Oral Health QUESTIONS
|
|
|
- Linda Park
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current guidelines for fluoride supplementation and be able to advise parents on toothbrushing and developing a dental home. CASE A family comes to you for well check-ups for both of their children after recently moving to town. Their children are Johnny, 2 years old, and Rose, 4 months old. They recently moved from a rural area of the country into the big city, and they are setting up all of their health care here in town, including trying to find a dentist. In the course of the interview, you learn that Johnny still goes to sleep with a bottle. He brushes his teeth every day and usually spreads the family toothpaste over his whole toothbrush. Mom has recently noticed some dark areas on his upper teeth. Rose is putting her hands in her mouth all the time, and mom thinks she might be teething, but otherwise is doing well. QUESTIONS 1. Mom gave Johnny fluoride supplements when he was a baby and wants advice on supplementing her children now. What do you counsel mom on fluoride and its risks and benefits? 2. What are the current recommendations for fluoride supplementation? 3. Mom is concerned about the changes in Johnny s teeth and would like some advice on what she can do about it. What can you tell mom about bottle caries? 4. Please provide the mom with appropriate anticipatory guidance and counseling regarding her children s tooth development. 5. How should mom care for her children s teeth and prevent them from getting cavities? 6. Mom agrees to take Johnny to the dentist and would like help deciding when Rose should see the dentist also. REFERENCES 1. Lewis CW, Milgram P. Fluoride. Pediatrics in Review. 2003; 24(10): Martof A. Dental Care: Consultation with the Specialist. Pediatrics in Review. 2001; 22(1): (go to oral health section) Policy Statement: Oral Health Risk Assessment Timing and Establishment of the Dental Home. Pediatrics. 2003; 111(5):
2 Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current guidelines for fluoride supplementation and be able to advise parents on toothbrushing and developing a dental home. CASE A family comes to you for well check-ups for both of their children after recently moving to town. Their children are Johnny, 2 years old, and Rose, 4 months old. They recently moved from a rural area of the country into the big city, and they are setting up all of their health care here in town, including trying to find a dentist. In the course of the interview, you learn that Johnny still goes to sleep with a bottle. He brushes his teeth every day and usually spreads the family toothpaste over his whole toothbrush. Mom has recently noticed some dark areas on his upper teeth. Rose is putting her hands in her mouth all the time, and mom thinks she might be teething, but otherwise is doing well. QUESTIONS 1. Mom gave Johnny fluoride supplements when he was a baby and wants advice on supplementing her children now. How do you counsel mom on fluoride and its benefits and risks? Fluoride is an element that acts to prevent dental caries. It is active in several ways, including enhancing tooth mineralization, stopping tooth demineralization, and working against the bacteria in the mouth that produce acid that leads to cavities. The risk of excessive intake of fluoride is developing fluorosis. Fluorosis in its most severe form is skeletal, which is very rare. Most fluorosis affects the enamel of teeth and causes anything from mild lacy markings on the enamel to striations and pitting of the teeth. The more severe form of enamel fluorosis actually puts one at greater risk for developing caries. The risk of fluorosis only applies to children under the age of 8, whose permanent teeth are still developing. In particular, children months are at greatest risk of suffering the adverse affects of excess fluoride as that is when the anterior permanent teeth are most vulnerable to fluorosis. There are many sources of fluoride, including community water, bottled water, foods and beverages, toothpaste, mouthrinses, and oral and topical supplements. Water is naturally fluoridated, but not always to optimal levels. Thus, fluoride is added to most community water according to region, and different areas have different amounts of fluoride (you can find the fluoride content of water in your area on the Optimal concentrations are 0.7 to 1.2 ppm. Most well-water has sub-optimal levels of fluoride. It is important to inform parents that in most urban areas, the level of fluoride in the community water is sufficient to provide a young child with protection prior to the age of brushing, but levels that exceed 2 ppm should not be given to children under the age of 8 due to an increased risk for fluorosis at that level. In addition, it is a little known fact that foods and beverages are usually
3 prepared using community water sources with fluoride, fluoride is entering diffusely via these products into communities, including those communities that do not fluoridate their water supply. Cooking with tap water in fluoridated communities also adds fluoride to foods. On the other hand, bottled or nursery water may or may not provide the infant with fluoride, as these water sources are not always fluoridated. Parents also need to understand that reverse osmosis and charcoal water filters can greatly decrease the amount of fluoride in the water cleaned with home water filtering systems. In Chicago, a 1 year old child needs about 1 liter of fluoridated water each day to meet fluoride needs. 2. What are the current recommendations for fluoride supplementation? The current guidelines for fluoride supplementation for children living in areas of unfluoridated community water are as follows: Water fluoride content (ppm) Age > to 0.6 > 0.6 Birth to 6 mo 0 mg 0 mg 0 mg 6 mo to 3 y 0.25 mg 0 mg 0 mg 3 y to 6 y 0.50 mg 0.25 mg 0 mg 6 y to 16 y 1.00 mg 0.50 mg 0 mg Considering the fact that this patient is living in an urban area that most likely has > 0.6 ppm fluoride in the water supply (when she previously lived in a rural area that may have had > 0.3), she does not need to supplement either of her children with oral fluoride. Please see the section on general anticipatory guidance and counseling regarding information on toothbrushing and the use of fluoride in toothpaste. 3. Mom is concerned about the changes in Johnny s teeth and would like advice on what she can do about it. What can you tell mom about bottle caries? Johnny has developed bottle caries. Putting a baby or child to bed with a bottle of milk or juice provides the teeth with prolonged contact with sugary substances, leading to the development of caries. These caries are usually found in the upper anterior teeth and the posterior teeth, because the lower front teeth are shielded from the fluid by the lip and tongue. Mom should be counseled to stop giving a bottle of milk or juice to Johnny at bedtime. Mom can be advised to simply wean Johnny off of the bottle altogether (one should counsel parents to stop using a bottle entirely around 12 to 14 months of age). Any bottle the mom may give at bedtime in the meantime should contain only water. In addition, Johnny should be referred to a dentist immediately for restoration or removal of the affected teeth. 4. Please provide the mom with appropriate anticipatory guidance and counseling regarding her children s tooth development? The following chart outlines the general timing of tooth development.
