Introduction. dnotify
|
|
|
- Norman Baker
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction In a multi-user, multi-process operating system, files are continually being created, modified and deleted, often by apparently unrelated processes. This means that any software that needs to keep aware of what is happening in a filesystem needs to employ a file monitoring technique. Monitoring, in this sense, means keeping a watch over a set of files, waiting for any of them to change. Applications that benefit from monitoring techniques include those that need to keep their displayed filesystem information up to date, long running server tools that should automatically reread their configuration files when those files change, applications that watch for and respond to unusual file modifications, system message file monitors, and so on. Most modern operating systems provide file monitoring facilities to give applications realtime information about changes to the filesystem. A variety of notification methods are used to tell the application when a change happens, ranging from an asynchronous signal being sent from the kernel, through to a user space tool printing the name of the changed file on its standard output. We ll take a look at some of the file monitoring facilities available to the Linux developer, starting with the lowest level mechanism and working up to the highest. dnotify All files are ultimately created, updated and deleted by the Linux kernel, so it makes sense that the most direct way for an application to learn that a file has changed is for the kernel to tell it. This is the idea behind the kernel s dnotify feature. dnotify stands for directory notification, and although the feature has been in the kernel for some time, it can only be relied upon in kernels and later, which was when a tiny but very important bug was fixed. dnotify works by sending a signal to a process that has asked to be informed when the content of a directory is changed. Being a low level feature, dnotify is normally used from C code. The developer needs to open the appropriate directory file for reading, then issue a fcntl(2) system call specifying the F_NOTIFY subcommand. Flags passed to this subcommand can specify which events the process wants to be notified about: file creation, deletion, access, modification, renaming, or access rights being set with chmod. By default, whenever any of the monitored operations happen to any file in the directory, the monitoring process will receive the SIGIO signal from the kernel. The signal used is configurable using the fcntl(2) F_SETSIG subcommand, and in order to ensure no signals are missed it is best to change the signal generated to one of the POSIX4 real-time ones, which can be queued. Note that we are talking about directory notification here, not files. If only a single file needs to be watched its directory should be dnotified and the file examined each time the monitoring process receives the signal. Listing 1 shows an example of some C code that watches a particular file waiting for it to be edited. #define _GNU_SOURCE #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <signal.h>
2 int requiredevent = 0; void eventhandler( int sig ) { requiredevent = 1; int main( int argc, char *argv[] ) { struct stat statbuf; struct sigaction action; int fd; char *dir; char *slashptr; char splitfilename[128]; if( argc!= 2 ) { printf( "Usage: %s filename", argv[0] ); if( lstat( argv[1], &statbuf ) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot lstat %s : %s\n", argv[1], strerror(errno) ); if(! S_ISREG( statbuf.st_mode ) ) { printf( "%s is not a regular file\n", argv[1] ); /* Find directory the file is in, or assume the current directory */ strncpy( splitfilename, argv[1], 127 ); if( (slashptr = rindex( splitfilename, '/' )) == NULL ) { dir = "."; else { *slashptr = 0; dir = splitfilename; /* Set up the signal handler */ action.sa_handler = eventhandler; sigemptyset( &action.sa_mask ); action.sa_flags = SA_RESTART; sigaction( SIGRTMIN, &action, NULL ); /* Open the directory the file is in */ if( (fd = open( dir, O_RDONLY )) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot open %s for reading : %s\n", dir, strerror(errno) ); /* Choose the signal I want to receive when the directory content changes */ if( fcntl( fd, F_SETSIG, SIGRTMIN) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot set signal : %s\n", strerror(errno) ); /* Ask for notification when a modification is made in the directory */ if( fcntl( fd, F_NOTIFY, DN_MODIFY DN_MULTISHOT ) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot fcntl %s : %s\n", dir, strerror(errno) ); /* Infinite loop - a real program would be doing stuff */ while( 1 ) { time_t modifiedtime; /* This demo has nothing to do, so just wait for a signal */ pause(); /* Check the flag which indicates the right signal has been received */ if( requiredevent ) {
3 /* Something has been modified in the directory - stat our file */ modifiedtime = statbuf.st_mtime; if( lstat( argv[1], &statbuf ) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot lstat %s : %s\n", argv[1], strerror(errno) ); /* If the modification time has changed, the file has been altered */ if( modifiedtime!= statbuf.st_mtime ) { printf( "File %s has been modified\n", argv[1] ); requiredevent = 0; This program finds the directory the given file is in, then starts monitoring that directory for file modifications. When a notification arrives, the program checks the monitored file with the lstat(2) system call to see if the modification time has been changed. Compile the example code with cc o checkchanged checkchanged.c and try it: > mkdir testdir > touch testdir/datafile >./checkchanged testdir/datafile Now, in another shell do something like echo data >> testdir/datafile. The checkchanged program immediately prints File testdir/datafile has been modified. This example uses the multishot feature of dnotify. Normally, once a notification is issued, dnotify stops monitoring since it is, by default, a single event system. If the DN_MULTISHOT flag is passed to the fcntl(2) F_NOTIFY subcommand, the monitoring stays in place and a signal is sent each and every time a change to the directory is made. FAM The main problem with dnotify is that it is Linux specific. It is also not particularly simple to work with, and if a lot of files need monitoring in lots of different directories, it can get rather complicated. Silicon Graphics Inc. s File Alteration Monitor, or FAM, was designed to simplify file monitoring, and to work on systems without a dnotify type feature. It is now one of SGI s contributions to the free software community. FAM ideally requires the operating system to have SGI s inode monitoring pseudo device driver available. This is called imon and is available for Linux as a kernel patch. There is also a patch available to FAM which allows it to use Linux s dnotify feature instead of imon, and this patch is applied to the FAM package by virtually all Linux distributors. Where neither imon nor dnotify are available, FAM falls back to polling for file changes. Although this might appear to defeat the object somewhat, it does have the advantage that a single process ends up doing all the polling for all monitoring applications. FAM comes in two parts: a daemon and a user level library. The system administrator will configure the daemon to either be started at boot time, or from xinetd as required. It is this daemon process that sits watching for file alterations. Applications, known as FAM clients, link to the user level library which provides routines to connect to the daemon and ask it to monitor a given set of files and/or directories. When a change
