Case Study: Long Term Performance Of HDPE Drainboards In The Gotthard Railway Tunnels ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION Advantages of Polymeric Drainboards
|
|
|
- Lesley Copeland
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Study: Long Term Performance Of HDPE Drainboards In The Gotthard Railway Tunnels Marcus Jablonka, Cosella-Dörken, Heinz Peter Raidt, Dörken GmbH & Co Kg, ABSTRACT Drainboards have been frequently employed in tunnel lining applications, both in cut-and-cover projects and in bored tunnels. The function of the drainage layer is to provide permanent relief of hydrostatic water pressure, while the waterproof liner prevents any ingress of water into the tunnel. Such systems are subject to high mechanical, physical, chemical and sometimes biological operational demands, both during the installation period as well as later in-situ during the service life. In order to provide adequate performance, drainage products must maintain their full integrity over the entire design life of the structure. While product specifications often avoid any reference to durability and long-term performance properties, it is clear that aging processes affect these polymeric materials. Hence, the durability and aging resistance of drainage membranes, like any polymeric products, is of primary concern. The first section of this paper describes advantages and concerns related to the usage of, and the design with polymeric drainboards in tunnel construction. In a second section, common degradation mechanisms associated with HDPE sheets are described. The third section describes stringent requirements for the Gotthard Alpine Railway Tunnel through the Swiss Alps, e.g. high ambient temperatures of up to 45 C and an expected service life of up to 100 years, which require outstanding aging resistance of polymeric drainage materials. The paper describes the methods deployed to investigate the long-term performance of HDPE drainboards, focusing on aging mechanisms identified in the second section. Details associated to test procedures developed to reflect the specific properties of drainboards are presented as well as the results obtained. A summary table shows recommended product specifications needed to confine the aging properties of dainboards and to design a system performing adequately throughout the entire lifetime of the structure. INTRODUCTION Damage to underground building structures ranks high in damage statistics of buildings (Abel et al., 1991). Identifying expected water exposure conditions is therefore an important step for proper planning of a waterproofing and drainage system. An effective drainage layer greatly improves and warrants the reliability of the waterproofing layer by relieving hydrostatic pressure caused by dammed-up seepage water. Furthermore, a drainboard can provide effective protection for a waterproofing liner against potential damage from mechanical impact and consequential moisture intrusion. Polymer based materials are commonly used to manufacture drainboards, providing inherent advantages as low weight, ease of application, etc. Sometimes such materials are even used where products with long expected service lifetimes are required. This paper reflects on advantages of using Polyethylene based drainboards, and on their performance criteria. Since organic materials are affected by physical and chemical ageing processes, long-term durability and possible concerns associated with the deployment of such polymeric products are also discussed. Degradation mechanisms of HDPE membranes are described and the requirements for long-term properties for drainage materials for new railway tunnels through the Swiss Alps with expected service lifetime requirements of up to 100 years (Flueeler et al., 2001) are discussed. Test procedures developed to reflect the specific properties of drainboards are presented, as well as the results obtained. A summary table shows recommended product specifications needed to confine the aging properties of dainboards and to design a system performing adequately throughout the entire lifetime of the structure. Advantages of Polymeric Drainboards Drainboards, generally comprised of a semi-rigid polymeric sheet with a 3-dimensional dimple structure, make an excellent drain on sub-grade structures (Koerner, 1997). Such products are commonly used to protect structures against moisture, to control ground water, and to reduce or eliminate hydrostatic pressure. Drainboards are also instrumental in tunnel lining applications to intercept artesian, fissure, and seepage water. Gravity forces can cause hydrostatic pressure build-up of water on sub-grade structures. The main objective of drainboards is to reduce or eliminate hydrostatic pressure against below grade structures by providing an effective drainage layer, and to prevent infiltration of water into the construction. A typical high-density polyethylene based drainboard is shown in Figure 1.
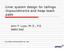
2 Figure 1: Typical HDPE drainboard In tunnel lining applications the drainage path for the water is provided by the air gap between the studded polymer core and the shotcrete surface. Figure 2 illustrates how seepage water passes through the shotcrete layer and is safely drained to the footer drain. Figure 2: Drainboard in tunnel lining application
3 Performance Criteria for Drainboards For a drainboard to function effectively throughout the lifetime of the structure, key performance criteria must be evaluated, also with respect to long-term durability. They can be categorized into mechanical properties, hydraulic properties, and durability. While drainboards are generally available with or without a geotextile laminated to the drainage core material, it should be noted that this paper only reflects on drainboard types without geotextiles. In this type of application a geotextile is not required since the shotcrete acts as a filter layer. Mechanical properties comprise the compression behavior of a drainboard, typically described as stress over strain. This material characteristic is important since the 3-dimensional membrane will be exposed to pressure, and its drainage capability is dependent on its compression resistance. An appropriate test method for determining the short-term compression behavior of a drainboard is ASTM D6364. While this test standard can give an indication of the momentary compression behavior of the material, it cannot, by itself, characterize the long-term compression behavior of the product. Other important mechanical properties of drainboards are breaking force and elongation, measurable according to ASTM D5035. In addition, the static and dynamic puncture resistance of these membranes is important. Dynamic puncture resistance reflects the product s ability to sustain the shock induced by the fall or impact of objects as may occur during installation. Static puncture reflects the ability of the product to sustain a local pressure. Appropriate test standards are CGSB 37-GP-56M and CGSB 37-GP-52M. Furthermore, hydraulic transmissivity and in-plane flow rate are important performance characteristics of a drainboard. These characteristics can be determined and described as per ASTM D4716. In order to characterize the long-term durability of drainboards, a number of standard test methods can be employed. For characterization of aging and oxidation, an oven-aging test as per ASTM D5721 and an OIT (Oxidative Induction Time) test as per ASTM D3895 are suitable in combination with compression behavior testing at different intervals of aging. Another degradation mechanism with relevance for HDPE drainboards is environmental stress-cracking. Generally suitable test methods to determine the environmental stress-cracking resistance (ESCR) are ASTM D1693 in most of the plastics industry, ASTM D5397 in the HDPE geomembrane industry, or ASTM F2136 in the HDPE pipe industry. However, the particular structure of drainboards (e.g., sheet thickness, presence of recycled polyethylene in co-extruded configurations) may not allow the use of these common tests. A test method referenced as Sageos GD001 (Stress Cracking Resistance of Dimpled Sheets) as described in Jablonka/Blond (2009), characterizes the ESCR of polyethylene-based drainboards. Durability of HDPE drainboards While polymers are being utilized in virtually every area of our life, the volume of polymers used in the above-mentioned applications represents only a fraction of the entire polymer market worldwide. The use of High Density Polyethylene in drainboards differs from many other applications since these membranes are intended to fulfill their function over long time periods. While some HDPE articles are made for short time periods only, drainboards are expected to fulfill their function for the lifetime of the structure typically in the range of 50 years or more. Durability concerns therefore need to be understood and evaluated. Most situations involving the expertise of a geotechnical engineer are dealt with under the aspect of ground water conditions, seepage, settlement, pressures, etc. Typically the short-term properties of materials are being evaluated without giving much consideration to their durability and potential degradation factors. Important to the durability of drainboards is their raw material formulation, the imposed in-service conditions, as well as the environmental conditions to which they will be exposed between manufacturing and the actual service life. The material formulation deserves special attention when recycled content is used in such membranes; especially if the membranes are made of 100% recycled HDPE. Since the use of recycled content in drainboards may potentially compromise their long-term durability, the intensity of the negative impact must be evaluated and understood in order to ensure that the key performance characteristics are maintained throughout the functional service life of these products. DEGRADATION MECHANISMS RELEVANT TO HDPE DRAINBOARDS Aging and degradation of polymers essentially takes place at the molecular level. Polymers are materials composed of large molecules of very high molecular weight. The cohesive forces of a polymer, which greatly affect the physical and chemical degradation mechanisms that can take place, are determined by the chemical composition of the polymer. The molecular structure of Polyethylene is shown in Figure 3.
