Presenter : Dr Yashpal Singh Rathore
|
|
|
- Douglas Rich
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Presenter : Dr Yashpal Singh Rathore 1
2 Narrowing of the spinal canal/lateral recess/ intervertebral foramen. Verbiest (1954) first established LCS as a clinical entity Annual incidence 5 cases / 100,000 individuals. By the age of 65 yrs, myelographic evidence of LCS is present in 17 60% of adults; Up to 80% aged >70 years. LCS most commonly involve L4-L5 level, followed byl3-l4 level. The natural history of lumbar canal stenosis is frequently benign, and many patients respond to conservative treatment. Surgery should be reserved for when medical treatment fails and leg symptoms are severe and functionally disabling. Johnsson, K. e. Acta Orthop. Scand. 66, (1995) Sasaki K (1995) Eur Spine J 4:71 6 2
3 Etiological Classification Primary stenosis Idiopathic stenosis Achondrodysplasia Secondary stenosis Degenerative Ossification of the ligamentum flavum & OPLL Metabolic or endocrine causes Infections Neoplastic Rheumatological conditions Posttraumatic or postoperative stenosis 3
4 Anatomical Classification Central stenosis (with or without lateral stenosis) Isolated lateral stenosis Foraminal stenosis A patho-morphological classification considers the underlying pathology such as: Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum Hypertrophy of the facet joints Osteophyte formations (spurs) Disc herniation Synovial facet joint cysts Vertebral displacements (anterior/lateral) 4
5 Ventral compression can be caused by medially bulging or protrusion of intervertebral discs. Lateral stenosis can be caused by lateral prolapse, stenosis of the neuroforamen or hypertrophy of the facet joints. 5
6 Dorsal view of lateral stenosis caused by hypertrophic facet joints and narrowing of the neuroforamen. 6
7 Corresponding lateral perspective of narrowed neuroforamen causing a lateral stenosis 7
8 Three-joint Complex A large tripod with the disc as the front support and two facet joints as the back supports Any alteration in one of these joints can lead to damage to the others 8
9 Standing/ walking provokes symptoms Pain/weakness in the legs Patients lean forward while walking to relieve symptoms Sitting or bending forward relieves symptoms 9
10 Cardinal symptom => Neurogenic claudication Numbness, weakness and discomfort in the legs while walking or prolonged standing, Regression of symptoms during sitting and rest. Distance decreases with increasing severity of the degenerative changes Radicular claudication Symptoms can be provoked during walking and prolonged standing but are localized to a nerve root dermatome Less frequent symptoms Mechanical low-back pain (worse on activity) Atypical leg pain (non-radicular distribution) Cauda equina syndrome (very rare) 10
11 Varied presentation Classically with neurogenic claudication Some may only have back pain Rarely painless progressive weakness 11
12 Root symptoms Unilateral No claudication Acute or chronic 12
13 Claudication Radicular pain Weakness is rare Acute or chronic 13
14 The most frequent physical findings Limited lumbar extension % Sensory deficit 32 58% Muscle weakness 18 52% Straight leg raising 10 90% Absent knee reflexes 10 50% Absent ankle reflexes 50 68% Katz JN, et al. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 20: , 1994 A reliable assessment of the walking distance is an important parameter for determining the outcome of surgical treatment. 14
15 Grade I Neurogenic intermittent claudication characterized by a reduced walking distance (caused by pain) and short intermittent sensory-motor deficits that at rest might be unremarkable, but can deteriorate while walking. Grade II Intermittent paresis refers to already persistent sensitivity deficits, loss of reflexes and intermittent paresis. Grade III Persistent, progressing paresis accompanied by partial regression of pain. Hufschmidt, A. & Lücking, C. H (eds) Neurologie Compact (Thieme, stuggart, 2006) 15
16 Intermittent claudication or vascular claudication Radiculopathies or polyneuropathies Intraspinal synovial cyst Disc prolapse Tethered cord or spina bifida Coxarthrosis or arthrosis of the iliosacral joint Abdominal aortic aneurysm Neoplasia (for e.g., tumor of myelon, spinal roots, meninges, bones) Inflammatory conditions (for e.g., spondylodiscitis, arachnoiditis) Dissociative syndromes 16
