Availability Guide for Deploying SQL Server on VMware vsphere. August 2009
|
|
|
- Jesse Hopkins
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Availability Guide for Deploying SQL Server on VMware vsphere August 2009
2 Contents Introduction...1 SQL Server 2008 with vsphere and VMware HA/DRS...2 Log Shipping Availability Option...4 Database Mirroring Failover Clustering Summary References Contents ii
3 Introduction When designing a SQL Server deployment, in addition to your SQL Server design, your operational readiness procedures should include availability and recoverability. There are several options available to Windows and SQL Server administrators that can ensure SQL Server availability. SQL Server availability is also an important consideration in meeting new or existing business service level agreements when designing virtual solutions for applications deployment. (The importance of performing regular backups in your SQL Server environment can also not be stressed enough, as a properly executed backup plan can significantly enhance your availability strategy.) In this document, we describe the various SQL Server availability options that system architects and administrators can choose from, and detail the steps for implementation in a VMware vsphere virtualized environment. The following table lists SQL Server availability options and their ability to meet various recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO). Table 1. SQL Server 2008 High Availability Options Technology Granularity RPO- Data Loss RTO - Downtime Failover Clustering Server No ~30sec + recovery Database Mirroring (High Safety Mode with Automatic Failover) Server, Database No < 3secs Log Shipping Database Possible transaction log Variable Database Mirroring (High Protection Configuration) Database Mirroring (High Performance Configuration) Database None < 3secs Database Some < 3secs Replication Publication Some Variable Before choosing any one option, evaluate your own business requirements to determine which scenario best meets your specific needs. The remaining sections in this document describe overall and detail steps for implementing each availability option using SQL Server This document assumes you have already configured VMware vsphere for best practices and have enabled VMware DRS, HA, and any other system functionality required by specific solutions. Introduction 1
4 SQL Server 2008 with vsphere and VMware HA/DRS Using only VMware vsphere with VMware HA/DRS provides high availability and host-level protection against hardware failure. VMware HA provides high availability for virtual machines by pooling them and the hosts they reside on into a cluster. Hosts in the cluster are monitored and in the event of a failure, the virtual machines on a failed host are restarted on alternate hosts. Use VMware HA when your business requirements dictate that you can have downtime and you don t want to tackle the complexities of configuring failover clustering, log shipping, or database mirroring. VMware HA allows you recover from host outages by restarting your SQL Server virtual machine on other surviving nodes in a VMware HA/DRS cluster. Crash consistency of the virtual machines is ensured during a host outage. Using VMware HA in combination with VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) facilitates automatic restart of virtual machines as well as intelligent load balancing of the entire VMware HA/DRS cluster. After a host failure, the virtual machines that were running on that host are automatically restarted on other surviving hosts in the cluster. During the restart of the virtual machines, VMware DRS will dynamically re-balance the cluster by intelligently relocating the virtual machines effectively optimizing the cluster resource utilization, all while providing the required resources to the virtual machines. Make sure that VMware HA and VMware DRS feature options are enabled for vsphere cluster. For more information on configuring a vsphere cluster and configuring VMware HA/DRS to provide high availability, see the VMware Availability Guide. SQL Server 2008 with vsphere and VMware HA/DRS 2
5 The adjacent screenshot shows that all of the ESX hosts are in a VMware HA cluster. In this configuration, a High Availability agent is running on each host in the cluster. This availability agent monitors each host for heartbeats. If a host in this cluster fails, all virtual machines that were running on that failed host will restart on another surviving host in the VMware HA cluster. SQL Server 2008 with vsphere and VMware HA/DRS 3
6 Log Shipping Availability Option The Log Shipping availability option typically provides lower cost automated transaction log backup and restore functionality, which provides redundancy at the database level. SQL Server provides the underlying framework for doing automated backup, copy and restore of transaction log files. SQL Server 2008 provides a sub-minute scheduling interval providing the ability to do quick backup and restores. Backups are performed on the primary SQL Server instance and restore performed on secondary SQL Server instance(s). Scheduling is done through SQL Server Agent jobs. As an availability strategy, the Log Shipping option does not provide any automatic failover capability and may allow some data loss, however the time synchronization interval is configurable, which gives users some level of control. (This data loss can occur due to corrupted, missing and possibly transaction log data that was not sent to the backup log file on the secondary server.) Log shipping can be used in conjunction with failover clustering to provide a good site failure redundancy with a low cost solution. You can use SQL Server log shipping to create multiple copies of your databases that can be used as a warm standby for recovery purposes, or to provide a database that can be used for reporting and to offload reporting and query functions off of the primary server, thereby improving overall performance and providing a better end user experience of the production SQL Server. To implement log shipping availability, you need to do the following: 1. Configure the primary SQL Server 2008 instance to ship transaction logs to the secondary server location. (You can use the SQL Server Management Studio, Transact-SQL statements, or you can run scripts using Transact-SQL to accomplish these tasks.) 2. After configuring Log Shipping, you need to verify correct operation of the Log Shipping configuration. You should also periodically monitor SQL Server Agent job activity to confirm that backup operations are being performed correctly. The following are step-by-step details of the log shipping implementation for a typical SQL Server 2008 configuration. Connect to the second SQL Server that is the target of the log shipping. Log Shipping Availability Option 4
7 Login to the second SQL Server. As you can now see, the second server CLSQLSRV02 instance is now attached in the SQL Server Management Studio Application. To start configuring your database to do log shipping to the secondary instance, right-click on the database to configure log shipping. In this case, this would be the DS2 database in the primary instance CLSQLSRV01. Before configuring log shipping, ensure that you have configured the following: Create a share for the transaction log backups (preferably not on the primary or secondary instance servers) Create a folder for each secondary server into which the transaction logs will be copied. Create a backup of the primary database and restore that database to the secondary server(s). You can manually backup/restore or allow the SQL Server Management Studio wizard to perform this action for you. In this example, we will use the SQL Server Management Studio to complete this action. A script is also available to accomplish the same set of tasks using Transact-SQL. Log Shipping Availability Option 5
8 On the "Database Properties page, select the "Transactions Log Shipping" option. Check the Enable this as a primary database in a log shipping configuration option. The grayed out "Transaction log backups" item now becomes available. Click the Backup Settings button to configure. Note that we have entered a network share, a local drive and folder for the transaction logs and also modified the backup job name to "Log_Shipping_Backup_DS2" to identify it more clearly. Click the Schedule button to configure the schedule option for the transaction log backups. Log Shipping Availability Option 6
9 We changed the name to "Log_Shipping Backup_Schedule_CLSQLSRV011" and modified the Daily Frequency from 15 minutes to 5 minutes. Click OK twice to accept the changes that you made to these screens. In the "Secondary Databases" section of the "Database Properties" screen, click the Add button to specify the secondary server(s). On the Secondary Database Settings screen click the Connect button to connect to the secondary server. Log Shipping Availability Option 7
10 Notice that we are making connection to the second instance on the CLSQLSRV02 server. Click Connect. On this screen you have multiple options of how to get the secondary database created on the secondary server. Because we do not have a copy of the database to restore either manually or through the wizard, we will elect to backup the database on the primary server and create, initialize and restore to the new database on the secondary server. Click the Restore Options button. Log Shipping Availability Option 8
11 In the "Restore Options" window, you will enter the paths on the local server to restore the database files and the logs files to. As a best practice, keep the drive letters and file paths identical to the primary server database and log paths to avoid any confusion. Click OK. Click the Copy Files Tab under the "Secondary Database" field and enter the file path for the transaction log files on the secondary server. Note: This should be a local file path, e.g., E:\DS2_Backups. Notice that we also changed the copy job name to "Log_Shipping_Copy_CLSQLSRV01_DS2" to improve the readability of the copy job name. Click the Schedule button to configure the copy job schedule settings. Log Shipping Availability Option 9
12 On this screen, we modified the schedule name and the daily frequency interval to 5 minutes from 15 minutes. Click OK to accept the changes made to this screen. Click the Restore Transaction Log Tab to configure the settings for this area. On this screen, we modified the "Database state when restoring backups" option to "Standby mode" and the "Restore Job" name to "Log_Shipping_Restore_CLSQLSRV 01_DS2". Placing the secondary database in standby mode will ensure that the database is available to queries and to offload some of the processing from the primary server all while keeping the database in synch with the primary database. Click the Schedule button to configure the schedule settings for the restore transaction log job. Log Shipping Availability Option 10
13 On this screen, we modified the job name and the "daily frequency interval to 5 minutes from 15 minutes. Click OK to continue. We are now ready to start SQL Server log shipping. Click OK to start the configuration and execution phases. Log Shipping Availability Option 11
14 Full backup and restore of the database to the secondary node is completed and was successful. The secondary database will be created and placed into read-only mode. In this mode, the secondary database will only accept updates from the primary instance using its shipped transaction logs. This screen shows that all attempted operations were successful and we are now ready to move forward with configuration of the log shipping configuration. Using the View Report option, you can view a summary of the operations that were executed as a result of configuring SQL Server log shipping. All operations were successful. You must ensure that you monitor all of the operations as you will not be able to continue until all operations complete successfully and you have a valid log shipping configuration. Log Shipping Availability Option 12
15 Notice that the secondary instance DS2 database is in standby and is fully synchronized with the primary DS2 instance database. Because the database is in Read-Only mode, end-users can only run queries against this database. This can be quite useful in that it can help to reduce the load on the primary database by allowing users to run reports and queries against the secondary database. In the SQL Server Agent Job Activity Monitor, you can monitor the progress of the Log Shipping configuration. This will monitor the health of the log shipping configuration and alert you to any anomalies that may have or are occurring within the configuration. Log Shipping Availability Option 13
16 In this screenshot we show the SQL Server Agent job activity monitor. You can see that a log is currently being backed up to the secondary SQL Server database involved in the log shipping configuration. In the screenshot above you can see that log Shipping is actually functioning as evidenced by the Log_Shipping_Backup_DS2 activity alert. When this log reaches the secondary DS2 database instance, it will be played into the DS2 database. Log Shipping Availability Option 14
17 Here is a snapshot of the transaction log backup directory on CLSQLSRV02 server. As you can see, there are many transaction logs in this folder. Take care to ensure that you allocate enough disk space to accommodate your transaction logs. These files are played into the instance database after they reach this folder. After a definable period, usually around 72 hours, they will be purged using an agent job. This job can be configured to suit your business requirements for availability Log Shipping Availability Option 15
