HP Smart Array Controller technology
|
|
|
- Roxanne York
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HP Smart Array Controller technology technology brief, 2 nd edition Abstract... 3 Introduction... 3 Storage trends... 3 Meeting data storage requirements... 4 High performance... 4 PCI Express technology... 4 SAS/SATA technology... 5 SAS-2 standard... 5 Mini SAS 4x cable connectors and receptacles... 6 High-performance processor... 6 Cache module benefits... 7 Read-ahead caching... 7 Write-back caching... 7 Balanced cache size... 8 RAID performance enhancements... 8 Disk striping... 8 Parity data... 8 Background RAID creation... 8 RAID 5 and RAID 6 read-modify-write...9 Striping across arrays... 9 RAID 1 load balancing... 9 Hardware RAID... 9 Smart Array performance... 9 Data availability RAID support Stripe size migration RAID migration Drive roaming Mirror splitting and recombining Online drive flash Recovery ROM Pre-Failure Warranty using S.M.A.R.T technology Automatic data recovery with rapid rebuild technology Online spare Dynamic sector repair ECC protection Battery-backed write cache... 16
2 Recovering data from battery-backed cache Selection criteria for battery-backed cache Types of batteries Battery replacement Alternatives to battery replacement Entry level RAID solutions Software RAID Zero Memory RAID Storage support and pathway redundancy Native Command Queuing Dual Domain support Tape device support Smart Array Advanced Pack Storage management Array Configuration Utility Option ROM Configuration for Arrays CPQONLIN HP Systems Insight Manager Performance monitoring Fault prediction Array Diagnostics Utility Summary Appendix A: Capacity growth technologies Array expansion Logical drive creation Logical drive extension For more information Call to action... 27
3 Abstract This technology brief describes specific functions of the HP Smart Array controller family and explains how Smart Array technology meets administrators requirements for capacity growth, high performance, data availability, and manageability. Introduction In today s networking environments, administrators face difficult online data storage problems and ever-increasing demands for performance. While PCI Express (PCIe) provides a high speed interface for data communication, the HP family of parallel SCSI, Serial Attached SCSI (SAS), and Serial ATA (SATA) Smart Array controllers addresses direct attach and storage area network (SAN) requirements. References made in this technology brief to the present generation of Smart Array controllers refers to those SAS-based, PCIe 2.0 compliant Smart Array controllers released in the first half of HP Smart Array controllers provide administrators with configuration, management, and diagnostics tools. These tools provide high levels of usability as well as consistency between generations of products. This continuity ensures that administrator can move data between servers and external storage enclosures, and between models of Smart Array controllers. For complete Smart Array controller compatibility and support information, see: Storage trends Four key trends influence network storage requirements today: Application complexity Network applications are becoming more complex, leading to larger files and the need to maintain more information online for immediate user access. Mission-critical migration More mission-critical data is moving to servers, either down from larger systems or up from paper-based processes. Server consolidation Multiple servers and applications are being consolidated onto fewer servers for increased control and centralized network management. Efficiency expectations Corporate information technology organizations are managing more applications and more data while at the same time reducing the size of their administrative staffs. These key trends generate four primary data storage requirements: Capacity growth Storage solutions must provide not only adequate capacity for today s applications but also flexibility for future growth. High performance Data storage subsystems must deliver enough performance to accommodate an increasing number of users while maintaining rapid response times. In many environments, the storage subsystem is the most critical determinant of overall system performance. Data availability Because businesses depend on their mission-critical data, it must be accessible at all times to maintain user productivity. Manageability Storage solutions must reduce the total cost of ownership by making network storage management intuitive, informative, and less time consuming. 3
4 Meeting data storage requirements The HP Smart Array controller family has an advanced intelligent architecture developed with a feature set that specifically addresses today s network data storage requirements: Capacity growth Administrators can expand server storage capacity while the server is operating. The HP online Array Configuration Utility (ACU) simplifies storage management for administrators who use fault-tolerant array configurations and experience capacity growth. Refer to appendix A for details about using array creation and expansion to increase capacity. High performance Smart Array controllers supply high levels of throughput and data bandwidth to support demanding workloads. The advanced intelligent architecture contains specialized modules that enhance performance significantly. Online array expansion, stripe size migration, RAID migration, configurable read/write cache sizes, rebuild priority, and configurable write-back caching for each logical drive empowers administrators to tune Smart Array controllers to meet performance demands. Data availability Smart Array controllers include a comprehensive set of fault-tolerance features that guard against disk drive and controller component failures, making online storage administration possible and reducing planned downtime. Manageability All Smart Array controllers use a common set of management software, reducing training requirements and technical expertise necessary to install and maintain HP server storage. The common data format among Smart Array controllers means customers can easily upgrade to future Smart Array products. High performance Smart Array controllers offer exceptional performance and reliability characteristics, with support for traditional parallel Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) technology as well as the latest SAS, SATA technology, and advanced RAID capabilities. PCI Express technology The present generation of Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) based Smart Array controllers released in the first half of 2009, and all ProLiant G6 servers support the PCIe 2.0 specification. PCIe 2.0 has a perlane signaling rate of 5 Gb/s double the per-lane signaling rate of PCIe 1.0 (Figure 1). Figure 1. PCIe data transfer rates Source Lane 1 Send Lane 1 Receive Lane n Send Lane n Receive Target Max. bandwidth (Send or receive) Total (Send and receive) Link size PCIe 1.0 PCIe 2.0 PCIe 1.0 PCIe 2.0 x1 250 MB/s 500 MB/s 500 MB/s 1 GB/s x4 1 GB/s 2 GB/s 2 GB/s 4 GB/s x8 2 GB/s 4 GB/s 4 GB/s 8 GB/s x16 4 GB/s 8 GB/s 8 GB/s 16 GB/s PCIe 2.0 is completely backward compatible with PCIe 1.0. A PCIe 2.0 device can be used in a PCIe 1.0 slot and a PCIe 1.0 device can be used in a PCIe 2.0 slot. Table 2 shows the level of interoperability between PCIe cards and PCIe slots. 4
5 Table 1. PCIe device interoperability PCIe device type x4 Connector x4 Link x8 Connector x4 Link x8 Connector x8 Link x16 Connector x8 Link x16 Connector x16 Link x4 card x4 operation x4 operation x4 operation x4 operation x4 operation x8 card Not allowed x4 operation x8 operation x8 operation x8 operation x16 card Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed x8 operation x16 operation SAS/SATA technology The newest serial, PCIe 2.0 capable Smart Array controllers use Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) technology, a point-to-point architecture in which each device connects directly to a SAS port rather than sharing a common bus as with parallel SCSI devices. Point-to-point links increase data throughput and improve the ability to locate and fix disk failures. More importantly, SAS architecture solves the parallel SCSI problems of clock skew and signal degradation at higher signaling rates. 1 The same Smart Array controllers are compatible with Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) technology and include the following features to enhance performance and maintain data availability and reliability: SAS and SATA compatibility The ability to use either SAS or SATA hard drives lets administrators deploy drive technology that fits each computing environment. HP Smart Array controllers can manage both SAS arrays and SATA arrays. Smart Array configuration utilities help administrators configure arrays correctly so that data remains available and reliable. SAS wide port operations Wide ports contain four single lane (1x) SAS connectors and the cabling bundles all four lanes together. SAS wide ports allow balanced SAS traffic distribution across the links for enhanced performance. In addition, wide ports provide redundancy by tolerating up to three physical link failures while maintaining the ability to communicate with the disk drives. The most common use of wide links is to a JBOD or to an internal server expander connecting to large numbers of drives. No special configuration is required for this functionality. SAS expanders Low-cost, high-speed switches called expanders can combine multiple single links to create wide ports and increase available bandwidth. SAS expander devices also offer higher system performance by expanding the number of hard drives that can be attached to an HP Smart Array controller. SAS expanders are an aggregation point for large numbers of drives or servers providing a common connection. By cascading expanders, administrators can chain multiple storage boxes together. For more information on the HP SAS Expander Card, go to SAS-2 standard The second-generation SAS (SAS-2) link speed 2 of 6 Gb/s is double the SAS-1 transfer rate. SAS-2 link speeds require SAS-2 compliant hard drives. SAS-2 eliminates the distinction between fanout and edge expanders by replacing them with self-configuring expanders. SAS-2 enables zoning for enhanced resource deployment, flexibility, security, and data traffic management. SAS-2 connections have the potential to deliver peak raw data bandwidth of up to 600 megabytes per second (MB/s) per physical link in each direction. SAS-2 devices are capable of sending and 1 For more information about SAS technology, refer to the HP technology brief titled Serial Attached SCSI storage technology available at 2 Serial Attached SCSI-2 (SAS-2) is an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard from the INCITS T10 Technical Committee on SCSI Storage Interfaces. SAS-2 is the successor to SAS-1.1 and SAS-1. 5
6 receiving data simultaneously across each physical link, which is known as full duplex. When effectively implemented, full duplex, 6 Gb/s SAS connections can deliver peak raw data bandwidth of up to 1200 MB/s between the controller and storage device. It is important to note that the SAS-2 data bandwidths described here are theoretical speeds identified by the SAS-2 standard. Real world performance will be affected by the performance of storage devices attached to the SAS-2 connection. Smart Array controllers, with releases beginning in the first quarter of 2009, incorporate SAS-2 connections. The SAS-2 standard is compatible with both Serial SCSI and Serial ATA protocols for communicating commands to SAS and SATA devices. SAS-2 compliant controllers are fully compatible with 1.5 Gb/s and 3 Gb/s SATA technology. For an up to date listing of HP Smart Array controllers that support the SAS-2 specification, see the Smart Array controller matrix: Mini SAS 4x cable connectors and receptacles Mini SAS 4x connectors and receptacles (Figure 2) are replacing SAS 4x connectors and receptacles in present generation Smart Array controllers. The ground pins in Mini SAS connectors can be used for power in active cables. Figure 2. The Mini SAS 4i connector (left) and receptacle (right) are replacing SAS 4x connectors and receptacles. For more detailed information on SAS technology and SAS-2 zoning, refer to the Serial Attached SCSI storage technology brief: High-performance processor HP Smart Array controllers use a variety of high-performance processors for managing the RAID system. The Power PC and MIPS processors are the most widely used among Smart Array controllers. The PowerPC processor is a 64-bit processor based on reduced instruction set computer (RISC) technology. The processor connects to its internal peripherals using separate 128-bit-wide read-andwrite buses, each running at 133 MHz. Power PC processors have a highly pipelined architecture that allows dual instruction fetch, decode, and out-of-order issue, as well as out-of-order dispatch, execution, and completion. The Power PC 6
