Type 2 Diabetes in Youth:
|
|
|
- Janice McCormick
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Collaborate Cultivate Educate PENS 2015 National Conference Type 2 Diabetes in Yo AAP Guidelines Type 2 Diabetes in Youth: Janet Silverstein, MD University of Florida September 30, 2014 Janet Silverste University of F Conflict of Interest Disclosure Conflicts of Interest Daichi Sankyo Research grant Novo Nordisk Research grant A conflict of interest exists when an individual is in a position to profit directly or indirectly through application of authority, influence, or knowledge in relation to the affairs of PENS. A conflict of interest also exists if a relative benefits or when the organization is adversely affected in any way. 1
2 Objectives Know how to differentiate type 1 from type 2 diabetes Understand glucose management: when to start insulin vs oral agents Know when to screen and how to manage the co-morbidities seen with type 2 diabetes in youth SEARCH Data in Youth <20 Years T1DM: 15,000 youth diagnosed annually Caucasians: 80% T1DM T2DM: 3700 youth diagnosed annually Native Americans: 80% T2DM Asian Pacific Islanders 70% African-Americans 58% Hispanics 46% Search for Diabetes Study Group Objectives To know how to differentiate type 1 from type 2 diabetes To understand when to start insulin vs oral agents 3. To know when to screen and how to manage the comorbidities seen with type 2 diabetes in youth 2
3 Case #1 Sarah Sarah is a 13 year old female who is seen for a school physical examination. Her only complaints were frequent urination of 3 weeks duration and having to get up at night to urinate. She has had no weight loss but has been feeling more tired than usual lately, which she attributes to late nights studying. She has a strong family history of type 2 diabetes in her mother and maternal grandfather Physical Examination Height was 5 ft 2 ins and weight 187 lbs. BMI was 34.2 kg/m2 BP 128/72 Acanthosis not present on her neck All else normal except for vaginal discharge of cottage cheese consistency POCT Laboratory Evaluation HbA1c 13.2% Urinalysis revealed 4+ glucose Moderate ketonuria What type of diabetes does this girl have? 3
4 What type of diabetes does Sarah have? Type 1 Type 2 MODY Unsure Short course Type 1 Not usually overweight Proportionate to obesity in general population 35-40% present with ketoacidosis 5% with a 1 st or 2 nd degree relative with type 1 Increased incidence of other autoimmune d/o: thyroid; adrenal; vitiligo; celiac Decreased C-peptide & Insulin No increase with glu challenge after 1 year Caucasians predominate 85% are overweight Indolent Course Type 2 33% with ketonuria 5-25% may have ketoacidosis % with 1 st or 2 nd degree relative with T2DM Increased incidence of metabolic syndrome: PCOS, AN (up to 90%), HTN, lipids Nl or increased C-P & Insulin Increase with glucose challenge after 1 year NA; AA; Latino; Asian; Pacific Islander Clinical Evaluation History Family History Ethnicity African Americans, Mexican, Hispanics, American Indians Physical Examination Acanthosis nigricans Blood Pressure Laboratory Evaluation Islet autoantibodies ICA, IAA, GAD, IA-2, ZnT8 C-Peptide / insulin levels -after 1 st year Lipid profile 4
5 Objectives To know how to differentiate type 1 from type 2 diabetes To understand diabetes management: when to start insulin vs oral agents 3. To know when to screen and how to manage the comorbidities seen with type 2 diabetes in youth Treatment Goals Weight reduction decreases insulin resistance Normoglycemia and normal HbA1c decreases microvascular disease Control co-morbidities of insulin resistance, the most important contributors to macrovascular disease Hypertension Dyslipidemia Acanthosis Hyperandrogenism: PCOS and hirsuitism Barriers to Adherence: Adolescent Psychosocial Issues DM is associated with depression and eating disorders - Binge eating associated with increased weight gain and high rate of depression (TODAY, Diabetes Care, June 2013) Desire for peer acceptance Doesn t want to be different; wants to be cool Stressful time of life: Stress is related to poor adherence and worsened metabolic control Rebellion against authority Listens to peers more than to parents or other adults Resentment about nagging Wants independence Parenting issues are key: punitive, supportive, too permissive, too controlling Risk taking behaviors Feels invulnerable Driving, Sex, Drugs, Alcohol, Smoking 5
6 Case 2 Johnny Johnny is seen for a sports physical examination. He is overweight and is trying to increase activity to help him lose weight. He is asymptomatic with no symptoms of polyuria or polydipsia. He has a strong family history of type 2 diabetes. Physical Examination/ POCT Labs BMI>95% for age, gender, and height BP 134/86 Acanthosis nigricans present on neck and axillae POCT Blood glucose 432 mg/dl HbA1c 12% Urine ketones small What would you do as initial treatment? Diet and exercise alone Diet and exercise plus metformin Diet and exercise plus insulin Diet and exercise plus metformin and insulin 6
