Comparison of Procedural Times for Ultrasound-Guided Perineural Catheter Insertion in Obese and Nonobese Patients
|
|
|
- Abraham Sharp
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of Procedural Times for Ultrasound-Guided Perineural Catheter Insertion in Obese and Nonobese Patients Edward R. Mariano, MD, MAS, Jay B. Brodsky, MD Article includes CME test Received March 14, 2011, from the Department of Anesthesia, University of California, San Diego, California USA; and Department of Anesthesia, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California USA. Revision requested April 8, Revised manuscript accepted for publication April 20, We thank Brian M. Ilfeld, MD, MS (University of California, San Diego), for invaluable editorial assistance and guidance during manuscript preparation. This project was support by the Departments of Anesthesiology, University of California, San Diego, and Stanford University School of Medicine, and the VA Palo Alto Health Care System (Palo Alto, CA). The contents of this article are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of these entities. Dr Mariano has received funding for other research investigations from Teleflex Medical (Research Triangle Park, NC) and Stryker Instruments (Kalamazoo, MI, USA) and previously conducted continuous peripheral nerve block workshops for Stryker Instruments. These companies had no input into any aspect of this study s conceptualization, design, and implementation; data collection, analysis, and interpretation; or manuscript preparation. Address correspondence to Edward R. Mariano, MD, MAS, Anesthesiology and Perioperative Care Service, VA Palo Alto Health Care System, 3801 Miranda Ave, 112A, Palo Alto, CA USA. emariano@stanford.edu. Abbreviations BMI, body mass index Objectives Perineural catheter insertion with ultrasound guidance alone has been described, but it remains unknown whether this new technique results in the same procedural time and success rate for obese and nonobese patients. We therefore tested the hypothesis that obese patients require more time for perineural catheter insertion compared to nonobese patients despite using ultrasound. Methods Data from 5 previously published randomized clinical trials comparing ultrasound- and stimulation-guided perineural catheter insertion techniques were reviewed, and patients who received ultrasound-guided catheters were divided into 2 groups: obese (body mass index 30 kg/m 2 ) and nonobese (body mass index <30 kg/m 2 ). A standardized ultrasound-guided nonstimulating catheter technique was used with mepivacaine, 1.5% (40 ml), as the initial bolus via the placement needle for the primary surgical nerve block. The primary outcome was the procedural time for perineural catheter insertion. Secondary outcomes included block efficacy, procedure-related pain, fluid leakage, vascular puncture, and catheter dislodgment. Results A sample of 120 patients was identified: 51 obese and 69 nonobese. All obese patients had successful catheter placement compared to 68 of 69 (98%) nonobese patients (P =.388). The time for perineural catheter insertion [median (10th 90th percentiles)] was 7 (4 12) minutes for obese patients versus 7 (4 15) minutes for nonobese patients (P =.732). There were no statistically significant differences in other secondary outcomes. Conclusions On the basis of this retrospective analysis, perineural catheter insertion is not prolonged in obese patients compared to nonobese patients when an ultrasoundguided technique is used. However, these results are only suggestive and require confirmation through prospective study. Key Words continuous peripheral nerve block; obesity; perineural catheter; ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia Obese patients presenting for eligible surgery may benefit considerably from regional anesthesia techniques because of their often difficult airways and increased sensitivities to anesthetic agents, muscle relaxants, and opioids. 1 Unfortunately, obesity is associated with technical difficulty in the performance of regional anesthesia procedures 2 as well as higher failure rates compared to nonobese patients. 3 Although the use of surface ultrasound guidance has been explored in the obese patient population for neuraxial blockade, 4,5 the effectiveness of ultrasound guidance for peri neural catheter insertion in the setting of obesity has not been explored to date by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2011; 30:
2 There has been increasing interest in placement techniques for perineural catheters using ultrasound guidance in recent years. 6 8 Compared to the traditional stimulating catheter technique, an exclusively ultrasound-guided approach results in high success rates for catheter insertion and reduces the procedural time However, it remains unknown whether this new ultrasound-guided technique results in the same procedural time and success rate in obese compared to non-obese patients. We therefore performed a pooled analysis of previously published clinical trial data to test the hypothesis that obese patients require more time for perineural catheter insertion compared to nonobese patients despite using an ultrasound-guided technique. Materials and Methods The Institutional Review Board (University of California, San Diego School of Medicine) reviewed the research plan and granted written exemption from Institutional Review Board approval. Prospectively gathered deindentified data from 5 previously published randomized clinical trials comparing ultrasound- and stimulation-guided perineural catheter insertion techniques 9 13 were reviewed. Data from the cohort of patients who underwent preoperative perineural catheter insertion using ultrasound alone were then divided into 2 groups: obese (body mass index [BMI] 30 kg/m 2 ) and nonobese (BMI <30 kg/m 2 ). During the original randomized clinical trials, each study patient received a nonstimulating perineural catheter using a standardized ultrasound-guided technique as previously described Review of the Catheter Insertion Technique Following standard American Society of Anesthesiologists monitoring guidelines and titration of intravenous sedatives, the procedural area was cleansed with chlorhexidine gluconate and isopropyl alcohol (ChloraPrep One-Step; Medi-Flex Hospital Products, Inc, Overland Park, KS), and a clear, sterile, fenestrated drape was applied. With the ultrasound transducer appropriate for the desired perineural catheter site (MicroMaxx; SonoSite, Inc, Bothell, WA) in a sterile sleeve, the target nerve was identified in a transverse cross-sectional view. Once the optimal image of the target nerve was obtained, a local anesthetic skin wheal was raised next to the ultrasound transducer. An 8.9-cm, 17-gauge Tuohy-tip needle (FlexTip; Arrow International, Reading, PA) was inserted through the skin wheal in plane beneath the ultrasound transducer and directed toward the target nerve. With the needle properly positioned, a local anesthetic solution (40 ml of mepivacaine, 1.5%, with epinephrine, μg/ml) was injected in divided doses circumferentially around the target nerve via the needle. A 19-gauge catheter (FlexTip; Arrow International) was then placed through the length of the needle and advanced 5 cm beyond the needle tip. Once a catheter had been inserted, the needle itself was withdrawn over the catheter. The injection port was attached to the end of the catheter, and the catheter tip position was inferred by injecting 1 ml of air via the catheter under ultrasound guidance, slightly withdrawn if necessary, and another 1 ml of air was injected to confirm accurate catheter tip placement. 14 The catheter was not tunneled farther but was dressed and secured with an anchoring device (StatLock; Venetec International, San Diego, CA). All catheters were placed by an attending physician with extensive experience in the ultrasound-guided technique or a regional anesthesia fellow or resident under the direct one-on-one supervision of the attending physician. Postoperatively, the patients were discharged with an portable electronic infusion pump (Pain Pump 2 Block- Aid; Stryker Instruments, Kalamazoo, MI) connected to the perineural catheter and programmed to deliver 0.2% ropivacaine (basal rate of 8 ml/h, patient-controlled bolus of 4 ml, and lockout interval of 30 minute). The patients were prescribed an oral opioid (5-mg oxycodone tablets) for breakthrough postoperative pain inadequately treated by the perineural ropivacaine infusion/bolus. Outcome Measurements The primary outcome was the procedural time for perineural catheter insertion in minutes starting when the ultrasound transducer first touched the patient and ending when the placement needle was withdrawn after catheter deployment. Secondary outcomes included block efficacy and procedure-related pain on a numeric rating scale of 0 to 10 (0, no discomfort; and 10, worst discomfort imaginable) immediately after catheter placement and fluid leakage, vascular puncture, and catheter dislodgment reported on postoperative day 1. Statistical Analysis Normality of distribution was determined using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (NCSS Statistical Software, Kaysville, UT). For normally distributed data, comparisons of independent samples were performed using the Student t test. For continuous data in distributions other than normal, the Mann-Whitney U test was used. Simple linear regression was performed to further analyze the as J Ultrasound Med 2011; 30:
3 sociation, if any, between the BMI and procedural time. The z test or Fisher exact test (n < 5 in any category) were used for comparisons of categorical variables. Two-sided P <.05 was considered statistically significant for the primary outcome. Because this study was a retrospective analysis of an existing data set, a post hoc calculation was performed to determine the power of the study to detect a 5-minute difference between groups (NCSS Statistical Software). Results From the original data set consisting of 240 patients who participated in previous randomized clinical trials, 9 13 a sample of 120 patients meeting study criteria (ie, catheters inserted using ultrasound guidance) was identified: 51 obese and 69 nonobese. Demographic, anthropometric, and catheter site data are presented in Table 1. Of note, obese patients were older [median (10th 90th percentiles)] versus nonobese patients [54 (30 68) and 45 (21 70), respectively; P =.035]. All obese patients had successful catheter placement per the protocol 9 13 compared to 68 of 69 (98%) nonobese patients (P=.388). The 1 patient who had a misplaced catheter was a 32-year-old man (BMI, 28 kg/m 2 ) who underwent ankle arthroscopy and had received a popliteal-sciatic perineural catheter preoperatively for postoperative analgesia. Despite reporting lack of cold sensation in the affected extremity before surgery, the patient had severe pain after emergence from general anesthesia with no evidence of sciatic nerve anesthesia despite a subsequent catheter bolus. The poplitealsciatic perineural catheter was replaced successfully in the postanesthesia care unit using ultrasound guidance. Primary Outcome The time for perineural catheter insertion [median (10th 90th percentiles)] was 7 (4 12) minutes for obese patients versus 7 (4 15) minutes for nonobese patients (P =.732). A post hoc power analysis was performed, and based on the sample size and prior assumptions (α =.05 and 5- minute SD from previously published study data), the present analysis had greater than 99.9% power to detect a 5-minute difference between groups. Secondary Outcomes A linear relationship did not exist between the BMI and procedural time (R 2 = 0.004). Procedure-related catheter insertion pain was similar for obese and nonobese patients [1 (0 4) versus 1 (0 4), respectively; P =.519]. There were no statistically significant differences in other secondary outcomes (Table 2). Table 1. Population Data and Procedural Information Obese Nonobese Characteristic (n = 51) (n = 69) P Age, y 54 (30 68) 45 (21 70).035 Sex, female/male 28/23 42/ Body mass index, kg/m 2 33 (30 41) 24 (21 28) <.001 Catheter insertion site Femoral Infraclavicular Interscalene Popliteal Values are reported as median (10th 90th percentiles) or number of patients, as indicated. Discussion When using the exclusively ultrasound-guided technique described in this study, perineural catheter insertion may be performed in the same amount of time and result in the same success rate for obese and nonobese patients. To our knowledge, a study evaluating the efficacy or efficiency of ultrasound-guided perineural catheter insertion specifically in obese patients has not been reported previously. The results of this study are specific to the technique and equipment used and cannot be extrapolated to other ultrasound-guided perineural catheter insertion techniques. For example, the technique used in this study relies on in-plane needle guidance and the insertion of a flexible epidural-type catheter to avoid bypassing the target nerve Other ultrasound-guided perineural catheter techniques incorporating less-flexible catheters use out-ofplane needle guidance to facilitate a needle approach that is nearly parallel to the target nerve. 6,15,16 The purpose of this study was not to compare various ultrasound-guided perineural catheter techniques. Therefore, we cannot draw conclusions regarding how well or poorly these alternative ultrasound-guided perineural catheter insertion techniques will compare to our technique in obese patients. Future research to determine the optimal ultrasound-guided perineural catheter equipment and insertion technique for obese and nonobese patients is warranted. Table 2. Secondary Outcomes Obese Nonobese Age, y (n = 51) (n = 69) P Fluid leakage at site Vascular puncture Catheter dislodged Values are reported as number of patients. J Ultrasound Med 2011; 30:
4 Catheter Placement Time The lack of a statistically significant difference in the catheter insertion time or success rate between obese and nonobese patients is in contrast to the results of a study by Nielsen and colleagues. 3 In that study, peripheral nerve blocks were placed without the aid of ultrasound guidance. Although it is tempting to speculate that ultrasound guidance is superior to traditional nerve localization techniques in obese patients, this theory is unproven currently and requires confirmation in randomized clinical trials. It is worth noting that 100% of the ultrasound-guided perineural catheters were placed successfully in the obese group, and 90% of the patients completed catheter insertion in 12 minutes or less. The time measurement in this study did not include setup time for the catheter and ultrasound equipment because this time was considered equal between the study groups. Combined Ultrasound Nerve Stimulation We elected to study a perineural catheter insertion technique relying exclusively on ultrasound guidance even though a combined technique may offer additional benefits over either technique alone Arguably, electrical stimulation may aid the practitioner in localizing a target nerve when the sonographic anatomy is difficult to discern, especially in the morbidly obese. At present, however, there is no clear evidence that electrical stimulation offers any additional benefit when combined with ultrasound guidance It is possible that stimulating perineural catheters may have an analgesic advantage over nonstimulating catheters, 13 but the ultrasound-guided stimulating perineural catheter placement technique 17,25 remains unproven in randomized clinical trials against perineural catheter insertion methods relying exclusively on ultrasound guidance or electrical stimulation. Study Limitations Although the data included in this analysis were gathered prospectively, 9 13 the study was retrospective in nature nonetheless and subject to sources of bias similar to other retrospective studies. Even if this study yielded statistically significant findings, confirmation by a prospective trial would be necessary before considering the results definitive. 26 Furthermore, failure to demonstrate the superiority of one technique over another is not proof of equivalency. Because this study was not a randomized clinical trial, the resulting group numbers was unbalanced, and the median age of the obese group was found to be older than that of the nonobese group. We do not believe that either of these factors influenced the results of the study. On the basis of the post hoc power analysis, our study had greater than 99.9% power to detect the anticipated difference between groups given the actual number of patients. We acknowledge the limited generalizability of the study given that the results apply specifically to the technique and associated equipment included in this investigation. Another potential limitation was that trainees placed nearly all of the perineural catheters included in this study, a factor that may also limit the generalizability of the results. Conclusions In summary, the results of this retrospective study do not show a statistically significant difference in the perineural catheter insertion time or success rate for obese patients compared to nonobese patients when an exclusively ultrasound-guided technique is used. These results do not necessarily apply to all ultrasound-guided perineural catheter insertion techniques or equipment. References 1. Casati A, Putzu M. Anesthesia in the obese patient: pharmacokinetic considerations. J Clin Anesth 2005; 17: Ranta P, Jouppila P, Spalding M, Jouppila R. The effect of maternal obesity on labour and labour pain. Anaesthesia 1995; 50: Nielsen KC, Guller U, Steele SM, Klein SM, Greengrass RA, Pietrobon R. Influence of obesity on surgical regional anesthesia in the ambulatory setting: an analysis of 9,038 blocks. Anesthesiology 2005; 102: Arzola C, Davies S, Rofaeel A, Carvalho JC. Ultrasound using the transverse approach to the lumbar spine provides reliable landmarks for labor epidurals. Anesth Analg 2007; 104: Balki M, Lee Y, Halpern S, Carvalho JC. Ultrasound imaging of the lumbar spine in the transverse plane: the correlation between estimated and actual depth to the epidural space in obese parturients. Anesth Analg 2009; 108: Swenson JD, Bay N, Loose E, et al. Outpatient management of continuous peripheral nerve catheters placed using ultrasound guidance: an experience in 620 patients. Anesth Analg 2006; 103: Sandhu NS, Manne JS, Medabalmi PK, Capan LM. Sonographically guided infraclavicular brachial plexus block in adults: a retrospective analysis of 1146 cases. J Ultrasound Med 2006; 25: Fredrickson MJ, Ball CM, Dalgleish AJ. A prospective randomized comparison of ultrasound guidance versus neurostimulation for interscalene catheter placement. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009; 34: Mariano ER, Cheng GS, Choy LP, et al. Electrical stimulation versus ultrasound guidance for popliteal-sciatic perineural catheter insertion: a randomized controlled trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009; 34: Mariano ER, Loland VJ, Bellars RH, et al. Ultrasound guidance versus electrical stimulation for infraclavicular brachial plexus perineural catheter insertion. J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28: J Ultrasound Med 2011; 30:
5 11. Mariano ER, Loland VJ, Sandhu NS, et al. Ultrasound guidance versus electrical stimulation for femoral perineural catheter insertion. J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28: Mariano ER, Loland VJ, Sandhu NS, et al. A trainee-based randomized comparison of stimulating interscalene perineural catheters with a new technique using ultrasound guidance alone. J Ultrasound Med 2010; 29: Mariano ER, Loland VJ, Sandhu NS, et al. Comparative efficacy of ultrasound-guided and stimulating popliteal-sciatic perineural catheters for postoperative analgesia. Can J Anaesth 2010; 57: Sandhu NS, Capan LM. Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular brachial plexus block. Br J Anaesth 2002; 89: Fredrickson MJ, Ball CM, Dalgleish AJ, Stewart AW, Short TG. A prospective randomized comparison of ultrasound and neurostimulation as needle end points for interscalene catheter placement. Anesth Analg 2009; 108: Ilfeld BM, Fredrickson MJ, Mariano ER. Ultrasound-guided perineural catheter insertion: three approaches but few illuminating data. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2010; 35: Mariano ER, Afra R, Loland VJ, et al. Continuous interscalene brachial plexus block via an ultrasound-guided posterior approach: a randomized, triple-masked, placebo-controlled study. Anesth Analg 2009; 108: Fredrickson MJ, Ball CM, Dalgleish AJ. Successful continuous interscalene analgesia for ambulatory shoulder surgery in a private practice setting. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2008; 33: Dhir S, Ganapathy S. Comparative evaluation of ultrasound-guided continuous infraclavicular brachial plexus block with stimulating catheter and traditional technique: a prospective-randomized trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2008; 52: Walker A, Roberts S. Stimulating catheters: a thing of the past? Anesth Analg 2007; 104: Beach ML, Sites BD, Gallagher JD. Use of a nerve stimulator does not improve the efficacy of ultrasound-guided supraclavicular nerve blocks. J Clin Anesth 2006; 18: Chan VW, Perlas A, McCartney CJ, Brull R, Xu D, Abbas S. Ultrasound guidance improves success rate of axillary brachial plexus block. Can J Anaesth 2007; 54: Gurkan Y, Acar S, Solak M, Toker K. Comparison of nerve stimulation vs. ultrasound-guided lateral sagittal infraclavicular block. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2008; 52: Dingemans E, Williams SR, Arcand G, et al. Neurostimulation in ultrasound-guided infraclavicular block: a prospective randomized trial. Anesth Analg 2007; 104: Mariano ER, Loland VJ, Ilfeld BM. Interscalene perineural catheter placement using an ultrasound-guided posterior approach. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2009; 34: Mariano ER, Ilfeld BM, Neal JM. Going fishing : the practice of reporting secondary outcomes as separate studies. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2007; 32: J Ultrasound Med 2011; 30:
Updated Guide to Billing for Regional Anesthesia (United States)
 Updated Guide to Billing for Regional Anesthesia (United States) Tae-Wu Edward Kim, MD* w Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System, Palo
Updated Guide to Billing for Regional Anesthesia (United States) Tae-Wu Edward Kim, MD* w Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System, Palo
Thoracic Epidural Catheterization Using Ultrasound in Obese Patients for Bariatric Surgery
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research in Obesity http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/obes/obes.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 538833, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014.538833 Research Article Thoracic Epidural
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research in Obesity http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/obes/obes.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 538833, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014.538833 Research Article Thoracic Epidural
Feasibility of an Infraclavicular Block With a Reduced Volume of Lidocaine With Sonographic Guidance
 Technical Advance Feasibility of an Infraclavicular Block With a Reduced Volume of Lidocaine With Sonographic Guidance NavParkash S. Sandhu, MD, Charanjeet S. Bahniwal, MD, Levon M. Capan, MD Objective.
Technical Advance Feasibility of an Infraclavicular Block With a Reduced Volume of Lidocaine With Sonographic Guidance NavParkash S. Sandhu, MD, Charanjeet S. Bahniwal, MD, Levon M. Capan, MD Objective.
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011
 Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Br J Anaesth. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2007 January 16.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Br J Anaesth. 2005 August ; 95(2): 250 254. The use of a stimulating catheter for total knee replacement surgery - preliminary results
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Br J Anaesth. 2005 August ; 95(2): 250 254. The use of a stimulating catheter for total knee replacement surgery - preliminary results
30. BASIC PEDIATRIC REGIONAL ANESTHESIA
 30. BASIC PEDIATRIC REGIONAL ANESTHESIA INTRODUCTION Military anesthesia providers often encounter pediatric patients while delivering medical care in the field. The application of regional anesthesia
30. BASIC PEDIATRIC REGIONAL ANESTHESIA INTRODUCTION Military anesthesia providers often encounter pediatric patients while delivering medical care in the field. The application of regional anesthesia
INTERSCALENE BLOCK AND OTHER ARTICLES ON ANESTHESIA FOR ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY NOT QUALIFYING AS EVIDENCE
 INTERSCALENE BLOCK AND OTHER ARTICLES ON ANESTHESIA FOR ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY NOT QUALIFYING AS EVIDENCE Hughes MS, Matava MJ, et al. Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block for Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery.
INTERSCALENE BLOCK AND OTHER ARTICLES ON ANESTHESIA FOR ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY NOT QUALIFYING AS EVIDENCE Hughes MS, Matava MJ, et al. Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block for Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery.
Femoral Nerve Block/3-in-1 Nerve Block
 Femoral Nerve Block/3-in-1 Nerve Block Femoral and/or 3-in-1 nerve blocks are used for surgical procedures on the front portion of the thigh down to the knee and postoperative analgesia. Both blocks are
Femoral Nerve Block/3-in-1 Nerve Block Femoral and/or 3-in-1 nerve blocks are used for surgical procedures on the front portion of the thigh down to the knee and postoperative analgesia. Both blocks are
Regional Anesthesia Fellowship at Wake Forest University
 Regional Anesthesia Fellowship at Wake Forest University Fellowship Director: Douglas Jaffe, DO Assistant Professor and Member - Section of Regional Anesthesia & Acute Pain Management (RAAPM) Department
Regional Anesthesia Fellowship at Wake Forest University Fellowship Director: Douglas Jaffe, DO Assistant Professor and Member - Section of Regional Anesthesia & Acute Pain Management (RAAPM) Department
The Impact of Regional Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes By Dr. David Nelson
 The Impact of Regional Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes By Dr. David Nelson As a private practice anesthesiologist, I am often asked: What are the potential benefits of regional anesthesia (RA)? My
The Impact of Regional Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes By Dr. David Nelson As a private practice anesthesiologist, I am often asked: What are the potential benefits of regional anesthesia (RA)? My
Ankle Block. Indications The ankle block is suitable for the following: Orthopedic and podiatry surgical procedures of the distal foot.
 Ankle Block The ankle block is a common peripheral nerve block. It is useful for procedures of the foot and toes, as long as a tourniquet is not required above the ankle. It is a safe and effective technique.
Ankle Block The ankle block is a common peripheral nerve block. It is useful for procedures of the foot and toes, as long as a tourniquet is not required above the ankle. It is a safe and effective technique.
