Psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacology. Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical. Department of Psychiatry, RVI
|
|
|
- Martina Short
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Regional Affective Disorders Service Psychopharmacology Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical Psychopharmacology Department of Psychiatry, RVI
2 Intro NOT a comprehensive review of everything you need to know about drug treatments of mental illness! Remember: 30% of patients visiting their GP have mental health problems 20-50% of patient in hospital out-patient clinics have mental health problems This is NOT some highly specialised area that you only need to have a vague knowledge of All doctors need to know something about psychotropic drugs
3 Plan General comments Brief overview of major groups of psychotropics Antidepressants Hypnotics/anxiolytics Antipsychotics Mood Stabilisers NOT Anti-dementia drugs Drugs used in addictions Drugs used for ADHD See Presentations and then Medical Student Senior Rotation, Autumn, 2007
4 The science of psychopharmacology Three classic studies
5 Efficacy of Drug Treatments - Antidepressants 100 MRC Antidepressant Trial, % recovered % improved ECT Imipramine Phenelzine Placebo
6 Efficacy of Drug Treatments - Antipsychotics Symptom ratings Johnstone et al Treatment of Schziophrenia β-flupenthixol Placebo α-flupenthixol Weeks * *
7 Efficacy of Drug Treatments - Lithium Prophylaxis Probability of remaining well Marker & Mander, 1989 Lithium Control Months
8 The clinical use of psychotropic Idiosyncratic reactions drugs e.g. amphetamine, SSRIs and migraine Lack of therapeutic ranges for drugs e.g. most antidepressants Enormous dosage ranges e.g. 10mg 1500mg chlorpromazine per day High rates of non-response Multiple classes of drugs Polypharmacy
9 Antidepressants TCAs SSRIs NaRIs SNRIs Antagonists MAOIs..and others currently available plus ones on the way
10 Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) H1 M1 NRI TCA α1 SRI N.B. also effects on cardiac and neuronal membrane excitability e.g. amitriptyline, lofepramine, imipramine Inhibit 5-HT and NA uptake Produces therapeutic effect Block of M 1, H 1, α 1 receptors produces side effects Poorly tolerated and toxic in overdose (except lofepramine)?amitriptyline more potent than SSRIs for severe depression
11 Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) SSRI SRI e.g. fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram Inhibit 5-HT uptake Produces therapeutic benefit depression OCD, Panic, anxiety Produces side effects Nausea Early increased anxiety Sexula dysfunction Well tolerated and good first line treatments
12 Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors (NaRIs) NRI NARI e.g. reboxetine (lofepramine) Inhibit NA uptake Produces therapeutic effect Produces side effects Well tolerated Alternative class for patients who fail an SSRI
13 Serotonin and Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) NRI SNRI DRI SRI e.g. venlafaxine, duloxetine Inhibit 5-HT and NA (and DA) uptake Produces therapeutic effect Produces side effects Similar to SSRI Better tolerated than TCAs and? more effective than SSRIs for severe depression therefore good second/third line treatment
14 Noradrenaline and Serotonin Selective Antagonist 5-HT2 5-HT3 H1 NaSSA α2 e.g. mirtazepine Blocks α 2 receptors Produces antidepressant effect (Increases 5-HT release) Blocks 5-HT 2 receptors Produces decreased anxiety Blocks H 1 receptors Produces sedation? more potent than SSRIs plus lacks sexual side effects, but causes marked weight gain. Used second line
15 5-HT 2 antagonist e.g. Trazodone Weakly blocks 5-HT uptake H1? effect 5-HT2 Trazodone SRI Blocks 5-HT 2 receptors? Main way produces benefit on depressive and anxiety symptoms α Blocks H1 receptors Produces sedation? Potency as mainline treatment but often used to augment SSRIs or SNRIs
16 Monamine Oxidase Inhibitors MAOI Traditional e.g. phenelzine, tranylcypromine Food & drug interaction RIMA e.g. moclobemide Increase levels of 5-HT, NA (and dopamine - traditionals) produces therapeutic benefit Second line for atypical depression, third line treatments for severe depression
17 NICE Clinical Guideline 23 December 2004 Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care
18 Guidance Good practice points for all Stepped care Step 1: Recognition of depression Step 2: Depression in primary care mild depression Step 3: Depression in primary care moderate to severe Step 4: Mental health services refractory, recurrent, atypical and psychotic depression Step 5: Depression requiring inpatient care
19 Step 2 Mild depression Antidepressants Not recommended for initial treatment Use if symptoms persist after other interventions depression associated with psychosocial problems past history of moderate to severe depression Recommended interventions Sleep and anxiety management Watchful waiting Structured exercise Guided self-help
20 Step 3 - moderate to severe depression Antidepressants Antidepressants should be routinely offered Address common concerns Inform about potential side effects and risk of discontinuation/withdrawal symptoms (particularly with paroxetine and venlafaxine) Inform about time delay in response Continue for at least 6 months from remission After 6 months review need for medication
21 Step 3 Choice of antidepressant SSRI in routine care fluoxetine or citalopram If response inadequate consider increasing dose to BNF limits If not effective switch antidepressant [C] Reasonable alternative to SSRIs = mirtazepine, but consider moclobemide, reboxetine, lofepramine. Venlafaxine or an older TCA for severe depression
22 Step 4 Atypical, psychotic and recurrent depression Atypical depression Hypersomnia, increased appetite, hypersensitive consider an MAOI (phenelzine) Psychotic depression Augment with an antipsychotic Recurrent depression Drugs If 2 or more episodes consider ADs for 2 years Use same dose of AD as for acute treatment Psychotherapies Consider CBT