4 Figure 3: Molecular structure of Polyethylene The characteristics of the polymer depend on intermolecular forces and are greatly influenced by the chain structure (i.e., chain length, linearity, branching, cross-linking, etc.), morphology (i.e., crystallinity), molecular weight distribution, irregularities (i.e., impurities), additives (i.e., color pigments, antioxidants, UV stabilizers, flame retardants, antistatic agents, etc.), as well as by the manufacturing process itself, during which the polymer is exposed to thermal and shear stresses initiatiating degradation mechanisms. Process conditions will also determine the effectiveness of mixing additives and stabilizers into the polymer, which can influence the morphology of the end product and the degree of stabilization against environmental factors like heat, UV, oxygen, etc. Essential aging and degradation mechanisms of polymers commonly used in geosynthetics, have been described in depth by Kay et al. (2004). HDPE is generally very resilient against environmental factors. Due to a low degree of branching Polyethylene has strong intermolecular forces and tensile strength. Being non-polar, it provides a very high resistance to chemicals. The permeability of Polyethylene to liquids and gases is very low. It is also very resilient to alkaline and acidic agents, as well as salt solutions. Polyethylene copolymers generally provide good low-temperature flexibility and increased environmental stress cracking resistance. Hence HDPE (copolymer) seems to be the ideal polymer to be used for drainboards. However, during their functional service life drainboards are exposed to several relevant degradation mechanisms. These aging mechanisms can, under certain circumstances, influence their properties and even reduce their durability and lifetime expectancy. Hence, the characteristics of the material used as well as the actual exposure conditions must be considered in order to evaluate the potential implication of these degradation mechanisms to the final product and its functional service life. One of the most relevant degradation mechanisms of HDPE is oxidation, which can occur in form of thermo-, photo-, and chemical oxidation. The long-term durability and performance of Polyethylene membranes can be ensured through adequate stabilization with antioxidants and UV stabilizers. In the presence of sensitizing agents HDPE can become sensitive to Environmental Stress Cracking, which next to oxidation is the most relevant degradation mechanism of this polymer. ASTM D883 explains stress cracking as an external or internal crack in a plastic caused by tensile stresses less than its short-term mechanical strength. This typically describes brittle cracking with little or no ductile drawing from the adjacent failure surfaces of the polymeric material. The occurrence of environmental stress cracking of stressed samples is linked to the presence of surfaceactive wetting agents such as alcohols and surfactants. The surface-active wetting agents don t chemically attack the polymer, nor do they produce any effect other than microscopically brittle-appearing fractures. The fractures initiate at microscopic imperfections in the material, and propagate through the crystalline regions of the polymer structure. In the absence of such surface-active wetting agents, these fractures would not occur in any reasonable time period under the same stress conditions. A polymers ability to resist environmental stress cracking is generally known as ESCR (Environmental Stress Crack Resistance). Different polymers exhibit varying levels of ESCR. It is important to know that the stress cracking susceptibility between different types of PE can be very different (Hsuan, 2000). Some grades of HDPE have very good ESCR, while other grades only show a marginal resilience. The principle variables that affect the ESCR in HDPE include the crystallinity, molecular weight (ESCR improves as molecular weight increases), the molecular weight distribution (generally a narrow molecular weight distribution shows poorer ESCR values than a broader distribution), branch length, and lamellar orientation (Lustiger, 1996). Naturally the ESCR testing conditions (i.e. reagent concentration, testing temperature, applied stress) also have a major influence on the ESCR that the tested sample will exhibit. Recycled content is also known to affect the ESCR of polymers. Historically, and practically, recycled materials do not perform as well as virgin polymers when subjected to Environmental Stress-Cracking (Develle et al., 2003). The effects of, as well as the resistance to environmental stress cracking of polyethylene based drainboards and a suitable test procedure have been discussed in depth by Jablonka/Blond (2009); the differences in environmental stress crack resistance of polyolefin based dimple sheets can be very significant as shown in Figure 4.
5 (a) No failure (b) Cracking (c) Severe cracking Figure 4: Environmental stress cracking on three different drainboard specimens after submersion in alkaline water at elevated temperature and lateral load Perhaps the most important factors governing the degradation rate of polymeric drainboards are the ambient ph value (Corbet et al., 1993) and the ambient temperature. As quantitatively described by the Arrhenius Equation the rate of degradation increases with an increase in ambient temperature. LONG-TERM PERFORMANCE OF HDPE DRAINBOARDS IN THE GOTTHARD ALPTRANSIT RAILWAY TUNNEL Durability Requirements As part of a new railway connection from the North to the South in Switzerland the Gotthard base tunnel is being built as double-shell tunnel. With a total length of 56.8 km the Gotthard tunnel is the longest tunnel in the world. Figure 5 shows a combination of a waterproofing system and a drainage layer between the shotcrete outer shell and the concrete inner shell. This design concept continuously drains seepage water away in order to protect the concrete shell against hydrostatic pressure, and to locally transfer high loads onto the concrete support structure. Figure 5: Detail of tunnel wall showing rock (1), shotcrete surface (2), drainboard (4), waterproofing (5), concrete liner (6) and drainage pipe (7)
6 At the base, where the mountain cover is up to 7,500 ft high, geothermal effects can generate rock temperatures of up to 45 C. Hence, the seepage water can also reach temperatures of up to 45 C. The water is mostly alkaline, but may also be acidic in some areas. The expected service lifetime for this tunnel is 100 years, with no major repairs being necessary for at least 50 years. There are currently no existing test standards with suitable criteria for such high loads and requirements, and available drainage materials previously had not been designed for or tested under comparable conditions. Hence a comprehensive product evaluation had to be performed. Durability Testing A number of different waterproofing systems and drainboards were tested in regards to their ageing resistance in a 24 months program. The test program has been described in depth by Flüeler et al. (2001). The drainage products that were submitted for testing were made from Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Polyamide and Polyester. These products included dimpled sheets (drainboards), nets, randomly oriented mats and non-woven geotextiles. This paper focuses on polyethylene-based drainboards only. The test program comprised existing test methods, that were augmented by additional procedures, e.g. aging resistance in oxygen-enriched water at elevated temperatures, compression creep tests between rough surfaces, tests under combined lateral loads and horizontal shear, as well as installation tests including the construction of the concrete support shell. Aging During the ageing part of the material evaluation the drainboard specimens were exposed to a number of different conditions for a period of 24 months: Water circulated at 23 C Water circulated at 45 C Water circulated at 70 C Alkaline water (saturated calcium-hydroxide solution) circulated at 50 C Acidic water (0.5% solution of sulphuric acid) circulated at 50 C Oxygen-enriched water circulated at 70 C and 3 bar pressure Environment with aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms Figure 6 shows the schematic of a pressure vessel for ageing of specimens in oxygen-enriched water at elevated temperature and pressure. Figure 6: Schematic of pressure vessel for ageing in oxygen-enriched water at elevated temperature and pressure
7 Five times during the test period specimens were tested for visual appearance, mass changes, in-plane water transmissivity and mechanical properties. In addition thermoanalytical tests were applied after 3, 6, 12 and 24 months to sufficiently characterize the aging behavior of the products. Furthermore the performance of the specimens under compression creep load was evaluated. Results The drainage materials generally reacted to acidic and alkaline exposure. Some polyamide and polyester based products decomposed in acidic water and embrittled in hot water (70 C) within 6 months. While the polyethylene based drainboard specimens with a weight of 1200 g/m 2 and a maximum compressive strength of 950 kn/m 2 - specifically formulated and stabilized to withstand the harsh environment - were relatively unaffected by these conditions, they did show noticeable effects of ageing in hot environments when submitted to compression creep load. However, in spite of large deformations of drainboards under such conditions they still proved to be fairly well suited as the water inlet pressure during in-plane water transmissivity tests under lateral loads remained consistently low. Figure 7: Inlet pressure of drainage water versus lateral compression load Minor visual changes such as loss of glance were detected on polyethylene based drainboards after 24 months exposure to all conditions. Only small changes were detected after exposure of the specimens to micro-organisms under aerobic or anaerobic soil conditions. The mass loss of 0.8% for polyethylene based drainboards after 24 months of ageing in water at 23 C was very low. After 24 months exposure to 70 C water the polyethylene based drainboard yielded a modest mass increase. After exposure to alkaline or acidic conditions the specimens also showed modest mass changes. The in-plane water transmissivity values of the drainboard specimens measured at a lateral load of 200 kn/m 2 after exposure, were generally not different from those measured in the as-received state. All exposure conditions as shown in Table 1 (Basler, 1998) could be met with a specially formulated polyethylene based drainboard.