With the shift away from costly preoperative
 BRIEF REPORTS Are Patients Comfortable Consenting to Clinical Anesthesia Research Trials on the Day of Surgery? Richard Brull, MD, Colin J. L. McCartney, MBChB, FRCA, FFARCSI, Vincent W. S. Chan, MD, FRCPC,
BRIEF REPORTS Are Patients Comfortable Consenting to Clinical Anesthesia Research Trials on the Day of Surgery? Richard Brull, MD, Colin J. L. McCartney, MBChB, FRCA, FFARCSI, Vincent W. S. Chan, MD, FRCPC,
INTRODUCTION BY ANDRÉ P BOEZAART MD, PHD
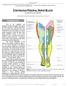 BY ANDRÉ P BOEZAART MD, PHD Author Affiliation: Department of Anesthesia, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA INTRODUCTION Due to the multiplicity and divergence of the nerve supply to the joints of the
BY ANDRÉ P BOEZAART MD, PHD Author Affiliation: Department of Anesthesia, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA INTRODUCTION Due to the multiplicity and divergence of the nerve supply to the joints of the
BEFORE THE ALABAMA BOARD OF NURSING IN THE MATTER OF: ) PETITION FOR ) DECLARATORY RULING STEVE SYKES, M.D., ) ) ) Petitioner. ) DECLARATORY RULING
 BEFORE THE ALABAMA BOARD OF NURSING IN THE MATTER OF: ) PETITION FOR ) DECLARATORY RULING STEVE SYKES, M.D., ) ) ) Petitioner. ) DECLARATORY RULING COMES NOW the Alabama Board of Nursing, by and through
BEFORE THE ALABAMA BOARD OF NURSING IN THE MATTER OF: ) PETITION FOR ) DECLARATORY RULING STEVE SYKES, M.D., ) ) ) Petitioner. ) DECLARATORY RULING COMES NOW the Alabama Board of Nursing, by and through
The ASA defines anesthesiology as the practice of medicine dealing with but not limited to:
 1570 Midway Pl. Menasha, WI 54952 920-720-1300 Procedure 1205- Anesthesia Lines of Business: All Purpose: This guideline describes Network Health s reimbursement of anesthesia services. Procedure: Anesthesia
1570 Midway Pl. Menasha, WI 54952 920-720-1300 Procedure 1205- Anesthesia Lines of Business: All Purpose: This guideline describes Network Health s reimbursement of anesthesia services. Procedure: Anesthesia
Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine Acute Pain Service Resident Goals and Objectives
 Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine Acute Pain Service Resident Goals and Objectives GOAL: SUPERVISION: OBJECTIVES: The Pain Medicine Resident will develop the knowledge and skills
Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine Acute Pain Service Resident Goals and Objectives GOAL: SUPERVISION: OBJECTIVES: The Pain Medicine Resident will develop the knowledge and skills
Dual Guidance. A Multimodal Approach to Nerve Location. Ralf Gebhard M.D., Admir Hadzic M.D., Ph.D., William Urmey M.D.
 Dual Guidance A Multimodal Approach to Nerve Location Ralf Gebhard M.D., Admir Hadzic M.D., Ph.D., William Urmey M.D. Published by B. Braun Melsungen AG Dual Guidance A Multimodal Approach to Nerve Location
Dual Guidance A Multimodal Approach to Nerve Location Ralf Gebhard M.D., Admir Hadzic M.D., Ph.D., William Urmey M.D. Published by B. Braun Melsungen AG Dual Guidance A Multimodal Approach to Nerve Location
r JOHNS HOPKINS HEALTHCARE Physician Guidelines Subject: Anesthesia Processing Guidelines Lines of Business: EHP, USFHP, Priority Partners
 Revision Date: 11/14/14 Last Reviewed Date: 11/14/14 Page 1 of 7 ACTION New Procedure Amending Procedure Number: Superseding Procedure Number: Repealing Procedure Number: REFERENCES: AMPT Committee ASA
Revision Date: 11/14/14 Last Reviewed Date: 11/14/14 Page 1 of 7 ACTION New Procedure Amending Procedure Number: Superseding Procedure Number: Repealing Procedure Number: REFERENCES: AMPT Committee ASA
TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS PLANE (TAP) BLOCK
 THE JOURNAL OF NEW YORK SCHOOL M a y 2 0 0 9 V o l u m e OF REGIONAL ANESTHESIA 1 2 TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS PLANE (TAP) BLOCK By Karim Mukhtar, MB BCh, MSc, FRCA Royal Liverpool and Broadgreen University
THE JOURNAL OF NEW YORK SCHOOL M a y 2 0 0 9 V o l u m e OF REGIONAL ANESTHESIA 1 2 TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS PLANE (TAP) BLOCK By Karim Mukhtar, MB BCh, MSc, FRCA Royal Liverpool and Broadgreen University
The Efficacy of Continuous Bupivacaine Infiltration Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 The Efficacy of Continuous Bupivacaine Infiltration Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Heinz R. Hoenecke, Jr., M.D., Pamela A. Pulido, R.N., B.S.N., Beverly A. Morris, R.N., C.N.P., and
The Efficacy of Continuous Bupivacaine Infiltration Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Heinz R. Hoenecke, Jr., M.D., Pamela A. Pulido, R.N., B.S.N., Beverly A. Morris, R.N., C.N.P., and
British Journal of Anaesthesia 101 (2): 250 4 (2008) doi:10.1093/bja/aen132 Advance Access publication May 30, 2008
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 11 (2): 25 4 (28) doi:1.193/bja/aen132 Advance Access publication May 3, 28 REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA International normalized ratio and prothrombin time values before the removal
British Journal of Anaesthesia 11 (2): 25 4 (28) doi:1.193/bja/aen132 Advance Access publication May 3, 28 REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA International normalized ratio and prothrombin time values before the removal
Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006.
 Citation Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006. Full Text An anesthesiologist inserted a 14-gauge peripheral
Citation Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006. Full Text An anesthesiologist inserted a 14-gauge peripheral
CODING AND COMPLIANCE NEW APPOINTMENT AND REAPPOINTMENT MODULE FOR ANESTHESIA FACULTY
 CODING AND COMPLIANCE NEW APPOINTMENT AND REAPPOINTMENT MODULE FOR ANESTHESIA FACULTY ANESTHESIA BILLING: MUST BE DOCUMENTED AS: Personally performed: you perform the case without a resident or a CRNA
CODING AND COMPLIANCE NEW APPOINTMENT AND REAPPOINTMENT MODULE FOR ANESTHESIA FACULTY ANESTHESIA BILLING: MUST BE DOCUMENTED AS: Personally performed: you perform the case without a resident or a CRNA
Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) Guidelines for the Management of Major Regional Analgesia
 PS03 2014 Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) Faculty of Pain Medicine Guidelines for the Management of Major Regional Analgesia 1. OVERVIEW This document is intended to apply to
PS03 2014 Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) Faculty of Pain Medicine Guidelines for the Management of Major Regional Analgesia 1. OVERVIEW This document is intended to apply to
2 Electrical Nerve. Stimulation. Ban C.H. Tsui. 2.1. Introduction
 2 Electrical Nerve Stimulation Ban C.H. Tsui 2.1. Introduction...................................................... 9 2.2. Electrophysiology.................................................. 10 2.2.1.
2 Electrical Nerve Stimulation Ban C.H. Tsui 2.1. Introduction...................................................... 9 2.2. Electrophysiology.................................................. 10 2.2.1.
LUMBAR PARAVERTEBRAL (PSOAS COMPARTMENT) BLOCK BY ANDRÉ P BOEZAART MD, PHD
 BY ANDRÉ P BOEZAART MD, PHD Author Affiliation: Department of Anesthesia, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA INTRODUCTION When evaluating the efficacy of centrally performed nerve blocks one must think
BY ANDRÉ P BOEZAART MD, PHD Author Affiliation: Department of Anesthesia, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA INTRODUCTION When evaluating the efficacy of centrally performed nerve blocks one must think
A BIBLIOGRAPHY OF PEER-REVIEWED JOURNAL ARTICLES
 ANESTHESIA CLOSED CLAIMS PROJECT A BIBLIOGRAPHY OF PEER-REVIEWED JOURNAL ARTICLES PROJECT OFFICE Anesthesia Closed Claims Project Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine University of Washington
ANESTHESIA CLOSED CLAIMS PROJECT A BIBLIOGRAPHY OF PEER-REVIEWED JOURNAL ARTICLES PROJECT OFFICE Anesthesia Closed Claims Project Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine University of Washington
Collaboration Anesthesia
 HPC hpcconnection.ca Nursing Neuro - axial Analgesia cross sector Pharmacists Intractable patient centered Opioids Interventional Consensus Collaboration Anesthesia Physicians epidural evidence based Intraspinal
HPC hpcconnection.ca Nursing Neuro - axial Analgesia cross sector Pharmacists Intractable patient centered Opioids Interventional Consensus Collaboration Anesthesia Physicians epidural evidence based Intraspinal
How To Treat Anesthetic With Local Anesthesia
 3. LOCAL ANESTHETICS INTRODUCTION Compared to general anesthesia with opioidbased perioperative pain management, regional anesthesia can provide benefits of superior pain control, improved patient satisfaction,
3. LOCAL ANESTHETICS INTRODUCTION Compared to general anesthesia with opioidbased perioperative pain management, regional anesthesia can provide benefits of superior pain control, improved patient satisfaction,
Anesthesia Coding and Compliance. Presented by: Melanie Lafferty June 2015
 Anesthesia Coding and Compliance Presented by: Melanie Lafferty June 2015 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement Melanie Lafferty, Vice President of Practice Management Medac, Inc. I have the following
Anesthesia Coding and Compliance Presented by: Melanie Lafferty June 2015 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement Melanie Lafferty, Vice President of Practice Management Medac, Inc. I have the following
OB PBLD L117 Labor and Delivery in the Age of Ebola Upper 20B-20C. PI PBLD L120 He's 15, Needs This Operation, and He's DNR!
