CMS Manual System Pub Medicare National Coverage Determinations
|
|
|
- Clarissa Wells
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMS Manual System Pub Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 21 Date: September 10, 2004 CHANGE REQUEST 3425 SUBJECT: Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for Diagnosing Brain Tumors I. SUMMARY OF CHANGES: Upon reconsideration of existing noncoverage policy, CMS determines that Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) used as a diagnostic tool for distinguishing indeterminate brain lesions and/or as an aid in conducting brain biopsies is not reasonable and necessary under section 1862(a)(1)(A) of the Social Security Act. Therefore, CMS reaffirms its existing noncoverage policy at section , of the National Coverage Determinations Manual (NCD) for all indications of MRS. In addition, sections 220.2, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and 220.3, Magnetic Resonance Angiography, are revised and reprinted with clerical/technical edits/clarifications. There are no substantive revisions and no changes to existing NCD policy. (This addition of of Pub is an NCD. The NCDs are binding on all carriers, fiscal intermediaries, quality improvement organizations, health maintenance organizations, competitive medical plans, and health care prepayment plans. Under 42 CFR (b), an NCD that expands coverage is also binding on Medicare Advantage Organizations. In addition, an administrative law judge may not review an NCD. (See 1869(f)(1)(A)(i) of the Social Security Act.) NEW/REVISED MATERIAL - EFFECTIVE DATE: 09/10/04 *IMPLEMENTATION DATE: 09/10/04 II. CHANGES IN MANUAL INSTRUCTIONS: (R = REVISED, N = NEW, D = DELETED) R/N/D CHAPTER/SECTION/SUBSECTION/TITLE R 1/Table of Contents R 1/220.2/Magnetic Resonance Imaging (See Effective Dates Below) N 1/ /Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (Effective September 10, 2004) R 1/220.3/Magnetic Resonance Angiography (See Effective Dates Below) *III. FUNDING: These instructions shall be implemented within your current operating budget. IV. ATTACHMENTS:
2 X Business Requirements X Manual Instruction Confidential Requirements One-Time Notification Recurring Update Notification *Medicare contractors only
3 Attachment - Business Requirements Pub Transmittal: Date: September 10, 2004 Change Request 3425 SUBJECT: Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for Diagnosing Brain Tumors I. GENERAL INFORMATION A. Background: Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) is an application of magnetic resonance imaging. It is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses strong magnetic fields to measure and analyze the chemical composition of human tissues. On March 22, 1994, CMS considered MRS an investigational procedure and issued a national noncoverage determination for all indications of MRS. B. Policy: Upon reconsideration of existing noncoverage policy, CMS determines that the evidence is not adequate to conclude that MRS used as a diagnostic tool for distinguishing indeterminate brain lesions and/or as an aid in conducting brain biopsies is reasonable and necessary under section 1862(a)(1)(A) of the Social Security Act. Therefore, CMS reaffirms its existing noncoverage policy at section of the NCD Manual for all indications of MRS. In addition, sections 220.2, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and 220.3, Magnetic Resonance Angiography, are revised and reprinted with clerical/technical edits/clarifications. There are no substantive revisions, and no changes to existing NCD policy. C. Provider Education: A Medlearn Matters provider education article related to this instruction will be available at shortly after the CR is released. You will receive notification of the article release via the established medlearn matters listserv. Contractors shall post this article, or a direct link to this article, on their Web site and include information about it in a listserv message within 1 week of the availability of the provider education article. In addition, the provider education article must be included in your next regularly scheduled bulletin. Contractors are free to supplement Medlearn Matters articles with localized information that would benefit their provider community in billing and administering the Medicare program correctly. II. BUSINESS REQUIREMENTS Shall" denotes a mandatory requirement "Should" denotes an optional requirement Requirement # Requirements Responsibility Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) used as a diagnostic tool for distinguishing indeterminate brain lesions is not considered a reasonable and necessary treatment and is not nationally covered by the Medicare program MRS used as an aid in conducting brain biopsies is not considered a reasonable and FIs and local Part B carriers FIs and local Part B carriers
4 necessary treatment and is not nationally covered by the Medicare program All other indications of MRS are not considered reasonable and necessary treatment and are not nationally covered by the Medicare program. FIs and local Part B carriers III. SUPPORTING INFORMATION AND POSSIBLE DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS A. Other Instructions: N/A X-Ref Requirement # Instructions B. Design Considerations: N/A X-Ref Requirement # Recommendation for Medicare System Requirements C. Interfaces: N/A D. Contractor Financial Reporting /Workload Impact: N/A E. Dependencies: N/A F. Testing Considerations: N/A IV. SCHEDULE, CONTACTS, AND FUNDING Effective Date: September 10, 2004 Implementation Date: September 10, 2004 Pre-Implementation Contact(s): Stuart Caplan, , Pat Brocato-Simons, These instructions shall be implemented within your current operating budget. Post-Implementation Contact(s): CMS ROs