4 Age Tooth eruption 6-10 months Lower central incisors 8-12 months Upper central incisors 9-16 months Lateral incisors 16 months - 3 First molars, canines, second molars (usually in that order) years 6 years and up Permanent teeth (central incisors first, then other incisors and molars Teenage years 3 rd molars Teething infants may be excessively drooly and cranky, and are often soothed by use of a chilled teething ring or appropriate dosing of an oral analgesic (i.e. acetaminophen or ibuprofen). Topical analgesics have not be shown to be beneficial, but can be used at small doses. Fever, diarrhea, and other systemic symptoms are often attributed to teething but have not been shown to be associated with teething in controlled studies. 5. How should mom care for her children s teeth and protect them against getting cavities? As soon as the baby s first teeth erupt, parents should begin to wash their children s teeth twice a day. This may be done at first by simply wiping with a wet cloth. As the child becomes old enough (nearing 1 year), the child can start brushing with a soft infant/child toothbrush in order for the child to learn the behavior of toothbrushing. In addition, teeth should be flossed once daily as soon as the teeth make contact with one another. A risk assessment should be used when counseling a family about the use of a fluoridated toothpaste in a child under the age of 2.5 years, due to the need to balance the need for fluoride protection with the higher risk of fluorosis, as these children will likely swallow large amounts of toothpaste. High risk children (those in non-fluoridated water areas, have siblings with significant tooth decay, are exposed to high levels of sugary substances, have visible plaque or white spots or caries on teeth, are of low socioeconomic status) may be advised to use a child s toothpaste that contains low levels of fluoride. When using fluoride toothpastes, parents should be counseled on using a pea-sized amount of toothpaste only, to minimize the risk of swallowed fluoride. Low risk children (those not falling into the above categories), should use non-fluoridated toothpastes only (if any toothpaste at all), since the risks of swallowing outweigh any potential benefits. Mom should be counseled on the avoidance of cariogenic foods, such as high sugar foods ( junk foods ) and those foods that get stuck in the teeth (i.e. raisins and peanut butter). One idea is limiting junk to 1 hour a week and promptly cleaning the teeth after ingestion of these foods. Juice should be limited to 1 cup a day (6 oz). Children should not ingest carbonated beverages. 6. Mom agrees to take Johnny to the dentist and would like help deciding when Rose should see the dentist also.