17 Sign & Symptoms Vascular Neurogenic Walking Distance Fixed Variable Type of Pain Cramps, Tightness Dull ache, numbness Relief at cessation of activity Immediate Delayed Back pain Rarely Occasionally Pain relief Standing Flexion & sitting Posture provocation Uncommon Common Walking uphill Pain No pain Bicycle riding Pain No pain Pulses Absent Normal Trophic changes Likely Absent Muscle atrophy Rarely occasionally 17
18 Screening exam Stenosis cannot be diagnosed Instability such as scoliosis or listhesis 18
19 Findings often associated with spinal stenosis Degenerative spondylolisthesis Degenerative scoliosis Congenitally narrow spinal canal Less reliable findings implying lateral recess or foraminal stenosis Disc space narrowing Isthmic spondylolisthesis Severe facet osteoarthritis 19
20 20
21 Excellent bony detail Difficult to diagnose stenosis Replaced by MRI May be useful for those who cannot have an MRI 21
22 Absolute stenosis Midsagittal lumbar canal diameter less than 10mm (physiological value is mm) Relative stenosis Midsagittal lumbar canal diameter mm Verbiest H (1979). Spine 4: The lateral recess can be considered stenotic if it has a diameter of <2 mm (physiological dia. 3 5 mm) 22
23 Gold standard Non-invasive Soft tissue visualization Sagittal images Visualization of foramen 23
24 Characteristic findings of spinal stenosis include: Thickened ligamentum flavum Facet joint hypertrophy Hourglass appearance of spinal canal on sagittal images Facet joint synovial cysts Trefoil appearance of the thecal sac (indicative of spinal lipomatosis) Short pedicles Vertebral endplate osteophytes Obliteration of the perineural fat in neural foramina in parasaggital T1WI is indicative of a foraminal stenosis 24
25 25
26 Excellent for intra-canal pathology Poor for foraminal pathology Replaced by MRI Invasive 1% spinal headache Recurrent stenosis Inability to obtain MRI 26
27 Excellent visualization of spinal canal Excellent for recurrent stenosis Invaluable in surgical planning 27
28 Multisegmental disc degeneration revealed by CT myelography. a A sagittal reformatted CT myelograph reveals a multisegmental severe disc degeneration, with disc space height reduction, vacuum phenomenon and endplate sclerosis of the lower lumbar spine, as well as thecal sac compressions at the L3 4 and L4 5 levels (arrows). b d Axial images show a circumscribed severe LCS of L3 4, with a typical hourglass constriction of the thecal sac (arrow) adjacent to relatively normal areas. 28
29 Neurophysiologic assessment is indicated: To confirm the clinical relevance of imaging findings in equivocal cases To identify a peripheral neuropathy To differentiate radiculopathy and mononeuropathy To differentiate non-specific neurological complaints 29
30 Rest Short term activity modification for acute pain Long term activity modification is not recommended Analgesic NSAIDS Paracetamol Narcotics Gabapentin Steroids Effective for acute pain Short duration therapy Spinal injection Epidural steroid Transforaminal root block Facet joint injection Calcitonin has been reported to improve the symptoms of neurogenic claudication Eskola A etal (1992) Calcif Tissue Int 50:
31 Avoid extension exercises acutely William Flexion Exercises Water aerobics Strengthening of weak muscle groups 31
32 Moderate to severe claudication symptoms Significant interference with lifestyle Progressive neurological deficits Cauda equina syndrome 32
33 Decompression (uni- /bilateral laminotomy or laminectomy) Decompression with non-instrumented fusion Decompression with instrumented fusion 33
34 Decompression of lateral recess Undercutting the ventral aspect of the facet joints and the associated ligamentum flavum. Medial facetectomy if necessary The traversing nerve root underneath the facet joint must be visualized 34
35 Selective decompression Surgical technique of choice in patients presenting with neurogenic claudication without relevant back pain Favourable indications Central stenosis predominantly due to flavum hypertrophy Nerve root claudication due to lateral recess stenosis Absence of degenerative spondylolisthesis and scoliosis Absence of osseous foraminal stenosis 35
36 Total laminectomy Thecal sac cannot be sufficiently decompressed or the access to the foramen is obliterated (foraminal stenosis) Laminectomy alone should be avoided in cases with preexisting instability such as: Degenerative spondylolisthesis Isthmic spondylolisthesis with secondary degenerative changes Degenerative scoliosis 36