7 flexibility features include independently configurable data cache arrays, write-back and write-through operation, and performance characteristics that increase cache memory allocation efficiency. Designed for extensive power management and maximum performance, Power PC processors provide increased throughput and a streamlined path to instruction completion, which means faster user access to data. The Smart Array P410, P411, and P212 controllers use an embedded MIPS storage processor. This reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) processor operates at 600 MHz, has 34K instruction and data caches, and a 32-bit multi-threading I/O. The MIPS processor uses a 4-way set associative write-back, and flexible thread policy manager with programmable quality of service (QoS) support. Cache module benefits With advanced read-ahead and write-back caching capabilities, the Smart Array controller cache module produces significant performance improvements for I/O operations. Read-ahead caching The HP Smart Array controller family uses an intelligent read-ahead algorithm that can anticipate data needs and reduce wait time. It can detect sequential read activity on single or multiple I/O threads and predict when sequential read requests will follow. The algorithm then reads ahead, or prefetches data, from the disk drives before the data is actually requested. When the read request occurs, the controller retrieves the data from high-speed cache memory in microseconds rather than from the disk drive in milliseconds. This adaptive read-ahead scheme provides excellent performance for sequential small block read requests. At the same time, the system is not penalized by random read patterns because read-ahead functionality is disabled when non-sequential read activity is detected. Thus, Smart Array controller technology overcomes the problem with some array controllers in the industry today that use fixed read-ahead schemes to increase sequential read performance but degrade random read performance. Write-back caching HP Smart Array controllers also use a caching scheme that allows host applications to continue without waiting for write operations to complete to the disk. This technique is also called postedwrites, or write-back caching. Without this type of caching, the controller must wait until write data is actually written to disk before returning completion status to the operating system. With write-back caching, the controller can post write data to high-speed cache memory and immediately return back completion status to the operating system. The write operation is completed in microseconds rather than milliseconds. Once write data is located in the cache, subsequent reads to the same disk location will be sourced from the cache. Subsequent writes to the same disk location will replace the data held in cache. This technique is called a read cache hit. This feature improves bandwidth and latency for applications that frequently write and read the same area of the disk. After write data is located in the cache, the controller finds opportunities to combine adjacent write transfers into a larger transfer that can efficiently move to the hard drive. This technique is called write coalescing. Hard drives achieve higher throughput when processing fewer large transfers instead of many small transfers. This feature improves write bandwidth whenever data is sequentially written to the controller using write command sizes smaller than the stripe size of the logical drive. With write data located in the cache, logical drives in RAID 5 and RAID 6 with advanced data guarding (ADG) configurations achieve higher write performance by combining adjacent write requests to form a full stripe of data. This technique is called full-stripe writes. Write operation for 7
8 RAID 5 and RAID 6 with ADG normally requires extra disk reads to compute the data for the parity drives. However, if all the data required for a full stripe is available in the cache, the controller does not require the extra disk reads. This feature improves write bandwidth whenever data is sequentially written to a logical drive in a RAID 5 or RAID 6 with ADG configuration. Data in the controller s write cache is written to disk later, at an optimal time for the controller. While the data is in cache, it is protected against memory chip failure by error checking and correction (ECC) DRAM technology and against system power loss by the integrated battery backup mechanism. Smart Array controllers avoid the risk of data loss by ensuring that the battery backup is present before enabling write-back cache. Hard drives provide an option to enable write-caching that is not battery backed. HP advises against enabling hard drive write cache because a power or equipment outage could result in data loss. Balanced cache size Smart Array controllers allow administrators to adjust how the cache is distributed for write-back and read-ahead operations. Administrators can configure the cache module for optimal performance for any storage need. The default setting configures the cache for 50 percent write-back operations and 50 percent read-ahead operations. Additionally, the cache module capacity can be upgraded to increase caching performance. RAID performance enhancements Smart Array controllers use several enhancements to increase RAID performance. Disk striping Striping combines several individual disk drives into a larger disk array containing one or more logical drives. Performance of the individual drives is aggregated to provide a single highperformance logical drive. The array controller evenly distributes the logical drive data into small stripes of data sequentially located across each member disk drive in the array. Administrators can adjust the stripe size to achieve optimal performance. Performance improves as the number of drives in the array increases. Parity data In a RAID 5 configuration, data protection is provided by distributed parity data. This parity data is calculated stripe by stripe from the user data that is written to all other blocks within that stripe. The blocks of parity data are distributed evenly over every physical drive within the logical drive. When a physical drive fails, data that was on the failed drive can be calculated from the remaining parity data and user data on the other drives in the array. This recovered data is usually written to an online spare drive through a process called a rebuild. RAID 6 (Advanced Data Guarding- ADG), like RAID 5, generates and stores parity information to protect against data loss caused by drive failure. With RAID 6 (ADG), however, two different sets of parity data are used so that data can still be preserved even if two drives fail. Each set of parity data uses a capacity equivalent to that of one of the constituent drives. This method is most useful when data loss is unacceptable but cost is also an important factor. RAID 6 (ADG) provides better protection for data than a RAID 5 configuration because of the additional parity information. Background RAID creation When a RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 6 logical drive is first created, the Smart Array controller must build the logical drive within the array before enabling certain advanced performance techniques. While the logical drive is created, the storage volume is accessible by the host with full fault tolerance. The Smart Array controller creates the logical drive whenever the controller is not busy; this is called background parity initialization. Parity initialization takes several hours to complete, depending on the size of the logical drive and how busy the host keeps the controller. Before parity initialization 8
9 completes, normal writes to RAID 5 and RAID 6 logical drives are slower because the controller must read the entire stripe to update the parity data and maintain fault tolerance. These writes during parity initialization are called regenerative writes or reconstructed writes. RAID 5 and RAID 6 read-modify-write After parity initialization is complete, writes to a RAID 5 or RAID 6 logical drive are typically faster because the controller does not read the entire stripe to update the parity data. Since the controller knows that the parity data is consistent with all the member drives in the stripe, the controller needs to read from only two hard drives during a RAID 5 write (or three hard drives for a RAID 6 write) to compute the parity data (regardless of array size). This technique is called a read-modify-write or backed-out writes. Striping across arrays RAID 50 and 60 methods stripe the data across multiple RAID/JBOD sets with different levels of parity. These nested RAID types allow users to configure arrays across HP Modular Smart Arrays (MSAs). RAID 50 (RAID 5+0) is a nested RAID method that uses RAID 0 block-level striping across RAID 5 arrays with distributed parity. RAID 50 will tolerate one drive failure in each spanned array without loss of data. RAID 50 configurations require a minimum of six drives and require less rebuild time than single RAID 5 arrays. RAID 60 (RAID 6+0) is a nested RAID method that uses RAID 0 block-level striping across multiple RAID 6 arrays with dual distributed parity. With the inclusion of dual parity, RAID 60 will tolerate the failure of two disks in each spanned array without loss of data. RAID 60 configurations require a minimum of eight drives. RAID 6 and 60 are available as an option with the Smart Array Advanced Pack (see section later in this paper) and are not supported on all HP Smart Array controllers. RAID 1 load balancing In general, the same stripe and array sizes RAID 0, RAID 5, and RAID 6 with ADG logical drives have the same read performance. RAID 1 logical drives contain two copies of the data. During reads to RAID 1 logical drives, the Smart Array controller issues read requests to either drive in the mirrored set. During a heavy read load, the Smart Array controller balances the number of requests between the two hard drives to achieve higher read bandwidth. This technique is called RAID 1 load balancing. Hardware RAID Today s operating systems offer basic RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5 disk management functions, called software RAID, to create logical drives that do not contain the operating system. Software RAID requires a significant amount of the server s resources to perform management functions. However, Smart Array controllers use a separate processor and memory subsystem for management functions. Furthermore, for Smart Array controllers the parity calculations required by RAID 5 and RAID 6 with ADG are performed by specialized hardware engines that maximize data throughput for disk write, rebuild, and regenerate read operations. Smart Array performance Figure 3 displays the results of HP testing for sequential read/write performance between Smart Array controller SA-P411, announced in April 2009, and the previous generation SA-P800. The data in Figure 3 is the result of testing on a ProLiant G5 DL380 server in a RAID 5 environment using the default 64KB stripe size. With the two controllers operating under the same constraints of 3Gb SAS and PCI-e Gen 1, the sequential write performance of the SA-P411was approximately 200 percent 9
10 higher than that of the SA-P800. The significant performance gains displayed the Smart Array P411 are a result of improvements to the Smart Array firmware and hardware. Figure 3. Sequential read/write performance for the Smart Array P800 and P411 controllers in a RAID 5 environment 250% RELATIVE PERFORMANCE (%) 200% 150% 100% 50% 0% KB SEQ 128KB SEQ 256KB SEQ 512KB SEQ 64KB SEQ 128KB SEQ 256KB SEQ 512KB SEQ READ READ READ READ WRITE WRITE WRITE WRITE Request Queue = SA-P411 SA-P800 The max I/O performance test results displayed in Figure 4 also show significant performance gains for the Smart Array P411 over the previous-generation P800 controller. Performance was similar in both read and write tests. 10
11 Figure 4. Max I/O read/write performance for the SA- P800 and SA-P411 controllers in a RAID 5 environment THROUGHPUT (IOPS) MAX READ I/O MAX WRITE I/O) SA-P411 SA-P800 Request Queue = The hardware and software specifications for the test results in Figures 3 and 4 were as follows: All testing used ProLiant DL380 G5 servers Smart Array P411 Firmware specifications: v1.62; Memory: 512 MB; Driver: HP Smart Array Controller Driver HpCISSs B25, RAID 5 (64 KB); Internal hard drives: 2 logical drives; External storage: 2 MSA60 with DRV; Drives: SEAGATE 15K 146GB large form factor SAS (HPDA- firmware version on the hard drives being tested) Smart Array P800 Firmware specifications: v5.26; Memory:512 MB; Driver: HpCISSs B25, RAID 5 (64 KB); Internal hard drives: 2 logical drives; External storage: 2 MSA60 with DRV; Drives: SEAGATE 15K 146GB large form factor SAS (HPDA) Data availability Smart Array controllers support online array expansion, logical drive extension, stripe size migration, and RAID migration. These technologies protect data and allow network administrators to modify the array without interrupting user access. Smart Array controllers can monitor I/O activity, track key parameters, predict potential problems, take corrective actions, provide automatic recovery, and deliver full fault management to protect against downtime. RAID support In 1989, HP (then Compaq) was the first company to introduce RAID subsystems in the network server marketplace. Today, RAID is an industry-standard technology and most online network data storage is protected with some level of RAID. Smart Array controllers support RAID levels 0, 1, 1+0, 5, 6 with ADG, 50, and 60. Today, only Smart Array controllers offer RAID 6 with ADG, which provides higher fault tolerance than RAID 5 with lower implementation costs than RAID 1+0 and greater usable capacity per unit density than RAID 1. 11