4 happens, the daemon sends the relevant information down a socket to the client application. An important difference between dnotify and FAM is that FAM doesn t work in an asynchronous way. The client program is expected to either block waiting for some information to arrive on its socket, or to occasionally poll the socket to see if anything has happened. If asynchronous behaviour is required by a FAM client, that client should fork off a dedicated process which can block on the socket, and which can send a signal to its parent when something happens. Working with FAM is a lot more straightforward than dnotify. The procedure is basically to open a connection to the daemon, use that connection to tell the daemon what you want to monitor, then either do a blocking read on the connection, or occasionally poll it, waiting for the daemon to tell you your file has changed. When you are finished monitoring, tell the daemon to stop, then close the connection. All of these steps are performed using calls to functions in the FAM library. See the documentation for details. Listing 2 shows a simple FAM client, written in C: #include <fam.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <signal.h> void ctrlccatcher( int sig ) { /* No action, just EINTR the system call */ int main( int argc, char *argv[] ) { FAMConnection famconn; FAMRequest famrequest; FAMEvent famevent; struct sigaction action; if( argc!= 2 ) { printf( "Usage: %s filename\n", argv[0] ); action.sa_handler = ctrlccatcher; sigemptyset( &action.sa_mask ); sigaction( SIGINT, &action, NULL ); if( FAMOpen( &famconn ) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot connect to FAM : %s\n", strerror(errno) ); if( FAMMonitorFile( &famconn, argv[1], &famrequest, NULL ) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot monitor file %s : %s\n", argv[1], strerror(errno) ); FAMClose( &famconn ); while( 1 ) { if( FAMNextEvent( &famconn, &famevent ) < 0 ) { if( errno == EINTR ) { printf( "Interrupted\n" ); break; printf( "Error retrieving next FAM event : %s\n", strerror(errno) ); FAMClose( &famconn ); if( famevent.code == FAMChanged ) {
5 printf( "FAM indicates file %s has changed\n", famevent.filename ); if( famevent.code == FAMDeleted ) { printf( "FAM indicates file %s has been deleted\n", famevent.filename ); if( FAMClose( &famconn ) < 0 ) { printf( "Cannot close FAM connection : %s\n", strerror(errno) ); exit( 0 ); This should be complied with a command like cc o famchanged lfam famchanged.c. The file to be monitored should be passed to the program as a command line argument, and must be an absolute pathname, starting with a /. For demonstration purposes this code makes the effort to trap a Ctrl-C and close the connection to the FAM daemon neatly. In normal practise it s safe to just exit the program and have the FAM connection close automatically. FAM can also be used from Perl, using the SGI::FAM module from CPAN. With this module you can write code like Listing 3: #!/usr/bin/perl -w use strict; use SGI::FAM; my $conn = new SGI::FAM; $conn->monitor( "/var/log/messages" ); while (1) { my $event = $conn->next_event; print $event->filename, " ", $event->type, "\n"; There s a Python FAM module too: #!/usr/bin/python import _fam conn = _fam.open() request = conn.monitorfile( "/var/log/messages", None ) while True: event = conn.nextevent() print event.filename, event.code2str() Being a user space tool, FAM can do a lot more than is possible with a kernel based facility like dnotify. For example, if a file to be monitored is in an NFS directory, FAM will attempt to contact the FAM daemon running on the NFS server. The server s FAM daemon will then do the actual monitoring, and when the file changes the information will be relayed via the local daemon to the client. If the server isn t running a FAM daemon then the local daemon will resort to polling the file. See the FAM documentation for details on how to configure this and other more specialised FAM features. FilesChanged If you only have a simple task which requires file monitoring it is often possible to do it from shell script. The fileschanged utility is a FAM client program designed to be used from a script. Although not as flexible as a hand coded FAM client, it is often a quick and simple solution to a problem.
6 fileschanged has recently been updated to version Previous versions contained a bug which prevented the tool working with bash under some circumstances. Ensure you have the latest version before experimenting with it. fileschanged takes the names of the files to monitor on its command line and can report when any of the files are created, deleted, changed or executed. When one of these actions happens, the name of the file is printed to standard output. This is simple, but effective. If you re working on a shared source tree, and you want to keep a log of which source files are being updated by your colleagues, you might take advantage of fileschanged s recursive directories feature, and run something like this: fileschanged r /shared/source/tree while read fd; do stat format= %n modified by %U at %y $fc done fileschanged is often used to monitor log files or incoming mailbox files. It s also possible to use it for more complex tasks such as watching and backing up rarely changed configuration files. Conclusion File monitoring is one of those issues of software development that is often classed as the icing on the cake. A user can always press F5 to refresh a file manager window, or send a SIGHUP to a program when they ve changed its configuration file, so automatically monitoring for changes isn t very often essential. It is, however, something which can make a program more intuitive, or easier to use. The system facilities that provide file monitoring are now widespread and mature, so users will always benefit if developers look for ways to utilise them.
Linux Syslog Messages in IBM Director
 Ever want those pesky little Linux syslog messages (/var/log/messages) to forward to IBM Director? Well, it s not built in, but it s pretty easy to setup. You can forward syslog messages from an IBM Director
Ever want those pesky little Linux syslog messages (/var/log/messages) to forward to IBM Director? Well, it s not built in, but it s pretty easy to setup. You can forward syslog messages from an IBM Director
Channel Access Client Programming. Andrew Johnson Computer Scientist, AES-SSG
 Channel Access Client Programming Andrew Johnson Computer Scientist, AES-SSG Channel Access The main programming interface for writing Channel Access clients is the library that comes with EPICS base Written
Channel Access Client Programming Andrew Johnson Computer Scientist, AES-SSG Channel Access The main programming interface for writing Channel Access clients is the library that comes with EPICS base Written
System Calls Related to File Manipulation
 KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS Information and Computer Science Department ICS 431 Operating Systems Lab # 12 System Calls Related to File Manipulation Objective: In this lab we will be
KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS Information and Computer Science Department ICS 431 Operating Systems Lab # 12 System Calls Related to File Manipulation Objective: In this lab we will be
Example of Standard API
 16 Example of Standard API System Call Implementation Typically, a number associated with each system call System call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface
16 Example of Standard API System Call Implementation Typically, a number associated with each system call System call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface
CS 103 Lab Linux and Virtual Machines
 1 Introduction In this lab you will login to your Linux VM and write your first C/C++ program, compile it, and then execute it. 2 What you will learn In this lab you will learn the basic commands and navigation
1 Introduction In this lab you will login to your Linux VM and write your first C/C++ program, compile it, and then execute it. 2 What you will learn In this lab you will learn the basic commands and navigation
Incremental Backup Script. Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems
 Incremental Backup Script Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems Last Updated Mar 18, 2008 2 Contents 1 Incremental Backup Script 5 1.1 Introduction.............................. 5 1.2 Design Issues.............................