5 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Manual Chapter 1 - Coverage Determinations Table of Contents (Rev.21, ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (See Effective Dates Below) Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (Effective September 10, 2004) Magnetic Resonance Angiography (See Effective Dates Below)
6 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (See Effective Dates Below) (Rev.21, Issued: , Effective: , Implementation: ) A. General 1. Method of Operation Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), formerly called nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), is a noninvasive method of graphically representing the distribution of water and other hydrogen-rich molecules in the human body. In contrast to conventional radiographs or computed tomography (CT) scans, in which the image is produced by x-ray beam attenuation by an object, MRI is capable of producing images by several techniques. In fact, various combinations of MRI production methods may be employed to emphasize particular characteristics of the tissue or body part being examined. The basic elements by which MRI produces an image are the density of hydrogen nuclei in the object being examined, their motion, the relaxation times, and the period of time required for the nuclei to return to their original states in the main, static magnetic field after being subjected to a brief additional magnetic field. These relaxation times reflect the physicalchemical properties of tissue and the molecular environment of its hydrogen nuclei. Only hydrogen atoms are present in human tissues in sufficient concentration for current use in clinical MRI. 2. General Clinical Utility Overall, MRI is a useful diagnostic imaging modality that is capable of demonstrating a wide variety of soft-tissue lesions with contrast resolution equal or superior to CT scanning in various parts of the body. Among the advantages of MRI are the absence of ionizing radiation and the ability to achieve high levels of tissue contrast resolution without injected iodinated radiological contrast agents. Recent advances in technology have resulted in development and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of new paramagnetic contrast agents for MRI that allow even better visualization in some instances. Multi-slice imaging and the ability to image in multiple planes, especially sagittal and coronal, have provided flexibility not easily available with other modalities. Because cortical (outer layer) bone and metallic prostheses do not cause distortion of MRI, it has been possible to visualize certain lesions and body regions with greater certainty than has been possible with CT. The use of MRI on certain soft tissue structures for the purpose of detecting disruptive, neoplastic, degenerative, or inflammatory lesions has now become established in medical practice. B. Nationally Covered Indications (Effective November 22, 1985) Although several uses of MRI are still considered investigational and some uses are clearly contraindicated, MRI is considered medically efficacious for a number of uses. Use the following descriptions as general guidelines or examples of what may be
7 considered covered rather than as a restrictive list of specific covered indications. Coverage is limited to MRI units that have FDA premarket approval, and such units must be operated within the parameters specified by the approval. In addition, the services must be reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of the specific patient involved. The MRI is useful in examining the head, central nervous system, and spine. Multiple sclerosis can be diagnosed with MRI and the contents of the posterior fossa are visible. The inherent tissue contrast resolution of MRI makes it an appropriate standard diagnostic modality for general neuroradiology. The MRI can assist in the differential diagnosis of mediastinal and retroperitoneal masses, including abnormalities of the large vessels such as aneurysms and dissection. When a clinical need exists to visualize the parenchyma of solid organs to detect anatomic disruption or neoplasia, this can be accomplished in the liver, urogenital system, adrenals, and pelvic organs without the use of radiological contrast materials. When MRI is considered reasonable and necessary, the use of paramagnetic contrast materials may be covered as part of the study. MRI may also be used to detect and stage pelvic and retroperitoneal neoplasms and to evaluate disorders of cancellous bone and soft tissues. It may also be used in the detection of pericardial thickening. Primary and secondary bone neoplasm and aseptic necrosis can be detected at an early stage and monitored with MRI. Patients with metallic prostheses, especially of the hip, can be imaged in order to detect the early stages of infection of the bone to which the prosthesis is