 ETHICS - Saturday, October 24 OB PBLD L117 Labor and Delivery in the Age of Ebola PI PBLD L120 He's 15, Needs This Operation, and He's DNR! PD PBLD L118 Sex, Drugs, and Rock 'N' Roll: An Anxious Adolescent
ETHICS - Saturday, October 24 OB PBLD L117 Labor and Delivery in the Age of Ebola PI PBLD L120 He's 15, Needs This Operation, and He's DNR! PD PBLD L118 Sex, Drugs, and Rock 'N' Roll: An Anxious Adolescent
Placement of Epidural Catheter for Pain Management Shane Bateman DVM, DVSc, DACVECC
 Placement of Epidural Catheter for Pain Management Shane Bateman DVM, DVSc, DACVECC Indications: Patients with severe abdominal or pelvic origin pain that is poorly responsive to other analgesic modalities.
Placement of Epidural Catheter for Pain Management Shane Bateman DVM, DVSc, DACVECC Indications: Patients with severe abdominal or pelvic origin pain that is poorly responsive to other analgesic modalities.
Comparison of spinal anesthesia with combined sciatic-femoral nerve block for outpatient knee arthroscopy
 Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2008) 20, 415 420 Original contribution Comparison of spinal anesthesia with combined sciatic-femoral nerve block for outpatient knee arthroscopy Felix R. Montes MD (Associate
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2008) 20, 415 420 Original contribution Comparison of spinal anesthesia with combined sciatic-femoral nerve block for outpatient knee arthroscopy Felix R. Montes MD (Associate
Complications Associated With Eye Blocks and Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Analysis
 Complications Associated With Eye Blocks and Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Analysis Lorri A. Lee, M.D., Karen L. Posner, Ph.D., Frederick W. Cheney, M.D.,
Complications Associated With Eye Blocks and Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Analysis Lorri A. Lee, M.D., Karen L. Posner, Ph.D., Frederick W. Cheney, M.D.,
Your anaesthetist may suggest that you have a spinal or epidural injection. These
 Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 11: Nerve damage associated with a spinal or epidural injection Your anaesthetist may suggest that you have a spinal or epidural injection. These injections
Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 11: Nerve damage associated with a spinal or epidural injection Your anaesthetist may suggest that you have a spinal or epidural injection. These injections
Changes in Practice: Evidence Based Nursing Revealed
 Changes in Practice: Evidence Based Nursing Revealed Gloria Spencer,, RN, MSPHN Sr. Nursing Instructor Nursing Education Department PACU Staff Nurses Yolanda Ayson, MSN, RN Maria Aguda, BSN, CPAN Imelda
Changes in Practice: Evidence Based Nursing Revealed Gloria Spencer,, RN, MSPHN Sr. Nursing Instructor Nursing Education Department PACU Staff Nurses Yolanda Ayson, MSN, RN Maria Aguda, BSN, CPAN Imelda
ULTRASOUND GUIDED FEMORAL NERVE BLOCK ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 284
 ULTRASOUND GUIDED FEMORAL NERVE BLOCK ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 284 15 TH APRIL 2013 Dr Suresh Kumar Jeyaraj, Specialty Doctor Dr Tim Pepall, Consultant Anaesthetist Frimley Park Hospital NHS foundation
ULTRASOUND GUIDED FEMORAL NERVE BLOCK ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 284 15 TH APRIL 2013 Dr Suresh Kumar Jeyaraj, Specialty Doctor Dr Tim Pepall, Consultant Anaesthetist Frimley Park Hospital NHS foundation
Pain Relief Options for Labor. Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support
 Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery Suite at Lucile Packard Children
Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery Suite at Lucile Packard Children
Regional anesthesia for outpatient surgery
 Anesthesiology Clin N Am 21 (2003) 289 303 Regional anesthesia for outpatient surgery Michael F. Mulroy, MD*, Susan B. McDonald, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center, Department of Anesthesia B2-AN, 1100 Ninth
Anesthesiology Clin N Am 21 (2003) 289 303 Regional anesthesia for outpatient surgery Michael F. Mulroy, MD*, Susan B. McDonald, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center, Department of Anesthesia B2-AN, 1100 Ninth
CHAP2-CPTcodes00000-01999_final103115.doc Revision Date: 1/1/2016
 CHAP2-CPTcodes00000-01999_final103115.doc Revision Date: 1/1/2016 CHAPTER II ANESTHESIA SERVICES CPT CODES 00000-09999 FOR NATIONAL CORRECT CODING INITIATIVE POLICY MANUAL FOR MEDICARE SERVICES Current
CHAP2-CPTcodes00000-01999_final103115.doc Revision Date: 1/1/2016 CHAPTER II ANESTHESIA SERVICES CPT CODES 00000-09999 FOR NATIONAL CORRECT CODING INITIATIVE POLICY MANUAL FOR MEDICARE SERVICES Current
Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Abstract Background Methods:
 Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Mousa Khoursheed, Ibtisam Al-Bader, Ali Mouzannar, Abdulla Al-Haddad, Ali Sayed, Ali Mohammad,
Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Mousa Khoursheed, Ibtisam Al-Bader, Ali Mouzannar, Abdulla Al-Haddad, Ali Sayed, Ali Mohammad,
NORTHSIDE ANESTHESIOLOGY CONSULTANTS AND PAIN MANAGEMENT SERVICES
 NORTHSIDE ANESTHESIOLOGY CONSULTANTS AND PAIN MANAGEMENT SERVICES K. Douglas Smith, M.D. Chairman John B. Neeld, Jr., M.D. Sheryl S. Dickman, M.D. Alan R. Kaplan, M.D. Thomas B. West, M.D. Michael E. Maffett,
NORTHSIDE ANESTHESIOLOGY CONSULTANTS AND PAIN MANAGEMENT SERVICES K. Douglas Smith, M.D. Chairman John B. Neeld, Jr., M.D. Sheryl S. Dickman, M.D. Alan R. Kaplan, M.D. Thomas B. West, M.D. Michael E. Maffett,
519.2 ANESTHESIA SERVICES. Background... 2. Policy... 2. 519.2.1 Covered Services... 2. 519.2.1.1 Anesthesiologist Directed Services...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION PAGE NUMBER Background... 2 Policy... 2 519.2.1 Covered Services... 2 519.2.1.1 Anesthesiologist Directed Services... 3 519.2.1.2 Emergency Anesthesia... 4 519.2.1.3 Monitored
TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION PAGE NUMBER Background... 2 Policy... 2 519.2.1 Covered Services... 2 519.2.1.1 Anesthesiologist Directed Services... 3 519.2.1.2 Emergency Anesthesia... 4 519.2.1.3 Monitored
INTERSCALENE BLOCK ANESTHESIA AT A AMBULATORY SURGERY CENTER PERFORMING PREDOMINATELY REGIONAL ANESTHESIA:
 INTERSCALENE BLOCK ANESTHESIA AT A AMBULATORY SURGERY CENTER PERFORMING PREDOMINATELY REGIONAL ANESTHESIA: A Prospective study of 133 patients undergoing shoulder surgery. Deborah Faryniarz MD, Christine
INTERSCALENE BLOCK ANESTHESIA AT A AMBULATORY SURGERY CENTER PERFORMING PREDOMINATELY REGIONAL ANESTHESIA: A Prospective study of 133 patients undergoing shoulder surgery. Deborah Faryniarz MD, Christine
devoted physicians. collaborative partners. metrics-driven quality.