Incremental Backup Script Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems Last Updated Mar 18, 2008 2 Contents 1 Incremental Backup Script 5 1.1 Introduction.............................. 5 1.2 Design Issues.............................
Setting up PostgreSQL
 Setting up PostgreSQL 1 Introduction to PostgreSQL PostgreSQL is an object-relational database management system based on POSTGRES, which was developed at the University of California at Berkeley. PostgreSQL
Setting up PostgreSQL 1 Introduction to PostgreSQL PostgreSQL is an object-relational database management system based on POSTGRES, which was developed at the University of California at Berkeley. PostgreSQL
Greenstone Documentation
 Greenstone Documentation Web library and Remote Collection Building with GLI Client Web Library. This enables any computer with an existing webserver to serve pre-built Greenstone collections. As with
Greenstone Documentation Web library and Remote Collection Building with GLI Client Web Library. This enables any computer with an existing webserver to serve pre-built Greenstone collections. As with
µtasker Document FTP Client
 Embedding it better... µtasker Document FTP Client utaskerftp_client.doc/1.01 Copyright 2012 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. FTP Log-In...4 3. FTP Operation Modes...4 4.
Embedding it better... µtasker Document FTP Client utaskerftp_client.doc/1.01 Copyright 2012 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. FTP Log-In...4 3. FTP Operation Modes...4 4.
Have both hardware and software. Want to hide the details from the programmer (user).
 Input/Output Devices Chapter 5 of Tanenbaum. Have both hardware and software. Want to hide the details from the programmer (user). Ideally have the same interface to all devices (device independence).
Input/Output Devices Chapter 5 of Tanenbaum. Have both hardware and software. Want to hide the details from the programmer (user). Ideally have the same interface to all devices (device independence).
Operating System Structures
 COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2015) Operating System Structures Zhi Wang Florida State University Content Operating system services User interface System calls System programs Operating
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2015) Operating System Structures Zhi Wang Florida State University Content Operating system services User interface System calls System programs Operating
GDB Tutorial. A Walkthrough with Examples. CMSC 212 - Spring 2009. Last modified March 22, 2009. GDB Tutorial
 A Walkthrough with Examples CMSC 212 - Spring 2009 Last modified March 22, 2009 What is gdb? GNU Debugger A debugger for several languages, including C and C++ It allows you to inspect what the program
A Walkthrough with Examples CMSC 212 - Spring 2009 Last modified March 22, 2009 What is gdb? GNU Debugger A debugger for several languages, including C and C++ It allows you to inspect what the program
Operating System Structure
 Operating System Structure Lecture 3 Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission Recap Computer architecture CPU, memory, disk, I/O devices Memory hierarchy Architectural
Operating System Structure Lecture 3 Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission Recap Computer architecture CPU, memory, disk, I/O devices Memory hierarchy Architectural
Setting Up a CLucene and PostgreSQL Federation
 Federated Desktop and File Server Search with libferris Ben Martin Abstract How to federate CLucene personal document indexes with PostgreSQL/TSearch2. The libferris project has two major goals: mounting
Federated Desktop and File Server Search with libferris Ben Martin Abstract How to federate CLucene personal document indexes with PostgreSQL/TSearch2. The libferris project has two major goals: mounting
White Paper. Real-time Capabilities for Linux SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux
 White Paper Real-time Capabilities for Linux SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux Abstract This white paper describes the real-time capabilities provided by SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux. software. REACT enables
White Paper Real-time Capabilities for Linux SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux Abstract This white paper describes the real-time capabilities provided by SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux. software. REACT enables
Version control. HEAD is the name of the latest revision in the repository. It can be used in subversion rather than the latest revision number.
 Version control Version control is a powerful tool for many kinds of work done over a period of time, including writing papers and theses as well as writing code. This session gives a introduction to a
Version control Version control is a powerful tool for many kinds of work done over a period of time, including writing papers and theses as well as writing code. This session gives a introduction to a
Lecture 24 Systems Programming in C
 Lecture 24 Systems Programming in C A process is a currently executing instance of a program. All programs by default execute in the user mode. A C program can invoke UNIX system calls directly. A system
Lecture 24 Systems Programming in C A process is a currently executing instance of a program. All programs by default execute in the user mode. A C program can invoke UNIX system calls directly. A system
Jorix kernel: real-time scheduling
 Jorix kernel: real-time scheduling Joris Huizer Kwie Min Wong May 16, 2007 1 Introduction As a specialized part of the kernel, we implemented two real-time scheduling algorithms: RM (rate monotonic) and
Jorix kernel: real-time scheduling Joris Huizer Kwie Min Wong May 16, 2007 1 Introduction As a specialized part of the kernel, we implemented two real-time scheduling algorithms: RM (rate monotonic) and
Leak Check Version 2.1 for Linux TM
 Leak Check Version 2.1 for Linux TM User s Guide Including Leak Analyzer For x86 Servers Document Number DLC20-L-021-1 Copyright 2003-2009 Dynamic Memory Solutions LLC www.dynamic-memory.com Notices Information
Leak Check Version 2.1 for Linux TM User s Guide Including Leak Analyzer For x86 Servers Document Number DLC20-L-021-1 Copyright 2003-2009 Dynamic Memory Solutions LLC www.dynamic-memory.com Notices Information
Linux/UNIX System Programming. POSIX Shared Memory. Michael Kerrisk, man7.org c 2015. February 2015
 Linux/UNIX System Programming POSIX Shared Memory Michael Kerrisk, man7.org c 2015 February 2015 Outline 22 POSIX Shared Memory 22-1 22.1 Overview 22-3 22.2 Creating and opening shared memory objects 22-10
Linux/UNIX System Programming POSIX Shared Memory Michael Kerrisk, man7.org c 2015 February 2015 Outline 22 POSIX Shared Memory 22-1 22.1 Overview 22-3 22.2 Creating and opening shared memory objects 22-10
1 Posix API vs Windows API
 1 Posix API vs Windows API 1.1 File I/O Using the Posix API, to open a file, you use open(filename, flags, more optional flags). If the O CREAT flag is passed, the file will be created if it doesnt exist.
