Achievements in Public Health, : Fluoridation of Drinking Water to Prevent Dental Caries
|
|
|
- Clarissa Park
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Weekly October 22, 1999 /48(41); The content, links, and pdfs are no longer maintained and might be outdated. The content on this page is being archived for historic and reference purposes only. For current, updated information see the MMWR website. Achievements in Public Health, : Fluoridation of Drinking Water to Prevent Dental Caries Fluoridation of community drinking water is a major factor responsible for the decline in dental caries (tooth decay) during the second half of the 20th century. The history of water fluoridation is a classic example of clinical observation leading to epidemiologic investigation and communitybased public health intervention. Although other fluoride-containing products are available, water fluoridation remains the most equitable and cost-effective method of delivering fluoride to all members of most communities, regardless of age, educational attainment, or income level. Dental Caries Dental caries is an infectious, communicable, multifactorial disease in which bacteria dissolve the enamel surface of a tooth (1). Unchecked, the bacteria then may penetrate the underlying dentin and progress into the soft pulp tissue. Dental caries can result in loss of tooth structure and discomfort. Untreated caries can lead to incapacitating pain, a bacterial infection that leads to pulpal necrosis, tooth extraction and loss of dental function, and may progress to an acute systemic infection. The major etiologic factors for this disease are specific bacteria in dental plaque (particularly Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli) on susceptible tooth surfaces and the availability of fermentable carbohydrates. At the beginning of the 20th century, extensive dental caries was common in the United States and in most developed countries (2). No effective measures existed for preventing this disease, and the most frequent treatment was tooth extraction. Failure to meet the minimum standard of having six opposing teeth was a leading cause of rejection from military service in both world wars (3,4). Pioneering oral epidemiologists developed an index to measure the prevalence of dental caries using the number of decayed, missing, or filled teeth (DMFT) or decayed, missing, or filled tooth surfaces (DMFS) (5) rather than merely presence of dental caries, in part because nearly all persons in most age groups in the United States had evidence of the disease. Application of the DMFT index in epidemiologic surveys throughout the United States in the 1930s and 1940s allowed quantitative distinctions in dental caries experience among communities--an innovation that proved critical in identifying a preventive agent and evaluating its effects. 1/8
2 History of Water Fluoridation Soon after establishing his dental practice in Colorado Springs, Colorado, in 1901, Dr. Frederick S. McKay noted an unusual permanent stain or "mottled enamel" (termed "Colorado brown stain" by area residents) on the teeth of many of his patients (6). After years of personal field investigations, McKay concluded that an agent in the public water supply probably was responsible for mottled enamel. McKay also observed that teeth affected by this condition seemed less susceptible to dental caries (7). Dr. F. L. Robertson, a dentist in Bauxite, Arkansas, noted the presence of mottled enamel among children after a deep well was dug in 1909 to provide a local water supply. A hypothesis that something in the water was responsible for mottled enamel led local officials to abandon the well in In 1930, H. V. Churchill, a chemist with Aluminum Company of America, an aluminum manufacturing company that had bauxite mines in the town, used a newly available method of spectrographic analysis that identified high concentrations of fluoride (13.7 parts per million [ppm]) in the water of the abandoned well (8). Fluoride, the ion of the element fluorine, almost universally is found in soil and water but generally in very low concentrations (less than 1.0 ppm). On hearing of the new analytic method, McKay sent water samples to Churchill from areas where mottled enamel was endemic; these samples contained high levels of fluoride ( ppm). The identification of a possible etiologic agent for mottled enamel led to the establishment in 1931 of the Dental Hygiene Unit at the National Institute of Health headed by Dr. H. Trendley Dean. Dean's primary responsibility was to investigate the association between fluoride and mottled enamel (see box). Adopting the term "fluorosis" to replace "mottled enamel," Dean conducted extensive observational epidemiologic surveys and by 1942 had documented the prevalence of dental fluorosis for much of the United States (9). Dean developed the ordinally scaled Fluorosis Index to classify this condition. Very mild fluorosis was characterized by small, opaque "paper white" areas affecting less than or equal to 25% of the tooth surface; in mild fluorosis, 26%-50% of the tooth surface was affected. In moderate dental fluorosis, all enamel surfaces were involved and susceptible to frequent brown staining. Severe fluorosis was characterized by pitting of the enamel, widespread brown stains, and a "corroded" appearance (9). Dean compared the prevalence of fluorosis with data collected by others on dental caries prevalence among children in 26 states (as measured by DMFT) and noted a strong inverse relation (10). This cross-sectional relation was confirmed in a study of 21 cities in Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio (11). Caries among children was lower in cities with more fluoride in their community water supplies; at concentrations greater than 1.0 ppm, this association began to level off. At 1.0 ppm, the prevalence of dental fluorosis was low and mostly very mild. The hypothesis that dental caries could be prevented by adjusting the fluoride level of community water supplies from negligible levels to ppm was tested in a prospective field study conducted in four pairs of cities (intervention and control) starting in 1945: Grand Rapids and Muskegon, Michigan; Newburgh and Kingston, New York; Evanston and Oak Park, Illinois; and Brantford and Sarnia, Ontario, Canada. After conducting sequential cross-sectional surveys in these communities over years, caries was reduced 50%-70% among children in the communities with fluoridated water (12). The prevalence of dental fluorosis in the intervention communities was comparable with what had been observed in cities where drinking water contained natural fluoride at 1.0 ppm. Epidemiologic investigations of patterns of water consumption and caries experience across different climates and geographic regions in the United States led in 1962 to the development of a recommended optimum range of fluoride concentration of ppm, with the lower concentration recommended for warmer climates (where water 2/8