23 Step 4 - Refractory depression Failure to respond to 2 or more ADs Consider the following options: ADs plus CBT Lithium augmentation Venlafaxine up to BNF limits SSRI + mianserin or mirtazepine [C] Consider phenelzine
24 Anxiolytics/hypnotics Benzodiazepines e.g. diazepam, lorazepam, chlordiazepoxide, temazepam Act on GABA A receptor complexes Relieve anxiety immediately, good for short term use Hypnotics are simply BZs with shorter half lifes S/E s - very few except dependency However antidepressants are the drugs of choice for treating anxiety but take longer to work
25 Antipsychotics Typicals/conventionals/first generation antipsychotics e.g. chlorpromazine, haloperidol Atypicals/second generation antipsychotics Clozapine Olanzapine Risperidone Quetiapine Aripiprazole Amisulpride Sulpiride
26 Tricyclic Antidepressant NRI H1 TCA SRI M1 α1 N.B. also effects on cardiac and neuronal membrane excitability
27 H1 M1 α1 N.B. also effects on cardiac and neuronal membrane excitability
28 Typical antipsychotics H1 M1 CPZ D2 α1 N.B. also effects on cardiac and neuronal membrane excitability E.g. chlorpromazine, haloperidol Block D 2 receptors Therapeutic effects EPS Also antagonise histamine, NA and acetylcholine receptors causing side effects Antipsychotic and sedative Used in schizophrenia, mania, psychotic depression NICE no longer recommend them first line
29 Atypical core pharmacology 5HT2A SGA D Stahl S M, Essential Psychopharmacology (2000)
30 Atypical rich pharmacology 5HT1A 5HT2A M1 H HT1D SRI 5HT2C NRI 5HT3 atypical antipsychotic D1 5HT6 D4 D3 D2 5HT Stahl S M, Essential Psychopharmacology (2000)
31 Clozapine the archetypal atypical 5HT1A 5HT2A M1 H HT2C 5HT3 5HT6 clozapine D4 D3 D2 D1 5HT Stahl S M, Essential Psychopharmacology (2000)
32 Clozapine Introduced in Europe in 1975 (but not UK) Less extrapyramidal symptoms than typicals Withdrawn due to cases of fatal neutropenia Kane et al. (1988) - large trial of treatment resistant schizophrenic patients (300+) failed at least three antipsychotics before entry all given high dose haloperidol - those who failed to respond randomised to chlorpromazine or clozapine 30% response to clozapine c.f. 4% to chlorpromazine significant effect on negative symptoms
33 Newer atypicals More recently introduced drugs Some more dopamine selective e.g. sulpiride, amisulpride Most recent dopamine partial agonist e.g. aripiprazole Most combined 5-HT 2 and D 2 antagonists e.g. risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine All pharmacologically differ
34 5HT2A 1 2 risperidone D2 5HT Stahl S M, Essential Psychopharmacology (2000)
35 5HT2A M1 H1 1 5HT2C 5HT3 5HT6 olanzapine D4 D3 D2 D Stahl S M, Essential Psychopharmacology (2000)
36 5HT2A H HT6 quetiapine D2 5HT Stahl S M, Essential Psychopharmacology (2000)
37 Atypicals Now first line antipsychotics for schizophrenia and mania (+ other effects in bipolar disorder) Less EPS quetiapine, olanzapine < risperidone amisulpiride, sulpiride, aripiprazole < convential antipsychotics Less hyperprolactinaemia quetiapine and olanzapine Still occurs with risperidone, amisulpiride and sulpiride Risk of weight gain, metabolic syndrome and diabetes clozapine, olzapine > quetiapine, risperidone > amisulpiride, sulpiride, aripiprazole? Differences in potency Clozapine used for TRS, but risk of blood disorders Olanzapine and risperidone possibly more potent than quetiapine in schizophrenia Quetiapine has possibly best evidence in bipolar disorder Depot risperidone available Expensive
38 NICE Clinical Guideline 1 December 2002 Core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia in primary and secondary care
39 Acute Episode Informed choice by patient If not able to do this then atypical If on typical and SEs are problematic or Sx control is inadequate, then atypical (otherwise remain on conventional) Single drug within BNF limits Avoid high doses and loading doses Treatment trials should be for periods of 6-8 weeks Progress, SEs and user satisfaction should be monitored closely Treat for 1-2 years, withdraw slowly and monitor for 2 years after withdrawal
40 What is a Mood Stabiliser Treats depression plus mania without making either pole worse and/or has prophylactic effects for both mania and depression Absence of a consensus definition NICE The guideline avoids the term mood stabiliser, because there is no agreed definition. The terms 'antimanic agent' or 'antimanic medication' are used for treatment of an acute episode, and 'prophylactic agent' or 'prophylactic medication' for long-term maintenance treatment
41 The course of Bipolar Disorder Mania Hypomania Euthymia Minor Depression Major Depression Preliminary Phase Preventative Phase
42 NICE Clinical Guideline 38 July 2006 Bipolar Disorder: The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care
43 Acute Mania Atypical antipsychotic (olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine) for those with severe mania If ineffective consider adding Li or valproate Valproate or Li if previous good response and compliance Avoid valproate in women of child baring potential Li only if less severe
44 Acute Depression First line: SSRI plus antimanic agent If on antimanic: SSRI or quetiapine (if not on antipsychotic) Avoid antidepressant monotherapy Taper antidepressants after symptoms reduced for 8 weeks
45 Long-term Treatment First line: lithium, olanzapine or valproate If fails monotherapy over 6 months Li + valp, Li + olanz, Valp + olanz If combination fails Consider lamotrigine (esp. freq. depressions), carbamazepine NOT antidepressants routinely