1 Posix API vs Windows API 1.1 File I/O Using the Posix API, to open a file, you use open(filename, flags, more optional flags). If the O CREAT flag is passed, the file will be created if it doesnt exist.
Unix System Calls. Dept. CSIE 2006.12.25
 Unix System Calls Gwan-Hwan Hwang Dept. CSIE National Taiwan Normal University 2006.12.25 UNIX System Overview UNIX Architecture Login Name Shells Files and Directories File System Filename Pathname Working
Unix System Calls Gwan-Hwan Hwang Dept. CSIE National Taiwan Normal University 2006.12.25 UNIX System Overview UNIX Architecture Login Name Shells Files and Directories File System Filename Pathname Working
Q N X S O F T W A R E D E V E L O P M E N T P L A T F O R M v 6. 4. 10 Steps to Developing a QNX Program Quickstart Guide
 Q N X S O F T W A R E D E V E L O P M E N T P L A T F O R M v 6. 4 10 Steps to Developing a QNX Program Quickstart Guide 2008, QNX Software Systems GmbH & Co. KG. A Harman International Company. All rights
Q N X S O F T W A R E D E V E L O P M E N T P L A T F O R M v 6. 4 10 Steps to Developing a QNX Program Quickstart Guide 2008, QNX Software Systems GmbH & Co. KG. A Harman International Company. All rights
Virtuozzo Virtualization SDK
 Virtuozzo Virtualization SDK Programmer's Guide February 18, 2016 Copyright 1999-2016 Parallels IP Holdings GmbH and its affiliates. All rights reserved. Parallels IP Holdings GmbH Vordergasse 59 8200
Virtuozzo Virtualization SDK Programmer's Guide February 18, 2016 Copyright 1999-2016 Parallels IP Holdings GmbH and its affiliates. All rights reserved. Parallels IP Holdings GmbH Vordergasse 59 8200
System Security Fundamentals
 System Security Fundamentals Alessandro Barenghi Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Politecnico di Milano alessandro.barenghi - at - polimi.it April 28, 2015 Lesson contents Overview
System Security Fundamentals Alessandro Barenghi Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Politecnico di Milano alessandro.barenghi - at - polimi.it April 28, 2015 Lesson contents Overview
System Calls and Standard I/O
 System Calls and Standard I/O Professor Jennifer Rexford http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~jrex 1 Goals of Today s Class System calls o How a user process contacts the Operating System o For advanced services
System Calls and Standard I/O Professor Jennifer Rexford http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~jrex 1 Goals of Today s Class System calls o How a user process contacts the Operating System o For advanced services
Xcode Project Management Guide. (Legacy)
 Xcode Project Management Guide (Legacy) Contents Introduction 10 Organization of This Document 10 See Also 11 Part I: Project Organization 12 Overview of an Xcode Project 13 Components of an Xcode Project
Xcode Project Management Guide (Legacy) Contents Introduction 10 Organization of This Document 10 See Also 11 Part I: Project Organization 12 Overview of an Xcode Project 13 Components of an Xcode Project
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 2: Operating System Structures Prof. Alan Mislove ([email protected]) Operating System Services Operating systems provide an environment for
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 2: Operating System Structures Prof. Alan Mislove ([email protected]) Operating System Services Operating systems provide an environment for
To connect to the cluster, simply use a SSH or SFTP client to connect to:
 RIT Computer Engineering Cluster The RIT Computer Engineering cluster contains 12 computers for parallel programming using MPI. One computer, cluster-head.ce.rit.edu, serves as the master controller or
RIT Computer Engineering Cluster The RIT Computer Engineering cluster contains 12 computers for parallel programming using MPI. One computer, cluster-head.ce.rit.edu, serves as the master controller or
TFTP Usage and Design. Diskless Workstation Booting 1. TFTP Usage and Design (cont.) CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming ------ TFTP + Errors
 CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming ------ TFTP + Errors Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina TFTP Usage and Design RFC 783, 1350 Transfer files between
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming ------ TFTP + Errors Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina TFTP Usage and Design RFC 783, 1350 Transfer files between
WhatsUp Gold v11 Features Overview
 WhatsUp Gold v11 Features Overview This guide provides an overview of the core functionality of WhatsUp Gold v11, and introduces interesting features and processes that help users maximize productivity
WhatsUp Gold v11 Features Overview This guide provides an overview of the core functionality of WhatsUp Gold v11, and introduces interesting features and processes that help users maximize productivity
Thirty Useful Unix Commands
 Leaflet U5 Thirty Useful Unix Commands Last revised April 1997 This leaflet contains basic information on thirty of the most frequently used Unix Commands. It is intended for Unix beginners who need a
Leaflet U5 Thirty Useful Unix Commands Last revised April 1997 This leaflet contains basic information on thirty of the most frequently used Unix Commands. It is intended for Unix beginners who need a
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus (FSAV) Table of Contents. FSAV 8.x and FSLS 7.x End of Life. FSAV 9.x and FSLS 9.x End of Life
 Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus (FSAV) Last update: 15 Jul 2015 Please see also the LISTSERV/F-Secure FAQ for further information. Table of Contents FSAV 4.x, 5.x and 7.x End of Life FSAV 8.x and FSLS 7.x
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus (FSAV) Last update: 15 Jul 2015 Please see also the LISTSERV/F-Secure FAQ for further information. Table of Contents FSAV 4.x, 5.x and 7.x End of Life FSAV 8.x and FSLS 7.x
Green Telnet. Making the Client/Server Model Green
 Green Telnet Reducing energy consumption is of growing importance. Jeremy and Ken create a "green telnet" that lets clients transition to a low-power, sleep state. By Jeremy Blackburn and Ken Christensen,
Green Telnet Reducing energy consumption is of growing importance. Jeremy and Ken create a "green telnet" that lets clients transition to a low-power, sleep state. By Jeremy Blackburn and Ken Christensen,
Instrumentation for Linux Event Log Analysis
 Instrumentation for Linux Event Log Analysis Rajarshi Das Linux Technology Center IBM India Software Lab [email protected] Hien Q Nguyen Linux Technology Center IBM Beaverton [email protected] Abstract
Instrumentation for Linux Event Log Analysis Rajarshi Das Linux Technology Center IBM India Software Lab [email protected] Hien Q Nguyen Linux Technology Center IBM Beaverton [email protected] Abstract
Data Migration from Magento 1 to Magento 2 Including ParadoxLabs Authorize.Net CIM Plugin Last Updated Jan 4, 2016
 Data Migration from Magento 1 to Magento 2 Including ParadoxLabs Authorize.Net CIM Plugin Last Updated Jan 4, 2016 This guide was contributed by a community developer for your benefit. Background Magento
Data Migration from Magento 1 to Magento 2 Including ParadoxLabs Authorize.Net CIM Plugin Last Updated Jan 4, 2016 This guide was contributed by a community developer for your benefit. Background Magento
CS355 Hw 3. Extended Shell with Job Control
 CS355 Hw 3 Due by the end of day Tuesday, Mar 18. Design document due on Thursday, Feb 27 in class. Written supplementary problems due on Thursday, March 6. Programming Assignment: You should team up with
CS355 Hw 3 Due by the end of day Tuesday, Mar 18. Design document due on Thursday, Feb 27 in class. Written supplementary problems due on Thursday, March 6. Programming Assignment: You should team up with
Command-Line Operations : The Shell. Don't fear the command line...