5 Previously, the AAP recommended children to first see a dentist at 3 years of age. The most recent ADA and AADP recommendation is to refer patients for a first dental visit between 12 and 18 months. This visit allows the child to be introduced to the idea of the dentist and for further evaluation of the child s oral health and anticipatory guidance for the family. It is best to call ahead and ensure that the dentist does accept young children, as there are some dentists who do not feel comfortable treating young patients. Children with special needs (i.e. developmental delay, trach/vent) should be referred to university or pediatric dentists for routine dental care. REFERENCES 1. Lewis CW, Milgram P. Fluoride. Pediatrics in Review. 2003; 24(10): Martof A. Dental Care: Consultation with the Specialist. Pediatrics in Review. 2001; 22(1): (go to oral health section) Policy Statement: Oral Health Risk Assessment Timing and Establishment of the Dental Home. Pediatrics. 2003; 111(5): Reviewed by Dr. Karen Goldstein
Oral Health Risk Assessment
 Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
THE TRUTH. What it is like to provide baby dental care. Beth Noel RDH, BS
 THE TRUTH What it is like to provide baby dental care Beth Noel RDH, BS Oral Health During Pregnancy Good oral health for infants starts during pregnancy 2012 Oral Health Care During Pregnancy : A National
THE TRUTH What it is like to provide baby dental care Beth Noel RDH, BS Oral Health During Pregnancy Good oral health for infants starts during pregnancy 2012 Oral Health Care During Pregnancy : A National
INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH
 INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH Infant Oral Health Material Developed by: J. Douglass BDS, DDS H. Silk MD A. Douglass MD of the University of Connecticut in cooperation with Connecticut
INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH Infant Oral Health Material Developed by: J. Douglass BDS, DDS H. Silk MD A. Douglass MD of the University of Connecticut in cooperation with Connecticut
Oral health care is vital for seniors
 Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH
 FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH The purpose of this monograph is to improve the oral health and overall pediatric health of children, birth to 5 years old, including those with disabilities
FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH The purpose of this monograph is to improve the oral health and overall pediatric health of children, birth to 5 years old, including those with disabilities
Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices
 Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices (Documentation, Coding, Charging, Billing & Measurement) The purpose of this document is to guide medical providers
Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices (Documentation, Coding, Charging, Billing & Measurement) The purpose of this document is to guide medical providers
Fluoride Products for Oral Health: Professional Information
 Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Your child s heart problem and dental care
 Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Dental Health Tip Cards
 A Parent s Guide Birth to SIX years Dental Health Tip Cards Six Dental Health Tip Cards are available from your local health region that highlight specific topics of interest regarding your child's dental
A Parent s Guide Birth to SIX years Dental Health Tip Cards Six Dental Health Tip Cards are available from your local health region that highlight specific topics of interest regarding your child's dental
Primary teeth are also called baby teeth. By age 3 years, there are usually 20 primary teeth.
 Primary teeth are also called baby teeth. By age 3 years, there are usually 20 primary teeth. The spacing between children s baby teeth is important because it allows enough room for the bigger, permanent
Primary teeth are also called baby teeth. By age 3 years, there are usually 20 primary teeth. The spacing between children s baby teeth is important because it allows enough room for the bigger, permanent
OPEN WIDE! Fun Science Activities Inside!
 OPEN WIDE! Fun Science Activities Inside! THINK BEFORE YOU DRINK Overview: In this experiment, kids may be surprised to learn how much sugar is in popular drinks and how this hidden sugar can damage teeth!
OPEN WIDE! Fun Science Activities Inside! THINK BEFORE YOU DRINK Overview: In this experiment, kids may be surprised to learn how much sugar is in popular drinks and how this hidden sugar can damage teeth!
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses. Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH. National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012
 Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children.
 An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children. Principal Investigator: Kristin Gebhard, MSIV Selective Advisor: Bruce Bernstein, Ph.D. Abstract:
An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children. Principal Investigator: Kristin Gebhard, MSIV Selective Advisor: Bruce Bernstein, Ph.D. Abstract:
How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums
 Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
Although largely preventable by early examination, identification of
 The Consequences of Untreated Dental Disease in Children Poor oral health in infants and children destroys more than just a smile. Although largely preventable by early examination, identification of individual
The Consequences of Untreated Dental Disease in Children Poor oral health in infants and children destroys more than just a smile. Although largely preventable by early examination, identification of individual
WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE
 WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE What Primary Care Providers Can Do To Improve Children s Oral Health Heidi Baines, MD Anchorage Neighborhood Health Center Alaska Academy of Family Physicians 27 th Annual Scientific
WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE What Primary Care Providers Can Do To Improve Children s Oral Health Heidi Baines, MD Anchorage Neighborhood Health Center Alaska Academy of Family Physicians 27 th Annual Scientific
Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements
 Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements Caregiver: How did your baby s last check-up go? Primary Feeding: Tell me about the kind of formula
Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements Caregiver: How did your baby s last check-up go? Primary Feeding: Tell me about the kind of formula
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay
 Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
A PARENT S GUIDE. Caring for Children s Teeth. Teething Toddlers to Teens, One Smile at a Time.
 A PARENT S GUIDE Caring for Children s Teeth. Teething Toddlers to Teens, One Smile at a Time. Oral Care in America THE ISSUE In May 2001, the Office of the Surgeon General released its first ever report
A PARENT S GUIDE Caring for Children s Teeth. Teething Toddlers to Teens, One Smile at a Time. Oral Care in America THE ISSUE In May 2001, the Office of the Surgeon General released its first ever report
1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth
 1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth Toddlers are often stubborn when it comes to the essentials of life; as any parent can attest, they
1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth Toddlers are often stubborn when it comes to the essentials of life; as any parent can attest, they