46 Bipolar treatments: some issues Lithium Narrow therapeutic index monitor levels 2 monthly Renal and thyroid dysfunction renal function + TFTs 6 monthly Sudden discontinuation 50% risk of mania Teratogenic Epsteins anomaly Valproate Not for women under 18 or of child baring potential Teratogenicity (neural tube), polycystic ovary Levels if ineffective, poor adherence or toxicity Lamotrigine Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome Slow dose titration
47 Clinical use of Drugs in Psychiatry Fundamental principles: Assessment of risk/benefits Consideration of costs Full discussion with patient Informed choice by patient Repeated monitoring and re-assessment Integration with other treatments
48 Conclusions Drugs are often the first line treatment in psychiatric illness However drugs are not the only mode of treatment Good evidence supports their use The use of psychotropics is complicated by: professional perceptions of illness patient perceptions of treatment Complexity of their pharmacology Normal good clinical practice is essential
Antidepressant treatment in adults
 Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY
 University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
NICE Clinical guideline 23
 NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
 TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services
 Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services DEPRESSION Pharmacological Treatment of Depression NICE guidelines suggest the following stepped care model also
Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services DEPRESSION Pharmacological Treatment of Depression NICE guidelines suggest the following stepped care model also
Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
Medications for bipolar disorder
 Medications for bipolar disorder Findings from Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing (Mitchell et al, 2004) In 12 months, only one-third saw a mental health professional 40% received
Medications for bipolar disorder Findings from Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing (Mitchell et al, 2004) In 12 months, only one-third saw a mental health professional 40% received
Preferred Practice Guidelines Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents
 These Guidelines are based in part on the following: American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry s Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Bipolar Disorder,
These Guidelines are based in part on the following: American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry s Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Bipolar Disorder,
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine
 Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION
 MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
NICE clinical guideline 90
 Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder. Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice
 Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS. Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health
 PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health Learning Objectives Learn basics about the various types of medications that
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health Learning Objectives Learn basics about the various types of medications that
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Depression Pathway. Patient Education Box 4. Guided self help Box 18. pg 11
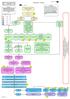 LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
Bipolar disorder. The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care NICE clinical guideline 38 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care NICE clinical guideline 38 Developed by the National Collaborating
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression
 Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
Conjoint Professor Brian Draper
 Chronic Serious Mental Illness and Dementia Optimising Quality Care Psychiatry Conjoint Professor Brian Draper Academic Dept. for Old Age Psychiatry, Prince of Wales Hospital, Randwick Cognitive Course
Chronic Serious Mental Illness and Dementia Optimising Quality Care Psychiatry Conjoint Professor Brian Draper Academic Dept. for Old Age Psychiatry, Prince of Wales Hospital, Randwick Cognitive Course
Treatments for Major Depression. Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are:
 Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Neuroscience An extra bit. Dr Sasha Gartside Institute of Neuroscience Newcastle University
 Neuroscience An extra bit Dr Sasha Gartside Institute of Neuroscience Newcastle University Drugs, receptors, and transporters Most psychoactive drugs interfere with neurotransmission The main targets are
Neuroscience An extra bit Dr Sasha Gartside Institute of Neuroscience Newcastle University Drugs, receptors, and transporters Most psychoactive drugs interfere with neurotransmission The main targets are
The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care
 Quick reference guide Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care Developed by the National Collaborating
Quick reference guide Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care Developed by the National Collaborating
Clinical Recommendations for Treatment of Bipolar Disorder for Hong Kong 2013
 Clinical Recommendations for Treatment of Bipolar Disorder for Hong Kong 2013 Version: March 2013 Objectives of Treatment Rapid control of symptoms especially agitation, impulsivity, aggression, suicidality
Clinical Recommendations for Treatment of Bipolar Disorder for Hong Kong 2013 Version: March 2013 Objectives of Treatment Rapid control of symptoms especially agitation, impulsivity, aggression, suicidality
Bipolar disorder GUIDELINE
 Bipolar disorder F Colin 1. Introduction Bipolar disorder (BD) presents in different phases over time and is often complicated by comorbid conditions such as substance-use disorders and anxiety disorders.