 Command-Line Operations : The Shell Don't fear the command line... Shell Graphical User Interface (GUI) Graphical User Interface : displays to interact with the computer - Open and manipulate files and
Command-Line Operations : The Shell Don't fear the command line... Shell Graphical User Interface (GUI) Graphical User Interface : displays to interact with the computer - Open and manipulate files and
PuTTY/Cygwin Tutorial. By Ben Meister Written for CS 23, Winter 2007
 PuTTY/Cygwin Tutorial By Ben Meister Written for CS 23, Winter 2007 This tutorial will show you how to set up and use PuTTY to connect to CS Department computers using SSH, and how to install and use the
PuTTY/Cygwin Tutorial By Ben Meister Written for CS 23, Winter 2007 This tutorial will show you how to set up and use PuTTY to connect to CS Department computers using SSH, and how to install and use the
Linux Kernel Architecture
 Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah [email protected] Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah [email protected] Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
PetaLinux SDK User Guide. Application Development Guide
 PetaLinux SDK User Guide Application Development Guide Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the "Materials") is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products.
PetaLinux SDK User Guide Application Development Guide Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the "Materials") is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products.
6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2003. Quiz II Solutions THIS IS AN OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES QUIZ.
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2003 Quiz II Solutions All problems are open-ended questions. In
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2003 Quiz II Solutions All problems are open-ended questions. In
CSC230 Getting Starting in C. Tyler Bletsch
 CSC230 Getting Starting in C Tyler Bletsch What is C? The language of UNIX Procedural language (no classes) Low-level access to memory Easy to map to machine language Not much run-time stuff needed Surprisingly
CSC230 Getting Starting in C Tyler Bletsch What is C? The language of UNIX Procedural language (no classes) Low-level access to memory Easy to map to machine language Not much run-time stuff needed Surprisingly
Command Line Interface Specification Linux Mac
 Command Line Interface Specification Linux Mac Online Backup Client version 4.1.x and higher 1. Introduction These modifications make it possible to access the BackupAgent Client software from the command
Command Line Interface Specification Linux Mac Online Backup Client version 4.1.x and higher 1. Introduction These modifications make it possible to access the BackupAgent Client software from the command
Installing Magento Extensions
 to Installing Magento Extensions by Welcome This best practice guide contains universal instructions for a smooth, trouble free installation of any Magento extension - whether by Fooman or another developer,
to Installing Magento Extensions by Welcome This best practice guide contains universal instructions for a smooth, trouble free installation of any Magento extension - whether by Fooman or another developer,
Introduction. What is an Operating System?
 Introduction What is an Operating System? 1 What is an Operating System? 2 Why is an Operating System Needed? 3 How Did They Develop? Historical Approach Affect of Architecture 4 Efficient Utilization
Introduction What is an Operating System? 1 What is an Operating System? 2 Why is an Operating System Needed? 3 How Did They Develop? Historical Approach Affect of Architecture 4 Efficient Utilization
HARFORD COMMUNITY COLLEGE 401 Thomas Run Road Bel Air, MD 21015 Course Outline CIS 110 - INTRODUCTION TO UNIX
 HARFORD COMMUNITY COLLEGE 401 Thomas Run Road Bel Air, MD 21015 Course Outline CIS 110 - INTRODUCTION TO UNIX Course Description: This is an introductory course designed for users of UNIX. It is taught
HARFORD COMMUNITY COLLEGE 401 Thomas Run Road Bel Air, MD 21015 Course Outline CIS 110 - INTRODUCTION TO UNIX Course Description: This is an introductory course designed for users of UNIX. It is taught
IBM Redistribute Big SQL v4.x Storage Paths IBM. Redistribute Big SQL v4.x Storage Paths
 Redistribute Big SQL v4.x Storage Paths THE GOAL The Big SQL temporary tablespace is used during high volume queries to spill sorts or intermediate data to disk. To improve I/O performance for these queries,
Redistribute Big SQL v4.x Storage Paths THE GOAL The Big SQL temporary tablespace is used during high volume queries to spill sorts or intermediate data to disk. To improve I/O performance for these queries,
FileBench's Multi-Client feature
 FileBench's Multi-Client feature Filebench now includes facilities to synchronize workload execution on a set of clients, allowing higher offered loads to the server. While primarily intended for network
FileBench's Multi-Client feature Filebench now includes facilities to synchronize workload execution on a set of clients, allowing higher offered loads to the server. While primarily intended for network
Programmation Systèmes Cours 7 IPC: FIFO
 Programmation Systèmes Cours 7 IPC: FIFO Stefano Zacchiroli [email protected] Laboratoire PPS, Université Paris Diderot - Paris 7 15 novembre 2011 URL http://upsilon.cc/zack/teaching/1112/progsyst/ Copyright
Programmation Systèmes Cours 7 IPC: FIFO Stefano Zacchiroli [email protected] Laboratoire PPS, Université Paris Diderot - Paris 7 15 novembre 2011 URL http://upsilon.cc/zack/teaching/1112/progsyst/ Copyright
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY. 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2005
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2005 Quiz II Solutions Average 84, median 83, standard deviation
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2005 Quiz II Solutions Average 84, median 83, standard deviation
LSN 10 Linux Overview
 LSN 10 Linux Overview ECT362 Operating Systems Department of Engineering Technology LSN 10 Linux Overview Linux Contemporary open source implementation of UNIX available for free on the Internet Introduced
LSN 10 Linux Overview ECT362 Operating Systems Department of Engineering Technology LSN 10 Linux Overview Linux Contemporary open source implementation of UNIX available for free on the Internet Introduced
How to Add a New System Call for Minix 3
 How to Add a New System Call for Minix 3 Karthick Jayaraman Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Syracuse University, Syracuse, New York 1. Introduction Minix3 has the micro-kernel architecture.