7 Targeted Glucose Control Base therapy on realistic glycemic goals Target both fasting and 2 hour postprandial glucose levels Implement step-wise approach Use whatever therapy necessary to achieve glycemic goals Glycemic Targets* Parameter Normal Reasonable Goals Fasting (or Preprandial) Glucose < Postprandial Glucose <140 <180 Bedtime BG < HbA 1c (DCCT Method) < 5.7 % <7.5%% Glucose values are plasma (mg/ml). *Combined WHO recommendations and ADA guidelines.. AAP T2DM Guidelines: Initial Treatment Clinicians must ensure that insulin therapy is initiated for children and adolescents with T2DM who are ketotic or in diabetic ketoacidosis who have venous or plasma blood glucose levels > 250 mg/dl whose Hemoglobin A1c is > 9 percent; or in whom the distinction between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is unclear. Copeland KC, Silverstein J, Moore KR, et al. Management of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2013;131:
8 Initial Treatment (contd) In all other instances, clinicians should start metformin as first-line therapy for children and adolescents at the time of diagnosis with T2DM, and initiate a lifestyle modification program including nutrition and physical activity. Initial Treatment of Blood Glucose Symptoms Blood Glucose Ketones Treatment No <250 Negative Metformin No >250 Negative Insulin ± Oral agents Yes >200s Negative Insulin Yes >200s Positive Insulin TODAY Study 699 youth with T2D followed for 3.86 years assigned to: Metformin 1000 mg BID Metformin + rosiglitazone 4 mg BID Metformin + lifestyle intervention, incl in-person visits in addition to quarterly clinic visits Primary endoint A1c <8% RESULTS Median time to failure 11.5 months Failure rates: metformin alone 51.7% metformin + rosiglitozone 38.6% - metformin + lifestyle 46.6% Zeitler, Hirst K, Pyle L and the TODAY Study Group. N Engl J Med 2012; 366(24):
9 TODAY Study Other Significant Findings Metformin + rosiglitazone more effective in girls than boys and only significantly different in girls Failure rates highest in African Americans: 52.8% African Americans 45% Hispanics 36.6% Caucasians Metformin alone less effective in AA (66.2% fail) than in Caucasians (44.9%) or Hispanics (44.0%) No difference in cardiovascular risk factors (lipids, microalbuminuria, BP) among groups Failure rates higher in boys p 0.03: 48.2% boys 44.3% girls BARIATRIC SURGERY Within 1 yr of surgery, RYGB improves fasting insulin, fasting glucose HOMA-IR even though patients were still obese (average BMI 35.8 kg/m2)* One year follow-up of 11 T2DM adolescents who underwent RYGB: 10 DCd oral hypoglycemics within 1 yr after surgery. The 1 patient who was insulin-dependent before surgery could not discontinue oral hypoglycemics but was less insulin-resistant and required lower doses of insulin.** * Lawson ML, Kirk S, Mitchell T et al a multicenter study from the Pediatric Bariatric Study Group. J Pediatr Surg 2006:41: Johnny and brother eating after school snack 9
10 Collaborate Cultivate Educate PENS 2015 National Conference AAP Monitoring Guidelines Blood Glucose Clinicians should advise patients to monitor finger-stick BG levels in those who: are taking insulin or other medications with a risk of hypoglycemia; or are initiating or changing their diabetes treatment regimen; or have not met treatment goals; or have intercurrent illnesses. AAP Monitoring Guidelines: HbA1c Clinicians should monitor Hemoglobin A1c (A1c) levels every three months Intensify treatment if treatment goals for BG and A1c levels are not being met. 1
11 Objectives To know how to differentiate type 1 from type 2 diabetes To understand diabetes management: when to start insulin vs oral agents 3. To know when to screen and how to manage the comorbidities seen with type 2 diabetes in youth Case 3 Corey Corey was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes 1 month ago. He is seen for his 1 month visit. Question : With what would you treat hypertension? ACE inhibitors Ca channel blockers Thiazide diuretics With what would you treat mictoalbuminuria? ACE inhibitors Ca channel blockers Thiazide diuretics With what would you treat dyslipidemia? Resins Fibrates Statins Because T2DM is but 1 comorbid condition of MS, tx must address all other co-morbidities 2