3 consumption was higher) and the higher concentration for colder climates (13). The effectiveness of community water fluoridation in preventing dental caries prompted rapid adoption of this public health measure in cities throughout the United States. As a result, dental caries declined precipitously during the second half of the 20th century. For example, the mean DMFT among persons aged 12 years in the United States declined 68%, from 4.0 in (14) to 1.3 in (CDC, unpublished data, 1999) (Figure 1). The American Dental Association, the American Medical Association, the World Health Organization, and other professional and scientific organizations quickly endorsed water fluoridation. Knowledge about the benefits of water fluoridation led to the development of other modalities for delivery of fluoride, such as toothpastes, gels, mouth rinses, tablets, and drops. Several countries in Europe and Latin America have added fluoride to table salt. Effectiveness of Water Fluoridation Early studies reported that caries reduction attributable to fluoridation ranged from 50% to 70%, but by the mid-1980s the mean DMFS scores in the permanent dentition of children who lived in communities with fluoridated water were only 18% lower than among those living in communities without fluoridated water (15). A review of studies on the effectiveness of water fluoridation conducted in the United States during found that caries reduction was 8%-37% among adolescents (mean: 26.5%) (16). Since the early days of community water fluoridation, the prevalence of dental caries has declined in both communities with and communities without fluoridated water in the United States. This trend has been attributed largely to the diffusion of fluoridated water to areas without fluoridated water through bottling and processing of foods and beverages in areas with fluoridated water and widespread use of fluoride toothpaste (17). Fluoride toothpaste is efficacious in preventing dental caries, but its effectiveness depends on frequency of use by persons or their caregivers. In contrast, water fluoridation reaches all residents of communities and generally is not dependent on individual behavior. Although early studies focused mostly on children, water fluoridation also is effective in preventing dental caries among adults. Fluoridation reduces enamel caries in adults by 20%-40% (16) and prevents caries on the exposed root surfaces of teeth, a condition that particularly affects older adults. Water fluoridation is especially beneficial for communities of low socioeconomic status (18). These communities have a disproportionate burden of dental caries and have less access than higher income communities to dental-care services and other sources of fluoride. Water fluoridation may help reduce such dental health disparities. Biologic Mechanism Fluoride's caries-preventive properties initially were attributed to changes in enamel during tooth development because of the association between fluoride and cosmetic changes in enamel and a belief that fluoride incorporated into enamel during tooth development would result in a more acidresistant mineral. However, laboratory and epidemiologic research suggests that fluoride prevents dental caries predominately after eruption of the tooth into the mouth, and its actions primarily are topical for both adults and children (1). These mechanisms include 1) inhibition of demineralization, 2) enhancement of remineralization, and 3) inhibition of bacterial activity in dental plaque (1). 3/8
4 Enamel and dentin are composed of mineral crystals (primarily calcium and phosphate) embedded in an organic protein/lipid matrix. Dental mineral is dissolved readily by acid produced by cariogenic bacteria when they metabolize fermentable carbohydrates. Fluoride present in solution at low levels, which becomes concentrated in dental plaque, can substantially inhibit dissolution of tooth mineral by acid. Fluoride enhances remineralization by adsorbing to the tooth surface and attracting calcium ions present in saliva. Fluoride also acts to bring the calcium and phosphate ions together and is included in the chemical reaction that takes place, producing a crystal surface that is much less soluble in acid than the original tooth mineral (1). Fluoride from topical sources such as fluoridated drinking water is taken up by cariogenic bacteria when they produce acid. Once inside the cells, fluoride interferes with enzyme activity of the bacteria and the control of intracellular ph. This reduces bacterial acid production, which directly reduces the dissolution rate of tooth mineral (19). Population Served by Water Fluoridation By the end of 1992, 10,567 public water systems serving 135 million persons in 8573 U.S. communities had instituted water fluoridation (20). Approximately 70% of all U.S. cities with populations of greater than 100,000 used fluoridated water. In addition, 3784 public water systems serving 10 million persons in 1924 communities had natural fluoride levels greater than or equal to 0.7 ppm. In total, 144 million persons in the United States (56% of the population) were receiving fluoridated water in 1992, including 62% of those served by public water systems. However, approximately 42,000 public water systems and 153 U.S. cities with populations greater than or equal to 50,000 have not instituted fluoridation. Cost Effectiveness and Cost Savings of Fluoridation Water fluoridation costs range from a mean of 31 cents per person per year in U.S. communities of greater than 50,000 persons to a mean of $2.12 per person in communities of less than 10,000 (1988 dollars) (21). Compared with other methods of community-based dental caries prevention, water fluoridation is the most cost effective for most areas of the United States in terms of cost per saved tooth surface (22). Water fluoridation reduces direct health-care expenditures through primary prevention of dental caries and avoidance of restorative care. Per capita cost savings from 1 year of fluoridation may range from negligible amounts among very small communities with very low incidence of caries to $53 among large communities with a high incidence of disease (CDC, unpublished data, 1999). One economic analysis estimated that prevention of dental caries, largely attributed to fluoridation and fluoride-containing products, saved $39 billion (1990 dollars) in dental-care expenditures in the United States during (23). Safety of Water Fluoridation Early investigations into the physiologic effects of fluoride in drinking water predated the first community field trials. Since 1950, opponents of water fluoridation have claimed it increased the risk for cancer, Down syndrome, heart disease, osteoporosis and bone fracture, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, low intelligence, Alzheimer disease, allergic reactions, and other health conditions (24). The safety and effectiveness of water fluoridation have been re-evaluated frequently, and no credible evidence supports an association between fluoridation and any of these 4/8
5 conditions (25). 21st Century Challenges Despite the substantial decline in the prevalence and severity of dental caries in the United States during the 20th century, this largely preventable disease is still common. National data indicate that 67% of persons aged years (26) and 94% of persons aged greater than or equal to 18 years (27) have experienced caries in their permanent teeth. Among the most striking results of water fluoridation is the change in public attitudes and expectations regarding dental health. Tooth loss is no longer considered inevitable, and increasingly adults in the United States are retaining most of their teeth for a lifetime (12). For example, the percentage of persons aged years who had lost all their permanent teeth decreased from 20.0% in (28) to 9.1% in (CDC, unpublished data, 1999). The oldest post-world War II "baby boomers" will reach age 60 years in the first decade of the 21st century, and more of that birth cohort will have a relatively intact dentition at that age than any generation in history. Thus, more teeth than ever will be at risk for caries among persons aged greater than or equal to 60 years. In the next century, water fluoridation will continue to help prevent caries among these older persons in the United States. Most persons in the United States support community water fluoridation (29). Although