 Regional Anesthesia and Multimodal Pain Management Improves Outcomes, Reduces Costs and Boosts Patient Satisfaction devoted physicians. collaborative partners. metrics-driven quality. usap.com jlrmedicalgroup.com
Regional Anesthesia and Multimodal Pain Management Improves Outcomes, Reduces Costs and Boosts Patient Satisfaction devoted physicians. collaborative partners. metrics-driven quality. usap.com jlrmedicalgroup.com
ANESTHESIA - Medicare
 ANESTHESIA - Medicare Policy Number: UM14P0008A2 Effective Date: August 19, 2014 Last Reviewed: January 1, 2016 PAYMENT POLICY HISTORY Version DATE ACTION / DESCRIPTION Version 2 January 1, 2016 Under
ANESTHESIA - Medicare Policy Number: UM14P0008A2 Effective Date: August 19, 2014 Last Reviewed: January 1, 2016 PAYMENT POLICY HISTORY Version DATE ACTION / DESCRIPTION Version 2 January 1, 2016 Under
*Reflex withdrawal from a painful stimulus is NOT considered a purposeful response.
 Analgesia and Moderate Sedation This Nebraska Board of Nursing advisory opinion is issued in accordance with Nebraska Revised Statute (NRS) 71-1,132.11(2). As such, this advisory opinion is for informational
Analgesia and Moderate Sedation This Nebraska Board of Nursing advisory opinion is issued in accordance with Nebraska Revised Statute (NRS) 71-1,132.11(2). As such, this advisory opinion is for informational
A Patient s Guide to PAIN MANAGEMENT. After Surgery
 A Patient s Guide to PAIN MANAGEMENT After Surgery C o m p a s s i o n a n d C o m m i t m e n t A Patient s Guide to Pain Management After Surgery If you re facing an upcoming surgery, it s natural to
A Patient s Guide to PAIN MANAGEMENT After Surgery C o m p a s s i o n a n d C o m m i t m e n t A Patient s Guide to Pain Management After Surgery If you re facing an upcoming surgery, it s natural to
Prerequisites. Authorization, Notification and Referral. Limitations ANESTHESIA SERVICES
 ANESTHESIA SERVICES Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for the administration of general and regional anesthesia, and supportive services performed in conjunction with covered obstetrical, surgical,
ANESTHESIA SERVICES Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for the administration of general and regional anesthesia, and supportive services performed in conjunction with covered obstetrical, surgical,
Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery
 Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine www.happypatient.org Updated 5/10 Why? To Help Control Postoperative Pain at Home A pump connected
Your Nerve Block &Home Pump For Arm/Hand Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine www.happypatient.org Updated 5/10 Why? To Help Control Postoperative Pain at Home A pump connected
The effects of adding epinephrine to ropivacaine for popliteal nerve block on the duration of postoperative analgesia: a randomized controlled trial
 Schoenmakers et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2015) 15:100 DOI 10.1186/s12871-015-0083-z RESEARCH ARTICLE The effects of adding epinephrine to ropivacaine for popliteal nerve block on the duration of postoperative
Schoenmakers et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2015) 15:100 DOI 10.1186/s12871-015-0083-z RESEARCH ARTICLE The effects of adding epinephrine to ropivacaine for popliteal nerve block on the duration of postoperative
Anesthesia Guidelines
 Anesthesia Guidelines Updated April 2012 Anesthesia BlueCross requires anesthesiologists and certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) to file claims using CPT anesthesia codes. We cover general
Anesthesia Guidelines Updated April 2012 Anesthesia BlueCross requires anesthesiologists and certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) to file claims using CPT anesthesia codes. We cover general
The MOD Experience after 1,000 Patients
 The MOD Experience after 1,000 Patients Sharon Conley MD PhD CPE, Chief Medical Officer, Avancen MOD Corporation Summary This paper reports the results of a survey from three hospitals and a skilled nursing
The MOD Experience after 1,000 Patients Sharon Conley MD PhD CPE, Chief Medical Officer, Avancen MOD Corporation Summary This paper reports the results of a survey from three hospitals and a skilled nursing
Post-operative Pain Management
 Post-operative Pain Management Total Hip Replacement www.ormc.org A member of the Greater Hudson Valley Health System Post-operative Pain MANAGEMENT Post-operative pain management after total joint replacement
Post-operative Pain Management Total Hip Replacement www.ormc.org A member of the Greater Hudson Valley Health System Post-operative Pain MANAGEMENT Post-operative pain management after total joint replacement
Clinical Site Resource Manual. Northport Medical Center- DCH
 Clinical Site Resource Manual Northport Medical Center- DCH Nurse Anesthesia Program School of Health Related Professions The University of Alabama at Birmingham TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1 CLINICAL SITE
Clinical Site Resource Manual Northport Medical Center- DCH Nurse Anesthesia Program School of Health Related Professions The University of Alabama at Birmingham TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1 CLINICAL SITE
EVALUATION OF EXPAREL
 EVALUATION OF EXPAREL USE VIA INFILTRATION INTO THE TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS PLANE FOR PROLONGED POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA IN SUBJECTS UNDERGOING OPEN ABDOMINAL HERNIA REPAIR Dennis E. Feierman, Mark Kronenfeld,
EVALUATION OF EXPAREL USE VIA INFILTRATION INTO THE TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS PLANE FOR PROLONGED POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA IN SUBJECTS UNDERGOING OPEN ABDOMINAL HERNIA REPAIR Dennis E. Feierman, Mark Kronenfeld,
The risk for permanent or severe nerve injury. Nerve Injury After Peripheral Nerve Block: Best Practices and Medical-Legal Protection Strategies
 PRINTER-FRIENDLY VERSION AVAILABLE AT ANESTHESIOLOGYNEWS.COM Nerve Injury After Peripheral Nerve Block: Best Practices and Medical-Legal Protection Strategies DAVID HARDMAN, MD, MBA Professor of Anesthesiology
PRINTER-FRIENDLY VERSION AVAILABLE AT ANESTHESIOLOGYNEWS.COM Nerve Injury After Peripheral Nerve Block: Best Practices and Medical-Legal Protection Strategies DAVID HARDMAN, MD, MBA Professor of Anesthesiology
PRACTICE GUIDELINE TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
There are four anesthesia categories as determined by CMS that affect payment of anesthesia services based on the provider rendering the services:
 PROVIDER BILLING GUIDELINES Anesthesia Background Qualified medical professionals administer anesthesia to relieve pain while at the same time monitoring and controlling the patients health and vital bodily
PROVIDER BILLING GUIDELINES Anesthesia Background Qualified medical professionals administer anesthesia to relieve pain while at the same time monitoring and controlling the patients health and vital bodily
Ultrasound Guided / Cadaver Course in Regional Anesthesia and Central Vascular Access
 Fifth Annual Ultrasound Guided / Cadaver Course in Regional Anesthesia and Central Vascular Access Best value for your CME dollars... Register today! May 30 31, 2015 An exciting opportunity to acquire
Fifth Annual Ultrasound Guided / Cadaver Course in Regional Anesthesia and Central Vascular Access Best value for your CME dollars... Register today! May 30 31, 2015 An exciting opportunity to acquire
LAW ANESTHESIA. the. Nerve Damage from Regional Blocks Placed In Anesthetized/Sedated Patients
 ANESTHESIA & the LAW A RISK MANAGEMENT NEWSLETTER DON T SETTLE. OWN. ISSUE 28 Nerve Damage from Regional Blocks Placed In Anesthetized/Sedated Patients W hether regional blocks should be placed in adult
ANESTHESIA & the LAW A RISK MANAGEMENT NEWSLETTER DON T SETTLE. OWN. ISSUE 28 Nerve Damage from Regional Blocks Placed In Anesthetized/Sedated Patients W hether regional blocks should be placed in adult
Anatomical Consideration and Brachial Plexus Anesthesia. Anatomy
 Brachial Plexus Anesthesia There are four approaches to the brachial plexus. These include the interscalene, supraclavicular, infraclavicular, and axillary approach. For the purposes of this lecture we
Brachial Plexus Anesthesia There are four approaches to the brachial plexus. These include the interscalene, supraclavicular, infraclavicular, and axillary approach. For the purposes of this lecture we
Objectives. Preoperative Cardiac Risk Stratification for Noncardiac Surgery. History
