Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services
|
|
|
- Juliana Carpenter
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services DEPRESSION Pharmacological Treatment of Depression NICE guidelines suggest the following stepped care model also see appendix 1 Do not use antidepressants routinely to treat persistent sub-threshold depressive symptoms or mild depression because the risk-benefit ratio is poor. However they should be considered for people with: o A past history of moderate or severe depression OR o Initial presentation of sub-threshold depressive symptoms that have been present for a long period (typically at least 2 years) OR o Sub-threshold depressive symptoms or mild depression that persist(s) after other interventions o Mild depression that complicates the care of a chronic physical health problem Antidepressants should be considered for people presenting with moderate depression. Antidepressants should be considered for people with a chronic physical health problem and presenting with moderate depression, after other interventions have been attempted or rejected by the person Antidepressants should be considered for people presenting with severe depression Antidepressants may be augmented with an atypical antipsychotic (the optimum dose and duration of treatment are unknown) for treatment of psychotic depression. Antidepressants should be given for 3-4 weeks; if there is no response at the optimal dose, then the drug should be changed. If there is a partial response, then continue for 2-4 weeks then reassess. Consider switching the antidepressant if the service user prefers to change or side effects develop or response is inadequate after 6-8 weeks. Be aware that there may be a delay of up to 2 weeks before onset of antidepressant effect. People taking antidepressants should be regularly reviewed, initially at 2 weeks then at intervals of at least 2 to 4 weeks for the first 3 months of treatment, and then at longer intervals if response is good. Antidepressant treatment should be continued for at least 6 months, extending to at least 2 years if there is a high risk of relapse. There is little evidence of difference in efficacy between different drugs but there are differences in side effect profiles; potential for interactions and safety in overdose. If drugs are equal in efficacy and safety, then the cost should be considered. NICE recommends a generic selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) as first choice. There is a possibility of increased anxiety, agitation and suicidal ideation in the first few weeks of antidepressant treatment Discuss antidepressant treatment choice, side effects and adherence with the service user and provide appropriate service user information leaflet. Appropriate psychological interventions (e.g. cognitive behavioural therapy, interpersonal therapy) should be considered, usually as an adjunct to antidepressants. 1
2 Safety Warnings Antidepressants are associated with an initial worsening of anxiety/agitation and an increased risk of suicidal thinking and behaviour. Monitor closely, at 2 weekly intervals, particularly at the start of treatment and when the dose is changed. Patients with high suicide risk or younger than 30 years should be reviewed weekly and then frequently until the risk is no longer clinically important. Abrupt discontinuation (sometimes reduced or missed doses) of antidepressants can lead to a withdrawal syndrome. Symptoms include dizziness, numbness and tingling, gastrointestinal disturbances, headaches, sweating, anxiety and sleep disturbance. Gradual discontinuation is advised. Use antidepressants with care in glaucoma, bipolar, prostate hypertrophy and seizures. Hyponatraemia has been associated with all antidepressants and should be considered in all those who develop drowsiness, confusion, or convulsions while on antidepressants. SSRIs can increase risk of bleeding. Caution is required in older adults and when used in combination with NSAIDS, aspirin or anticoagulants. Gastroprotection may be required. SSRIs can increase risk of falls and osteoporotic fractures in people over 50 years. Serotonin syndrome (agitation, confusion, tremor, hypereflexia, myoclonus and hyperthermia) can occur with serotonergic drugs and requires emergency management. Adverse Effects and Interactions SSRIs are better tolerated and safer in overdose than other antidepressants. Common side effects of SSRIs are headache, nausea, and anxiety/agitation, especially when starting treatment (usually settle on continued treatment). Other side effects are insomnia, tremor, akathisia, sweating, paraethesias, sexual dysfunction, including diminished libido and difficulty with erection and orgasm, muscle/joint pain, hyponatraemia, bruising/bleeding, weight changes and manic or psychotic symptoms. Tricyclic antidepressants have similar efficacy to SSRIs but are more likely to be discontinued because of side-effects and are toxic in overdose. Common side effects of tricyclics include anxiety, drowsiness, dizziness, agitation, confusion, anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention and blurred vision); cardiovascular effects (hypotension, tachycardia, arrhythmias and other ECG changes - baseline ECG is advised, where appropriate); hepatic effects, changes in blood sugar, increased appetite, weight gain and sexual dysfunction can occur. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) can have dangerous interactions with some foods and drugs, and should be reserved for initiation by consultants. Service users prescribed MAOIs require careful monitoring (blood pressure) and advice on dietary and drug interactions. When changing antidepressants, a suitable washout period (usually at least 14 days) should be allowed before or after using MAOIs. Mirtazapine has few antimuscarinic effects, but causes sedation during initial treatment and is associated with weight gain and blood dyscrasias. Relevant NICE Guidance NICE Clinical Guideline (CG90). Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update). October Available at NICE Clinical Guideline (CG91). Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: Treatment and management. October Available at NICE clinical guideline (CG28). Depression in children and young people. September 2005 Available at: (rapid update expected March 2015). NICE Pathways: Depression NICE quality standards: Depression in adults quality standard Mar Depression in children and young people Sept
3 Depression First Line: Relative Cost Notes Citalopram Has less drug/drug interactions; prolongs QT interval; contraindicated with other drugs that prolong QT Escitalopram Has less drug/drug interactions; prolongs QT interval; contraindicated with other drugs that prolong QT Sertraline Sertraline has a superior tolerability and is preferred in cardiac disease Mirtazapine /Orodispersible Useful where weight is not a concern and sedation is preferable; caution in liver impairment. Rare cases of bone marrow depression. Use with caution where there are risk factors for QT prolongation Fluoxetine Long half life useful if compliance is an issue Second Line: Relative Cost Notes Venlafaxine - More toxic in overdose than SSRIs; higher risk of discontinuation reaction Amitriptyline Titrate slowly toxic in overdose Lofepramine Least cardiotoxic of TCAs Trazodone Useful in anxiety and agitation where sedation is required Paroxetine Higher incidence of discontinuation symptoms. Drug/drug interactions common Third Line: Relative Cost Notes [Seek Consultant Opinion before prescribing] Fluvoxamine Nausea a problem; drug/drug interactions common; Caution in hepatic or renal impairment; Bradycardia with ECG changes has been noted; Duloxetine Expensive; Little or no advantages over other antidepressants; care needed to use correct dosage regimen; associated with nausea and headache, and can also increase blood pressure. Imipramine Less sedating than other tricyclics with moderate antimuscarinic activity Clomipramine Useful if OCD symptoms are present as well Doxepin - Moderate sedative effects Moclobemide Use alone need to be careful with diet difficult to switch from 3
4 Depression continued Fourth Line: Relative Cost Notes [Seek Consultant Opinion before prescribing] Phenelzine Dietary problems. Washout period required when switching. Useful for atypical depression Mianserin Regular blood counts needed Trimipramine Useful where sedation is required Nortriptyline Less postural hypotension and lower cardiotoxicity than other tricyclics Agomelatine Liver function test required before and during use; Expensive; Specialist initiation and hospital use only Reboxetine Poor response rate and low tolerability; May lower serum potassium; Not licensed in older adults. Other Notes [Seek Consultant Opinion before prescribing] ECT Consider for severe, life-threatening depression when a rapid response is required, or when other treatments have failed OR for moderate depression unresponsive to multiple drug treatments and psychological treatment Benzodiazepine - Short-term treatment (usually no longer than 2 weeks) if anxiety, agitation and/or insomnia are a problem; Avoid in chronic anxiety symptoms; Use with caution in people at risk of falls. Augmentation Relative Cost Notes [Seek Consultant Opinion before prescribing] Add Lithium - Use in treatment resistant depression baseline and routine monitoring and blood tests needed Add Tryptophan Use in treatment resistant depression blood tests needed; Unlicensed in the UK; Named patient only Add Antipsychotic - Useful for depression with psychotic symptoms; monitor weight, lipids, glucose levels, side effects Not Recommended Notes Dosulepin Avoid due to increased cardiac risk and toxicity in overdose. Should not be started in new patients. St John s Wort - Avoid due to uncertainty about appropriate dose, persistence of effect, variation in available preparations and risk of serious interactions with other drugs Augmentation with valproate, lamotrigine, carbamazepine, buspirone, pindolol - Not routinely recommended because of insufficient evidence of effectiveness 4