37 Segmental instability (degenerative spondylolisthesis and scoliosis) Iatrogenic pars defect Greater than 50% facet joint resection Concomitant moderate to severe back pain Necessity for a wide decompression Recurrent spinal stenosis 37
38 X-Stop Implant Inter- spinous process Device Mimics bending or sitting Daycare surgery done in less than one hour Quicker recovery No manipulation of nerves or entrance into spinal canal Less potential risks Used only in select patients Symptoms must be relieved with sitting or bending forward 38
39 Typical complications of both decompression and fusion surgery Dura / vessel lacerations Epidural hematomas Inadequate decompression with significant residual stenosis Instability Re-ossification The complication rates for decompression surgery (during and after the surgical procedure) range from 14% to 35%. Thome, C. et al. J. Neurosurg. Spine 3, (2005) Benz, r. J. et al Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 384, (2001) 39
40 Unilateral Laminotomy for B/L microdecompression: 520 levels/374pts 88% improved VAS 5yr follow up 0.8% instability None reoperated Costa F et.al. JNS-Spine 2007;7(6): Clinical results of decompressive laminectomy Patient satisfaction varies from 57% to 81% with regard to excellent to good results. Iguchi T etal. J Spinal Disord Tech 2002 ; 15:93 9 Iguchi T etal. Spine 2000 ; 25:
41 In patients with imaging-confirmed spinal stenosis without spondylolisthesis and leg symptoms persisting for at least 12 weeks, surgery was superior to nonsurgical treatment in relieving symptoms and improving function. Surgery resulted in better improvement in pain and function than non-operative treatment for stenosis at 2yrs. 17% crossover to surgery. James N. Weinstein et.al; NEJM 2008; 358: ;Feb 21,
42 81 surgery, 67 non-op Surgery group more severe symptoms 1 year f/u (p=0.003) 55% surgery improved 28% non-op improved 5 year f/u (p=0.05) 70% surgery improved 52% non-op improved Atlas SJ Spine 1996; 21(15)
43 Surgery better for leg pain and back related function but equal to non-op management for pt. satisfaction, back pain and primary surgery relief at 8-10yrs. 39% non-ops had surgery 23% reoperation Atlas SJ et al. Spine 2005;30(8):
44 Prospective study of long term outcomes 78 88% success at 6 wk 6 mo Fell to ~70% at 1 year Javid MJ ;J Neurosurg 89;1, 1998 Cochrane Systematic Review 2005 No scientific evidence for spinal stenosis surgery Van Tulder ;Eur Spine J
45 THANK YOU 45
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
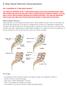 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic & Spine Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital
 Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic & Spine Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Classification Pathology Clinical features Imaging Treatment Options Outcomes Definition: 1. Narrowing
Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic & Spine Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Classification Pathology Clinical features Imaging Treatment Options Outcomes Definition: 1. Narrowing
Spinal Surgery 2. Teaching Aims. Common Spinal Pathologies. Disc Degeneration. Disc Degeneration. Causes of LBP 8/2/13. Common Spinal Conditions
 Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Cervical Spine Surgery. Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar. Dr Michelle Atkinson. Friday October 21 st 2011. Cervical Disc Herniation
 Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Introduction Lumbar spinal stenosis is defined as reduction in the diameter of the spinal canal, lateral nerve canals or neural foramina. The stenosis may involve multiple level
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Introduction Lumbar spinal stenosis is defined as reduction in the diameter of the spinal canal, lateral nerve canals or neural foramina. The stenosis may involve multiple level
Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis
 Low Back Pains Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis JMAJ 46(10): 439 444, 2003 Katsuro TOMITA Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kanazawa University Abstract: Lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Low Back Pains Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis JMAJ 46(10): 439 444, 2003 Katsuro TOMITA Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kanazawa University Abstract: Lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