18 Database Mirroring The Database Mirroring availability option provides complete protection against data loss and fast recovery through automatic failover. Database mirroring maintains a redundant database by shipping log files to mirror servers when the transactions are committed on the principal server. Use database mirroring when you need to maintain multiple copies of your data and to create a warm standby of your SQL Server database environment. You should note that SQL Server database mirroring is performed at the database level. Only user databases can be mirrored. This can give you flexibility over SQL Server failover clustering in that you don t need to include all of your databases in the cluster. You can pick and choose which database(s) to mirror. There is also no single point of failure, as in SQL Server failover clustering, in which the storage can become unavailable or corrupted. There are three modes in which database mirroring operates: High Availability mode (High Safety) A principal server, mirror server, and witness server are required. This mode sets the transaction safety to FULL thereby using synchronous I/O between the principal and mirror servers. The principal server will wait for an acknowledgement from the mirror server that the shipped transaction has been applied on the mirror server. In the event of failure at the principal server, the witness server will form a quorum and fail over to the mirror server. You do not lose any data as a result of the transaction safety mode being configured as FULL. High Protection mode A principal server and mirror server are required. Transaction safety mode is set to FULL. This uses synchronous I/O between the principal and mirror servers. In the event of a failure of the principal server, you will need to manually fail over to the mirror server as there is no witness server to perform quorum and automate failover. High Performance mode A principal server and a mirror server are required. Transaction safety is set to OFF and as a result, asynchronous I/O is used between the principal and mirror servers. In this mode, the principal server does not wait for an acknowledgement from the mirror server that all transactions have been recorded on the mirror server. The client application gets a confirmation that a transaction has been committed as soon as the principal server writes the transaction to the log. In the event of failure or unavailability of the principal server, you will need to manually fail over to the mirror server. There is the possibility of data loss as some transactions might be in flight during the failure of the principal server. To implement SQL Server database mirroring: 1. First install SQL Server on two servers and create your database(s) on the principal server. 2. You must then perform a full backup of the principal server database(s) and transaction logs. 3. After you have completed your backup, you must then restore your backup to the mirror SQL Server and configure the database for mirroring. 4. For this scenario, we will configure a SQL Server database mirroring configuration that is in High Safety mode. During this process, you configure security for the principal, mirror and witness servers (if you will be using High Safety Mode.) In High Safety mode, all updates to the database are done synchronously. There is a small performance hit for using this option, but using the high safety mode ensures that your database recovery point objective (RPO) is as close to real-time as possible. 5. After you have completed database mirroring configuration, you can then establish your mirroring session. Database Mirroring 16
19 The following are step-by-step details of database mirroring configuration for a typical SQL Server 2008 setup. These tasks should be performed from the Principal Server. Choose the database that is to be the target for database mirroring, right-click and select Back up database. On this screen you will choose the options for creating a backup of the selected database. Choose the FULL recovery model and backup type. You will also need to choose a location for your backup. Note: ensure your backup location has ample space to store the database and transaction log backups. Database Mirroring 17
20 Click the OK button to execute the backup using your configured options. This summary box show that the full database backup completed successfully. Database Mirroring 18
21 Now we must perform a full backup of the transaction logs for that same database. Follow the previous steps for creating the full transaction log backup. Take care to ensure that you have allocated enough disk space to accommodate the transaction log backup. Here again we are choosing a location for our full transaction log backup. This summary box show that the full transaction log backup completed successfully Database Mirroring 19
22 On the mirror server, you must perform the restore of the database using the NORECOVERY switch to the secondary SQL Server. NORECOVERY forces the database to remain in the restoring state after the restore operation. We must choose this option as we still need to restore any transaction logs that were not applied to the database when the full database backup was taken. Here you can see from the screenshot the SQL Server database restore has completed successfully. The database will now be in a restoring state and will remain in that state until a failover occurs. Database Mirroring 20
23 Here we are restoring the transaction logs to the secondary SQL Server again with the NORECOVERY switch. After Database Mirroring has been established on the primary in a High Safety Automatic Failover scenario, you will find that the DS2 database on the Mirror server CLSQLSRV02 cannot be accessed as it is performing a mirroring function and is only available in the case of failover. Database Mirroring 21
24 An error is generated when you try to access the database on the mirrored server. Right-click and select the DS2 > Tasks > Mirror option which brings up the Database properties window for your chosen database. Database Mirroring 22
25 Click the Configure Security Button to start the SQL Server Configure Database Security Wizard. Database Mirroring 23
26 Configure the security to include a Witness server for automatic failover. You will choose endpoint names and ports for the database mirroring configuration. Endpoints are ports that are configured to provide secure access to the mirrored database instances. In High Safety Mode you must configure a third server to act as a witness to monitor the availability of the principal and mirror SQL Servers. All data will be encrypted through these connections. In this document we show configuration from the SQL Server Management Studio but this can also be configured using SQL commands. Here we are electing to configure a witness server for the SQL Server database mirroring configuration. The witness server will be used to monitor availability of the principal and mirror servers. Should the principal server become unavailable, the witness server will reconfigure quorum and perform a failover to the mirror server. Database Mirroring 24
27 On this screen, we will choose to implement a witness server. This will enable us to implement the High Availability (High Safety) database mirroring mode. Choose your listener port and Endpoint name. Here we chose listener port 5022 and DS2_Mirroring for the Endpoint name. This was an out-of-box or default listener port. Based on your security policies, you may configure a different listener port for use. Click Next to continue. Database Mirroring 25
28 On the Mirror Server Instance Screen, click the Connect button to connect to the mirror server instance. Click Connect on the Connect To Server screen to connect to the mirror instance. Database Mirroring 26
29 Choose your listener port and Endpoint name. Again, we chose listener port 5022 and DS2_Mirroring for the Endpoint name. Click Next. Expand the Database Engine on the Network Servers Tab and select your SQL Server to host the Witness Instance. Database Mirroring 27
30 Here we selected the KLADSRV02 server on which we are running SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition although the Witness can be hosted on any edition of SQL Server and any OS (Windows XP to Windows Server 2008). Click OK to continue. On the Connect To Server, click Connect. Database Mirroring 28
31 Choose your listener port and Endpoint name. Once again, we have chosen listener port 5022 and DS2_Mirroring for the Endpoint name. Click Next. On the Service Accounts screen, you must choose the accounts you wish to use to connect to the instances for mirroring. They will be created automatically if they don't exist. In some cases, you might have to pre-create the service accounts. Note: A single service account could be used for the three instances (Principal, Mirror, and Witness). This should be determined based on your corporate security policies. Database Mirroring 29
32 This is the completion summary screen. It details all of the actions that you wish to perform. Review it carefully before proceeding with the mirroring session. Click Finish when you are ready to proceed with the configuration. Do not proceed unless you get success messages for all Endpoint configurations. Click Close. Database Mirroring 30
33 You will get a popup notification detailing all of the Endpoint configurations as well as the Operating Mode for the mirroring session. Click the Start Mirroring button when you are ready to start mirroring the chosen database instance. Notice the status window message: Status: Synchronized: the databases are fully synchronized Database Mirroring 31
34 In the Object Explorer, you will now see that DS2 database on Server CLSQLSRV01 is now the Principal Mirror server in a High Safety Database Mirroring Configuration. After failover to the mirrored database, the mirror now becomes the principal database and the former principal database now becomes the mirrored copy of the database which is available to clients to connect and process queries. For failover of SQL clients, your application must support client redirection. Database Mirroring 32
35 If you try to get the properties for the new mirrored (former principal) database you will receive an error message. To monitor the state of the database mirror, right-click the DS2 database and select Tasks > Launch Database Mirroring > Monitor. Database Mirroring 33
36 You can also monitor the synchronization history. The metrics shown here were taken from the principal database history. You can also monitor the synchronization history. These metrics were taken from the mirror database history. Database Mirroring 34
37 After failover, the mirrored instance is now the principal mirrored database and you can now open the properties to get information on the database. On the properties page under the database mirroring option, you can see that the databases are now synchronized. This took approximately 1-1/2 seconds to fail over and 3 seconds to stabilize. The database was available for access in about 3 seconds with no data loss. Database Mirroring 35
38 Failover Clustering The Failover Clustering option is a more expensive solution for providing SQL Server availability. It provides very good protection in the case of hardware failure. Failover to a passive node is fairly quick (anywhere between 1-5 minutes depending upon the state of the cluster and database). Failover Clustering provides service availability but does not provide data redundancy like database mirroring and log shipping. Data protection has to be provided at the storage level or by combining with other solutions. Failover Clustering provides instance-level protection built on Windows Failover Clustering. Nodes of the cluster are typically co-located within the same site or datacenter to provide local availability but can also be deployed regionally. Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC) are possible using geographically dispersed clustering solutions. These solutions can be difficult to design, implement, and maintain from a cost and operational standpoint. Implementing SQL Server failover clustering involves a number of steps: 1. Create a virtual machine and install all tested and critical updates and service packs. You should template this virtual machine using sysprep and deploy your virtual machines from templates. This will significantly reduce the time needed to provision your virtual machines. 2. Create a new VMware vsphere virtual switch or port group and add a second network adapter to the cluster s primary node virtual machine to carry cluster heartbeat communications. If using vsphere, select the vmxnet-3 adapters for your public and heartbeat adapters. 3. After completing the network configuration, you map your storage array LUNs as Raw Device Mappings (RDM) to the primary virtual machine. Keep in mind you need to set up a separate vscsi controller for clustered disks as clustered disks cannot reside on the same vscsi controller as the OS boot drive. You also should map your database and log LUNs on separate vscsi adapters. NOTE: Details on virtual machine setup for use in Microsoft clusters is provide in the VMware Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Services guide. 4. Following setup of the SQL Server 2008 primary node virtual machine, you can configure the virtual machine of the secondary SQL Server node. 5. When you are finished with the secondary node, you need to install Microsoft.NET application server roles, configure associated role services, and add the failover cluster feature to both primary and secondary virtual machines in the cluster. a. On the primary node, open the Disk Manager and bring all newly presented disks online and, using DiskPart, align your disks to prevent split I/Os. b. On the secondary virtual machine, open the Disk Manager utility to bring disks online to the secondary node virtual machine. Map the disk letters exactly as they are mapped on the primary virtual machine. c. Use the Microsoft Cluster validation wizard to validate a cluster configuration. When validating a cluster for the first time, you MUST run ALL tests and all tests must pass to be a Microsoft supported failover cluster solution. 6. After completion of the validation, use Microsoft Failover Cluster Management options to create a Windows Server failover cluster to support a clustered SQL Server 2008 instance(s). You will then use the Failover Cluster Management tools to configure the Cluster Quorum or witness drive and settings to specify failover conditions for the cluster. 7. With the cluster now fully configured and functional, configure the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC). SQL Server uses the MSDTC for distributed queries, replication, and two-phase commit transactions. Failover Clustering 36
39 To configure the MSDTC, you open the Microsoft Failover Cluster Management console to configure a service or application. The console provides a High Availability Wizard to configure MSDTC to perform the SQL Server cluster failover. 8. The last step is to actually install SQL Server 2008 on the failover cluster primary node. The procedure to add an additional cluster node to a clustered SQL Server instance is similar to the failover cluster installation of SQL Server. You can perform this task, from either the primary or second node of the Windows Server failover cluster. 9. With SQL Server node installation complete, perform instance failover tests. The following are step-by-step details of failover clustering configuration for a typical SQL Server 2008 setup. This is a screenshot of a VMware vsphere cluster. It should be noted that Windows failover clustering is not supported in a vsphere cluster. This means that DRS and VMotion will not function in that the VMs are engaged in bus sharing mode (sharing virtual disks between ESX servers). Any servers hosting VMs that are using windows failover clusters should be removed from a HA/DRS cluster. Failover Clustering 37
40 Create a new virtual switch or virtual port group to carry the cluster heartbeat communications. As you can see, We created the Heartbeat network as a virtual port group on an existing vswitch called vswitch1. Listed below are the properties for the Heartbeat port group that we created. Failover Clustering 38
41 Add a second adapter in the virtual machine properties to carry your cluster communications traffic. Here we have added a second vnic adapter in the virtual machine properties and we have connected this added vnic to the Heartbeat port group. Step 1. Once you are done with the network configuration, you can now start to add your virtual disks to the virtual machine for the cluster. This is detailed in the VMware "Setup for Microsoft Cluster Services" guide available on the VMware website. Click the Next button to continue configuration. Failover Clustering 39
42 Step 2. We will not cover the zoning of storage in this guide as this should be completed by your SAN Administrator before configuring a SQL Server 2008 Failover cluster. Select the "Raw Device Mappings" radio button and click Next to continue. As you can see in the screen display, there are a number of LUNs that we can select from for use in the SQL Server 2008 failover cluster. We will use all of the LUNs presented here. Table 2 provides a description of the LUNs used. Failover Clustering 40