12 Atherosclerosis begins in childhood: Autopsy Studies Bogalusa Heart Study (BHS): 2-15 year olds Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis (PADY): year olds in Youth Raised coronary lesions in 7% BHS and 24% PADY Body mass index VLDL, LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides Blood pressure Complications Occur Early in T2DM Frequency Within 1.3 Years of DM Onset Microalbuminuria 28% (7% at 3 mos) Hypertension 36% Mean A1c 7.3%...thus, not due to poor BG control Eppens MC, et al. Diabetes Care 2006;29(6): Complications Occur Early: TODAY Trial months after diagnosis 34% with HTN 54% with hypertriglyceridemia 10% with high LDL-C 20% with microalbuminuria 14% with non-proliferative retinopathy 3
13 COMPLICATION RATE IN TODAY STUDY TODAY Study Group. Diabetes Care. June 2013; 36: BASELINE (n=699) 12 Months (n=512) 24 months (n=404) 36 months (n-264) LDL-C (mg/dl)mean 130 or on meds (%) TG (mg/dl) mean <150 (%) or on meds (%) Apo B (mg/l) p< hscrp (%) > p= CV Risk Factors in T2DM vs T1DM SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Population based study of 2096 youth 0-19 y.o. CVD risk factors: Waist circumference >90% sbp or dbp >90% HDL-C <40 mg/dl, TG > 110 mg/dl 2 or more CV Risk Factors in: 15% T1DM 90% T2DM HTN TG HDL-C WC MS Rodriguez BL, et al. Diabetes Care 29: , 2006 T1DM T2DM TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS Because of the many CV risk factors associated with insulin resistance, T2DM has earlier severe complications than T1DM in childhood. Vascular disease may be present at diagnosis because of the insidious onset and unknown duration of diabetes preceding diagnosis Thus, test for complications (urine albumin, eye exam, lipids) at T2DM dx!!! 4
14 LIPIDS Recommendations for Lipid Treatment: Basic Guidelines Treatment should be based on lipid values obtained after diabetes treatment initiated Initial treatment: diet & exercise if LDL-C >100 Pharmacologic rx should be considered if medical nutrition therapy has failed after 3-6 months, even if chronic hyperglycemia is present Medications should be instituted if LDL is > 160 mg/dl Medication should be considered if LDL is based on the child's CVD risk profile Recommendations for Diet Portion Size (palm, fist) Avoid sugared drinks MyPlate Snacks no more than 100 cals No eating out of box or bag Wait 15 minutes before seconds- then salad 5
15 AAP Key Action Statements Clinicians encourage youth with T2DM to Engage in moderate-to-vigorous exercise for at least 60 minutes daily -May need to increase gradually Limit non- academic screen time to less than 2 hours a day. Drug Therapy LDL-C HDL-C TG Statins 18-55% 5-15% 7-30% Bile acid sequestrant 15-30% 3-5% May increase Fibrates 10-20% 20-30% 20-50% Ezetimibe 18% Niacin 5-25% 15-35% 25-50% 6
16 Anti-inflammatory actions of statins Statins VBWG Lymphocyte LDL LFA-1 Selective block ICAM-1 HMG-CoA reductase activity NO production Geranylgeranyl PP Farnesyl PP + + Reduced prenylation Increased stability of mrna Rho protein Increased transcription NOS mrna oxldl NO Inactivation NO Monocyte Reduced adhesion Decreased activation NF- B Endothelial cell LFA-1 = lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 Sposito AC, Chapman J. ATVB. 2002;22: Statins Concerns over statin use: Elevated transaminase levels %, reversible and dose related Muscle symptoms (myositis, weakness, rhabdomyolysis) - Risk of severe myositis <0.1% Tolerability Pasternak RC, et al. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:7 572 Summary for Clinical Management of Safety Issues Measure baseline AST, ALT before statin use Can continue statins if ALT/AST are <3X upper limits of normal if monitor closely D/C statin if muscle symptoms appear and measure CPK If CPK is WNL or <3X normal, can continue statin and monitor symptoms. Consider dose reduction Statin must be discontinued if CPK is >10X normal Pasternak RC, et al. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:
17 Clinical Management of Statins Measure baseline AST, ALT before statin use Can continue statins if ALT/AST are <3X upper limits of normal if monitor closely D/C statin if muscle symptoms appear and measure CPK If CPK is WNL or <3X normal, can continue statin and monitor symptoms. Consider dose reduction Statin must be discontinued if CPK is >10X normal Pasternak RC, et al. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:7-572 MICROALBUMINURIA & BLOOD PRESSURE Microalbuminuria Normal <30 mg/gm creat on spot urine Represents inflammatory state of vessels Increased in white coat HTN and non-dippers Obtain 2 additional urine samples at least 1 month apart over the next 3-6 months Ideally with first morning void If all 3 abnormal, treat with ACE-I 8