12 Stripe size migration Using the ACU, administrators can change the stripe size of a logical drive without any downtime. Stripe size migration can improve logical drive in response to changes in the read/write environment. Each RAID level has a default value designed to provide good performance across many types of applications. Table 2 shows the default values and the range of stripe sizes available for each RAID level. Table 2 provides a generic overview of stripe sizes for the listed RAID levels and is generally applicable to the present generation of Smart Array controllers. These values can change for certain controllers and storage device implementations. Users should consult configuration documentation for the specific controller and storage device in question. Table 2. Stripe sizes available per RAID level Fault-tolerance level Default in KB Available stripe sizes (KB) RAID , 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 RAID 1 or , 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 RAID , 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 RAID 6 with ADG * 16 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 RAID , 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512 RAID 60 * 16 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 * Requires a valid SAAP license key Certain applications, especially those performing mostly one type of transaction, write transactions for example, may require adjusting stripe size to achieve optimal performance. Table 3 lists recommended stripe sizes for general types of server applications. Administrators can start with these general recommendations and then fine tune to determine the best overall performance for a particular application. The ACU allows administrators to make these changes online without disruption or data loss. Table 3. Recommended stripe sizes Type of server application Mixed read/write Mainly sequential read (such as audio/video applications) Mainly write (such as image manipulation applications) Suggested stripe size change Accept default value Larger stripe sizes Smaller stripes for RAID 5, RAID 6 with ADG Larger stripes for RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 1+0 NOTE: Different controllers may have different stripe sizes. Users should consult the controller user guide for more details. RAID migration Using the ACU, administrators can also change the RAID level of the logical drive without down time. Administrators can perform RAID migration to increase raw data storage capacity, improve performance by increasing the number of spindles in a logical drive, or change fault-tolerance (RAID) configurations. Table 4 summarizes RAID levels and the amount of space required for each type of fault tolerance. 12
13 Table 4. Summary of RAID methods RAID 0 (striping) RAID 1 (mirroring) RAID 1+0 (striping and mirroring) RAID 5 (distributed data guarding) RAID 6 with ADG (advanced data guarding) Usable drive space* 100% 50% 50% 67% to 93% 50% to 96% Usable drives N N/2 N/2 N-1 N-2 Minimum number of drives Tolerant of single drive failure? No Yes Yes Yes Yes Tolerant of multiple simultaneous drive failures? No No Yes, if failed drives not mirrored to each other No Yes Read performance High High High High High Write performance High Medium Medium Low Low Relative cost Low High High Medium Medium * The values for usable drive space are calculated assuming a maximum of 14 physical drives of the same capacity (or a maximum of 56 for RAID 6 with ADG) with no online spares. HP recommends not exceeding these maximum figures (excluding any allowable online spares) when configuring a drive array due to the increased likelihood of logical drive failure with more hard drives. Drive roaming HP Smart Array controllers support drive roaming, which allows administrators to move hard drives and arrays while maintaining data availability. Drive roaming allows administrators to move one or more hard drives that are members of a configured logical drive to a different bay position as long as the new bay position is accessible by the same controller. In addition, it allows administrators to move a complete array from one controller to another, even if controllers are in different servers. Mirror splitting and recombining Mirror splitting is a task that splits an array with one or more RAID 1 or RAID 1+0 logical drives into two identical new arrays with RAID 0 logical drives. This is useful for administrators who want to replicate a configuration or need to build a backup before performing a risky operation. Using the ACU, administrators can also recombine a split mirrored array. Beginning with the present generation of SAS-based Smart Array controller controllers, the Smart Array Advanced Pack (SAAP) is required to use mirror splitting and recombining. For support information regarding mirror splitting on specific controllers, see the controller Quickspecs. More information about mirror splitting can be found in the technology brief RAID 1(+0): breaking mirrors and rebuilding drives at: 13
14 NOTE: An array cannot be split if it contains logical drives in RAID 0, RAID 5, or RAID 6 with ADG configurations. An array can be split or re-mirrored only when the server is offline and operating in the standard configuration mode of the ACU. When a split mirrored array is recombined, all data on the second array is destroyed. For more information, refer to the product documentation. Online drive flash Serial-based Smart Array controllers support online drive flashing, which saves time when updating firmware. Instead of taking the hard disk drive (HDD) offline before loading a new firmware image, administrators can download an updated HDD firmware image to the supported Smart Array controller and update all of the HDDs the next time the server is rebooted. This greatly reduces the time involved in updating disk drive firmware. Recovery ROM HP Smart Array controllers store a redundant copy of the controller firmware image to protect against data corruption. If the active firmware image becomes corrupt, Smart Array controllers use the redundant firmware image and continue operating. The recovery read-only memory (ROM) provides protection against power outages during firmware flashing. Pre-Failure Warranty using S.M.A.R.T technology HP (then Compaq) pioneered failure prediction technology for hard disk drives by developing monitoring tests run by Smart Array controllers. Called monitoring and performance (M&P), or drive parameter tracking, these tests externally monitor hard drive attributes such as seek times, spin-up times, and media defects to detect changes that could indicate potential failure. HP worked with the hard drive industry to help develop a diagnostic and failure prediction capability known as Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.). Over the years, as S.M.A.R.T. matured, HP used both M&P and S.M.A.R.T. to support hard drive failure prediction technology for Pre-Failure Warranty replacement of hard drives. S.M.A.R.T. has matured to the point that HP relies exclusively on this technology for hard drive failure prediction to support Pre-Failure Warranty. Since 1997, all HP SCSI, SAS, and SATA server-class hard drives have incorporated S.M.A.R.T. technology. S.M.A.R.T. hard have the capacity to inform the host when a hard drive is experiencing abnormal operation likely to lead to drive failure. S.M.A.R.T. improves failure prediction technology by placing monitoring capabilities within the hard disk drive. These monitoring routines are more accurate than the original M&P tests because they are designed for a specific drive type and have direct access to internal performance, calibration, and error measurements. S.M.A.R.T. uses internal performance indicators and real-time monitoring and analysis to improve data protection and fault prediction capability beyond that of the original M&P tests. In addition, HP Smart Array controllers proactively scan the hard drive media during idle time and repair, or report, any media defects detected. S.M.A.R.T. can often predict a problem before failure occurs. HP Smart Array controllers recognize S.M.A.R.T. error codes and notify HP Systems Insight Manager 3 (SIM) whenever a potential problem arises. HP SIM, in turn, immediately notifies administrators of drive failures. The drive parameter tracking feature allows Smart Array controllers to warn of potential drive problems before they occur. 3 For a more detailed discussion of HP Systems Insight Manager, refer to the HP Systems Insight Manager section. 14
15 HP drives that fail to meet the expected criteria may be eligible for replacement under the HP Pre-Failure Warranty. Automatic data recovery with rapid rebuild technology When a hard drive in an array is replaced, Smart Array controllers use the fault-tolerance information on the remaining drives in the array to reconstruct the missing data and write it to the replacement drive. This process is called automatic data recovery, or rebuild. If fault tolerance is compromised, the data cannot be reconstructed and is likely to be permanently lost. The latest generation of HP Smart Array controllers includes rapid rebuild technology for accelerating the rebuild process. Rapid rebuild technology comprises several features that result in substantially quicker rebuild time. Faster rebuild time reduces the risk of logical drive failure by restoring logical drives back to full fault tolerance before a subsequent drive failure can occur. Generally, a rebuild operation requires approximately 15 to 30 seconds per gigabyte for RAID 5 or RAID 6 with ADG logical drives. However, actual rebuild time depends on several factors, including the amount of I/O activity occurring during the rebuild operation, the number of disk drives in the logical drive, the rebuild priority setting, and the disk drive performance. The ACU allows administrators to view progress of the rebuild and set the priority for the rebuild operation. Online spare Smart Array controllers enable administrators to designate an unlimited number of drives as online spares to arrays containing one or more fault-tolerant logical drives. The same spare drive can be assigned to multiple arrays as a global spare. Smart Array configuration utilities ensure that SAS hard drives can only be assigned as spares for SAS arrays (and likewise, SATA hard drives for SATA arrays). During system operation, these spare drives remain up and running but not active; that is, no I/O operations are performed to them during normal array operation. Spare drives are held in reserve in case one of the active drives in the array should fail, and then an online spare drive is selected as the replacement hard drive. If an active drive fails during system operation, the controller automatically begins rebuilding each fault-tolerant logical drive onto the online spare; no administrator action is required. Once the rebuild operation is complete, the system is fully fault-tolerant once again. The failed drive can be replaced at a convenient time. Once an administrator installs a replacement drive, the controller will restore data automatically from the failed drive to the new drive. At that point, the original online global spare, as shown in Figure 5, will return to standby mode. 15
16 Figure 5. RAID 5 with an online spare drive Smart Array Controller User data Parity data Online spare Dynamic sector repair Under normal operating conditions, disk drive media can often develop defects over time, caused by variances in the drive mechanisms. To protect data from media defects, HP built a dynamic sector repair feature into Smart Array controllers. During inactive periods, Smart Array controllers configured with a fault-tolerant logical drive perform a background surface analysis, continually scanning all drives for media defects. During busy periods, Smart Array controllers can also detect media defects when a bad sector is accessed. If a Smart Array controller finds a recoverable media defect, the controller automatically remaps the bad sector to a reserve area on the hard drive. If the controller finds an unrecoverable media defect and a fault-tolerant logical drive is configured, the controller automatically regenerates the data and writes it to the remapped reserved area on the hard drive. ECC protection HP Smart Array cache modules use ECC technology to protect cache data. DRAM is accessed by transferring read-or-write data 32 or 64 bits at time, depending on the type of cache module. The ECC scheme generates 8 bits of check data for every 32 or 64 bits of regular data. This check data can be used not only to detect data errors, but also to correct them. Data errors could originate inside the DRAM chip or across the memory bus. Battery-backed write cache HP Smart Array controllers ensure that data is protected in a location isolated from server failures before acknowledging that the data transfer has completed. The write-back cache allows the controller to acknowledge transfer completion before the data is physically stored in the hard drive. To improve disk write performance, data is temporarily stored in battery-backed write cache (BBWC), which uses DRAM and is substantially quicker when compared to the disk drive. Battery power is required for RAID controllers to perform operations such as write-back cache, array expansion, logical drive extension, stripe size migration, and RAID migration. Recovering data from battery-backed cache If an unexpected server shutdown occurs while data is held in battery-backed cache, Smart Array controllers automatically signal the memory chips to enter a self refresh state and the controller initiates battery power, or system auxiliary power if present. An amber LED, available either on the cache module or battery pack, begins flashing to indicate that data is trapped in the cache. Smart Array controllers automatically write this data to disk when power is restored to the system. If power is not restored within the specified backup duration, the batteries may become drained of power. If that happens, posted-write data in the cache will be lost. Once system power is restored, the batteries will 16