the proportion of the U.S. population drinking fluoridated water increased fairly quickly from 1945 into the 1970s, the rate of increase has been much lower in recent years. This slowing in the expansion of fluoridation is attributable to several factors: 1) the public, some scientists, and policymakers may perceive that dental caries is no longer a public health problem or that fluoridation is no longer necessary or effective; 2) adoption of water fluoridation can require political processes that make institution of this public health measure difficult; 3) opponents of water fluoridation often make unsubstantiated claims about adverse health effects of fluoridation in attempts to influence public opinion (24); and 4) many of the U.S. public water systems that are not fluoridated tend to serve small populations, which increases the per capita cost of fluoridation. These barriers present serious challenges to expanding fluoridation in the United States in the 21st century. To overcome the challenges facing this preventive measure, public health professionals at the national, state, and local level will need to enhance their promotion of fluoridation and commit the necessary resources for equipment, personnel, and training. Reported by Div of Oral Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, CDC. References 1. Featherstone JD. Prevention and reversal of dental caries: role of low level fluoride. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1999;27: Burt BA. Influences for change in the dental health status of populations: an historical perspective. J Public Health Dent 1978;38: Britten RH, Perrott GSJ. Summary of physical findings on men drafted in world war. Pub Health Rep 1941;56: Klein H. Dental status and dental needs of young adult males, rejectable, or acceptable for military service, according to Selective Service dental requirements. Pub Health Rep 1941; 56: Klein H, Palmer CE, Knutson JW. Studies on dental caries. I. Dental status and dental needs of elementary school children. Pub Health Rep 1938;53: /8
6 6. McKay FS, Black GV. An investigation of mottled teeth: an endemic developmental imperfection of the enamel of the teeth, heretofore unknown in the literature of dentistry. Dental Cosmos 1916;58: McKay FS. Relation of mottled enamel to caries. J Am Dent A 1928;15: Churchill HV. Occurrence of fluorides in some waters of the United States. J Ind Eng Chem 1931;23: Dean HT. The investigation of physiological effects by the epidemiological method. In: Moulton FR, ed. Fluorine and dental health. Washington, DC: American Association for the Advancement of Science 1942: Dean HT. Endemic fluorosis and its relation to dental caries. Public Health Rep 1938;53: Dean HT. On the epidemiology of fluorine and dental caries. In: Gies WJ, ed. Fluorine in dental public health. New York, New York: New York Institute of Clinical Oral Pathology, 1945: Burt BA, Eklund SA. Dentistry, dental practice, and the community. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: WB Saunders, Public Health Service. Public Health Service drinking water standards--revised Washington, DC: US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, PHS publication no National Center for Health Statistics. Decayed, missing, and filled teeth among youth years--united States. Rockville, Maryland: US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Health Resources Administration, Vital and health statistics, vol 11, no DHEW publication no. (HRA) Brunelle JA, Carlos JP. Recent trends in dental caries in US children and the effect of water fluoridation. J Dent Res 1990;69: Newbrun E. Effectiveness of water fluoridation. J Public Health Dent 1989;49: Horowitz HS. The effectiveness of community water fluoridation in the United States. J Public Health Dent 1996;56: Riley JC, Lennon MA, Ellwood RP. The effect of water fluoridation and social inequalities on dental caries in 5-year-old children. Int J Epidemiol 1999;28: Shellis RP, Duckworth RM. Studies on the cariostatic mechanisms of fluoride. Int Dent J 1994;44(3 suppl 1): CDC. Fluoridation census Atlanta, Georgia: US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, CDC, National Center for Prevention Services, Division of Oral Health, Ringelberg ML, Allen SJ, Brown LJ. Cost of fluoridation: 44 Florida communities. J Public Health Dent 1992;52: Burt BA, ed. Proceedings for the workshop: cost effectiveness of caries prevention in dental public health. J Public Health Dent 1989;49(5, special issue): Brown LJ, Beazoglou T, Heffley D. Estimated savings in U.S. dental expenditures, Public Health Rep 1994;109: Hodge HC. Evaluation of some objections to water fluoridation. In: Newbrun E, ed. Fluorides and dental caries. 3rd ed. Springfield, Illinois: Charles C. Thomas, 1986: National Research Council. Health effects of ingested fluoride. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, Kaste LM, Selwitz RH, Oldakowski RJ, Brunelle JA, Winn DM, Brown LJ. Coronal caries in the primary and permanent dentition of children and adolescents 1-17 years of age: United States, J Dent Res 1996;75: Winn DM, Brunelle JA, Selwitz RH, et al. Coronal and root caries in the dentition of adults in the United States, J Dent Res 1996;75: /8
7 28. National Center for Health Statistics. Decayed, missing, and filled teeth in adults--united States, Rockville, Maryland: US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Health Resources Administration, Vital and health statistics vol 11, no. 23. DHEW publication no. (HRA) American Dental Association Survey Center consumers' opinions regarding community water fluoridation. Chicago, Illinois: American Dental Association, Figure 1 Return to top. Disclaimer All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from ASCII text into HTML. This conversion may have resulted in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users should not rely on this HTML document, but are referred to the electronic PDF version and/or the original MMWR paper copy for the official text, figures, and tables. An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC ; telephone: (202) Contact GPO for current prices. 7/8
8 **Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to Page converted: 10/21/1999 HOME ABOUT MMWR MMWR SEARCH DOWNLOADS RSS CONTACT POLICY DISCLAIMER ACCESSIBILITY Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 1600 Clifton Rd, MailStop E-90, Atlanta, GA 30333, U.S.A Department of Health and Human Services This page last reviewed 5/2/01 8/8
Achievements in Public Health, 1900 1999
 October 22, 1999 / Vol. 48 / No. 41 933 Fluoridation of Drinking Water to Prevent Dental Caries 941 Progress Toward Poliomyelitis Eradication Nepal, 1996 1999 944 Update: West Nile Virus Encephalitis New
October 22, 1999 / Vol. 48 / No. 41 933 Fluoridation of Drinking Water to Prevent Dental Caries 941 Progress Toward Poliomyelitis Eradication Nepal, 1996 1999 944 Update: West Nile Virus Encephalitis New
3. Preventing bacteria from producing sufficient organic acid to demineralize tooth surface.
 FACT SHEET - Dental Health : Vol. 1 No. 4 January 1998 Fluoride Used for Dental Caries Prevention Piyada Prasertsom. DDS. MSc. Dental Health Division, Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Tel:
FACT SHEET - Dental Health : Vol. 1 No. 4 January 1998 Fluoride Used for Dental Caries Prevention Piyada Prasertsom. DDS. MSc. Dental Health Division, Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Tel:
Fluoride Products for Oral Health: Professional Information
 Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Drinking optimally fluoridated water is a safe, simple and effective way to help prevent and reduce tooth decay in the whole population.