18 Hypertension and T2DM DM and glucose intolerance double risk of HTN Cause of HTN is multifactorial Volume expansion Stiff vessels Decreased NO mediated vasodilitation Increased angiotensin activity BP Treatment Initial treatment: dietary (limit salt) and lifestyle interventions for weight reduction & exercise If BP doesn t reach target of 95% for age, gender, height within 3-6 months, treatment with anti-hypertensive agent should be initiated ACE-I is rx of choice Anti-hypertensive Anti-thrombotic: inhibits platelet aggregation & endothelin Vasodilation: production of angiotensin ; bradykinin levels Limits smooth muscle proliferation & plaque rupture Slows progression of nephropathy & retinopath If AER > 30 mg/d, > 20 mg/min, or > 30 mg/gm creatinine, strive to maintain BP 120/75 Dose titrated to maintain BP< 90% Consider adding meds if goals not reached with ACE alone We do a Poor Job of Treating HTN and hyperlipidemia: SEARCH Study Preliminary Results Lipid levels were measured in 2843 children with overweight 19% had Total cholesterol 200 mg/dl 14% had LDL-C 130 mg/dl 7% had TG 200 mg/dl 1% on lipid lowering meds 4% on metformin 9
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY. Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
DR. Trinh Thi Kim Hue
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE CHILD AND ADOLESCENT DR. Trinh Thi Kim Hue CONTENTS Definition Diagnosis Treatment Comorbidities and Complications Comorbidities and Complications Screening for T2D References DEFINITION
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE CHILD AND ADOLESCENT DR. Trinh Thi Kim Hue CONTENTS Definition Diagnosis Treatment Comorbidities and Complications Comorbidities and Complications Screening for T2D References DEFINITION
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help?
 Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION. Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D.
 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee
 Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest. Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007
 Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Nutrition. Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT
 1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group. Learning Objectives. Background. CAPA 2015 Annual Conference
 Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health?
 Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin resistance syndrome in Children
 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin resistance syndrome in Children Anil R Kumar MD Pediatric Endocrinology MCV/VCU, Richmond VA Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM) has increased in children
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin resistance syndrome in Children Anil R Kumar MD Pediatric Endocrinology MCV/VCU, Richmond VA Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM) has increased in children
Diabetes Complications
 Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
DISCLOSURES RISK ASSESSMENT. Stroke and Heart Disease -Is there a Link Beyond Risk Factors? Daniel Lackland, MD
 STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention.
 Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention. Professor Paolo Pozzilli University Campus Bio-Medico, Rome Institute of Cell & Molecular Science, Queen Mary, University of
Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention. Professor Paolo Pozzilli University Campus Bio-Medico, Rome Institute of Cell & Molecular Science, Queen Mary, University of
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Insulin Resistance and PCOS: A not uncommon reproductive disorder
 Insulin Resistance and PCOS: A not uncommon reproductive disorder Joyce L. Ross, MSN, CRNP, CS, FNLA, FPCNA Diplomate Accrediation Council for Clinical Lipidology President Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses
Insulin Resistance and PCOS: A not uncommon reproductive disorder Joyce L. Ross, MSN, CRNP, CS, FNLA, FPCNA Diplomate Accrediation Council for Clinical Lipidology President Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Family History and Diabetes. Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional
 Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Treatment of diabetes In order to survive, people with type 1 diabetes must have insulin delivered by a pump or injections.
 National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
Diabetes Dispatch. Children with Type 2 Diabetes: How do we treat them? A L A S K A N A T I V E D I A B E T E S T E A M. Inside this issue:
 A L A S K A N A T I V E D I A B E T E S T E A M Diabetes Dispatch Volume 8, Issue 1 Spring 2013 Compiled by Justin Park, Pharm.D. Candidate Type 2 diabetes is a relatively new disease in children and adolescents.
A L A S K A N A T I V E D I A B E T E S T E A M Diabetes Dispatch Volume 8, Issue 1 Spring 2013 Compiled by Justin Park, Pharm.D. Candidate Type 2 diabetes is a relatively new disease in children and adolescents.