8 Exposure conditions Change in Mass Change in Mechanical Strength Transmissivity Water at 23C 4% -20% > 10-4 [m2/s] Water at 45C 5% -30% > 10-4 [m2/s] Water at 70C 7% -50% > 10-4 [m2/s] 0.5% sulphuric acid at 50C 7% -50% > 10-4 [m2/s] Aqueous saturated calciumhydroxide 7% -50% > 10-4 [m2/s] solution Aerobic micro-organisms in soil 7% No requirements No requirements at 29C, 98% relative humidity Anaerobic micro-organisms in 7% No requirements No requirements soil at 29C, 98% relative humidity Table 1: Exposure conditions, criteria and requirements after 24 months aging for polymeric drainboards Summary Polymer based drainboards are affected by physical and chemical aging processes. Degradation mechanisms and aging processes of HDPE membranes as well as requirements for long-term properties for drainage materials for the Swiss AlpTransit tunnels with expected service lifetime requirements of up to 100 years were discussed in this paper. Test procedures that have been developed to characterize the aging behavior of such products were presented. The results from the extensive test program showed that standard waterproofing/drainage systems would be unable to fulfill the requirements for the AlpTransit Base Tunnels. However, refined systems were able to prove their suitability to fulfill the stringent requirements. A specially formulated polyethylene based drainboard underwent an stringent test procedure. Drainboard samples were aged over a 24-month period. During the aging period the specimens were submerged in acidic and alkaline solutions at 50 C, and in oxygen-enriched water at 70 C and then tested again. All required product specifications needed to confine the ageing properties of dainboards, could be met. REFERENCES Abel, R., Dahmen, G., Lamers, R., Oswald, R., Schnapauff, V. and Wilmes, K. (1991). Bauschadensschwerpunkte bei Sanierungs- und Instandhaltungsmassnahmen, Aachener Institut für Bauschadensforschung und angewandte Bauphysik. Basler, E., Zulassungsprüfung für Abdichtungssysteme für die Basistunnel der AlpTransit Gotthard und Lötschberg, Bewerberunterlagen, Anforderungswerte Corbet, S., King, J. (1993). Geotextiles in filtration and drainage, Thomas Telford Services, London, Great Britain. Flüeler, P., Böhni, H. (2001). The Sealing of Deep-seated Alpine Railway Tunnels New Evaluation Procedure for Waterproofing Systems, 11 th Symposium Techtextil Hsuan, Y.G. (2000). Data Base of Field Incidents used to establish HDPE Geomembrane stress crack resistance specification, Geotextiles and Geomembranes, Vo.18, p Jablonka, M., Blond, E. (2009). Long Term Performance Requirements for HDPE Drainboards, Geosynthetics 2009, Salt Lake City, USA Kay, D., Blond, E., Mlynarek, J. (2004). Geosynthetics Durability: A Polymer Chemistry Issue, 57 th Canadian Geotechnical Conference, GeoQuebec Koerner, R. M. (1997). Designing with Geosynthetics, 4 th edition, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA Lustiger, A. (1996). Understanding Environmental Stress Cracking in Polyethylene, Medical Plastics and Biomaterials Magazine, p. 8.
Naue GmbH&Co.KG. Quality Control and. Quality Assurance. Manual. For Geomembranes
 Naue GmbH&Co.KG Quality Control and Quality Assurance Manual For Geomembranes July 2004 V.O TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Quality Assurance and Control 2.1 General 2.2 Quality management acc. to
Naue GmbH&Co.KG Quality Control and Quality Assurance Manual For Geomembranes July 2004 V.O TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Quality Assurance and Control 2.1 General 2.2 Quality management acc. to
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance Of Polyethylene
 Introduction to Environmental Stress Cracking and ESCR Over the past decade, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) materials have improved significantly and now meet more stringent performance standards; some
Introduction to Environmental Stress Cracking and ESCR Over the past decade, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) materials have improved significantly and now meet more stringent performance standards; some
High Performance PSA in Sheet Membrane in Water Protection
 High Performance PSA in Sheet Membrane in Water Protection Xia Cao, Senior R&D Chemist, W. R. Grace, Cambridge MA 02140 Jyoti Seth, Strategic Program Leader, W. R. Grace, Cambridge MA 02140 Concrete is
High Performance PSA in Sheet Membrane in Water Protection Xia Cao, Senior R&D Chemist, W. R. Grace, Cambridge MA 02140 Jyoti Seth, Strategic Program Leader, W. R. Grace, Cambridge MA 02140 Concrete is
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance of Polyethylene Pipe Materials
 Environmental Stress Crack Resistance of Polyethylene Pipe Materials ROBERT B. TAMPA, Product Development and Service Engineer* Abstract Slow crack growth is a phenomenon that can occur in most plastics.
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance of Polyethylene Pipe Materials ROBERT B. TAMPA, Product Development and Service Engineer* Abstract Slow crack growth is a phenomenon that can occur in most plastics.
Drainage Composites. The ready-made solution to sub soil drainage
 Drainage Composites The ready-made solution to sub soil drainage The Ready-Made Solution to Sub Soil Drainage Drainage Composites are prefabricated subsurface-drainage products which directly replace conventional
Drainage Composites The ready-made solution to sub soil drainage The Ready-Made Solution to Sub Soil Drainage Drainage Composites are prefabricated subsurface-drainage products which directly replace conventional
MICRO PLASTICS MOLDED NYLON 6/6 FASTENERS MECHANICAL TEST DATA - UNC - UNF SECTION
 MICRO PLASTICS MOLDED NYLON 6/6 FASTENERS MECHANICAL TEST DATA - UNC - UNF Nylon 6/6 meets MIL-M20693B "A" Type 1, LP410A, and ASTM D789-66 Type 1, GDE 2 All test performed per ASTM specifications. Parts
MICRO PLASTICS MOLDED NYLON 6/6 FASTENERS MECHANICAL TEST DATA - UNC - UNF Nylon 6/6 meets MIL-M20693B "A" Type 1, LP410A, and ASTM D789-66 Type 1, GDE 2 All test performed per ASTM specifications. Parts
GRI Test Method GM13* Test Methods, Test Properties and Testing Frequency for High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Smooth and Textured Geomembranes
 Geosynthetic Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII GRI Test Method GM13* Revision 14: January 6, 2016 Revision schedule on
Geosynthetic Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII GRI Test Method GM13* Revision 14: January 6, 2016 Revision schedule on
100 Year Service Life of Polypropylene And Polyethylene Gravity Sewer Pipes. Summary Technical Report
 December 2014 100 Year Service Life of Polypropylene And Polyethylene Gravity Sewer Pipes A TEPPFA Project in cooperation with Borealis and LyondellBasell Summary Technical Report (Based on Extracts of
December 2014 100 Year Service Life of Polypropylene And Polyethylene Gravity Sewer Pipes A TEPPFA Project in cooperation with Borealis and LyondellBasell Summary Technical Report (Based on Extracts of
EUROPEAN AND INTERNATIONAL GEOTEXTILE STANDARDS. A SHORT GUIDE (revised version)
 EUROPEAN AND INTERNATIONAL GEOTEXTILE STANDARDS A SHORT GUIDE (revised version) by Dr Fred Foubert (Centexbel), secretary to CEN/TC 189 Geosynthetics Important note: This short guide means to be an introduction
EUROPEAN AND INTERNATIONAL GEOTEXTILE STANDARDS A SHORT GUIDE (revised version) by Dr Fred Foubert (Centexbel), secretary to CEN/TC 189 Geosynthetics Important note: This short guide means to be an introduction
Current opportunities of sprayed waterproofing membrane. Frank Clement Technical Manager Sprayable Membranes MEYCO Global Underground Construction
 Current opportunities of sprayed waterproofing membrane Frank Clement Technical Manager Sprayable Membranes MEYCO Global Underground Construction 1 What would we like to achieve? 2 What is desired? 3 and
Current opportunities of sprayed waterproofing membrane Frank Clement Technical Manager Sprayable Membranes MEYCO Global Underground Construction 1 What would we like to achieve? 2 What is desired? 3 and
HIGH PERFORMANCE PRE-APPLIED SYSTEM FOR BLIND SIDE & BELOW GRADE WATERPROOFING APPLICATIONS
 BSW HIGH PERFORMANCE PRE-APPLIED SYSTEM FOR BLIND SIDE & BELOW GRADE WATERPROOFING APPLICATIONS BSW is a fully reinforced Pre-Applied system membrane designed for horizontal and vertical external blind-side
BSW HIGH PERFORMANCE PRE-APPLIED SYSTEM FOR BLIND SIDE & BELOW GRADE WATERPROOFING APPLICATIONS BSW is a fully reinforced Pre-Applied system membrane designed for horizontal and vertical external blind-side
rhuesker HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES Product- Portfolio HUESKER Engineering with Geosynthetics
 HUESKER Engineering with Geosynthetics rhuesker HUESKER Product- HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr SKER HUESKER Portfolio HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES Engineering with Geosynthetics HUESKER Synthetic