How to Add a New System Call for Minix 3 Karthick Jayaraman Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Syracuse University, Syracuse, New York 1. Introduction Minix3 has the micro-kernel architecture.
Title: Documentation for the Pi-UPS-Monitor-App
 Title: Documentation for the Pi-UPS-Monitor-App Version: 0.01 Date: 09.01.14 Table of Content 1. PURPOSE, OR WHAT PIUSVMONITOR DOES...3 2. PACKAGE CONTENTS...4 3. INSTALLATION...5 4. USAGE...6 5. CONSOLE
Title: Documentation for the Pi-UPS-Monitor-App Version: 0.01 Date: 09.01.14 Table of Content 1. PURPOSE, OR WHAT PIUSVMONITOR DOES...3 2. PACKAGE CONTENTS...4 3. INSTALLATION...5 4. USAGE...6 5. CONSOLE
Statel Robot Service Help. 2004... Eurostat
 Statel Robot Service Help 2 SRS help 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview The objective of the STATEL Robot Service is to provide an automatic tool to automate file transfer in a process pipeline using STATEL.
Statel Robot Service Help 2 SRS help 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview The objective of the STATEL Robot Service is to provide an automatic tool to automate file transfer in a process pipeline using STATEL.
Using NSM for Event Notification. Abstract. with DM3, R4, and Win32 Devices
 Using NSM for Event Notification with DM3, R4, and Win32 Devices Abstract This document explains why Native Synchronization Methods (NSM) is the best solution for controlling synchronization of DM3, R4,
Using NSM for Event Notification with DM3, R4, and Win32 Devices Abstract This document explains why Native Synchronization Methods (NSM) is the best solution for controlling synchronization of DM3, R4,
How to Write a Simple Makefile
 Chapter 1 CHAPTER 1 How to Write a Simple Makefile The mechanics of programming usually follow a fairly simple routine of editing source files, compiling the source into an executable form, and debugging
Chapter 1 CHAPTER 1 How to Write a Simple Makefile The mechanics of programming usually follow a fairly simple routine of editing source files, compiling the source into an executable form, and debugging
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Computer Science Division. P. N. Hilfinger
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Computer Science Division CS 61B Fall 2012 P. N. Hilfinger Version Control and Homework Submission 1 Introduction Your
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Computer Science Division CS 61B Fall 2012 P. N. Hilfinger Version Control and Homework Submission 1 Introduction Your
Automatic Generation of Time-lapse Animations
 Automatic Generation of Time-lapse Animations Stephen B. Jenkins Institute for Aerospace Research National Research Council Ottawa, Canada Presented at YAPC::Canada Ottawa, Ontario May 2003 Abstract A
Automatic Generation of Time-lapse Animations Stephen B. Jenkins Institute for Aerospace Research National Research Council Ottawa, Canada Presented at YAPC::Canada Ottawa, Ontario May 2003 Abstract A
CLC Server Command Line Tools USER MANUAL
 CLC Server Command Line Tools USER MANUAL Manual for CLC Server Command Line Tools 2.5 Windows, Mac OS X and Linux September 4, 2015 This software is for research purposes only. QIAGEN Aarhus A/S Silkeborgvej
CLC Server Command Line Tools USER MANUAL Manual for CLC Server Command Line Tools 2.5 Windows, Mac OS X and Linux September 4, 2015 This software is for research purposes only. QIAGEN Aarhus A/S Silkeborgvej
Source Code Management for Continuous Integration and Deployment. Version 1.0 DO NOT DISTRIBUTE
 Source Code Management for Continuous Integration and Deployment Version 1.0 Copyright 2013, 2014 Amazon Web Services, Inc. and its affiliates. All rights reserved. This work may not be reproduced or redistributed,
Source Code Management for Continuous Integration and Deployment Version 1.0 Copyright 2013, 2014 Amazon Web Services, Inc. and its affiliates. All rights reserved. This work may not be reproduced or redistributed,
NBU651 BMR. Avi Weinberger
 NBU651 BMR Avi Weinberger Bare Metal Restore Overview BMR automates system recovery by restoring the operating system, the system configuration, and all system and data files with two steps: Run one command
NBU651 BMR Avi Weinberger Bare Metal Restore Overview BMR automates system recovery by restoring the operating system, the system configuration, and all system and data files with two steps: Run one command
OLCF Best Practices. Bill Renaud OLCF User Assistance Group
 OLCF Best Practices Bill Renaud OLCF User Assistance Group Overview This presentation covers some helpful information for users of OLCF Staying informed Some aspects of system usage that may differ from
OLCF Best Practices Bill Renaud OLCF User Assistance Group Overview This presentation covers some helpful information for users of OLCF Staying informed Some aspects of system usage that may differ from
Tail call elimination. Michel Schinz
 Tail call elimination Michel Schinz Tail calls and their elimination Loops in functional languages Several functional programming languages do not have an explicit looping statement. Instead, programmers
Tail call elimination Michel Schinz Tail calls and their elimination Loops in functional languages Several functional programming languages do not have an explicit looping statement. Instead, programmers
Frysk The Systems Monitoring and Debugging Tool. Andrew Cagney
 Frysk The Systems Monitoring and Debugging Tool Andrew Cagney Agenda Two Use Cases Motivation Comparison with Existing Free Technologies The Frysk Architecture and GUI Command Line Utilities Current Status
Frysk The Systems Monitoring and Debugging Tool Andrew Cagney Agenda Two Use Cases Motivation Comparison with Existing Free Technologies The Frysk Architecture and GUI Command Line Utilities Current Status
CS197U: A Hands on Introduction to Unix
 CS197U: A Hands on Introduction to Unix Lecture 4: My First Linux System J.D. DeVaughn-Brown University of Massachusetts Amherst Department of Computer Science [email protected] 1 Reminders After
CS197U: A Hands on Introduction to Unix Lecture 4: My First Linux System J.D. DeVaughn-Brown University of Massachusetts Amherst Department of Computer Science [email protected] 1 Reminders After
Source Code Management/Version Control
 Date: 3 rd March 2005 Source Code Management/Version Control The Problem: In a typical software development environment, many developers will be engaged in work on one code base. If everyone was to be
Date: 3 rd March 2005 Source Code Management/Version Control The Problem: In a typical software development environment, many developers will be engaged in work on one code base. If everyone was to be
Type-C Hypervisors. @DustinKirkland Ubuntu Product & Strategy Canonical Ltd.