17 automatically recharge if needed. Battery recharge takes between 30 minutes and 2 hours, depending on the remaining capacity level. In the event of a server failure, the Smart Array controller and all of the drives can be moved to another server to allow writing the data in the write cache to the drives. In the event of a controller failure, the cache module containing posted-write data can be moved to a new Smart Array controller. However, to preserve the cached data, the new Smart Array controller must be attached to the original drives for which the posted-write data is intended. Administrators should be aware of a special concern when using an embedded RAID controller with battery-backed cache. If the server board fails, the replacement board must be the same model server board so that the controller type and drive bays are the same. The cache module, battery pack, and drives must be moved to the replacement system to extract the data from the battery-backed cache. Selection criteria for battery-backed cache HP Smart Array battery cells, battery enclosures, and contacts are custom designed to preserve the integrity of business-critical information beyond the minimum specified backup duration. HP Smart Array battery cells were selected to achieve the specified three-year backup life in typical server environments. A dedicated battery microcontroller continuously monitors the HP Smart Array battery pack for signs of damage, including an open battery terminal, partial battery short, charge timeouts, and over discharge conditions. Battery status information is indicated with an LED, power-on self-test (POST) messages, event messages to the host, ACU information pages, ADU, and within HP SIM. The battery microcontroller automatically disables the battery-backed cache features any time it detects battery damage or the charge level falls below the required limits to achieve the specified backup duration. The battery microcontroller automatically restores battery-backed cache features when the microcontroller detects a replacement battery or when battery recharging is complete. Highend HP RAID controller designs contain two batteries to protect against a single battery cell failure while data is held in cache. For detailed technical information on all HP cache options and controller compatibility, go to Types of batteries HP Smart Array controllers use rechargeable Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) button cell batteries specifically designed for longer life at the temperatures found inside rack-mounted servers. Typical capacity reduction for the HP Smart Array battery pack is 5 to 10 percent over a 3-year period, depending on server temperature and number of discharge cycles. NiMH cells are also environmentally friendly, since they do not contain harmful lead, mercury, or cadmium material. Additionally, NiMH chemistry does not suffer capacity memory effects that can lower battery capacity. For example, memory capacity of Nickel Cadmium (NiCD) batteries is reduced when the batteries are exposed to short discharge cycles. Lithium Ion (Li-Ion) batteries are typically smaller than NiMH batteries, but their capacity is permanently reduced at high temperatures and they are usually limited to 100 full discharge cycles. The HP 650 mah P-Series battery has the same form factor as previous versions and extends battery life up to 48 hours before recharging is necessary. Battery replacement HP Smart Array controllers include serviceable battery packs which allow tool-free battery pack replacement with no need to replace either the Smart Array controller or the detachable cache module. 17
18 Alternatives to battery replacement If it is not possible or desirable to replace the batteries, administrators have three options to disable write-back cache and avoid losing critical data: 1. The ACU provides a method for adjusting the read-and-write cache ratio to 100 percent read cache. 2. The ACU provides a method to disable the array accelerator for each logical drive, which disables both read-ahead and write-back cache. 3. Administrators can replace an existing RAID controller with a newer Smart Array controller model. NOTE: If the write cache is turned off, some write performance degradation may occur. For more information about Smart Array controller battery configuration and specifications download the HP Smart Array Controllers for HP ProLiant Servers User Guide : mpid=reg_r1002_usen Entry level RAID solutions Software RAID HP has developed a software RAID solution based on the Smart Array firmware. The B110i SATA Software RAID supports the ACU, ACU-CLI (command line tool), SNMP agents, and Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) providers. The B110i features an OS-specific driver from HP that uses the embedded ICH10R controller. The B110i supports RAID 0, 1, and 1+0 and a maximum of two logical drives. The B100i supports up to four 1.5G or 3G SATA drives. Administrators can migrate drives to a Smart Array controller in a seamless procedure that maintains the user data and RAID configuration. The ProLiant DL320 G6 server supports the B110i. For a listing of the complete feature set and support information for the B110i SATA Software RAID, download the B110i user guide at Zero Memory RAID Using Zero Memory RAID (ZMR), administrators can create a RAID 0-1 configuration without additional memory. ZMR uses memory embedded in the controller, approximately 1K in size, and supports limited configurations. ZMR supports up to eight drives in Zero Memory Mode, or seven drives and one tape drive. ZMR does not include caching; however, all systems can be upgraded to a BBWC memory module that can significantly increase performance. ZMR is supported on present generation Smart Array controllers for internal, direct connections only. This includes the Smart Array P410, P410i, P212, and P712 controllers. Consequently, the P212 controller does not include ZMR on the external connector. Modular Smart Array (MSA) products are not supported in ZMR mode. NOTE: The P212 controller can only be upgraded to 256 MB BBWC, so it does not support 512 MB BBWC. 18
19 NOTE: Smart Array Advanced Pack is not available on Zero Memory configurations. Storage support and pathway redundancy HP Smart Array controllers support Native Command Queuing and Dual Domain providing increased performance and redundancy on the storage network. Smart Array controllers continue to support tape back up devices. Native Command Queuing Native Command Queuing (NCQ) increases SATA HDD performance by internally prioritizing read/write command execution. This reduces unnecessary drive head movement which results in increased performance, especially in server or storage-type applications where multiple simultaneous read/write requests are common. Without NCQ, the drive can process and complete only one command at a time. NCQ must be supported and turned on in both the controller and the drive. Dual Domain support Dual Domain SAS creates redundant pathways from servers to storage devices. These redundant paths reduce or eliminate single points of failure within the storage network and increase data availability. Dual domain SAS implementations can tolerate host bus adapter (HBA) failure, external cable failure, expander failure, or failure in a spanned disk (JBOD). Dual Domain support is available for the HP Smart Array P800 attached to an MSA60/70 with the HP StorageWorks Dual Domain I/O Module Option (AG779A). Dual Domain support requires HP Smart Array firmware v5.10 or higher and dual-port SAS drives. Dual Domain supports Multi-Initiator JBOD Clusters. I/O Module Option with the HP SC44Ge Host Bus Adapter supports HP-UX and OpenVMS on select HP Integrity servers only. Dual Domain is also supported by HP Serviceguard software on HP-UX with HP-UX 11iv2 and 11iv3 only. Tape device support Smart Array controllers support tape back-up devices. The One Button Disaster Recovery (OBDR) ProLiant server/controller compatibility matrix for currently shipping HP products is available at Smart Array Advanced Pack HP Smart Array Advanced Pack (SAAP) firmware provides advanced functionality within Smart Array controllers. This firmware further enhances performance, reliability, and availability of data. SAAP is hosted on the Smart Array controller hardware firmware stack. It can be enabled beginning with the present generation of Smart Array controllers. SAAP requires a license key for activation. After activation, administrators can use several standard capabilities: RAID 6 with Advanced Data Guarding (ADG) protects against failure of any two drives. It requires a minimum of four drives, but only two will be available for data. ADG can tolerate multiple simultaneous drive failures without downtime or data loss and is ideal for applications requiring 19
20 large logical volumes, because it can safely protect a single volume of up to 56 disk drives. RAID ADG also offers lower implementation costs and greater usable capacity per U than RAID 1. RAID 60 allows administrators to split the RAID storage across multiple external boxes. It requires a minimum of eight drives, but only four will be available for data. NOTE: HP BladeSystem servers do not support RAID 6 and 60. Advanced Capacity Expansion (ACE) automates higher capacity migration using capacity transformation to remove logical drives by shrinking and then expanding them online. Standard drive migration and expansion remain unchanged. Mirror Splitting and Recombining in Offline Mode breaks a RAID 1 configuration into two RAID 0 configurations. This is similar to a scaled down rollback functionality that requires two disk drives. Drive Erase completely erases physical disks or logical volumes. This capability is useful when decommissioning, redeploying, or returning hard drives. Video On Demand Performance Optimization optimizes performance of video on demand and improves latency during video streaming. More information about SAAP is available at NOTE: At a minimum, a 256 MB cache and battery kit is required to enable the SAAP license key. SAAP is not available on Zero Memory Configurations. Storage management To improve data storage management, HP Smart Array controllers include built-in intelligence that makes it easier for administrators to configure, modify, expand, manage, and monitor storage. HP provides five utilities for managing an array on a Smart Array controller: ACU (Array Configuration Utility) ACU is the main tool for configuring arrays on HP Smart Array controllers. It exists in three interface formats; the ACU GUI, the ACU CLI, and ACU Scripting. All three formats have separate executables: Starting with version , ACU Scripting is now a standalone application that is distributed with the ACU CLI application. In ACU versions prior to , the scripting executable was provided with the ACU GUI component. Users familiar with the previous versions of ACU Scripting must now install the ACU CLI application to obtain the scripting executable. The new ACU scripting executable (hpacuscripting) replaces the former executable (cpqacuxe) in all scripts. ORCA (Option ROM Configuration for Arrays) A simple ROM-based configuration utility CPQONLIN A menu-based configuration utility specifically for servers using Novell NetWare HP System Insight Manager Extensible, secure management suite for server and storage environments ADU (Array Diagnostic Utility) A diagnostic and reporting utility for Smart Array controllers. With the introduction of version or later of ACU or HPACUCLI, ADU is no longer provided as a separate utility but now has its functionality integrated with ACU and HPACUCLI. 20
21 For more information about storage management and using these utilities, see the Configuring Arrays on HP Smart Array Controllers Reference Guide, available at: Table 6 summarizes the capabilities of ACU, ORCA, and CPQONLIN utilities. Table 6. Summary of HP configuration utility features Utility features ACU ORCA CPQONLIN Uses a graphical interface Yes No No Available in languages other than English Yes No No Executable at any time Yes No Yes Available on disc Yes No No Uses a wizard to suggest the optimum configuration for an unconfigured controller Yes No Yes Describes configuration errors Yes No No Creating and deleting arrays and logical drives Yes Yes Yes Assigning RAID level Yes Yes Yes Sharing spare drives among several arrays Yes No Yes Assigning multiple spare drives per array Yes No Yes Setting stripe size Yes No Yes Migrating RAID level or stripe size Yes No Yes Configuring controller settings Yes No Yes Expanding an array Yes No Yes Creating multiple logical drives per array Yes No Yes Setting of boot controller No Yes No Array Configuration Utility The ACU 4 is a browser-based graphical application that helps configure Smart Array controllers. The ACU is also supported on the HP MSA family of entry-level SAN products. This provides administrators with a seamless set of tools to use with both HP Smart Array direct-attached storage (DAS) and HP SAN-attached storage. The ACU runs online on Microsoft Windows Server and Linux operating systems. Because the ACU is available on a bootable disc, an administrator using other operating systems 5 can run the utility offline by booting the system from the SmartStart or Server Storage Support Software disc. 4 For more information about the ACU, refer to 5 Refer to product documentation to verify operating system support. 21
22 The ACU also contains a command line interface (ACU-CLI), offering a quicker way to deploy multiple servers by automating creation of arrays and logical drives. Configuration information for the ACU is available at Option ROM Configuration for Arrays Option ROM Configuration for Arrays (ORCA) is an alternative method of viewing, creating, and deleting multiple arrays and logical drives during system power up. ORCA is designed for administrators who have minimal configuration requirements. The ACU is recommended for more advanced array configurations. CPQONLIN CPQONLIN is a configuration utility that runs online on Novell NetWare. It functions like the ACU in this environment. Refer to the HP Smart Array controller documentation for more information about using CPQONLIN. HP Systems Insight Manager HP Systems Insight Manager is a client/server tool for integrated server environment management. Based on SNMP, it is capable of monitoring more than 1,200 system-wide parameters for performance and other operational characteristics of Smart Array controller storage. The program displays configuration information, operating system device driver version numbers, controller firmware version numbers, Pre-Failure Warranty information, and operating statistics. Performance monitoring HP SIM gives administrators a window to look at low-level performance characteristics of Smart Array controllers in the environment. It monitors three basic Smart Array controller performance parameters for proactive storage subsystem management: I/O commands per second Average command latency Local processor utilization Analyzing these key parameters can assist administrators in fine tuning configurations for performance. HP SIM can graphically chart performance over time for each of these parameters. Fault prediction A background task monitors several key drive parameters and notifies HP SIM if a drive fails to meet certain factory-preset criteria. HP SIM alerts the administrator to the potential problem. Array Diagnostics Utility The HP Array Diagnostics Utility (ADU) is an in-depth diagnostic and reporting utility for all Smart Array controllers. The ADU quickly identifies problems such as incorrect versions of firmware, improperly installed drives, inappropriate error rates, and failed batteries on the array accelerator board. The ADU displays a detailed analysis of the system configuration. If the cause is not apparent, the ADU can generate a full report for administrators to fax or to HP customer service for phone support. 22