Bipolar disorder F Colin 1. Introduction Bipolar disorder (BD) presents in different phases over time and is often complicated by comorbid conditions such as substance-use disorders and anxiety disorders.
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATION USE FOR PERSONS WITH INTELLECTUAL DISABILITIES
 INTRODUCTION A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATION USE FOR PERSONS WITH INTELLECTUAL DISABILITIES Individuals with intellectual disabilities are not uncommonly prescribed psychotropic medications.
INTRODUCTION A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATION USE FOR PERSONS WITH INTELLECTUAL DISABILITIES Individuals with intellectual disabilities are not uncommonly prescribed psychotropic medications.
CLINICIAN INTERVIEW COMPLEXITIES OF BIPOLAR DISORDER. Interview with Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD
 COMPLEXITIES OF BIPOLAR DISORDER Interview with Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD Dr Nemeroff is the Reunette W. Harris Professor and Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Emory
COMPLEXITIES OF BIPOLAR DISORDER Interview with Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD Dr Nemeroff is the Reunette W. Harris Professor and Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Emory
Major Depression. What is major depression?
 Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Anxiety Disorders Drug Treatment Guidelines
 Western Australian Psychotropic Drugs Committee Anxiety Disorders Drug Treatment Guidelines August 2008 www.watag.org.au Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Psychological or pharmacological treatment?...
Western Australian Psychotropic Drugs Committee Anxiety Disorders Drug Treatment Guidelines August 2008 www.watag.org.au Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Psychological or pharmacological treatment?...
Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents
 TREATMENT GUIDELINES Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Guideline 7 Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Description There are few controlled trials to guide practitioners
TREATMENT GUIDELINES Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Guideline 7 Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Description There are few controlled trials to guide practitioners
TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER
 TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2002. 1 For Continuing Medical
TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2002. 1 For Continuing Medical
Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression
 Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression Special Report on New Depression Treatment Technology Based on 2010 APA Practice Guidelines Best Practices Guideline for the Treatment of Patients
Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression Special Report on New Depression Treatment Technology Based on 2010 APA Practice Guidelines Best Practices Guideline for the Treatment of Patients
Depre r s e sio i n o i n i a dults Yousuf Al Farsi
 Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
Ttreatment algorithms were discussed in a previous article. 1
 The Texas Medication Algorithm Project: Report of the Texas Consensus Conference Panel on Medication Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder M. Lynn Crismon, Pharm.D.; Madhukar Trivedi, M.D.; Teresa A.
The Texas Medication Algorithm Project: Report of the Texas Consensus Conference Panel on Medication Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder M. Lynn Crismon, Pharm.D.; Madhukar Trivedi, M.D.; Teresa A.
Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center
 Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center First Line Medications SSRIs Prozac (Fluoxetine): 5-605 mg Zoloft (Sertraline):
Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center First Line Medications SSRIs Prozac (Fluoxetine): 5-605 mg Zoloft (Sertraline):
Pharmacological management of unipolar depression
 Acta Psychiatr Scand 2013: 127 (Suppl. 443): 6 23 All rights reserved DOI: 10.1111/acps.12122 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd ACTA PSYCHIATRICA SCANDINAVICA Clinical overview
Acta Psychiatr Scand 2013: 127 (Suppl. 443): 6 23 All rights reserved DOI: 10.1111/acps.12122 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd ACTA PSYCHIATRICA SCANDINAVICA Clinical overview
What are the best treatments?
 What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
If you are not clear about why an antidepressant has been suggested for you, ask your doctor.