3. Preventing bacteria from producing sufficient organic acid to demineralize tooth surface.
 FACT SHEET - Dental Health : Vol. 1 No. 4 January 1998 Fluoride Used for Dental Caries Prevention Piyada Prasertsom. DDS. MSc. Dental Health Division, Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Tel:
FACT SHEET - Dental Health : Vol. 1 No. 4 January 1998 Fluoride Used for Dental Caries Prevention Piyada Prasertsom. DDS. MSc. Dental Health Division, Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Tel:
First Dental Visit by Age One
 CONTINUING EDUCATION August 2004 First Dental Visit by Age One A guide to the new recommendations Recommended by American Dental Association American Academy of Pediatrics American Academy of Pediatric
CONTINUING EDUCATION August 2004 First Dental Visit by Age One A guide to the new recommendations Recommended by American Dental Association American Academy of Pediatrics American Academy of Pediatric
Dental Health and Epilepsy
 Dental Health and Epilepsy Good dental health is important to everyone. But it is especially important for people who take antiepileptic medications. Certain antiepileptic drugs and other medications can
Dental Health and Epilepsy Good dental health is important to everyone. But it is especially important for people who take antiepileptic medications. Certain antiepileptic drugs and other medications can
Karen L Carson MD, FAAP
 Karen L Carson MD, FAAP Dental varnish application as a covered benefit first presented by Dr. Ben Hoffman and Albert Bourbon, PA November, 2007 at the NM Pediatric Society Council Meeting Who is the Pediatric
Karen L Carson MD, FAAP Dental varnish application as a covered benefit first presented by Dr. Ben Hoffman and Albert Bourbon, PA November, 2007 at the NM Pediatric Society Council Meeting Who is the Pediatric
Promoting Oral Health
 Promoting Oral Health Oral diseases are among the most prevalent health problems in the United States. The 198 Surgeon General's Report to the Nation listed dental disease as a critical health problem
Promoting Oral Health Oral diseases are among the most prevalent health problems in the United States. The 198 Surgeon General's Report to the Nation listed dental disease as a critical health problem
SAMPLE. Your Child s Teeth. Parents. Helpful Tips for Parents and Caregivers W177
 Parents Your Child s Teeth Helpful Tips for Parents and Caregivers Produced in cooperation with the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (www.aapd.org) and the American Association of Orthodontists
Parents Your Child s Teeth Helpful Tips for Parents and Caregivers Produced in cooperation with the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (www.aapd.org) and the American Association of Orthodontists
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
Fluoride Strengthens Teeth
 Fluoride Strengthens Teeth Two hard-boiled eggs Fluoride gel or solution, 4 to 6 oz. (from dental office) Three clean plastic containers Several cans of dark soda Water 1. Place a hard-boiled egg in one
Fluoride Strengthens Teeth Two hard-boiled eggs Fluoride gel or solution, 4 to 6 oz. (from dental office) Three clean plastic containers Several cans of dark soda Water 1. Place a hard-boiled egg in one
Final Report Format. Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum
 Final Report Format Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum State /Territory: Maryland Person submitting report: Linda Zang Activities originally proposed and how they relate
Final Report Format Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum State /Territory: Maryland Person submitting report: Linda Zang Activities originally proposed and how they relate
The state of children s oral health in England
 The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions. Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes
 Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Non-carious dental conditions
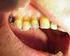 Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
oral health During Pregnancy & Early Childhood: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Health Professionals F e b r u a r y
 oral health During Pregnancy & Early Childhood: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Health Professionals F e b r u a r y 2 0 1 0 Acknowledgments: The CDA Foundation would like to thank the project s co-chairs,
oral health During Pregnancy & Early Childhood: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Health Professionals F e b r u a r y 2 0 1 0 Acknowledgments: The CDA Foundation would like to thank the project s co-chairs,
The Importance of Dental Care. in Huntington Disease
 Huntington s New South Wales The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease Supported by NSW Health 1 2 The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease It should be stated at the outset that the
Huntington s New South Wales The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease Supported by NSW Health 1 2 The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease It should be stated at the outset that the
FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS
 1 FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS Smiles for Life A National Oral Health Curriculum Society of Teachers of Family Medicine Group on Oral Health SMILES FOR LIFE is a comprehensive oral health
1 FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS Smiles for Life A National Oral Health Curriculum Society of Teachers of Family Medicine Group on Oral Health SMILES FOR LIFE is a comprehensive oral health
GRADE THREE DENTAL HEALTH
 GRADE THREE DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 3 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: TEETH HAVE MANY FUNCTIONS PREPARATION: 1 Several mirrors 2 A copy of the three different kinds of teeth
GRADE THREE DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 3 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: TEETH HAVE MANY FUNCTIONS PREPARATION: 1 Several mirrors 2 A copy of the three different kinds of teeth
VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO!
 VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO! 2012-2013 Annual Report The Varnish! Michigan Babies Too! Program was developed as an incentive for medical providers to have oral health training and begin an oral health
VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO! 2012-2013 Annual Report The Varnish! Michigan Babies Too! Program was developed as an incentive for medical providers to have oral health training and begin an oral health
Ann A. Stueck, MSN,RN
 Integrating Bright Futures into Public Health at the State and Local Levels Oral Health Theme Murray L. Katcher, MD, PhD, FAAP Moderator Chief Medical Officer for Community Health Promotion State MCH Medical
Integrating Bright Futures into Public Health at the State and Local Levels Oral Health Theme Murray L. Katcher, MD, PhD, FAAP Moderator Chief Medical Officer for Community Health Promotion State MCH Medical
4th-5th grade Lesson Plan
 4th-5th grade Lesson Plan Curriculum Guide Objective: The student will be able to explain why sodas, chewing gum, and candy are bad for our teeth. 1) Guiding Questions How and why do cavities form on our
4th-5th grade Lesson Plan Curriculum Guide Objective: The student will be able to explain why sodas, chewing gum, and candy are bad for our teeth. 1) Guiding Questions How and why do cavities form on our
Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
 Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments Introduction If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you're not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently
Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments Introduction If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you're not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients
 Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Drinking optimally fluoridated water is a safe, simple and effective way to help prevent and reduce tooth decay in the whole population.
 1 Water Fluoridation Water Fluoridation What is fluoride? Fluoride is a common natural element found in air, soil, fresh water, sea water, plants and lots of foods. It is known to have a protective effect
1 Water Fluoridation Water Fluoridation What is fluoride? Fluoride is a common natural element found in air, soil, fresh water, sea water, plants and lots of foods. It is known to have a protective effect
Table of Contents. Grades Preschool 1 (Ages 4-7)...3. Grades 2 3 (Ages 7-9)...19. Grades 4 6 (Ages 9-12)...38
 Table of Contents HAPPY TEETH! Grades Preschool 1 (Ages 4-7)...3 A LIFETIME OF HEALTHY HAPPY TEETH! Grades 2 3 (Ages 7-9)...19 TEETH TO TREASURE! Grades 4 6 (Ages 9-12)...38 Legends for A-Maze-ing Message
Table of Contents HAPPY TEETH! Grades Preschool 1 (Ages 4-7)...3 A LIFETIME OF HEALTHY HAPPY TEETH! Grades 2 3 (Ages 7-9)...19 TEETH TO TREASURE! Grades 4 6 (Ages 9-12)...38 Legends for A-Maze-ing Message
Healthy Smile, Healthy Child
 Healthy Smile, Healthy Child ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR WELL CHILD PROVIDERS This publication was prepared in conjunction with Healthy Smile, Healthy Child ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR WELL CHILD PROVIDERS ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Healthy Smile, Healthy Child ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR WELL CHILD PROVIDERS This publication was prepared in conjunction with Healthy Smile, Healthy Child ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR WELL CHILD PROVIDERS ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
State of North Carolina. Medicaid Dental Review
 State of North Carolina Medicaid Dental Review October 2010 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is committed to improving pediatric dental care in the Medicaid program
State of North Carolina Medicaid Dental Review October 2010 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is committed to improving pediatric dental care in the Medicaid program
Smile Smarts! AN ORAL HEALTH CURRICULUM FOR PRESCHOOL - GRADE 8
 Smile Smarts! AN ORAL HEALTH CURRICULUM FOR PRESCHOOL - GRADE 8 FLEXIBLE, MODULAR LESSON PLANS SUPPORT MATERIALS HANDS-ON CLASSROOM DEMONSTRATIONS STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEETS SUGGESTIONS FOR FURTHER ORAL HEALTH
Smile Smarts! AN ORAL HEALTH CURRICULUM FOR PRESCHOOL - GRADE 8 FLEXIBLE, MODULAR LESSON PLANS SUPPORT MATERIALS HANDS-ON CLASSROOM DEMONSTRATIONS STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEETS SUGGESTIONS FOR FURTHER ORAL HEALTH
WHY MASS MEDICATION WITH FLUORIDE MUST STOP NOW! Alliance for Natural Health International Position Paper September 2012
 ANH International The Atrium, Curtis Road Dorking, Surrey RH4 1XA United Kingdom e: info@anhinternational.org t: +44 (0)1306 646 600 f: +44 (0)1306 646 552 www.anhinternational.org ANH-Intl Regional Offices
ANH International The Atrium, Curtis Road Dorking, Surrey RH4 1XA United Kingdom e: info@anhinternational.org t: +44 (0)1306 646 600 f: +44 (0)1306 646 552 www.anhinternational.org ANH-Intl Regional Offices
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH
 GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
Use of a Risk Assessment Tool in Primary Care
 Use of a Risk Assessment Tool in Primary Care Can old dogs learn new tricks? Suzanne Boulter, MD, FAAP Adjunct Professor of Pediatrics Dartmouth Medical School Learning Points Opportunities and challenges
Use of a Risk Assessment Tool in Primary Care Can old dogs learn new tricks? Suzanne Boulter, MD, FAAP Adjunct Professor of Pediatrics Dartmouth Medical School Learning Points Opportunities and challenges
Dental Care for Infants
 Dental Care for Infants Ivonne Ganem, DMD, MPH Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce387/ce387.aspx Disclaimer: Participants
Dental Care for Infants Ivonne Ganem, DMD, MPH Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce387/ce387.aspx Disclaimer: Participants
Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs
 Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs Disclosure statement: I have no relevant financial relationships, conflicts of interest, or commercial support to
Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs Disclosure statement: I have no relevant financial relationships, conflicts of interest, or commercial support to
Unit: Fluoride in Drinking Water/Alternate Source of Fluoride
 Unit: Fluoride in Drinking Water/Alternate Source of Fluoride Understandings: Fluoridated water is safe and helps to prevent tooth decay. Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth. Fluoride toothpaste
Unit: Fluoride in Drinking Water/Alternate Source of Fluoride Understandings: Fluoridated water is safe and helps to prevent tooth decay. Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth. Fluoride toothpaste
NC History. Access Problems. The Partnership. Funding. Into the Mouths of Babes. Kelly Haupt, RDH, MHA Project Coordinator.