attached. Disc Disease Diagnosis (Effective March 22, 1994) The MRI may also be covered to diagnose disc disease without regard to whether radiological imaging has been tried first to diagnose the problem. Gating Devices and Surface Coils (Effective March 4,1991) Gating devices that eliminate distorted images caused by cardiac and respiratory movement cycles are now considered state-of-the-art techniques and may be covered. Surface and other specialty coils may also be covered, as they are used routinely for high resolution imaging where small limited regions of the body are studied. They produce high signal-to-noise ratios resulting in images of enhanced anatomic detail. C. Contraindications and Nationally Noncovered Indications 1. Contraindications The MRI is not covered when the following patient-specific contraindications are present. It is not covered for patients with cardiac pacemakers or with metallic clips on vascular aneurysms. MRI during a viable pregnancy is also contraindicated at this time. The danger inherent in bringing ferromagnetic materials within range of MRI units generally
8 constrains the use of MRI on acutely ill patients requiring life support systems and monitoring devices that employ ferromagnetic materials. In addition, the long imaging time and the enclosed position of the patient may result in claustrophobia, making patients who have a history of claustrophobia unsuitable candidates for MRI procedures. 2. Nationally Noncovered Indications The CMS has determined that blood flow measurement, imaging of cortical bone and calcifications, and procedures involving spatial resolution of bone and calcifications, are not considered reasonable and necessary indications within the meaning of section 1862(a)(1)(A) of the Social Security Act, and are therefore noncovered. D. Other All other uses of MRI for which CMS has not specifically indicated coverage or noncoverage continue to be eligible for coverage through individual local contractor discretion. (This NCD last reviewed September 2004.) Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (Effective September 10, 2004) (Rev.21, Issued: , Effective: , Implementation: ) A. General Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) is an application of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses strong magnetic fields to measure and analyze the chemical composition of human tissues. On March 22, 1994, CMS considered MRS an investigational procedure and issued a national noncoverage determination for all indications of MRS. B. Nationally Covered Indications Not applicable. C. Nationally Noncovered Indications After thorough review and reconsideration of the existing national noncoverage determination for MRS, as well as the available evidence for the use of MRS as a diagnostic tool for distinguishing indeterminate brain lesions, and/or as an aid in conducting brain biopsies, CMS has determined that the evidence is not adequate to conclude that MRS is reasonable and necessary within the meaning of section 1862(a)(1)(A) of the Social Security Act, for use in the diagnosis of brain tumors.
9 Therefore, CMS reaffirms its current national noncoverage determination for all indications of MRS. D. Other Not applicable. (This NCD last reviewed September 2004.) Magnetic Resonance Angiography (See Effective Dates Below) (Rev.21, Issued: , Effective: , Implementation: ) A. General Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a non-invasive diagnostic test that is an application of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). By analyzing the amount of energy released from tissues exposed to a strong magnetic field, MRA provides images of normal and diseased blood vessels as well as visualization and quantification of blood flow through these vessels. Phase contrast (PC) and time-of-flight (TOF) are the available MRA techniques at the time these instructions are being issued. PC measures the difference between the phases of proton spins in tissue and blood and measures both the venous and arterial blood flow at any point in the cardiac cycle. TOF measures the difference between the amount of magnetization of tissue and blood and provides information on the structure of blood vessels, thus indirectly indicating blood flow. Two-dimensional (2D) and threedimensional (3D) images can be obtained using each method. Contrast-enhanced MRA (CE-MRA) involves blood flow imaging after the patient receives an intravenous injection of a contrast agent. Gadolinium, a non-ionic element, is the foundation of all contrast agents currently in use. Gadolinium affects the way in which tissues respond to magnetization, resulting in better visualization of structures when compared to un-enhanced studies. Unlike ionic (i.e., iodine-based) contrast agents used in conventional contrast angiography (CA), allergic reactions to gadolinium are extremely rare. Additionally, gadolinium does not cause the kidney failure occasionally seen with ionic contrast agents. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is a computeraugmented form of CA that obtains digital blood flow images as contrast agent courses through a blood vessel. The computer subtracts bone and other tissue from the image, thereby improving visualization of blood vessels. Physicians elect to use a specific MRA or CA technique based upon clinical information from each patient. In a National Coverage Analysis Decision Memorandum issued on April 15, 2003, CMS reviewed scientific and clinical literature on MRA, and set forth its basis for the