 1 Water Fluoridation Water Fluoridation What is fluoride? Fluoride is a common natural element found in air, soil, fresh water, sea water, plants and lots of foods. It is known to have a protective effect
1 Water Fluoridation Water Fluoridation What is fluoride? Fluoride is a common natural element found in air, soil, fresh water, sea water, plants and lots of foods. It is known to have a protective effect
Introduction. Review of the Literature
 Source: Journal of Dental Hygiene, Vol. 82, No. 1, January 2008 Relationship of Naturally Occurring Fluoride in Carroll County, Maryland to Aquifers,Well Depths, and Fluoride Supplementation Prescribing
Source: Journal of Dental Hygiene, Vol. 82, No. 1, January 2008 Relationship of Naturally Occurring Fluoride in Carroll County, Maryland to Aquifers,Well Depths, and Fluoride Supplementation Prescribing
DEDICATION ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ABOUT FLUORIDATION FACTS
 Fluoridation Facts DEDICATION This 2005 edition of Fluoridation Facts is dedicated to Dr. Herschel Horowitz, talented researcher, renowned dental epidemiologist and tireless advocate of community water
Fluoridation Facts DEDICATION This 2005 edition of Fluoridation Facts is dedicated to Dr. Herschel Horowitz, talented researcher, renowned dental epidemiologist and tireless advocate of community water
Policy Statement. Fluoridation of Public Drinking Water. Updated 04 June 2014. I. Introduction
 Policy Statement Fluoridation of Public Drinking Water Updated 04 June 2014 I. Introduction Communities throughout the United States have utilized the fluoridation of drinking water supplies for over 60
Policy Statement Fluoridation of Public Drinking Water Updated 04 June 2014 I. Introduction Communities throughout the United States have utilized the fluoridation of drinking water supplies for over 60
WATER FLUORIDATION QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 WATER FLUORIDATION QUESTIONS & ANSWERS April 2012 1 Acknowledgement I would like to acknowledge and extend my heartfelt gratitude to the many individuals who have supported this project and made valuable
WATER FLUORIDATION QUESTIONS & ANSWERS April 2012 1 Acknowledgement I would like to acknowledge and extend my heartfelt gratitude to the many individuals who have supported this project and made valuable
STATISTICAL BRIEF #117
 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey STATISTICAL BRIEF #117 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality March 2006 Children s Dental Visits and Expenses, United States, 2003 Erwin Brown, Jr. Introduction Regular
Medical Expenditure Panel Survey STATISTICAL BRIEF #117 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality March 2006 Children s Dental Visits and Expenses, United States, 2003 Erwin Brown, Jr. Introduction Regular
DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY
 DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY S. К. Matelo, Т. V. Kupets Dental fluorosis is attributed to the group of non-carious diseases of type one, in other words to a
DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY S. К. Matelo, Т. V. Kupets Dental fluorosis is attributed to the group of non-carious diseases of type one, in other words to a
First Dental Visit by Age One
 CONTINUING EDUCATION August 2004 First Dental Visit by Age One A guide to the new recommendations Recommended by American Dental Association American Academy of Pediatrics American Academy of Pediatric
CONTINUING EDUCATION August 2004 First Dental Visit by Age One A guide to the new recommendations Recommended by American Dental Association American Academy of Pediatrics American Academy of Pediatric
CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry
 CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry CAMBRA stands for "CAries Management By Risk Assessment" and should be your standard for treating patients. In simple terms, here's why. By Drs. Douglas A. Young,
CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry CAMBRA stands for "CAries Management By Risk Assessment" and should be your standard for treating patients. In simple terms, here's why. By Drs. Douglas A. Young,
Fluoride. Introduction
 Fluoride Introduction Most fluoride in the body is found in bones and teeth, due to its high affinity for calcium and calcium phosphate. Ingestion of and topical treatment with fluoride is effective in
Fluoride Introduction Most fluoride in the body is found in bones and teeth, due to its high affinity for calcium and calcium phosphate. Ingestion of and topical treatment with fluoride is effective in
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS. brought to you by:
 CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
Alberta Health, Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health
 lberta Health, Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Notice to the reader on Review of Water Fluoridation October 1, 2010 November 7, 2014 November 7, 2014 Notice to the reader Re: Review of Water
lberta Health, Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Notice to the reader on Review of Water Fluoridation October 1, 2010 November 7, 2014 November 7, 2014 Notice to the reader Re: Review of Water
FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH
 FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH The purpose of this monograph is to improve the oral health and overall pediatric health of children, birth to 5 years old, including those with disabilities
FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH The purpose of this monograph is to improve the oral health and overall pediatric health of children, birth to 5 years old, including those with disabilities
Maintaining good dental health among children in the United
 133 CHILD INDICATORS Child Indicators: Dental Health Eugene M. Lewit Nancy Kerrebrock Maintaining good dental health among children in the United States today should be easy: regular tooth brushing, flossing,
133 CHILD INDICATORS Child Indicators: Dental Health Eugene M. Lewit Nancy Kerrebrock Maintaining good dental health among children in the United States today should be easy: regular tooth brushing, flossing,
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology
 Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
Water Fluoridation- All you need to know...
 Water Fluoridation- All you need to know... Dental decay is the most common chronic disease in children, affecting 5-8 times as many children than asthma (1). The use of water fluoridation for the prevention
Water Fluoridation- All you need to know... Dental decay is the most common chronic disease in children, affecting 5-8 times as many children than asthma (1). The use of water fluoridation for the prevention
WHY MASS MEDICATION WITH FLUORIDE MUST STOP NOW! Alliance for Natural Health International Position Paper September 2012
 ANH International The Atrium, Curtis Road Dorking, Surrey RH4 1XA United Kingdom e: info@anhinternational.org t: +44 (0)1306 646 600 f: +44 (0)1306 646 552 www.anhinternational.org ANH-Intl Regional Offices
ANH International The Atrium, Curtis Road Dorking, Surrey RH4 1XA United Kingdom e: info@anhinternational.org t: +44 (0)1306 646 600 f: +44 (0)1306 646 552 www.anhinternational.org ANH-Intl Regional Offices
Oral Health QUESTIONS
 Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current
Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current
Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample of Children Ages 6-8
 Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample of Children Ages 6-8 Area of Technology and Health Services Delivery Health Services Organization Regional Oral Health Program July 2004 Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample
Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample of Children Ages 6-8 Area of Technology and Health Services Delivery Health Services Organization Regional Oral Health Program July 2004 Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample
COMMUNITY WATER FLUORIDATION IN AMERICA: DENTAL BENEFITS AND SAFETY
 COMMUNITY WATER FLUORIDATION IN AMERICA: DENTAL BENEFITS AND SAFETY Michael W. Easley, D.D.S., M.P.H., Associate Professor Department of Oral Biology; School of Dental Medicine State University of New
COMMUNITY WATER FLUORIDATION IN AMERICA: DENTAL BENEFITS AND SAFETY Michael W. Easley, D.D.S., M.P.H., Associate Professor Department of Oral Biology; School of Dental Medicine State University of New
Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children. we design therapies to treat or remineralize early carious lesions?
 Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children Dr. Stephen H. Abrams Dental caries is the most common oral disease we treat in paediatric dentistry. We place restorations to
Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children Dr. Stephen H. Abrams Dental caries is the most common oral disease we treat in paediatric dentistry. We place restorations to
Oral Health Risk Assessment
 Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
Evidence Review: Dental Health Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health
 Evidence Review: Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health March 2014 (update from September 2006) This is a review of evidence and best practice that should be seen as a guide to understanding
Evidence Review: Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health March 2014 (update from September 2006) This is a review of evidence and best practice that should be seen as a guide to understanding
REPORT OF THE FORT COLLINS FLUORIDE TECHNICAL STUDY GROUP
 REPORT OF THE FORT COLLINS FLUORIDE TECHNICAL STUDY GROUP April 2003 The following agencies collaborated on the Fort Collins Fluoride Technical Study Group Process: Fort Collins Utility Department Health
REPORT OF THE FORT COLLINS FLUORIDE TECHNICAL STUDY GROUP April 2003 The following agencies collaborated on the Fort Collins Fluoride Technical Study Group Process: Fort Collins Utility Department Health
Fluoridation Position Statement
 Fluoridation Position Statement Part B of the Oral Health Strategy relates to a separate document on a detailed Oral Health Strategy for the CDHB 1 PART A Fluoridation position statement 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Fluoridation Position Statement Part B of the Oral Health Strategy relates to a separate document on a detailed Oral Health Strategy for the CDHB 1 PART A Fluoridation position statement 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Achievements in Public Health, 1900 1999
 October 22, / Vol. 48 / No. 41 933 Fluoridation of Drinking Water to Prevent Dental Caries 941 Progress Toward Poliomyelitis Eradication Nepal, 1996 944 Update: West Nile Virus Encephalitis New York, 955
October 22, / Vol. 48 / No. 41 933 Fluoridation of Drinking Water to Prevent Dental Caries 941 Progress Toward Poliomyelitis Eradication Nepal, 1996 944 Update: West Nile Virus Encephalitis New York, 955
BENEFITS AND RISKS OF WATER FLUORIDATION
 BENEFITS AND RISKS OF WATER FLUORIDATION An Update of the 1996 Federal-Provincial Sub-committee Report Prepared under contract for: Public Health Branch, Ontario Ministry of Health First Nations and Inuit
BENEFITS AND RISKS OF WATER FLUORIDATION An Update of the 1996 Federal-Provincial Sub-committee Report Prepared under contract for: Public Health Branch, Ontario Ministry of Health First Nations and Inuit
Water Fluoridation: A briefing on the York University Systematic Review and Subsequent Research Developments
 Water Fluoridation: A briefing on the York University Systematic Review and Subsequent Research Developments The York University Systematic Review 1. This systematic review, subsequently referred to as
Water Fluoridation: A briefing on the York University Systematic Review and Subsequent Research Developments The York University Systematic Review 1. This systematic review, subsequently referred to as
The Chococeutical way of Life. He lthy Teeth. Xylitol tooth re-mineralization chocolates
 The Chococeutical way of Life He lthy Teeth Xylitol tooth re-mineralization chocolates Xyl ceuticals approach to Preventive Dentistry The Problem The new Approach For many years, Preventive Dentistry has
The Chococeutical way of Life He lthy Teeth Xylitol tooth re-mineralization chocolates Xyl ceuticals approach to Preventive Dentistry The Problem The new Approach For many years, Preventive Dentistry has
School-Based Oral Health Care. A Choice for Michigan Children.indd 1
 School-Based Oral Health Care A Choice for Michigan Children School Based Oral Health Care: A Choice for Michigan Children is part of an information set meant to serve as a guideline for school personnel
School-Based Oral Health Care A Choice for Michigan Children School Based Oral Health Care: A Choice for Michigan Children is part of an information set meant to serve as a guideline for school personnel
Dental Public Health Activity Descriptive Report
 Dental Public Health Activity Descriptive Report Practice Number: 24002 Submitted By: Office of Oral Health, Massachusetts Department of Public Health Submission Date: January 2002 Last Updated: January
Dental Public Health Activity Descriptive Report Practice Number: 24002 Submitted By: Office of Oral Health, Massachusetts Department of Public Health Submission Date: January 2002 Last Updated: January
Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows
 Issue Brief PROJECT Children s NAME Dental Campaign Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows Dental decay remains the most common chronic childhood disease in the United States. 1 More
Issue Brief PROJECT Children s NAME Dental Campaign Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows Dental decay remains the most common chronic childhood disease in the United States. 1 More
Health Priority: Access to Primary and Preventive Health Services Objective 4: Access to Oral Health Services
 Health Priority: Access to Primary and Preventive Health Services Objective 4: Access to Oral Health Services Long Term (2010) Subcommittee Outcome Objective: By 2010, increase by 10 percentage points
Health Priority: Access to Primary and Preventive Health Services Objective 4: Access to Oral Health Services Long Term (2010) Subcommittee Outcome Objective: By 2010, increase by 10 percentage points
Submission: REF Fluoridation Plants Including the Ballina Shire Council Marom Creek Supply
 4 th February 2010 Attn: The General Manager Rous Water water@rouswater.nsw.gov.au Submission prepared by Jo Immig NTN Coordinator Submission: REF Fluoridation Plants Including the Ballina Shire Council
4 th February 2010 Attn: The General Manager Rous Water water@rouswater.nsw.gov.au Submission prepared by Jo Immig NTN Coordinator Submission: REF Fluoridation Plants Including the Ballina Shire Council
Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians
 Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians Approved CDA Board of Directors May 2010 Preamble A daily regimen of brushing and flossing is an important part of good oral health while equitable
Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians Approved CDA Board of Directors May 2010 Preamble A daily regimen of brushing and flossing is an important part of good oral health while equitable
Dental Health Services in Canada
 Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
America s Oral Health
 a me r i c a s Most Trusted D e n t a l l P a n America s Oral Health The Role of Dental Benefits Compiled and published by Delta Dental Plans Association, this report cites data from a number of industry
a me r i c a s Most Trusted D e n t a l l P a n America s Oral Health The Role of Dental Benefits Compiled and published by Delta Dental Plans Association, this report cites data from a number of industry
Oral Health Program. Strategic Plan. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 Oral Health Program Strategic Plan 2011 2014 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Chronic
Oral Health Program Strategic Plan 2011 2014 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Chronic
U.S. Public Health Service Recommendation for Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water for the Prevention of Dental Caries
 Reports and Recommendations U.S. Public Health Service Recommendation for Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water for the Prevention of Dental Caries U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Federal
Reports and Recommendations U.S. Public Health Service Recommendation for Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water for the Prevention of Dental Caries U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Federal
Role of Dental Public Health Professionals in Community Alliances
 Role of Dental Public Health Professionals in Community Alliances Michael Garrett, DDS Through a community-based health assessment and planning process, oral health was noted to be a significant concern
Role of Dental Public Health Professionals in Community Alliances Michael Garrett, DDS Through a community-based health assessment and planning process, oral health was noted to be a significant concern
Vermont Oral Health Plan 2014
 Vermont Oral Health Plan 2014 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION TO VERMONT ORAL HEALTH PLAN 2013... 3 THE BURDEN OF ORAL DISEASE IN VERMONT... 6 Children... 6 Adults... 8 Older Adults... 10 Disparities...