43 Table 2. LUN Attributes LUN ID LUN Size LUN Purpose vscsi Adapter OS (VMFS) 42 GB OS Boot drive 0:0 Non-shared DATA (VMFS) 40GB OS Data drive (SQL binaries) 0:1 Non-shared Cluster (0) 1GB QUORUM LUN 1:0 Shared (clustered) Cluster (1) 4GB DTC LUN 1:1 Shared (clustered) SQL Server (60) 100GB SQL Database LUN 2:0 Shared (clustered) SQL Server (61) 50GB SQL Transaction Log LUN 1:2 Shared (clustered) SQL Server (62) 35GB TempDB Database LUN 2:1 Shared (clustered) We selected LUN 0 to add to the virtual machine. NOTE: All clustered disks must be attached to a SCSI/RAID controller that is separate from the controller to which the OS Boot drive is attached. Click Next to continue with the configuration. Failover Clustering 41
44 Step 3. Here you have the option of storing the mapping file with the virtual machine or on a datastore that has common access to all nodes in the VMware datacenter. We have chosen to store the mapping file on common storage in a location created by the first virtual machine that maps the storage. In this case, it is datastore EMCCX40VMFS03 in a folder called "CLSQLSRV01". Click Next to continue the configuration. Step 4. Select the Physical radio button to bypass the virtualization layer and allow the virtual machine to directly access the presented LUNS as well as access the array based tools and utilities. NOTE: Using this mode does not allow the creation of VMware snapshots although hardware (array-based) snapshots are available. Click Next to continue the configuration. Failover Clustering 42
45 Step 5. In this step, we have place the Quorum LUN on a different vscsi adapter (SCSI adapter 1). As mentioned earlier, the clustered disks must be attached to a separate vscsi adapter than the adapter to which the OS Boot disk is attached. The OS Boot disk is currently attached to vscsi adapter 0. Click Next to continue with the configuration. Here we see the summary page of the configuration that we selected. Click the Finish button to complete the addition of the first LUN to the virtual machine. Failover Clustering 43
46 Step 6. Here you can see that the new vscsi adapter and Raw Data Mapping (RDM) are ready to be added. By clicking OK, the vscsi adapter and RDM will be added to the virtual machine. But before we add the vscsi adapter to the virtual machine, there are two changes we need to make to the vscsi adapter. We need to enable the Physical mode by selecting the Physical radio button and we also need to change the "SCSI Controller Type" to the SAS adapter as Windows Server 2008 no longer supports SCSI-2 reservations. The "LSI Logic SAS" adapter supports SCSI-3 reservations. Here we have changed the "SCSI Bus Sharing" mode to physical mode. Under the SCSI Controller Type", click the Change Type... button and select the "LSI Logic SAS Controller". Failover Clustering 44
47 Click the OK button to continue the configuration. Click OK to complete the configuration for the first LUN. Repeat Steps 1-6 to add any additional LUNs that you need for your virtual machine. Keep in mind that you should use different vscsi adapters for your database and transaction logs (TLOGS). In this example, we will use the vscsi 2 adapter for the SQL and TempDB databases and the vscsi 1 adapter for TLOGS. Adding the MSDTC LUN required for SQL failover clustering. Failover Clustering 45
48 This LUN will be added on the same controller as the Quorum LUN as SCSI ID 1:1. Note hard disk 3 on SCSI ID 1:0. This is the Quorum LUN required for clustering. We have mapped this LUN to SCSI 1:1. Failover Clustering 46
49 Again, we see the summary screen before confirming selections. Click the Finish and then the OK button to apply these settings. This will create a new vscsi adapter 2 and map the LUN to this adapter. Failover Clustering 47
50 This display shows confirmation that we have mapped this LUN to SCSI 2:0. Here again, we see the summary screen before confirming selections. Click the Finish and then the OK button to apply these settings. Failover Clustering 48
51 Because this is a new vscsi adapter, you will need to enable SCSI Bus Sharing and change its type to the "LSI Logic SAS" adapter type. Under "SCSI Controller Type", click the Change Type... button and select "LSI Logic SAS Controller". Selection of the LSI Logic SAS adapter type. Click the OK button to apply the changes. Failover Clustering 49
52 Here we map the TempDB LUN. We map this LUN to the same vscsi adapter as the SQL Database LUN is attached to, vscsi adapter 2. As you can see, we have chosen vscsi adapter 2 for mapping to this LUN. Note that there is already a LUN on SCSI ID 2:0. This is the SQL database LUN. Failover Clustering 50
53 LUN settings are confirmed for vscsi ID 2:1. Summary screen confirming settings. We will now map the last LUN, the TLOG LUN, to the virtual machine. Failover Clustering 51
54 We will map this drive to the vscsi adapter 1. This is the adapter that the cluster (Quorum and MSDTC) LUNs are attached to. Notice the two LUN mappings preceding the selected SCSI target ID. These are the Quorum id 1:0 and the MSDTC id 1:1 LUNs. Failover Clustering 52
55 LUN settings are confirmed for vscsi ID 1:2. Summary screen confirming our settings. Failover Clustering 53
56 This is what the virtual machine settings should look like after initial configuration. Take note of vscsi adapter 0 and notice that it is not in SCSI Bus Sharing mode. This is because the adapter holds the OS Boot and data drives which do not require it to be in SCSI Bus Sharing mode. This adapter should not be placed in Bus Sharing Mode as there is no need to share it with other virtual machines; this would also result in data corruption as well as an unsupported Microsoft OS configuration. Now that we have mapped the LUNs to the primary virtual machine node, we must now map the LUNS to the secondary virtual machine node. We need to select the secondary node of the cluster CLSQLSRV02 and edit its settings to map the LUNs to this virtual machine. Failover Clustering 54
57 Leave vscsi adapter 1 in its default state of SCSI Bus Sharing mode of "None". Click the Add button and select hard disk. This time, instead of adding a Raw Device Mapping (RDM), we are going to add a previously created hard disk. Take care to map each disk to the same vscsi adapter on this virtual machine (node) as you mapped to on the first virtual machine (node) of the cluster. Failover Clustering 55
58 Notice that we have selected the "Use an existing virtual disk" option. Also note that the Raw Device Mappings option is not available for selection. Click the Next button to continue. You will be presented with a dialog box that asks for a path to the virtual disk that you want to map to this virtual machine. Click the Browse button to choose from the selection of available disks to map. Remember that we stored the mapping files on the SAN datastore "EMCCX40VMFS03" The files will be located in a folder on this datastore called "CLSQLSRV01". Failover Clustering 56
59 Here we have selected the datastore containing our virtual disk mapping files. After we have selected the datastore "EMCCX40VMFS03", you can see that there is a folder called "CLSQLSRV01". This folder was created on this datastore after we mapped the LUNs from the first virtual machine (node) of the cluster "CLSQLSRV01". Failover Clustering 57
60 If you refer to the size of the mapped LUNs listed in Table 2. LUN Attributes, provided earlier in this document, you will see that the sizes match up with the earlier table listing. We have selected the first virtual disk. Using the information provided in Table 2. LUN Attributes, we will map this virtual disk to SCSI ID 1:0. You will need to repeat this process for the remaining virtual disks. We will map one more virtual disk. Click OK to proceed with the configuration. Failover Clustering 58
61 The full path to the virtual disk is displayed in the disk file path field. Click the Next button to continue with the configuration. We have mapped this virtual disk to SCSI ID 1:0. Failover Clustering 59
62 Here is confirmation of the mapped virtual disk. Click the Next button to continue. Summary screen confirming the settings. Click Finish and OK buttons to apply these settings. Failover Clustering 60
63 Here again we show the selection of the LSI Logic SAS adapter type. Click the OK button to apply the changes. Do not forget to change the SCSI Bus Sharing mode to physical and the vscsi adapter type to LSI Logic SAS. Click the OK button to apply these settings. Failover Clustering 61
64 Notice that we have selected the "Use an existing virtual disk" option. Also note that the Raw Device Mappings option is not available for selection. Click the Next button to continue. You will be presented with a dialog box that asks for a path to the virtual disk that you want to map to this virtual machine. Click the Browse button to choose from the selection of available disks to map. Remember that we stored the mapping files on the SAN datastore "EMCCX40VMFS03" The files will be located in a folder on this datastore called "CLSQLSRV01". Failover Clustering 62
65 Here we have selected the datastore containing our virtual disk mapping files. After we have selected the datastore "EMCCX40VMFS03". You can see that there is a folder called "CLSQLSRV01". This folder was created on this datastore after we mapped the LUNs from the first virtual machine (node) of the cluster "CLSQLSRV01". Failover Clustering 63
66 We are now selecting the MSDTC virtual disk, which we will map to SCSI ID 1:1. The full path to the virtual disk is displayed in this dialog box. Click the Next button to continue the configuration. Failover Clustering 64
67 We are mapping this virtual disk to SCSI ID 1:1. Confirmation of mapped settings. Click the Next button to continue. Failover Clustering 65
68 Summary screen of configuration settings. Click the Finish and OK buttons to apply these settings. Notice that we have selected the "Use an existing virtual disk" option. Also note that the Raw Device Mappings option is not available for selection. Click the Next button to continue. You will be presented with a dialog box that asks for a path to the virtual disk that you want to map to this virtual machine. Failover Clustering 66
69 Click the Browse button to choose from the selection of available disks to map. Remember that we stored the mapping files on the SAN datastore "EMCCX40VMFS03" The files will be located in a folder on this datastore called "CLSQLSRV01". Here we have selected the datastore containing our virtual disk mapping files. Failover Clustering 67
70 After we have selected the datastore "EMCCX40VMFS03", you can see that there is a folder called "CLSQLSRV01". This folder was created on this datastore after we mapped the LUNs from the first virtual machine (node) of the cluster "CLSQLSRV01". If you refer to the size of the mapped LUNs in Table 2, provided earlier in this document, you will see that the sizes match up with the table listing. Failover Clustering 68
71 Mapping the database virtual disk and attaching this virtual disk to vscsi ID 2:0. Click the OK button to continue. Full path to virtual disk is displayed in this dialog box. Click the Next button to continue the configuration. Failover Clustering 69
72 Mapping this virtual disk to vscsi ID 2:0. Confirmation of vscsi ID of 2:0. Failover Clustering 70
73 Summary screen of settings. Because we are adding a new vscsi adapter 2, we will need to configure this adapter as previously configured earlier in this document. Failover Clustering 71
74 New vscsi adapter 2 with the required changes. Click the OK button to apply all changes. Continue to map your virtual disks until they have all been mapped to the appropriate vscsi adapters and vscsi IDs. After you have configured all of your LUNs to both virtual machines (nodes) of the cluster, you can now proceed with powering on the first virtual machine to configure the shared disks from the operating system layer. Any errors during power-on indicate that there are problems with the components (disks, network, etc.) within the virtual machine. Failover Clustering 72
75 Login to the OS and open the disk manager. On the primary node in the Disk Manager, you will see all of the drives that you mapped to this virtual machine as Raw Data Mapping (RDMs). Notice that all of the drives are offline. You will need to bring all of the disks to an online state. You do this by selecting the drive label, e.g., Disk 2, right-click the drive label, and select "Online". Failover Clustering 73
76 Here, we have selected Disk 3 and brought it to an online state. After initializing and formatting this drive, it will be available for use. After configuration, all of your drives should be in an online state. Open a command window and run the DiskPart program to format your disks with a 64bit alignment from the operating system level. This will provide performance gains as tracks will be aligned for the SQL application and the chance of split writes will be reduced significantly. Failover Clustering 74
77 Type DiskPart at the command line to run the DiskPart utility. The "list disk" command will print out a listing of all of the disks known to the system. We will perform actions on disks starting with Disk 4 through 6 as the Quorum and MSDTC drives don't need to be 64bit aligned. The "select disk" command will select a disk to perform some action on. Here we have selected Disk 4 to 64bit align and label. Failover Clustering 75
78 The command "create partition primary align=64" creates a primary partition on the selected disk and 64bit aligns the track boundaries at the OS layer. We will now use the "label" command to create a label on the selected disk. The "assign" command creates a drive letter of your choice on the selected drive. Here we have assigned the letter L to the drive because this drive is meant to hold the transaction logs for the SQL Server database. Once you have aligned all of your data and log file disks, exit the DiskPart utility and open the Disk Manager utility to format your aligned disks. You should now format them using NTFS and a 64K block size to preserve alignment. Be sure to perform a full format on all of the aligned disks. Failover Clustering 76
79 Note the format parameters for the Database disk Volume label "DBASE", File System "NTFS" and Allocation Unit Size "32K 64K". Also note that the "Perform a quick format" box is not selected. Confirm here to proceed with the format of the disk(s). Format the remainder of your disks this way. Here you can see that we have started the format on all of the disks and they are proceeding to format. Failover Clustering 77
80 Your disk manager display should be similar to this screen display after all of your disks have been properly formatted. After formatting is complete, your disks are ready for use. You can now close the server manager utility. As you can see from the Windows Explorer, the formatted disks are now available for use and we are now ready to configure the secondary virtual machine (node) of the cluster. After configuration of the secondary virtual machine (node), you should immediately install.net v3.5 with Service pack 1 on both virtual machines (nodes) of the cluster. These are freely downloadable from the Microsoft website. Failover Clustering 78