23 Summary HP Smart Array controllers are powerful I/O solutions for today s most demanding network data storage requirements. Smart Array controller technology combines an advanced feature set and fullspectrum, hardware-based fault management with exceptional performance characteristics. Smart Array controllers provide solutions for all four primary data storage requirements: capacity growth, high performance, data availability, and manageability. Smart Array controllers represent patented HP technology and continue the HP commitment to providing the most complete and advanced storage solutions for server customers. HP is the only server provider with a seamless storage solution set that spans the range from embedded Smart Array controllers in servers to plug-in PCI Smart Array controllers to SAN-attached MSA storage. The tools used for managing and configuring storage are the same in all of those environments. Data sets are compatible across all of those environments, The HP universal drive strategy allows customers to easily migrate data from DAS to SAN. 23
24 Appendix A: Capacity growth technologies The Smart Array controller family includes a standard toolset that administrators can use to configure array controllers, expand an existing array configuration by adding disk drives, or reconfigure an array by extending logical drive sizes. Before this innovation, expanding the storage capacity attached to an array controller required a time-consuming backup-reconfigure-restore cycle. Array expansion Array expansion is the process of adding physical drives to an array that has already been configured. The logical drives that exist in the array before the expansion takes place are unchanged; only the amount of free space in the array changes. For example, suppose an existing array consists of four physical drives and the administrator wants to expand the array to six physical drives. This is like having four glasses full of water and dividing that water from the original four glasses among six glasses (Figure A1). The amount of water (the size of the logical drive) has not changed it has merely been redistributed, or expanded, into a larger number of containers (drives). Figure A1. Array expansion redistributes an array into a larger number of physical drives. The size of the logical drive does not change. Thus, if an existing array is nearly filled with logical drives, an administrator can add new physical drives and initiate an array expansion using the ACU. The ACU automatically checks the drive hardware configuration to ensure the array expansion. Then, the existing logical drive is distributed across all physical drives in the expanded array without affecting any existing data. If the array being expanded contains more than one logical drive, data is redistributed one logical drive at a time. The expansion process is entirely independent of the operating system. For example, if a 10-gigabyte (GB) logical drive is expanded from four drives into six drives, the operating system is unaware of the change. The amount of time it takes to complete an online array expansion depends on subsystem I/O activity, the size of the logical drives on the array, fault-tolerance level, the number of disk drives in the new array, disk drive performance, and the priority level of the array expansion. Administrators can monitor array expansion completion progress within the ACU. 24
25 The ACU allows administrators to set the priority of array expansion operations. A high-priority setting prioritizes the array expansion operation over I/O requests. A low-priority setting is the ACU default setting and gives I/O commands precedence over array expansion. During idle time, when no I/O commands are active, the array expansion operation runs at full speed regardless of the priority setting. Logical drive creation Once the array capacity is expanded, the added capacity can be used to create a new logical drive (Figure A2) or to extend the size of an existing logical drive (described in the Logical drive extension section). Figure A2. After array expansion, the administrator can use the free space by creating a new logical drive. For example, if every department in a company has its own logical drive and a new department is created, the administrator might need to create an entirely new logical drive for that department. However, many administrators wish to extend the size of their logical drive after array expansion. Logical drive extension lets administrators increase logical drive size if the existing drive is running out of storage space. 25
26 Logical drive extension Logical drive extension increases the storage space of a logical drive (Figure A3). During this process, an administrator adds new storage space to an existing logical drive on the same array. An administrator may have gained this new storage space either by array expansion or by deleting another logical drive on the same array. Figure A3. Logical drive extension grows the size of a logical drive. The operating system must be aware of changes to the logical drive size. Refer to operating system documentation for additional information. 26
27 For more information For additional information, refer to the resources listed below. Resource description Web address Smart Array controllers HP hard disk drive products HP Modular Smart Array external storage systems HP ProLiant servers HP SAS Technology Configuring Arrays on HP Smart Array Controllers Reference Guide RAID 6 with HP Advanced Data Guarding technology Smart Array RAID Controllers Support Matrix Smart Array Advanced Pack c /c pdf anual/c /c pdf Serial Attached SCSI storage technology brief Redundancy in enterprise storage networks using dual-domain SAS configurations HP Smart Array controllers for HP ProLiant Servers User Guide HP One-Button Disaster Recovery (OBDR) Solution for ProLiant c /c pdf. c /c pdf c /c pdf?jumpid=reg_r1002_usen tml Call to action Send comments about this paper to [email protected]. 2004, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. TC090807TB, August
HP Smart Array Controller technology
 HP Smart Array Controller technology technology brief Abstract... 3 Storage trends... 3 Meeting data storage requirements... 4 Capacity growth... 4 Array expansion... 5 Logical drive creation... 6 Logical
HP Smart Array Controller technology technology brief Abstract... 3 Storage trends... 3 Meeting data storage requirements... 4 Capacity growth... 4 Array expansion... 5 Logical drive creation... 6 Logical
HP Smart Array controller technology
 HP Smart Array controller technology Technology brief, 4 th edition Introduction... 2 Smart Array performance factors... 2 Smart Array processing engine... 2 Hardware tuning... 3 Cache module performance
HP Smart Array controller technology Technology brief, 4 th edition Introduction... 2 Smart Array performance factors... 2 Smart Array processing engine... 2 Hardware tuning... 3 Cache module performance
QuickSpecs. Models HP Smart Array E200 Controller. Upgrade Options Cache Upgrade. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array E200 is HP's first entry level PCI Express (PCIe) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The full size card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR1-266 memory. The E200 is ideal
Overview The HP Smart Array E200 is HP's first entry level PCI Express (PCIe) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The full size card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR1-266 memory. The E200 is ideal
Models Smart Array 6402A/128 Controller 3X-KZPEC-BF Smart Array 6404A/256 two 2 channel Controllers
 Overview The SA6400A is a high-performance Ultra320, PCI-X array controller. It provides maximum performance, flexibility, and reliable data protection for HP OpenVMS AlphaServers through its unique modular
Overview The SA6400A is a high-performance Ultra320, PCI-X array controller. It provides maximum performance, flexibility, and reliable data protection for HP OpenVMS AlphaServers through its unique modular
HP Smart Array 5i Plus Controller and Battery Backed Write Cache (BBWC) Enabler
 Overview HP Smart Array 5i Plus Controller and Battery Backed Write Cache (BBWC) Enabler Models Smart Array 5i Plus Controller and BBWC Enabler bundled Option Kit (for ProLiant DL380 G2, ProLiant DL380
Overview HP Smart Array 5i Plus Controller and Battery Backed Write Cache (BBWC) Enabler Models Smart Array 5i Plus Controller and BBWC Enabler bundled Option Kit (for ProLiant DL380 G2, ProLiant DL380
How To Use An Hp Smart Array P212 (Sas) With A 1-Year Warranty On A 2 Terabyte Hard Drive (Sata) And A 1 Terabyte (Sasa) Hard Drive With A 2-Year License (S
 Overview The HP Smart Array P212 is HP's entry level PCI Express (PCIe) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory. The P212
Overview The HP Smart Array P212 is HP's entry level PCI Express (PCIe) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory. The P212
QuickSpecs. HP Smart Array 5312 Controller. Overview
 Overview Models 238633-B21 238633-291 (Japan) Feature List: High Performance PCI-X Architecture High Capacity Two Ultra 3 SCSI channels support up to 28 drives Modular battery-backed cache design 128 MB
Overview Models 238633-B21 238633-291 (Japan) Feature List: High Performance PCI-X Architecture High Capacity Two Ultra 3 SCSI channels support up to 28 drives Modular battery-backed cache design 128 MB
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF. Compaq RAID on a Chip Technology EXECUTIVE SUMMARY CONTENTS
 TECHNOLOGY BRIEF August 1999 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISSD Technology Communications CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Introduction 3 Subsystem Technology 3 Processor 3 SCSI Chip4 PCI Bridge
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF August 1999 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISSD Technology Communications CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Introduction 3 Subsystem Technology 3 Processor 3 SCSI Chip4 PCI Bridge
Smart Array technology: advantages of battery-backed cache
 Smart Array technology: advantages of battery-backed cache technology brief Abstract... 2 Introduction... 2 Role of cache in the storage system... 2 Need for a battery-backed cache... 2 Recovering data
Smart Array technology: advantages of battery-backed cache technology brief Abstract... 2 Introduction... 2 Role of cache in the storage system... 2 Need for a battery-backed cache... 2 Recovering data
QuickSpecs. What's New Boot from Tape. Models HP Smart Array P411 Controller
 Overview The HP Smart Array P411 is HP's external connect only, PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller for Integrity rack optimized servers. The low profile, half height card
Overview The HP Smart Array P411 is HP's external connect only, PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller for Integrity rack optimized servers. The low profile, half height card
Intel RAID Controllers
 Intel RAID Controllers Best Practices White Paper April, 2008 Enterprise Platforms and Services Division - Marketing Revision History Date Revision Number April, 2008 1.0 Initial release. Modifications
Intel RAID Controllers Best Practices White Paper April, 2008 Enterprise Platforms and Services Division - Marketing Revision History Date Revision Number April, 2008 1.0 Initial release. Modifications
HP Smart Array Controllers and basic RAID performance factors
 Technical white paper HP Smart Array Controllers and basic RAID performance factors Technology brief Table of contents Abstract 2 Benefits of drive arrays 2 Factors that affect performance 2 HP Smart Array
Technical white paper HP Smart Array Controllers and basic RAID performance factors Technology brief Table of contents Abstract 2 Benefits of drive arrays 2 Factors that affect performance 2 HP Smart Array
HP Array Technologies
 19 6717-4 CH13.qxd 9/15/04 5:11 PM Page 253 T H I R T E E N HP Array Technologies Chapter Syllabus 13.1 Advantages of HP Smart Array Controllers 13.2 HP Array Controller Utilities 13.3 Array Controller
19 6717-4 CH13.qxd 9/15/04 5:11 PM Page 253 T H I R T E E N HP Array Technologies Chapter Syllabus 13.1 Advantages of HP Smart Array Controllers 13.2 HP Array Controller Utilities 13.3 Array Controller
DELL RAID PRIMER DELL PERC RAID CONTROLLERS. Joe H. Trickey III. Dell Storage RAID Product Marketing. John Seward. Dell Storage RAID Engineering
 DELL RAID PRIMER DELL PERC RAID CONTROLLERS Joe H. Trickey III Dell Storage RAID Product Marketing John Seward Dell Storage RAID Engineering http://www.dell.com/content/topics/topic.aspx/global/products/pvaul/top
DELL RAID PRIMER DELL PERC RAID CONTROLLERS Joe H. Trickey III Dell Storage RAID Product Marketing John Seward Dell Storage RAID Engineering http://www.dell.com/content/topics/topic.aspx/global/products/pvaul/top
QuickSpecs. Models. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P812 is HP's 24 port Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller with PCI Express (PCIe). This high performance SAS RAID controller provides high levels of reliability for HP
Overview The HP Smart Array P812 is HP's 24 port Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller with PCI Express (PCIe). This high performance SAS RAID controller provides high levels of reliability for HP
QuickSpecs. What's New. HP Smart Array P411 Controller. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P411 is HP's external connect only, PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory.
Overview The HP Smart Array P411 is HP's external connect only, PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory.