 Antidepressants Aims of the leaflet This leaflet is for anyone who wants to know more about antidepressants. It discusses how they work, why they are prescribed, their effects and side-effects, and alternative
Antidepressants Aims of the leaflet This leaflet is for anyone who wants to know more about antidepressants. It discusses how they work, why they are prescribed, their effects and side-effects, and alternative
Psychiatric Medication Information
 Psychiatric Medication Information A Guide for Patients & Carers 3 rd Edition (November 2013) Revised & Updated St Vincent s Hospital & The University of Melbourne Professor David Castle Chair of Psychiatry
Psychiatric Medication Information A Guide for Patients & Carers 3 rd Edition (November 2013) Revised & Updated St Vincent s Hospital & The University of Melbourne Professor David Castle Chair of Psychiatry
Bipolar disorder. Understanding NICE guidance
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Bipolar disorder NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Bipolar disorder NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Depression. The treatment and management of depression in adults. This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Improving the Recognition and Treatment of Bipolar Depression
 Handout for the Neuroscience Education Institute (NEI) online activity: Improving the Recognition and Treatment of Bipolar Depression Learning Objectives Apply evidence-based tools that aid in differentiating
Handout for the Neuroscience Education Institute (NEI) online activity: Improving the Recognition and Treatment of Bipolar Depression Learning Objectives Apply evidence-based tools that aid in differentiating
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease
 Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults
 Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines
 MOH CLINICL PRCTICE GUIELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines College of Family Physicians, Singapore cademy of Medicine, Singapore Executive summary of recommendations etails of recommendations
MOH CLINICL PRCTICE GUIELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines College of Family Physicians, Singapore cademy of Medicine, Singapore Executive summary of recommendations etails of recommendations
Bipolar Disorder. Mania is the word that describes the activated phase of bipolar disorder. The symptoms of mania may include:
 Bipolar Disorder What is bipolar disorder? Bipolar disorder, or manic depression, is a medical illness that causes extreme shifts in mood, energy, and functioning. These changes may be subtle or dramatic
Bipolar Disorder What is bipolar disorder? Bipolar disorder, or manic depression, is a medical illness that causes extreme shifts in mood, energy, and functioning. These changes may be subtle or dramatic
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over
 Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Overview of Mental Health Medication Trends
 America s State of Mind Report is a Medco Health Solutions, Inc. analysis examining trends in the utilization of mental health related medications among the insured population. The research reviewed prescription
America s State of Mind Report is a Medco Health Solutions, Inc. analysis examining trends in the utilization of mental health related medications among the insured population. The research reviewed prescription
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents.
 Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
ATYPICALS ANTIPSYCHOTIC MEDICATIONS
 The atypical antipsychotics are a class of drugs that are used to treat a number of behavioral health disorders, including schizophrenia, other psychotic disorders, mood disorders, and behavioral agitation
The atypical antipsychotics are a class of drugs that are used to treat a number of behavioral health disorders, including schizophrenia, other psychotic disorders, mood disorders, and behavioral agitation
Depression Flow Chart
 Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Published 09 September 2013 1. 09 August 2013
 aripiprazole 5mg, 10mg, 15mg, 30mg tablets, 10mg, 15mg orodispersible tablets, 1mg/mL oral solution (Abilify ) SMC No. (891/13) Otsuka Pharmaceutical (UK) Ltd 09 August 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium
aripiprazole 5mg, 10mg, 15mg, 30mg tablets, 10mg, 15mg orodispersible tablets, 1mg/mL oral solution (Abilify ) SMC No. (891/13) Otsuka Pharmaceutical (UK) Ltd 09 August 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium
Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90
 Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
Handy charts to help people compare the medications for mental health conditions
 Handy charts Handy charts to help people compare the medications for mental health conditions Contents: 1. Acute Psychiatric Emergency 2. ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) 3. Alcohol Dependence
Handy charts Handy charts to help people compare the medications for mental health conditions Contents: 1. Acute Psychiatric Emergency 2. ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) 3. Alcohol Dependence
and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Issue date: November 2005
 Issue date: November 2005 Treating obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD) and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Understanding NICE guidance information for people with OCD
Issue date: November 2005 Treating obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD) and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Understanding NICE guidance information for people with OCD
These guidelines are intended to support General Practitioners in the care of their patients with dementia both in the community and in care homes.
