Spinal Decompression: Laminectomy & Laminotomy
|
|
|
- Avice Morgan
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
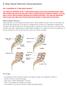
1 Spinal Decompression: Laminectomy & Laminotomy Overview Narrowing of the spinal canal, a condition called spinal stenosis can cause chronic pain, numbness, and muscle weakness in your arms or legs (Fig. 1). The condition primarily afflicts elderly people and is caused by degenerative changes that result in enlargement of the facet joints and thickening of the ligaments. Constriction of the spinal cord and nerves may be effectively relieved with a spinal decompression procedure if your symptoms have not improved with physical therapy or medications. This surgery requires a hospital stay from 1 to 3 days and recovery takes between 4 to 6 weeks. What is spinal decompression? Spinal decompression can be performed anywhere along the spine from the neck (cervical) to the lower back (lumbar). The procedure is performed through a surgical incision in the back (posterior). The lamina is the bone that forms the backside of the spinal canal and makes a roof over the spinal cord. Removing the lamina and other soft tissues gives more room for the nerves and allows for removal of bone spurs. Depending on the extent of stenosis, one vertebra (single-level) or more (multilevel) may be involved. There are several types of decompression surgery: Laminectomy is the removal of the entire bony lamina, a portion of the enlarged facet joints, and the thickened ligaments overlying the spinal cord and nerves. Laminotomy is the removal of a small portion of the lamina and ligaments, usually on one side. Using this method the natural support of the lamina is left in place, decreasing the chance of postoperative spinal instability. Sometimes an endoscope may be used, allowing for a smaller, less invasive incision. Foraminotomy is the removal of bone around the neural foramen - the space between vertebrae where the nerve root exits the spinal canal. This method is used when disc degeneration has caused the height of the foramen to collapse, resulting in a pinched nerve. It can be performed with a laminectomy or laminotomy. Laminaplasty is the expansion of the spinal canal by cutting the laminae on one side and swinging them open like a door. It is used only in the cervical area. Figure 1. (top view of vertebra) Spinal stenosis is a degenerative disease that causes narrowing of the spinal canal, enlargement of the facet joints, stiffening of the ligaments, and bony overgrowth. As the spinal canal narrows, it presses on the spinal cord and nerves, causing them to become swollen and inflamed. In some cases, spinal fusion may be done at the same time to help stabilize sections of the spine treated with laminectomy. Fusion uses a combination of bone graft, screws, and rods to connect two separate vertebrae together into one new piece of bone. Fusing the joint prevents the spinal stenosis from recurring and can help eliminate pain from an unstable spine. Who is a candidate? You may be a candidate for decompression if you have: significant pain, weakness, or numbness in your leg or foot leg pain worse than back pain not improved with physical therapy or medication difficulty walking or standing that affects your quality of life diagnostic tests (MRI, CT, myelogram) that show stenosis in the central canal or lateral recess. > 1
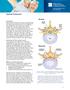
2 The surgical decision Decompression surgery for spinal stenosis is elective, except in the rare instance of cauda equina syndrome or rapidly progressing neurologic deficits. Your doctor may recommend treatment options, but only you can decide whether surgery is right for you. Be sure to look at all the risks and benefits before making a decision. Decompression does not cure spinal stenosis nor eliminate arthritis; it only relieves some of the symptoms. Unfortunately, the symptoms may recur as the degenerative process that produces stenosis continues. Who performs the procedure? A neurosurgeon or an orthopedic surgeon can perform spine surgery. Many spine surgeons have specialized training in complex spine surgery. Ask your surgeon about their training, especially if your case is complex or you ve had more than one spinal surgery. Figure 2. A skin incision is made down the middle of your back and the muscles overlying the vertebrae are dissected off the bone and moved to the side. What happens before surgery? You may be scheduled for presurgical tests (e.g., blood test, electrocardiogram, chest X-ray) several days before surgery. In the doctors office you will sign consent forms and fill out paperwork so that the surgeon knows your medical history (allergies, medicines/vitamins, bleeding history, anesthesia reactions, previous surgeries). You may wish to donate blood several weeks before surgery. You should stop taking all non-steroidal antiinflammatory medicines (Naprosyn, Advil, Motrin, Nuprin, Aleve, etc.) and blood thinners (coumadin, aspirin, etc.) one week before surgery. Additionally, stop smoking, chewing tobacco, and drinking alcohol one week before and 2 weeks after surgery as these activities can cause bleeding problems. Patients are admitted to the hospital the morning of the procedure. No food or drink is permitted past midnight the night before surgery. An intravenous (IV) line is placed in your arm. An anesthesiologist will explain the effects of anesthesia and its risks. Figure 3. A laminectomy involves removal of the entire lamina and ligament. Multiple laminae can be removed. What happens during surgery? There are seven steps of the procedure. The operation generally lasts 1 to 3 hours. Step 1: prepare the patient You will lie on your back on the operative table and be given anesthesia. Once asleep you will be rolled over onto your stomach with your chest and sides supported by pillows. The area where the surgery is to be performed will be cleansed and prepped. If a fusion is planned and you have decided to use your own bone, the hip area will be cleansed and prepped to obtain a bone graft. If you ve decided to use donor bone, a hip incision is unnecessary. Step 2: incision A skin incision is made down the middle of your back over the appropriate vertebrae (Fig. 2). The Figure 4. A laminotomy makes a small window by removing bone of the lamina above and below. The spinous process is not removed. > 2
3 length of the incision depends on how many laminectomies are to be performed. The strong back muscles are split down the middle and moved to either side exposing the lamina of each vertebra. Step 3: laminectomy or laminotomy Once the bone is exposed, an X-ray is taken to verify the correct vertebra. Laminectomy: The surgeon removes the bony spinous process. Next, the bony lamina is removed with a drill or bone-biting tools. The thickened ligamentum flavum that connects the laminae of the vertebra below with the vertebra above is removed (Fig. 3). This is repeated for each affected vertebrae. Laminotomy: In some cases, the surgeon may not want to remove the entire protective bony lamina. A small opening of the lamina above and below the spinal nerve may be enough to relieve compression (Fig. 4). Laminotomy can be done on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral) and on multiple vertebrae levels. Step 4: decompress the spinal cord Once the lamina and ligamentum flavum are removed the protective covering of the spinal cord (dura mater) is visible. The surgeon can gently retract the protective sac of the spinal cord and nerve root to remove bone spurs and thickened ligament. Step 5: decompress the spinal nerve The facet joints, which are directly over the nerve roots, may be undercut (trimmed) to give the nerve roots more room (Fig 5). Called a foraminotomy, this maneuver enlarges the neural foramen (where the spinal nerves exit the spinal canal). If a herniated disc is causing compression the surgeon will perform a discectomy. Step 6: fusion (if necessary) If you have spinal instability or have laminectomies to multiple vertebrae, a fusion may be performed. Fusion is the joining of two vertebrae with a bone graft held together with hardware such as plates, rods, hooks, pedicle screws, or cages. The goal of the bone graft is to join the vertebrae above and below to form one solid piece of bone. There are several ways to create a fusion. The right one for you depends on your own choice and your doctor s recommendation. The most common type of fusion is called the posterolateral fusion. The topmost layer of bone on the transverse processes is removed with a drill to create a bed for the bone graft to grow. Bone graft, taken from the top of your hip, is placed along the posterolateral bed. The surgeon may reinforce the fusion with metal rods and screws inserted into the vertebrae. The back muscles are laid over the bone graft to hold it in place. Figure 5. The enlarged facet joints are trimmed to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves. Step 7: closure The muscle and skin incisions are sewn together with sutures or staples. What happens after surgery? You will wake up in the postoperative recovery area, called the PACU. Your blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration will be monitored, and your pain will be addressed. Once awake you will be moved to a regular room where you ll increase your activity level (sitting in a chair, walking). If you ve had a fusion, a brace may need to be worn. In 1 to 2 days you ll be released from the hospital and given discharge instructions. Discharge instructions: Discomfort 1. After surgery, pain is managed with narcotic medication. Because narcotic pain pills are addictive, they are used for a limited period (4 to 8 weeks). Their regular use may also cause constipation, so drink lots of water and eat high fiber foods. Laxatives (e.g., Dulcolax, Senokot, Milk of Magnesia) can be bought without a prescription. Thereafter, pain is managed with acetaminophen (e.g., Tylenol). Restrictions 2. If you have had a fusion, do not use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (e.g., aspirin; ibuprofen, Advil, Motrin, Nuprin; naproxen sodium, Aleve) for six months after surgery. NSAIDs may cause bleeding and interfere with bone healing. 3. Do not drive for 2 to 4 weeks after surgery or until discussed with your surgeon. 4. Avoid sitting for long periods of time. > 3