HUESKER Engineering with Geosynthetics rhuesker HUESKER Product- HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr SKER HUESKER Portfolio HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES Engineering with Geosynthetics HUESKER Synthetic
USE OF GEOSYNTHETICS FOR FILTRATION AND DRAINAGE
 USE OF GEOSYNTHETICS FOR FILTRATION AND DRAINAGE Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Functions of a Filter Retain particles of the base
USE OF GEOSYNTHETICS FOR FILTRATION AND DRAINAGE Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 Functions of a Filter Retain particles of the base
EUROPEAN AND INTERNATIONAL GEOTEXTILE STANDARDS
 EUROPEAN AND INTERNATIONAL GEOTEXTILE STANDARDS A SHORT GUIDE (updated version 2014) by Dr. Fred Foubert (Centexbel), secretary to CEN/TC 189 Geosynthetics IMPORTANT NOTE: This short guide means to be
EUROPEAN AND INTERNATIONAL GEOTEXTILE STANDARDS A SHORT GUIDE (updated version 2014) by Dr. Fred Foubert (Centexbel), secretary to CEN/TC 189 Geosynthetics IMPORTANT NOTE: This short guide means to be
GSI. Geosynthetic Institute GRI. 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GII GAI GCI. GRI Test Method GM21
 Geosynthetic Institute 4 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 133-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII Revision 4: December 17, 2012 Revision schedule on pg. 11 GRI Test Method GM21
Geosynthetic Institute 4 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 133-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII Revision 4: December 17, 2012 Revision schedule on pg. 11 GRI Test Method GM21
Worldwide tank building applications using PP-Sheets: The effect of Foaming on properties
 Worldwide tank building applications using PP-Sheets: The effect of Foaming on properties Marcus Hoffmann 1, Dominic Müller 1, Marco Stallmann 1, Matt Curtis 2 1 Simona AG Teichweg 16, 55606 Kirn, Germany
Worldwide tank building applications using PP-Sheets: The effect of Foaming on properties Marcus Hoffmann 1, Dominic Müller 1, Marco Stallmann 1, Matt Curtis 2 1 Simona AG Teichweg 16, 55606 Kirn, Germany
Product Guide Specification
 Reef Industries, Inc. 9209 Almeda Genoa Rd. Houston, Texas 77075 Toll Free (800) 231-6074 Phone (713) 507-4251 Fax (713) 507-4295 Web Site www.reefindustries.com E-Mail ri@reefindustries.com Product Guide
Reef Industries, Inc. 9209 Almeda Genoa Rd. Houston, Texas 77075 Toll Free (800) 231-6074 Phone (713) 507-4251 Fax (713) 507-4295 Web Site www.reefindustries.com E-Mail ri@reefindustries.com Product Guide
Cavity Drain R20 is manufactured from1.0mm thick black high density polyethylene with studs approximately 20mm high.
 CI/SfB Tn6 L6813 September 2013 RIW CAVITY DRAIN R20 R20 is manufactured from1.0mm thick black high density polyethylene with studs approximately 20mm high. Other systems are available for specific uses,
CI/SfB Tn6 L6813 September 2013 RIW CAVITY DRAIN R20 R20 is manufactured from1.0mm thick black high density polyethylene with studs approximately 20mm high. Other systems are available for specific uses,
Membrane for tunnels and underground construction
 System Platon Membrane for tunnels and underground construction Drainage Protection Waterproofing Dry and healthy buildings The Isola history quality through innovation CONTENT The Isola History Air Gap
System Platon Membrane for tunnels and underground construction Drainage Protection Waterproofing Dry and healthy buildings The Isola history quality through innovation CONTENT The Isola History Air Gap
Elastoseal EPDM Tanking System Waterproofing of basements, foundations and cut-and-cover tunnels
 Elastoseal EPDM Tanking System Waterproofing of basements, foundations and cut-and-cover tunnels EPDM Rubber - facts about EPDM Product range Elastoseal EPDM Tanking membrane can either be supplied in
Elastoseal EPDM Tanking System Waterproofing of basements, foundations and cut-and-cover tunnels EPDM Rubber - facts about EPDM Product range Elastoseal EPDM Tanking membrane can either be supplied in
Native InDesign 2890 SaniTite Brochure 1/8" 100 300 CMYK April 17, 07
 Sanitary Sewer Pipe Tough pipe for a tough environment SaniTite Sanitary Sewer Pipe delivers the features that engineers, contractors and municipalities demand durability, performance, handling, toughness
Sanitary Sewer Pipe Tough pipe for a tough environment SaniTite Sanitary Sewer Pipe delivers the features that engineers, contractors and municipalities demand durability, performance, handling, toughness
Liner system design for tailings impoundments and heap leach pads
 Liner system design for tailings impoundments and heap leach pads John F. Lupo, Ph.D., P.E. AMEC E&E TAILINGS & MINE WASTE 08, VAIL Liner Systems Liner systems Environmental containment of process solutions
Liner system design for tailings impoundments and heap leach pads John F. Lupo, Ph.D., P.E. AMEC E&E TAILINGS & MINE WASTE 08, VAIL Liner Systems Liner systems Environmental containment of process solutions
How To Test A Wrap N Drain X Dampproofing System
 National Research Council Canada Institute for Research in Construction Conseil national de recherches Canada Institut de recherche en construction CCMC 13094-R &&0& EVALUATION DIVISION 07111 REPORT Issued
National Research Council Canada Institute for Research in Construction Conseil national de recherches Canada Institut de recherche en construction CCMC 13094-R &&0& EVALUATION DIVISION 07111 REPORT Issued
GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE
 GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE Prof. J. N. Mandal Department of civil engineering, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Tel.022-25767328 email: cejnm@civil.iitb.ac.in Module - 4
GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE Prof. J. N. Mandal Department of civil engineering, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Tel.022-25767328 email: cejnm@civil.iitb.ac.in Module - 4
DRAINAGE MATS For Vertical: Flow 15-P For Horizontal: Flow 18-H
 DRAINAGE MATS For Vertical: Flow 15-P For Horizontal: Flow 18-H Soil Drainage Mat with Built-In Protection Layer POLYGUARD DRAINAGE MATS are three-part prefabricated geocomposite drain consisting of a
DRAINAGE MATS For Vertical: Flow 15-P For Horizontal: Flow 18-H Soil Drainage Mat with Built-In Protection Layer POLYGUARD DRAINAGE MATS are three-part prefabricated geocomposite drain consisting of a
SKER HUESKER HUESKER geogrid HUESKER HUESKER for HUESKERHUES SKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES SKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES
 rhuesker HUESKER Fortrac HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr rhuesker Flexible HUESKER HUESKER low-extension HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr SKER HUESKER HUESKER geogrid HUESKER HUESKER for HUESKERHUES SKER HUESKERHUES
rhuesker HUESKER Fortrac HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr rhuesker Flexible HUESKER HUESKER low-extension HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr SKER HUESKER HUESKER geogrid HUESKER HUESKER for HUESKERHUES SKER HUESKERHUES
Safety containment systems for hydrocarbon tanks
 Safety containment systems for hydrocarbon tanks Daniele Cazzuffi CESI SpA, Via Rubattino 54, 134 Milano, Italy cazzuffi@cesi.it ABSTRACT In the recent years, geosynthetics (and specifically geomembranes)
Safety containment systems for hydrocarbon tanks Daniele Cazzuffi CESI SpA, Via Rubattino 54, 134 Milano, Italy cazzuffi@cesi.it ABSTRACT In the recent years, geosynthetics (and specifically geomembranes)
REHABILITATION OF UNDERGROUND SEWER LATERAL PIPES WITH CURED-IN-PLACE-PIPE LINER SECTION 02542
 1.0 INTENT REHABILITATION OF UNDERGROUND SEWER LATERAL PIPES 1.01 It is the intent of this specification to provide for the reconstruction of pipelines and conduits by the installation of a resin-impregnated
1.0 INTENT REHABILITATION OF UNDERGROUND SEWER LATERAL PIPES 1.01 It is the intent of this specification to provide for the reconstruction of pipelines and conduits by the installation of a resin-impregnated
KALPANA INDUSTRIES LTD. TECHNICAL DATA SHEET
 1 KALPANA INDUSTRIES LTD. TECHNICAL DATA SHEET KI XL - 03 / KI-SC 10 TWO COMPONENT AMBIENT CURABLE POLYETHYLENE COMPOUND FOR INSULATION OF LOW VOLTAGE POWER CABLE DESCRIPTION : KI polyethylene compound
1 KALPANA INDUSTRIES LTD. TECHNICAL DATA SHEET KI XL - 03 / KI-SC 10 TWO COMPONENT AMBIENT CURABLE POLYETHYLENE COMPOUND FOR INSULATION OF LOW VOLTAGE POWER CABLE DESCRIPTION : KI polyethylene compound
Stabilenka HUESKER. and Separation. Engineering with Geosynthetics SKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES
 HUESKER Engineering with Geosynthetics rhuesker HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr rhuesker HUESKER Woven HUESKER HUESKER Fabrics HUESKER HUESKERr SKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES rhuesker
HUESKER Engineering with Geosynthetics rhuesker HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERr rhuesker HUESKER Woven HUESKER HUESKER Fabrics HUESKER HUESKERr SKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKER HUESKERHUES rhuesker
Geosynthetic Research Institute. 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441.