UPPER LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION WITH CENTRAL AND FAR LATERAL STENOTIC CHANGES RESULTING IN ANTERIOR THIGH PAIN
 Cox Technic Case Report #60 sent 5/13/08 1 UPPER LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION WITH CENTRAL AND FAR LATERAL STENOTIC CHANGES RESULTING IN ANTERIOR THIGH PAIN History, Examination & Imaging Review: A 53-year-old
Cox Technic Case Report #60 sent 5/13/08 1 UPPER LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION WITH CENTRAL AND FAR LATERAL STENOTIC CHANGES RESULTING IN ANTERIOR THIGH PAIN History, Examination & Imaging Review: A 53-year-old
Lumbar spinal stenosis JA Shipley MMed(Orth) Department Orthopaedic Surgery, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
 Page 42 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Autumn 2008 CLINICAL ARTICLE C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Lumbar spinal stenosis JA Shipley MMed(Orth) Department Orthopaedic Surgery, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Page 42 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Autumn 2008 CLINICAL ARTICLE C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Lumbar spinal stenosis JA Shipley MMed(Orth) Department Orthopaedic Surgery, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
OUTLINE. Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP. Treatment. Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear. Non-Surgical Surgical
 DISCOGENIC PAIN OUTLINE Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear Treatment Non-Surgical Surgical Facet Joints: bear 20% of weight Discs bear 80% of weight Neural Foramen
DISCOGENIC PAIN OUTLINE Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear Treatment Non-Surgical Surgical Facet Joints: bear 20% of weight Discs bear 80% of weight Neural Foramen
How To Understand The Anatomy Of A Lumbar Spine
 Sciatica: Low back and Leg Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Options Presented by Devesh Ramnath, MD Orthopaedic Associates Of Dallas Baylor Spine Center Sciatica Compression of the spinal nerves in the back
Sciatica: Low back and Leg Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Options Presented by Devesh Ramnath, MD Orthopaedic Associates Of Dallas Baylor Spine Center Sciatica Compression of the spinal nerves in the back
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R.
 Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
1 REVISOR 5223.0070. (4) Pain associated with rigidity (loss of motion or postural abnormality) or
 1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: 07/24/2013 Comments: Policy Accepted during 2013 Annual Review with no changes.
 Health Plan Coverage Policy ARBenefits Approval: 01/01/2012 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: 07/24/2013 Comments: Policy Accepted during 2013 Annual Review with no changes. Title: Minimally Invasive,
Health Plan Coverage Policy ARBenefits Approval: 01/01/2012 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: 07/24/2013 Comments: Policy Accepted during 2013 Annual Review with no changes. Title: Minimally Invasive,
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
IP'Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 A Patient's G uide to IP'Lumbar Spinal Stenosis X*STOP Interspinous Process Decompression This patient information guide is made possible through cooperation between your physician and St. Francis Medical
A Patient's G uide to IP'Lumbar Spinal Stenosis X*STOP Interspinous Process Decompression This patient information guide is made possible through cooperation between your physician and St. Francis Medical
Research Article Partial Facetectomy for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis
 Advances in Orthopedics, Article ID 534658, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/534658 Research Article Partial Facetectomy for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis Kevin Kang, 1 Juan Carlos Rodriguez-Olaverri,
Advances in Orthopedics, Article ID 534658, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/534658 Research Article Partial Facetectomy for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis Kevin Kang, 1 Juan Carlos Rodriguez-Olaverri,
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances?
 Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: lumbar_spine_fusion_surgery 9/2010 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Low back pain
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: lumbar_spine_fusion_surgery 9/2010 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Low back pain
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica. Alexander Ching, MD
 Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Overview Anatomy of the spinal canal What is spinal stenosis? > 1
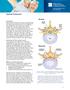 Spinal Stenosis Overview Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of your spinal canal and nerve root canal along with the enlargement of your facet joints. Most commonly it is caused by osteoarthritis and your
Spinal Stenosis Overview Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of your spinal canal and nerve root canal along with the enlargement of your facet joints. Most commonly it is caused by osteoarthritis and your
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica. Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS
 Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
LOW BACK PAIN. common of these conditions include: muscle strain ( pulled muscle ), weak core muscles
 LOW BACK PAIN Most episodes of low back pain are caused by relatively harmless conditions. The most common of these conditions include: muscle strain ( pulled muscle ), weak core muscles (abdominal and
LOW BACK PAIN Most episodes of low back pain are caused by relatively harmless conditions. The most common of these conditions include: muscle strain ( pulled muscle ), weak core muscles (abdominal and
Surgical Treatment for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Dynamic Interspinous Distraction Interlaminar Stabilization Implant - Coflex
 International 31st Course For Percutaneous Endoscopic Spinal Surgery And Complementary Minimal Invasive Techniques Zurich, Switzerland January 24-25, 2013 Surgical Treatment for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
International 31st Course For Percutaneous Endoscopic Spinal Surgery And Complementary Minimal Invasive Techniques Zurich, Switzerland January 24-25, 2013 Surgical Treatment for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
The outcome of Microscopic Selective Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.28, No.4, December 2006 The outcome of Microscopic Selective Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis A.Aziz Mohammed, CABS, FRCS (Ortho, Tr)* Tariq El Kalifa,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.28, No.4, December 2006 The outcome of Microscopic Selective Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis A.Aziz Mohammed, CABS, FRCS (Ortho, Tr)* Tariq El Kalifa,
Subject: BlueCross BlueShield of North Carolina Lumbar Spine Fusion Surgery Notification
 , 2010 Don W. Bradley, M.D. Senior Vice President, Healthcare & Chief Medical Officer Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina 5901 Chapel Hill Road Durham, NC 27707 Subject: BlueCross BlueShield of
, 2010 Don W. Bradley, M.D. Senior Vice President, Healthcare & Chief Medical Officer Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina 5901 Chapel Hill Road Durham, NC 27707 Subject: BlueCross BlueShield of
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer. Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU
 Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants
 White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Chronic Low Back Pain. Do I have to see this patient?
 Chronic Low Back Pain. Do I have to see this patient? Wayne State University Update in Internal Medicine: Rahul Vaidya MD FRCSc Chief of Orthopedic Surgery Detroit Medical Center Professor of Orthopaedic
Chronic Low Back Pain. Do I have to see this patient? Wayne State University Update in Internal Medicine: Rahul Vaidya MD FRCSc Chief of Orthopedic Surgery Detroit Medical Center Professor of Orthopaedic
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine. Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Anatomy review Pathophysiology of degenerative disc disease Common sequelae of disk
Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Anatomy review Pathophysiology of degenerative disc disease Common sequelae of disk
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
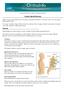 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy. Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883
 Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
There are four main regions of the back; the cervical (C), thoracic (T), lumbar (L), and sacral (S) regions
 Low Back Pain Overview Low back pain is one of the most common disorders in the United States. About 80 percent of people have at least one episode of low back pain during their lifetime. Factors that
Low Back Pain Overview Low back pain is one of the most common disorders in the United States. About 80 percent of people have at least one episode of low back pain during their lifetime. Factors that
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Materclass: Surgical management of lumbar spinal stenosis:
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Materclass: Surgical management of lumbar spinal stenosis: Presented By: Michelle Emsley Senior Spinal In-Patient Physiotherapist Learning objectives Indications Evidence Post operative
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Materclass: Surgical management of lumbar spinal stenosis: Presented By: Michelle Emsley Senior Spinal In-Patient Physiotherapist Learning objectives Indications Evidence Post operative
Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease
 Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A Member of Caregroup Harvard Medical School Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease Michael Barnett, HMS III Core Radiology Clerkship BIDMC PCE Overview Patient Presentation:
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A Member of Caregroup Harvard Medical School Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease Michael Barnett, HMS III Core Radiology Clerkship BIDMC PCE Overview Patient Presentation:
CONCOMITANT COMBINED DEGENERATIVE COMPRESSION OF THE SPINAL CORD AND CAUDA EQUINA: A REPORT ON THREE CASES
 CASE REPORT CONCOMITANT COMBINED DEGENERATIVE COMPRESSION OF THE SPINAL CORD AND CAUDA EQUINA: A REPORT ON THREE CASES Atanas Davarski 1, Ivo Kehayov 1, Tanya Kitova 2, Christo Zhelyazkov 1, Borislav Kitov
CASE REPORT CONCOMITANT COMBINED DEGENERATIVE COMPRESSION OF THE SPINAL CORD AND CAUDA EQUINA: A REPORT ON THREE CASES Atanas Davarski 1, Ivo Kehayov 1, Tanya Kitova 2, Christo Zhelyazkov 1, Borislav Kitov
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Cervical Spine Radiculopathy: Convervative Treatment. Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, MD Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Cervical Spine Radiculopathy: Convervative Treatment Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, MD Orthopaedic Surgeon Laboratory for the Research of the Musculoskeletal System, University of Athens & IASO General Hospital,
Cervical Spine Radiculopathy: Convervative Treatment Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, MD Orthopaedic Surgeon Laboratory for the Research of the Musculoskeletal System, University of Athens & IASO General Hospital,
Cervical Conditions: Diagnosis and Treatments
 Cervical Conditions: Diagnosis and Treatments Mark R Mikles, M.D. Cervical Conditions: Diagnosis and Treatment Cervical conditions Neck Pain Radiculopathy Myelopathy 1 Cervical Conditions: Diagnosis and
Cervical Conditions: Diagnosis and Treatments Mark R Mikles, M.D. Cervical Conditions: Diagnosis and Treatment Cervical conditions Neck Pain Radiculopathy Myelopathy 1 Cervical Conditions: Diagnosis and
POST SURGICAL RETURN OF RIGHT LEG PAIN. TREATED SUCCESSFULLY WITH COX FLEXION DISTRACTION DECOMPRESSION ADJUSTING
 POST SURGICAL RETURN OF RIGHT LEG PAIN. TREATED SUCCESSFULLY WITH COX FLEXION DISTRACTION DECOMPRESSION ADJUSTING A 47 year old white married female was seen for the chief complaint of low back and right
POST SURGICAL RETURN OF RIGHT LEG PAIN. TREATED SUCCESSFULLY WITH COX FLEXION DISTRACTION DECOMPRESSION ADJUSTING A 47 year old white married female was seen for the chief complaint of low back and right
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
Lower Back Pain. Introduction. Anatomy
 Lower Back Pain Introduction Back pain is the number one problem facing the workforce in the United States today. To illustrate just how big a problem low back pain is, consider these facts: Low back pain
Lower Back Pain Introduction Back pain is the number one problem facing the workforce in the United States today. To illustrate just how big a problem low back pain is, consider these facts: Low back pain
Balloon Kyphoplasty. Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures.
 Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
The Surgical Spine. Sergio Rivero M.D.
 The Surgical Spine Sergio Rivero M.D. Goals: Review Current literature in spinal surgery. To utilize evidence based medicine to treat spinal pathology. It is much more important to know what sort of a
The Surgical Spine Sergio Rivero M.D. Goals: Review Current literature in spinal surgery. To utilize evidence based medicine to treat spinal pathology. It is much more important to know what sort of a
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION. Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg
 NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg CONTENTS I. Incidence of L.B.P. II. Anatomy Review III. IV. Disc Degeneration, Bulge, and Herniation Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression 1. History
NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg CONTENTS I. Incidence of L.B.P. II. Anatomy Review III. IV. Disc Degeneration, Bulge, and Herniation Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression 1. History
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon
The Spine and Aging LOW BACK PAIN
 The Spine and Aging Disorders of the spine are extremely common as we age. Problems with the aging spine include spinal stenosis, disc herniation, spinal instability, fractures as a result of osteoporosis,
The Spine and Aging Disorders of the spine are extremely common as we age. Problems with the aging spine include spinal stenosis, disc herniation, spinal instability, fractures as a result of osteoporosis,
REVIEW DECISION. Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009
 REVIEW DECISION Re: Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009 Date: Review Officer: Lyall Zucko The worker requests a review of the decision of WorkSafeBC (the Board) dated
REVIEW DECISION Re: Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009 Date: Review Officer: Lyall Zucko The worker requests a review of the decision of WorkSafeBC (the Board) dated
Practice Guidelines For Low Back Pain
 Consumers Guide Practice Guidelines For Low Back Pain Copyright 2008 American Chronic Pain Association Page 1 Written by: Penney Cowan Founder Executive Director American Chronic Pain Association Editors:
Consumers Guide Practice Guidelines For Low Back Pain Copyright 2008 American Chronic Pain Association Page 1 Written by: Penney Cowan Founder Executive Director American Chronic Pain Association Editors:
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN
 MEDICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: 2015T0004W Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS COVERAGE RATIONALE APPLICABLE CODES..
MEDICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: 2015T0004W Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS COVERAGE RATIONALE APPLICABLE CODES..