4 5. Do not lift anything heavier than 10 pounds (e.g., gallon of milk). Do not bend or twist at the waist. 6. Housework and yard-work are not permitted until the first follow-up office visit. This includes gardening, mowing, vacuuming, ironing, and loading/unloading the dishwasher, washer, or dryer. 7. Postpone sexual activity until your follow-up appointment unless your surgeon specifies otherwise. 8. Do not smoke. Smoking delays healing by increasing the risk of complications (e.g., infection) and inhibits the bones' ability to fuse. Activity 9. You may need help with daily activities (e.g., dressing, bathing) for the first few weeks. Fatigue is common. Let pain be your guide. 10. Gradually return to your normal activities. Walking is encouraged; start with a short distance and gradually increase to 1 to 2 miles daily. A physical therapy program may be recommended. 11. If applicable, know how to wear the brace before you leave the hospital. Wear for daily activities (excluding sleep) unless instructed otherwise. Bathing/Incision Care 12. You may shower 4 days after surgery unless instructed otherwise. 13. Staples or stitches, which remain in place when you go home, will need to be removed. Ask your surgeon or call the office to find out when. When to Call Your Doctor 14. If your temperature exceeds 101 F or if the incision begins to separate or show signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, or drainage. What are the results? Decompressive laminectomy is successful in relieving leg pain in 70% of patients allowing significant improvement in function (ability to perform normal daily activities) and markedly reduced level of pain and discomfort. 1 However, back pain may not be relieved and 17% of older adults need another operation. 2 Symptoms may return after a few years. Decompressive laminotomy is successful in relieving back pain (72%) and leg pain (86%), and in improving walking ability (88%). 3 Endoscopic laminotomy results in less blood loss, shorter hospital stay, and less postoperative pain medication than an open laminotomy. The results of the surgery are largely up to you. It is important to keep a positive attitude and diligently perform your physical therapy exercises. Maintaining a weight that is appropriate for your height can significantly reduce pain. Do not expect your back to be as good as new. You need to be mindful that you ll always have a bad back and will need to use correct posture and lifting techniques to avoid re-injury. What are the risks? No surgery is without risks. General complications of any surgery include bleeding, infection, blood clots, and reactions to anesthesia. If spinal fusion is done at the same time as a laminectomy, there is greater risk of complications. The following are risks that should be considered: Vertebrae failing to fuse. Among many reasons why vertebrae fail to fuse, common ones include smoking, osteoporosis, obesity, and malnutrition. Smoking is by far the greatest factor that can prevent fusion. Nicotine is a toxin that inhibits bone-growing cells. If you continue to smoke after your spinal surgery, you could undermine the fusion process. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a potentially serious condition caused when blood clots form inside the veins of your legs. If the clots break free and travel to your lungs, lung collapse or even death is a risk. However, there are several ways to treat or prevent DVT. If your blood is moving it is less likely to clot, so an effective treatment is getting you out of bed as soon as possible. Support hose and pulsatile stockings keep the blood from pooling in the veins. Drugs such as aspirin, Heparin, Lovenox, or Coumadin are also commonly used. Hardware fracture. The metal screws, rods and plates used to stabilize your spine are called hardware. The hardware may move or break before your vertebrae are completely fused. If this occurs, a second surgery may be needed to fix or replace the hardware. Bone graft migration. In rare cases (1 to 2%), the bone graft can move from the correct position between the vertebrae soon after surgery. This is more likely to occur if hardware (plates and screws) are not used to secure the bone graft. It s also more likely to occur if multiple vertebral levels are fused. If this occurs, a second surgery may be necessary. Transitional syndrome (adjacent-segment disease). This syndrome occurs when the vertebrae above or below a fusion take on extra stress. The added stress can eventually degenerate the adjacent vertebrae and cause pain. > 4