 Drexel U N I V E R S I T Y Geosynthetic Research Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII Standard Guide for GRI Standard GC8
Drexel U N I V E R S I T Y Geosynthetic Research Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII Standard Guide for GRI Standard GC8
GRI Test Method GM17*
 Geosynthetic Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII Revision 12: November 4, 2015 Revision schedule on pg. 11 GRI Test Method
Geosynthetic Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII Revision 12: November 4, 2015 Revision schedule on pg. 11 GRI Test Method
Interpretation of clogging effects on the hydraulic behavior of ion treated geotextiles
 9 th International Conference on Geosynthetics, Brazil, 2010 Interpretation of clogging effects on the hydraulic behavior of ion treated geotextiles Lee, K. W. Department of Civil Engineering, Dongseo
9 th International Conference on Geosynthetics, Brazil, 2010 Interpretation of clogging effects on the hydraulic behavior of ion treated geotextiles Lee, K. W. Department of Civil Engineering, Dongseo
Evaluation of HDPE Geomembrane Liners for Unconventional Gas Extraction Brine Associated Water
 Evaluation of HDPE Geomembrane Liners for Unconventional Gas Extraction Brine Associated Water Daniel Tan, Engr., Solmax International Asia Pacific Sdn. Bhd., Malaysia, dtan@solmax.com Robert Denis, P.E.,
Evaluation of HDPE Geomembrane Liners for Unconventional Gas Extraction Brine Associated Water Daniel Tan, Engr., Solmax International Asia Pacific Sdn. Bhd., Malaysia, dtan@solmax.com Robert Denis, P.E.,
Secondary Containment Comparison ATI Ultra COAT vs HDPE
 When choosing a secondary containment system it must be chosen based on its ability to withstand long term contact with the natural elements (weather), whatever the tanks hold (unrefined oil, fuels, acids,
When choosing a secondary containment system it must be chosen based on its ability to withstand long term contact with the natural elements (weather), whatever the tanks hold (unrefined oil, fuels, acids,
SPECIFICATIONS FOR PRECAST MODULAR BLOCK RETAINING WALL SYSTEM (revised 11/5/13)
 Page 1 of 7 STONE STRONG SYSTEMS SPECIFICATIONS FOR PRECAST MODULAR BLOCK RETAINING WALL SYSTEM (revised ) PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Description A. Work includes furnishing and installing precast modular blocks
Page 1 of 7 STONE STRONG SYSTEMS SPECIFICATIONS FOR PRECAST MODULAR BLOCK RETAINING WALL SYSTEM (revised ) PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Description A. Work includes furnishing and installing precast modular blocks
Laboratory and Field Performance Assessment of Geocomposite Alternative to Gravel Drainage Overliner in Heap Leach Pads
 Laboratory and Field Performance Assessment of Geocomposite Alternative to Gravel Drainage Overliner in Heap Leach Pads Aigen Zhao, PhD, PE, GSE Environmental, LLC, USA Mark Harris, GSE Environmental,
Laboratory and Field Performance Assessment of Geocomposite Alternative to Gravel Drainage Overliner in Heap Leach Pads Aigen Zhao, PhD, PE, GSE Environmental, LLC, USA Mark Harris, GSE Environmental,
Construction. SikaProof A-08 Edge, A-12 Edge. Fully bonded FPO sheet membrane in L-shape for the SikaProof A waterproofing system. Product Description
 Product Data Sheet Edition 15/10/2014 Identification no: 02 07 04 10 300 0 000002 SikaProof A Edge SikaProof A-08 Edge, A-12 Edge Fully bonded FPO sheet membrane in L-shape for the SikaProof A waterproofing
Product Data Sheet Edition 15/10/2014 Identification no: 02 07 04 10 300 0 000002 SikaProof A Edge SikaProof A-08 Edge, A-12 Edge Fully bonded FPO sheet membrane in L-shape for the SikaProof A waterproofing
EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF THE BIOLOGICAL CLOGGING OF DRAINAGE GEOCOMPOSITE AT THE BOTOM OF LANDFILL
 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF THE BIOLOGICAL CLOGGING OF DRAINAGE GEOCOMPOSITE AT THE BOTOM OF LANDFILL Yves Durkheim, Afitex, France Stéphane FOURMONT, Afitex, France Carole BLOQUET, Sita, France ABSTRACT
EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF THE BIOLOGICAL CLOGGING OF DRAINAGE GEOCOMPOSITE AT THE BOTOM OF LANDFILL Yves Durkheim, Afitex, France Stéphane FOURMONT, Afitex, France Carole BLOQUET, Sita, France ABSTRACT
MaxCell Technical Manual Design Parameters
 MaxCell Technical Manual Design Parameters Breaking Strength by Product Style, lbs Product Style Standard MaxCell Fire Resistant MaxCell Test Method 4 Cell 2,750 2,200 ASTM D 5 Bellcore 5 5.. Cell 2,50
MaxCell Technical Manual Design Parameters Breaking Strength by Product Style, lbs Product Style Standard MaxCell Fire Resistant MaxCell Test Method 4 Cell 2,750 2,200 ASTM D 5 Bellcore 5 5.. Cell 2,50
Testing and appraisal of Lucobit polymer effect as an additive on asphalt mixture performance
 Abstract Testing and appraisal of polymer effect as an additive on asphalt mixture performance Hamid Sabbagh mollahosseini*,golazin Yadollahi**, Ershad Amoosoltani*** *, ***Executive of Engineering and
Abstract Testing and appraisal of polymer effect as an additive on asphalt mixture performance Hamid Sabbagh mollahosseini*,golazin Yadollahi**, Ershad Amoosoltani*** *, ***Executive of Engineering and
A Guide to Structural Waterproofing
 A Guide to Structural Waterproofing Part One Waterproofing Protection For Below Ground Structures 1 2012 W. R. Grace & Co Benjamin J. Brooks Table of Contents Grace Around The World Reference Material
A Guide to Structural Waterproofing Part One Waterproofing Protection For Below Ground Structures 1 2012 W. R. Grace & Co Benjamin J. Brooks Table of Contents Grace Around The World Reference Material
Tunnels & Arches OLDROYD THE ULTIMATE WATERPROOF MEMBRANE SYSTEM
 P r o d u c t a p p l i c a t i o n s a n d t e c h n i c a l i n f o r m a t i o n 5 Tunnels & Arches V OLDROYD THE ULTIMATE WATERPROOF MEMBRANE SYSTEM V Create dry usable space with the original X pattern
P r o d u c t a p p l i c a t i o n s a n d t e c h n i c a l i n f o r m a t i o n 5 Tunnels & Arches V OLDROYD THE ULTIMATE WATERPROOF MEMBRANE SYSTEM V Create dry usable space with the original X pattern
PVC PIPE PERFORMANCE FACTORS
 PVC PIPE PERFORMANCE FACTORS PVC pipe, like all flexible pipe products, is very dependent on the surrounding soil for its structural capacity, in addition, the pipe material must have sufficient inherent
PVC PIPE PERFORMANCE FACTORS PVC pipe, like all flexible pipe products, is very dependent on the surrounding soil for its structural capacity, in addition, the pipe material must have sufficient inherent
DENSO WATERPROOFING SYSTEMS
 DENSO WATERPROOFING SYSTEMS Approved Quality Management System AS/NZS ISO 9001:2008 Lloyds Register Certificate N o Mel 0927759 Denso (Australia) Pty Ltd A MEMBER OF WINN & COALES INTERNATIONAL 411 413
DENSO WATERPROOFING SYSTEMS Approved Quality Management System AS/NZS ISO 9001:2008 Lloyds Register Certificate N o Mel 0927759 Denso (Australia) Pty Ltd A MEMBER OF WINN & COALES INTERNATIONAL 411 413
Chapter 2 Basis of design and materials
 Chapter 2 Basis of design and materials 2.1 Structural action It is necessary to start a design by deciding on the type and layout of structure to be used. Tentative sizes must be allocated to each structural