10 following coverage policy. Below are the only indications for which Medicare coverage is allowed for MRA. B. Nationally Covered Indications 1. Head and Neck Studies have proven that MRA is effective for evaluating flow in internal carotid vessels of the head and neck. However, not all potential applications of MRA have been shown to be reasonable and necessary. All of the following criteria must apply in order for Medicare to provide coverage for MRA of the head and neck: a. MRA is used to evaluate the carotid arteries, the circle of Willis, the anterior, middle or posterior cerebral arteries, the vertebral or basilar arteries or the venous sinuses; b. MRA is used to verify the need for anticipated surgery for conditions that include, but are not limited to, tumor, aneurysms, vascular malformations, vascular occlusion, or thrombosis. Within this broad category of disorders, medical necessity is the underlying determinant of the need for an MRA. Because MRA and CA perform the same diagnostic function, the medical records should clearly justify and demonstrate the existence of medical necessity; and c. MRA and contrast angiography (CA) are not expected to be performed on the same patient for diagnostic purposes prior to the application of anticipated therapy. Only one of these tests will be covered routinely unless the physician can demonstrate the medical need to perform both tests. 2. Peripheral Arteries of Lower Extremities Studies have proven that MRA of peripheral arteries is useful in determining the presence and extent of peripheral vascular disease in lower extremities. This procedure is noninvasive and has been shown to find occult vessels in some patients for which those vessels were not apparent when CA was performed. Medicare will cover either MRA or CA to evaluate peripheral arteries of the lower extremities. However, both MRA and CA may be useful is some cases, such as: a. A patient has had CA and this test was unable to identify a viable run-off vessel for bypass. When exploratory surgery is not believed to be a reasonable medical course of action for this patient, MRA may be performed to identify the viable runoff vessel; or b. A patient has had MRA, but the results are inconclusive. 3. Abdomen and Pelvis
11 a. Pre-operative Evaluation of Patients Undergoing Elective Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Repair (Effective July 1, 1999) The MRA is covered for pre-operative evaluation of patients undergoing elective AAA repair if the scientific evidence reveals MRA is considered comparable to CA in determining the extent of AAA, as well as in evaluating aortoiliac occlusion disease and renal artery pathology that may be necessary in the surgical planning of AAA repair. These studies also reveal that MRA could provide a net benefit to the patient. If preoperative CA is avoided, then patients are not exposed to the risks associated with invasive procedures, contrast media, end-organ damage, or arterial injury. b. Imaging the Renal Arteries and the Aortoiliac Arteries in the Absence of AAA or Aortic Dissection (Effective July 1, 2003) The MRA coverage is expanded to include imaging the renal arteries and the aortoiliac arteries in the absence of AAA or aortic dissection. MRA should be obtained in those circumstances in which using MRA is expected to avoid obtaining CA, when physician history, physical examination, and standard assessment tools provide insufficient information for patient management, and obtaining an MRA has a high probability of positively affecting patient management. However, CA may be ordered after obtaining the results of an MRA in those rare instances where medical necessity is demonstrated. 4. Chest a. Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism Current scientific data has shown that diagnostic pulmonary MRAs are improving due to recent developments such as faster imaging capabilities and gadolinium-enhancement. However, these advances in MRA are not significant enough to warrant replacement of pulmonary angiography in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism for patients who have no contraindication to receiving intravenous iodinated contrast material. Patients who are allergic to iodinated contrast material face a high risk of developing complications if they undergo pulmonary angiography or computed tomography angiography. Therefore, Medicare will cover MRA of the chest for diagnosing a suspected pulmonary embolism only when it is contraindicated for the patient to receive intravascular iodinated contrast material. b. Evaluation of Thoracic Aortic Dissection and Aneurysm Studies have shown that MRA of the chest has a high level of diagnostic accuracy for pre-operative and post-operative evaluation of aortic dissection of aneurysm. Depending on the clinical presentation, MRA is used as an alternative to other non-invasive imaging technologies, such as transesophageal echocardiography and CT. Generally, Medicare will provide coverage only for MRA or for CA when used as a diagnostic test. However, if both MRA and CA of the chest are used, the physician must demonstrate the medical need for performing these tests.