 This is a new guideline. These guidelines are intended to support General Practitioners in the care of their patients with dementia both in the community and in care homes. It incorporates NICE clinical
This is a new guideline. These guidelines are intended to support General Practitioners in the care of their patients with dementia both in the community and in care homes. It incorporates NICE clinical
Making sense of coming off psychiatric drugs. coming off psychiatric drugs
 Making sense of coming off psychiatric drugs coming off psychiatric drugs Making sense of coming off psychiatric drugs Many people would like to stop their psychiatric medication, but coming off can be
Making sense of coming off psychiatric drugs coming off psychiatric drugs Making sense of coming off psychiatric drugs Many people would like to stop their psychiatric medication, but coming off can be
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview
 Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
1/23/2014 TOPICS PHARMACOLOGY: UPDATES AND REVIEW. Elizabeth Reeve MD HealthPartners Medical Group Gillette Children s Specialty Heath Care
 PHARMACOLOGY: UPDATES AND REVIEW Elizabeth Reeve MD HealthPartners Medical Group Gillette Children s Specialty Heath Care TOPICS General pharmacology concepts when prescribing for children and adults When
PHARMACOLOGY: UPDATES AND REVIEW Elizabeth Reeve MD HealthPartners Medical Group Gillette Children s Specialty Heath Care TOPICS General pharmacology concepts when prescribing for children and adults When
Disclosures Christer Allgulander
 How Patients With Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Are Treated in Specialized Care: A Pharmacoepidemiological Case Register Study in Sweden Christer Allgulander MD, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden Jan
How Patients With Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Are Treated in Specialized Care: A Pharmacoepidemiological Case Register Study in Sweden Christer Allgulander MD, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden Jan
Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults
 Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults Introduction The partial update of the guideline on Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder
Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults Introduction The partial update of the guideline on Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder
Unipolar Depression Management Protocol
 Unipolar Depression Management Protocol All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Unipolar depression or Major Depressive Disorder means that the patient feels persistent low mood or
Unipolar Depression Management Protocol All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Unipolar depression or Major Depressive Disorder means that the patient feels persistent low mood or
There are four groups of medications most likely to be used for depression: Antidepressants Antipsychotics Mood stabilisers Augmenting agents.
 What this fact sheet covers: Physical treatments (medication, ECT and TMS) Psychological treatments Self-help & alternative therapies Key points to remember Where to get more information. Introduction
What this fact sheet covers: Physical treatments (medication, ECT and TMS) Psychological treatments Self-help & alternative therapies Key points to remember Where to get more information. Introduction
Evidence-based best practice interventions for the treatment of mood disorders: Annotated Information Package
 Evidence-based best practice interventions for the treatment of mood disorders: Annotated Information Package September 2007 Evidence-based best practice interventions for the treatment of mood disorders:
Evidence-based best practice interventions for the treatment of mood disorders: Annotated Information Package September 2007 Evidence-based best practice interventions for the treatment of mood disorders:
Depression in Long-Term Care
 Depression in Long-Term Care Annette Carron, DO, CMD, FACOI, FAAHPM Director Geriatrics and Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Slide 1 OBJECTIVES Know and understand: Incidence and morbidity of depressive
Depression in Long-Term Care Annette Carron, DO, CMD, FACOI, FAAHPM Director Geriatrics and Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Slide 1 OBJECTIVES Know and understand: Incidence and morbidity of depressive
An Investigation of Atypical Antidepressants
 An Investigation of Atypical Antidepressants An Interactive Qualifying Project Report submitted to the Faculty of WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree
An Investigation of Atypical Antidepressants An Interactive Qualifying Project Report submitted to the Faculty of WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree
How to Identify and Diagnose Depression
 Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
Why are antidepressants used to treat IBS? Some medicines can have more than one action (benefit) in treating medical problems.
 The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD What are functional GI disorders? There are more
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD What are functional GI disorders? There are more
New Treatments. For Bipolar Disorder. Po W. Wang, MD Clinical Associate Professor Bipolar Disorders Clinic Stanford University School of Medicine
 New Treatments For Bipolar Disorder Po W. Wang, MD Clinical Associate Professor Bipolar Disorders Clinic Stanford University School of Medicine Abbott Laboratories AstraZeneca Bristol-Myers Squibb Corcept
New Treatments For Bipolar Disorder Po W. Wang, MD Clinical Associate Professor Bipolar Disorders Clinic Stanford University School of Medicine Abbott Laboratories AstraZeneca Bristol-Myers Squibb Corcept
Psychiatric Medications: Pearls and Pitfalls. The majority of medications used in patients with psychiatric diagnoses have more than one use.