 Type-C Hypervisors @DustinKirkland Ubuntu Product & Strategy Canonical Ltd. Canonical is the company behind Ubuntu 2004 600+ FOUNDATION EMPLOYEES 30+ COUNTRIES London Beijing Boston Shanghai Taipei What
Type-C Hypervisors @DustinKirkland Ubuntu Product & Strategy Canonical Ltd. Canonical is the company behind Ubuntu 2004 600+ FOUNDATION EMPLOYEES 30+ COUNTRIES London Beijing Boston Shanghai Taipei What
Title: SharePoint Advanced Training
 416 Agriculture Hall Michigan State University 517-355- 3776 http://support.anr.msu.edu [email protected] Title: SharePoint Advanced Training Document No. - 106 Revision Date - 10/2013 Revision No. -
416 Agriculture Hall Michigan State University 517-355- 3776 http://support.anr.msu.edu [email protected] Title: SharePoint Advanced Training Document No. - 106 Revision Date - 10/2013 Revision No. -
Parallelization: Binary Tree Traversal
 By Aaron Weeden and Patrick Royal Shodor Education Foundation, Inc. August 2012 Introduction: According to Moore s law, the number of transistors on a computer chip doubles roughly every two years. First
By Aaron Weeden and Patrick Royal Shodor Education Foundation, Inc. August 2012 Introduction: According to Moore s law, the number of transistors on a computer chip doubles roughly every two years. First
Computer Systems II. Unix system calls. fork( ) wait( ) exit( ) How To Create New Processes? Creating and Executing Processes
 Computer Systems II Creating and Executing Processes 1 Unix system calls fork( ) wait( ) exit( ) 2 How To Create New Processes? Underlying mechanism - A process runs fork to create a child process - Parent
Computer Systems II Creating and Executing Processes 1 Unix system calls fork( ) wait( ) exit( ) 2 How To Create New Processes? Underlying mechanism - A process runs fork to create a child process - Parent
Performance analysis of a Linux based FTP server
 Performance analysis of a Linux based FTP server A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Technology by Anand Srivastava to the Department of Computer Science
Performance analysis of a Linux based FTP server A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Technology by Anand Srivastava to the Department of Computer Science
QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions. Linux Database Server Manager Installation and Configuration Guide
 QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions Linux Database Server Manager Installation and Configuration Guide Copyright Copyright 2007 Intuit Inc. All rights reserved. STATEMENTS IN THIS DOCUMENT REGARDING THIRD-PARTY
QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions Linux Database Server Manager Installation and Configuration Guide Copyright Copyright 2007 Intuit Inc. All rights reserved. STATEMENTS IN THIS DOCUMENT REGARDING THIRD-PARTY
CS420: Operating Systems OS Services & System Calls
 NK YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVANIA HG OK 2 YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVAN OS Services & System Calls James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts,
NK YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVANIA HG OK 2 YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVAN OS Services & System Calls James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts,
An Example VHDL Application for the TM-4
 An Example VHDL Application for the TM-4 Dave Galloway Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto March 2005 Introduction This document describes a simple
An Example VHDL Application for the TM-4 Dave Galloway Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto March 2005 Introduction This document describes a simple
Writing Scripts with PHP s PEAR DB Module
 Writing Scripts with PHP s PEAR DB Module Paul DuBois [email protected] Document revision: 1.02 Last update: 2005-12-30 As a web programming language, one of PHP s strengths traditionally has been to make
Writing Scripts with PHP s PEAR DB Module Paul DuBois [email protected] Document revision: 1.02 Last update: 2005-12-30 As a web programming language, one of PHP s strengths traditionally has been to make
Hadoop Basics with InfoSphere BigInsights
 An IBM Proof of Technology Hadoop Basics with InfoSphere BigInsights Part: 1 Exploring Hadoop Distributed File System An IBM Proof of Technology Catalog Number Copyright IBM Corporation, 2013 US Government
An IBM Proof of Technology Hadoop Basics with InfoSphere BigInsights Part: 1 Exploring Hadoop Distributed File System An IBM Proof of Technology Catalog Number Copyright IBM Corporation, 2013 US Government
Improved metrics collection and correlation for the CERN cloud storage test framework
 Improved metrics collection and correlation for the CERN cloud storage test framework September 2013 Author: Carolina Lindqvist Supervisors: Maitane Zotes Seppo Heikkila CERN openlab Summer Student Report
Improved metrics collection and correlation for the CERN cloud storage test framework September 2013 Author: Carolina Lindqvist Supervisors: Maitane Zotes Seppo Heikkila CERN openlab Summer Student Report
Device Management API for Windows* and Linux* Operating Systems
 Device Management API for Windows* and Linux* Operating Systems Library Reference September 2004 05-2222-002 INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS
Device Management API for Windows* and Linux* Operating Systems Library Reference September 2004 05-2222-002 INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS
Writing a C-based Client/Server
 Working the Socket Writing a C-based Client/Server Consider for a moment having the massive power of different computers all simultaneously trying to compute a problem for you -- and still being legal!
Working the Socket Writing a C-based Client/Server Consider for a moment having the massive power of different computers all simultaneously trying to compute a problem for you -- and still being legal!