Vermont Oral Health Plan 2014 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION TO VERMONT ORAL HEALTH PLAN 2013... 3 THE BURDEN OF ORAL DISEASE IN VERMONT... 6 Children... 6 Adults... 8 Older Adults... 10 Disparities...
Determiniation of Flouride Ion in Well Waters of Eastwood School District, Wood, County, Ohio
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 85, Issue 5 (December, 185) 185-12 Determiniation of Flouride Ion in
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 85, Issue 5 (December, 185) 185-12 Determiniation of Flouride Ion in
AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
Oral health care is vital for seniors
 Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Review of Fluoridation and Regulation Issues
 Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Review of Fluoridation and Regulation Issues Mary Tiemann Specialist in Environmental Policy January 3, 2011 Congressional Research Service CRS Report for Congress Prepared
Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Review of Fluoridation and Regulation Issues Mary Tiemann Specialist in Environmental Policy January 3, 2011 Congressional Research Service CRS Report for Congress Prepared
SAMPLE DENTAL SEALANT AGENCY PROTOCOL
 SAMPLE DENTAL SEALANT AGENCY PROTOCOL Wisconsin Department of Health and Family Services Division of Public Health April 25, 2005 Table of Contents I. Sample Dental Sealant Policy...3 II. III. IV. Sample
SAMPLE DENTAL SEALANT AGENCY PROTOCOL Wisconsin Department of Health and Family Services Division of Public Health April 25, 2005 Table of Contents I. Sample Dental Sealant Policy...3 II. III. IV. Sample
Ohio Public Health Association
 Ohio Public Health Association Dental Care Access: A Public Health Issue April 17 th, 2014 Presented by: Audia Ellis, MSN, RN, FNP BC audiaellis@yahoo.com Objectives Evaluate the current state of dental
Ohio Public Health Association Dental Care Access: A Public Health Issue April 17 th, 2014 Presented by: Audia Ellis, MSN, RN, FNP BC audiaellis@yahoo.com Objectives Evaluate the current state of dental
Healthy People (HP) 2010
 The military oral health care system as a model for eliminating disparities in oral health Jeffrey J. Hyman, DDS, PhD; Britt C. Reid, DDS, PhD; Susan W. Mongeau, DDS, MPH; Andrew K. York, DMD, MPH Healthy
The military oral health care system as a model for eliminating disparities in oral health Jeffrey J. Hyman, DDS, PhD; Britt C. Reid, DDS, PhD; Susan W. Mongeau, DDS, MPH; Andrew K. York, DMD, MPH Healthy
Water Fluoridation and Public Health
 Water Fluoridation and Public Health FACULTY OF PUBLIC HEALTH MEDICINE ROYAL COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS OF IRELAND Dr. M. O Connor Dr. P. Fitzpatrick Dr. H. Johnson Dr. L. Thornton October 1999 CONTENTS Preface
Water Fluoridation and Public Health FACULTY OF PUBLIC HEALTH MEDICINE ROYAL COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS OF IRELAND Dr. M. O Connor Dr. P. Fitzpatrick Dr. H. Johnson Dr. L. Thornton October 1999 CONTENTS Preface
Fluoride Strengthens Teeth
 Fluoride Strengthens Teeth Two hard-boiled eggs Fluoride gel or solution, 4 to 6 oz. (from dental office) Three clean plastic containers Several cans of dark soda Water 1. Place a hard-boiled egg in one
Fluoride Strengthens Teeth Two hard-boiled eggs Fluoride gel or solution, 4 to 6 oz. (from dental office) Three clean plastic containers Several cans of dark soda Water 1. Place a hard-boiled egg in one
The Oral Health of Older Americans
 CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION National Center for Health Statistics March 2001 Aging Trends No. 3 The Oral Health of Older Americans The Aging Trends series was developed with support from
CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION National Center for Health Statistics March 2001 Aging Trends No. 3 The Oral Health of Older Americans The Aging Trends series was developed with support from
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme
 The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
State of Mississippi. Oral Health Plan
 State of Mississippi Oral Health Plan 2006 2010 Vision Statement: We envision a Mississippi where every child enjoys optimal oral health; where prevention and health education are emphasized and treatment
State of Mississippi Oral Health Plan 2006 2010 Vision Statement: We envision a Mississippi where every child enjoys optimal oral health; where prevention and health education are emphasized and treatment
Adult oral health and dental visiting in Australia
 Adult oral health and dental visiting in Australia Results from the National Dental Telephone Interview Survey 2010 JE Harford and S Islam Dental statistics and research series No. 65 DENTAL STATISTICS
Adult oral health and dental visiting in Australia Results from the National Dental Telephone Interview Survey 2010 JE Harford and S Islam Dental statistics and research series No. 65 DENTAL STATISTICS
Natural fluoride Content of Drinking Water in Two District Areas in Iraq and Yemen (A comparative study).