12 While the intent of this policy is to provide reimbursement for either MRA or CA, CMS is also allowing flexibility for physicians to make appropriate decisions concerning the use of these tests based on the needs of individual patients. CMS anticipates, however, low utilization of the combined use of MRA and CA. As a result, CMS encourages contractors to monitor the use of these tests and, where indicated, requires evidence of the need to perform both MRA and CA. C. Nationally Noncovered Indications All other uses of MRA for which CMS has not specifically indicated coverage continue to be noncovered. D. Other Not applicable. (This NCD last reviewed September 2004.)
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers
 2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers How can we subscribe to the Coding Clinic for ICD-9 guidelines and updates? The American Hospital Association publishes this quarterly newsletter.
2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers How can we subscribe to the Coding Clinic for ICD-9 guidelines and updates? The American Hospital Association publishes this quarterly newsletter.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
Imaging of Acute Stroke. Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group
 Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Diagnostic Imaging Prior Review Code List 3 rd Quarter 2016
 Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers
 CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
Table 11: Pros and Cons of 1.5 T MRI vs. 3.0 T MRI; Safety and Technical Issues, and Clinical Applications
 Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
The Lewin Group undertook the following steps to identify the guidelines relevant to the 11 targeted procedures:
 Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016
 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
Mississippi Medicaid. Provider Reference Guide. For Part 203. Physician Services
 Mississippi Medicaid Provider Reference Guide For Part 203 Physician Services This is a companion document to the Mississippi Administrative Code Title 23 and must be utilized as a reference only. January
Mississippi Medicaid Provider Reference Guide For Part 203 Physician Services This is a companion document to the Mississippi Administrative Code Title 23 and must be utilized as a reference only. January
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs for Chronic Heart Failure (20.10.1)
 National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs for Chronic Heart Failure (20.10.1) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.10.1 Manual Section
National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs for Chronic Heart Failure (20.10.1) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.10.1 Manual Section
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray)
 Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION. CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST
 CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST 70480 CT ORBIT W/O CONTRAST 70481 CT ORBIT W/ CONTRAST 70482
CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST 70480 CT ORBIT W/O CONTRAST 70481 CT ORBIT W/ CONTRAST 70482
76641 Ultrasound, breast, unilateral, real time with image documentation, including axilla when performed; complete 76642 limited
 2015 CPT Code Update The ACR, either alone or in conjunction with other specialty societies, worked on a number of code proposals for the 2015 code cycle. This update provides a listing of code changes
2015 CPT Code Update The ACR, either alone or in conjunction with other specialty societies, worked on a number of code proposals for the 2015 code cycle. This update provides a listing of code changes
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006. SUBJECT: Changes Conforming to CR3648 for Therapy Services
 CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006 Change
CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006 Change
RADIOLOGY 2014 CPT Codes
 RADIOLOGY 2014 CPT Codes Radiology 2014 CPT Codes CMS has issued 36 new procedure codes (one is a radiation therapy code) for CY 2014 that directly pertain to radiology with 26 of those codes the result
RADIOLOGY 2014 CPT Codes Radiology 2014 CPT Codes CMS has issued 36 new procedure codes (one is a radiation therapy code) for CY 2014 that directly pertain to radiology with 26 of those codes the result
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Medicare Part B. Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests
 Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests This article from Medicare B News Issue 223 dated October 21, 2005 is being updated and reprinted to ensure that the Noridian Administrative
Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests This article from Medicare B News Issue 223 dated October 21, 2005 is being updated and reprinted to ensure that the Noridian Administrative
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults
 CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
Computed Tomography (CT) - Body
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
MRI Ordering Guide: MRA/MRV TO SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT: CALL (860) 714-XRAY (714-9729) or FAX REQUISITION TO (860) 714-8002
 SAINT SAINT FRANCIS Hospital and Hospital Medical and Medical Center Center MRI Ordering Guide: MRA/MRV MRA Abdomen AAA (abdominal aortic aneurysm Dissection Mesenteric Ischemia MRA Abdomen With & Without