81 Click run to install the.net v3.5 service pack 1 update. Do this on both virtual machines (nodes). Preparing to load the installation screen. Click the Next button to continue. Failover Clustering 79
82 On this screen the.net application is being repaired or reverted to its default installation state. Setup completed successfully. Failover Clustering 80
83 Next we need to install the Application Server Role on both virtual machines (nodes) of the cluster. Open the server manager console and select roles. Click the Add Roles link and this will open the Add Roles Wizard. Select the Application Server Role and click the Next button to continue configuration of the role. Failover Clustering 81
84 Overview of the Application Server role screen. Click the Next button to continue configuration. In the "Select Role Services" under "Distributed Transactions" select "Incoming Remote Transactions" and "Outgoing Remote Transactions" options as these are required by the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC). Click the Next button to continue configuration and installation of this role. Failover Clustering 82
85 Role configuration confirmation screen. Click the Install button to continue. Summary screen indicating that the Application Server Role has completed successfully without incident. Proceed with the configuration of the Application Server Role on the secondary virtual machine (node) of the cluster. Next we must proceed to add the Failover Cluster Feature to both virtual machines (nodes) that will participate in the Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Cluster. In the Server manager, select the "Features" container to start configuration of the Failover Cluster Feature. Failover Clustering 83
86 Click the Add Features link to start the "Add Features" Wizard. Select the Failover Cluster feature from the listed features. Click the Next button to confirm features selections. Click the Install button to install the selected feature. Ensure that you complete this task on both virtual machines (nodes) of the cluster. Failover Clustering 84
87 Installation in progress. This screen shows that the installation of the failover cluster feature was successful. Ensure that this wizard completes successfully on both virtual machines (nodes) of the cluster. Click the Close button to complete the wizard and close the server manager. Next we must validate that the virtual machines (nodes) will function properly and produce a Microsoft supported cluster configuration. We do this by running the Cluster Validation Wizard included with the Windows Server 2008 OS. To run the Cluster validation wizard, under Administrator Tools, select the "Failover Cluster Management" console. We will perform this task from the primary node of the cluster. Failover Clustering 85
88 Start the secondary virtual machine (node) of the cluster "CLSQLSRV02". If you experience any issues starting the secondary virtual machine (node), check to ensure that you have correctly mapped your virtual disks on the secondary virtual machine (node) of the cluster. Startup of the secondary virtual machine (node). Failover Clustering 86
89 Notice in the disk manager utility that the disks we configured on the primary virtual machine are available to the secondary virtual machine, but are offline. Follow the procedures described earlier in this document to bring the disks online. No formatting should be necessary as all of the offline disks are shared and have been 64bit aligned and formatted by the primary virtual machine (node) of the cluster. You will have to change the drive letters to match the drive letters of the primary virtual machine (node) of the cluster. Confirm the drive letter change and click the Yes button to apply the change. Failover Clustering 87
90 Your disk manager display should look similar to this one after you have corrected the drive letters. You may now close the server manager utility. This completes the drive configuration procedures required for forming the Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition cluster. At this point, you should check network connectivity to ensure that the Public LAN and Cluster communications networks are functioning properly. You should perform these steps from both virtual machines (nodes) of the cluster. Here we have opened a command window and issued the ping command to test connectivity of the public and cluster heartbeat networks. You should perform this test from both virtual machines (nodes) before proceeding to the configuration of a Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition cluster. After ensuring that public and heartbeat communications are functioning properly, we can then proceed to cluster configuration. We will start this from the primary virtual machine (node) of the cluster. Failover Clustering 88
91 On the primary node of the proposed Windows Server failover cluster, click to open the Failover Cluster Management console. To validate a cluster configuration, click the Validate a configuration link. Failover Clustering 89
92 Validation Before You Begin Dialog screen. Click the Next button to continue. Enter the servers to be validated. Failover Clustering 90
93 We have entered the two SQL Server cluster nodes CLSQLSRV01 and CLSQLSRV02 for validation. Click the Next button to continue. When validating a failover cluster configuration for the first time, you must run ALL tests. Click the Next button to continue. Failover Clustering 91
94 Shown here is the validation confirmation screen. You should view the list of items on the checklist so you are familiar with what is being tested. Click the Next button to continue. The Windows failover cluster validation tests are now in progress. Failover Clustering 92
95 Disk validation in progress. The failover cluster validation is performing disk arbitration tests at this point in the validation. Failover Clustering 93
96 Disk arbitration is continuing and we are almost done with the validation testing. Here you can see that the cluster validation tests passed. You may view the report for all of the details about the tests that were performed. Click the Finish button to continue. You may now proceed to creation of the Windows Server 2008 Enterprise cluster. Click the Create A Cluster link to proceed with the creation and configuration of a new cluster. Failover Clustering 94
97 Create Cluster Wizard Before You Begin. Click the Next button to continue. Enter the names of the servers that form the cluster and click the Next button to continue. Failover Clustering 95
98 Click the Next button to continue. On the next screen, enter the name for the cluster, and IP address for the cluster virtual address. We have given the cluster name of W2K8EECLUS and as the cluster virtual IP address. Click the Next button to continue configuration of the cluster. Failover Clustering 96
99 Confirmation of our cluster settings. Click the Next button to continue. Wizard is configuring the cluster. Failover Clustering 97
100 The cluster is now formed. View the report to get details of the configuration, ensure that the cluster was properly created, and verify that there were no warnings or errors. Click the Finish button to complete the cluster configuration. To manage the newly created cluster, click the Manage a Cluster link. Failover Clustering 98
101 Select the cluster that you want to manage and click the OK button to continue. Configuring your QUORUM drive. Open the Failover Cluster Management console. Right-click on the cluster name, select the More Actions option, and click Configure Cluster settings. The "Configure Cluster Quorum" settings wizard opens. Failover Clustering 99
102 Select the Configure Cluster Quorum settings. This will allow you to choose the Quorum (now called a witness drive). The "Before You Begin" advisory screen displays. Please read the information on this screen before configuration of the Quorum Disk settings. Click the Next button to continue. Failover Clustering 100
103 When building a two node failover cluster, be sure to select the Node and Disk Majority option as this will allow the cluster to sustain a node failure while maintaining quorum through the Quorum (witness disk). As you can see in this screenshot we have selected Volume Q as our Quorum (Witness disk). Click the Next button to continue the configuration of the Witness Disk. Failover Clustering 101
104 Here is the configuration confirmation screen. Click the Next button to continue. Successful completion summary screen. Click the Finish button to close the wizard. Failover Clustering 102
105 In this screenshot you can see the configuration settings of the Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition cluster. Note that there are two networks (Public and Heartbeat) and five shared hard disks (Quorum, MSDTC, DBase, TempDB and Tlog) shared disks. This is the active node of the cluster as it has all of the resources allocated to it. With the cluster configured and fully functional, we will now need to configure the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC). Clustered SQL Server uses the MSDTC service for distributed queries, replication functionality and twophase commit transactions. Ensure that you have an available IP address for the MSDTC configuration. To configure the MSDTC, open the Failover Cluster Management console and right-click the cluster name. On the Server and Applications context menu select Configure a Service or Application. When the High Availability Wizard Before You Begin screen is displayed, click the Next button to continue with configuration. Failover Clustering 103
106 From this screen, select the Distributed Transaction Coordinator (DTC) option from the list of applications and services. Click the Next button to continue the configuration. Notice the name of the service. We have given the service an IP address of Click the Next button to continue configuration of the DTC service. Failover Clustering 104
107 Select the disk that will be used to hold the MSDTC logging and consistency information. Here we have chosen the M drive. We have designated this drive as the MSDTC drive by giving it the letter M. Click the Next button to continue with the configuration. Here we show the configuration settings confirmation screen. Click the Next button to continue with the configuration. Failover Clustering 105
108 Here, the wizard is configuring the cluster storage to be used for the clustered MSDTC application. Here, the wizard is configuring the network name and IP address to be used for the clustered MSDTC application. Failover Clustering 106
109 Summary screen showing the successful configuration of MSDTC service. View the report to get detailed configuration information. Click the Finish button to complete the configuration. Here we have a summary display of the MSDTC service and its status. Notice the resources required for the service: a NetBIOS name (W2K8EECLUSDTC), an IP address ( ), and a disk (Volume M) to store logging and consistency information for the service. Notice that all resources and dependencies are in an Online state and are functioning properly. You should now restart this computer to ensure that all service and resources fail over and are restarted properly within the cluster. This is also a requirement before installing SQL Server 2008 in a failover cluster. There is a system restart rule that is checked and, if it fails, you cannot proceed with the installation. Failover Clustering 107
110 To install SQL Server 2008, you can run the setup from the SQL Server 2008 DVD or ISO. Select the New SQL Server Failover Cluster installation option under the installation link. The SQL Server setup wizard will start. Failover Clustering 108
111 Here we see the selection of the Installation options and the New SQL Server failover cluster option. Select to continue configuration. The wizard is Processing our selections. Failover Clustering 109
112 The Setup Support Rules checks for issues that might prevent you from successfully installing a SQL Server failover cluster. Notice the red X in the results window. Here we see that a restart of the computer on which we are trying to install SQL Server 2008 requires a reboot. Failover Clustering 110
113 After restarting the computer, all setup support tests passed without incident. We are now ready to proceed with the installation of SQL Server 2008 in a failover cluster configuration. Click the OK button to continue. Here the wizard is loading the SQL Server failover cluster configuration screen. Failover Clustering 111
114 Enter your product key or, if this is a Proof of Concept deployment, you can select the Enterprise Evaluation option, but note that evaluation option installations will be activated with a 180-day expiration. You must accept the Microsoft End User License Agreement (EULA) to continue the installation. After you have accepted the EULA, Click the Next button to continue the installation of SQL Server. Failover Clustering 112
115 Click the Install button to install the required setup support files. Here we see the successful completion of the Setup Support Rules for the SQL Server failover cluster installation. Click the Next button to continue. Failover Clustering 113
116 On the Instance Features screen, select only the options that you require for your installation. Click the Next button to continue the configuration. On this screen you must provide the SQL cluster network name and Instance root directory. The network name will be used by clients on the network to connect to the SQL Server instance. We have left the default instance name of MSSQLSERVER. Click the Next button to continue the configuration and installation. Failover Clustering 114
117 On the Disk Space Requirements review screen, ensure that you have enough disk space to proceed with the SQL Server failover cluster installation. Click the Next button to continue. Select the Cluster Resource Group to use for the SQL failover cluster. You can use the provided name or choose your own name by typing one in the dialog box. We have used the default name. Once you have selected a name, click the Next button to continue with the configuration and installation of the SQL Server failover cluster. Failover Clustering 115
118 On the Cluster Disk Selection screen you must select the disk resources that will be part of the SQL Server failover cluster resource group. Here we have chosen all of the remaining disks as they will designated for SQL user database, tempdb database and the transaction log files. Once you have completed your disk selection, click the Next button to continue with the configuration and installation. Windows Server 2008 clusters allow you to use DHCP for Application Resource Groups, so you must decide whether or not you want to use DHCP for your application resource group. Here we have chosen to use a static IP address for the SQL Server failover cluster resource group. We have disabled my IPv6 protocol at the adapter level so the IPv6 protocol does not display here. If you have not disabled your IPv6 protocols, then you should uncheck the IPv6 box that would be displayed here. Click the Next button to continue with configuration and installation of your SQL failover cluster. Failover Clustering 116
119 On this screen keep the default selection and click the Next button to continue with the configuration and installation of the SQL Server failover cluster. For more information on using security identifiers (SIDs) with SQL Server, see the Microsoft MSDN article: ms On the Server Configuration screen, we have chosen to use the same service account for all SQL Server services but you should configure these settings according to your business security policies. Click the Next button to continue with the configuration and installation. Failover Clustering 117