Chapter 2 Basis of design and materials 2.1 Structural action It is necessary to start a design by deciding on the type and layout of structure to be used. Tentative sizes must be allocated to each structural
CONCRETE SEGMENTAL RETAINING WALL SYSTEM
 CONCRETE SEGMENTAL RETAINING WALL SYSTEM PART 1: GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 1.01 Work Included A. Work shall consist of furnishing and constructing a Rockwood Classic 8 with PCS unit segmental retaining wall
CONCRETE SEGMENTAL RETAINING WALL SYSTEM PART 1: GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 1.01 Work Included A. Work shall consist of furnishing and constructing a Rockwood Classic 8 with PCS unit segmental retaining wall
EVALUATION ACCORDING TO ASTM F
 Bodycote Report EVALUATION ACCORDING TO ASTM F 2023 Evaluation of the chlorine resistance according to ASTM F 2023 of the PB pipe material PB4267 GREY Mattias Svedberg RESTRICTED DISTRIBUTION SE-611 82
Bodycote Report EVALUATION ACCORDING TO ASTM F 2023 Evaluation of the chlorine resistance according to ASTM F 2023 of the PB pipe material PB4267 GREY Mattias Svedberg RESTRICTED DISTRIBUTION SE-611 82
Prestressed Concrete Pipe Fitness for Service and Repair
 Prestressed Concrete Pipe Fitness for Service and Repair Rasko Ojdrovic rpojdrovic@sgh.com 781-907-9231 IAEA - EPRI 15 October 2014 www.sgh.com SGH Pipeline Experience More than 25 years of research, analysis,
Prestressed Concrete Pipe Fitness for Service and Repair Rasko Ojdrovic rpojdrovic@sgh.com 781-907-9231 IAEA - EPRI 15 October 2014 www.sgh.com SGH Pipeline Experience More than 25 years of research, analysis,
GRI Standard Practice GT7 * Determination of the Long-Term Design Strength of Geotextiles
 Geosynthetic Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII adopted -1989 Rev. 1 1992 Rev. 2 (editorial) 2012 GRI Standard Practice
Geosynthetic Institute 475 Kedron Avenue Folsom, PA 19033-1208 USA TEL (610) 522-8440 FAX (610) 522-8441 GEI GRI GSI GAI GCI GII adopted -1989 Rev. 1 1992 Rev. 2 (editorial) 2012 GRI Standard Practice
Introduction: Background of the OIT Test:
 The Effect of Hindered Phenol Stabilizers on Oxygen Induction Time (OIT) Measurements, and The Use of OIT Measurements to Predict Long Term Thermal Stability Philip Jacoby, Vice President of Technology,
The Effect of Hindered Phenol Stabilizers on Oxygen Induction Time (OIT) Measurements, and The Use of OIT Measurements to Predict Long Term Thermal Stability Philip Jacoby, Vice President of Technology,
Interior Walls below and above ground OLDROYD THE ULTIMATE WATERPROOF MEMBRANE SYSTEM
 P r o d u c t a p p l i c a t i o n s a n d t e c h n i c a l i n f o r m a t i o n 2 below and above ground V OLDROYD THE ULTIMATE WATERPROOF MEMBRANE SYSTEM V The flexible, fast and cost-effective answer
P r o d u c t a p p l i c a t i o n s a n d t e c h n i c a l i n f o r m a t i o n 2 below and above ground V OLDROYD THE ULTIMATE WATERPROOF MEMBRANE SYSTEM V The flexible, fast and cost-effective answer
M n = (DP)m = (25,000)(104.14 g/mol) = 2.60! 10 6 g/mol
 14.4 (a) Compute the repeat unit molecular weight of polystyrene. (b) Compute the number-average molecular weight for a polystyrene for which the degree of polymerization is 25,000. (a) The repeat unit
14.4 (a) Compute the repeat unit molecular weight of polystyrene. (b) Compute the number-average molecular weight for a polystyrene for which the degree of polymerization is 25,000. (a) The repeat unit
Specification Guidelines: Allan Block Modular Retaining Wall Systems
 Specification Guidelines: Allan Block Modular Retaining Wall Systems The following specifications provide Allan Block Corporation's typical requirements and recommendations. At the engineer of record's
Specification Guidelines: Allan Block Modular Retaining Wall Systems The following specifications provide Allan Block Corporation's typical requirements and recommendations. At the engineer of record's
INTERIOR WALLS AND BASEMENTS CHOOSING THE RIGHT MEMBRANE FOR INTERIOR WALLS. Multi-Layer Technology provides increased strength.
 INTERIOR WALLS AND BASEMENTS CHOOSING THE RIGHT MEMBRANE FOR INTERIOR WALLS Multi-Layer Technology provides increased strength. Specifically designed for interior applications. Compatible with most internal
INTERIOR WALLS AND BASEMENTS CHOOSING THE RIGHT MEMBRANE FOR INTERIOR WALLS Multi-Layer Technology provides increased strength. Specifically designed for interior applications. Compatible with most internal
The Most Advanced Name in Drainage Systems. Sanitary Sewer Pipe
 The Most Advanced Name in Drainage Systems Sanitary Sewer Pipe SaniTite Sanitary Sewer Pipe delivers the features that engineers, contractors and municipalities demand durability, performance, handling,
The Most Advanced Name in Drainage Systems Sanitary Sewer Pipe SaniTite Sanitary Sewer Pipe delivers the features that engineers, contractors and municipalities demand durability, performance, handling,
Moisture and Resilient Floor Covering
 Moisture and Resilient Floor Covering Moisture related failures of resilient floor coverings installed over concrete have focused unfairly over the years on the premise that the flooring product itself
Moisture and Resilient Floor Covering Moisture related failures of resilient floor coverings installed over concrete have focused unfairly over the years on the premise that the flooring product itself
Oil and Gas Containment Systems
 FRONT COVER Oil and Gas Containment Systems FACING THE CHALLENGE Oil and natural gas production is one of the most hazardous and complex industries in the world. In addition to typical day-to-day business
FRONT COVER Oil and Gas Containment Systems FACING THE CHALLENGE Oil and natural gas production is one of the most hazardous and complex industries in the world. In addition to typical day-to-day business
NRC INSPECTION MANUAL
 NRC INSPECTION MANUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURE 88001 LLUR ON-SITE CONSTRUCTION PROGRAM APPLICABILITY: 2600, 2801 88001-01 INSPECTION OBJECTIVES 01.01 To determine by direct observation if on-site construction
NRC INSPECTION MANUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURE 88001 LLUR ON-SITE CONSTRUCTION PROGRAM APPLICABILITY: 2600, 2801 88001-01 INSPECTION OBJECTIVES 01.01 To determine by direct observation if on-site construction
Long term performance of polymers
 1.0 Introduction Long term performance of polymers Polymer materials exhibit time dependent behavior. The stress and strain induced when a load is applied are a function of time. In the most general form
1.0 Introduction Long term performance of polymers Polymer materials exhibit time dependent behavior. The stress and strain induced when a load is applied are a function of time. In the most general form
pdi PLASTIC DRUM INSTITUTE Plastic Drum Paneling Issues
 pdi PLASTIC DRUM INSTITUTE Plastic Drum Paneling Issues PANELING BACKGROUND This report will explain the causes of paneling and suggest some possible ways to eliminate or minimize the paneling of plastic
pdi PLASTIC DRUM INSTITUTE Plastic Drum Paneling Issues PANELING BACKGROUND This report will explain the causes of paneling and suggest some possible ways to eliminate or minimize the paneling of plastic
100.02 Civil engineering Fibertex Geotextiles
 C O N S T R U C T I O N 100.02 Civil engineering C O N S T R Constructing with Fibertex offers a full range of nonwoven geotextiles designed for use in many different foundation structures within civil