COSC 6397 Big Data Analytics. Distributed File Systems (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014. HDFS Basics
 COSC 6397 Big Data Analytics Distributed File Systems (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 HDFS Basics An open-source implementation of Google File System Assume that node failure rate is high Assumes a small
COSC 6397 Big Data Analytics Distributed File Systems (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 HDFS Basics An open-source implementation of Google File System Assume that node failure rate is high Assumes a small
CASHNet Secure File Transfer Instructions
 CASHNet Secure File Transfer Instructions Copyright 2009, 2010 Higher One Payments, Inc. CASHNet, CASHNet Business Office, CASHNet Commerce Center, CASHNet SMARTPAY and all related logos and designs are
CASHNet Secure File Transfer Instructions Copyright 2009, 2010 Higher One Payments, Inc. CASHNet, CASHNet Business Office, CASHNet Commerce Center, CASHNet SMARTPAY and all related logos and designs are
Outlook Web App (OWA) To create a new message:
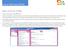 What you ll see in Mail 1. Create a new message by clicking New mail. 2. Folder list. The folder list includes the folders in your mailbox. It may include other folders, such as Favorites and archive folders.
What you ll see in Mail 1. Create a new message by clicking New mail. 2. Folder list. The folder list includes the folders in your mailbox. It may include other folders, such as Favorites and archive folders.
Sophos Anti-Virus for Linux configuration guide. Product version: 9
 Sophos Anti-Virus for Linux configuration guide Product version: 9 Document date: September 2015 Contents 1 About this guide...5 2 About Sophos Anti-Virus for Linux...6 2.1 What Sophos Anti-Virus does...6
Sophos Anti-Virus for Linux configuration guide Product version: 9 Document date: September 2015 Contents 1 About this guide...5 2 About Sophos Anti-Virus for Linux...6 2.1 What Sophos Anti-Virus does...6
Code Estimation Tools Directions for a Services Engagement
 Code Estimation Tools Directions for a Services Engagement Summary Black Duck software provides two tools to calculate size, number, and category of files in a code base. This information is necessary
Code Estimation Tools Directions for a Services Engagement Summary Black Duck software provides two tools to calculate size, number, and category of files in a code base. This information is necessary
SysPatrol - Server Security Monitor
 SysPatrol Server Security Monitor User Manual Version 2.2 Sep 2013 www.flexense.com www.syspatrol.com 1 Product Overview SysPatrol is a server security monitoring solution allowing one to monitor one or
SysPatrol Server Security Monitor User Manual Version 2.2 Sep 2013 www.flexense.com www.syspatrol.com 1 Product Overview SysPatrol is a server security monitoring solution allowing one to monitor one or
Linux command line. An introduction to the Linux command line for genomics. Susan Fairley
 Linux command line An introduction to the Linux command line for genomics Susan Fairley Aims Introduce the command line Provide an awareness of basic functionality Illustrate with some examples Provide
Linux command line An introduction to the Linux command line for genomics Susan Fairley Aims Introduce the command line Provide an awareness of basic functionality Illustrate with some examples Provide
Extreme computing lab exercises Session one
 Extreme computing lab exercises Session one Michail Basios ([email protected]) Stratis Viglas ([email protected]) 1 Getting started First you need to access the machine where you will be doing all
Extreme computing lab exercises Session one Michail Basios ([email protected]) Stratis Viglas ([email protected]) 1 Getting started First you need to access the machine where you will be doing all
Module 816. File Management in C. M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University
 M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University Aim Learning objectives Content After working through this module you should be able to create C programs that create an use both text and binary files. After working
M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University Aim Learning objectives Content After working through this module you should be able to create C programs that create an use both text and binary files. After working
Linux Driver Devices. Why, When, Which, How?
 Bertrand Mermet Sylvain Ract Linux Driver Devices. Why, When, Which, How? Since its creation in the early 1990 s Linux has been installed on millions of computers or embedded systems. These systems may
Bertrand Mermet Sylvain Ract Linux Driver Devices. Why, When, Which, How? Since its creation in the early 1990 s Linux has been installed on millions of computers or embedded systems. These systems may
Linux System Administration on Red Hat
 Linux System Administration on Red Hat Kenneth Ingham September 29, 2009 1 Course overview This class is for people who are familiar with Linux or Unix systems as a user (i.e., they know file manipulation,
Linux System Administration on Red Hat Kenneth Ingham September 29, 2009 1 Course overview This class is for people who are familiar with Linux or Unix systems as a user (i.e., they know file manipulation,
System Administration
 Performance Monitoring For a server, it is crucial to monitor the health of the machine You need not only real time data collection and presentation but offline statistical analysis as well Characteristics
Performance Monitoring For a server, it is crucial to monitor the health of the machine You need not only real time data collection and presentation but offline statistical analysis as well Characteristics
OFBiz Addons goals, howto use, howto manage. Nicolas Malin, Nov. 2012
 OFBiz Addons goals, howto use, howto manage Nicolas Malin, Nov. 2012 Agenda History of a birth Addons principle Addons and their environment (extensive program) Conclusion Once upon a time The history
OFBiz Addons goals, howto use, howto manage Nicolas Malin, Nov. 2012 Agenda History of a birth Addons principle Addons and their environment (extensive program) Conclusion Once upon a time The history
Yocto Project Eclipse plug-in and Developer Tools Hands-on Lab
 Yocto Project Eclipse plug-in and Developer Tools Hands-on Lab Yocto Project Developer Day San Francisco, 2013 Jessica Zhang Introduction Welcome to the Yocto Project Eclipse plug-in
Yocto Project Eclipse plug-in and Developer Tools Hands-on Lab Yocto Project Developer Day San Francisco, 2013 Jessica Zhang Introduction Welcome to the Yocto Project Eclipse plug-in
Networks. Inter-process Communication. Pipes. Inter-process Communication
 Networks Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Inter-process Communication process CS 217 process Network 1 2 Inter-process Communication Sockets o Processes can
Networks Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Inter-process Communication process CS 217 process Network 1 2 Inter-process Communication Sockets o Processes can
OS: IPC I. Cooperating Processes. CIT 595 Spring 2010. Message Passing vs. Shared Memory. Message Passing: Unix Pipes
 Cooperating Processes Independent processes cannot affect or be affected by the execution of another process OS: IPC I CIT 595 Spring 2010 Cooperating process can affect or be affected by the execution
Cooperating Processes Independent processes cannot affect or be affected by the execution of another process OS: IPC I CIT 595 Spring 2010 Cooperating process can affect or be affected by the execution