5 Treatment of Resistant or Refractory Depression This requires a flexible approach Escalate antidepressant doses for an adequate duration Switch drugs ensuring that all drug classes have been tried optimally Augment the antidepressant with other drugs or combine two antidepressants Assure compliance Manage ADRs that may reduce compliance Monitor and review outcome of treatment Offer high-intensity psychological interventions eg CBT Options include 1 st choice Add lithium well established recommended by NICE Use combinations of antidepressants e.g. mirtazapine & venlafaxine OR an SSRI Add liothyronine (T3) 20mcg 50mcg daily may be better tolerated than lithium Augmentation of current therapy with bupropion or buspirone (less evidence-based) Use other antidepressants e.g. nortriptyline (TCA) or tranylcypromine (MAOI) 2 nd choice Add lamotrigine, max 200mg daily SSRI and up to 60mg buspirone daily Venlafaxine >225mg daily recommended by NICE; 3 nd choice Consider for severe, life-threatening depression when a rapid response is required, or when other treatments have failed OR for moderate depression unresponsive to multiple drug treatments and psychological treatment For further options please contact the Pharmacy department 5
6 Usual Recommended Treatment of Depression in Chronic Medical Conditions Co-morbidity Post stroke Diabetes Cardiovascular disease Epilepsy Hepatic Old age Renal impairment Recommended treatment In all chronic conditions any possible drug interactions must be considered as a matter of priority SSRIs Mirtazapine (small effect on INR causing an increase to INR) SSRIs fluoxetine best supported by data Venlafaxine Mirtazapine SSRIs preferably sertraline especially if also prescribed flecainide, propafenone. SSRIs not recommended if also prescribed warfarin, heparin or aspirin Mirtazapine Check choices with Medicines Information before use of any antidepressant Paroxetine SSRIs Mirtazapine In Parkinson s disease do not use SSRIs with MAO-B inhibitors e.g. selegiline Check choices with Medicines Information before use of any antidepressant Elderly Consider lower doses and increase slowly. Also consider co-morbidity Musculoskeletal disease SSRIs not recommended to be used with NSAIDs. If essential use a gastroprotective agent at the same time Migraine In people receiving triptans use mirtazapine / trazodone / mianserin or reboxetine If the above options for recommended treatments in co-morbidity have been used without an improvement in symptoms, then please contact the Pharmacy Department for more detailed and individualised advice. 6
7 Appendix 1 The Stepped-Care Model The least intrusive, most effective intervention is provided first. If a person does nor benefit from that intervention, or declines an intervention, they should be offered an appropriate intervention from the next step Focus of the intervention Nature of the intervention Step 4 Severe and complex depression 1 ; risk to life; severe self neglect Medication, high-intensity psychological interventions, electroconvulsive therapy, crisis service, combined treatments, multiprofessional and inpatient care Step 3 Persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression with inadequate response to initial interventions; moderate and severe depression Medication, high-intensity psychological interventions, combined treatments, collaborative care 2 and referral for further assessment and interventions Step 2 Persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms; mild to moderate depression Low-intensity psychological and psychosocial interventions, medication and referral for further assessment and interventions Step 1 All known and suspected presentations of depression Assessment, support, psychoeducation, active monitoring and referral for further assessment and interventions 1 Complex depression includes depression that shows an inadequate response to multiple treatments, is complicated by psychotic symptoms and/or is associated with significant psychiatric comorbidity or psychosocial factors 2 only for depression where the person also has a chronic physical health problem and associated functional impairment 7
8 Appendix 2 Relative Side Effects of Antidepressants Drug Some of the main side effects Drowsiness Weight gain Nausea Anticholinergic Sexual Cardiac effects effects problems Citalopram Sertraline Fluoxetine Escitalopram Mirtazapine o o o + Venlafaxine Moclobemide Amitriptyline Clomipramine Imipramine Nortriptyline Lofepramine Trazodone o Paroxetine Fluvoxamine Reboxetine o o o Duloxetine Phenelzine Agomelatine o o o o o ++ Tryptophan + o + o o + Lithium o o = relatively common; ++ = moderately common + = uncommon 0 = little or no effect 8
9 References 1. NICE Clinical Guideline (CG90). Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) NICE Clinical Guideline (CG91). Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: Treatment and management NICE clinical guideline (CG28). Depression in children and young people (rapid update March 2015). 4. BAP Consensus Guidelines. Evidence-based guidelines for treating depressive disorders with antidepressants: A revision of the 2000 British Association for Psychopharmacology guidelines (2008) BNF online (British Medical Association and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain). Online BNF online at: 6. Martindale The complete drug reference online at: [subscription required] 7. SPCs for all the drugs referred to in this guideline can be found in the Electronic Medicines Compendium ( 8. Bazire. Psychotropic Drug Directory Lloyd-Reinhold Communications. 9. The Maudsley Guidelines 11 th edition and online at The Maudsley Guidelines 11th edition and online at (NHS athens password required) 10. MHRA Drug Safety Update. Antidepressants: risk of fractures MHRA Drug Safety Update. Agomelatine (Valdoxan): risk of liver toxicity reminder to test liver function before and during treatment MHRA Drug Safety Update. Citalopram and escitalopram: QT interval prolongation new maximum daily dose restrictions (including in elderly patients), contraindications, and warnings MHRA Drug Safety Update. Antidepressants: suicidal thoughts and behaviour - summary report. 9