C O N S T R U C T I O N 100.02 Civil engineering C O N S T R Constructing with Fibertex offers a full range of nonwoven geotextiles designed for use in many different foundation structures within civil
PEX Pipes for Service Line Applications
 PEX Pipes for Service Line Applications Introduction to PPI Introduction to PEX pipes for water service Industry standards and tests Reasons for using PEX pipes for water service PEX installation for water
PEX Pipes for Service Line Applications Introduction to PPI Introduction to PEX pipes for water service Industry standards and tests Reasons for using PEX pipes for water service PEX installation for water
Study of durability of sprayed concrete
 Study of durability of sprayed concrete ADAM HUBÁČEK, RUDOLF HELA Department of Technology of Building Materials and Components Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering Veveří 95, 602
Study of durability of sprayed concrete ADAM HUBÁČEK, RUDOLF HELA Department of Technology of Building Materials and Components Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering Veveří 95, 602
synthetic waterproofing systems
 GreeN roofing Waterproofing systems with SINTOFOIL TpO/Fpa membranes synthetic waterproofing systems Recently, green roofing systems have been attracting increasing interest because of the significant
GreeN roofing Waterproofing systems with SINTOFOIL TpO/Fpa membranes synthetic waterproofing systems Recently, green roofing systems have been attracting increasing interest because of the significant
INSTALLATION GUIDE. americanwick.com 800.242.WICK (9425)
 INSTALLATION GUIDE americanwick.com 800.242.WICK (9425) American Wick Drain SITEDRAIN prefabricated drainage products may be installed in a variety of civil construction applications including: retaining
INSTALLATION GUIDE americanwick.com 800.242.WICK (9425) American Wick Drain SITEDRAIN prefabricated drainage products may be installed in a variety of civil construction applications including: retaining
INVESTIGATING AND REMEDIATING LEAKS IN BELOW GRADE STRUCTURES AND UNDER PLAZAS
 INVESTIGATING AND REMEDIATING LEAKS IN BELOW GRADE STRUCTURES AND UNDER PLAZAS JUSTIN HENSHELL, FAIA, FASTM HENSHELL & BUCCELLATO, RED BANK, NJ B U I L D I N G E N V E L O P E T E C H N O L O G Y S Y M
INVESTIGATING AND REMEDIATING LEAKS IN BELOW GRADE STRUCTURES AND UNDER PLAZAS JUSTIN HENSHELL, FAIA, FASTM HENSHELL & BUCCELLATO, RED BANK, NJ B U I L D I N G E N V E L O P E T E C H N O L O G Y S Y M
Waterproofing of Tunnels under Water Pressure
 1 1. INTRODUCTION...3 1.1. General...3 1.2. Products of RENOLIT...3 1.3. Requirements of the waterproofing materials...3 1.3.1. Water tightness...3 1.3.2. Flexibility...3 1.3.3. Chemical resistance...3
1 1. INTRODUCTION...3 1.1. General...3 1.2. Products of RENOLIT...3 1.3. Requirements of the waterproofing materials...3 1.3.1. Water tightness...3 1.3.2. Flexibility...3 1.3.3. Chemical resistance...3
CHARACTERIZATION OF POLYMERS BY TMA. W.J. Sichina, National Marketing Manager
 PERKIN ELMER Polymers technical note CHARACTERIZATION OF POLYMERS BY W.J. Sichina, National Marketing Manager Thermomechanical analysis () is one of the important characterization techniques in the field
PERKIN ELMER Polymers technical note CHARACTERIZATION OF POLYMERS BY W.J. Sichina, National Marketing Manager Thermomechanical analysis () is one of the important characterization techniques in the field
SIENA STONE GRAVITY RETAINING WALL INSTALLATION SPECIFICATIONS. Prepared by Risi Stone Systems Used by permission.
 SIENA STONE GRAVITY RETAINING WALL INSTALLATION SPECIFICATIONS Prepared by Risi Stone Systems Used by permission. 1-800-UNILOCK www.unilock.com FOREWORD This outline specification has been prepared for
SIENA STONE GRAVITY RETAINING WALL INSTALLATION SPECIFICATIONS Prepared by Risi Stone Systems Used by permission. 1-800-UNILOCK www.unilock.com FOREWORD This outline specification has been prepared for
DISTRIBUTION PIPING MATERIALS: BUILDING HYDRONIC SYSTEM MANAGEMENT. Jim Riley, Texas A&M University February 10, 2015
 DISTRIBUTION PIPING MATERIALS: BUILDING HYDRONIC SYSTEM MANAGEMENT Jim Riley, Texas A&M University February 10, 2015 Piping at Texas A&M 2 History of Distribution Piping at Texas A&M Concrete reinforced
DISTRIBUTION PIPING MATERIALS: BUILDING HYDRONIC SYSTEM MANAGEMENT Jim Riley, Texas A&M University February 10, 2015 Piping at Texas A&M 2 History of Distribution Piping at Texas A&M Concrete reinforced
Mechanically stabilized layers in road construction
 Mechanically stabilized layers in road construction Zikmund Rakowski, Jacek Kawalec Tensar International, UK, Technical University of Silesia, Poland Abstract: Effective and economical technologies are
Mechanically stabilized layers in road construction Zikmund Rakowski, Jacek Kawalec Tensar International, UK, Technical University of Silesia, Poland Abstract: Effective and economical technologies are
BELOW GRADE & PLAZA WATERPROOFING SELECTION PROCESS
 BELOW GRADE & PLAZA WATERPROOFING SELECTION PROCESS PAUL BUCCELLATO AIA, RWC HENSHELL & BUCCELLATO, RED BANK, NJ B U I L D I N G E N V E L O P E T E C H N O L O G Y S Y M P O S I U M O C T O B E R 2 0
BELOW GRADE & PLAZA WATERPROOFING SELECTION PROCESS PAUL BUCCELLATO AIA, RWC HENSHELL & BUCCELLATO, RED BANK, NJ B U I L D I N G E N V E L O P E T E C H N O L O G Y S Y M P O S I U M O C T O B E R 2 0
Solutions for tunneling and mining. Waterproofing. Expanding Horizons Underground. Expanding horizons underground
 Solutions for tunneling and mining Waterproofing Expanding Horizons Underground Expanding horizons underground The Bonded Waterproofing Concept An innovative approach, the MASTERSEAL 345 waterproofing
Solutions for tunneling and mining Waterproofing Expanding Horizons Underground Expanding horizons underground The Bonded Waterproofing Concept An innovative approach, the MASTERSEAL 345 waterproofing
TPO: Getting Better With Age
 TPO: Getting Better With Age By Michael Mendoza, TPO product manager, Firestone Building Products Thermoplastic polyolefin has matured. By any criteria, TPO is no longer the new kid on the block when it
TPO: Getting Better With Age By Michael Mendoza, TPO product manager, Firestone Building Products Thermoplastic polyolefin has matured. By any criteria, TPO is no longer the new kid on the block when it
DELTA Premium Moisture Management Systems for Foundations.
 DELTA protects property. Saves energy. Creates comfort. DELTA Premium Moisture Management Systems for Foundations. DELTA Premium Moisture Management Systems provide the best protection for foundations.
DELTA protects property. Saves energy. Creates comfort. DELTA Premium Moisture Management Systems for Foundations. DELTA Premium Moisture Management Systems provide the best protection for foundations.
Pipes and Fittings for Gravity Sewer Mains. SewerMAX
 SewerMAX High resistance to tree root intrusion and groundwater infiltration lightweight for ease of installation low embodied energy for environmental benefits long service life Excellent chemical resistance
SewerMAX High resistance to tree root intrusion and groundwater infiltration lightweight for ease of installation low embodied energy for environmental benefits long service life Excellent chemical resistance
Geosynthetic Mining Solutions at Copper Tailings Dams: A Review of the State of Practice in Chile.