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Natural fluoride Content of Drinking Water in Two District Areas in Iraq and Yemen (A comparative study). Faraed D Salman BDS, MSc (Assis Prof) May Gh Al Ajrab BDS, MSc (Assist Lect) Dept
ISSN: 1812 1217 Natural fluoride Content of Drinking Water in Two District Areas in Iraq and Yemen (A comparative study). Faraed D Salman BDS, MSc (Assis Prof) May Gh Al Ajrab BDS, MSc (Assist Lect) Dept
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements
 Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Dental Disparities and Access to Fluoridation in Massachusetts
 Dental Disparities and Access to Fluoridation in Massachusetts Background Percentage of ages 17 and under living in poverty Disparities in oral health exist for the children of Massachusetts 1 and for
Dental Disparities and Access to Fluoridation in Massachusetts Background Percentage of ages 17 and under living in poverty Disparities in oral health exist for the children of Massachusetts 1 and for
Oral health in Iran. Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran
 International Dental Journal (2004) 54, 367 372 Oral health in Iran Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran The health network in the Islamic Republic (I.R.) of Iran is an integrated public health system with
International Dental Journal (2004) 54, 367 372 Oral health in Iran Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran The health network in the Islamic Republic (I.R.) of Iran is an integrated public health system with
dental fillings facts About the brochure:
 dental fillings facts About the brochure: Your dentist is dedicated to protecting and improving oral health while providing safe dental treatment. This fact sheet provides information you need to discuss
dental fillings facts About the brochure: Your dentist is dedicated to protecting and improving oral health while providing safe dental treatment. This fact sheet provides information you need to discuss
State Program Title: Public Health Dental Program. State Program Strategy:
 State Program Title: Public Health Dental Program State Program Strategy: The Public Health Dental Program provides policy direction for oral health issues to promote the development of cost-effective
State Program Title: Public Health Dental Program State Program Strategy: The Public Health Dental Program provides policy direction for oral health issues to promote the development of cost-effective
Promoting Oral Health
 Promoting Oral Health Oral diseases are among the most prevalent health problems in the United States. The 198 Surgeon General's Report to the Nation listed dental disease as a critical health problem
Promoting Oral Health Oral diseases are among the most prevalent health problems in the United States. The 198 Surgeon General's Report to the Nation listed dental disease as a critical health problem
Tooth Decay. What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth.
 Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Non-carious dental conditions
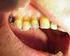 Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children.
 An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children. Principal Investigator: Kristin Gebhard, MSIV Selective Advisor: Bruce Bernstein, Ph.D. Abstract:
An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children. Principal Investigator: Kristin Gebhard, MSIV Selective Advisor: Bruce Bernstein, Ph.D. Abstract:
INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH
 INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH Infant Oral Health Material Developed by: J. Douglass BDS, DDS H. Silk MD A. Douglass MD of the University of Connecticut in cooperation with Connecticut
INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH Infant Oral Health Material Developed by: J. Douglass BDS, DDS H. Silk MD A. Douglass MD of the University of Connecticut in cooperation with Connecticut
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses. Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH. National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012
 Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
How To Prevent Dental Caries
 This report may be used, in whole or in part, as the basis for development of clinical practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, or a basis for reimbursement and coverage policies. AHRQ
This report may be used, in whole or in part, as the basis for development of clinical practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, or a basis for reimbursement and coverage policies. AHRQ
Oral health and dental care in Australia
 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia: Key facts
Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia: Key facts
Despite substantial improvements in oral health
 Articles Recommendations on Selected Interventions to Prevent Dental Caries, Oral and Pharyngeal Cancers, and Sports-Related Craniofacial Injuries Task Force on Community Preventive Services Medical Subject
Articles Recommendations on Selected Interventions to Prevent Dental Caries, Oral and Pharyngeal Cancers, and Sports-Related Craniofacial Injuries Task Force on Community Preventive Services Medical Subject
FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS
 1 FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS Smiles for Life A National Oral Health Curriculum Society of Teachers of Family Medicine Group on Oral Health SMILES FOR LIFE is a comprehensive oral health
1 FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS Smiles for Life A National Oral Health Curriculum Society of Teachers of Family Medicine Group on Oral Health SMILES FOR LIFE is a comprehensive oral health
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients
 Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
The Role of Physicians in Children s Oral Health
 In This Monitor: Preventive Oral Health, Primary Care, Children s Coverage December 2008 The Role of Physicians in Children s Oral Health Chris Cantrell Introduction Twenty-five state Medicaid programs
In This Monitor: Preventive Oral Health, Primary Care, Children s Coverage December 2008 The Role of Physicians in Children s Oral Health Chris Cantrell Introduction Twenty-five state Medicaid programs
Building Better Oral Health Communities
 Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Activity 4 answers: Care of natural teeth Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Prepared by Ms
Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Activity 4 answers: Care of natural teeth Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Prepared by Ms
Paul Glassman DDS, MA, MBA Professor and Director of Community Oral Health University of the Pacific School of Dentistry San Francisco, CA
 Paul Glassman DDS, MA, MBA Professor and Director of Community Oral Health University of the Pacific School of Dentistry San Francisco, CA pglassman@pacific.edu We re Getting Older! U.S. Census. The Older
Paul Glassman DDS, MA, MBA Professor and Director of Community Oral Health University of the Pacific School of Dentistry San Francisco, CA pglassman@pacific.edu We re Getting Older! U.S. Census. The Older
MI Paste. GC America Inc. Advancing the Art and Science of Dentistry
 MI Paste PROfessionally SPECified Tooth Treatment Delivering Bio-Available Calcium and Phosphate TM Contains 002265 PROSPEC MI Paste 10-Pack Contains: 10 Tubes of MI Paste (40g each), two tubes of each
MI Paste PROfessionally SPECified Tooth Treatment Delivering Bio-Available Calcium and Phosphate TM Contains 002265 PROSPEC MI Paste 10-Pack Contains: 10 Tubes of MI Paste (40g each), two tubes of each
FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS
 FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS THIS INFORMATION IS SUPPORTED BY MASSHEALTH AND IS CREATED IN CONJUNCTION WITH MATERIALS FROM: Society of Teachers in Family
FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS THIS INFORMATION IS SUPPORTED BY MASSHEALTH AND IS CREATED IN CONJUNCTION WITH MATERIALS FROM: Society of Teachers in Family
Perspectives on the Science Supporting Florida s Public Health Policy for Community Water Fluoridation
 Florida Journal of Environmental Health, Vol. 191, Dec. 2005, pp.14-20. Perspectives on the Science Supporting Florida s Public Health Policy for Community Water Fluoridation Michael W. Easley, DDS, MPH