QuickSpecs. What's New. HP Smart Array P410 Controller Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P410 is HP's PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory. The P410 is ideal
Overview The HP Smart Array P410 is HP's PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory. The P410 is ideal
QuickSpecs. What's New. HP Smart Array P410 Controller. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P410 is HP's PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory. The P410 is ideal
Overview The HP Smart Array P410 is HP's PCI Express (PCIe) 2.0 Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The low profile, half height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-800 memory. The P410 is ideal
QuickSpecs. Models. Overview
 Overview The is an enterprise-class 6 Gb/s controller that provides improved performance, greater external attach rate and lower maintenance. P421 controller is ideal for RAID 0/1, 1+0, 5, and 50. RAID
Overview The is an enterprise-class 6 Gb/s controller that provides improved performance, greater external attach rate and lower maintenance. P421 controller is ideal for RAID 0/1, 1+0, 5, and 50. RAID
QuickSpecs. What's New. At A Glance. Models. HP StorageWorks SB40c storage blade. Overview
 DA - 12587 Worldwide Version 5 2.16.2007 Page 1 Overview The HP StorageWorks SB40c is a half-height c-class storage blade supporting up to six hot-plug Small Form Factor (SFF) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)
DA - 12587 Worldwide Version 5 2.16.2007 Page 1 Overview The HP StorageWorks SB40c is a half-height c-class storage blade supporting up to six hot-plug Small Form Factor (SFF) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)
As enterprise data requirements continue
 Storage Introducing the Dell PERC 6 Family of SAS RAID ControlLers By Bhanu Prakash Dixit Sanjay Tiwari Kedar Vaze Joe H. Trickey III The Dell PowerEdge Expandable RAID Controller (PERC) 6 family of enterprise-class
Storage Introducing the Dell PERC 6 Family of SAS RAID ControlLers By Bhanu Prakash Dixit Sanjay Tiwari Kedar Vaze Joe H. Trickey III The Dell PowerEdge Expandable RAID Controller (PERC) 6 family of enterprise-class
QuickSpecs. Models. HP Dynamic Smart Array B320i Controller. Overview
 Overview HP Dynamic Smart array provides more customer choice with higher levels of data protection for embedded controllers, these data protection levels were earlier only available to standup controllers.
Overview HP Dynamic Smart array provides more customer choice with higher levels of data protection for embedded controllers, these data protection levels were earlier only available to standup controllers.
QuickSpecs. Models. HP Smart Array P731m Controller. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P731m is a PCI-Express (PCIe) 3.0 mezzanine card supporting direct attached storage for the HP ProLiant Gen8 BladeSystem servers. It is one of the highest performing controllers
Overview The HP Smart Array P731m is a PCI-Express (PCIe) 3.0 mezzanine card supporting direct attached storage for the HP ProLiant Gen8 BladeSystem servers. It is one of the highest performing controllers
Redundancy in enterprise storage networks using dual-domain SAS configurations
 Redundancy in enterprise storage networks using dual-domain SAS configurations technology brief Abstract... 2 Introduction... 2 Why dual-domain SAS is important... 2 Single SAS domain... 3 Dual-domain
Redundancy in enterprise storage networks using dual-domain SAS configurations technology brief Abstract... 2 Introduction... 2 Why dual-domain SAS is important... 2 Single SAS domain... 3 Dual-domain
RAID Technology Overview
 RAID Technology Overview HP Smart Array RAID Controllers HP Part Number: J6369-90050 Published: September 2007 Edition: 1 Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. Legal Notices Copyright
RAID Technology Overview HP Smart Array RAID Controllers HP Part Number: J6369-90050 Published: September 2007 Edition: 1 Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. Legal Notices Copyright
IBM ^ xseries ServeRAID Technology
 IBM ^ xseries ServeRAID Technology Reliability through RAID technology Executive Summary: t long ago, business-critical computing on industry-standard platforms was unheard of. Proprietary systems were
IBM ^ xseries ServeRAID Technology Reliability through RAID technology Executive Summary: t long ago, business-critical computing on industry-standard platforms was unheard of. Proprietary systems were
Assessing RAID ADG vs. RAID 5 vs. RAID 1+0
 White Paper October 2001 Prepared by Industry Standard Storage Group Compaq Computer Corporation Contents Overview...3 Defining RAID levels...3 Evaluating RAID levels...3 Choosing a RAID level...4 Assessing
White Paper October 2001 Prepared by Industry Standard Storage Group Compaq Computer Corporation Contents Overview...3 Defining RAID levels...3 Evaluating RAID levels...3 Choosing a RAID level...4 Assessing
RAID 5 rebuild performance in ProLiant
 RAID 5 rebuild performance in ProLiant technology brief Abstract... 2 Overview of the RAID 5 rebuild process... 2 Estimating the mean-time-to-failure (MTTF)... 3 Factors affecting RAID 5 array rebuild
RAID 5 rebuild performance in ProLiant technology brief Abstract... 2 Overview of the RAID 5 rebuild process... 2 Estimating the mean-time-to-failure (MTTF)... 3 Factors affecting RAID 5 array rebuild
Configuring ThinkServer RAID 500 and RAID 700 Adapters. Lenovo ThinkServer
 Configuring ThinkServer RAID 500 and RAID 700 Adapters Lenovo ThinkServer October 4, 2011 Contents Overview... 4 RAID 500 features... 4 RAID 700 features... 4 RAID Overview... 4 Choosing the RAID Level...
Configuring ThinkServer RAID 500 and RAID 700 Adapters Lenovo ThinkServer October 4, 2011 Contents Overview... 4 RAID 500 features... 4 RAID 700 features... 4 RAID Overview... 4 Choosing the RAID Level...
Chapter 6. 6.1 Introduction. Storage and Other I/O Topics. p. 570( 頁 585) Fig. 6.1. I/O devices can be characterized by. I/O bus connections
 Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 6.1 Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 6.1 Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Education. Servicing the IBM ServeRAID-8k Serial- Attached SCSI Controller. Study guide. XW5078 Release 1.00
 Education Servicing the IBM ServeRAID-8k Serial- Attached SCSI Controller Study guide XW5078 Release 1.00 May 2006 Servicing the IBM ServeRAID-8k Serial- Attached SCSI (SAS) Controller Overview The ServeRAID
Education Servicing the IBM ServeRAID-8k Serial- Attached SCSI Controller Study guide XW5078 Release 1.00 May 2006 Servicing the IBM ServeRAID-8k Serial- Attached SCSI (SAS) Controller Overview The ServeRAID
QuickSpecs. What's New Support for HP MSA 2040 Storage. Models. HP Smart Array P712m Controller. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P712m mezzanine card is the preferred high value solution for 6Gb/s Shared SAS Storage for the HP ProLiant BladeSystem servers. It is one of the highest performing controllers
Overview The HP Smart Array P712m mezzanine card is the preferred high value solution for 6Gb/s Shared SAS Storage for the HP ProLiant BladeSystem servers. It is one of the highest performing controllers
HP Smart Array P400 Controller User Guide
 HP Smart Array P400 Controller User Guide October 2005 (First Edition) Part Number 399716-001 Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change
HP Smart Array P400 Controller User Guide October 2005 (First Edition) Part Number 399716-001 Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change
QuickSpecs. What's New. Models. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P212 is HP's entry level PCI Express (PCIe) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The Low Profile, Half Height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-266 memory. The P212
Overview The HP Smart Array P212 is HP's entry level PCI Express (PCIe) Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) RAID controller. The Low Profile, Half Height card has 8 ports and utilizes DDR2-266 memory. The P212
VTrak 15200 SATA RAID Storage System
 Page 1 15-Drive Supports over 5 TB of reliable, low-cost, high performance storage 15200 Product Highlights First to deliver a full HW iscsi solution with SATA drives - Lower CPU utilization - Higher data
Page 1 15-Drive Supports over 5 TB of reliable, low-cost, high performance storage 15200 Product Highlights First to deliver a full HW iscsi solution with SATA drives - Lower CPU utilization - Higher data
New Advanced RAID Level for Today's Larger Storage Capacities: Advanced Data Guarding
 White Paper October 2000 Prepared by Storage Products Group Compaq Computer Corporation Contents Introduction...2 What customers can expect from Compaq RAID ADG solution...3 RAID ADG Features and Benefits...3
White Paper October 2000 Prepared by Storage Products Group Compaq Computer Corporation Contents Introduction...2 What customers can expect from Compaq RAID ADG solution...3 RAID ADG Features and Benefits...3
Benefits of Intel Matrix Storage Technology
 Benefits of Intel Matrix Storage Technology White Paper December 2005 Document Number: 310855-001 INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
Benefits of Intel Matrix Storage Technology White Paper December 2005 Document Number: 310855-001 INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
HP A7143A RAID160 SA Controller Support Guide
 HP A7143A RAID160 SA Controller Support Guide Installation and Administration of the HP A7143A PCI 4-Channel RAID160 SA SCSI Controller HP-UX Manufacturing Part Number : J6369-90026 E0512 Printed in the
HP A7143A RAID160 SA Controller Support Guide Installation and Administration of the HP A7143A PCI 4-Channel RAID160 SA SCSI Controller HP-UX Manufacturing Part Number : J6369-90026 E0512 Printed in the
QuickSpecs. HP StorageWorks Modular Smart Array 500 G2. Overview
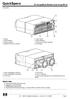 Overview 1. Display 5. Power Switch 2. Display Buttons 6. Status Indicators 3. Display Indicators 7. Redundant Controller Slot Blank 4. Modular Smart Array Controller 8. Drive Bay(s) 1. Power Supply/Blower
Overview 1. Display 5. Power Switch 2. Display Buttons 6. Status Indicators 3. Display Indicators 7. Redundant Controller Slot Blank 4. Modular Smart Array Controller 8. Drive Bay(s) 1. Power Supply/Blower
RAID-01 (ciss) B.11.31.1005 mass storage driver release notes, edition 2
 RAID-01 (ciss) B.11.31.1005 mass storage driver release notes, edition 2 HP-UX 11i v3 HP Part Number: 5991-0448_ed2 Published: August 2010 Edition: 2 Copyright 2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company,
RAID-01 (ciss) B.11.31.1005 mass storage driver release notes, edition 2 HP-UX 11i v3 HP Part Number: 5991-0448_ed2 Published: August 2010 Edition: 2 Copyright 2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company,
Smart Array Technology: Basics and Advantages of Battery-Backed Cache
 White Paper February 2001 Prepared by Industry Standard Server Group, Storage Products Division Compaq Computer Corporation Contents Introduction...3 Cache Use...3 Battery Backing of Cache...3 Compaq Implementations
White Paper February 2001 Prepared by Industry Standard Server Group, Storage Products Division Compaq Computer Corporation Contents Introduction...3 Cache Use...3 Battery Backing of Cache...3 Compaq Implementations
The Advantages of Multi-Port Network Adapters in an SWsoft Virtual Environment
 The Advantages of Multi-Port Network Adapters in an SWsoft Virtual Environment Introduction... 2 Virtualization addresses key challenges facing IT today... 2 Introducing Virtuozzo... 2 A virtualized environment
The Advantages of Multi-Port Network Adapters in an SWsoft Virtual Environment Introduction... 2 Virtualization addresses key challenges facing IT today... 2 Introducing Virtuozzo... 2 A virtualized environment
Intel Rapid Storage Technology
 Intel Rapid Storage Technology User Guide August 2011 Revision 1.0 1 Document Number: XXXXXX INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
Intel Rapid Storage Technology User Guide August 2011 Revision 1.0 1 Document Number: XXXXXX INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
HP Smart Array SAS Controllers for Integrity Servers Support Guide
 HP Smart Array SAS Controllers for Integrity Servers Support Guide HP-UX 11i v2 and 11i v3 Abstract This document describes how to install, configure, and troubleshoot HP Smart Array SAS controllers on
HP Smart Array SAS Controllers for Integrity Servers Support Guide HP-UX 11i v2 and 11i v3 Abstract This document describes how to install, configure, and troubleshoot HP Smart Array SAS controllers on
Best Practices RAID Implementations for Snap Servers and JBOD Expansion
 STORAGE SOLUTIONS WHITE PAPER Best Practices RAID Implementations for Snap Servers and JBOD Expansion Contents Introduction...1 Planning for the End Result...1 Availability Considerations...1 Drive Reliability...2
STORAGE SOLUTIONS WHITE PAPER Best Practices RAID Implementations for Snap Servers and JBOD Expansion Contents Introduction...1 Planning for the End Result...1 Availability Considerations...1 Drive Reliability...2
This user guide describes features that are common to most models. Some features may not be available on your computer.