Antidepressant treatment in adults
 Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
NICE Clinical guideline 23
 NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
NICE clinical guideline 90
 Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
 TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine
 Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Depression. The treatment and management of depression in adults. This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90
 Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
Depression Pathway. Patient Education Box 4. Guided self help Box 18. pg 11
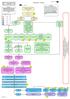 LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
What are the best treatments?
 What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY
 University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION
 MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup. Shared Care Template
 GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) for the treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Body Dysmorphic
GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) for the treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Body Dysmorphic
Treatments for Major Depression. Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are:
 Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder. Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice
 Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
Major Depression. What is major depression?
 Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease
 Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Depression Flow Chart
 Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacology. Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical. Department of Psychiatry, RVI
 Regional Affective Disorders Service Psychopharmacology Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical Psychopharmacology Department of Psychiatry, RVI Intro NOT
Regional Affective Disorders Service Psychopharmacology Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical Psychopharmacology Department of Psychiatry, RVI Intro NOT
Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in Primary Care, Adult 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com 40 05 17 035 3/03 Once a primary care patient presents with depressive symptoms, the primary care physician makes
Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com 40 05 17 035 3/03 Once a primary care patient presents with depressive symptoms, the primary care physician makes
NHS FORTH VALLEY Drug Treatment of Depression
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Drug Treatment of Depression Endorsed by: Primary Care Prescribing Group Primary Care Drug and Therapeutics Committee Area Drug and Therapeutics Committee Depression ICP Group Approved
NHS FORTH VALLEY Drug Treatment of Depression Endorsed by: Primary Care Prescribing Group Primary Care Drug and Therapeutics Committee Area Drug and Therapeutics Committee Depression ICP Group Approved
Depression. Medicines To Help You
 Medicines To Help You Depression Use this guide to help you talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse about your medicines for depression. The guide lists all of the FDA-approved products now available
Medicines To Help You Depression Use this guide to help you talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse about your medicines for depression. The guide lists all of the FDA-approved products now available
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults
 Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia
 Ref No. E040 Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Consultant s contact details (p.3) And send One copy to: 1.
Ref No. E040 Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Consultant s contact details (p.3) And send One copy to: 1.
These guidelines are intended to support General Practitioners in the care of their patients with dementia both in the community and in care homes.
 This is a new guideline. These guidelines are intended to support General Practitioners in the care of their patients with dementia both in the community and in care homes. It incorporates NICE clinical
This is a new guideline. These guidelines are intended to support General Practitioners in the care of their patients with dementia both in the community and in care homes. It incorporates NICE clinical
If you are not clear about why an antidepressant has been suggested for you, ask your doctor.