 Preoperative Cardiac Risk Stratification for Noncardiac Surgery Kimberly Boddicker, MD FACC Essentia Health Heart and Vascular Center 27 th Heart and Vascular Conference May 13, 2011 Objectives Summarize
Preoperative Cardiac Risk Stratification for Noncardiac Surgery Kimberly Boddicker, MD FACC Essentia Health Heart and Vascular Center 27 th Heart and Vascular Conference May 13, 2011 Objectives Summarize
Interscalene Block. Nancy A. Brown, MD
 Interscalene Block Nancy A. Brown, MD What is an Interscalene Block? An Interscalene block is a form of regional anesthesia used in conjunction with general anesthesia for surgeries of the shoulder and
Interscalene Block Nancy A. Brown, MD What is an Interscalene Block? An Interscalene block is a form of regional anesthesia used in conjunction with general anesthesia for surgeries of the shoulder and
Status Active. Reimbursement Policy Section: Anesthesia Services Policy Number: RP - Anesthesia - 001 Anesthesia Effective Date: June 1, 2015
 Status Active Reimbursement Policy Section: Anesthesia Services Policy Number: RP - Anesthesia - 001 Anesthesia Effective Date: June 1, 2015 Anesthesia Policy Description: Definitions: This policy addresses
Status Active Reimbursement Policy Section: Anesthesia Services Policy Number: RP - Anesthesia - 001 Anesthesia Effective Date: June 1, 2015 Anesthesia Policy Description: Definitions: This policy addresses
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE BONE MARROW ASPIRATION
 I. Definition: This protocol covers the task of bone marrow aspiration by an Allied Health Professional. The purpose of this standardized procedure is to allow the Allied Health Professional to safely
I. Definition: This protocol covers the task of bone marrow aspiration by an Allied Health Professional. The purpose of this standardized procedure is to allow the Allied Health Professional to safely
Revisiting the anatomy of the ilio-inguinal / iliohypogastric nerve block
 Original article Revisiting the anatomy of the ilio-inguinal / iliohypogastric nerve block Albert-Neels van Schoor 1, Marius C Bosman 1, Adrian T Bosenberg 2, 1 Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine,
Original article Revisiting the anatomy of the ilio-inguinal / iliohypogastric nerve block Albert-Neels van Schoor 1, Marius C Bosman 1, Adrian T Bosenberg 2, 1 Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine,
Comparison of the effects between clonidine and epinephrine added with bupivacine in brachial plexus block.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2014), PP 54-58 Comparison of the effects between clonidine and epinephrine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2014), PP 54-58 Comparison of the effects between clonidine and epinephrine
A new way of thinking. Philips Sparq regional anesthesia and pain medicine ultrasound system
 A new way of thinking Philips Sparq regional anesthesia and pain medicine ultrasound system Introducing Philips Sparq Breakthrough technology should not make your life more complex. Quite the opposite.
A new way of thinking Philips Sparq regional anesthesia and pain medicine ultrasound system Introducing Philips Sparq Breakthrough technology should not make your life more complex. Quite the opposite.
Acute & Chronic Pain Management (requiring opioid analgesics) in Patients Receiving Pharmacotherapy for Opioid Addiction
 Acute & Chronic Pain Management (requiring opioid analgesics) in Patients Receiving Pharmacotherapy for Opioid Addiction June 9, 2011 Tufts Health Care Institute Program on Opioid Risk Management Daniel
Acute & Chronic Pain Management (requiring opioid analgesics) in Patients Receiving Pharmacotherapy for Opioid Addiction June 9, 2011 Tufts Health Care Institute Program on Opioid Risk Management Daniel
Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Kalpesh Ganatra,MD Diplomate, American Board of Sleep Medicine
 Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Kalpesh Ganatra,MD Diplomate, American Board of Sleep Medicine Disclosures. This activity is supported by an education grant from Trivalley
Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Kalpesh Ganatra,MD Diplomate, American Board of Sleep Medicine Disclosures. This activity is supported by an education grant from Trivalley
Program Specification for Master Degree Anesthesia, ICU and Pain Management
 Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Program type: Single Program Specification for Master Degree Anesthesia, ICU and Pain Management Department offering program: Anesthesia, intensive care and pain management
Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Program type: Single Program Specification for Master Degree Anesthesia, ICU and Pain Management Department offering program: Anesthesia, intensive care and pain management
Military Advanced Regional Anesthesia and Analgesia handbook
 Military Advanced Regional Anesthesia and Analgesia handbook Published by the Office of The Surgeon General Department of the Army, United States of America US Army Medical Center and School Fort Sam Houston,
Military Advanced Regional Anesthesia and Analgesia handbook Published by the Office of The Surgeon General Department of the Army, United States of America US Army Medical Center and School Fort Sam Houston,
DISCHARGE CRITERIA FOR PHASE I & II- POST ANESTHESIA CARE
 REFERENCES: The Joint Commission Accreditation Manual for Hospitals American Society of Post Anesthesia Nurses: Standards of Post Anesthesia Nursing Practice (1991, 2002). RELATED DOCUMENTS: SHC Administrative
REFERENCES: The Joint Commission Accreditation Manual for Hospitals American Society of Post Anesthesia Nurses: Standards of Post Anesthesia Nursing Practice (1991, 2002). RELATED DOCUMENTS: SHC Administrative
A randomized controlled trial of fentanyl for abortion pain
 A randomized controlled trial of fentanyl for abortion pain Mollie J. Rawling, MB, ChB, and Ellen R. Wiebe, MD Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada OBJECTIVE: Our aim was to find out whether intravenous
A randomized controlled trial of fentanyl for abortion pain Mollie J. Rawling, MB, ChB, and Ellen R. Wiebe, MD Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada OBJECTIVE: Our aim was to find out whether intravenous
Intraocular Pressure and Quality of Blockade in Peribulbar Anesthesia Using Ropivacaine or Lidocaine with Adrenaline: A Double-Blind Randomized Study
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2004, Ropivacaine 204, 203-208 in Peribulbar Block: a Comparison with Lidocaine 203 Intraocular Pressure and Quality of Blockade in Peribulbar Anesthesia Using Ropivacaine or Lidocaine
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2004, Ropivacaine 204, 203-208 in Peribulbar Block: a Comparison with Lidocaine 203 Intraocular Pressure and Quality of Blockade in Peribulbar Anesthesia Using Ropivacaine or Lidocaine
Anesthesia Policy. Approved By 3/11/2015
 Anesthesia Policy Policy Number 2015R0032D Annual Approval Date 3/11/2015 Approved By Payment Policy Oversight Committee IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY You are responsible for submission
Anesthesia Policy Policy Number 2015R0032D Annual Approval Date 3/11/2015 Approved By Payment Policy Oversight Committee IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY You are responsible for submission
Pain Relief during Labour and Delivery: What Are My Options?
 Pain Relief during Labour and Delivery: What Are My Options? To help you prepare for the birth of your baby, this booklet answers some of the questions you may have about pain relief options. You should
Pain Relief during Labour and Delivery: What Are My Options? To help you prepare for the birth of your baby, this booklet answers some of the questions you may have about pain relief options. You should
Pediatric Neuraxial Anesthesia from Caudals, to Thoracic Epidurals, to Awake Spinals. Disclosure
 Pediatric Neuraxial Anesthesia from Caudals, to Thoracic Epidurals, to Awake Spinals Martin Müller, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Anesthesia Iowa Symposium XIII May 4, 2013 Disclosure No
Pediatric Neuraxial Anesthesia from Caudals, to Thoracic Epidurals, to Awake Spinals Martin Müller, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Anesthesia Iowa Symposium XIII May 4, 2013 Disclosure No
CALIFORNIA ASSOCIATION OF NURSE ANESTHETISTS CRNA SCOPE OF PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 CALIFORNIA ASSOCIATION OF NURSE ANESTHETISTS CRNA SCOPE OF PRACTICE GUIDELINES The following offers guidance on the scope of practice for Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs) in California.