120 On the Account Provisioning Tab of this display, we chose Mixed mode authentication because our application uses SQL authentication but you must select configuration options based on your own applications requirements. Click the Data Directories Tab to configure the location of your database and logfiles. Configure all of the database, logs, and backup directory locations, keeping in mind that all of these locations must be on the clustered shared disks. If you want to use the new FILESTREAM feature, select the FILESTREAM Tab and configure settings. (We will not make use of it here.) Click the Next button to continue the configuration and installation of the SQL Server 2008 failover cluster. Failover Clustering 118
121 On the Error and Usage screen, we have selected to send error data to Microsoft. You should configure settings based on your own company security policies. Click the Next button to continue with the configuration and installation of the SQL Server failover cluster. On the Cluster Installation Rules screen, you can see that all applicable tests passed without incident. If any test fails, view the failed information, correct the failure, and re-run the tests. Click the Next button to continue. Failover Clustering 119
122 Here is the summary of our configuration settings. These will be stored in a file indicated by the configuration file path location. Be sure to view the configuration settings before proceeding to ensure that you have all of your desired settings. When done, click the Install button to proceed with the installation of the SQL Server failover cluster. SQL Server failover cluster installation is now in progress. Failover Clustering 120
123 SQL Server failover cluster installation continues. SQL Server failover cluster installation successful completion. You now have a clustered instance of SQL Server 2008, but we still need to make that clustered SQL instance highly available. From here, we will proceed to add a second node to the clustered SQL instance. Click the Close button to finish. Failover Clustering 121
124 The procedure to add an additional cluster node to a clustered SQL Server instance is similar to the failover cluster installation of SQL Server. We will describe the process in following screenshots. We chose to add the node to the SQL Server failover cluster from the second node of the Windows Server failover cluster. You could also accomplish this task as from the primary node of the Windows Server failover cluster. From the SQL Server Installation Center choose the Add node to a SQL Server failover cluster option. The wizard is starting the Setup Support Rules wizard which will identify any issues that might prevent you from adding an additional node to a SQL Server failover cluster. Failover Clustering 122
125 Ensure that all of the Setup Support Rules pass and click the OK button to continue with the configuration. Starting the Setup Support Files wizard. Failover Clustering 123
126 Click the Install button to install the Setup Support Files required to add the node to the SQL failover cluster. Starting the Setup Support Rules wizard. Failover Clustering 124
127 Again, ensure that all of your Setup Support Rules pass and click the Next button to continue with the configuration and installation. Here you need to enter your product key to continue with the configuration and installation. Failover Clustering 125
128 Accept the End User License Agreement (EULA) and click the Next button to continue with the addition of an additional node the SQL Server failover cluster. Here the installer program picks up the information that is relevant to the SQL Server failover clustered instance and is ready to validate the service accounts that will run the SQL Server services. Failover Clustering 126
129 Enter the password information for the SQL Server service accounts that you used to build the first node of the cluster. Click the Next button to continue the configuration and installation of the second node addition to the SQL Server failover cluster. Configure this screen according to your company security policies. Click the Next button to continue the configuration and installation. Failover Clustering 127
130 Correct any failures or warnings on this screen and re-run Add Node Rules. When you have passed all checks, click the Next button to continue the configuration and installation. This is the Ready To Add Node confirmation screen. Ensure that all settings meet with your approval before proceeding. When ready, click the Install button to add an additional node to the SQL Server failover cluster. Failover Clustering 128
131 The Add Node setup process has completed successfully. Click the Next button to complete the installation. Setup process is complete. Click the Close button to close the wizard. Perform any instance failover tests to ensure that your SQL Server failover clustered instance is functioning properly. Failover Clustering 129
132 The SQL Server failover clustered instance is currently owned by cluster node CLSQLSRV01. We will perform a manual failover to the secondary node of the cluster CLSQLSRV02. As you can see on this screen, we are moving the SQL Server clustered resources to node CLSQLSRV02. Currently, the SQL Server clustered resources are owned by cluster node CLSQLSRV01. Failover Clustering 130
133 Looking at this screenshot at the Current Owner field, you can see that the SQL Server clustered resources are now owned by cluster node CLSQLSRV02. Summary When planning a SQL Server deployment, your operational readiness procedures should also include provisions to ensure availability and recoverability. Evaluate your business requirements to determine the specific availability options that would satisfy your business requirements. Once you have narrowed down your options, this document should help you with details and descriptions of the chosen availability option. References Documents listed here provide additional information relevant to implementing high availability for SQL Server 2008 that is available on the VMware web site or from other third parties. VMware Solutions web site located at Additional product information and documentation for using VMware Infrastructure is located at Failover Clustering 131
134
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service
 Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESX 4.0 ESXi 4.0 vcenter Server 4.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESX 4.0 ESXi 4.0 vcenter Server 4.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Microsoft SharePoint 2010 on VMware Availability and Recovery Options. Microsoft SharePoint 2010 on VMware Availability and Recovery Options
 This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws. This product is covered by one or more patents listed at http://www.vmware.com/download/patents.html. VMware
This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws. This product is covered by one or more patents listed at http://www.vmware.com/download/patents.html. VMware
Deploy App Orchestration 2.6 for High Availability and Disaster Recovery
 Deploy App Orchestration 2.6 for High Availability and Disaster Recovery Qiang Xu, Cloud Services Nanjing Team Last Updated: Mar 24, 2015 Contents Introduction... 2 Process Overview... 3 Before you begin...
Deploy App Orchestration 2.6 for High Availability and Disaster Recovery Qiang Xu, Cloud Services Nanjing Team Last Updated: Mar 24, 2015 Contents Introduction... 2 Process Overview... 3 Before you begin...
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service
 Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service Update 1 ESX 4.0 ESXi 4.0 vcenter Server 4.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service Update 1 ESX 4.0 ESXi 4.0 vcenter Server 4.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until
Setup for Microsoft Cluster Service ESX Server 3.0.1 and VirtualCenter 2.0.1
 ESX Server 3.0.1 and VirtualCenter 2.0.1 Setup for Microsoft Cluster Service Revision: 20060818 Item: XXX-ENG-QNNN-NNN You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on our Web site at http://www.vmware.com/support/
ESX Server 3.0.1 and VirtualCenter 2.0.1 Setup for Microsoft Cluster Service Revision: 20060818 Item: XXX-ENG-QNNN-NNN You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on our Web site at http://www.vmware.com/support/
SQL Server Mirroring. Introduction. Setting up the databases for Mirroring
 SQL Server Mirroring The purpose of this document is to describe in detail the process of configuring Secret Server and SQL Server 2008 for a high-availability environment using Mirroring. The contents
SQL Server Mirroring The purpose of this document is to describe in detail the process of configuring Secret Server and SQL Server 2008 for a high-availability environment using Mirroring. The contents
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service
 Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESX 4.1 ESXi 4.1 vcenter Server 4.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESX 4.1 ESXi 4.1 vcenter Server 4.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Installing and Configuring a. SQL Server 2012 Failover Cluster
 Installing and Configuring a SQL Server 2012 Failover Cluster Edwin M Sarmiento Applies to: SQL Server 2012 SQL Server 2014 P a g e 1 Copyright This document is provided as-is. Information and views expressed
Installing and Configuring a SQL Server 2012 Failover Cluster Edwin M Sarmiento Applies to: SQL Server 2012 SQL Server 2014 P a g e 1 Copyright This document is provided as-is. Information and views expressed
Dell PowerVault MD32xx Deployment Guide for VMware ESX4.1 Server
 Dell PowerVault MD32xx Deployment Guide for VMware ESX4.1 Server A Dell Technical White Paper PowerVault MD32xx Storage Array www.dell.com/md32xx THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND
Dell PowerVault MD32xx Deployment Guide for VMware ESX4.1 Server A Dell Technical White Paper PowerVault MD32xx Storage Array www.dell.com/md32xx THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service
 Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service Update 1 ESXi 5.1 vcenter Server 5.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service Update 1 ESXi 5.1 vcenter Server 5.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Administering and Managing Failover Clustering
 24_0672329565_ch18.qxd 9/7/07 8:37 AM Page 647 CHAPTER 18 Administering and Managing Failover Clustering Failover clustering is one of four SQL Server 2005 highavailability alternatives. Other SQL Server
24_0672329565_ch18.qxd 9/7/07 8:37 AM Page 647 CHAPTER 18 Administering and Managing Failover Clustering Failover clustering is one of four SQL Server 2005 highavailability alternatives. Other SQL Server
Administering and Managing Log Shipping
 26_0672329565_ch20.qxd 9/7/07 8:37 AM Page 721 CHAPTER 20 Administering and Managing Log Shipping Log shipping is one of four SQL Server 2005 high-availability alternatives. Other SQL Server 2005 high-availability
26_0672329565_ch20.qxd 9/7/07 8:37 AM Page 721 CHAPTER 20 Administering and Managing Log Shipping Log shipping is one of four SQL Server 2005 high-availability alternatives. Other SQL Server 2005 high-availability
StarWind Virtual SAN Installing & Configuring a SQL Server 2012 Failover Cluster
 #1 HyperConverged Appliance for SMB and ROBO StarWind Virtual SAN Installing & Configuring a SQL Server 2012 Failover JANUARY 2015 TECHNICAL PAPER Trademarks StarWind, StarWind Software and the StarWind
#1 HyperConverged Appliance for SMB and ROBO StarWind Virtual SAN Installing & Configuring a SQL Server 2012 Failover JANUARY 2015 TECHNICAL PAPER Trademarks StarWind, StarWind Software and the StarWind
Bosch Video Management System High availability with VMware
 Bosch Video Management System High availability with VMware en Technical Note Bosch Video Management System Table of contents en 3 Table of contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Restrictions 4 2 Overview 5 3
Bosch Video Management System High availability with VMware en Technical Note Bosch Video Management System Table of contents en 3 Table of contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Restrictions 4 2 Overview 5 3
Drobo How-To Guide. Use a Drobo iscsi Array as a Target for Veeam Backups
 This document shows you how to use a Drobo iscsi SAN Storage array with Veeam Backup & Replication version 5 in a VMware environment. Veeam provides fast disk-based backup and recovery of virtual machines
This document shows you how to use a Drobo iscsi SAN Storage array with Veeam Backup & Replication version 5 in a VMware environment. Veeam provides fast disk-based backup and recovery of virtual machines
Implementing disaster recovery solutions with IBM Storwize V7000 and VMware Site Recovery Manager
 Implementing disaster recovery solutions with IBM Storwize V7000 and VMware Site Recovery Manager A step-by-step guide IBM Systems and Technology Group ISV Enablement January 2011 Table of contents Abstract...
Implementing disaster recovery solutions with IBM Storwize V7000 and VMware Site Recovery Manager A step-by-step guide IBM Systems and Technology Group ISV Enablement January 2011 Table of contents Abstract...
BEST PRACTICES GUIDE: VMware on Nimble Storage
 BEST PRACTICES GUIDE: VMware on Nimble Storage Summary Nimble Storage iscsi arrays provide a complete application-aware data storage solution that includes primary storage, intelligent caching, instant
BEST PRACTICES GUIDE: VMware on Nimble Storage Summary Nimble Storage iscsi arrays provide a complete application-aware data storage solution that includes primary storage, intelligent caching, instant
Deploying Remote Desktop Connection Broker with High Availability Step-by-Step Guide
 Deploying Remote Desktop Connection Broker with High Availability Step-by-Step Guide Microsoft Corporation Published: May 2010 Abstract This guide describes the steps for configuring Remote Desktop Connection
Deploying Remote Desktop Connection Broker with High Availability Step-by-Step Guide Microsoft Corporation Published: May 2010 Abstract This guide describes the steps for configuring Remote Desktop Connection
Moving the TRITON Reporting Databases
 Moving the TRITON Reporting Databases Topic 50530 Web, Data, and Email Security Versions 7.7.x, 7.8.x Updated 06-Nov-2013 If you need to move your Microsoft SQL Server database to a new location (directory,
Moving the TRITON Reporting Databases Topic 50530 Web, Data, and Email Security Versions 7.7.x, 7.8.x Updated 06-Nov-2013 If you need to move your Microsoft SQL Server database to a new location (directory,
SQL AlwaysOn Availability Groups (AAG) on Tintri
 TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER SQL AlwaysOn Availability Groups (AAG) on Tintri Best Practices Guide V1.0 Rev Oct 2014 www.tintri.com Contents Intended Audience... 4 Executive Summary... 4 Assumptions... 4 Microsoft
TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER SQL AlwaysOn Availability Groups (AAG) on Tintri Best Practices Guide V1.0 Rev Oct 2014 www.tintri.com Contents Intended Audience... 4 Executive Summary... 4 Assumptions... 4 Microsoft
SQL Server AlwaysOn. Michal Tinthofer 11. Praha 2013. What to avoid and how to optimize, deploy and operate. Michal.Tinthofer@Woodler.