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus
 Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
Management of Diabetes in the Elderly. Sylvia Shamanna Internal Medicine (R1)
 Management of Diabetes in the Elderly Sylvia Shamanna Internal Medicine (R1) Case 74 year old female with frontal temporal lobe dementia admitted for prolonged delirium and frequent falls (usually in the
Management of Diabetes in the Elderly Sylvia Shamanna Internal Medicine (R1) Case 74 year old female with frontal temporal lobe dementia admitted for prolonged delirium and frequent falls (usually in the
How To Treat Dyslipidemia
 An International Atherosclerosis Society Position Paper: Global Recommendations for the Management of Dyslipidemia Introduction Executive Summary The International Atherosclerosis Society (IAS) here updates
An International Atherosclerosis Society Position Paper: Global Recommendations for the Management of Dyslipidemia Introduction Executive Summary The International Atherosclerosis Society (IAS) here updates
Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075
 Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯
 The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
MANAGEMENT OF LIPID DISORDERS: IMPLICATIONS OF THE NEW GUIDELINES
 MANAGEMENT OF LIPID DISORDERS: IMPLICATIONS OF THE NEW GUIDELINES Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest EXPLAINING
MANAGEMENT OF LIPID DISORDERS: IMPLICATIONS OF THE NEW GUIDELINES Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest EXPLAINING
Primary Care Management of Women with Hyperlipidemia. Julie Marfell, DNP, BC, FNP, Chairperson, Department of Family Nursing
 Primary Care Management of Women with Hyperlipidemia Julie Marfell, DNP, BC, FNP, Chairperson, Department of Family Nursing Objectives: Define dyslipidemia in women Discuss the investigation process leading
Primary Care Management of Women with Hyperlipidemia Julie Marfell, DNP, BC, FNP, Chairperson, Department of Family Nursing Objectives: Define dyslipidemia in women Discuss the investigation process leading
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
DIABETES MELLITUS GUIDELINES
 DIABETES MELLITUS GUIDELINES Virginia Premier Health Plan Virginia Premier Health Plan, Clinical Practice Guideline-Diabetes 1. Population screening a. Indications i. Adults of any age with body mass index
DIABETES MELLITUS GUIDELINES Virginia Premier Health Plan Virginia Premier Health Plan, Clinical Practice Guideline-Diabetes 1. Population screening a. Indications i. Adults of any age with body mass index
ADULT HYPERTENSION PROTOCOL STANFORD COORDINATED CARE
 I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines for the monitoring of antihypertensive therapy in adult patients and to define the roles and responsibilities of the collaborating clinical pharmacist and pharmacy resident.
I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines for the monitoring of antihypertensive therapy in adult patients and to define the roles and responsibilities of the collaborating clinical pharmacist and pharmacy resident.
Type 1 Diabetes ( Juvenile Diabetes)
 Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
ETIOLOGIC CLASSIFICATION. Type I diabetes Type II diabetes
 DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
Challenges in Glycemic Control in Adult and Geriatric Patients. Denyse Gallagher, APRN-BC, CDE Endocrinology Nurse Practitioner
 Challenges in Glycemic Control in Adult and Geriatric Patients Denyse Gallagher, APRN-BC, CDE Endocrinology Nurse Practitioner Provide an overview of diabetes prevalence; discuss challenges and barriers
Challenges in Glycemic Control in Adult and Geriatric Patients Denyse Gallagher, APRN-BC, CDE Endocrinology Nurse Practitioner Provide an overview of diabetes prevalence; discuss challenges and barriers
Nutrition Therapy in Diabetes Mellitus. Dorothy Debrah Diabetes Specialist Dietitian University Hospital, Llandough. Wales, UK February 2012
 Nutrition Therapy in Diabetes Mellitus. Dorothy Debrah Diabetes Specialist Dietitian University Hospital, Llandough. Wales, UK February 2012 University Hospital Llandough DIABETES MELLITUS. Definition:
Nutrition Therapy in Diabetes Mellitus. Dorothy Debrah Diabetes Specialist Dietitian University Hospital, Llandough. Wales, UK February 2012 University Hospital Llandough DIABETES MELLITUS. Definition:
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes?
 Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
DIABETES YOUR GUIDE TO
 YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
Tuberculosis And Diabetes. Dr. hanan abuelrus Prof.of internal medicine Assiut University
 Tuberculosis And Diabetes Dr. hanan abuelrus Prof.of internal medicine Assiut University TUBERCULOSIS FACTS More than 9 million people fall sick with tuberculosis (TB) every year. Over 1.5 million die
Tuberculosis And Diabetes Dr. hanan abuelrus Prof.of internal medicine Assiut University TUBERCULOSIS FACTS More than 9 million people fall sick with tuberculosis (TB) every year. Over 1.5 million die
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY. 12a. FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline. Diabetes Mellitus
 CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline Diabetes Mellitus Part I: 1. Which one of the following statements about type 2 diabetes is not accurate? a. Diabetics are at increased risk of experiencing
CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline Diabetes Mellitus Part I: 1. Which one of the following statements about type 2 diabetes is not accurate? a. Diabetics are at increased risk of experiencing
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Part XII Insulin Resistance By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner September 15, 2005
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Part XII By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner September 15, 2005 As we approach the end of our extended series on cardiovascular disease risk factors,
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Part XII By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner September 15, 2005 As we approach the end of our extended series on cardiovascular disease risk factors,
Diabetes and Obesity in Children. Janie Berquist, RN, BSN, MPH, CDE Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Kansas City, MO
 Diabetes and Obesity in Children Janie Berquist, RN, BSN, MPH, CDE Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Kansas City, MO Diabetes and Obesity in Children What is Diabetes? How are Diabetes and Obesity
Diabetes and Obesity in Children Janie Berquist, RN, BSN, MPH, CDE Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Kansas City, MO Diabetes and Obesity in Children What is Diabetes? How are Diabetes and Obesity
High Blood Cholesterol
 National Cholesterol Education Program ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference 1 Step 1 2 Step 2 3 Step 3 Determine lipoprotein levels obtain complete lipoprotein profile after 9- to 12-hour
National Cholesterol Education Program ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference 1 Step 1 2 Step 2 3 Step 3 Determine lipoprotein levels obtain complete lipoprotein profile after 9- to 12-hour
2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Athersclerotic Risk
 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Athersclerotic Risk Lynne T Braun, PhD, CNP, FAHA, FAAN Professor of Nursing, Nurse Practitioner Rush University Medical Center 2
2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Athersclerotic Risk Lynne T Braun, PhD, CNP, FAHA, FAAN Professor of Nursing, Nurse Practitioner Rush University Medical Center 2
Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals
 Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals Lanita. S. White, Pharm.D. Director, UAMS 12 th Street Health and Wellness Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, UAMS College of Pharmacy
Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals Lanita. S. White, Pharm.D. Director, UAMS 12 th Street Health and Wellness Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, UAMS College of Pharmacy
Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record. Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD
 Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Defined by the National Kidney Foundation Either a decline in
Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Defined by the National Kidney Foundation Either a decline in
PRESCRIBING GUIDELINES FOR LIPID LOWERING TREATMENTS for SECONDARY PREVENTION
 Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee PRESCRIBING GUIDELINES FOR LIPID LOWERING TREATMENTS for SECONDARY PREVENTION For guidance on Primary Prevention please see NICE guidance http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg181
Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee PRESCRIBING GUIDELINES FOR LIPID LOWERING TREATMENTS for SECONDARY PREVENTION For guidance on Primary Prevention please see NICE guidance http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg181
INSULIN TREATMENT FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT
 INSULIN TREATMENT FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT APIRADEE SRIWIJITKAMOL DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITOL QUESTION 1 1. ท านเคยเป นแพทย
INSULIN TREATMENT FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT APIRADEE SRIWIJITKAMOL DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITOL QUESTION 1 1. ท านเคยเป นแพทย
Diabetes and Heart Disease
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Diabetes, Type 2. RelayClinical Patient Education Sample Topic Diabetes, Type 2. What is type 2 diabetes? How does it occur?
 What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
Statins and Risk for Diabetes Mellitus. Background
 Statins and Risk for Diabetes Mellitus Kevin C. Maki, PhD, FNLA Midwest Center for Metabolic & Cardiovascular Research and DePaul University, Chicago, IL 1 Background In 2012 the US Food and Drug Administration
Statins and Risk for Diabetes Mellitus Kevin C. Maki, PhD, FNLA Midwest Center for Metabolic & Cardiovascular Research and DePaul University, Chicago, IL 1 Background In 2012 the US Food and Drug Administration
NCT00272090. sanofi-aventis HOE901_3507. insulin glargine
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: Generic drug name:
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: Generic drug name:
The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx:
 James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
Diabetes Mellitus. Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes Mellitus
 Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
Diabetes Mellitus 1. Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions
 Diabetes Mellitus 1 Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions 1. A 46-year-old man presents for his annual physical. He states that he has been going to the bathroom more frequently than
Diabetes Mellitus 1 Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions 1. A 46-year-old man presents for his annual physical. He states that he has been going to the bathroom more frequently than
Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat?
 Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat? After eating, most food is turned into glucose, the body s main source of energy. 1 Normal Blood
Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat? After eating, most food is turned into glucose, the body s main source of energy. 1 Normal Blood
Prevention of and the Screening for Diabetes Part I Insulin Resistance By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner January 19, 2012
 Prevention of and the Screening for Diabetes Part I Insulin Resistance By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner January 19, 2012 In 2002, SETMA began a relationship with Joslin Diabetes
Prevention of and the Screening for Diabetes Part I Insulin Resistance By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner January 19, 2012 In 2002, SETMA began a relationship with Joslin Diabetes
An Interprofessional Approach to Diabetes Management
 Disclosures An Interprofessional Approach to Diabetes Management Principal in DiabetesReframed, LLC. Inventor of U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 61/585,483 METHODS OF USING A DIABETES CROSS- DISCIPLINARY
Disclosures An Interprofessional Approach to Diabetes Management Principal in DiabetesReframed, LLC. Inventor of U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 61/585,483 METHODS OF USING A DIABETES CROSS- DISCIPLINARY
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Prognosis and Treatment
 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Prognosis and Treatment Zachary Henry, M.D. Assistant Professor UVA Gastroenterology & Hepatology October 28, 2015 Overview Case Presentation Prognosis Effects of fibrosis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Prognosis and Treatment Zachary Henry, M.D. Assistant Professor UVA Gastroenterology & Hepatology October 28, 2015 Overview Case Presentation Prognosis Effects of fibrosis
Diabetes Fundamentals
 Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Where Do We Stand in 2012? David M. Kendall, MD Distinguished Medical Fellow Lilly Diabetes Associate Professor of Medicine University of MInnesota Disclosure - Duality
Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Where Do We Stand in 2012? David M. Kendall, MD Distinguished Medical Fellow Lilly Diabetes Associate Professor of Medicine University of MInnesota Disclosure - Duality
Section 5: Type 2 Diabetes
 SECTION OVERVIEW Definition and Symptoms Blood Glucose Monitoring Healthy Eating Physical Activity Oral Medication Insulin Sharps Disposal Definition and Symptoms Type 2 diabetes is occurring more frequently
SECTION OVERVIEW Definition and Symptoms Blood Glucose Monitoring Healthy Eating Physical Activity Oral Medication Insulin Sharps Disposal Definition and Symptoms Type 2 diabetes is occurring more frequently
Cardiovascular disease physiology. Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 14, 2011
 Cardiovascular disease physiology Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 14, 2011 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics Recommendations The disease process
Cardiovascular disease physiology Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 14, 2011 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics Recommendations The disease process
G:\ CDM\BHCIG Diabetes Pathway FINAL September 05.doc 1
 G:\ CDM\BHCIG Diabetes Pathway FINAL September 05.doc 1 BHCiG: TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT PATHWAY MODEL INTRODUCTION What is the aim of the model? To improve the capacity of primary care health practitioners
G:\ CDM\BHCIG Diabetes Pathway FINAL September 05.doc 1 BHCiG: TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT PATHWAY MODEL INTRODUCTION What is the aim of the model? To improve the capacity of primary care health practitioners
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
JNC-8 Blood Pressure and ACC/AHA Cholesterol Guideline Updates. January 30, 2014
 JNC-8 Blood Pressure and ACC/AHA Cholesterol Guideline Updates January 30, 2014 GOALS Review key recommendations from recently published guidelines on blood pressure and cholesterol management Discuss
JNC-8 Blood Pressure and ACC/AHA Cholesterol Guideline Updates January 30, 2014 GOALS Review key recommendations from recently published guidelines on blood pressure and cholesterol management Discuss
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
 Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Patient Tool #1 Understanding Diabetes and Psychiatric Illness: A Guide for Individuals, Families, and Caregivers Type 2 Diabetes,
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Patient Tool #1 Understanding Diabetes and Psychiatric Illness: A Guide for Individuals, Families, and Caregivers Type 2 Diabetes,
Diabetes mellitus. Lecture Outline
 Diabetes mellitus Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis II. Epidemiology III. Causes of diabetes IV. Health Problems and Diabetes V. Treating Diabetes VI. Physical activity and diabetes 1 Diabetes Disorder characterized
Diabetes mellitus Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis II. Epidemiology III. Causes of diabetes IV. Health Problems and Diabetes V. Treating Diabetes VI. Physical activity and diabetes 1 Diabetes Disorder characterized
Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word picture puzzle slides.
 Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word picture puzzle slides. Example: = Head Over Heels Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word
Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word picture puzzle slides. Example: = Head Over Heels Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
 Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Professional Tool #1: Screening and Monitoring in a High-Risk Population: Questions and Answers Overview of Cardiometabolic
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Professional Tool #1: Screening and Monitoring in a High-Risk Population: Questions and Answers Overview of Cardiometabolic
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net
 1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
Diabetes: The Numbers
 Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME
 1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN
1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN
Absolute cardiovascular disease risk management
 Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk management This quick reference guide is for use by health professionals for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk management This quick reference guide is for use by health professionals for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires
 Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
Diabetes epidemics- classification and prevalence Grazyna Sypniewska
 Diabetes epidemics- classification and prevalence Grazyna Sypniewska Dept.of Laboratory Medicine, Collegium Medicum N Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland 14th EFLM Postgraduate Course, Dubrovnik 2014
Diabetes epidemics- classification and prevalence Grazyna Sypniewska Dept.of Laboratory Medicine, Collegium Medicum N Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland 14th EFLM Postgraduate Course, Dubrovnik 2014
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes
 Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world. Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ)
 Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ) Overview Pathogenesis of T2DM Aims of treatment The place of glycaemic control Strategies to improve glycaemic
Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ) Overview Pathogenesis of T2DM Aims of treatment The place of glycaemic control Strategies to improve glycaemic
Chapter 4 Type 2 Diabetes
 Chapter 4 Type 2 Diabetes (previously referred to as adult onset diabetes or non-insulin dependent diabetes) H. Peter Chase, MD Cindy Cain, RN, CDE Philip Zeitler, MD This is the most common type of diabetes
Chapter 4 Type 2 Diabetes (previously referred to as adult onset diabetes or non-insulin dependent diabetes) H. Peter Chase, MD Cindy Cain, RN, CDE Philip Zeitler, MD This is the most common type of diabetes
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know
 Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Markham Stouffville Hospital
 Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin. 4. Not meeting glycemic goals with oral hypoglycemic agents or
 A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin When to Start Insulin: 1. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels >250 mg/dl or 2. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) >10% or 3. Random plasma glucose consistently >300 mg/dl
A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin When to Start Insulin: 1. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels >250 mg/dl or 2. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) >10% or 3. Random plasma glucose consistently >300 mg/dl
Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Lipids Hypercholesterolaemia is an important reversible risk factor for cardiovascular disease and should be tackled aggressively in all diabetic patients. In Type 1 patients,
Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Lipids Hypercholesterolaemia is an important reversible risk factor for cardiovascular disease and should be tackled aggressively in all diabetic patients. In Type 1 patients,
Type 2 Diabetes. Tabinda Dugal GP Day 4/05/16
 Type 2 Diabetes Tabinda Dugal GP Day 4/05/16 Diabetes Diabetes.a growing health crisis in Britain 869m per year 10% of NHS budget Projections.. 5 million by 2025 Youngest patient? T2DM Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Tabinda Dugal GP Day 4/05/16 Diabetes Diabetes.a growing health crisis in Britain 869m per year 10% of NHS budget Projections.. 5 million by 2025 Youngest patient? T2DM Type 2 diabetes
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics
 Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes
 Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes Section 1 1 of 4 Curriculum Module II 1 Diagnosis, classification and presentation of diabetes Slide 2 of 48 Polyurea Definition of diabetes Slide 3
Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes Section 1 1 of 4 Curriculum Module II 1 Diagnosis, classification and presentation of diabetes Slide 2 of 48 Polyurea Definition of diabetes Slide 3
Secondary Stroke Prevention Luke Bradbury, MD 10/4/14 Fall WAPA Conferfence
 Guidelines Secondary Stroke Prevention Luke Bradbury, MD 10/4/14 Fall WAPA Conferfence Stroke/TIA Nearly 700,000 ischemic strokes and 240,000 TIAs every year in the United States Currently, the risk for
Guidelines Secondary Stroke Prevention Luke Bradbury, MD 10/4/14 Fall WAPA Conferfence Stroke/TIA Nearly 700,000 ischemic strokes and 240,000 TIAs every year in the United States Currently, the risk for
Initiation and Adjustment of Insulin Regimens
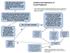 Start with bedtime intermediateacting insulin or bedtime or morning long-acting insulin (can initiate with 10 units or 0.2 units per kg) Initiation and Adjustment of Insulin Regimens Insulin regimens should
Start with bedtime intermediateacting insulin or bedtime or morning long-acting insulin (can initiate with 10 units or 0.2 units per kg) Initiation and Adjustment of Insulin Regimens Insulin regimens should