 Psychiatric Medications: Pearls and Pitfalls Rule #1 The majority of medications used in patients with psychiatric diagnoses have more than one use. Without access to the patient s medical record, to review
Psychiatric Medications: Pearls and Pitfalls Rule #1 The majority of medications used in patients with psychiatric diagnoses have more than one use. Without access to the patient s medical record, to review
Psychotropic Medication in Pregnancy/Lactation. Mercy Hospital for Women. 2nd Edition. www.mercy.com.au
 Psychotropic Medication in Pregnancy/ 2nd Edition www.mercy.com.au Mercy Hospital for Women Psychotropic Medication in Pregnancy/ 2nd Edition General Points: None of the Psychotropic medications have been
Psychotropic Medication in Pregnancy/ 2nd Edition www.mercy.com.au Mercy Hospital for Women Psychotropic Medication in Pregnancy/ 2nd Edition General Points: None of the Psychotropic medications have been
Bipolar Disorder. MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 5/2011. Singapore Medical Association. Academy of Medicine, Singapore
 Bipolar Disorder MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 5/2011 College of Family Physicians, Singapore Academy of Medicine, Singapore Singapore Medical Association November 2011 Levels of evidence and grades
Bipolar Disorder MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 5/2011 College of Family Physicians, Singapore Academy of Medicine, Singapore Singapore Medical Association November 2011 Levels of evidence and grades
TEXAS MEDICATION ALGORITHM PROJECT PROCEDURAL MANUAL
 TEXAS MEDICATION ALGORITHM PROJECT PROCEDURAL MANUAL BIPOLAR DISORDER ALGORITHMS M. Lynn Crismon, PharmD, BCPP Tami R. Argo, PharmD, MS, BCPP Sherrie D. Bendele, BS Trisha Suppes, MD, PhD 2007, Texas Department
TEXAS MEDICATION ALGORITHM PROJECT PROCEDURAL MANUAL BIPOLAR DISORDER ALGORITHMS M. Lynn Crismon, PharmD, BCPP Tami R. Argo, PharmD, MS, BCPP Sherrie D. Bendele, BS Trisha Suppes, MD, PhD 2007, Texas Department
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: a pharmacological treatment approach
 Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: a pharmacological treatment approach Professor Alasdair Vance Head, Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics University of Melbourne Royal Children s Hospital
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: a pharmacological treatment approach Professor Alasdair Vance Head, Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics University of Melbourne Royal Children s Hospital
Depression in children and young people. Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care
 NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
A Manic Episode is defined by a distinct period during which there is an abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood.
 Bipolar disorder Bipolar (manic-depressive illness) is a recurrent mode disorder. The patient may feel stable at baseline level but experience recurrent shifts to an emotional high (mania or hypomania)
Bipolar disorder Bipolar (manic-depressive illness) is a recurrent mode disorder. The patient may feel stable at baseline level but experience recurrent shifts to an emotional high (mania or hypomania)
1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the
 1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
Understanding Antipsychotic Medications
 Understanding Antipsychotic Medications NARSAD RESEARCH National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression 60 Cutter Mill Road, Suite 404 Great Neck, NY 11021 516-829-0091 1-800-829-8289 516-487-6930
Understanding Antipsychotic Medications NARSAD RESEARCH National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression 60 Cutter Mill Road, Suite 404 Great Neck, NY 11021 516-829-0091 1-800-829-8289 516-487-6930
Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder Second Edition
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR THE Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder Second Edition WORK GROUP ON BIPOLAR DISORDER Robert M.A. Hirschfeld, M.D., Chair Charles L. Bowden, M.D. Michael J. Gitlin, M.D.
PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR THE Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder Second Edition WORK GROUP ON BIPOLAR DISORDER Robert M.A. Hirschfeld, M.D., Chair Charles L. Bowden, M.D. Michael J. Gitlin, M.D.
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression
 Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
American Psychiatric Association
 Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder (Revision) American Psychiatric Association Originally published in April 2002. A guideline watch, summarizing significant developments
Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder (Revision) American Psychiatric Association Originally published in April 2002. A guideline watch, summarizing significant developments
GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup. Shared Care Template
 GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) for the treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Body Dysmorphic
GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) for the treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Body Dysmorphic
Treating Major Depressive Disorder
 Treating Major Depressive Disorder A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Third Edition, originally published in October 2010.
Treating Major Depressive Disorder A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Third Edition, originally published in October 2010.
Paxil/Paxil-CR (paroxetine)
 Generic name: Paroxetine Available strengths: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg tablets; 10 mg/5 ml oral suspension; 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg controlled-release tablets (Paxil-CR) Available in generic: Yes, except
Generic name: Paroxetine Available strengths: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg tablets; 10 mg/5 ml oral suspension; 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg controlled-release tablets (Paxil-CR) Available in generic: Yes, except
Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia
 Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia Trust, team and patient information Q1. Patient's DIS number... Q2. Patient s residence: Home Residential Home Nursing Home
Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia Trust, team and patient information Q1. Patient's DIS number... Q2. Patient s residence: Home Residential Home Nursing Home
TEXAS MEDICATION ALGORITHM PROJECT PROCEDURAL MANUAL
 TEXAS MEDICATION ALGORITHM PROJECT PROCEDURAL MANUAL MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER ALGORITHMS Brandon Suehs, PharmD Tami R. Argo, PharmD, MS, BCPP Sherrie D. Bendele, BS M. Lynn Crismon, PharmD, BCPP Madhukar
TEXAS MEDICATION ALGORITHM PROJECT PROCEDURAL MANUAL MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER ALGORITHMS Brandon Suehs, PharmD Tami R. Argo, PharmD, MS, BCPP Sherrie D. Bendele, BS M. Lynn Crismon, PharmD, BCPP Madhukar
Data Based Medicine Paper: Dependence and Withdrawal
 Data Based Medicine Paper: Dependence and Withdrawal Author: Dr. David Healy Date Last Revised: 7 June 2012 Contents TREATMENT GROUPS... 2 DRUG GROUPS... 2 ALL DRUGS ACT ON EVERYTHING... 3 DRUG WITHDRAWAL
Data Based Medicine Paper: Dependence and Withdrawal Author: Dr. David Healy Date Last Revised: 7 June 2012 Contents TREATMENT GROUPS... 2 DRUG GROUPS... 2 ALL DRUGS ACT ON EVERYTHING... 3 DRUG WITHDRAWAL
SESSION K2. When SSRIs Are Not Enough, What Then?