 SQL Server AlwaysOn What to avoid and how to optimize, deploy and operate. 11. ročník největší odborné IT konference v ČR! Michal Tinthofer [email protected] Praha 2013 Overview Introduction
SQL Server AlwaysOn What to avoid and how to optimize, deploy and operate. 11. ročník největší odborné IT konference v ČR! Michal Tinthofer [email protected] Praha 2013 Overview Introduction
GoGrid Implement.com Configuring a SQL Server 2012 AlwaysOn Cluster
 GoGrid Implement.com Configuring a SQL Server 2012 AlwaysOn Cluster Overview This documents the SQL Server 2012 Disaster Recovery design and deployment, calling out best practices and concerns from the
GoGrid Implement.com Configuring a SQL Server 2012 AlwaysOn Cluster Overview This documents the SQL Server 2012 Disaster Recovery design and deployment, calling out best practices and concerns from the
Barracuda Backup Vx. Virtual Appliance Deployment. White Paper
 Barracuda Backup Vx Virtual Appliance Deployment White Paper DOCUMENT SCOPE This document provides guidance and best practices on designing and deploying Barracuda Backup Vx Virtual Appliance on VMware
Barracuda Backup Vx Virtual Appliance Deployment White Paper DOCUMENT SCOPE This document provides guidance and best practices on designing and deploying Barracuda Backup Vx Virtual Appliance on VMware
VMware for Bosch VMS. en Software Manual
 VMware for Bosch VMS en Software Manual VMware for Bosch VMS Table of Contents en 3 Table of contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Restrictions 4 2 Overview 5 3 Installing and configuring ESXi server 6 3.1 Installing
VMware for Bosch VMS en Software Manual VMware for Bosch VMS Table of Contents en 3 Table of contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Restrictions 4 2 Overview 5 3 Installing and configuring ESXi server 6 3.1 Installing
Microsoft SQL Server on VMware Availability and Recovery Options
 This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws. This product is covered by one or more patents listed at http://www.vmware.com/download/patents.html. VMware
This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws. This product is covered by one or more patents listed at http://www.vmware.com/download/patents.html. VMware
Solution Brief Availability and Recovery Options: Microsoft Exchange Solutions on VMware
 Introduction By leveraging the inherent benefits of a virtualization based platform, a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 deployment on VMware Infrastructure 3 offers a variety of availability and recovery
Introduction By leveraging the inherent benefits of a virtualization based platform, a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 deployment on VMware Infrastructure 3 offers a variety of availability and recovery
SQL Server 2012/2014 AlwaysOn Availability Group
 SQL Server 2012/2014 AlwaysOn Availability Group Part 1 - Introduction v1.0-2014 - G.MONVILLE Summary SQL Server 2012 AlwaysOn - Introduction... 2 AlwaysOn Features... 2 AlwaysOn FCI (Failover Cluster
SQL Server 2012/2014 AlwaysOn Availability Group Part 1 - Introduction v1.0-2014 - G.MONVILLE Summary SQL Server 2012 AlwaysOn - Introduction... 2 AlwaysOn Features... 2 AlwaysOn FCI (Failover Cluster
WhatsUp Gold v16.3 Installation and Configuration Guide
 WhatsUp Gold v16.3 Installation and Configuration Guide Contents Installing and Configuring WhatsUp Gold using WhatsUp Setup Installation Overview... 1 Overview... 1 Security considerations... 2 Standard
WhatsUp Gold v16.3 Installation and Configuration Guide Contents Installing and Configuring WhatsUp Gold using WhatsUp Setup Installation Overview... 1 Overview... 1 Security considerations... 2 Standard
Hyper-V Cloud Practice Builder. Disaster Recovery Using DPM 2010
 Hyper-V Cloud Practice Builder Disaster Recovery Using DPM 2010 The Hyper-V Cloud Practice Builder from Microsoft Enterprise Services can help Microsoft partners by: Accelerating practice development by
Hyper-V Cloud Practice Builder Disaster Recovery Using DPM 2010 The Hyper-V Cloud Practice Builder from Microsoft Enterprise Services can help Microsoft partners by: Accelerating practice development by
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service
 Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESXi 5.0 vcenter Server 5.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESXi 5.0 vcenter Server 5.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document
Microsoft SMB File Sharing Best Practices Guide
 Technical White Paper Microsoft SMB File Sharing Best Practices Guide Tintri VMstore, Microsoft SMB 3.0 Protocol, and VMware 6.x Author: Neil Glick Version 1.0 06/15/2016 @tintri www.tintri.com Contents
Technical White Paper Microsoft SMB File Sharing Best Practices Guide Tintri VMstore, Microsoft SMB 3.0 Protocol, and VMware 6.x Author: Neil Glick Version 1.0 06/15/2016 @tintri www.tintri.com Contents
ClearPass Policy Manager 6.3
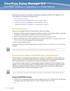 ClearPass Policy Manager 6.3 Tech Note: Installing or Upgrading on a Virtual Machine This document describes the procedures for installing and upgrading ClearPass Policy Manager 6.3 on a Virtual Machine.
ClearPass Policy Manager 6.3 Tech Note: Installing or Upgrading on a Virtual Machine This document describes the procedures for installing and upgrading ClearPass Policy Manager 6.3 on a Virtual Machine.
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service
 Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESXi 5.5 vcenter Server 5.5 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service ESXi 5.5 vcenter Server 5.5 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document
Drobo How-To Guide. Cloud Storage Using Amazon Storage Gateway with Drobo iscsi SAN
 The Amazon Web Services (AWS) Storage Gateway uses an on-premises virtual appliance to replicate a portion of your local Drobo iscsi SAN (Drobo B1200i, left below, and Drobo B800i, right below) to cloudbased
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) Storage Gateway uses an on-premises virtual appliance to replicate a portion of your local Drobo iscsi SAN (Drobo B1200i, left below, and Drobo B800i, right below) to cloudbased
istorage Server: High-Availability iscsi SAN for Windows Server 2008 & Hyper-V Clustering
 istorage Server: High-Availability iscsi SAN for Windows Server 2008 & Hyper-V Clustering Tuesday, Feb 21 st, 2012 KernSafe Technologies, Inc. www.kernsafe.com Copyright KernSafe Technologies 2006-2012.
istorage Server: High-Availability iscsi SAN for Windows Server 2008 & Hyper-V Clustering Tuesday, Feb 21 st, 2012 KernSafe Technologies, Inc. www.kernsafe.com Copyright KernSafe Technologies 2006-2012.
EXPRESSCLUSTER X for Windows Quick Start Guide for Microsoft SQL Server 2014. Version 1
 EXPRESSCLUSTER X for Windows Quick Start Guide for Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Version 1 NEC EXPRESSCLUSTER X 3.x for Windows SQL Server 2014 Quick Start Guide Document Number ECX-MSSQL2014-QSG, Version
EXPRESSCLUSTER X for Windows Quick Start Guide for Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Version 1 NEC EXPRESSCLUSTER X 3.x for Windows SQL Server 2014 Quick Start Guide Document Number ECX-MSSQL2014-QSG, Version
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution
 EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Release 3.0 User Guide P/N 300-999-671 REV 02 Copyright 2007-2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in the USA.
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Release 3.0 User Guide P/N 300-999-671 REV 02 Copyright 2007-2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in the USA.
IMPROVING VMWARE DISASTER RECOVERY WITH EMC RECOVERPOINT Applied Technology
 White Paper IMPROVING VMWARE DISASTER RECOVERY WITH EMC RECOVERPOINT Applied Technology Abstract EMC RecoverPoint provides full support for data replication and disaster recovery for VMware ESX Server
White Paper IMPROVING VMWARE DISASTER RECOVERY WITH EMC RECOVERPOINT Applied Technology Abstract EMC RecoverPoint provides full support for data replication and disaster recovery for VMware ESX Server
Contents. SnapComms Data Protection Recommendations
 Contents Abstract... 2 SnapComms Solution Environment... 2 Concepts... 3 What to Protect... 3 Database Failure Scenarios... 3 Physical Infrastructure Failures... 3 Logical Data Failures... 3 Service Recovery
Contents Abstract... 2 SnapComms Solution Environment... 2 Concepts... 3 What to Protect... 3 Database Failure Scenarios... 3 Physical Infrastructure Failures... 3 Logical Data Failures... 3 Service Recovery
How To Create An Easybelle History Database On A Microsoft Powerbook 2.5.2 (Windows)
 Introduction EASYLABEL 6 has several new features for saving the history of label formats. This history can include information about when label formats were edited and printed. In order to save this history,
Introduction EASYLABEL 6 has several new features for saving the history of label formats. This history can include information about when label formats were edited and printed. In order to save this history,
Using EonStor FC-host Storage Systems in VMware Infrastructure 3 and vsphere 4
 Using EonStor FC-host Storage Systems in VMware Infrastructure 3 and vsphere 4 Application Note Abstract This application note explains the configure details of using Infortrend FC-host storage systems
Using EonStor FC-host Storage Systems in VMware Infrastructure 3 and vsphere 4 Application Note Abstract This application note explains the configure details of using Infortrend FC-host storage systems
Protecting SQL Server Databases. 1997-2008 Software Pursuits, Inc.
 Protecting SQL Server Databases 1997-2008 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Overview of the Backup Process... 2 Configuring SQL Server to Perform Scheduled Backups... 3 Configuring SureSync Relation
Protecting SQL Server Databases 1997-2008 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Overview of the Backup Process... 2 Configuring SQL Server to Perform Scheduled Backups... 3 Configuring SureSync Relation
ArCycle vmbackup. for VMware/Hyper-V. User Guide
 ArCycle vmbackup for VMware/Hyper-V User Guide 2 Copyright Copyright ArCycle Software, Ltd., 2011-2014. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
ArCycle vmbackup for VMware/Hyper-V User Guide 2 Copyright Copyright ArCycle Software, Ltd., 2011-2014. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
Using SQL Database Mirroring to Improve Citrix XenApp Server Farm Disaster Recovery Capabilities
 Using SQL Database Mirroring to Improve Citrix XenApp Server Farm Disaster Recovery Capabilities www.citrix.com Summary... 3 Environment... 3 SQL Server Configuration... 3 XenApp Server Configuration...
Using SQL Database Mirroring to Improve Citrix XenApp Server Farm Disaster Recovery Capabilities www.citrix.com Summary... 3 Environment... 3 SQL Server Configuration... 3 XenApp Server Configuration...
Clustering VirtualCenter 2.5 Using Microsoft Cluster Services
 Clustering VirtualCenter 2.5 Using Microsoft Cluster Services This paper documents the steps to successfully implement a high availability solution for VirtualCenter 2.5 using Microsoft s cluster services.
Clustering VirtualCenter 2.5 Using Microsoft Cluster Services This paper documents the steps to successfully implement a high availability solution for VirtualCenter 2.5 using Microsoft s cluster services.