 RAID User Guide Copyright 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Intel is a trademark of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks
RAID User Guide Copyright 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Intel is a trademark of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks
HP StorageWorks 20 Modular Smart Array Overview
 Overview 1. Mounting bracket covers (bezel ears) 2. Disk drive in bay 3 3. Disk drive in bay 6 1. Arrow buttons (for future use) 5. Enclosure fault LED - Glows amber when any other LED in the 2. enclosure
Overview 1. Mounting bracket covers (bezel ears) 2. Disk drive in bay 3 3. Disk drive in bay 6 1. Arrow buttons (for future use) 5. Enclosure fault LED - Glows amber when any other LED in the 2. enclosure
Dell PowerEdge RAID Controller Cards H700 and H800 Technical Guide
 PowerEdge RAID Controller Cards H700 and H800 Technical Guide Enterprise-class controllers designed for performance, reliability, and fault tolerance. This document is for informational purposes only.
PowerEdge RAID Controller Cards H700 and H800 Technical Guide Enterprise-class controllers designed for performance, reliability, and fault tolerance. This document is for informational purposes only.
QuickSpecs. Models. HP Smart Array P721m Controller. Overview
 Overview The HP Smart Array P721m is a PCI-Express (PCIe) 3.0 mezzanine card supporting direct attached SAS Storage for the HP ProLiant Gen8 BladeSystem servers. It is one of the highest performing controllers
Overview The HP Smart Array P721m is a PCI-Express (PCIe) 3.0 mezzanine card supporting direct attached SAS Storage for the HP ProLiant Gen8 BladeSystem servers. It is one of the highest performing controllers
technology brief RAID Levels March 1997 Introduction Characteristics of RAID Levels
 technology brief RAID Levels March 1997 Introduction RAID is an acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks (originally Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) coined in a 1987 University of California
technology brief RAID Levels March 1997 Introduction RAID is an acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks (originally Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) coined in a 1987 University of California
HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8 1000 mailbox 2GB mailbox resiliency Exchange 2010 storage solution
 Technical white paper HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8 1000 mailbox 2GB mailbox resiliency Exchange 2010 storage solution Table of contents Overview 2 Disclaimer 2 Features of the tested solution 2 Solution description
Technical white paper HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8 1000 mailbox 2GB mailbox resiliency Exchange 2010 storage solution Table of contents Overview 2 Disclaimer 2 Features of the tested solution 2 Solution description
Intel Matrix Storage Manager 8.x
 Intel Matrix Storage Manager 8.x User's Manual January 2009 Revision 1.0 Document Number: XXXXXX INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
Intel Matrix Storage Manager 8.x User's Manual January 2009 Revision 1.0 Document Number: XXXXXX INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
ESATA PCI CARD. User s Manual
 ESATA PCI CARD User s Manual Introduction... 3 System Requirements... 3 RAID Introduction... 3 BIOS Configuration Utility... 5 Configuring Arrays... 5 RAID Mode Definitions... 5 BIOS Configuration Utility...
ESATA PCI CARD User s Manual Introduction... 3 System Requirements... 3 RAID Introduction... 3 BIOS Configuration Utility... 5 Configuring Arrays... 5 RAID Mode Definitions... 5 BIOS Configuration Utility...
Definition of RAID Levels
 RAID The basic idea of RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is to combine multiple inexpensive disk drives into an array of disk drives to obtain performance, capacity and reliability that exceeds
RAID The basic idea of RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is to combine multiple inexpensive disk drives into an array of disk drives to obtain performance, capacity and reliability that exceeds
Distribution One Server Requirements
 Distribution One Server Requirements Introduction Welcome to the Hardware Configuration Guide. The goal of this guide is to provide a practical approach to sizing your Distribution One application and
Distribution One Server Requirements Introduction Welcome to the Hardware Configuration Guide. The goal of this guide is to provide a practical approach to sizing your Distribution One application and
SAN Conceptual and Design Basics
 TECHNICAL NOTE VMware Infrastructure 3 SAN Conceptual and Design Basics VMware ESX Server can be used in conjunction with a SAN (storage area network), a specialized high speed network that connects computer
TECHNICAL NOTE VMware Infrastructure 3 SAN Conceptual and Design Basics VMware ESX Server can be used in conjunction with a SAN (storage area network), a specialized high speed network that connects computer
3 Port PCI Express 2.0 SATA III 6 Gbps RAID Controller Card w/ msata Slot and HyperDuo SSD Tiering
 3 Port PCI Express 2.0 SATA III 6 Gbps RAID Controller Card w/ msata Slot and HyperDuo SSD Tiering StarTech ID: PEXMSATA343 The PEXMSATA343 3-Port PCI Express 2.0 SATA Card with HyperDuo adds an internal
3 Port PCI Express 2.0 SATA III 6 Gbps RAID Controller Card w/ msata Slot and HyperDuo SSD Tiering StarTech ID: PEXMSATA343 The PEXMSATA343 3-Port PCI Express 2.0 SATA Card with HyperDuo adds an internal
Using RAID6 for Advanced Data Protection
 Using RAI6 for Advanced ata Protection 2006 Infortrend Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents The Challenge of Fault Tolerance... 3 A Compelling Technology: RAI6... 3 Parity... 4 Why Use RAI6...
Using RAI6 for Advanced ata Protection 2006 Infortrend Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents The Challenge of Fault Tolerance... 3 A Compelling Technology: RAI6... 3 Parity... 4 Why Use RAI6...
QuickSpecs. HP StorageWorks 60 Modular Smart Array. Overview
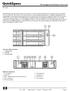 Overview The enclosure is a 2U Serial Attach SCSI (SAS) disk drive storage enclosure supporting 3.5" SAS or Serial ATA (SATA) drives. This enclosure delivers industry-leading data performance, availability,
Overview The enclosure is a 2U Serial Attach SCSI (SAS) disk drive storage enclosure supporting 3.5" SAS or Serial ATA (SATA) drives. This enclosure delivers industry-leading data performance, availability,
Performance Report Modular RAID for PRIMERGY
 Performance Report Modular RAID for PRIMERGY Version 1.1 March 2008 Pages 15 Abstract This technical documentation is designed for persons, who deal with the selection of RAID technologies and RAID controllers
Performance Report Modular RAID for PRIMERGY Version 1.1 March 2008 Pages 15 Abstract This technical documentation is designed for persons, who deal with the selection of RAID technologies and RAID controllers
Accelerating Server Storage Performance on Lenovo ThinkServer
 Accelerating Server Storage Performance on Lenovo ThinkServer Lenovo Enterprise Product Group April 214 Copyright Lenovo 214 LENOVO PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION AS IS WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER
Accelerating Server Storage Performance on Lenovo ThinkServer Lenovo Enterprise Product Group April 214 Copyright Lenovo 214 LENOVO PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION AS IS WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER
Xanadu 130. Business Class Storage Solution. 8G FC Host Connectivity and 6G SAS Backplane. 2U 12-Bay 3.5 Form Factor
 RAID Inc Xanadu 200 100 Series Storage Systems Xanadu 130 Business Class Storage Solution 8G FC Host Connectivity and 6G SAS Backplane 2U 12-Bay 3.5 Form Factor Highlights Highest levels of data integrity
RAID Inc Xanadu 200 100 Series Storage Systems Xanadu 130 Business Class Storage Solution 8G FC Host Connectivity and 6G SAS Backplane 2U 12-Bay 3.5 Form Factor Highlights Highest levels of data integrity
File System & Device Drive. Overview of Mass Storage Structure. Moving head Disk Mechanism. HDD Pictures 11/13/2014. CS341: Operating System
 CS341: Operating System Lect 36: 1 st Nov 2014 Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati File System & Device Drive Mass Storage Disk Structure Disk Arm Scheduling RAID
CS341: Operating System Lect 36: 1 st Nov 2014 Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati File System & Device Drive Mass Storage Disk Structure Disk Arm Scheduling RAID
Price/performance Modern Memory Hierarchy
 Lecture 21: Storage Administration Take QUIZ 15 over P&H 6.1-4, 6.8-9 before 11:59pm today Project: Cache Simulator, Due April 29, 2010 NEW OFFICE HOUR TIME: Tuesday 1-2, McKinley Last Time Exam discussion
Lecture 21: Storage Administration Take QUIZ 15 over P&H 6.1-4, 6.8-9 before 11:59pm today Project: Cache Simulator, Due April 29, 2010 NEW OFFICE HOUR TIME: Tuesday 1-2, McKinley Last Time Exam discussion
HP Array Configuration Utility User Guide
 HP Array Configuration Utility User Guide January 2006 (First Edition) Part Number 416146-001 Copyright 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change
HP Array Configuration Utility User Guide January 2006 (First Edition) Part Number 416146-001 Copyright 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change
High Density RocketRAID 2711 + Rocket EJ220 Device Board Data RAID Installation Guide
 High Density RocketRAID 2711 + Rocket EJ220 Device Board Data RAID Installation Guide Introduction The HighPoint High Density Storage Solutions hammer down high density storage cost over a single mini-
High Density RocketRAID 2711 + Rocket EJ220 Device Board Data RAID Installation Guide Introduction The HighPoint High Density Storage Solutions hammer down high density storage cost over a single mini-
HP AD397A rx2660 SAS Smart Array P400 Controller Installation Guide Manufacturing Part Number: AD397-9001A February 2007
 HP AD397A rx2660 SAS Smart Array P400 Controller Installation Guide Manufacturing Part Number: AD397-9001A February 2007 United States Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P.. Legal Notices
HP AD397A rx2660 SAS Smart Array P400 Controller Installation Guide Manufacturing Part Number: AD397-9001A February 2007 United States Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P.. Legal Notices
HARDWARE GUIDE. MegaRAID SCSI 320-2 RAID Controller
 HARDWARE GUIDE MegaRAID SCSI 320-2 RAID Controller November 2002 This document contains proprietary information of LSI Logic Corporation. The information contained herein is not to be used by or disclosed
HARDWARE GUIDE MegaRAID SCSI 320-2 RAID Controller November 2002 This document contains proprietary information of LSI Logic Corporation. The information contained herein is not to be used by or disclosed
QuickSpecs. HP Dynamic Smart Array Controllers. Models HP Dynamic Smart Array RAID Controllers. HP Dynamic Smart Array Controllers.
 Overview HP Dynamic Smart Array is a RAID solution combining a storage host bus adapter (HBA) and proprietary software components. Eliminating most of the hardware RAID controller components and relocating
Overview HP Dynamic Smart Array is a RAID solution combining a storage host bus adapter (HBA) and proprietary software components. Eliminating most of the hardware RAID controller components and relocating
Post-production Video Editing Solution Guide with Microsoft SMB 3 File Serving AssuredSAN 4000
 Post-production Video Editing Solution Guide with Microsoft SMB 3 File Serving AssuredSAN 4000 Dot Hill Systems introduction 1 INTRODUCTION Dot Hill Systems offers high performance network storage products
Post-production Video Editing Solution Guide with Microsoft SMB 3 File Serving AssuredSAN 4000 Dot Hill Systems introduction 1 INTRODUCTION Dot Hill Systems offers high performance network storage products
4 Channel 6-Port SATA 6Gb/s PCIe RAID Host Card
 4 Channel 6-Port SATA 6Gb/s PCIe RAID Host Card User Manual Model: UGT-ST644R All brand names and trademarks are properties of their respective owners www.vantecusa.com Contents: Chapter 1: Introduction...