Florida Journal of Environmental Health, Vol. 191, Dec. 2005, pp.14-20. Perspectives on the Science Supporting Florida s Public Health Policy for Community Water Fluoridation Michael W. Easley, DDS, MPH
Oral health and dental care in Australia
 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures 2011 Sergio Chrisopoulos Research Associate Katie Beckwith Research Officer Jane Harford Research Fellow Australian Research Centre for Population
Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures 2011 Sergio Chrisopoulos Research Associate Katie Beckwith Research Officer Jane Harford Research Fellow Australian Research Centre for Population
Oral Health Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Physicians
 2015 Oral Health Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Physicians CPT Codes: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are developed and maintained by the American Medical Association. The codes consist
2015 Oral Health Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Physicians CPT Codes: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are developed and maintained by the American Medical Association. The codes consist
Dental Public Health Activities & Practices
 Dental Public Health Activities & Practices Practice Number: 15001 Submitted By: Oral Health Program, Idaho Department of Health and Welfare Submission Date: April 2002 Last Updated: April 2002 Name of
Dental Public Health Activities & Practices Practice Number: 15001 Submitted By: Oral Health Program, Idaho Department of Health and Welfare Submission Date: April 2002 Last Updated: April 2002 Name of
How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums
 Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
DENTAL COVERAGE AND CARE FOR LOW-INCOME CHILDREN: THE ROLE OF MEDICAID AND SCHIP
 July 2008 DENTAL COVERAGE AND CARE FOR LOW-INCOME CHILDREN: THE ROLE OF MEDICAID AND SCHIP Tooth decay is the most common chronic illness among children. Although it is firmly established that oral health
July 2008 DENTAL COVERAGE AND CARE FOR LOW-INCOME CHILDREN: THE ROLE OF MEDICAID AND SCHIP Tooth decay is the most common chronic illness among children. Although it is firmly established that oral health
Oral Health Program. Fluoridation Plan. Wisconsin Department of Health Services
 Wisconsin Department of Health Services Oral Health Program Fluoridation Plan 2010 Cooperative Agreement CDC DP08-802 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Acknowledgements Authors: Midge Pfeffer,
Wisconsin Department of Health Services Oral Health Program Fluoridation Plan 2010 Cooperative Agreement CDC DP08-802 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Acknowledgements Authors: Midge Pfeffer,
Dental Public Health Activities & Practices
 Dental Public Health Activities & Practices Practice Number: 24002 Submitted By: Office of Oral Health, Massachusetts Department of Public Health Submission Date: January 2002 Last Updated: January 2002
Dental Public Health Activities & Practices Practice Number: 24002 Submitted By: Office of Oral Health, Massachusetts Department of Public Health Submission Date: January 2002 Last Updated: January 2002
Adverse Health Effects from Fluoride in Drinking Water
 Adverse Health Effects from Fluoride in Drinking Water Comments to the Water Quality and Operations Committee Metropolitan Water District Los Angeles, California August 20, 2007 Kathleen M. Thiessen, Ph.D.
Adverse Health Effects from Fluoride in Drinking Water Comments to the Water Quality and Operations Committee Metropolitan Water District Los Angeles, California August 20, 2007 Kathleen M. Thiessen, Ph.D.
Comparison of Association of Dental Caries in Relation with Body Mass Index (BMI) in Government and Private School Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Association of Dental Caries in Relation with Body Mass Index (BMI) in Government and Private School Children 1 1 1 1 Prashanth S.T, Venkatesh Babu, Vivek Dhruv Kumar, Amitha
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Association of Dental Caries in Relation with Body Mass Index (BMI) in Government and Private School Children 1 1 1 1 Prashanth S.T, Venkatesh Babu, Vivek Dhruv Kumar, Amitha
A healthcare professional guide to oral care for older patients. The Seattle Pathway
 A healthcare professional guide to oral care for older patients The Seattle Pathway Introduction In 2013 a group of experts met in Seattle, Washington to define a care pathway for oral care in older patients.
A healthcare professional guide to oral care for older patients The Seattle Pathway Introduction In 2013 a group of experts met in Seattle, Washington to define a care pathway for oral care in older patients.
The state of children s oral health in England
 The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079)
 Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079) My name is Cindi Sherwood and I am speaking in opposition to House Bill 2079. My background is that I was trained
Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079) My name is Cindi Sherwood and I am speaking in opposition to House Bill 2079. My background is that I was trained
4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009
 4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
 BISPHOSPHONATE RELATED OSTEONECROSIS OF THE JAW (BRONJ) BISPHOSPHONATES AND WHAT HAPPENS TO BONE VINCENT E. DIFABIO, DDS, MS MEMBER OF THE COMMITTEE ON HEALTHCARE AND ADVOCACY FROM THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION
BISPHOSPHONATE RELATED OSTEONECROSIS OF THE JAW (BRONJ) BISPHOSPHONATES AND WHAT HAPPENS TO BONE VINCENT E. DIFABIO, DDS, MS MEMBER OF THE COMMITTEE ON HEALTHCARE AND ADVOCACY FROM THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION
Early Childhood and the Crisis in Oral Health. Dr. Stephen Abrams Dr. Ian McConnachie
 Early Childhood and the Crisis in Oral Health Dr. Stephen Abrams Dr. Ian McConnachie Today as Part of a Continuum Current state of government action and ODA lobbying IADR 2008 ODA Special Report on Tooth
Early Childhood and the Crisis in Oral Health Dr. Stephen Abrams Dr. Ian McConnachie Today as Part of a Continuum Current state of government action and ODA lobbying IADR 2008 ODA Special Report on Tooth
WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE
 WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE What Primary Care Providers Can Do To Improve Children s Oral Health Heidi Baines, MD Anchorage Neighborhood Health Center Alaska Academy of Family Physicians 27 th Annual Scientific
WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE What Primary Care Providers Can Do To Improve Children s Oral Health Heidi Baines, MD Anchorage Neighborhood Health Center Alaska Academy of Family Physicians 27 th Annual Scientific
Your child s heart problem and dental care
 Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Variation in Urban and Rural Water Fluoride Levels in Ontario
 Professional I s s u e s Variation in Urban and Rural Water Fluoride Levels in Ontario James Yarmolinsky; Savithiri Ratnapalan, MBBS, MRCP, FAAP, FRCPC, MEd; David J. Kenny, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) Contact Author
Professional I s s u e s Variation in Urban and Rural Water Fluoride Levels in Ontario James Yarmolinsky; Savithiri Ratnapalan, MBBS, MRCP, FAAP, FRCPC, MEd; David J. Kenny, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) Contact Author
1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth
 1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth Toddlers are often stubborn when it comes to the essentials of life; as any parent can attest, they
1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth Toddlers are often stubborn when it comes to the essentials of life; as any parent can attest, they
prestige varie ty cre ativity Dental Hygiene Word of Mouth Careers in the Dental Profession flexibility security challenges re s p e ct
 prestige varie ty cre ativity Dental Hygiene Word of Mouth Careers in the Dental Profession flexibility security challenges re s p e ct page 1 prestige It s very rewarding to be able variety to have a
prestige varie ty cre ativity Dental Hygiene Word of Mouth Careers in the Dental Profession flexibility security challenges re s p e ct page 1 prestige It s very rewarding to be able variety to have a