5 Nerve damage or persistent pain. Any operation on the spine comes with the risk of damaging the nerves or spinal cord. Damage can cause numbness or even paralysis. However, the most common cause of persistent pain is nerve damage from the disc herniation itself. Some disc herniations may permanently damage a nerve making it unresponsive to decompressive surgery. In these cases, spinal cord stimulation or other treatments may provide relief. Be sure to go into surgery with realistic expectations about your pain. Discuss your expectations with your doctor. Sources & links If you have more questions, please contact the Mayfield Clinic & Spine Institute at or Sources 1) Hu SS, et al. (2000). Stenosis of the lumbar spine. In HB Skinner, ed., Current Diagnosis and Treatment in Orthopedics, 2nd ed., pp New York: McGraw-Hill. 2) Turner JA, Ersek M, Herron L, Deyo R. Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: Attempted metaanalysis of the literature. Spine 1992; 17:1-8. 3) Khoo L, Fessler RG. Microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for the treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery 51:S146-54, 2002 Links Glossary anesthesiologist: a doctor who specializes in monitoring your life functions during surgery so that you don t feel pain. annulus (annulus fibrosis): tough fibrous outer wall of an intervertebral disc. anterior: from the front. cauda equina syndrome: dull pain and loss of feeling in the buttocks, genitals, and/or thigh with impaired bladder and bowel function; caused by compression of the spinal nerve roots. cervical: the neck portion of the spine made up of seven vertebrae. decompression: opening or removal of bone to relieve pressure and pinching of the spinal nerves. discectomy: a type of surgery in which herniated disc material is removed so that it no longer irritates and compresses the nerve root. facet joints: joints located on the top and bottom of each vertebra that connect the vertebrae to each other and permit back motion. foraminotomy: surgical enlargement of the intervertebral foramen through which the spinal nerves pass from the spinal cord to the body. Performed to relieve pressure and pinching of the spinal nerves. fusion: to join together two separate bones into one to provide stability. herniated disc: a condition in which disk material protrudes through the disk wall and irritates surrounding nerves causing pain. lamina: flat plates of bone originating from the pedicles of the vertebral body that form the posterior outer wall of the spinal canal and protect the spinal cord. Sometimes called the vertebral arch. spinal instability: abnormal movement between two vertebrae that can cause pain or damage the spinal cord and nerves. vertebra (plural vertebrae): one of 33 bones that form the spinal column, they are divided into 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal. Only the top 24 bones are moveable. updated > reviewed by > Robert Bohinski, MD, Mayfield Clinic / University of Cincinnati Department of Neurosurgery, Cincinnati, Ohio Mayfield Certified Health Info materials are written and developed by the Mayfield Clinic & Spine Institute. We comply with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information. This information is not intended to replace the medical advice of your health care provider. Mayfield Clinic > 5
Lumbar or Thoracic Fusion +/- Decompression
 Lumbar or Thoracic Fusion +/- Decompression PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS
Lumbar or Thoracic Fusion +/- Decompression PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances?
 Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION AND FUSION
 ANTERIOR CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION AND FUSION NOTE: PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS FOR 2 WEEKS
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION AND FUSION NOTE: PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS FOR 2 WEEKS
Low Back Surgery. Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you.
 Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion
 Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion or Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion
 Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion or Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen,
Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion or Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen,
Overview Anatomy of the spinal canal What is spinal stenosis? > 1
 Spinal Stenosis Overview Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of your spinal canal and nerve root canal along with the enlargement of your facet joints. Most commonly it is caused by osteoarthritis and your
Spinal Stenosis Overview Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of your spinal canal and nerve root canal along with the enlargement of your facet joints. Most commonly it is caused by osteoarthritis and your
Neck Surgery (Cervical spine surgery) Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you.