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
Clinical Guideline. Low Back Pain Orthopaedics. Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department. 1 Purpose. 2 Background
 Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain. Seth Cheatham, MD
 Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain Seth Cheatham, MD 262 Seth A. Cheatham, MD VCU Sports Medicine I have no financial disclosures. Focus on clinical situations where a referral to an orthopaedic surgeon
Orthopaedic Approach to Back Pain Seth Cheatham, MD 262 Seth A. Cheatham, MD VCU Sports Medicine I have no financial disclosures. Focus on clinical situations where a referral to an orthopaedic surgeon
Lumbar Spine Stenosis: A Common Cause of Back and Leg Pain. Low back pain resulting from degenerative disease of the lumbosacral.
 Lumbar Spine Stenosis: A Common Cause of Back and Leg Pain Lumbar spine stenosis most commonly affects the middle-aged and elderly population. Entrapment of the cauda equina roots by hypertrophy of the
Lumbar Spine Stenosis: A Common Cause of Back and Leg Pain Lumbar spine stenosis most commonly affects the middle-aged and elderly population. Entrapment of the cauda equina roots by hypertrophy of the
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN. Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
https://www.laserspineinstitute.com/back_problems/foraminal_stenosis/e...
 Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery
 Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES SPONDYLOLISTHESIS AND SPONDYLOLYSIS
 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES SPONDYLOLISTHESIS AND SPONDYLOLYSIS MPC 01414 ICD-9 756.12; 738.41; 756.11 DEFINITION Spondylolisthesis is generally defined as an anterior or posterior slipping or displacement
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES SPONDYLOLISTHESIS AND SPONDYLOLYSIS MPC 01414 ICD-9 756.12; 738.41; 756.11 DEFINITION Spondylolisthesis is generally defined as an anterior or posterior slipping or displacement
Spine conditionsnew treatments. Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Spine conditionsnew treatments Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Certainties of life Death Taxes Back pain New Advances Minimal access surgery Indirect Lumbar decompression Dynamic
Spine conditionsnew treatments Ben Okafor FRCS FRCS.orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Certainties of life Death Taxes Back pain New Advances Minimal access surgery Indirect Lumbar decompression Dynamic
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Image-guided Spine Procedures for Relief of Severe Lower Back Pain:
 Image-guided Spine Procedures for Relief of Severe Lower Back Pain: A Guide to Epidural Steroid Injection, Facet Joint Injection, and Selective Nerve Root Block. PETER H TAKEYAMA MD HENRY WANG MD PhD SVEN
Image-guided Spine Procedures for Relief of Severe Lower Back Pain: A Guide to Epidural Steroid Injection, Facet Joint Injection, and Selective Nerve Root Block. PETER H TAKEYAMA MD HENRY WANG MD PhD SVEN
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion
 Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Page 1 of 42 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Revised April 2014 Number: 0743 Policy I. Aetna considers cervical laminectomy (and/or
Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Page 1 of 42 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Spinal Surgery: Laminectomy and Fusion Revised April 2014 Number: 0743 Policy I. Aetna considers cervical laminectomy (and/or
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, The Cervical Spine. What is the Cervical Spine?
 Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
Spine DJD Nomenclature. Sonia K Ghei, MD
 Spine DJD Nomenclature Sonia K Ghei, MD Recommendations of the Combined Task Forces of the North American Spine Society, American Society of Spine Radiology, and American Society of Neuroradiology http://www.asnr.org/spine_nomenclature/
Spine DJD Nomenclature Sonia K Ghei, MD Recommendations of the Combined Task Forces of the North American Spine Society, American Society of Spine Radiology, and American Society of Neuroradiology http://www.asnr.org/spine_nomenclature/
SPINE AND NECK SURGERY: MAKING A DECISION THAT S RIGHT FOR YOU
 1. GET THE FACTS: Back and neck pain affects 8 out of 10 people at some point in their life. Acute back and neck pain comes on suddenly and usually lasts from a few days to a few weeks. Chronic back and
1. GET THE FACTS: Back and neck pain affects 8 out of 10 people at some point in their life. Acute back and neck pain comes on suddenly and usually lasts from a few days to a few weeks. Chronic back and
Advanced Practice Provider Academy
 (+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
(+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN
 CLINICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: PAIN 019.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS..
CLINICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: PAIN 019.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS..
Sample Treatment Protocol
 Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Surgical Procedures and Clinical Results of Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Canal Stenosis
 Surgical Procedures and Clinical Results of Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Canal Stenosis Munehito Yoshida, Akitaka Ueyoshi, Kazuhiro Maio, Masaki Kawai, and Yukihiro Nakagawa Summary. The purpose
Surgical Procedures and Clinical Results of Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Canal Stenosis Munehito Yoshida, Akitaka Ueyoshi, Kazuhiro Maio, Masaki Kawai, and Yukihiro Nakagawa Summary. The purpose
AMA Guides 6 th Edition AADEP SPINE EXAMPLES
 AMA Guides 6 th Edition AADEP SPINE EXAMPLES 1 Questions? James B. Talmage MD, Occupational Health Center, 315 N. Washington Ave, Suite 165 Cookeville, TN 38501 Phone 931-526-1604 (Fax 526-7378) [email protected]
AMA Guides 6 th Edition AADEP SPINE EXAMPLES 1 Questions? James B. Talmage MD, Occupational Health Center, 315 N. Washington Ave, Suite 165 Cookeville, TN 38501 Phone 931-526-1604 (Fax 526-7378) [email protected]
Surgical Guideline for Lumbar Fusion (Arthrodesis)
 I. Introduction Surgical Guideline for Lumbar Fusion (Arthrodesis) The purpose of this guideline is: A. To provide utilization review staff with the information necessary to make recommendations about
I. Introduction Surgical Guideline for Lumbar Fusion (Arthrodesis) The purpose of this guideline is: A. To provide utilization review staff with the information necessary to make recommendations about
TWO CONTRASTING CASES OF SCIATIC RADICULOPATHY: ONE WITH NORMAL MRI AND ONE WITH A FREE FRAGMENT. WHAT S A CHIROPRACTOR TO DO?
 Cox Case Report #59 by Dr. James Cox published 4/08 1 TWO CONTRASTING CASES OF SCIATIC RADICULOPATHY: ONE WITH NORMAL MRI AND ONE WITH A FREE FRAGMENT. WHAT S A CHIROPRACTOR TO DO? A 26-year-old, white,
Cox Case Report #59 by Dr. James Cox published 4/08 1 TWO CONTRASTING CASES OF SCIATIC RADICULOPATHY: ONE WITH NORMAL MRI AND ONE WITH A FREE FRAGMENT. WHAT S A CHIROPRACTOR TO DO? A 26-year-old, white,
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
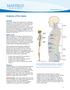 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Axial Loading during MR Imaging Can Influence Treatment Decision for Symptomatic Spinal Stenosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:170 174, February 2004 Axial Loading during MR Imaging Can Influence Treatment Decision for Symptomatic Spinal Stenosis Akio Hiwatashi, Barbro Danielson, Toshio Moritani, Robert
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:170 174, February 2004 Axial Loading during MR Imaging Can Influence Treatment Decision for Symptomatic Spinal Stenosis Akio Hiwatashi, Barbro Danielson, Toshio Moritani, Robert
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Review Article Minimal Invasive Decompression for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 645321, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/645321 Review Article Minimal Invasive Decompression for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Victor Popov 1 and David G. Anderson 1,
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 645321, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/645321 Review Article Minimal Invasive Decompression for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Victor Popov 1 and David G. Anderson 1,
Microdecompression on Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Surgery
 14 Classification of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis I- Congenital Idiopathic Achondroplasia Osteopetrosis II- Acquired Degenerative Central Lateral recess or foraminal Degenerative spondylolisthesis Idiopathic
14 Classification of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis I- Congenital Idiopathic Achondroplasia Osteopetrosis II- Acquired Degenerative Central Lateral recess or foraminal Degenerative spondylolisthesis Idiopathic
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
A review of spinal problems
 Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
Spinal Decompression
 Spinal Decompression Spinal decompression is just one more tool we have to treat radiculopathy. With appropriate education and exercises, this modality has been proven to assist in the resolution of symptoms
Spinal Decompression Spinal decompression is just one more tool we have to treat radiculopathy. With appropriate education and exercises, this modality has been proven to assist in the resolution of symptoms
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