 37th Annual Advanced Practice in Primary and Acute Care Conference: October 9-11, 2014 SESSION K2 3:55 When SSRIs Are Not Enough, What Then? Scott MacHaffie, MN, ARNP S E S S I O N Session Description:
37th Annual Advanced Practice in Primary and Acute Care Conference: October 9-11, 2014 SESSION K2 3:55 When SSRIs Are Not Enough, What Then? Scott MacHaffie, MN, ARNP S E S S I O N Session Description:
NHS FORTH VALLEY Drug Treatment of Depression
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Drug Treatment of Depression Endorsed by: Primary Care Prescribing Group Primary Care Drug and Therapeutics Committee Area Drug and Therapeutics Committee Depression ICP Group Approved
NHS FORTH VALLEY Drug Treatment of Depression Endorsed by: Primary Care Prescribing Group Primary Care Drug and Therapeutics Committee Area Drug and Therapeutics Committee Depression ICP Group Approved
POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS
 Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant
Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant
Treatment of depression drug therapies and ECT
 Ch.08.qxd 8/18/04 12:13 PM Page 99 Treatment of depression drug therapies and ECT 8 GENERAL QUESTIONS 8.1 GPs are being asked to diagnose and treat depression effectively, yet there are so many different
Ch.08.qxd 8/18/04 12:13 PM Page 99 Treatment of depression drug therapies and ECT 8 GENERAL QUESTIONS 8.1 GPs are being asked to diagnose and treat depression effectively, yet there are so many different
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines
 TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 01 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Post-traumatic stress disorder
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 01 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Post-traumatic stress disorder
TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER
 TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2002. A guideline watch,
TREATING BIPOLAR DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2002. A guideline watch,
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES. Depression
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
Generalised anxiety disorder in adults
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: anxiety Generalised anxiety disorder in adults diagnosis and management Key concepts: Anxiety disorders are the most frequently seen mental disorders in primary care Generalised
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: anxiety Generalised anxiety disorder in adults diagnosis and management Key concepts: Anxiety disorders are the most frequently seen mental disorders in primary care Generalised
4 DRUGS USED TO RELIEVE BEHAVIOURAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL SYMPTOMS OF DEMENTIA
 DEMENTIA Q&A 4 DRUGS USED TO RELIEVE BEHAVIOURAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL SYMPTOMS OF DEMENTIA People with dementia may at some point in their illness develop behavioural or psychological symptoms. While it is
DEMENTIA Q&A 4 DRUGS USED TO RELIEVE BEHAVIOURAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL SYMPTOMS OF DEMENTIA People with dementia may at some point in their illness develop behavioural or psychological symptoms. While it is
The pharmacological management of anxiety disorders
 Anxiety s z Review The pharmacological management of anxiety s Stephen Bleakley MRPharmS, MSc, FCMHP, Simon JC Davies DM (Oxon), MBBS (Lond), MRCPsych, MSc (LSHTM), MSc (Maastricht/Florence) Progress in
Anxiety s z Review The pharmacological management of anxiety s Stephen Bleakley MRPharmS, MSc, FCMHP, Simon JC Davies DM (Oxon), MBBS (Lond), MRCPsych, MSc (LSHTM), MSc (Maastricht/Florence) Progress in
Chapter 18 Drugs Used for Psychoses Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of psychotic behavior Describe major indications for the use of
 Chapter 18 Drugs Used for Psychoses Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of psychotic behavior Describe major indications for the use of antipsychotic agents Identify common adverse effects
Chapter 18 Drugs Used for Psychoses Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of psychotic behavior Describe major indications for the use of antipsychotic agents Identify common adverse effects
The Pharmacological Management of Depression in the Adult Person with Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities (MR/DD)
 The Pharmacological Management of Depression in the Adult Person with Mental Retardation and (MR/DD) 1. Overview Multiple classes of medications are available for treatment of depression in the patient
The Pharmacological Management of Depression in the Adult Person with Mental Retardation and (MR/DD) 1. Overview Multiple classes of medications are available for treatment of depression in the patient
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults. (update) and
 Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