FioranoMQ 9. High Availability Guide
 FioranoMQ 9 High Availability Guide Copyright (c) 1999-2008, Fiorano Software Technologies Pvt. Ltd., Copyright (c) 2008-2009, Fiorano Software Pty. Ltd. All rights reserved. This software is the confidential
FioranoMQ 9 High Availability Guide Copyright (c) 1999-2008, Fiorano Software Technologies Pvt. Ltd., Copyright (c) 2008-2009, Fiorano Software Pty. Ltd. All rights reserved. This software is the confidential
Drobo How-To Guide. Use a Drobo iscsi Array as a Target for Veeam Backups
 This document shows you how to use a Drobo iscsi array with Veeam Backup & Replication version 6.5 in a VMware environment. Veeam provides fast disk-based backup and recovery of virtual machines (VMs),
This document shows you how to use a Drobo iscsi array with Veeam Backup & Replication version 6.5 in a VMware environment. Veeam provides fast disk-based backup and recovery of virtual machines (VMs),
VMware vsphere Data Protection 6.0
 VMware vsphere Data Protection 6.0 TECHNICAL OVERVIEW REVISED FEBRUARY 2015 Table of Contents Introduction.... 3 Architectural Overview... 4 Deployment and Configuration.... 5 Backup.... 6 Application
VMware vsphere Data Protection 6.0 TECHNICAL OVERVIEW REVISED FEBRUARY 2015 Table of Contents Introduction.... 3 Architectural Overview... 4 Deployment and Configuration.... 5 Backup.... 6 Application
Veritas Storage Foundation High Availability for Windows by Symantec
 Veritas Storage Foundation High Availability for Windows by Symantec Simple-to-use solution for high availability and disaster recovery of businesscritical Windows applications Data Sheet: High Availability
Veritas Storage Foundation High Availability for Windows by Symantec Simple-to-use solution for high availability and disaster recovery of businesscritical Windows applications Data Sheet: High Availability
Direct Storage Access Using NetApp SnapDrive. Installation & Administration Guide
 Direct Storage Access Using NetApp SnapDrive Installation & Administration Guide SnapDrive overview... 3 What SnapDrive does... 3 What SnapDrive does not do... 3 Recommendations for using SnapDrive...
Direct Storage Access Using NetApp SnapDrive Installation & Administration Guide SnapDrive overview... 3 What SnapDrive does... 3 What SnapDrive does not do... 3 Recommendations for using SnapDrive...
SAN Conceptual and Design Basics
 TECHNICAL NOTE VMware Infrastructure 3 SAN Conceptual and Design Basics VMware ESX Server can be used in conjunction with a SAN (storage area network), a specialized high speed network that connects computer
TECHNICAL NOTE VMware Infrastructure 3 SAN Conceptual and Design Basics VMware ESX Server can be used in conjunction with a SAN (storage area network), a specialized high speed network that connects computer
SQL Server Database Administrator s Guide
 SQL Server Database Administrator s Guide Copyright 2011 Sophos Limited. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by
SQL Server Database Administrator s Guide Copyright 2011 Sophos Limited. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by
SnapManager 1.0 for Virtual Infrastructure Best Practices
 NETAPP TECHNICAL REPORT SnapManager 1.0 for Virtual Infrastructure Best Practices John Lockyer, NetApp January 2009 TR-3737 LEVERAGING NETAPP DATA ONTAP FOR VMWARE BACKUP, RESTORE, AND DISASTER RECOVERY
NETAPP TECHNICAL REPORT SnapManager 1.0 for Virtual Infrastructure Best Practices John Lockyer, NetApp January 2009 TR-3737 LEVERAGING NETAPP DATA ONTAP FOR VMWARE BACKUP, RESTORE, AND DISASTER RECOVERY
Configure SQL database mirroring
 App Orchestration 2.0 Configure SQL database mirroring Prepared by: Mohit Menghnani Commissioning Editor: Linda Belliveau Version: 4.0 Last Updated: December 12, 2013 Page 1 Contents Overview... 3 Configure
App Orchestration 2.0 Configure SQL database mirroring Prepared by: Mohit Menghnani Commissioning Editor: Linda Belliveau Version: 4.0 Last Updated: December 12, 2013 Page 1 Contents Overview... 3 Configure
Clustering ExtremeZ-IP 4.1
 Clustering ExtremeZ-IP 4.1 Installing and Configuring ExtremeZ-IP 4.x on a Cluster Version: 1.3 Date: 10/11/05 Product Version: 4.1 Introduction This document provides instructions and background information
Clustering ExtremeZ-IP 4.1 Installing and Configuring ExtremeZ-IP 4.x on a Cluster Version: 1.3 Date: 10/11/05 Product Version: 4.1 Introduction This document provides instructions and background information
StarWind iscsi SAN Software: Using StarWind with VMware ESX Server
 StarWind iscsi SAN Software: Using StarWind with VMware ESX Server www.starwindsoftware.com Copyright 2008-2010. All rights reserved. COPYRIGHT Copyright 2008-2010. All rights reserved. No part of this
StarWind iscsi SAN Software: Using StarWind with VMware ESX Server www.starwindsoftware.com Copyright 2008-2010. All rights reserved. COPYRIGHT Copyright 2008-2010. All rights reserved. No part of this
QUANTIFY INSTALLATION GUIDE
 QUANTIFY INSTALLATION GUIDE Thank you for putting your trust in Avontus! This guide reviews the process of installing Quantify software. For Quantify system requirement information, please refer to the
QUANTIFY INSTALLATION GUIDE Thank you for putting your trust in Avontus! This guide reviews the process of installing Quantify software. For Quantify system requirement information, please refer to the
VMware@SoftLayer Cookbook Disaster Recovery (DR)
 VMware@SoftLayer Cookbook Disaster Recovery (DR) IBM Global Technology Services: Khoa Huynh ([email protected]) Daniel De Araujo ([email protected]) Bob Kellenberger ([email protected]) VMware: Merlin
VMware@SoftLayer Cookbook Disaster Recovery (DR) IBM Global Technology Services: Khoa Huynh ([email protected]) Daniel De Araujo ([email protected]) Bob Kellenberger ([email protected]) VMware: Merlin
Building a Penetration Testing Virtual Computer Laboratory
 Building a Penetration Testing Virtual Computer Laboratory User Guide 1 A. Table of Contents Collaborative Virtual Computer Laboratory A. Table of Contents... 2 B. Introduction... 3 C. Configure Host Network
Building a Penetration Testing Virtual Computer Laboratory User Guide 1 A. Table of Contents Collaborative Virtual Computer Laboratory A. Table of Contents... 2 B. Introduction... 3 C. Configure Host Network
VMware vsphere Data Protection 5.8 TECHNICAL OVERVIEW REVISED AUGUST 2014
 VMware vsphere Data Protection 5.8 TECHNICAL OVERVIEW REVISED AUGUST 2014 Table of Contents Introduction.... 3 Features and Benefits of vsphere Data Protection... 3 Additional Features and Benefits of
VMware vsphere Data Protection 5.8 TECHNICAL OVERVIEW REVISED AUGUST 2014 Table of Contents Introduction.... 3 Features and Benefits of vsphere Data Protection... 3 Additional Features and Benefits of
TECHNICAL PAPER. Veeam Backup & Replication with Nimble Storage
 TECHNICAL PAPER Veeam Backup & Replication with Nimble Storage Document Revision Date Revision Description (author) 11/26/2014 1. 0 Draft release (Bill Roth) 12/23/2014 1.1 Draft update (Bill Roth) 2/20/2015
TECHNICAL PAPER Veeam Backup & Replication with Nimble Storage Document Revision Date Revision Description (author) 11/26/2014 1. 0 Draft release (Bill Roth) 12/23/2014 1.1 Draft update (Bill Roth) 2/20/2015
TGL VMware Presentation. Guangzhou Macau Hong Kong Shanghai Beijing
 TGL VMware Presentation Guangzhou Macau Hong Kong Shanghai Beijing The Path To IT As A Service Existing Apps Future Apps Private Cloud Lots of Hardware and Plumbing Today IT TODAY Internal Cloud Federation
TGL VMware Presentation Guangzhou Macau Hong Kong Shanghai Beijing The Path To IT As A Service Existing Apps Future Apps Private Cloud Lots of Hardware and Plumbing Today IT TODAY Internal Cloud Federation
WHITE PAPER: ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS. Symantec Backup Exec Continuous Protection Server Continuous Protection for Microsoft SQL Server Databases
 WHITE PAPER: ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS Symantec Backup Exec Continuous Protection Server Continuous Protection for Microsoft SQL Server Databases White Paper: Enterprise Solutions Symantec Backup Exec Continuous
WHITE PAPER: ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS Symantec Backup Exec Continuous Protection Server Continuous Protection for Microsoft SQL Server Databases White Paper: Enterprise Solutions Symantec Backup Exec Continuous
Quick Start - Virtual Server idataagent (VMware)
 Page 1 of 24 Quick Start - Virtual Server idataagent (VMware) TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW Introduction Key Features Complete Virtual Machine Protection Granular Recovery of Virtual Machine Data Minimal
Page 1 of 24 Quick Start - Virtual Server idataagent (VMware) TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW Introduction Key Features Complete Virtual Machine Protection Granular Recovery of Virtual Machine Data Minimal
How to configure Failover Clustering for Hyper-V hosts on HP ProLiant c-class server blades with All-in-One SB600c storage blade
 How to configure Failover Clustering for Hyper-V hosts on HP ProLiant c-class server blades with All-in-One SB600c storage blade Executive summary... 2 System requirements... 2 Hardware requirements...
How to configure Failover Clustering for Hyper-V hosts on HP ProLiant c-class server blades with All-in-One SB600c storage blade Executive summary... 2 System requirements... 2 Hardware requirements...
Installing and Using the vnios Trial
 Installing and Using the vnios Trial The vnios Trial is a software package designed for efficient evaluation of the Infoblox vnios appliance platform. Providing the complete suite of DNS, DHCP and IPAM
Installing and Using the vnios Trial The vnios Trial is a software package designed for efficient evaluation of the Infoblox vnios appliance platform. Providing the complete suite of DNS, DHCP and IPAM
VMware Certified Professional 5 Data Center Virtualization (VCP5-DCV) Exam
 Exam : VCP5-DCV Title : VMware Certified Professional 5 Data Center Virtualization (VCP5-DCV) Exam Version : DEMO 1 / 9 1.Click the Exhibit button. An administrator has deployed a new virtual machine on
Exam : VCP5-DCV Title : VMware Certified Professional 5 Data Center Virtualization (VCP5-DCV) Exam Version : DEMO 1 / 9 1.Click the Exhibit button. An administrator has deployed a new virtual machine on
How to Backup and Restore a VM using Veeam
 How to Backup and Restore a VM using Veeam Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Assumptions... 3 Add ESXi Server... 4 Backup a VM... 6 Restore Full VM... 12 Appendix A: Install Veeam Backup & Replication
How to Backup and Restore a VM using Veeam Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Assumptions... 3 Add ESXi Server... 4 Backup a VM... 6 Restore Full VM... 12 Appendix A: Install Veeam Backup & Replication
Virtual Server Agent v9 with VMware. March 2011
 Virtual Server Agent v9 with VMware March 2011 Contents Summary... 3 Backup Transport Methods... 3 Deployment Scenarios... 3 VSA Installation Requirements... 4 VSA Patch Requirements... 4 VDDK Installation...
Virtual Server Agent v9 with VMware March 2011 Contents Summary... 3 Backup Transport Methods... 3 Deployment Scenarios... 3 VSA Installation Requirements... 4 VSA Patch Requirements... 4 VDDK Installation...
