes Mellitus JMAJ 45(5): 197 21, 22 Yuichi YAMAUCHI Attending Director, Division of Psychosomatic Medicine, Miyagi Chuou Hospital Abstract: Diabetes mellitus is not a simple
Stress-related Diseases Diabetes Mellitus JMAJ 45(5): 197 21, 22 Yuichi YAMAUCHI Attending Director, Division of Psychosomatic Medicine, Miyagi Chuou Hospital Abstract: Diabetes mellitus is not a simple
Overview of Diabetes Management. By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health
 Overview of Diabetes Management By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health Objectives: Describe the pathophysiology of diabetes. From a multiorgan systems viewpoint. Identify the types of diabetes.
Overview of Diabetes Management By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health Objectives: Describe the pathophysiology of diabetes. From a multiorgan systems viewpoint. Identify the types of diabetes.
Statistical Analysis Using SPSS for Windows Getting Started (Ver. 2014/11/6) The numbers of figures in the SPSS_screenshot.pptx are shown in red.
 Statistical Analysis Using SPSS for Windows Getting Started (Ver. 2014/11/6) The numbers of figures in the SPSS_screenshot.pptx are shown in red. 1. How to display English messages from IBM SPSS Statistics
Statistical Analysis Using SPSS for Windows Getting Started (Ver. 2014/11/6) The numbers of figures in the SPSS_screenshot.pptx are shown in red. 1. How to display English messages from IBM SPSS Statistics
PERINATAL NUTRITION. Nutrition during pregnancy and lactation. Nutrition during infancy.
 PERINATAL NUTRITION Nutrition during pregnancy and lactation Nutrition during infancy. Rama Bhat, MD. Department of Pediatrics, University of Illinois Hospital Chicago, Illinois. Nutrition During Pregnancy
PERINATAL NUTRITION Nutrition during pregnancy and lactation Nutrition during infancy. Rama Bhat, MD. Department of Pediatrics, University of Illinois Hospital Chicago, Illinois. Nutrition During Pregnancy
Diabetes Complications
 Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