 Into the Mouths of Babes NC Oral Screening and Varnish Project Kelly Haupt, RDH, MHA Project Coordinator NC History 25% of ALL children entering kindergarten have visible, untreated decay 20% of indigent
Into the Mouths of Babes NC Oral Screening and Varnish Project Kelly Haupt, RDH, MHA Project Coordinator NC History 25% of ALL children entering kindergarten have visible, untreated decay 20% of indigent
Evidence Review: Dental Health Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health
 Evidence Review: Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health March 2014 (update from September 2006) This is a review of evidence and best practice that should be seen as a guide to understanding
Evidence Review: Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health March 2014 (update from September 2006) This is a review of evidence and best practice that should be seen as a guide to understanding
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology
 Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY
 DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY S. К. Matelo, Т. V. Kupets Dental fluorosis is attributed to the group of non-carious diseases of type one, in other words to a
DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY S. К. Matelo, Т. V. Kupets Dental fluorosis is attributed to the group of non-carious diseases of type one, in other words to a
How To Prevent Dental Caries
 This report may be used, in whole or in part, as the basis for development of clinical practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, or a basis for reimbursement and coverage policies. AHRQ
This report may be used, in whole or in part, as the basis for development of clinical practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, or a basis for reimbursement and coverage policies. AHRQ
Preventive Pediatric Dental Care. Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203
 Preventive Pediatric Dental Care Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Patient comfort and safety 1. All children are treated using the
Preventive Pediatric Dental Care Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Patient comfort and safety 1. All children are treated using the
dental fillings facts About the brochure:
 dental fillings facts About the brochure: Your dentist is dedicated to protecting and improving oral health while providing safe dental treatment. This fact sheet provides information you need to discuss
dental fillings facts About the brochure: Your dentist is dedicated to protecting and improving oral health while providing safe dental treatment. This fact sheet provides information you need to discuss
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme
 The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
Tooth Decay. What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth.
 Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP
 1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
When Kids Require General Anesthesia Dentistry
 North Texas Dentistry a business and lifestyle magazine for north texas dentists When Kids Require General Anesthesia Dentistry Children 1st Dental & Surgery Center cover feature An anesthesiologist monitors
North Texas Dentistry a business and lifestyle magazine for north texas dentists When Kids Require General Anesthesia Dentistry Children 1st Dental & Surgery Center cover feature An anesthesiologist monitors
Submission: REF Fluoridation Plants Including the Ballina Shire Council Marom Creek Supply
 4 th February 2010 Attn: The General Manager Rous Water water@rouswater.nsw.gov.au Submission prepared by Jo Immig NTN Coordinator Submission: REF Fluoridation Plants Including the Ballina Shire Council
4 th February 2010 Attn: The General Manager Rous Water water@rouswater.nsw.gov.au Submission prepared by Jo Immig NTN Coordinator Submission: REF Fluoridation Plants Including the Ballina Shire Council
Building Better Oral Health Communities
 Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Activity 4 answers: Care of natural teeth Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Prepared by Ms
Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Activity 4 answers: Care of natural teeth Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Prepared by Ms
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS. brought to you by:
 CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
MassHealth Dental Benefit Booklet
 MassHealth Dental Benefit Booklet January 2012 3 Serving the MassHealth Program* January 2012 Dear MassHealth Member, We have some important news about the MassHealth dental program that you need to know.
MassHealth Dental Benefit Booklet January 2012 3 Serving the MassHealth Program* January 2012 Dear MassHealth Member, We have some important news about the MassHealth dental program that you need to know.