Backups and Maintenance
 Backups and Maintenance Backups and Maintenance Objectives Learn how to create a backup strategy to suit your needs. Learn how to back up a database. Learn how to restore from a backup. Use the Database
Backups and Maintenance Backups and Maintenance Objectives Learn how to create a backup strategy to suit your needs. Learn how to back up a database. Learn how to restore from a backup. Use the Database
High Availability and Disaster Recovery for Exchange Servers Through a Mailbox Replication Approach
 High Availability and Disaster Recovery for Exchange Servers Through a Mailbox Replication Approach Introduction Email is becoming ubiquitous and has become the standard tool for communication in many
High Availability and Disaster Recovery for Exchange Servers Through a Mailbox Replication Approach Introduction Email is becoming ubiquitous and has become the standard tool for communication in many
Symantec Storage Foundation High Availability for Windows
 Symantec Storage Foundation High Availability for Windows Storage management, high availability and disaster recovery for physical and virtual Windows applications Data Sheet: High Availability Overview
Symantec Storage Foundation High Availability for Windows Storage management, high availability and disaster recovery for physical and virtual Windows applications Data Sheet: High Availability Overview
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service
 Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service Update 1 ESXi 6.0 vcenter Server 6.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service Update 1 ESXi 6.0 vcenter Server 6.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the
Zerto Virtual Manager Administration Guide
 Zerto Virtual Manager Administration Guide AWS Environment ZVR-ADVA-4.0U2-01-23-07-15 Copyright 2015, Zerto Ltd. All rights reserved. Information in this document is subject to change without notice and
Zerto Virtual Manager Administration Guide AWS Environment ZVR-ADVA-4.0U2-01-23-07-15 Copyright 2015, Zerto Ltd. All rights reserved. Information in this document is subject to change without notice and
Advanced VMware Training
 Goals: Demonstrate VMware Fault Tolerance in action Demonstrate Host Profile Usage How to quickly deploy and configure several vsphere servers Discuss Storage vmotion use cases Demonstrate vcenter Server
Goals: Demonstrate VMware Fault Tolerance in action Demonstrate Host Profile Usage How to quickly deploy and configure several vsphere servers Discuss Storage vmotion use cases Demonstrate vcenter Server
RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines
 RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines Version 4.3 Administrator's Guide P/N 302-001-905 REV 01 EMC CONFIDENTIAL Copyright 2014-2015 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in USA. Published July, 2015
RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines Version 4.3 Administrator's Guide P/N 302-001-905 REV 01 EMC CONFIDENTIAL Copyright 2014-2015 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in USA. Published July, 2015
Introduction to Hyper-V High- Availability with Failover Clustering
 Introduction to Hyper-V High- Availability with Failover Clustering Lab Guide This lab is for anyone who wants to learn about Windows Server 2012 R2 Failover Clustering, focusing on configuration for Hyper-V
Introduction to Hyper-V High- Availability with Failover Clustering Lab Guide This lab is for anyone who wants to learn about Windows Server 2012 R2 Failover Clustering, focusing on configuration for Hyper-V
Moving the Web Security Log Database
 Moving the Web Security Log Database Topic 50530 Web Security Solutions Version 7.7.x, 7.8.x Updated 22-Oct-2013 Version 7.8 introduces support for the Web Security Log Database on Microsoft SQL Server
Moving the Web Security Log Database Topic 50530 Web Security Solutions Version 7.7.x, 7.8.x Updated 22-Oct-2013 Version 7.8 introduces support for the Web Security Log Database on Microsoft SQL Server
Overview... 1 Requirements... 1. Installing Roles and Features... 3. Creating SQL Server Database... 9 Setting Security Logins...
 Contents CHAPTER 1 IMail Server using Failover Clustering Overview... 1 Requirements... 1 CHAPTER 2 IIS Installing Roles and Features... 3 CHAPTER 3 Configuring Storage Area Network Requirements... 5 Connecting
Contents CHAPTER 1 IMail Server using Failover Clustering Overview... 1 Requirements... 1 CHAPTER 2 IIS Installing Roles and Features... 3 CHAPTER 3 Configuring Storage Area Network Requirements... 5 Connecting
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution
 EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Release 8.2 User Guide P/N 302-000-658 REV 01 Copyright 2007-2014 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in the USA.
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Release 8.2 User Guide P/N 302-000-658 REV 01 Copyright 2007-2014 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in the USA.
VirtualCenter Database Maintenance VirtualCenter 2.0.x and Microsoft SQL Server
 Technical Note VirtualCenter Database Maintenance VirtualCenter 2.0.x and Microsoft SQL Server This document discusses ways to maintain the VirtualCenter database for increased performance and manageability.
Technical Note VirtualCenter Database Maintenance VirtualCenter 2.0.x and Microsoft SQL Server This document discusses ways to maintain the VirtualCenter database for increased performance and manageability.
Virtualizing your Datacenter
 Virtualizing your Datacenter with Windows Server 2012 R2 & System Center 2012 R2 Part 2 Hands-On Lab Step-by-Step Guide For the VMs the following credentials: Username: Contoso\Administrator Password:
Virtualizing your Datacenter with Windows Server 2012 R2 & System Center 2012 R2 Part 2 Hands-On Lab Step-by-Step Guide For the VMs the following credentials: Username: Contoso\Administrator Password:
Using Emergency Restore to recover the vcenter Server has the following benefits as compared to the above methods:
 Executive Summary This document provides certain best practices with regards to the Emergency Restore feature in vsphere Data Protection 5.5 release. It also describes the methods and processes to be used
Executive Summary This document provides certain best practices with regards to the Emergency Restore feature in vsphere Data Protection 5.5 release. It also describes the methods and processes to be used
This article Includes:
 Log shipping has been a mechanism for maintaining a warm standby server for years. Though SQL Server supported log shipping with SQL Server 2000 as a part of DB Maintenance Plan, it has become a built-in
Log shipping has been a mechanism for maintaining a warm standby server for years. Though SQL Server supported log shipping with SQL Server 2000 as a part of DB Maintenance Plan, it has become a built-in
VMware Data Recovery. Administrator's Guide EN-000193-00
 Administrator's Guide EN-000193-00 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at: http://www.vmware.com/support/ The VMware Web site also provides the latest product
Administrator's Guide EN-000193-00 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at: http://www.vmware.com/support/ The VMware Web site also provides the latest product
Virtual Appliance Setup Guide
 Virtual Appliance Setup Guide 2015 Bomgar Corporation. All rights reserved worldwide. BOMGAR and the BOMGAR logo are trademarks of Bomgar Corporation; other trademarks shown are the property of their respective
Virtual Appliance Setup Guide 2015 Bomgar Corporation. All rights reserved worldwide. BOMGAR and the BOMGAR logo are trademarks of Bomgar Corporation; other trademarks shown are the property of their respective
GlobalSCAPE DMZ Gateway, v1. User Guide
 GlobalSCAPE DMZ Gateway, v1 User Guide GlobalSCAPE, Inc. (GSB) Address: 4500 Lockhill-Selma Road, Suite 150 San Antonio, TX (USA) 78249 Sales: (210) 308-8267 Sales (Toll Free): (800) 290-5054 Technical
GlobalSCAPE DMZ Gateway, v1 User Guide GlobalSCAPE, Inc. (GSB) Address: 4500 Lockhill-Selma Road, Suite 150 San Antonio, TX (USA) 78249 Sales: (210) 308-8267 Sales (Toll Free): (800) 290-5054 Technical
Support Document: Microsoft SQL Server - LiveVault 7.6X
 Contents Preparing to create a Microsoft SQL backup policy... 2 Adjusting the SQL max worker threads option... 2 Preparing for Log truncation... 3 Best Practices... 3 Microsoft SQL Server 2005, 2008, or
Contents Preparing to create a Microsoft SQL backup policy... 2 Adjusting the SQL max worker threads option... 2 Preparing for Log truncation... 3 Best Practices... 3 Microsoft SQL Server 2005, 2008, or
12 NETWORK MANAGEMENT
 12 NETWORK MANAGEMENT PROJECTS Project 12.1 Project 12.2 Project 12.3 Project 12.4 Understanding Key Concepts Backing Up and Restoring Data Monitoring Computer Activity Configuring SNMP Support 276 Networking
12 NETWORK MANAGEMENT PROJECTS Project 12.1 Project 12.2 Project 12.3 Project 12.4 Understanding Key Concepts Backing Up and Restoring Data Monitoring Computer Activity Configuring SNMP Support 276 Networking
VMware Virtual Machine File System: Technical Overview and Best Practices
 VMware Virtual Machine File System: Technical Overview and Best Practices A VMware Technical White Paper Version 1.0. VMware Virtual Machine File System: Technical Overview and Best Practices Paper Number:
VMware Virtual Machine File System: Technical Overview and Best Practices A VMware Technical White Paper Version 1.0. VMware Virtual Machine File System: Technical Overview and Best Practices Paper Number:
Quick Start Guide. User Manual. 1 March 2012
 Quick Start Guide User Manual 1 March 2012 This document outlines the steps to install SAMLite system into a single box of server and configure it to run for passive collection (domain login script). This
Quick Start Guide User Manual 1 March 2012 This document outlines the steps to install SAMLite system into a single box of server and configure it to run for passive collection (domain login script). This
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution
 EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Version 8.2 Service Pack 1 User Guide 302-001-235 REV 01 Copyright 2007-2015 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Version 8.2 Service Pack 1 User Guide 302-001-235 REV 01 Copyright 2007-2015 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published
Atlantis ILIO Persistent VDI for Flash Arrays Administration Guide Atlantis Computing Inc. Atlantis ILIO 4.1. Document Version 1.0
 Atlantis ILIO Persistent VDI for Flash Arrays Atlantis Computing Inc. Atlantis ILIO 4.1 Document Version 1.0 Copyrights Atlantis ILIO Persistent VDI for Flash Arrays Document Version 1.0 2007-2015 Atlantis
Atlantis ILIO Persistent VDI for Flash Arrays Atlantis Computing Inc. Atlantis ILIO 4.1 Document Version 1.0 Copyrights Atlantis ILIO Persistent VDI for Flash Arrays Document Version 1.0 2007-2015 Atlantis
VMware vsphere-6.0 Administration Training
 VMware vsphere-6.0 Administration Training Course Course Duration : 20 Days Class Duration : 3 hours per day (Including LAB Practical) Classroom Fee = 20,000 INR Online / Fast-Track Fee = 25,000 INR Fast
VMware vsphere-6.0 Administration Training Course Course Duration : 20 Days Class Duration : 3 hours per day (Including LAB Practical) Classroom Fee = 20,000 INR Online / Fast-Track Fee = 25,000 INR Fast
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution
 EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Version 9.0 User Guide 302-001-755 REV 01 Copyright 2007-2015 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in USA. Published
EMC NetWorker Module for Microsoft for Windows Bare Metal Recovery Solution Version 9.0 User Guide 302-001-755 REV 01 Copyright 2007-2015 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published in USA. Published
Introduction. Setup of Exchange in a VM. VMware Infrastructure
 Introduction VMware Infrastructure is deployed in data centers for deploying mission critical applications. Deployment of Microsoft Exchange is a very important task for the IT staff. Email system is an
Introduction VMware Infrastructure is deployed in data centers for deploying mission critical applications. Deployment of Microsoft Exchange is a very important task for the IT staff. Email system is an
1. Server 2008 - Microsoft FEP 2010 - Instalation
 1. Server 2008 - Microsoft FEP 2010 - Instalation 1 2. Windows XP x86 (32bit) - Microsoft FEP 2010 Instalation 2 3 2.1. 4 System Requirements Microsoft Forefront Endpoint Protection 2010 1 System Requirements
1. Server 2008 - Microsoft FEP 2010 - Instalation 1 2. Windows XP x86 (32bit) - Microsoft FEP 2010 Instalation 2 3 2.1. 4 System Requirements Microsoft Forefront Endpoint Protection 2010 1 System Requirements
VMware Site Recovery Manager with EMC RecoverPoint
 VMware Site Recovery Manager with EMC RecoverPoint Implementation Guide EMC Global Solutions Centers EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters Hopkinton MA 01748-9103 1.508.435.1000 www.emc.com Copyright
VMware Site Recovery Manager with EMC RecoverPoint Implementation Guide EMC Global Solutions Centers EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters Hopkinton MA 01748-9103 1.508.435.1000 www.emc.com Copyright
VMware vsphere Data Protection 6.1
 VMware vsphere Data Protection 6.1 Technical Overview Revised August 10, 2015 Contents Introduction... 3 Architecture... 3 Deployment and Configuration... 5 Backup... 6 Application Backup... 6 Backup Data
VMware vsphere Data Protection 6.1 Technical Overview Revised August 10, 2015 Contents Introduction... 3 Architecture... 3 Deployment and Configuration... 5 Backup... 6 Application Backup... 6 Backup Data
Veritas Cluster Server Database Agent for Microsoft SQL Configuration Guide
 Veritas Cluster Server Database Agent for Microsoft SQL Configuration Guide Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003 5.0 11293743 Veritas Cluster Server Database Agent for Microsoft SQL Configuration Guide Copyright
Veritas Cluster Server Database Agent for Microsoft SQL Configuration Guide Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003 5.0 11293743 Veritas Cluster Server Database Agent for Microsoft SQL Configuration Guide Copyright