 Antidepressants Aims of the leaflet This leaflet is for anyone who wants to know more about antidepressants. It discusses how they work, why they are prescribed, their effects and side-effects, and alternative
Antidepressants Aims of the leaflet This leaflet is for anyone who wants to know more about antidepressants. It discusses how they work, why they are prescribed, their effects and side-effects, and alternative
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Assessing the Effectiveness of Medications. Administering Medications
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 32 Psychopharmacologic Nursing Interventions Assessing the Effectiveness of Medications Include how well the medications are helping the client to
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 32 Psychopharmacologic Nursing Interventions Assessing the Effectiveness of Medications Include how well the medications are helping the client to
Paxil/Paxil-CR (paroxetine)
 Generic name: Paroxetine Available strengths: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg tablets; 10 mg/5 ml oral suspension; 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg controlled-release tablets (Paxil-CR) Available in generic: Yes, except
Generic name: Paroxetine Available strengths: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg tablets; 10 mg/5 ml oral suspension; 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg controlled-release tablets (Paxil-CR) Available in generic: Yes, except
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over
 Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression
 Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
Document name: ANTIDEPRESSANTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION. Portfolio Document type: Staff group to whom it applies: Distribution: How to access:
 Document name: ANTIDEPRESSANTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION. Portfolio Document type: Antidepressants for the treatment of depression in line with NICE CG90 (October 2009) and NICE CG28 - Management
Document name: ANTIDEPRESSANTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION. Portfolio Document type: Antidepressants for the treatment of depression in line with NICE CG90 (October 2009) and NICE CG28 - Management
Antidepressants. Understanding psychiatric medications. Information for consumers, families and friends. Titles in the.
 Titles in the Understanding psychiatric medications series include: Antidepressants Antipsychotics Benzodiazepines Mood Stabilizers Understanding psychiatric medications Antidepressants For more information
Titles in the Understanding psychiatric medications series include: Antidepressants Antipsychotics Benzodiazepines Mood Stabilizers Understanding psychiatric medications Antidepressants For more information
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression
 Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
Bipolar disorder. The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care NICE clinical guideline 38 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care NICE clinical guideline 38 Developed by the National Collaborating
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression
 Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Issue date: November 2005
 Issue date: November 2005 Treating obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD) and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Understanding NICE guidance information for people with OCD
Issue date: November 2005 Treating obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD) and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Understanding NICE guidance information for people with OCD
1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the
 1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
Anxiety Disorders Drug Treatment Guidelines
 Western Australian Psychotropic Drugs Committee Anxiety Disorders Drug Treatment Guidelines August 2008 www.watag.org.au Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Psychological or pharmacological treatment?...
Western Australian Psychotropic Drugs Committee Anxiety Disorders Drug Treatment Guidelines August 2008 www.watag.org.au Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Psychological or pharmacological treatment?...
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview
 Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Treatment for Anxiety Disorders in Primary Care
 Treatment for Anxiety Disorders in Primary Care Dr Terence Leong Associate Consultant Dept of Psychological Medicine Research Clinical Care Education 1 1.1 Topic goes here Project number 14.12.08 Copyright
Treatment for Anxiety Disorders in Primary Care Dr Terence Leong Associate Consultant Dept of Psychological Medicine Research Clinical Care Education 1 1.1 Topic goes here Project number 14.12.08 Copyright
Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour. Pharmacovigilance Working Party. January 2008
 Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour Pharmacovigilance Working Party January 2008 PhVWP PAR January 2008 Page 1/15 1. Introduction The Pharmacovigilance Working Party has on a number of
Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour Pharmacovigilance Working Party January 2008 PhVWP PAR January 2008 Page 1/15 1. Introduction The Pharmacovigilance Working Party has on a number of
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå. aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí=
 `çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines
 MOH CLINICL PRCTICE GUIELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines College of Family Physicians, Singapore cademy of Medicine, Singapore Executive summary of recommendations etails of recommendations
MOH CLINICL PRCTICE GUIELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines College of Family Physicians, Singapore cademy of Medicine, Singapore Executive summary of recommendations etails of recommendations
find out about... tricyclic antidepressants a publication from
 find out about... tricyclic antidepressants a publication from Why have I been prescribed this drug? Tricyclic and related Antidepressants (TCAs) are prescribed for people suffering from depression or
find out about... tricyclic antidepressants a publication from Why have I been prescribed this drug? Tricyclic and related Antidepressants (TCAs) are prescribed for people suffering from depression or
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance
 Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Treating Major Depressive Disorder
 Treating Major Depressive Disorder A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Third Edition, originally published in October 2010.