 Neck Surgery (Cervical spine surgery) Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. 1 Neck Surgery (cervical spine surgery) Table of contents Page Why do I need neck surgery?... 2 What kinds
Neck Surgery (Cervical spine surgery) Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. 1 Neck Surgery (cervical spine surgery) Table of contents Page Why do I need neck surgery?... 2 What kinds
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (LLIF or XLIF)
 Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (LLIF or XLIF) NOTE: PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Aleve, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Mobic, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS
Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (LLIF or XLIF) NOTE: PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Aleve, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Mobic, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon
Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide
 Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 5: Page 7: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Surgery Before Surgery Medications Day of Surgery Evening
Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 5: Page 7: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Surgery Before Surgery Medications Day of Surgery Evening
Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
A whiplash injury, most commonly due to a car crash, causes neck pain. See separate leaflet called 'Whiplash Injury' for details.
 Neck Pain in Adults Who gets neck pain and what are the causes? Neck pain is common. More than half of people develop a bout of neck pain at some time in their life. One survey done in the UK found that,
Neck Pain in Adults Who gets neck pain and what are the causes? Neck pain is common. More than half of people develop a bout of neck pain at some time in their life. One survey done in the UK found that,
SPINE AND NECK SURGERY: MAKING A DECISION THAT S RIGHT FOR YOU
 1. GET THE FACTS: Back and neck pain affects 8 out of 10 people at some point in their life. Acute back and neck pain comes on suddenly and usually lasts from a few days to a few weeks. Chronic back and
1. GET THE FACTS: Back and neck pain affects 8 out of 10 people at some point in their life. Acute back and neck pain comes on suddenly and usually lasts from a few days to a few weeks. Chronic back and
Patient Guide to Neck Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
Lower Back Pain. Introduction. Anatomy
 Lower Back Pain Introduction Back pain is the number one problem facing the workforce in the United States today. To illustrate just how big a problem low back pain is, consider these facts: Low back pain
Lower Back Pain Introduction Back pain is the number one problem facing the workforce in the United States today. To illustrate just how big a problem low back pain is, consider these facts: Low back pain
Surgery for cervical disc prolapse or cervical osteophyte
 Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Consent for Lumbar Spine Surgery and Fusion at
 STEPHEN MARANO, M.D. JAMES COOK PA-C Consent for Lumbar Spine Surgery and Fusion at Patient Name: Patient Diagnosis: Lumbar Spinal Stenosis (Narrowing of the canal where the spinal cord and nerves are
STEPHEN MARANO, M.D. JAMES COOK PA-C Consent for Lumbar Spine Surgery and Fusion at Patient Name: Patient Diagnosis: Lumbar Spinal Stenosis (Narrowing of the canal where the spinal cord and nerves are
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION
 SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
Patients with pain in the neck, arm, low back, or leg (sciatica) may benefit from ESI. Specifically, those with the following conditions:
 Overview An epidural steroid injection (ESI) is a minimally invasive procedure that can help relieve neck, arm, back, and leg pain caused by inflamed spinal nerves. ESI may be performed to relieve pain
Overview An epidural steroid injection (ESI) is a minimally invasive procedure that can help relieve neck, arm, back, and leg pain caused by inflamed spinal nerves. ESI may be performed to relieve pain
Consent for Anterior Cervical Discectomy With Fusion and a Metal Plate at
 STEPHEN MARANO, M.D. JAMES COOK PA-C Consent for Anterior Cervical Discectomy With Fusion and a Metal Plate at Patient Name: Patient Diagnosis: Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease (wear and tear on the
STEPHEN MARANO, M.D. JAMES COOK PA-C Consent for Anterior Cervical Discectomy With Fusion and a Metal Plate at Patient Name: Patient Diagnosis: Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease (wear and tear on the
BRYAN. Cervical Disc System. Patient Information
 BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
SPINAL FUSION. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Lumbar Decompression and Stabilisation for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis
 Lumbar Decompression and Stabilisation for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent investigations and consultation
Lumbar Decompression and Stabilisation for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent investigations and consultation
Cervical Disk Surgery
 Cervical Disk Surgery Relieving Symptoms with Decompression and Fusion CONSIDER CERVICAL DISK SURGERY Do you suffer from nagging neck and arm pain or weakness caused by a disk problem in your upper (cervical)
Cervical Disk Surgery Relieving Symptoms with Decompression and Fusion CONSIDER CERVICAL DISK SURGERY Do you suffer from nagging neck and arm pain or weakness caused by a disk problem in your upper (cervical)
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
 A Patient s Guide to Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
A Patient s Guide to Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy
 Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Are Cervical Stenosis and Myelopathy? The cervical spine (neck) is made up of a series of connected bones called
Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Are Cervical Stenosis and Myelopathy? The cervical spine (neck) is made up of a series of connected bones called
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, The Cervical Spine. What is the Cervical Spine?
 Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Patient Guide. Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
Posterior Cervical Decompression Surgery Guide
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Surgery Guide 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 4: Page 6: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: Page 13: Page 15: Frequently Asked Questions The Cervical Spine Cervical
Posterior Cervical Decompression Surgery Guide 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 4: Page 6: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: Page 13: Page 15: Frequently Asked Questions The Cervical Spine Cervical
IP'Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 A Patient's G uide to IP'Lumbar Spinal Stenosis X*STOP Interspinous Process Decompression This patient information guide is made possible through cooperation between your physician and St. Francis Medical
A Patient's G uide to IP'Lumbar Spinal Stenosis X*STOP Interspinous Process Decompression This patient information guide is made possible through cooperation between your physician and St. Francis Medical
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE:
 James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE: 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand
James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE: 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery What is it and how will it benefit patients?
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery What is it and how will it benefit patients? Dr Raoul Pope MBChB, FRACS, Neurosurgeon and Minimally Invasive Spine Surgeon Concord Hospital and Mater Private Hospital Sydney
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery What is it and how will it benefit patients? Dr Raoul Pope MBChB, FRACS, Neurosurgeon and Minimally Invasive Spine Surgeon Concord Hospital and Mater Private Hospital Sydney
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Spinal Injections. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions. Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789)
 Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
How to Care for Yourself after Lumbar Posterior Decompression
 How to Care for Yourself after Lumbar Posterior Decompression What is Lumbar Posterior Decompression? Lumbar Posterior Decomposition is the removal of part of or all of the bone that covers the back of
How to Care for Yourself after Lumbar Posterior Decompression What is Lumbar Posterior Decompression? Lumbar Posterior Decomposition is the removal of part of or all of the bone that covers the back of
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Anterior Cervical Discectomy
 Anterior Cervical Discectomy Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 4: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been
Anterior Cervical Discectomy Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 4: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been
Lumbar Micro-Discectomy
 Lumbar Micro-Discectomy David M. Montgomery, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon Lisa A. Olds, RN, BSN, ONC Spine Nurse Clinician Oakland Orthopaedic Surgeons, PLLC 30575 Woodward Avenue, Suite 100 Royal Oak,
Lumbar Micro-Discectomy David M. Montgomery, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon Lisa A. Olds, RN, BSN, ONC Spine Nurse Clinician Oakland Orthopaedic Surgeons, PLLC 30575 Woodward Avenue, Suite 100 Royal Oak,
Carpal Tunnel Release. Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist
 Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
There are four main regions of the back; the cervical (C), thoracic (T), lumbar (L), and sacral (S) regions
 Low Back Pain Overview Low back pain is one of the most common disorders in the United States. About 80 percent of people have at least one episode of low back pain during their lifetime. Factors that
Low Back Pain Overview Low back pain is one of the most common disorders in the United States. About 80 percent of people have at least one episode of low back pain during their lifetime. Factors that
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report
 The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report BACK INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Back Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report BACK INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Back Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
1 REVISOR 5223.0070. (4) Pain associated with rigidity (loss of motion or postural abnormality) or
 1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
A Healthy Lumbar Spine... 2. A Problem Lumbar Spine... 3. Understanding Your Surgery... 4. Preparing for Surgery... 5. Day of Surgery...
 Table of Contents A Healthy Lumbar Spine................. 2 A Problem Lumbar Spine................. 3 Understanding Your Surgery.............. 4 Preparing for Surgery.................... 5 Day of Surgery.........................
Table of Contents A Healthy Lumbar Spine................. 2 A Problem Lumbar Spine................. 3 Understanding Your Surgery.............. 4 Preparing for Surgery.................... 5 Day of Surgery.........................