SAINT SAINT FRANCIS Hospital and Hospital Medical and Medical Center Center MRI Ordering Guide: MRA/MRV MRA Abdomen AAA (abdominal aortic aneurysm Dissection Mesenteric Ischemia MRA Abdomen With & Without
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
SUTTER MEDICAL CENTER, SACRAMENTO Department of Cardiovascular Disease Cardiology - Delineation of Privileges
 INITIAL: [ ] RENEWED: [ ] DATE: ADDITIONAL: [ ] Privileges are granted for Sutter General Hospital, Sutter Memorial Hospital, Sutter Center for Psychiatry, Sutter Oaks Midtown and the Capitol Pavilion
INITIAL: [ ] RENEWED: [ ] DATE: ADDITIONAL: [ ] Privileges are granted for Sutter General Hospital, Sutter Memorial Hospital, Sutter Center for Psychiatry, Sutter Oaks Midtown and the Capitol Pavilion
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA. Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005
 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
Procedure Codes. RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY
 Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
Local Coverage Article: Endovascular Repair of Aortic Aneurysms (A53124)
 Local Coverage Article: Endovascular Repair of Aortic Aneurysms (A53124) Contractor Information Contractor Name Novitas Solutions, Inc. Article Information General Information Article ID A53124 Original
Local Coverage Article: Endovascular Repair of Aortic Aneurysms (A53124) Contractor Information Contractor Name Novitas Solutions, Inc. Article Information General Information Article ID A53124 Original
Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006. SUBJECT: Bariatric Surgery for Treatment of Morbid Obesity
 CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006 Change
CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006 Change
Health Care Careers in the Field of Imaging. Shari Workman, MSM,PHR,CIR MultiCare Health System Senior Recruiter/Employment Specialist
 Health Care Careers in the Field of Imaging Shari Workman, MSM,PHR,CIR MultiCare Health System Senior Recruiter/Employment Specialist What is Health Care Imaging? Technologists working with patients, using
Health Care Careers in the Field of Imaging Shari Workman, MSM,PHR,CIR MultiCare Health System Senior Recruiter/Employment Specialist What is Health Care Imaging? Technologists working with patients, using
Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Basics of Skilled Nursing Facility Consolidated Billing (SNF-CB) Medicare Part A and B Presentation March 19, 2013
 Basics of Skilled Nursing Facility Consolidated Billing (SNF-CB) Medicare Part A and B Presentation March 19, 2013 2 Agenda Skilled Care Defined Background on SNF-CB Under Arrangements Inclusions and Exclusions
Basics of Skilled Nursing Facility Consolidated Billing (SNF-CB) Medicare Part A and B Presentation March 19, 2013 2 Agenda Skilled Care Defined Background on SNF-CB Under Arrangements Inclusions and Exclusions
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease)
 Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION
 CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION CINDY WEILAND AND SANDRA L. KATANICK Continued innovations in noninvasive testing equipment provide skilled sonographers and physicians with the technology
CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION CINDY WEILAND AND SANDRA L. KATANICK Continued innovations in noninvasive testing equipment provide skilled sonographers and physicians with the technology
NOVOSTE BETA-CATH SYSTEM
 HOSPITAL INPATIENT AND OUTPATIENT BILLING GUIDE FOR THE NOVOSTE BETA-CATH SYSTEM INTRAVASCULAR BRACHYTHERAPY DEVICE This guide is intended solely for use as a tool to help hospital billing staff resolve
HOSPITAL INPATIENT AND OUTPATIENT BILLING GUIDE FOR THE NOVOSTE BETA-CATH SYSTEM INTRAVASCULAR BRACHYTHERAPY DEVICE This guide is intended solely for use as a tool to help hospital billing staff resolve
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
CT scan. Useful information. Contents. This information is about CT scans. There are sections on
 CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
The Field. Radiologic technologists take x-rays and administer nonradioactive materials into patients' bloodstreams for diagnostic purposes.
 Radiologic Technologist Overview The Field - Specialty Areas - Preparation - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Radiologic technologists
Radiologic Technologist Overview The Field - Specialty Areas - Preparation - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Radiologic technologists
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Bon Secours St. Mary s Hospital School of Medical Imaging Course Descriptions by Semester 18 Month Program
 Bon Secours St. Mary s Hospital School of Medical Imaging Course Descriptions by Semester 18 Month Program First Semester RAD 1101 Patient Care, Ethics, Law and Diversity Credits This 16 week course prepares
Bon Secours St. Mary s Hospital School of Medical Imaging Course Descriptions by Semester 18 Month Program First Semester RAD 1101 Patient Care, Ethics, Law and Diversity Credits This 16 week course prepares
Group Critical Illness Insurance Provides lump-sum cash benefits that can help with daily expenses
 What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for A Plus Benefits
What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for A Plus Benefits
Radiologic Technology (RAD, CLE) courses are open only to Radiologic Technology majors.
 RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (A.A.S Degree) Director: Prof. Virginia Mishkin, M.S., R.T. (R) (M) (QM) A radiologic technologist is a skilled professional who provides a specialized health care service. This rewarding
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (A.A.S Degree) Director: Prof. Virginia Mishkin, M.S., R.T. (R) (M) (QM) A radiologic technologist is a skilled professional who provides a specialized health care service. This rewarding
The Medical Imaging Detective
 Solving Medical Mysteries with Imaging Richard S. Breiman, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging (Medical Imaging Detective) UCSF The Medical Imaging Detective Peering into the Patient to
Solving Medical Mysteries with Imaging Richard S. Breiman, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging (Medical Imaging Detective) UCSF The Medical Imaging Detective Peering into the Patient to
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
The ASA defines anesthesiology as the practice of medicine dealing with but not limited to:
 1570 Midway Pl. Menasha, WI 54952 920-720-1300 Procedure 1205- Anesthesia Lines of Business: All Purpose: This guideline describes Network Health s reimbursement of anesthesia services. Procedure: Anesthesia
1570 Midway Pl. Menasha, WI 54952 920-720-1300 Procedure 1205- Anesthesia Lines of Business: All Purpose: This guideline describes Network Health s reimbursement of anesthesia services. Procedure: Anesthesia
Purpose Members of the Department of Cardiology will provide cardiology services to patients of McLaren Greater Lansing.
 Purpose Members of the Department of Cardiology will provide cardiology services to patients of McLaren Greater Lansing. Qualifications To be eligible for core privileges in the Department of Cardiology,
Purpose Members of the Department of Cardiology will provide cardiology services to patients of McLaren Greater Lansing. Qualifications To be eligible for core privileges in the Department of Cardiology,
US Reimbursement Guide
 US Reimbursement Guide The information with this notice is general reimbursement information only. It is not legal advice, nor is it about how to code, complete or submit any particular claim for payment.
US Reimbursement Guide The information with this notice is general reimbursement information only. It is not legal advice, nor is it about how to code, complete or submit any particular claim for payment.
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology)
 STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
What is Radiology and Radiologic Technology?
 What is Radiology and Radiologic Technology? Note: Prospective CSI Radiologic Technology students are encouraged to print this document out and study it thoroughly before applying for admission to the
What is Radiology and Radiologic Technology? Note: Prospective CSI Radiologic Technology students are encouraged to print this document out and study it thoroughly before applying for admission to the
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
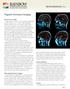 Magnetic Resonance Imaging What are the uses of MRI? To begin, not only are there a variety of scanning methodologies available, but there are also a variety of MRI methodologies available which provide
Magnetic Resonance Imaging What are the uses of MRI? To begin, not only are there a variety of scanning methodologies available, but there are also a variety of MRI methodologies available which provide
MRI EXAM CPT CODE REFERENCE
 I EXAM REFERENCE Use this reference to quickly determine the correct exam for your patients based on the indications described herein and the for the order. Creatine levels should be obtained prior to
I EXAM REFERENCE Use this reference to quickly determine the correct exam for your patients based on the indications described herein and the for the order. Creatine levels should be obtained prior to
CT Scan. CT Angiography, Neck, W/O Contrast Matl(s), Followed By Contrast Matl(s), W/Image
 CT Scan CPT 70450 CT Scan, Head/Brain; W/O Contrast Matl 70460 CT Scan, Head/Brain; W/Contrast Matl(s) 70470 CT Scan, Head/Brain; W/O Contrast Matl, Then W/Contrast Matl(s) 70480 CT Scan, Orbit/Sella/Posterior
CT Scan CPT 70450 CT Scan, Head/Brain; W/O Contrast Matl 70460 CT Scan, Head/Brain; W/Contrast Matl(s) 70470 CT Scan, Head/Brain; W/O Contrast Matl, Then W/Contrast Matl(s) 70480 CT Scan, Orbit/Sella/Posterior
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Topic 2. Physical bases of ID (1) Bases of ultrasonography. Ultrasound (US). The Doppler effect. Interventionist ultrasonography.