Treating Major Depressive Disorder A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Third Edition, originally published in October 2010.
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES. Depression
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents
 TREATMENT GUIDELINES Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Guideline 7 Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Description There are few controlled trials to guide practitioners
TREATMENT GUIDELINES Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Guideline 7 Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Description There are few controlled trials to guide practitioners
Depre r s e sio i n o i n i a dults Yousuf Al Farsi
 Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center
 Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center First Line Medications SSRIs Prozac (Fluoxetine): 5-605 mg Zoloft (Sertraline):
Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center First Line Medications SSRIs Prozac (Fluoxetine): 5-605 mg Zoloft (Sertraline):
Pharmacotherapy of BPSD. Pharmacological interventions. Anti-dementia drugs. Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence
 Pharmacotherapy of BPSD Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence Pharmacological interventions Reducing medication errors. Reducing potentially inappropriate medication prescription.
Pharmacotherapy of BPSD Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence Pharmacological interventions Reducing medication errors. Reducing potentially inappropriate medication prescription.
Medications for bipolar disorder
 Medications for bipolar disorder Findings from Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing (Mitchell et al, 2004) In 12 months, only one-third saw a mental health professional 40% received
Medications for bipolar disorder Findings from Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing (Mitchell et al, 2004) In 12 months, only one-third saw a mental health professional 40% received
Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression
 Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression Special Report on New Depression Treatment Technology Based on 2010 APA Practice Guidelines Best Practices Guideline for the Treatment of Patients
Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression Special Report on New Depression Treatment Technology Based on 2010 APA Practice Guidelines Best Practices Guideline for the Treatment of Patients
Why are antidepressants used to treat IBS? Some medicines can have more than one action (benefit) in treating medical problems.
 The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD What are functional GI disorders? There are more
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD What are functional GI disorders? There are more
Review of Pharmacological Pain Management
 Review of Pharmacological Pain Management CHAMP Activities are possible with generous support from The Atlantic Philanthropies and The John A. Hartford Foundation The WHO Pain Ladder The World Health Organization
Review of Pharmacological Pain Management CHAMP Activities are possible with generous support from The Atlantic Philanthropies and The John A. Hartford Foundation The WHO Pain Ladder The World Health Organization
IMR ISSUES, DECISIONS AND RATIONALES The Final Determination was based on decisions for the disputed items/services set forth below:
 Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
ANTIDEPRESSANT MEDICINES. A GUIDE for ADULTS With DEPRESSION
 ANTIDEPRESSANT MEDICINES A GUIDE for ADULTS With DEPRESSION August 2007 FAST FACTS ON ANTIDEPRESSANTS The antidepressants in this guide work for treating depression. Most people can find one that makes
ANTIDEPRESSANT MEDICINES A GUIDE for ADULTS With DEPRESSION August 2007 FAST FACTS ON ANTIDEPRESSANTS The antidepressants in this guide work for treating depression. Most people can find one that makes
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS. Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health
 PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health Learning Objectives Learn basics about the various types of medications that
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health Learning Objectives Learn basics about the various types of medications that
Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia
 Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia Trust, team and patient information Q1. Patient's DIS number... Q2. Patient s residence: Home Residential Home Nursing Home
Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia Trust, team and patient information Q1. Patient's DIS number... Q2. Patient s residence: Home Residential Home Nursing Home
POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS
 Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant
Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant
A Manic Episode is defined by a distinct period during which there is an abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood.
 Bipolar disorder Bipolar (manic-depressive illness) is a recurrent mode disorder. The patient may feel stable at baseline level but experience recurrent shifts to an emotional high (mania or hypomania)
Bipolar disorder Bipolar (manic-depressive illness) is a recurrent mode disorder. The patient may feel stable at baseline level but experience recurrent shifts to an emotional high (mania or hypomania)
DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 1 DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for depression and any history of depression? 2. Did staff
1 DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for depression and any history of depression? 2. Did staff
What You Should Know
 What You Should Know Will this medicine work for me? The antidepressants presented in this decision aid all work the same for treating depression. Most people with depression can find one that can make
What You Should Know Will this medicine work for me? The antidepressants presented in this decision aid all work the same for treating depression. Most people with depression can find one that can make
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents.
 Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
North of Tyne Area Prescribing Committee
 North of Tyne Area Prescribing Committee ANTIPSYCHOTICS IN PSYCHOSIS, BIPOLAR DISORDER AND AUGMENTATION THERAPY IN TREATMENT RESISTANT DEPRESSION Information for Primary Care Updated November 2013 This
North of Tyne Area Prescribing Committee ANTIPSYCHOTICS IN PSYCHOSIS, BIPOLAR DISORDER AND AUGMENTATION THERAPY IN TREATMENT RESISTANT DEPRESSION Information for Primary Care Updated November 2013 This
Medicines for Treating Depression. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Treating Depression A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor or other health care professional has told you that you have depression. Your doctor
Medicines for Treating Depression A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor or other health care professional has told you that you have depression. Your doctor
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine Clinical Indication: Treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease (AD)
 SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AND INFORMATION FOR GPS Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine Clinical Indication: Treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Version: 3 Date Approved: June 2011 Review
SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AND INFORMATION FOR GPS Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine Clinical Indication: Treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Version: 3 Date Approved: June 2011 Review
How to Identify and Diagnose Depression
 Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
Remeron (mirtazapine)
 Remeron (mirtazapine) FDA ALERT [07/2005] Suicidal Thoughts or Actions in Children and Adults Patients with depression or other mental illnesses often think about or attempt suicide. Closely watch anyone
Remeron (mirtazapine) FDA ALERT [07/2005] Suicidal Thoughts or Actions in Children and Adults Patients with depression or other mental illnesses often think about or attempt suicide. Closely watch anyone
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: a pharmacological treatment approach
 Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: a pharmacological treatment approach Professor Alasdair Vance Head, Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics University of Melbourne Royal Children s Hospital
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: a pharmacological treatment approach Professor Alasdair Vance Head, Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics University of Melbourne Royal Children s Hospital
PTSD Evidence Based Practice Recommendations
 PTSD Evidence ased Practice Recommendations Jason's ox est Practice Group Dr. Sam Moreno, Michelle Schnack Compilation & consolidation of the research and recommendations located in: The VA/DoD Clinical
PTSD Evidence ased Practice Recommendations Jason's ox est Practice Group Dr. Sam Moreno, Michelle Schnack Compilation & consolidation of the research and recommendations located in: The VA/DoD Clinical
DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource
 E-Resource March, 2015 DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource Depression affects approximately 20% of the general population
E-Resource March, 2015 DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource Depression affects approximately 20% of the general population
The Antidepressants: Treating Depression. Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price
 The Antidepressants: Treating Depression Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Antidepressants can improve the symptoms of depression, but they can also have serious side effects.
The Antidepressants: Treating Depression Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Antidepressants can improve the symptoms of depression, but they can also have serious side effects.
Medication Guide. Cymbalta. (duloxetine delayed-release capsules)
 Medication Guide 1 Cymbalta [sim-ball-tah] (duloxetine delayed-release capsules) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Cymbalta and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Medication Guide 1 Cymbalta [sim-ball-tah] (duloxetine delayed-release capsules) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Cymbalta and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Depression in children and young people. Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care
 NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Medication Guide SYMBYAX. (SIM-be-ax)
 1 Medication Guide SYMBYAX (SIM-be-ax) (olanzapine and fluoxetine) Capsule Read the Medication Guide that comes with SYMBYAX before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new
1 Medication Guide SYMBYAX (SIM-be-ax) (olanzapine and fluoxetine) Capsule Read the Medication Guide that comes with SYMBYAX before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults. (update) and
 Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen (aripiprazole)
 EMA/303592/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen (aripiprazole) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen, which details the measures
EMA/303592/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen (aripiprazole) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen, which details the measures
Depression Treatment Guide
 Depression Treatment Guide DSM V Criteria for Major Depressive Disorders A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous
Depression Treatment Guide DSM V Criteria for Major Depressive Disorders A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous
TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER
 TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2002. 1 For Continuing Medical
TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2002. 1 For Continuing Medical
POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm
 E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