4 Channel 6-Port SATA 6Gb/s PCIe RAID Host Card User Manual Model: UGT-ST644R All brand names and trademarks are properties of their respective owners www.vantecusa.com Contents: Chapter 1: Introduction...
Q & A From Hitachi Data Systems WebTech Presentation:
 Q & A From Hitachi Data Systems WebTech Presentation: RAID Concepts 1. Is the chunk size the same for all Hitachi Data Systems storage systems, i.e., Adaptable Modular Systems, Network Storage Controller,
Q & A From Hitachi Data Systems WebTech Presentation: RAID Concepts 1. Is the chunk size the same for all Hitachi Data Systems storage systems, i.e., Adaptable Modular Systems, Network Storage Controller,
OPTIMIZING SERVER VIRTUALIZATION
 OPTIMIZING SERVER VIRTUALIZATION HP MULTI-PORT SERVER ADAPTERS BASED ON INTEL ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY As enterprise-class server infrastructures adopt virtualization to improve total cost of ownership (TCO)
OPTIMIZING SERVER VIRTUALIZATION HP MULTI-PORT SERVER ADAPTERS BASED ON INTEL ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY As enterprise-class server infrastructures adopt virtualization to improve total cost of ownership (TCO)
Maximizing Server Storage Performance with PCI Express and Serial Attached SCSI. Article for InfoStor November 2003 Paul Griffith Adaptec, Inc.
 Filename: SAS - PCI Express Bandwidth - Infostor v5.doc Maximizing Server Storage Performance with PCI Express and Serial Attached SCSI Article for InfoStor November 2003 Paul Griffith Adaptec, Inc. Server
Filename: SAS - PCI Express Bandwidth - Infostor v5.doc Maximizing Server Storage Performance with PCI Express and Serial Attached SCSI Article for InfoStor November 2003 Paul Griffith Adaptec, Inc. Server
How to register. Who should attend Services, both internal HP and external
 mm Servicing HP Rack and Tower Server Solutions - Rev 12.31 Course data sheet Certification: Exam(s): The Learning Center: Format: Recommended Duration: How to register HP ATP - Rack and Tower Server Solutions
mm Servicing HP Rack and Tower Server Solutions - Rev 12.31 Course data sheet Certification: Exam(s): The Learning Center: Format: Recommended Duration: How to register HP ATP - Rack and Tower Server Solutions
RAID EzAssist Configuration Utility Quick Configuration Guide
 RAID EzAssist Configuration Utility Quick Configuration Guide DB15-000277-00 First Edition 08P5520 Proprietary Rights Notice This document contains proprietary information of LSI Logic Corporation. The
RAID EzAssist Configuration Utility Quick Configuration Guide DB15-000277-00 First Edition 08P5520 Proprietary Rights Notice This document contains proprietary information of LSI Logic Corporation. The
RAID. RAID 0 No redundancy ( AID?) Just stripe data over multiple disks But it does improve performance. Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 29
 RAID Redundant Array of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks Use multiple smaller disks (c.f. one large disk) Parallelism improves performance Plus extra disk(s) for redundant data storage Provides fault tolerant
RAID Redundant Array of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks Use multiple smaller disks (c.f. one large disk) Parallelism improves performance Plus extra disk(s) for redundant data storage Provides fault tolerant
white paper A CASE FOR VIRTUAL RAID ADAPTERS Beyond Software RAID
 white paper A CASE FOR VIRTUAL RAID ADAPTERS Beyond Software RAID Table of Contents 1. Abstract...3 2. Storage Configurations...4 3. RAID Implementation...4 4. Software RAID.4-5 5. Hardware RAID Adapters...6
white paper A CASE FOR VIRTUAL RAID ADAPTERS Beyond Software RAID Table of Contents 1. Abstract...3 2. Storage Configurations...4 3. RAID Implementation...4 4. Software RAID.4-5 5. Hardware RAID Adapters...6
PCI Express 2.0 SATA III RAID Controller Card with Internal Mini-SAS SFF-8087 Connector
 PCI Express 2.0 SATA III RAID Controller Card with Internal Mini-SAS SFF-8087 Connector StarTech ID: PEXSAT34SFF The PEXSAT34SFF PCI Express SATA Controller Card enables 4 AHCI SATA III connections to
PCI Express 2.0 SATA III RAID Controller Card with Internal Mini-SAS SFF-8087 Connector StarTech ID: PEXSAT34SFF The PEXSAT34SFF PCI Express SATA Controller Card enables 4 AHCI SATA III connections to
IBM System Storage DS5020 Express
 IBM DS5020 Express Manage growth, complexity, and risk with scalable, high-performance storage Highlights Mixed host interfaces support (Fibre Channel/iSCSI) enables SAN tiering Balanced performance well-suited
IBM DS5020 Express Manage growth, complexity, and risk with scalable, high-performance storage Highlights Mixed host interfaces support (Fibre Channel/iSCSI) enables SAN tiering Balanced performance well-suited
This chapter explains how to update device drivers and apply hotfix.
 MegaRAID SAS User's Guide Areas Covered Before Reading This Manual This section explains the notes for your safety and conventions used in this manual. Chapter 1 Overview This chapter explains an overview
MegaRAID SAS User's Guide Areas Covered Before Reading This Manual This section explains the notes for your safety and conventions used in this manual. Chapter 1 Overview This chapter explains an overview
Configuring RAID for Optimal Performance
 Configuring RAID for Optimal Performance Intel RAID Controller SRCSASJV Intel RAID Controller SRCSASRB Intel RAID Controller SRCSASBB8I Intel RAID Controller SRCSASLS4I Intel RAID Controller SRCSATAWB
Configuring RAID for Optimal Performance Intel RAID Controller SRCSASJV Intel RAID Controller SRCSASRB Intel RAID Controller SRCSASBB8I Intel RAID Controller SRCSASLS4I Intel RAID Controller SRCSATAWB
HP MSA 2040. Table of contents. Best practices. Technical white paper
 Technical white paper HP MSA 2040 Best practices Table of contents About this document... 3 Intended audience... 3 Prerequisites... 3 Related documentation... 3 Introduction... 3 General best practices...
Technical white paper HP MSA 2040 Best practices Table of contents About this document... 3 Intended audience... 3 Prerequisites... 3 Related documentation... 3 Introduction... 3 General best practices...
EMC Backup and Recovery for Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enabled by EMC Celerra Unified Storage
 EMC Backup and Recovery for Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enabled by EMC Celerra Unified Storage Applied Technology Abstract This white paper describes various backup and recovery solutions available for SQL
EMC Backup and Recovery for Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enabled by EMC Celerra Unified Storage Applied Technology Abstract This white paper describes various backup and recovery solutions available for SQL
actitape LTO-3 and LTO-4 internal SCSI and SAS Quick Start Guide
 actitape LTO-3 and LTO-4 internal SCSI and SAS Quick Start Guide Page 1 of 11 Introduction This poster describes how to install your ActiTape LTO half-height internal tape drives with SCSI and SAS interface.
actitape LTO-3 and LTO-4 internal SCSI and SAS Quick Start Guide Page 1 of 11 Introduction This poster describes how to install your ActiTape LTO half-height internal tape drives with SCSI and SAS interface.
HP and Mimosa Systems A system for email archiving, recovery, and storage optimization white paper
 HP and Mimosa Systems A system for email archiving, recovery, and storage optimization white paper Mimosa NearPoint for Microsoft Exchange Server and HP StorageWorks 1510i Modular Smart Array Executive
HP and Mimosa Systems A system for email archiving, recovery, and storage optimization white paper Mimosa NearPoint for Microsoft Exchange Server and HP StorageWorks 1510i Modular Smart Array Executive
What is RAID--BASICS? Mylex RAID Primer. A simple guide to understanding RAID
 What is RAID--BASICS? Mylex RAID Primer A simple guide to understanding RAID Let's look at a hard disk... Several platters stacked on top of each other with a little space in between. One to n platters
What is RAID--BASICS? Mylex RAID Primer A simple guide to understanding RAID Let's look at a hard disk... Several platters stacked on top of each other with a little space in between. One to n platters
HP Direct-Connect External SAS Storage for HP BladeSystem Solutions Deployment Guide
 HP Direct-Connect External SAS Storage for HP BladeSystem Solutions Deployment Guide This document provides device overview information, installation best practices and procedural overview, and illustrated
HP Direct-Connect External SAS Storage for HP BladeSystem Solutions Deployment Guide This document provides device overview information, installation best practices and procedural overview, and illustrated
Management of VMware ESXi. on HP ProLiant Servers
 Management of VMware ESXi on W H I T E P A P E R Table of Contents Introduction................................................................ 3 HP Systems Insight Manager.................................................
Management of VMware ESXi on W H I T E P A P E R Table of Contents Introduction................................................................ 3 HP Systems Insight Manager.................................................
HP D3600 Disk Enclosure 4,000 Mailbox Resiliency Exchange 2013 Storage Solution
 Technical white paper HP D3600 Disk Enclosure 4,000 Mailbox Resiliency Exchange 2013 Storage Solution Table of contents Overview... 2 Disclaimer... 2 Features of the tested solution... 2 HP D3600 Disk
Technical white paper HP D3600 Disk Enclosure 4,000 Mailbox Resiliency Exchange 2013 Storage Solution Table of contents Overview... 2 Disclaimer... 2 Features of the tested solution... 2 HP D3600 Disk
6Gb/s MegaRAID SAS RAID Controllers
 6Gb/s MegaRAID SAS RAID Controllers User Guide 41450-04, Rev. B 41450-04B Revision History Version and Date Description of Changes 41450-04, Rev. B, Updated the environmental conditions for the RAID controllers.
6Gb/s MegaRAID SAS RAID Controllers User Guide 41450-04, Rev. B 41450-04B Revision History Version and Date Description of Changes 41450-04, Rev. B, Updated the environmental conditions for the RAID controllers.
HARDWARE GUIDE. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 RAID Controller
 HARDWARE GUIDE MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 RAID Controller September 2002 This document contains proprietary information of LSI Logic Corporation. The information contained herein is not to be used by or disclosed
HARDWARE GUIDE MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 RAID Controller September 2002 This document contains proprietary information of LSI Logic Corporation. The information contained herein is not to be used by or disclosed
Contents. Overview. Drive Policy RAID 500 features. Disable BGI RAID 700 features. Management Tasks Choosing the RAID Level.
 Configuring ThinkServer RAID 500 and RAID 700 Adapters Contents Overview 2 Drive Policy 28 RAID 500 features 2 Disable BGI 28 RAID 700 features 2 Adapter Properties 28 RAID Overview 2 Management Tasks
Configuring ThinkServer RAID 500 and RAID 700 Adapters Contents Overview 2 Drive Policy 28 RAID 500 features 2 Disable BGI 28 RAID 700 features 2 Adapter Properties 28 RAID Overview 2 Management Tasks