Baby Teeth with Plaque
 Baby Teeth with Plaque Plaque is a sticky, colorless layer of germs and saliva that sits on the teeth and gums. When plaque is left on the teeth and gums, it hardens and becomes tartar or calculus. When
Baby Teeth with Plaque Plaque is a sticky, colorless layer of germs and saliva that sits on the teeth and gums. When plaque is left on the teeth and gums, it hardens and becomes tartar or calculus. When
Dental Admission Form
 Dental Admission Form PERSONAL HISTORY All of the information which you provide on this form will be held in the strictest confidence. Although some questions may seem unimportant at the time, they may
Dental Admission Form PERSONAL HISTORY All of the information which you provide on this form will be held in the strictest confidence. Although some questions may seem unimportant at the time, they may
Brushy Brushalotamus in Your Classroom Teacher's Guide for Pre-K Programs
 Brushy Brushalotamus in Your Classroom Teacher's Guide for Pre-K Programs 2012 Colgate-Palmolive Company. All Rights Reserved. A Global Oral Health Initiative. Dear Educator, Welcome to the Colgate Bright
Brushy Brushalotamus in Your Classroom Teacher's Guide for Pre-K Programs 2012 Colgate-Palmolive Company. All Rights Reserved. A Global Oral Health Initiative. Dear Educator, Welcome to the Colgate Bright
Activity: Can You Identify the Age?
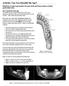 Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
A 3-Step Approach to Improving Quality Outcomes in Safety Net Dental Programs
 A 3-Step Approach to Improving Quality Outcomes in Safety Net Dental Programs The Future: Quality Outcome Measures Using CAMBRA Bob Russell, DDS, MPH The Future Increase Federal Funding to Expand FQHCs
A 3-Step Approach to Improving Quality Outcomes in Safety Net Dental Programs The Future: Quality Outcome Measures Using CAMBRA Bob Russell, DDS, MPH The Future Increase Federal Funding to Expand FQHCs
Innovative State Practices for Improving The Provision of Medicaid Dental Services:
 Innovative State Practices for Improving The Provision of Medicaid Dental Services: SUMMARY OF EIGHT STATE REPORTS: (Alabama, Arizona, Maryland, Nebraska, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Texas and Virginia)
Innovative State Practices for Improving The Provision of Medicaid Dental Services: SUMMARY OF EIGHT STATE REPORTS: (Alabama, Arizona, Maryland, Nebraska, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Texas and Virginia)
FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS
 FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS THIS INFORMATION IS SUPPORTED BY MASSHEALTH AND IS CREATED IN CONJUNCTION WITH MATERIALS FROM: Society of Teachers in Family
FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS THIS INFORMATION IS SUPPORTED BY MASSHEALTH AND IS CREATED IN CONJUNCTION WITH MATERIALS FROM: Society of Teachers in Family
Water Fluoridation- All you need to know...
 Water Fluoridation- All you need to know... Dental decay is the most common chronic disease in children, affecting 5-8 times as many children than asthma (1). The use of water fluoridation for the prevention
Water Fluoridation- All you need to know... Dental decay is the most common chronic disease in children, affecting 5-8 times as many children than asthma (1). The use of water fluoridation for the prevention
Dental health following cancer treatment
 Dental health following cancer treatment Treatment for cancer often increases the risk for dental problems. As a cancer survivor, it is important for you to understand the reasons why dental care is especially
Dental health following cancer treatment Treatment for cancer often increases the risk for dental problems. As a cancer survivor, it is important for you to understand the reasons why dental care is especially
Fluoride. Introduction
 Fluoride Introduction Most fluoride in the body is found in bones and teeth, due to its high affinity for calcium and calcium phosphate. Ingestion of and topical treatment with fluoride is effective in
Fluoride Introduction Most fluoride in the body is found in bones and teeth, due to its high affinity for calcium and calcium phosphate. Ingestion of and topical treatment with fluoride is effective in
Dental Health Guide. School Nurses
 Dental Health Guide Dental Health for Guide School fornurses School Nurses Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services 2014 Missouri Department of
Dental Health Guide Dental Health for Guide School fornurses School Nurses Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services 2014 Missouri Department of
The Effect of Dental Rehabilitation on the Body Weight of Children with Early Childhood Caries
 The Effect of Dental Rehabilitation on the Body Weight of Children with Early Childhood Caries George Acs, Richard Shulman, Man Wai Ng, Steven Chussid Purpose: Methods: Results: The purpose of this study
The Effect of Dental Rehabilitation on the Body Weight of Children with Early Childhood Caries George Acs, Richard Shulman, Man Wai Ng, Steven Chussid Purpose: Methods: Results: The purpose of this study
ITI BASIC ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 ITI BASIC ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MANUAL How To Teach Groups And Individuals Basic Oral Hygiene Procedures 2009 INTERNATIONAL TRAINING INSTITUTE www.iticourses.com 1000 O Malley Road, Suite 104 Anchorage,
ITI BASIC ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MANUAL How To Teach Groups And Individuals Basic Oral Hygiene Procedures 2009 INTERNATIONAL TRAINING INSTITUTE www.iticourses.com 1000 O Malley Road, Suite 104 Anchorage,
New York State Developmental Disabilities Planning Council