 SUBJECT GENERAL RADIOLOGY AND PHYSICAL MEDICINE CREDITS Total 6.5 Theory 3 Practical 3.5 GENERAL OBJECTIVES As part of the syllabus of the Faculty of Medicine, Radiology and Physical Medicine deals with
SUBJECT GENERAL RADIOLOGY AND PHYSICAL MEDICINE CREDITS Total 6.5 Theory 3 Practical 3.5 GENERAL OBJECTIVES As part of the syllabus of the Faculty of Medicine, Radiology and Physical Medicine deals with
Imaging Technology. Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist
 Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Letter of Intent. Radiologic Technician Program. AAS Degree in Radiologic Technology
 Letter of Intent Radiologic Technician Program AAS Degree in Radiologic Technology Office of the Provost and Department of Nursing Table of Contents 1. Purposes and goals 2. Need for the Curriculum 3.
Letter of Intent Radiologic Technician Program AAS Degree in Radiologic Technology Office of the Provost and Department of Nursing Table of Contents 1. Purposes and goals 2. Need for the Curriculum 3.
Patient Information Booklet. Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
 Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects
 Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects This document lists sample learning objectives by subject matter The numerical ranking in parenthesis following
Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects This document lists sample learning objectives by subject matter The numerical ranking in parenthesis following
European Academy of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology
 European Academy of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology Framework for Specialist Training in Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology Background The scope of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology DMFR (Dental and Maxillofacial
European Academy of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology Framework for Specialist Training in Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology Background The scope of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology DMFR (Dental and Maxillofacial
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in General Surgery
 Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in General Surgery 2010 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation of the
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in General Surgery 2010 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation of the
CT Angiography (CTA) What is CT Angiography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING SERVICES
 DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING SERVICES Policy NHP reimburses contracted providers for medically necessary diagnostic imaging services delivered in non-institutional settings such as an office or free-standing facility,
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING SERVICES Policy NHP reimburses contracted providers for medically necessary diagnostic imaging services delivered in non-institutional settings such as an office or free-standing facility,
RADIOLOGY HOUSE STAFF MANUAL
 RADIOLOGY HOUSE STAFF MANUAL The Department of Radiology offers a wide range of services/procedures and operates 12 divisions/sections, which are listed separately below. The procedures offered are listed
RADIOLOGY HOUSE STAFF MANUAL The Department of Radiology offers a wide range of services/procedures and operates 12 divisions/sections, which are listed separately below. The procedures offered are listed
American Heritage Life Insurance Company
 Policy GVAP1 pays the following benefits for covered on and off the job accidental injuries that result within 90 days (180 days for Accidental Death or Dismemberment) from the date of the accident. A
Policy GVAP1 pays the following benefits for covered on and off the job accidental injuries that result within 90 days (180 days for Accidental Death or Dismemberment) from the date of the accident. A
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts
 Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
First Year. PT7040- Clinical Skills and Examination II
 First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
Froedtert Hospital School of Radiology Curriculum Analysis Grid. Clinical Practice
 Professional Curriculum Clinical Practice Procedural Performance Clinical Competency Basic Principles of Digital Radiography Image Acquisition Image Acquisition Errors Fundamental Principles of Exposure
Professional Curriculum Clinical Practice Procedural Performance Clinical Competency Basic Principles of Digital Radiography Image Acquisition Image Acquisition Errors Fundamental Principles of Exposure
Embedded Systems in Healthcare. Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008
 Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Group Critical Illness Insurance Provides lump-sum cash benefits that can help with daily expenses
 What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for Catholic
What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for Catholic
ST. DAVID S MEDICAL CENTER CARDIOLOGY - Special, Invasive, Diagnostic, or High-Risk Procedure Requirements
 ST. DAVID S MEDICAL CENTER CARDIOLOGY - Special, Invasive, Diagnostic, or High-Risk Procedure Requirements Cardiac Catheterization & Peripheral Angiography Completion of a fellowship in Cardiovascular
ST. DAVID S MEDICAL CENTER CARDIOLOGY - Special, Invasive, Diagnostic, or High-Risk Procedure Requirements Cardiac Catheterization & Peripheral Angiography Completion of a fellowship in Cardiovascular
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program. 2010-2011 Assessment Report
 Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2010-2011 Assessment Report 1 I. Introduction II. III. IV. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2010-2011 Assessment Report 1 I. Introduction II. III. IV. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program