 Geosynthetic Mining Solutions at Copper Tailings Dams: A Review of the State of Practice in Chile. Carlos Cacciuttolo, Engineering Council, Chile. Jack Caldwell, Robertson GeoConsultants, Canada. Scott
Geosynthetic Mining Solutions at Copper Tailings Dams: A Review of the State of Practice in Chile. Carlos Cacciuttolo, Engineering Council, Chile. Jack Caldwell, Robertson GeoConsultants, Canada. Scott
The Most Advanced Name in Drainage Systems. Geotextile Products
 The Most Advanced Name in Drainage Systems Geotextile Products ADS MEETs YOUR Geotextile NEEDS Advanced Drainage Systems, Inc. (ADS) single wall and N12 dual wall pipe have become the industry standard
The Most Advanced Name in Drainage Systems Geotextile Products ADS MEETs YOUR Geotextile NEEDS Advanced Drainage Systems, Inc. (ADS) single wall and N12 dual wall pipe have become the industry standard
WATERPROOFING OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FLAT ROOF 12
 WATERPROOFING OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FLAT ROOF 12 87 88 GOOD INDUSTRY PRACTICES 12 WATERPROOFING OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FLAT ROOF 12.1 BACKGROUND Most roofs in Singapore are constructed using reinforced
WATERPROOFING OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FLAT ROOF 12 87 88 GOOD INDUSTRY PRACTICES 12 WATERPROOFING OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FLAT ROOF 12.1 BACKGROUND Most roofs in Singapore are constructed using reinforced
SECTION 02720 SANITARY SEWER AND STORM DRAIN SYSTEMS
 SECTION 02720 SANITARY SEWER AND STORM DRAIN SYSTEMS PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. The requirements for pipe material and installation in sewer and drainage collection systems. All materials
SECTION 02720 SANITARY SEWER AND STORM DRAIN SYSTEMS PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. The requirements for pipe material and installation in sewer and drainage collection systems. All materials
GENERAL PROPERTIES //////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 ALLOY 625 DATA SHEET //// Alloy 625 (UNS designation N06625) is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy possessing excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion over a broad range of corrosive conditions,
ALLOY 625 DATA SHEET //// Alloy 625 (UNS designation N06625) is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy possessing excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion over a broad range of corrosive conditions,
Radiation Curable Components and Their use in Hard, Scratch Resistant Coating Applications
 Radiation Curable Components and Their use in Hard, Scratch Resistant Coating Applications William Schaeffer Steven Tyson Indu Vappala Robert Kensicki Sartomer USA, LLC 502 Thomas Jones Way Exton, PA 19343
Radiation Curable Components and Their use in Hard, Scratch Resistant Coating Applications William Schaeffer Steven Tyson Indu Vappala Robert Kensicki Sartomer USA, LLC 502 Thomas Jones Way Exton, PA 19343
Introduction: Consumables - Part of the Identification System
 Consumables - The Basics A presentation from: Introduction: Consumables - Part of the Identification System You have spent many hours researching, selecting, and getting approval for your new data collection
Consumables - The Basics A presentation from: Introduction: Consumables - Part of the Identification System You have spent many hours researching, selecting, and getting approval for your new data collection
Moisture Mitigation for Concrete Slabs
 Moisture Mitigation for Concrete Slabs A brief description of alternative methods for dealing with slab moisture problems By Peter A. Craig M oisture-related problems with floor coverings and coatings
Moisture Mitigation for Concrete Slabs A brief description of alternative methods for dealing with slab moisture problems By Peter A. Craig M oisture-related problems with floor coverings and coatings
Sarah Chung, Ken Oliphant, Patrick Vibien and Jingguo Zhang Jana Laboratories Inc., Aurora, Ontario, Canada
 AN EXAMINATION OF THE RELATIVE IMPACT OF COMMON POTABLE WATER DISINFECTANTS (CHLORINE, CHLORAMINES AND CHLORINE DIOXIDE) ON PLASTIC PIPING SYSTEM COMPONENTS Sarah Chung, Ken Oliphant, Patrick Vibien and
AN EXAMINATION OF THE RELATIVE IMPACT OF COMMON POTABLE WATER DISINFECTANTS (CHLORINE, CHLORAMINES AND CHLORINE DIOXIDE) ON PLASTIC PIPING SYSTEM COMPONENTS Sarah Chung, Ken Oliphant, Patrick Vibien and
The AQUAFIN Approach to Concrete Repair
 Concrete Repair Building Product Systems Waterproofing & Concrete Restoration Decorative Coatings Moisture Vapor Remediation & Flooring Injection Grouting The AQUAFIN Approach to Concrete Repair www.aquafin.net
Concrete Repair Building Product Systems Waterproofing & Concrete Restoration Decorative Coatings Moisture Vapor Remediation & Flooring Injection Grouting The AQUAFIN Approach to Concrete Repair www.aquafin.net
CONCRETE SEGMENTAL RETAINING WALL SYSTEM
 CONCRETE SEGMENTAL RETAINING WALL SYSTEM PART 1: GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 1.01 Work Included A. Work shall consist of furnishing and constructing a Rockwood Vintage TM unit segmental retaining wall (SRW)
CONCRETE SEGMENTAL RETAINING WALL SYSTEM PART 1: GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 1.01 Work Included A. Work shall consist of furnishing and constructing a Rockwood Vintage TM unit segmental retaining wall (SRW)
Composite Design Fundamentals. David Richardson
 Composite Design Fundamentals David Richardson Contents A review of the fundamental characteristics of composites Stiffness and Strength Anisotropic Role of fibre, matrix and interface Composite failure
Composite Design Fundamentals David Richardson Contents A review of the fundamental characteristics of composites Stiffness and Strength Anisotropic Role of fibre, matrix and interface Composite failure
HW 10. = 3.3 GPa (483,000 psi)
 HW 10 Problem 15.1 Elastic modulus and tensile strength of poly(methyl methacrylate) at room temperature [20 C (68 F)]. Compare these with the corresponding values in Table 15.1. Figure 15.3 is accurate;
HW 10 Problem 15.1 Elastic modulus and tensile strength of poly(methyl methacrylate) at room temperature [20 C (68 F)]. Compare these with the corresponding values in Table 15.1. Figure 15.3 is accurate;
September 2007. September 2013. Consulting Structural and Civil Engineers. 100 St John Street London EC1M 4EH. info @ akt-uk.com www.akt-uk.
 Consulting Structural and Civil Engineers 100 St John Street London EC1M 4EH T +44 (0) 20 7250 7777 F +44 (0) 20 7250 7555 info @ akt-uk.com www.akt-uk.com 3290 A031234 The 196-222 Joseph Kings Bloggs
Consulting Structural and Civil Engineers 100 St John Street London EC1M 4EH T +44 (0) 20 7250 7777 F +44 (0) 20 7250 7555 info @ akt-uk.com www.akt-uk.com 3290 A031234 The 196-222 Joseph Kings Bloggs
Preliminary Comments
 GRI-GM17 Specification Linear Low Density Polyethylene Geomembranes spec covers smooth and textured LLDPE thicknesses 0.50-3.00 mm (20-120 mils) formulated density 0.939 g/cc silent on flat die or blown
GRI-GM17 Specification Linear Low Density Polyethylene Geomembranes spec covers smooth and textured LLDPE thicknesses 0.50-3.00 mm (20-120 mils) formulated density 0.939 g/cc silent on flat die or blown
Nomex KD Technology. DuPont TM. DuPont s Heritage in Hot Gas Filtration Application. For over 4 decades, a filter media made of Nomex
 DuPont s Heritage in Hot Gas Filtration Application For over 4 decades, a filter media made of Nomex brand fibre has been considered as the state of the art product in typical filtration applications such
DuPont s Heritage in Hot Gas Filtration Application For over 4 decades, a filter media made of Nomex brand fibre has been considered as the state of the art product in typical filtration applications such
Plastics and Polymer Business. Properties enhancement for Plastics
 News Letter Vol. 18, issue October-December, 2012 Hyperdispersants and Coupling Agents for Thermoplastics and Thermosets Solplus, Ircolplus and Solsperse hyperdispersants and coupling agents have been
News Letter Vol. 18, issue October-December, 2012 Hyperdispersants and Coupling Agents for Thermoplastics and Thermosets Solplus, Ircolplus and Solsperse hyperdispersants and coupling agents have been
SECTION 02612 NONREINFORCED CONCRETE SEWER PIPE
 SECTION 02612 PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: Furnishing and installing nonreinforced concrete sewer pipe. Provide concrete sewer pipe less than 12 inches in diameter, and in other sizes
SECTION 02612 PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: Furnishing and installing nonreinforced concrete sewer pipe. Provide concrete sewer pipe less than 12 inches in diameter, and in other sizes
ATI 2205 ATI 2205. Technical Data Sheet. Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES. (UNS S31803 and S32205)
 ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
Waterproofing of tunnels under infiltrating water RENOLIT ALKORGEO. Underground structures
 Waterproofing of tunnels under infiltrating water RENOLIT ALKORGEO Underground structures RENOLIT ALKORGEO Underground structures RENOLIT Belgium N.V. Industriepark de Bruwaan 9 9700 Oudenaarde Belgium
Waterproofing of tunnels under infiltrating water RENOLIT ALKORGEO Underground structures RENOLIT ALKORGEO Underground structures RENOLIT Belgium N.V. Industriepark de Bruwaan 9 9700 Oudenaarde Belgium
constructive solutions Fosroc total waterproofing protection of below-ground structures
 constructive solutions Fosroc total waterproofing protection of below-ground structures Our profile Since the company s beginnings over 50 years ago, Fosroc has developed into an International leader in
constructive solutions Fosroc total waterproofing protection of below-ground structures Our profile Since the company s beginnings over 50 years ago, Fosroc has developed into an International leader in