 References: American Academy of Pediatrics. (2003). Oral Health Risk Assessment Timing and Establishment of the Dental Home. Pediatrics, 111(5), 1113-1116. Retrieved July 30, 2008 from http://aappolicy.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/pediatrics;111/5/1113
References: American Academy of Pediatrics. (2003). Oral Health Risk Assessment Timing and Establishment of the Dental Home. Pediatrics, 111(5), 1113-1116. Retrieved July 30, 2008 from http://aappolicy.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/pediatrics;111/5/1113
School-Based Oral Health Care. A Choice for Michigan Children.indd 1
 School-Based Oral Health Care A Choice for Michigan Children School Based Oral Health Care: A Choice for Michigan Children is part of an information set meant to serve as a guideline for school personnel
School-Based Oral Health Care A Choice for Michigan Children School Based Oral Health Care: A Choice for Michigan Children is part of an information set meant to serve as a guideline for school personnel
Managing Mouth Sores
 Managing Mouth Sores The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Managing Mouth Sores The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
U.S. Public Health Service Recommendation for Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water for the Prevention of Dental Caries
 Reports and Recommendations U.S. Public Health Service Recommendation for Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water for the Prevention of Dental Caries U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Federal
Reports and Recommendations U.S. Public Health Service Recommendation for Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water for the Prevention of Dental Caries U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Federal
Like us on Facebook! 3rd Quarter 2014 PARA INFORMACIÓN ACERCA DE TENNCARE IN ESPAÑOL, LLAME AL 1-866-311-4290.
 3rd Quarter 2014 BlueCareSM TennCareSelect PARA INFORMACIÓN ACERCA DE TENNCARE IN ESPAÑOL, LLAME AL 1-866-311-4290. ect Members under age 21 For BlueCare and TennCareSel Teen Wellness Checkups: What s
3rd Quarter 2014 BlueCareSM TennCareSelect PARA INFORMACIÓN ACERCA DE TENNCARE IN ESPAÑOL, LLAME AL 1-866-311-4290. ect Members under age 21 For BlueCare and TennCareSel Teen Wellness Checkups: What s
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners
 USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
Dental care is the most common unmet health care
 P R O F E S S I O N A L I S S U E S Development and Testing of an Audio-visual Aid for Improving Infant Oral Health through Primary Caregiver Education Lisa H. Alsada, DDS, FCAM, P Mgr, FCIM Michael J.
P R O F E S S I O N A L I S S U E S Development and Testing of an Audio-visual Aid for Improving Infant Oral Health through Primary Caregiver Education Lisa H. Alsada, DDS, FCAM, P Mgr, FCIM Michael J.
FOLFOX Chemotherapy. This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy.
 FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
Understanding Dental Implants
 Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Introduction to Dental Anatomy
 Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research What do I need to know about dry mouth? Dry mouth is the feeling that
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research What do I need to know about dry mouth? Dry mouth is the feeling that
dental care every day
 dental care every day A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
dental care every day A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location
![[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location](/thumbs/31/14971568.jpg) Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
Dental services. in Bath and North East Somerset, Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire
 Dental services in Bath and North East Somerset, Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire Contents Finding an NHS dentist 1 What can I do to avoid dental disease? 2 Information about sugar 2 Dental
Dental services in Bath and North East Somerset, Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire Contents Finding an NHS dentist 1 What can I do to avoid dental disease? 2 Information about sugar 2 Dental
CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION.
 CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION. ١ G.V. BLACK who is known as the father of operative dentistry,he classified carious lesions into groups according to their locations in permanent
CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION. ١ G.V. BLACK who is known as the father of operative dentistry,he classified carious lesions into groups according to their locations in permanent
Dental Health Services in Canada
 Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
SAY THIS, NOT THAT: Tips for talking about Community Water Fluoridation
 SAY THIS, NOT THAT: Tips for talking about Community Water Fluoridation Many people take for granted that community water fluoridation (CWF) in the U.S. is a safe and well-accepted public health practice,
SAY THIS, NOT THAT: Tips for talking about Community Water Fluoridation Many people take for granted that community water fluoridation (CWF) in the U.S. is a safe and well-accepted public health practice,
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003
 Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
Looking for Affordable Dental Care in Madison and Dane County?
 Looking for Affordable Dental Care in Madison and Dane County? Caring for your teeth and gums is an important part of your health. Dental care can be difficult to obtain, especially if you have Medical
Looking for Affordable Dental Care in Madison and Dane County? Caring for your teeth and gums is an important part of your health. Dental care can be difficult to obtain, especially if you have Medical