CALIFORNIA ASSOCIATION OF NURSE ANESTHETISTS CRNA SCOPE OF PRACTICE GUIDELINES The following offers guidance on the scope of practice for Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs) in California.
Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia
 Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia Several local anesthetics are used for spinal anesthesia. These include procaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine. Local anesthetics
Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia Several local anesthetics are used for spinal anesthesia. These include procaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine. Local anesthetics
Comparison of Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block and 3-in-1 Block in Adults Undergoing Knee Arthroscopy and Meniscal Repair
 Comparison of Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block and 3-in-1 Block in Adults Undergoing Knee Arthroscopy and Meniscal Repair LT Jerrol B. Wallace, CRNA, MSN, NC, USN LT Joseph A. Andrade, CRNA, MSN, NC, USN
Comparison of Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block and 3-in-1 Block in Adults Undergoing Knee Arthroscopy and Meniscal Repair LT Jerrol B. Wallace, CRNA, MSN, NC, USN LT Joseph A. Andrade, CRNA, MSN, NC, USN
2.0 Synopsis. Vicodin CR (ABT-712) M05-765 Clinical Study Report R&D/07/095. (For National Authority Use Only) to Part of Dossier: Volume:
 2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
Top-up for Cesarean section. Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern
 Top-up for Cesarean section Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern In which situations? 2 What exactly is a Top-up? 3 C-section, NOW!! Emergency C-section requires a rapid onset of sustained analgesia
Top-up for Cesarean section Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern In which situations? 2 What exactly is a Top-up? 3 C-section, NOW!! Emergency C-section requires a rapid onset of sustained analgesia
Sonographically Guided Ilioinguinal Nerve Block
 Technical Advance Sonographically Guided Ilioinguinal Nerve Block Michael Gofeld, MD, Monique Christakis, MD, FRCPC Objective. The aim of this study was to describe a sonographically guided ilioinguinal
Technical Advance Sonographically Guided Ilioinguinal Nerve Block Michael Gofeld, MD, Monique Christakis, MD, FRCPC Objective. The aim of this study was to describe a sonographically guided ilioinguinal
Ten Steps to Coding Anesthesia Services
 Ten Steps to Coding Anesthesia Services AAPC National Conference Orlando, Florida April 2013 Chandra Stephenson, CPC, CPC-H, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CEMC, CFPC, CGSC, CIMC, COSC Disclaimer The information
Ten Steps to Coding Anesthesia Services AAPC National Conference Orlando, Florida April 2013 Chandra Stephenson, CPC, CPC-H, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CEMC, CFPC, CGSC, CIMC, COSC Disclaimer The information
ANESTHESIA. Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery
 ANESTHESIA & YOU Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery T oday the majority of patients who undergo surgery or diagnostic tests do not need to stay overnight in the hospital. In most cases, you will be well
ANESTHESIA & YOU Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery T oday the majority of patients who undergo surgery or diagnostic tests do not need to stay overnight in the hospital. In most cases, you will be well
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Anesthesia Coding and Compliance. Presented by: Melanie Lafferty July 2014
 Anesthesia Coding and Compliance Presented by: Melanie Lafferty July 2014 Introduction The target for this training is to provide you with a basic understanding of anesthesia coding and compliance in regards
Anesthesia Coding and Compliance Presented by: Melanie Lafferty July 2014 Introduction The target for this training is to provide you with a basic understanding of anesthesia coding and compliance in regards
Medical Coverage Policy Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC)
 Medical Coverage Policy Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC) Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2004 Policy Last Updated: 1/8/2013 Prospective review is recommended/required.
Medical Coverage Policy Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC) Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2004 Policy Last Updated: 1/8/2013 Prospective review is recommended/required.
Placement of peripheral intravenous (IV) The use of ultrasound for placement of intravenous catheters
 The use of ultrasound for placement of intravenous catheters Capt Hector Aponte, CRNA, MSN, USAF, NC Aviano, Italy Capt Said Acosta, CRNA, MSN, USAF, NC Crestview, Florida Donald Rigamonti, PhD Arlington,
The use of ultrasound for placement of intravenous catheters Capt Hector Aponte, CRNA, MSN, USAF, NC Aviano, Italy Capt Said Acosta, CRNA, MSN, USAF, NC Crestview, Florida Donald Rigamonti, PhD Arlington,
Richard C. Clarke, M.D. Texas Tech University Health Science Center. Anesthesiology Residency March 1999- March 2001 Lubbock Texas.
 Curriculum Vitae Richard C. Clarke, M.D. Education Texas Tech University Health Science Center. Anesthesiology Residency March 1999- March 2001 Lubbock Texas. Tulane University Hospital. New Orleans, Louisiana.
Curriculum Vitae Richard C. Clarke, M.D. Education Texas Tech University Health Science Center. Anesthesiology Residency March 1999- March 2001 Lubbock Texas. Tulane University Hospital. New Orleans, Louisiana.
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Low Back Pain Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Ultrasound Evaluation of Low Back Pain Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
VA SAN DIEGO HEALTHCARE SYSTEM MEMORANDUM 118-28 SAN DIEGO, CA
 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENT-CONTROLLED ANALGESIA (PCA) AND PATIENT- CONTROLLED EPIDURAL ANALGESIA (PCEA) FOR ACUTE PAIN MANAGEMENT 1. PURPOSE: To assure the safe and effective use of patient controlled analgesia
GUIDELINES FOR PATIENT-CONTROLLED ANALGESIA (PCA) AND PATIENT- CONTROLLED EPIDURAL ANALGESIA (PCEA) FOR ACUTE PAIN MANAGEMENT 1. PURPOSE: To assure the safe and effective use of patient controlled analgesia
Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients
 Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Jennifer Kuhns, Pharm.D. Pharmacy Practice Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or potential
Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Jennifer Kuhns, Pharm.D. Pharmacy Practice Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or potential
Anesthesia Billing: 101. Presented by: Medi-Corp, Inc www.medi-corp.com
 Anesthesia Billing: 101 Presented by: Medi-Corp, Inc www.medi-corp.com Disclaimer Statement The material enclosed is based on information that is in effect at the time of this presentation. This presentation
Anesthesia Billing: 101 Presented by: Medi-Corp, Inc www.medi-corp.com Disclaimer Statement The material enclosed is based on information that is in effect at the time of this presentation. This presentation
The use of ultrasound by anesthesiologists has dramatically
 SPECIAL ARTICLE The American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine and the European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy Joint Committee Recommendations for Education and Training
SPECIAL ARTICLE The American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine and the European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy Joint Committee Recommendations for Education and Training
BMC Research Notes. Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Nomaqhawe Moyo *, Farai D. Madzimbamuto and Samson Shumbairerwa
 DOI 10.1186/s13104-016-1864-2 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Adding a transversus abdominis plane block to parenteral opioid for postoperative analgesia following trans abdominal hysterectomy
DOI 10.1186/s13104-016-1864-2 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Adding a transversus abdominis plane block to parenteral opioid for postoperative analgesia following trans abdominal hysterectomy
The subdural space lies between the arachnoid and
 Case Report 607 Extensive Sensory Block Caused by Accidental Subdural Catheterization during Epidural Labor Analgesia Sheng-Huan Chen, MD; Ho-Yen Chiueh 1, MD; Chao-Tsen Hung, MD; Shih-Chang Tsai, MD;
Case Report 607 Extensive Sensory Block Caused by Accidental Subdural Catheterization during Epidural Labor Analgesia Sheng-Huan Chen, MD; Ho-Yen Chiueh 1, MD; Chao-Tsen Hung, MD; Shih-Chang Tsai, MD;
The most important room in the hospital : that s
 ECRI Institute Perspectives Postanesthesia care action plan aims to ensure optimal patient safety The most important room in the hospital : that s what a landmark 1969 case in Canada Laidlaw v. Lions Gate
ECRI Institute Perspectives Postanesthesia care action plan aims to ensure optimal patient safety The most important room in the hospital : that s what a landmark 1969 case in Canada Laidlaw v. Lions Gate