We ve got your back. Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery
 We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
Spine Surgery - Wallis Ligament Stabilisation
 Spine Surgery - Wallis Ligament Stabilisation An Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department 0161 419 4060 August 2011 Every Patient Matters TO47 2 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy
Spine Surgery - Wallis Ligament Stabilisation An Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department 0161 419 4060 August 2011 Every Patient Matters TO47 2 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy
How To Understand The Anatomy Of A Lumbar Spine
 Sciatica: Low back and Leg Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Options Presented by Devesh Ramnath, MD Orthopaedic Associates Of Dallas Baylor Spine Center Sciatica Compression of the spinal nerves in the back
Sciatica: Low back and Leg Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Options Presented by Devesh Ramnath, MD Orthopaedic Associates Of Dallas Baylor Spine Center Sciatica Compression of the spinal nerves in the back
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Patient information for cervical spinal fusion.
 Patient information for cervical spinal fusion. Introduction This booklet has been compiled to help you understand spinal cervical fusion surgery and postoperative rehabilitation. Anatomy The cervical
Patient information for cervical spinal fusion. Introduction This booklet has been compiled to help you understand spinal cervical fusion surgery and postoperative rehabilitation. Anatomy The cervical
Cervical Spondylosis. Understanding the neck
 Page 1 of 5 Cervical Spondylosis This leaflet is aimed at people who have been told they have cervical spondylosis as a cause of their neck symptoms. Cervical spondylosis is a 'wear and tear' of the vertebrae
Page 1 of 5 Cervical Spondylosis This leaflet is aimed at people who have been told they have cervical spondylosis as a cause of their neck symptoms. Cervical spondylosis is a 'wear and tear' of the vertebrae
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica. Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS
 Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
A review of spinal problems
 Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW
 BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF).
 Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Primary and revision lumbar discectomy. (nerve root decompression)
 Primary and revision lumbar discectomy (nerve root decompression) The aim of this leaflet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a lumbar discectomy. It explains the benefits,
Primary and revision lumbar discectomy (nerve root decompression) The aim of this leaflet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a lumbar discectomy. It explains the benefits,
https://www.laserspineinstitute.com/back_problems/foraminal_stenosis/e...
 Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C. clinical study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION
 www.southerarizonaspine.com POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns,
www.southerarizonaspine.com POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns,
Balloon Kyphoplasty. Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures.
 Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
Risks of Spinal Surgery
 Risks of Spinal Surgery Infection One of the more common potential complications of any surgery is a wound infection. In spinal surgery this can be a very severe problem. It occurs in 1.5 percent to 3
Risks of Spinal Surgery Infection One of the more common potential complications of any surgery is a wound infection. In spinal surgery this can be a very severe problem. It occurs in 1.5 percent to 3
Presented by Zoran Maric, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon May 22, 2010
 Presented by Zoran Maric, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon May 22, 2010 1 cervical area thoracic area lumbar area sacrum coccyx Mayfield Clinic 2 3 4 5 Zoran Maric, MD Spine Surgery Procedures How to Document
Presented by Zoran Maric, M.D. Orthopaedic Spine Surgeon May 22, 2010 1 cervical area thoracic area lumbar area sacrum coccyx Mayfield Clinic 2 3 4 5 Zoran Maric, MD Spine Surgery Procedures How to Document
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica. Alexander Ching, MD
 Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
Lumbar Spine Surgery What to Expect
 Lumbar Spine Surgery What to Expect You have been scheduled for lumbar spine surgery and are probably wondering what to expect with your surgical journey. We will discuss pre- operative tasks, the day
Lumbar Spine Surgery What to Expect You have been scheduled for lumbar spine surgery and are probably wondering what to expect with your surgical journey. We will discuss pre- operative tasks, the day
Spinal Fusion: Preparing for Surgery
 Spinal Fusion: Preparing for Surgery A GUIDE TO YOUR CHILD S SURGERY he diagnosis of a spinal deformity, such as scoliosis or kyphosis, can be overwhelming. These conditions often require surgical treatment
Spinal Fusion: Preparing for Surgery A GUIDE TO YOUR CHILD S SURGERY he diagnosis of a spinal deformity, such as scoliosis or kyphosis, can be overwhelming. These conditions often require surgical treatment
